Chemistry Terms & Definitions: Nucleic Acids, Carbs & Proteins
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What are subatomic particles?
protons, neutrons, electrons (make up atom)
What is an atom?
Smallest unit of element
What are molecules?
two or more atoms bonded together
What are macromolecules?
large, complex, organic molecules
What are the 4 macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
What are carbohydrates result?
glucose and cellulose
What are lipids result?
fats and phospholipids
What are proteins result?
enzymes and antibodies
What do carbohydrates serve as?
fuel and building materials
What are the groups of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
What are monosaccharides?
one simple sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose)
What are disaccharides?
two monosaccharides joined by covalent bond
What are polysaccharides?
long chains of monosaccharides liked by glycosidic bonds
What is the storage in polysaccharides?
starch and glycogen
What is starch?
storage form of glucose in plants
What is glycogen?
Storage form of glucose in animals
What are structural of polysaccharides?
Cellulose and chitin
What is cellulose?
straight, unbranched structure of fiber like strands (cell walls)
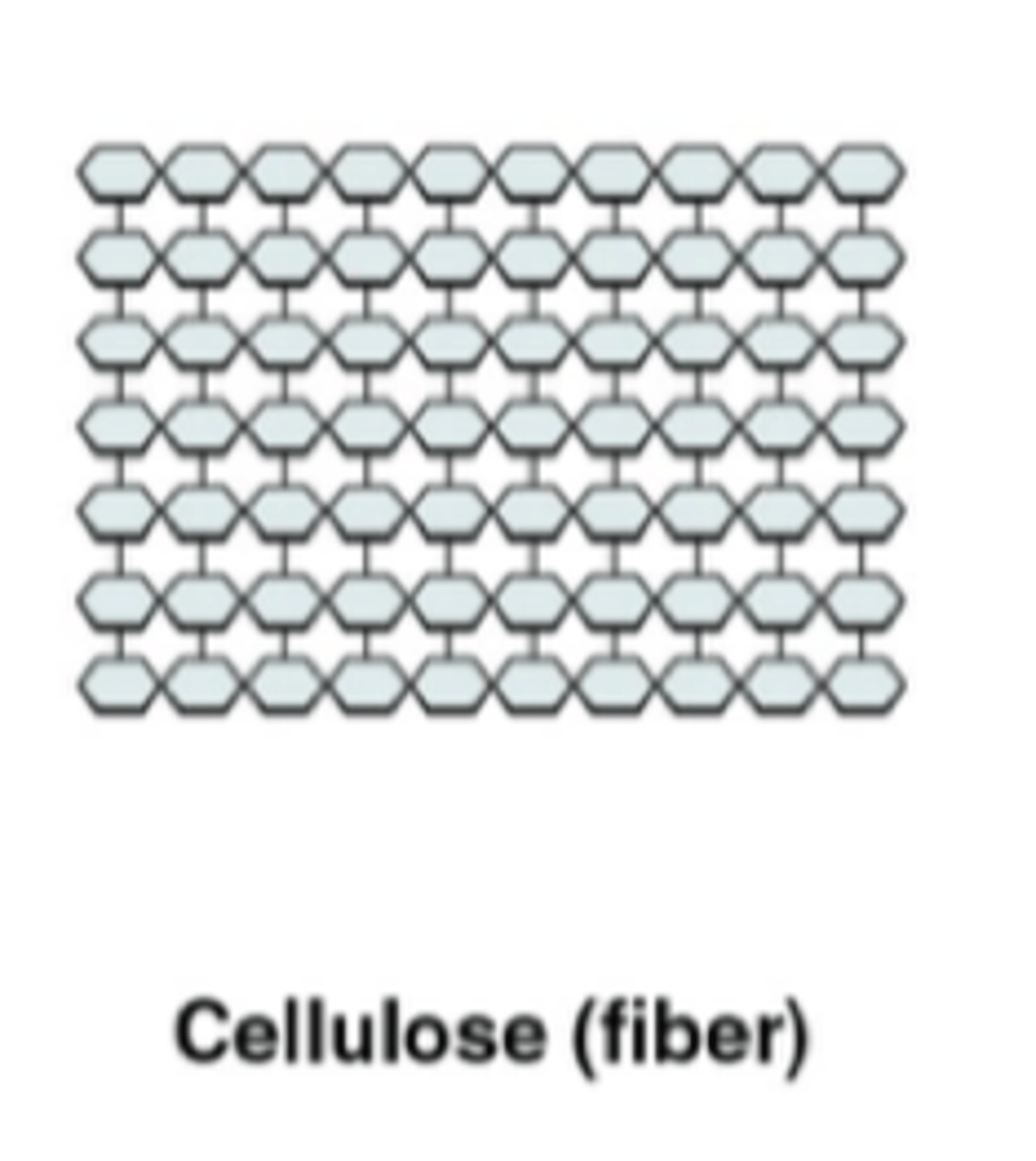
What is chitin?
structural polysaccharide in insects
What are lipids characteristics?
non-polar, hydrophobic molecules
What are the 3 types of lipids?
