Biological molecules
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I want to die
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Name the three monosaccharides
Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose
What comprises Maltose?
Two alpha glucose molecules joined together
What comprises Sucrose?
a glucose and a fructose molecules
What comprises Lactose?
a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
Where water molecules break apart chemical bond
Describe the non reducing sugar test
Add benedicts reagent to a sample and heat it in a water bath that has been brought to boil.
If the test is positive it will form a coloured precipitate (blue green, yellow, orange, red ) depending on concentration
If the result is negative, you need to get a sample of the test solution, adding dilute hydrochloric acid and carefully heat it in a water bath that has been brought to boil.
you then neutralise it sodium hydrogencarbonate
you carry out the test for reducing sugar where a positive result should form
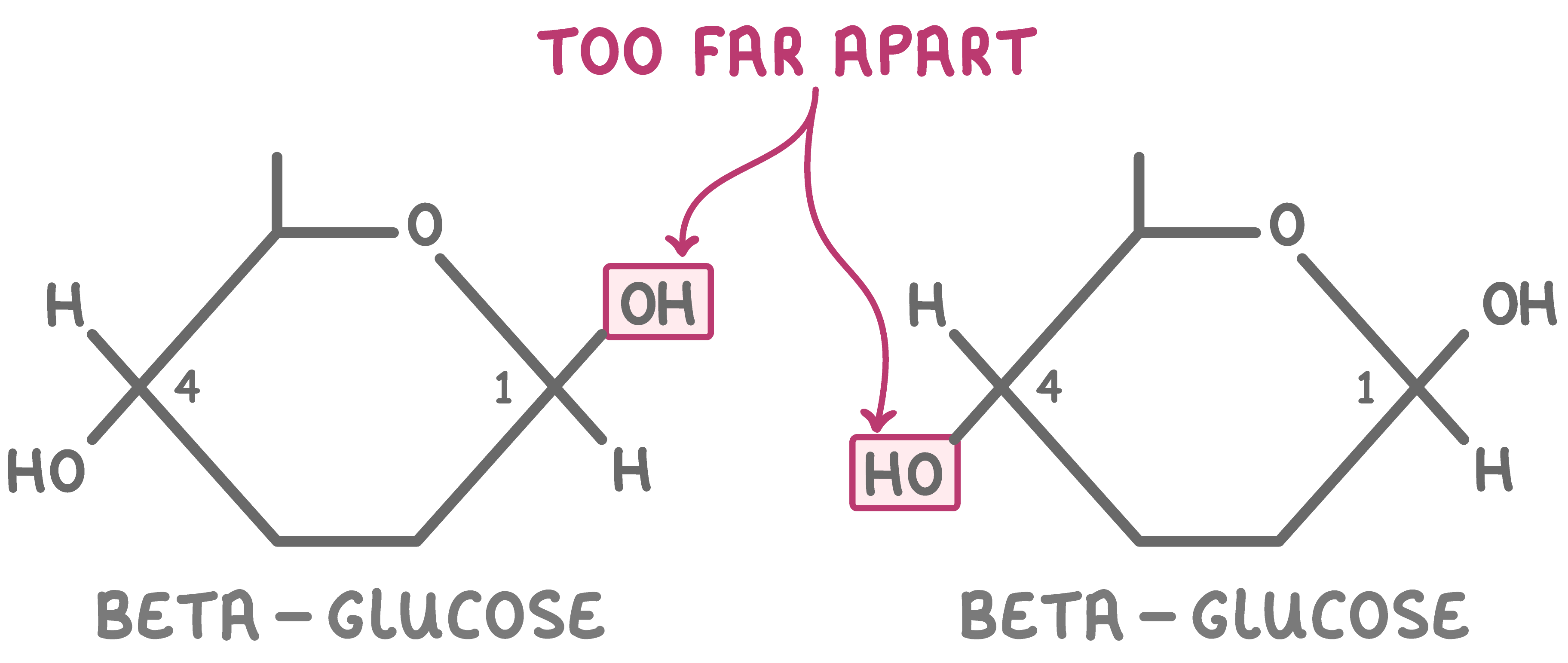
Draw a beta glucose molecule
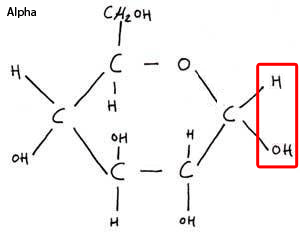
Draw an alpha glucose molecule
Starch - the difference between amylopectin and amylose
Amylose is long unbranched chain of alpha glucose. The angles of the glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure, almost like a cylinder. This makes it compact, so its really good for storage because you can fit more into a small space.
on the other hand amylose is a long branched chain of alpha glucose. It side branches allow the enzymes that break down the molecule to get at the glycosidic bonds easily which means that the glucose can be released quickly.
Describe the structure of cellulose
Cellulose is made of long unbranched chains of beta-glucose
each second beta glucose molecule is inverted
when the beta glucose molecules bond, they form straight cellulose chains
the cellulose chains are linked together by hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres called microfibrils. The strong fibres means cellulose provides structural support for cells.
Describe the structure of a triglyceride
A triglyceride has three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule
A fatty acid has a double bond with carbon and oxygen, a single bond with an r ground and a hydroxide
Triglycerides are joined together in a condensation reaction
Whats the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid?
Saturated fatty acids don’t have any double bonds between their carbon atoms. The fatty acid is saturated with hydrogen.
Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond between carbon atoms, which cause the chain to kink
What is the structure for a phospholipid?
Phospholipids have a similar structure to triglycerides, however one of the fatty acids have been replaced by a phosphate group
How does the structure of a triglyceride relate to their function
The long hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acid contains lots of chemical energy - a load of energy is released when they’re broken down. Because of trhese ails, lipids contain more energy than carbohydrates
How does the structure of phopspholipids relate to their function.
Phospholipids - their heads are hydrophylic and their tails are hydrophobic so they can form a double layer with their heads facing out towards the water on either side.
Describe the test for lipids
Add ethanol and water to the test tube - shake and a white emulsion should form.