P4: Energy Resources and Energy Transfers
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
energy stores
Chemical - fuel, food, batteries
Electrostatic - energy stored when charged particles (electrons and protons) are in an electrical field and can attract or repel each other —> stationary e.g. balloon sticking to a wall
Magnetic - magnets storing energy —> similar to electrostatic but magnets in a magnetic field —> caused by electrons spinning or moving in wires/materials —> moving e.g. magnets repelling each other
Thermal - heat energy
Elastic potential - stretched and compressed
Nuclear - stored in atom nuclei
Gravitational potential - stored when lifted
Kinetic - moving objects
energy transfers
Heating - conduction, convection, radiation
Electrically - current flow
Radiation - light and sound waves
Mechanically - by a force moving
3 types of thermal energy transfer
conduction - heat through solids —> vibrating particles pass energy
convection - heat through fluids (liquids and gases) —> hot rise, cold sinks —> forms a current
radiation - heat by infrared waves —> no particles needed
what are dark, matte surfaces good at
absorbing and emitting radiation
what are shiny, white surfaces good at
reflect radiation well
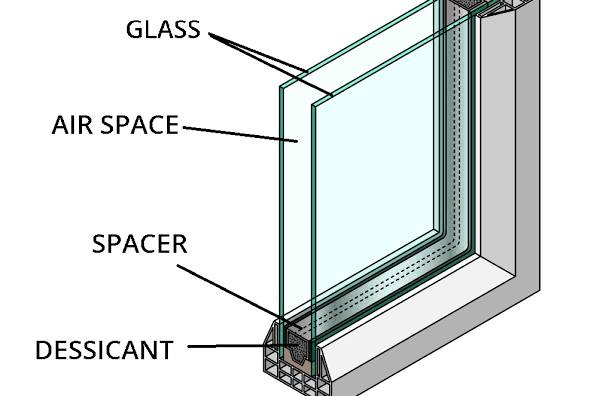
how to reduce unwanted energy transfer
insulation —> foam + double glazing (two layers of glass with a space of air between them)
trapped air prevents convection
shiny surfaces reduce radiation
what is the law of conservation of energy
GPE lost = KE gained when falling
energy isn’t made or gained or lost
what are the energy transfers for electricity generation
fuel (chemical or nuclear)
thermal
kinetic (turbines)
electrical
fossil fuels pros + cons
pros = reliable, generates lots of energy
cons = pollution, non-renewable
nuclear pros + cons
pros = no CO2, generates lots of energy
cons = expensive, radioactive waste
solar pros + cons
pros = no pollution, renewable
cons = weather-dependant, expensive
wind pros + cons
pros = clean, renewable
cons = noisy, unreliable
hydroelectric pros + cons
pros = reliable, can start producing electricity quickly —> water is stored in dam —> water is released —> turbines start moving
cons = requires building a dam which can flood large areas + disrupt river ecosystems
geothermal pros + cons
pros = constant source —> underground
cons = only in certain areas
tidal/wave pros + cons
pros = predictable/reliable —> waves move and turbines move —> generates electricity
cons = expensive + limited locations