Integrals & Riemann Sum Function Behavior & Approximation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
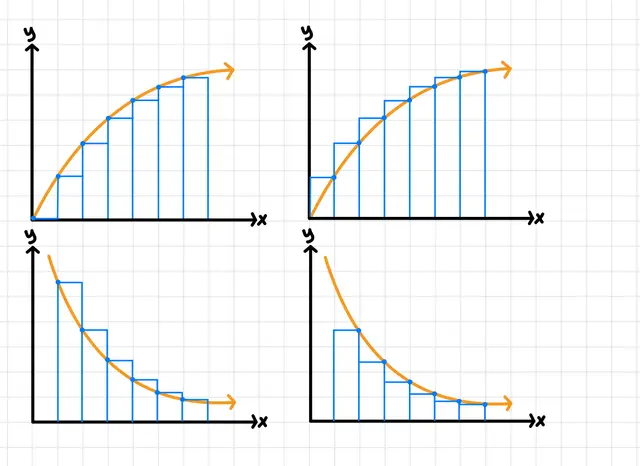
If the function behavior is increasing, a left Riemann sum would be an (underestimate/overestimate/cannot be determined).
underestimate
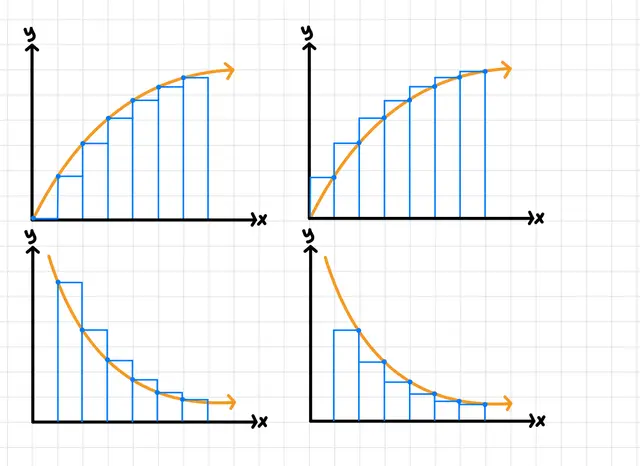
If the function behavior is decreasing, a left Riemann sum would be an (underestimate/overestimate/cannot be determined).
overestimate
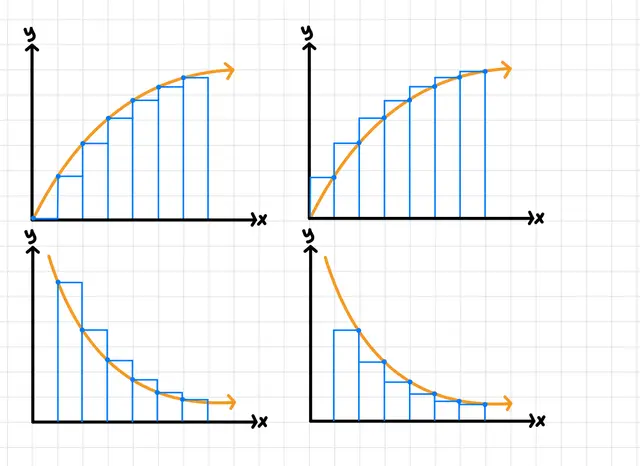
If the function behavior is increasing, a right Riemann sum would be an (underestimate/overestimate/cannot be determined).
overestimate
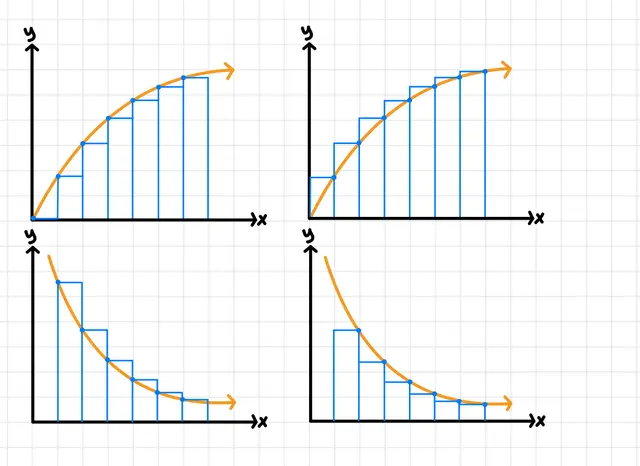
If the function behavior is decreasing, a right Riemann sum would be an (underestimate/overestimate/cannot be determined).