triglycerides (fats), phospholipids, steroids
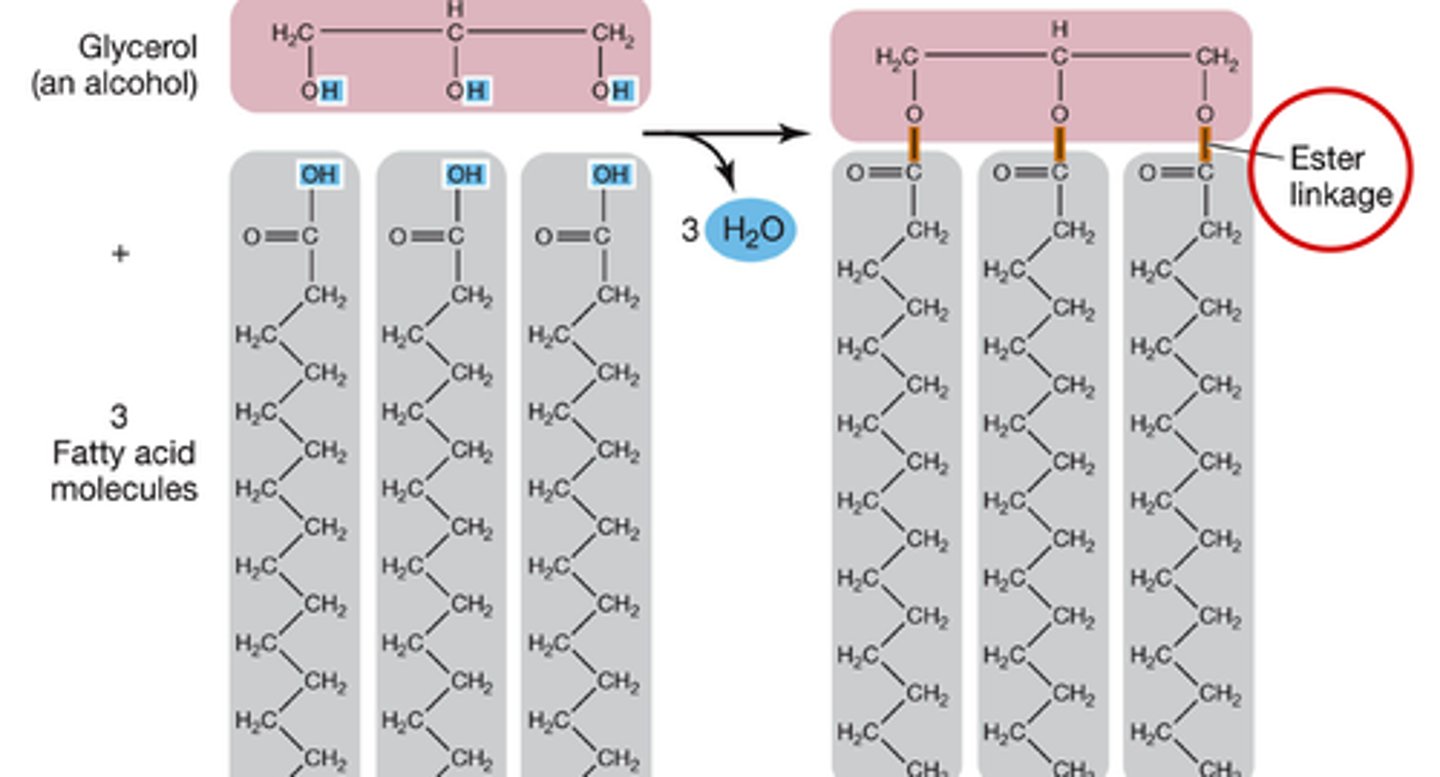
What are triglycerides?
made of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
joined by ester bonds
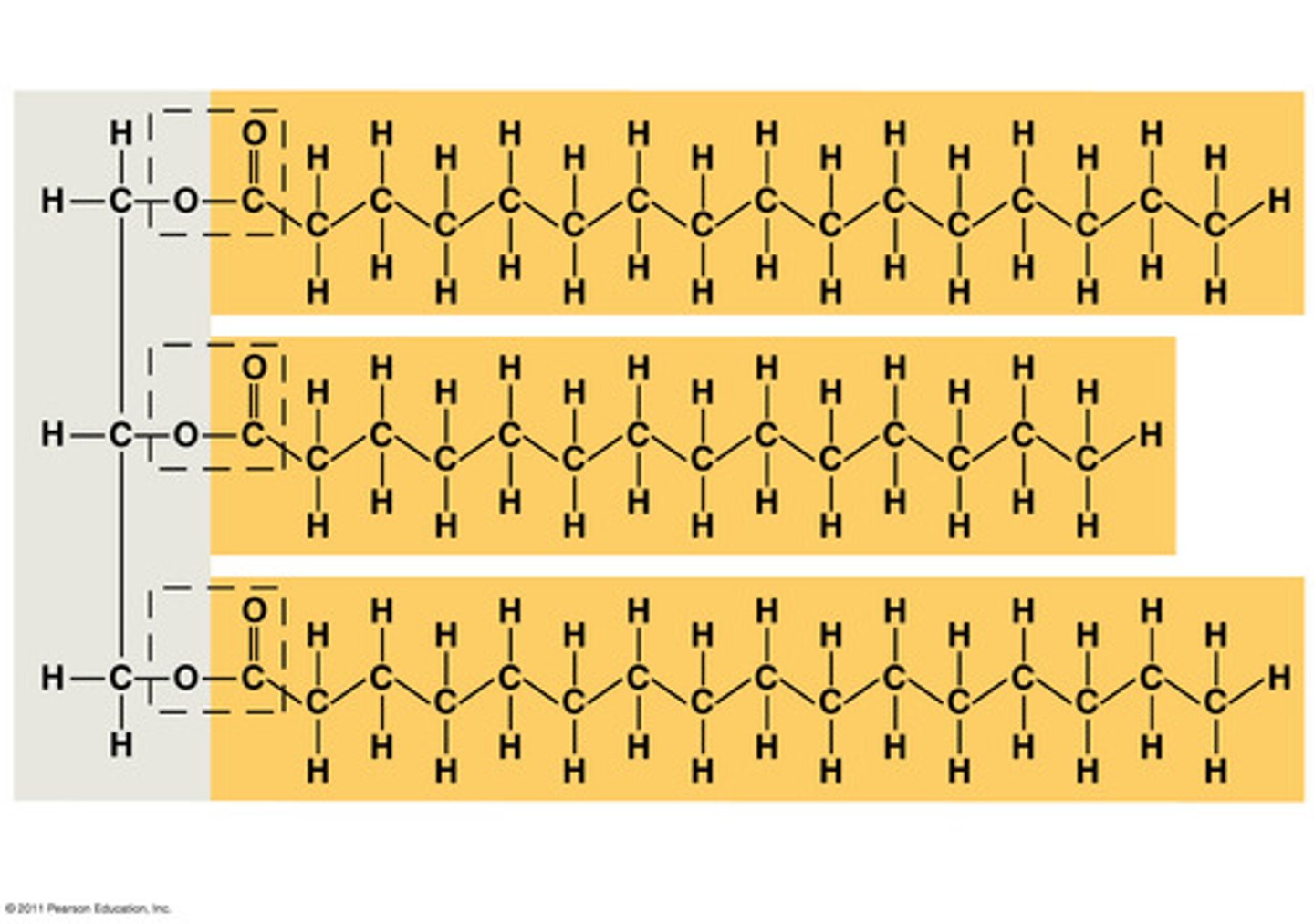
What are saturated fats?
