Magnetism + the Motor Effect (Topic 12)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything on the checklist for Magnetism + the Motor Effect (Topic 12)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the Two Types of Magnets?
PERMANENT MAGNETS → ALWAYS produce a MAGNETIC FIELD
INDUCED MAGNETS → ONLY produce a MAGNETIC FIELD when NEAR ANOTHER MAGNET (when in another Magnet’s Magnetic Field)
What are the Three Magnetic Materials?
IRON
NICKEL
COBALT
What affects how Quickly a Magnet Loses its Magnetism?
SOFTNESS:
e.g Steel is magnetically ‘HARD’ → Used in PERMANENT MAGNETS
e.g Iron is magnetically ‘SOFT’ → Used in TEMPORARY MAGNETS
What are the Rules for Attraction + Repulsion?
LIKE Poles REPEL
OPPOSITE Poles ATTRACT
What is a Magnetic Field?
A REGION around a Magnet where OTHER MAGNETS experience a NON-CONTACT FORCE acting on them
How to Draw a Magnetic Field?
Field Lines point TOWARDS SOUTH POLE
MORE LINES = MORE STRENGTH
Field lines get FURTHER APART when moving AWAY from Magnet
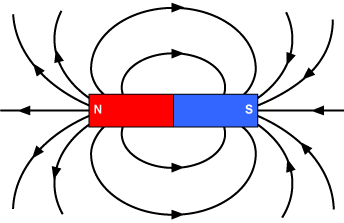
What does the Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet look like?
CLOSE FIELD LINES at POLES
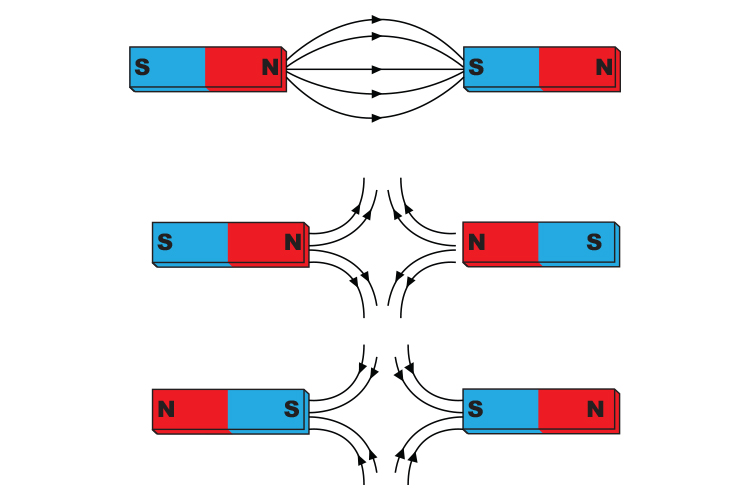
What does the Magnetic Field around Two Opposite Poles look like?
UNIFORM FIELD:
EVENLY SPACED
PARALLEL
STRAIGHT LINES
Why do Magnets Attract/Repel according to Magnetic Fields?
Field Lines of OPPOSITE Poles POINT IN SAME DIRECTION → JOIN UP → ATTRACT
Field Lines of LIKE POLES point in OPPOSITE DIRECTIONS → REPEL
How to Use a Plotting Compass to show the Field Lines of an Object?
Put PLOTTING COMPASS near Magnet
MARK DIRECTION of NEEDLE with a DOT
Move COMPASS to DOT you drew
Repeat STEPS 2 + 3 until back at Magnet → ONE FIELD LINE DRAWN
Repeat STEPS 1-4 until MULTIPLE Field Lines drawn
What does a Compass show about the Earth?
Compass ALWAYS points NORTH → Earth has a MAGNETIC FIELD → INNER CORE must be MAGNETIC
What is Electromagnetism?
