Muscle Length Testing Exam Review
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
muscle length testing
A procedure involving passive stretching of a muscle in the opposite direction of its action.
proximally
where does stabilization occur in muscle length testing?
Watch for any compensation.
What should be monitored during muscle length testing?
passive insufficiency
A condition where a two-joint muscle is lengthened to its fullest extent at both joints.
The full range of motion of each joint that the muscle crosses.
What does passive insufficiency prevent?
active insufficiency
A condition where a two-joint muscle is maximally shortened across both joints.
When a two-joint muscle is fully shortened at both joints, its ability to produce force decreases.
What happens to force output during active insufficiency?
Flexibility
the ability of muscles, joints and tissues to move through an unrestricted, pain free range of motion
inversion/eversion
Compensation for gastroc/soleus testing
-Posterior Pelvic Tilt
-Knee Flexion
-Elevation of the non-test limb off the table
What are the compensations for straight leg raise testing?
-Low back extension
-Anterior pelvic tilt
-Trunk Rotation
What are the compensations for pec major testing?
-Trunk/pelvic rotation
-Anterior or lateral pelvic tilt
-Hip flexion or internal rotation
What are the compensations for obers/modified obers ?
The patient should be lying on the flexed non-test limb.
What position should the patient be in for Stabilization for Ober's/Modified Ober's?
Anterior/upward pressure is applied to prevent pelvic tilt or rotation.
What type of pressure is applied to the pelvis during Stabilization for Ober's/Modified Ober's?
-Anterior Pelvic Tilt
-Thoracic/lumbar extension
Compensation for the lats
Decrease
Does anterior pelvic tilting increase or decrease the apparent hamstring length?
Increase
Does posterior pelvic tilting increase or decrease the apparent hamstring length?
Supine with both legs extended
What position should the patient be in for the Straight Leg Raise (SLR) procedure?
Passively flexes the test hip with the knee in full extension
What does the SPTA do during the Straight Leg Raise (SLR) procedure?
Supine position with the tested hip and knee flexed.
What is the position of the patient during the Soleus testing procedure?
Passively dorsiflex the left ankle.
What action does the SPTA perform during the Soleus testing procedure?
Supine hook lying with arms interlaced behind head
What position should the patient be in for the Pec Major General Muscle Length Testing?
Arms are passively dropped, elbows toward the table
What is the procedure for the arms during the Pec Major General Muscle Length Testing?
- supine hook lying
- arms resting at the sides
- elbows extended and palms upward
What position should the patient be in for testing the length of the Pec Major Clavicular Head muscle?
Bend the arm to a 90° angle with the shoulder turned outward and the elbow straight.
What is the initial step in testing the muscle length of the clavicular head of the pectoralis major?
Slowly abduct the arm to 90°.
What is the second step in the muscle length testing procedure for the clavicular head of the pectoralis major?
- supine hook lying
- arms resting at the sides
- elbows extended and palms upward
What position should the patient be in for the Pec Major Sternal Head Muscle Length Testing?
Bend the arm to a 90° angle with the shoulder turned outward and the elbow straight.
What is the first step in the Pec Major Sternal Head Muscle Length Testing procedure?
Slowly abduct the arm to 135°.
What is the final step in testing the length of the Pec Major Sternal Head muscle?
Patient is in supine with arms resting on the abdomen or to the side.
What is the starting position for pec minor muscle length testing?
Elbows should be supported with a towel roll.
How should the elbows be supported during pec minor muscle length testing?
The patient should be in hooklying to ensure the back is flat on the table.
What position should the patient's back be in during pec minor muscle length testing?
Rectus Femoris
What muscle is Ely's test for?
tensor fasciae latae
What muscle is Ober's Test for?
Iliopsoas
What muscle is the prone extension test for?
- Rectus Femoris
- Illiopsoas
- TFL
- Sartorius
Which muscles can Thomas/Modified Thomas test for?
Both knees are brought to the chest while lying supine on the plinth.
What is the Thomas Test?
One knee is lowered while lying supine on the plinth.
What is the Modified Thomas Test?
Hamstring
What muscle is straight leg raise test for?
proximal hamstring
What portion of the hamstring does straight leg raise test for?
Distal hamstring
What portion of the hamstring does 90/90 test for?
The knee is bent to 90 degrees.
What is the knee position in Ober's test?
The knee is extended.
What is the knee position in Modified Ober's test?
Less than 20 degrees of dorsiflexion.
What is a positive result in the Soleus Muscle Length Test?
20 degrees or greater (≥ 20) of dorsiflexion.
What is a negative result in the Soleus Muscle Length Test?
Less than 10 degrees of dorsiflexion.
What indicates a positive Gastroc Muscle Length Test?
10 degrees or greater (≥10) of dorsiflexion.
What indicates a negative Gastroc Muscle Length Test?
Proximal
What part of the hamstring is straight leg raise test for?