contain NO double bonds (solid)
What are unsaturated fats?
have 1 or more double bond (liquid)
What are phospholipids?
Two fatty acids, glycerol, and a phosphate group
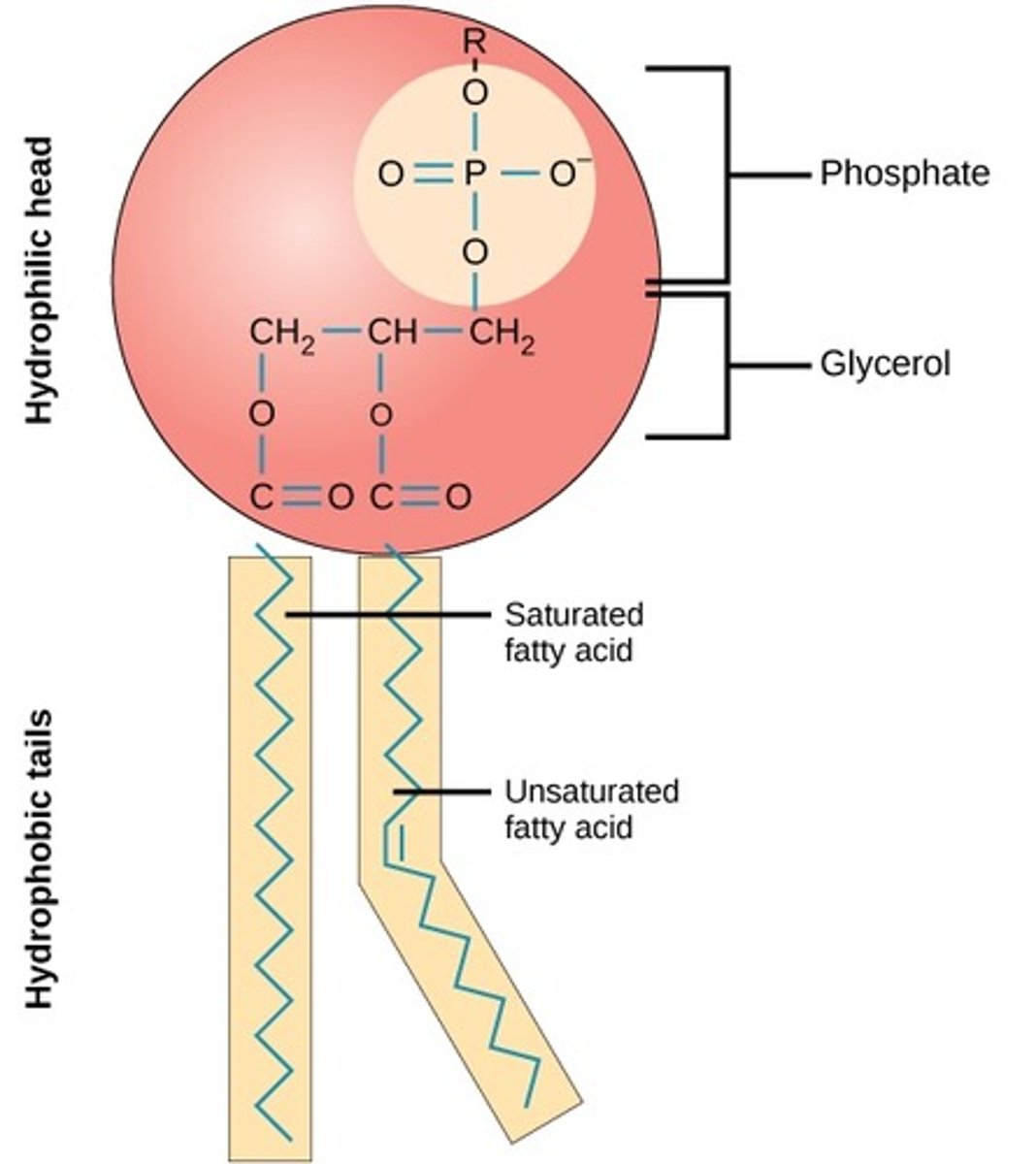
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails creating cell membranes
What are steroids?