underestimate
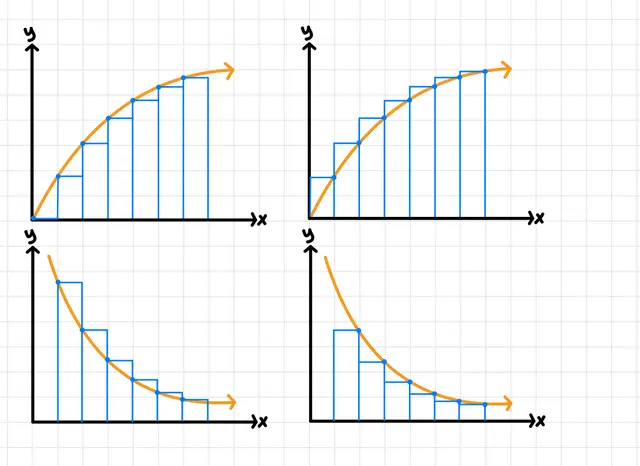
You can tell whether a left or right Riemann sum will over or underestimate because of the function’s (increasing or decreasing trends/concavity).
both
If a function goes from concave up to concave down, a left or right Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
cannot be determined
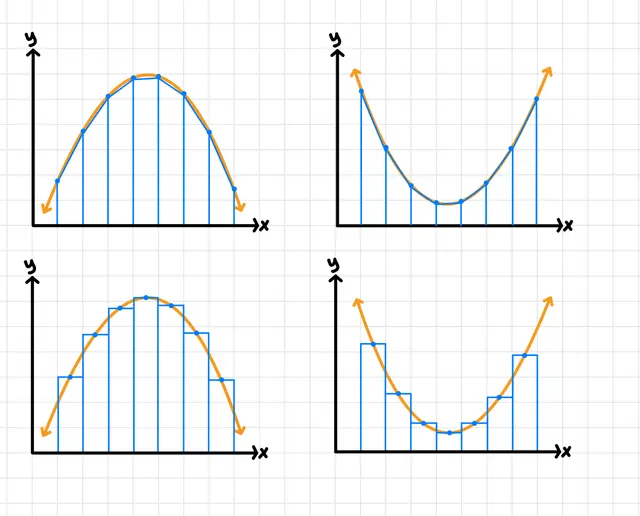
If a function is concave up, a trapezoidal Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
overestimate
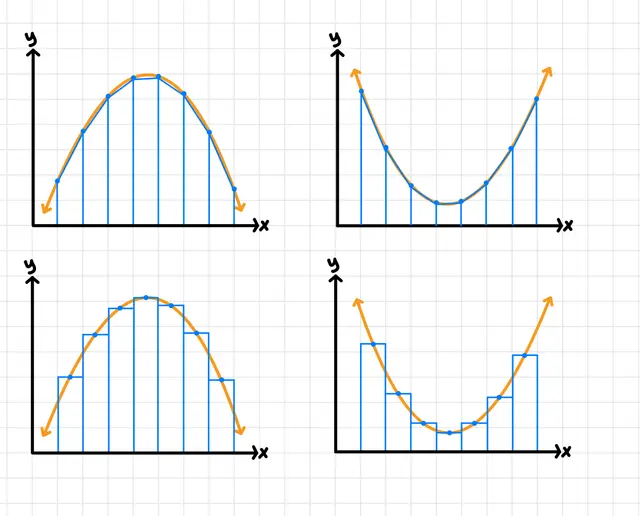
If a function is concave down, a trapezoidal Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
underestimate
If a function goes from concave up to concave down, a trapezoidal Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
cannot be determined
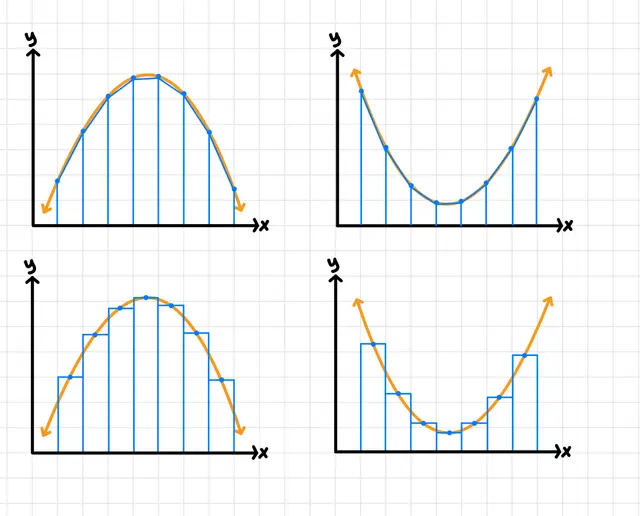
You can tell whether a midpoint Riemann sum will over or underestimate because of the function’s (increasing or decreasing trends/concavity).
concavity
