Topic 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Last updated 4:03 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
How to work outSurface area to volume ratio and how does an organisms size affect it?
* The surface area of an organism divided by its volume
* the larger the organism, the smaller the ratio
* the larger the organism, the smaller the ratio
2
New cards
Factors affecting gas exchange:
* diffusion distance
* surface area
* concentration gradient
* temperature
* surface area
* concentration gradient
* temperature
3
New cards
What is Ventilation?
* Inhaling and exhaling in humans
* controlled by diaphragm and antagonistic interaction of internal and external intercostal muscles
* controlled by diaphragm and antagonistic interaction of internal and external intercostal muscles
4
New cards
What is Inspiration?
* External intercostal muscles contract and internal relax
* pushing ribs up and out diaphragm contracts and flattens
* air pressure in lungs drops below atmospheric pressure as lung volume increases
* air moves in down pressure gradient
* pushing ribs up and out diaphragm contracts and flattens
* air pressure in lungs drops below atmospheric pressure as lung volume increases
* air moves in down pressure gradient
5
New cards
What is Expiration?
* External intercostal muscles relax and internal contract
* pulling ribs down and in
* diaphragm relaxes and domes
* air pressure in lungs increases above atmospheric pressure as lung volume decreases
* air forced out down pressure gradient
* pulling ribs down and in
* diaphragm relaxes and domes
* air pressure in lungs increases above atmospheric pressure as lung volume decreases
* air forced out down pressure gradient
6
New cards
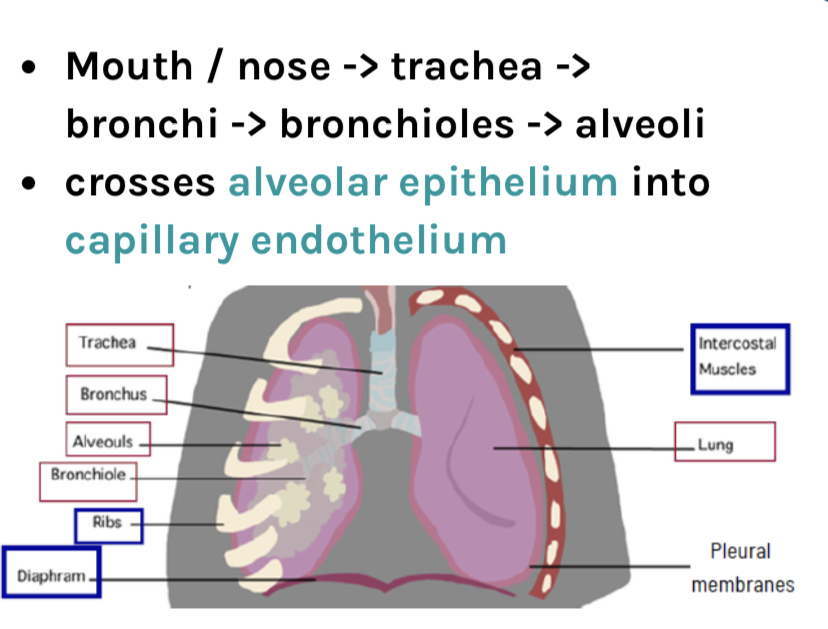
Describe the Passage of gas exchange:
* Mouth / nose → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
* crosses alveolar epithelium into capillary endothelium
* crosses alveolar epithelium into capillary endothelium
7
New cards
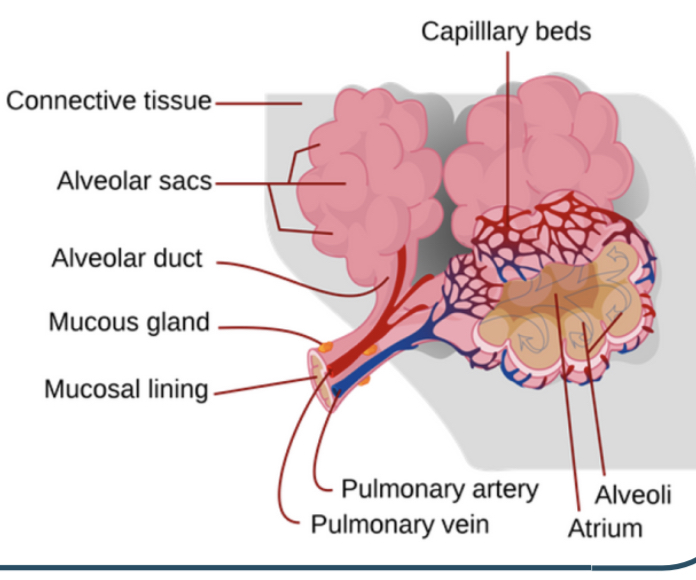
Describe Alveoli’s structure:
* Tiny air sacs
* highly abundant in each lung - 300 million
* surrounded by the capillary network
* epithelium 1 cell thick
* highly abundant in each lung - 300 million
* surrounded by the capillary network
* epithelium 1 cell thick
8
New cards
Why do large organisms need specialised exchange surface?