MAGNETIC FIELD created by a CURRENT
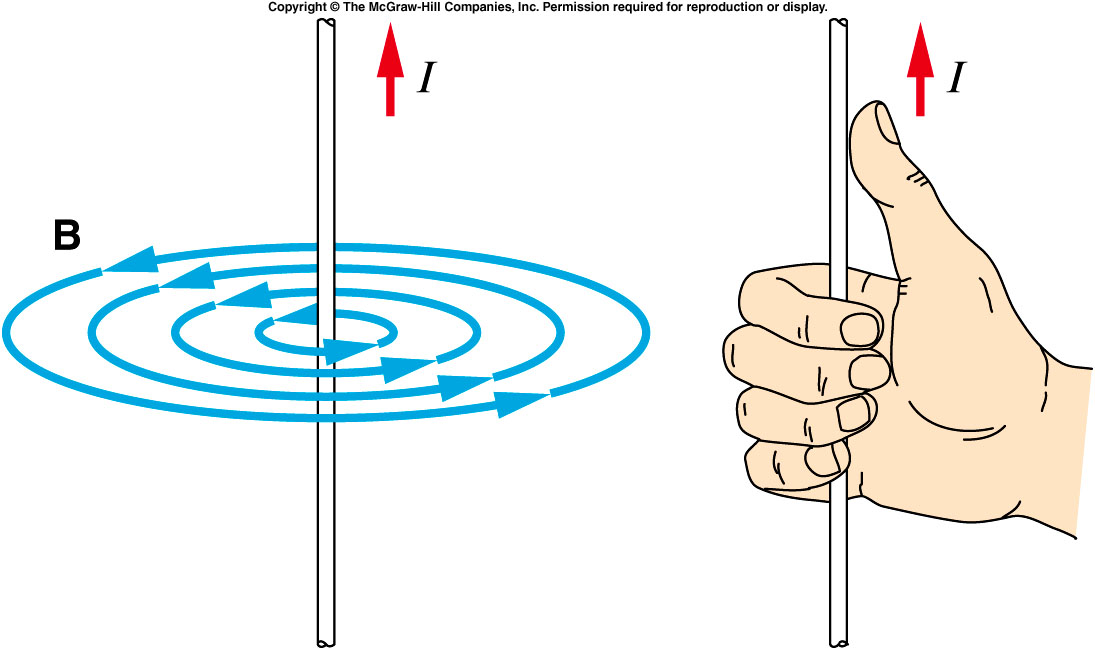
What does the Magnetic Field around a Current-carrying Wire look like?
CIRCLES
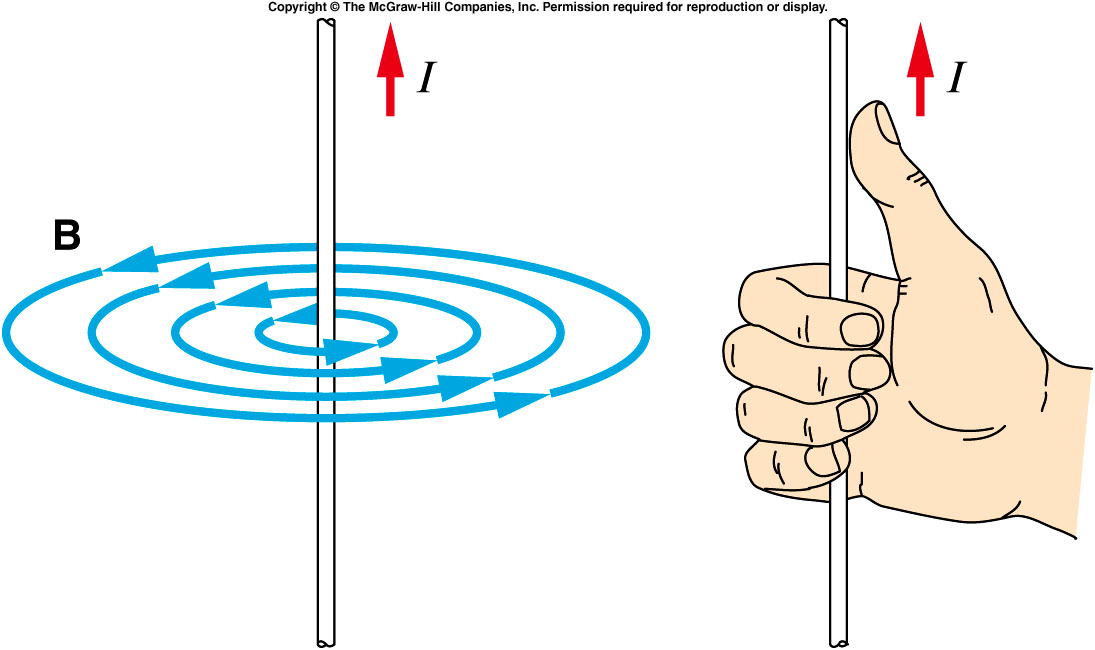
How to Work Out the Direction of the Magnetic Field in a Current-carrying Wire?