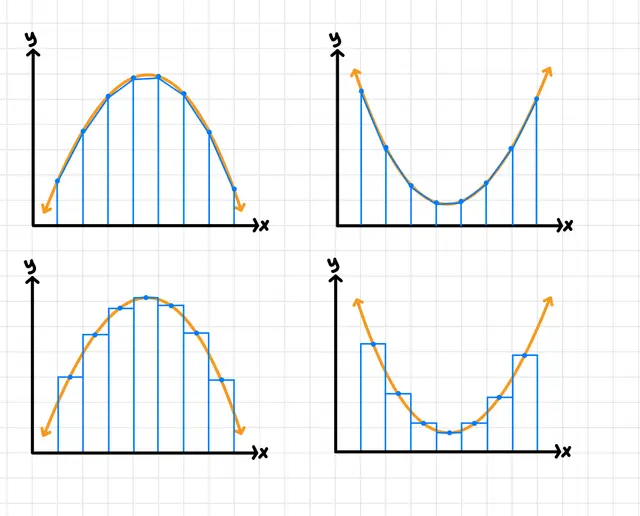
If a function is concave up, a midpoint Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
underestimate
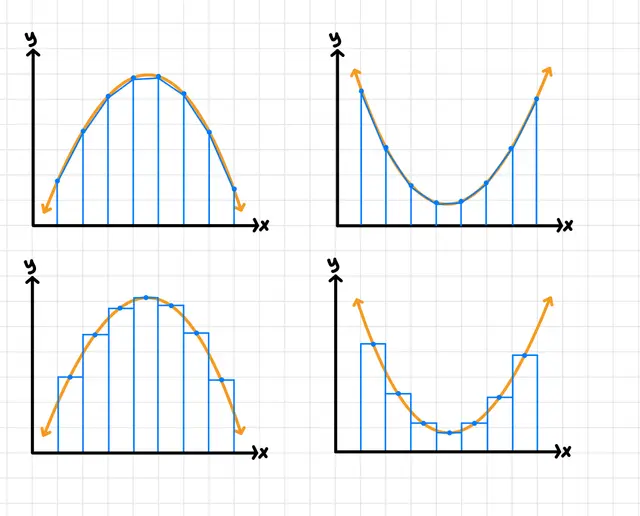
If a function is concave down, a midpoint Riemann sum will (overestimate/underestimate/cannot be determined).
overestimate
When the derivative f is positive, the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
increasing
When the derivative f is negative, the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
decreasing
When the derivative f is increasing, the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
concave up
When the derivative f is decreasing, the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
concave down
When the derivative f changes signs (crosses the x-axis), the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
at a local minimum/maximum
When the derivative f reaches a local extrema, the antiderivative
g\left(x\right)=\int_0^{x}\!f\left(t\right)\,dt is…
at an inflection point