4 ringed carbon structure
What is a common steroid?
cholesterol
What is an ester linkage?
formed through dehydration reactions between hydroxyl and carbonyl groups
What are proteins made of?
amino acids linked by peptide bonds
What are structural functions in proteins?
provide support and shape (folding/coiling)
What are enzymatic functions in proteins?
speed up biochemical reactions
What are hormonal functions in proteins?
coordinate cellular activities
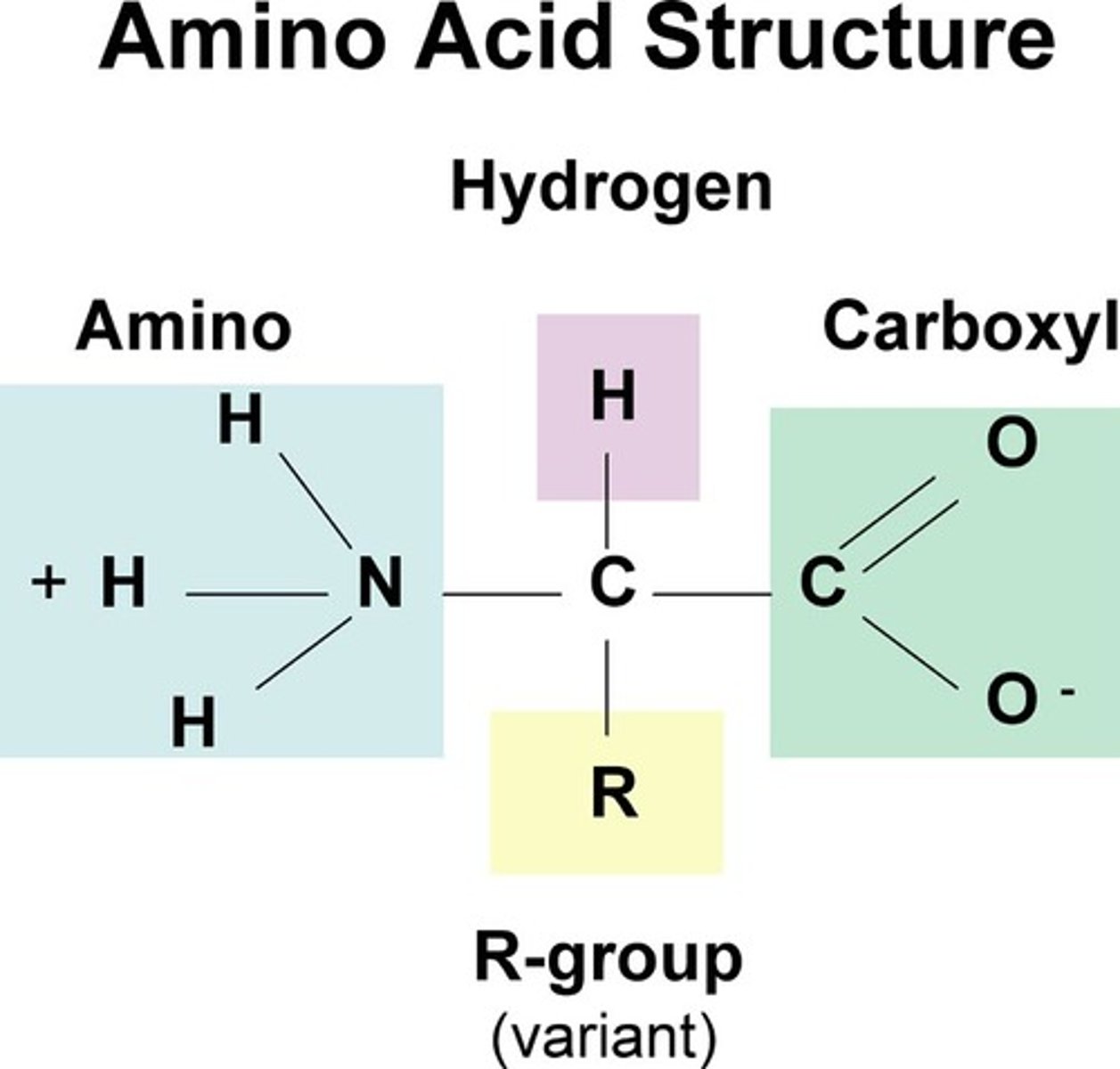
Describe the structure of an amino acid
-amino group (NH2)
-carboxyl group (COOH)
-hydrogen atom (H)
-R group
What is an R group?
side chain that varies with each amino acid and determines its properties
What is nonpolar group?
hydrophobic, often inside of proteins
What are polar groups?
hydrophilic, interact with water and often exterior
What are charged groups?
acidic or basic, can form ionic bonds
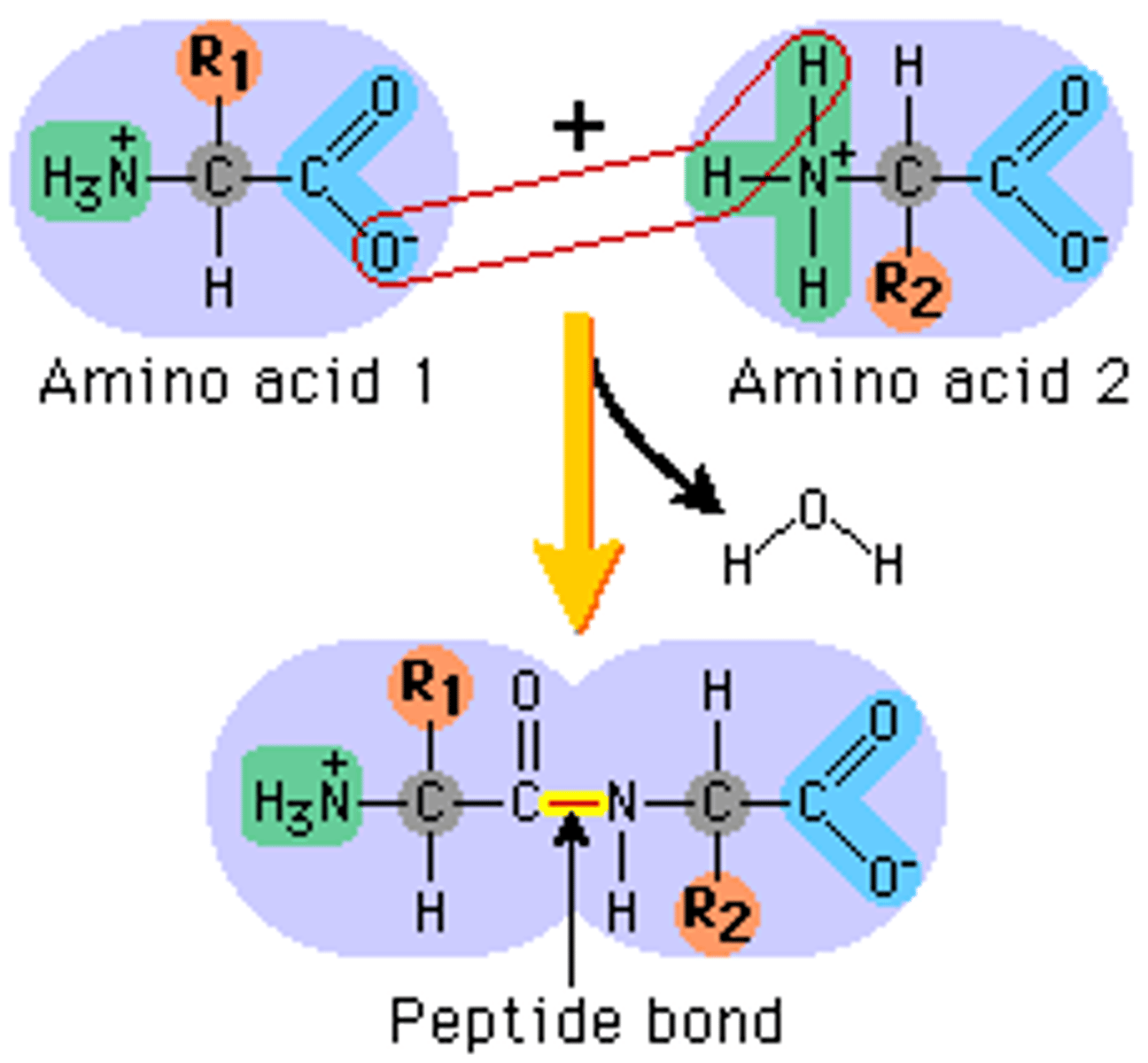
What are peptide bonds?
form between amino group and carboxyl group in amino acids through dehydration reactions