Distal
What part of the hamstring does 90/90 hamstring test for?
Thigh lifts off the table (indicating hip flexion).
What indicates a positive result in the Thomas Test for Iliopsoas?
Thigh remains flat on the table.
What indicates a negative result in the Thomas Test for Iliopsoas?
abducted hip and hip IR
Thomas Test: Positive Test for TFL
abducted hip and hip ER
Thomas Test: Positive Test for Sartorius
- less than 80 degrees of knee flexion
- the thigh flat on the table
What indicates a positive Thomas Test for Rectus Femoris?
- 80 degrees or greater of knee flexion
- the thigh flat on the table
What indicates a negative Thomas Test for Rectus Femoris?
It indicates hip flexion.
What does it indicate if the thigh is off the table during the Thomas/Modified Thomas Test?
Knee flexion is less than 80 degrees.
What knee flexion degree shows tightness in the rectus femoris and iliopsoas muscles during the Thomas or Modified Thomas Test?
If the knee is straight and the thigh falls to the table, it means the rectus femoris is tight.
How can an SPTA figure out if it's the rectus femoris or iliopsoas that's doing the hip flexion during the Thomas test?
Pec minor
Which muscle is most likely tight with rounded shoulders posture?
posterior acromion to the plinth
To test for pec minor tightness, you are measuring the distance from the ________ to the _________
The quadriceps must activate to prevent knee flexion.
What happens if the line of gravity falls posterior to the axis of rotation at the knee?
Quadriceps
Which muscle group prevents knee flexion when the line of gravity is behind the knee's axis of rotation?
The hamstrings must activate to prevent knee extension.
What happens if the line of gravity falls anterior to the axis of rotation at the knee?
Hamstrings
Which muscle group activates to prevent knee extension when the line of gravity is anterior to the axis of rotation at the knee?
Swayback Posture
-flattened lumbar curve and trunk angled posteriorly
Military Posture
-increased lumbar lordosis
-low back extensors and hip flexors are tight
Flatback Posture
-decreased lumbar curve
-increased posterior pelvic tilt & hip flexion
Validity
how ACCURATE a tool is
Reliability
how CONSISTENT a tool is
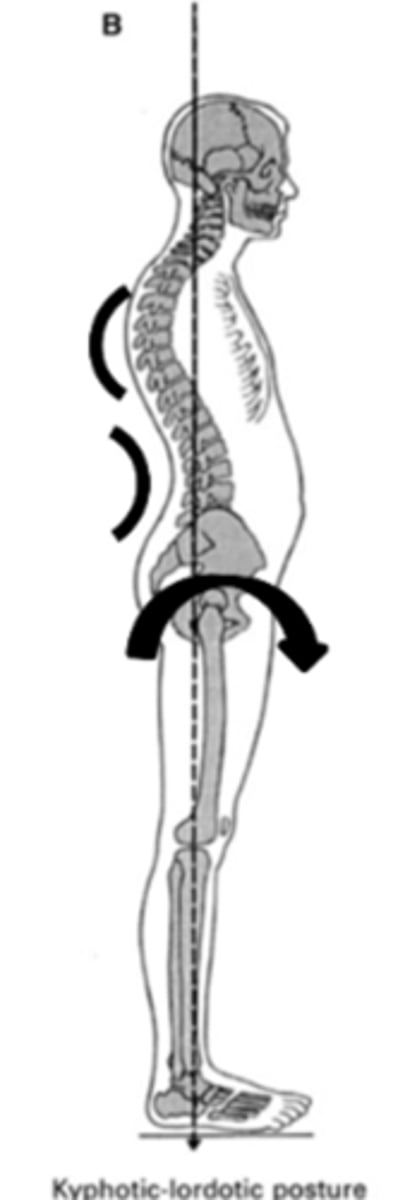
Kyphotic/Lordotic Posture
- increased thoracic kyphosis
- increased lumbar lordosis
- tight low back extensors
Cross-Sectional Study
data is collected from different participants at a single point in time to assess the prevalence
Longitudinal Study
Tracks the same participants over time to observe changes
Experimental Study
used to establish cause and effect
Non-Experimental Study
the researcher collects data without introducing an intervention
It measures the physical bone length of your legs.
What does true/actual leg length measure?
It measures how your legs look from the outside.
What does apparent leg length measure?
Pelvic tilt, muscle imbalances, posture, etc.
What can cause one leg to appear shorter than the other?
Supine
What position should the patient be in for measuring true leg length?
From the ASIS to the umbilicus
What is the first measurement taken when measuring true leg length?
To ensure the pelvis is aligned
Why is the measurement from ASIS to the umbilicus taken?
Correct the pelvis alignment with a bridge
What should be done if the pelvis is not aligned during measurement?
From ASIS to ipsilateral medial malleolus
What is the second measurement taken for true leg length?
Activates the abdominals and hip extensors which work in a muscle synergy
How does a bridge work to bring the pelvis to neutral?