RIGHT HAND THUMB RULE:
Point THUMB in DIRECTION of CURRENT + CURL FINGERS → Direction of FINGERS is DIRECTION OF FIELD
What are the Two Factors that affect how Strong the Magnetic Field of a Current-Carrying Wire is?
SIZE OF CURRENT
DISTANCE FROM WIRE
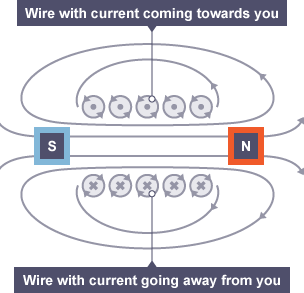
How to Draw a Wire where the Current is Away/Towards you?
Away - CROSS
Towards - POINT
→ Like a DART (looks like X when Moving Away from you)
What is a Solenoid + What does its Magnetic Field look like?
Solenoid → COIL of Wire
Magnetic Field → Field Lines JOIN to form a STRONGER, ALMOST UNIFORM Field ALONG THE CENTRE
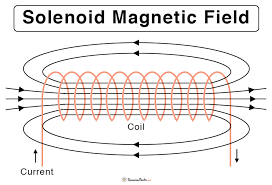
What are the Four Factors that affect how Strong the Magnetic Field of a Solenoid is?
SIZE OF CURRENT
DISTANCE FROM WIRE
NUMBER OF TURNS
IRON CORE in CENTRE of Solenoid → Becomes INDUCED MAGNET
What are (two) Uses of Permanent Magnets?
COMPASS
FRIDGE MAGNETS
What is a Use of Electromagnets?
CRANES
What is the Motor Effect?
If you put a CURRENT-CARRYING WIRE through a MAGNETIC FIELD → the TWO MAGNETIC FIELDS INTERACT → FORCE on WIRE
What are the Three Factors that affect how Strong the Motor Effect is?
Wire at RIGHT ANGLE to Magnetic Field → Strongest
SIZE OF CURRENT
STRENGTH OF MAGNETIC FIELD
What is the Formula for Size of the Force in the Motor Effect?
F = BIL
FORCE = MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY (Strength of Magnetic Field) x CURRENT x LENGTH (of Wire in Magnetic Field)
How to Work Out the Direction of the Force of the Motor Effect?
FLEMING’S LEFT HAND RULE:
THUMB is Direction of FORCE/MOTION
FIRST FINGER is Direction of FIELD
SECOND FINGER is Direction of CURRENT
How does a D.C Motor Work?
COIL of Wire (free to rotate) is placed in a MAGNETIC FIELD
DC Current flows through Wire → FORCE on EACH SIDE OF WIRE acts in DIFFERENT DIRECTION (due to Current being in Opposite Direction)
→ COIL SPINS
EVERY HALF TURN (e.g when Vertical), the SPLIT RING COMMUTATOR SWITCHES the CONTACTS of the Loop → REVERSES CURRENT DIRECTION
→ COIL SPINS in SAME DIRECTION
How to Switch the Direction of a Motor?
SWAP CURRENT DIRECTION (e.g by swapping polarity)
SWAP POLES OF MAGNET
How does a Loudspeaker Work?
COIL of Wire (free to rotate) is placed in a MAGNETIC FIELD
AC Current flows through Wire → FORCE produced which KEEPS SWITCHING DIRECTION
The Wire is connected to a PAPER CONE which also MOVES + KEEPS SWITCHING DIRECTION → SOUND WAVE
How is the Frequency of the Sound Wave produced by the Loudspeaker Controlled?
Same as the FREQUENCY of the AC Current