List the levels of biological organization from smallest to largest
subatomic, electron, nucleolus, protons and neutrons, atom, molecule, macromolecules, monomer, polymer
What biological macromolecules have ester linkages?
lipids
What biological macromolecules have glycosidic linkages?
carbohydrates
What biological macromolecules have peptide bonds?
proteins
What are ester linkages?
a covalent bond that links lipids
What functional groups make up carbhydrates?
hydroxyl and carbonyl
What are amino acids structure?
both carboxyl and amino groups that differ in properties due to R groups
What is hydrolysis?
The separation of two macromolecules by adding water.
What do dehydration reactions do?
form new, longer, bonds by removing water molecule
Carbohydrates serve as what?
energy availability (processing) and structure (organization)
What are the 4 levels of protein structure?
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
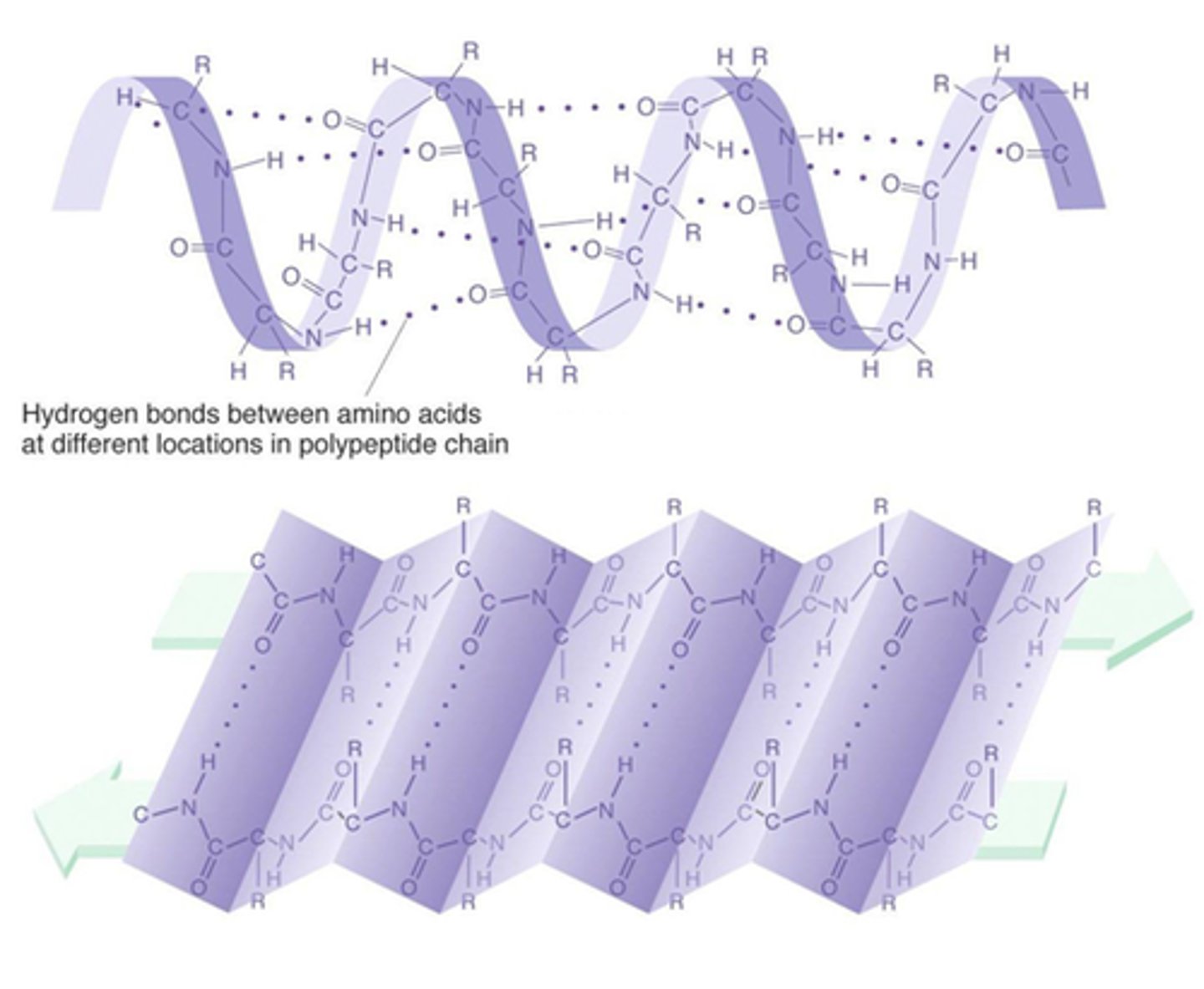
What is a proteins secondary structure?