* They have a small surface area to volume ratio
* higher metabolic rate - demands efficient gas exchange
* specialised organs e.g. lungs / gills designed for exchange
* higher metabolic rate - demands efficient gas exchange
* specialised organs e.g. lungs / gills designed for exchange
9
New cards
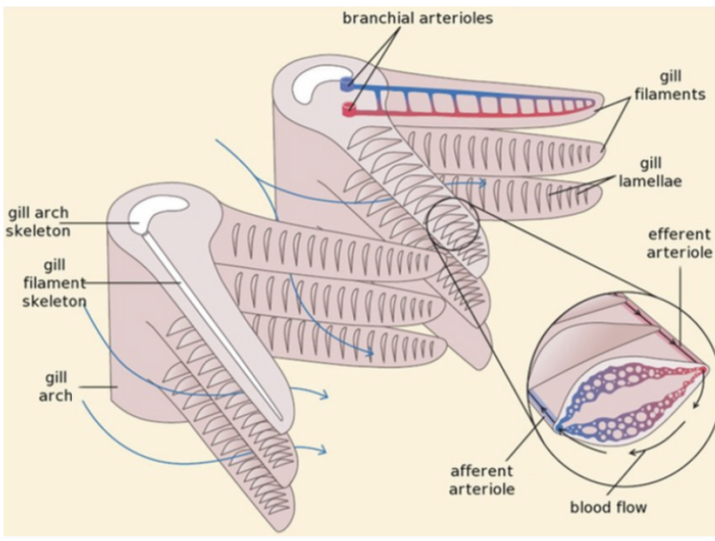
Describe the Fish gill anatomy:
* Fish gills are stacks of gill filaments
* each filament is covered with gill lamellae at right angles
* each filament is covered with gill lamellae at right angles
10
New cards
How does fish gas exchange surface provide a large surface area?
* Many gill filaments covered in many gill lamellae are positioned at right angles
* creates a large surface area for efficient diffusion
* creates a large surface area for efficient diffusion
11
New cards
Describe the Countercurrent flow:
* When water flows over gills in opposite direction to flow of blood in capillaries
* equilibrium not reached
* diffusion gradient maintained across entire length of gill lamellae
* equilibrium not reached
* diffusion gradient maintained across entire length of gill lamellae
12
New cards
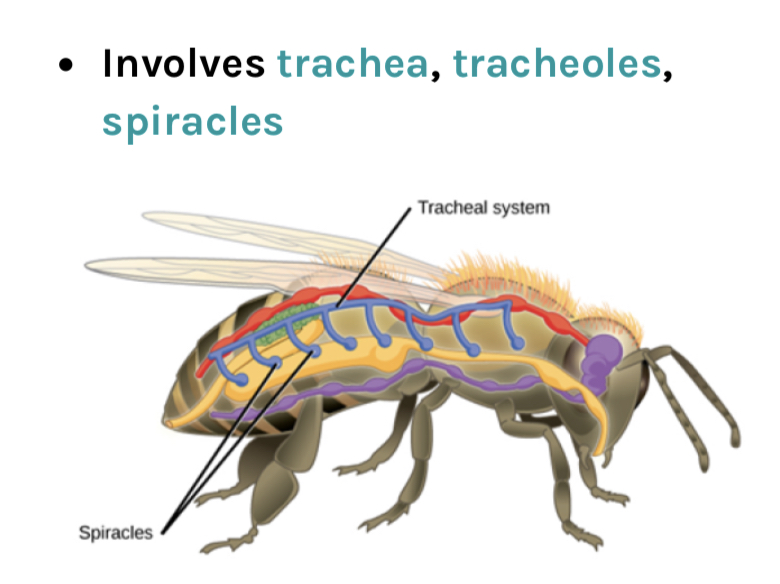
Name the three structures in the tracheal system:
Involves trachea, tracheoles, spiracles
13
New cards
How does the tracheal system provide a large surface area?