folding or coiling into either an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet
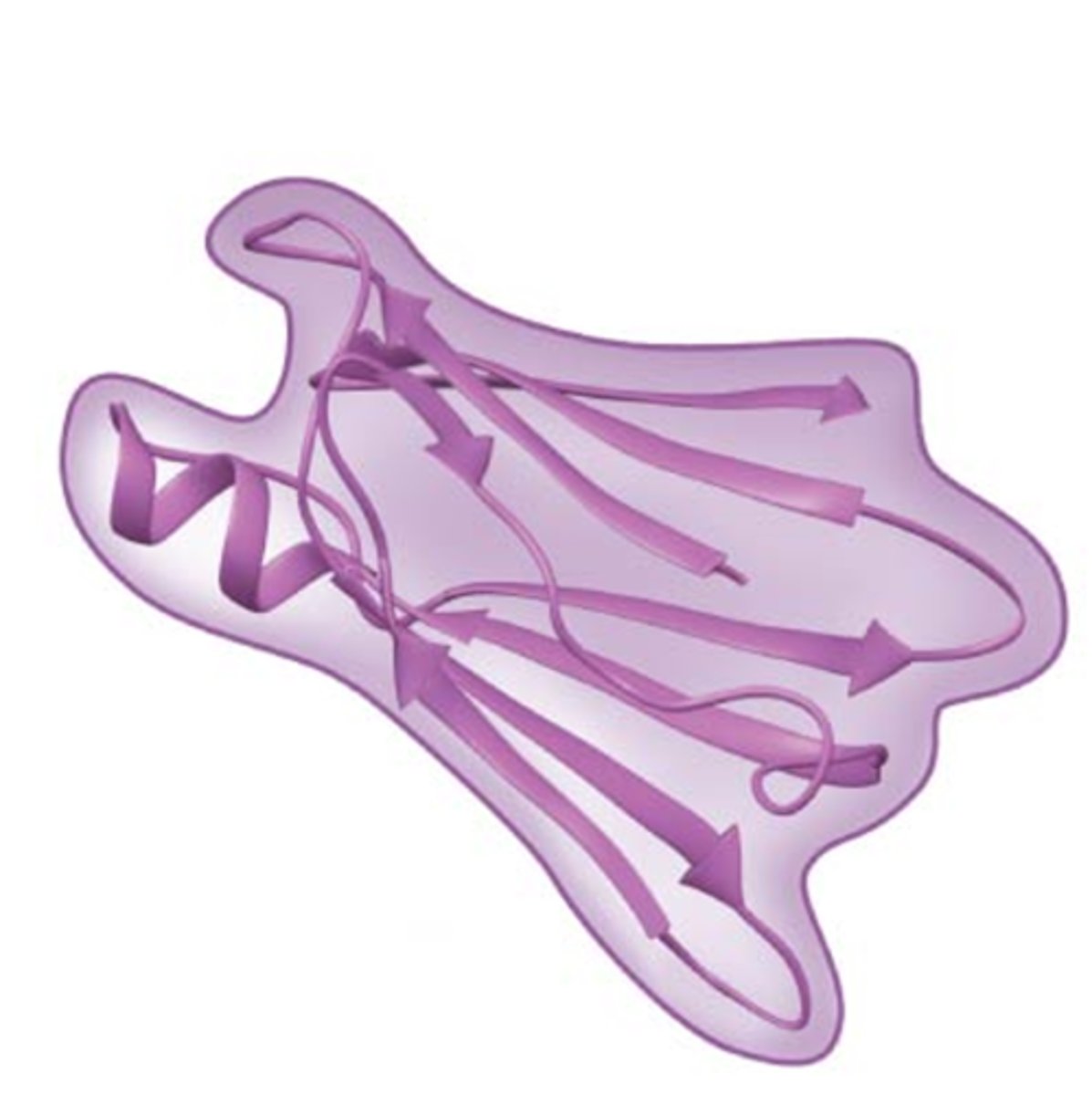
What is a proteins tertiary structure?
The overall three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide
What is a proteins quaternary structure?
overall protein structure made of 2 or more polypeptides
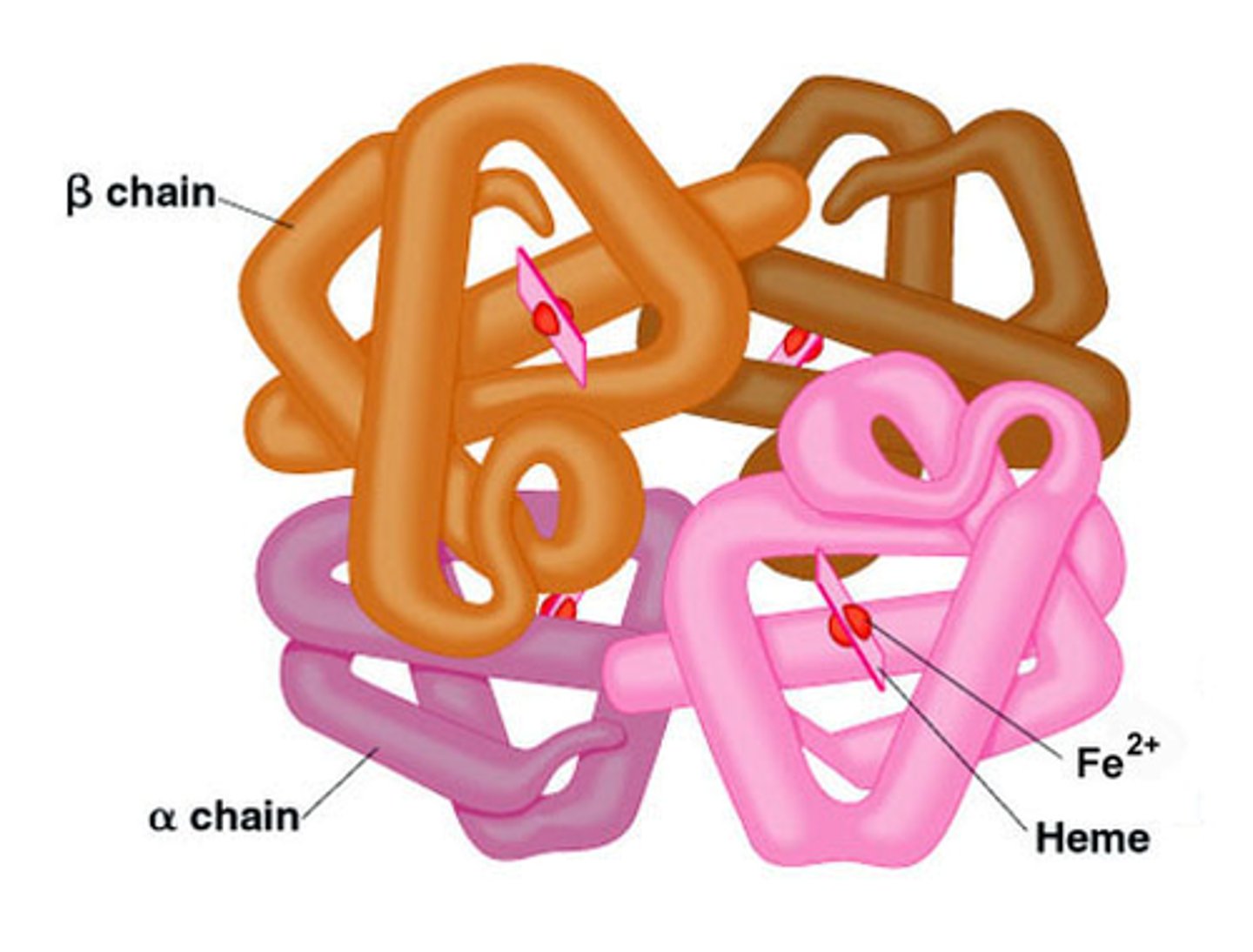
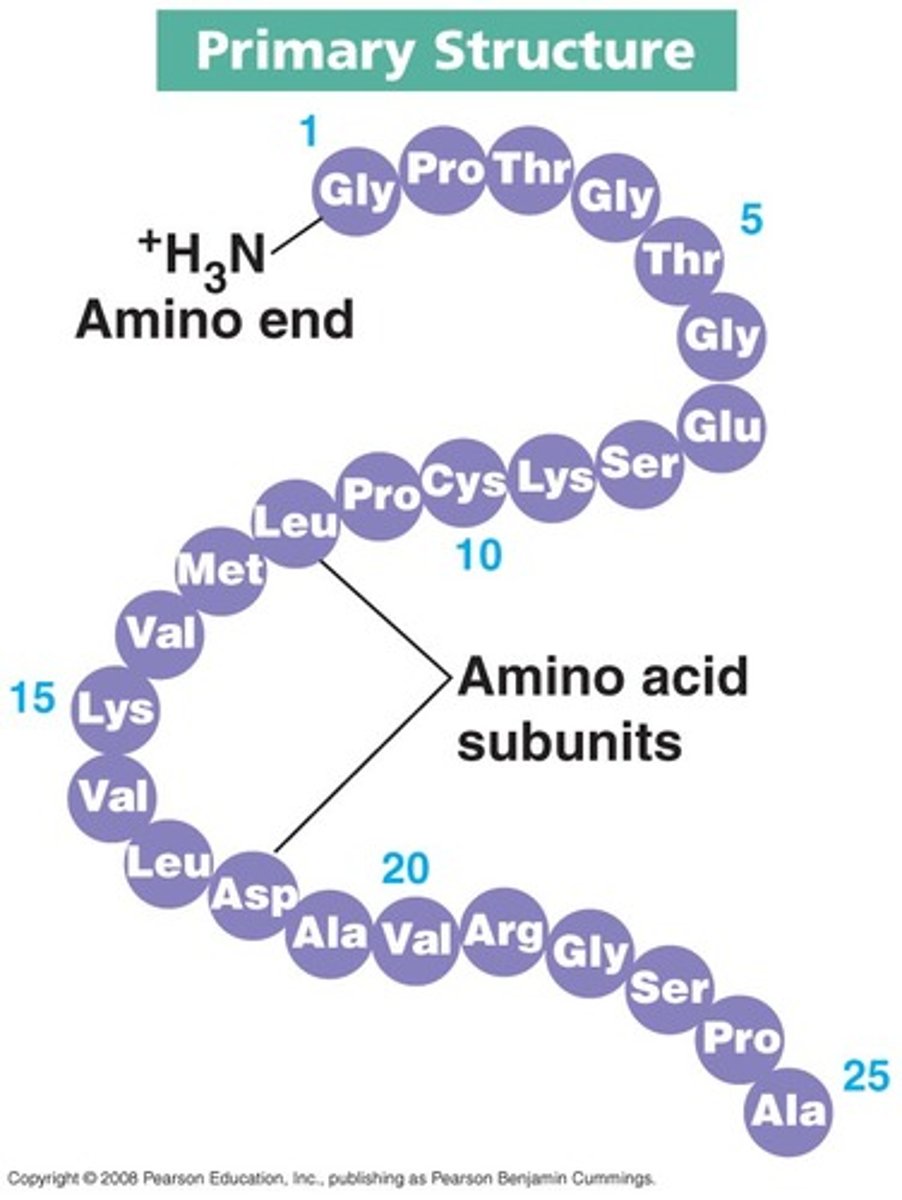
What is a proteins primary structure?