* Highly branched tracheoles
* large number of tracheoles
* filled in ends of tracheoles moves into tissues during exercise
* so larger surface area for gas exchange
* large number of tracheoles
* filled in ends of tracheoles moves into tissues during exercise
* so larger surface area for gas exchange
14
New cards
What is the purpose of Fluid-filled tracheole ends?
* Adaptation to increase movement of gases
* when insect flies and muscles respire anaerobically - lactate produced
* water potential of cells lowered, so water moves from tracholes to cells by osmosis
* gases diffuse faster in air
* when insect flies and muscles respire anaerobically - lactate produced
* water potential of cells lowered, so water moves from tracholes to cells by osmosis
* gases diffuse faster in air
15
New cards
How do insects limit water loss?
* Small surface area to volume ratio
* waterproof exoskeleton
* spiracles can open and close to reduce water loss
* thick waxy cuticle - increases diffusion distance so less evaporation
* waterproof exoskeleton
* spiracles can open and close to reduce water loss
* thick waxy cuticle - increases diffusion distance so less evaporation
16
New cards
What are the Dicotyledonous plants leaf tissues?
Key structures involved are mesophyll layers
(palisade and spongy mesophyll)
stomata created by guard cells
(palisade and spongy mesophyll)
stomata created by guard cells
17
New cards
Describe the Gas exchange in plants?
* Palisade mesophyll is site of photosynthesis
* oxygen produced and carbon dioxide used creates a concentration gradient
* oxygen diffuses through air space in spongy mesophyll and diffuse out stomata
* oxygen produced and carbon dioxide used creates a concentration gradient
* oxygen diffuses through air space in spongy mesophyll and diffuse out stomata
18
New cards
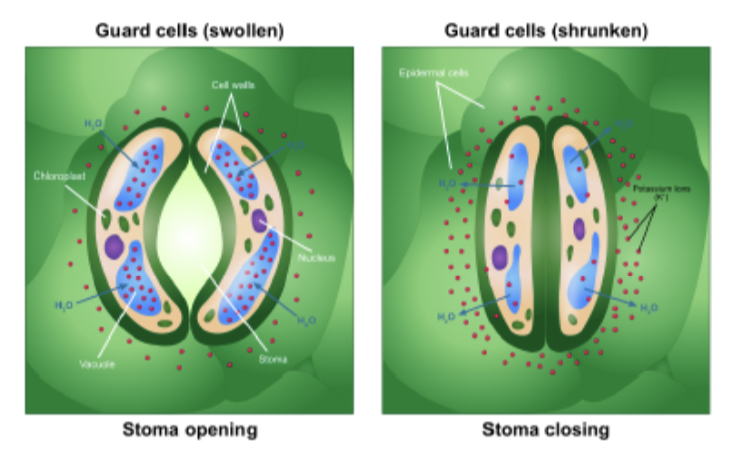
What is the Role of guard cells?