sequence of amino acids (growing chain)
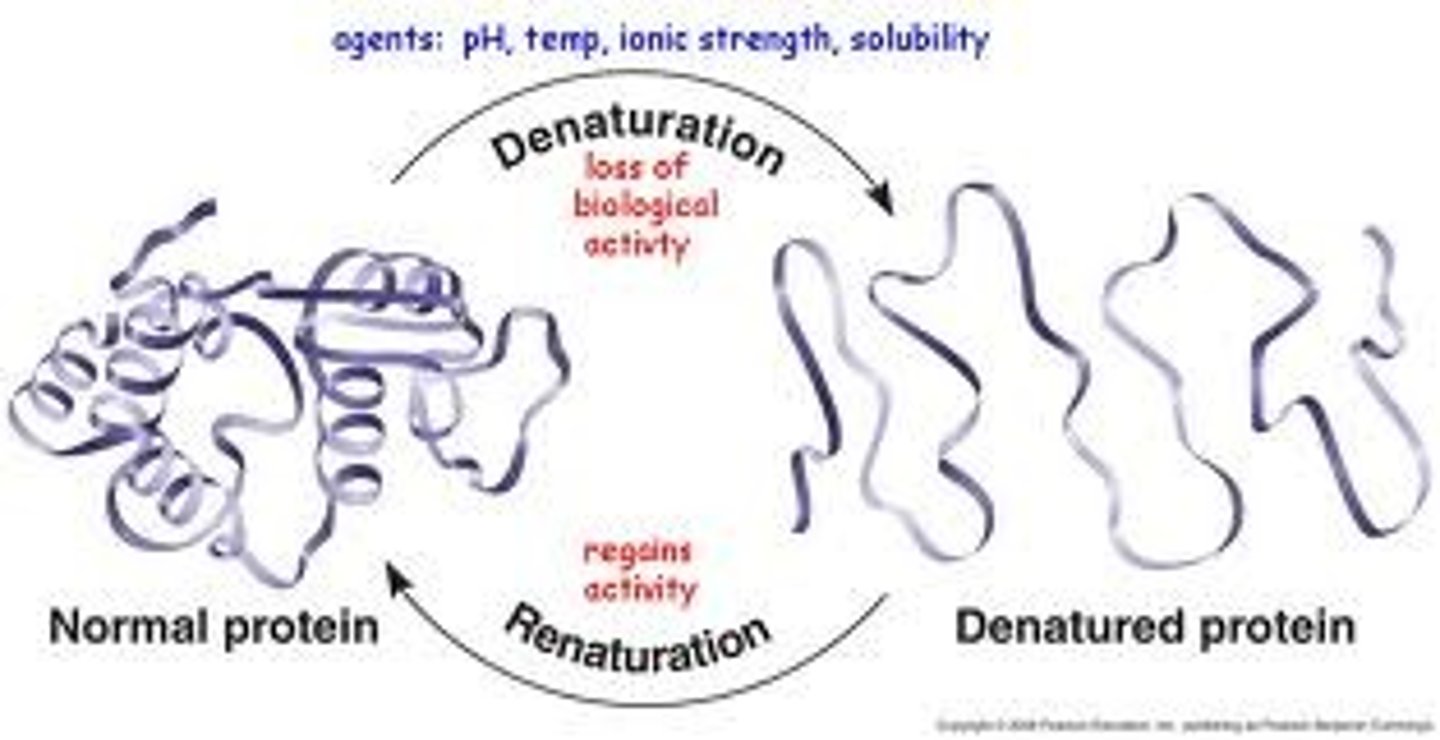
What is denaturation?
protein unravels/loses og shape changing function due to chemicals/head
What is a pyrimidine?
single-ringed nitrogenous base (ATU)
What determines the function of a protein?
Amino acid sequence, shape and structure, and whether or not its been denatured
What is a purine?
a double-ringed nitrogenous base (A and G)
Sometimes, Elephants, Point and Nag, About, Moles, Mighty, Migration, Patterns
Subatomic, electron, protons and neutrons (nucleus), atom, molecule, macromolecules, monomers, polymer
What functional groups make up lipids?
hydroxyl and carboxyl but have less oxygen
What functional groups make up nucleic acids?
Amine group (+) phosphate group (-) and sugar
What functional groups make up protein?
amino and carboxyl and R group
Are carbohydrates polar and nonpolar?
non polar
Are lipids polar and nonpolar?
nonpolar (phospholipids are both)
Are nucleic acids polar and nonpolar?
polar
Are proteins polar and nonpolar?
polar sides, but R-group can be either
What are nucleic acids bonds?
hydrogen bonds
What are proteins bonds?
peptides, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds
What are carboohydrates monomer?
monosaccharide
What are lipids monomer?
They dont have one
What are nucleic acids monomer?
nucleotides
What are proteins monomer?
amino acids
What terms go with carbohydrates?
glycerol
What terms go with lipids?
steroids and saturated/unsaturated
What terms go with nucleic acids?
DNA, RNA, ATP and purine/pyrimidines
What terms go with proteins?
denaturation, conformation (folding/3D structure)
How are carbohydrates used?
short term energy storage and structure
How are lipids used?
long term energy storage and chemical massagers
How are nucleic acids used?
NOT storage, but energy processing, messengers, and information
How are proteins used?
The body uses protein for energy when carbs aren't available.