* swell - open stomata
* shrink - closed stomata
* at night they shrink, reducing water loss by evaporation
* shrink - closed stomata
* at night they shrink, reducing water loss by evaporation
19
New cards
What are Xerophytic plants?
* Plants adapted to survive in dry environments with limited water (e.g. marram grass/cacti)
* structural features for efficient gas exchange but limiting water loss
* structural features for efficient gas exchange but limiting water loss
20
New cards
What are the Adaptations of xerophyte?
* Adaptations to trap moisture to increase humidity -> lowers water potential inside plant so less water lost via osmosis
* sunken stomata
* curled leaves
* hairs
* thick cuticle reduces loss by evaporation
* longer root network
* sunken stomata
* curled leaves
* hairs
* thick cuticle reduces loss by evaporation
* longer root network
21
New cards
What is Digestion?
* Process where large insoluble biological molecules are hydrolysed into smaller soluble molecules
* so they can be absorbed across cell membranes
* so they can be absorbed across cell membranes
22
New cards
What are the Locations of carbohydrate digestion?
Mouth → duodenum → ileum
23
New cards
What are the Locations of protein digestion?
Stomach → duodenum → ileum
24
New cards
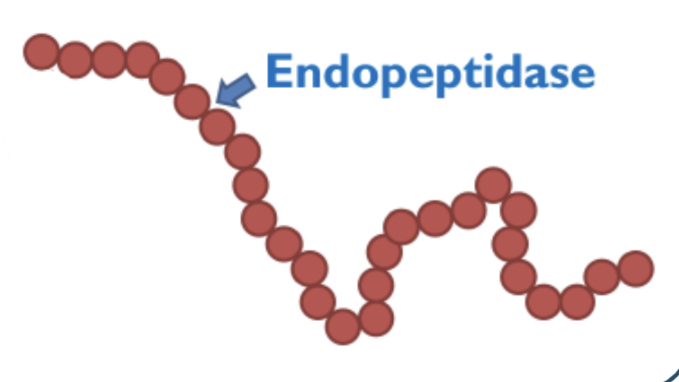
What is the role of Endopeptidases?
* Break peptide bonds between amino acids in the middle of the chain
* creates more ends for exopeptidases for efficient hydrolysis
* creates more ends for exopeptidases for efficient hydrolysis
25
New cards
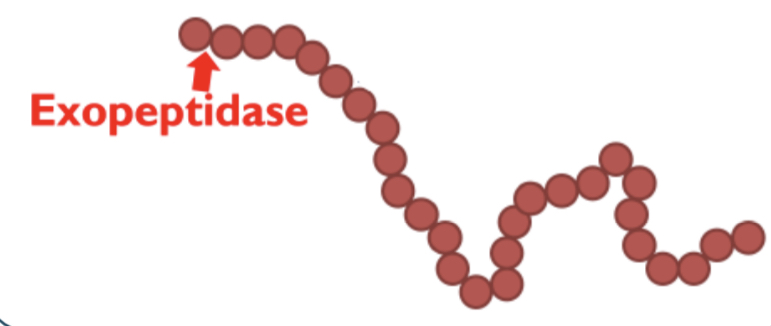
What is the role of Exopeptidases?
Break peptide bonds between amino acids at the ends of polymer chain
26
New cards
What is the role of Membrane- bound dipeptidases?
Break peptide bond between two amino acids
27
New cards
Describe the Digestion of lipids:
* Digestion by lipase (chemical)
* emulsified by bile salts (physical)
* lipase produced in pancreas
* bile salts produced in liver and stored in gall bladder
* emulsified by bile salts (physical)
* lipase produced in pancreas
* bile salts produced in liver and stored in gall bladder
28
New cards
What is the use of Lipase and where is it produced?
* Produced in pancreas
* Breaks ester bonds in triglycerides to form :
* monoglycerides
* glycerol
* fatty acids
* Breaks ester bonds in triglycerides to form :
* monoglycerides
* glycerol
* fatty acids
29
New cards
What is the Role of bile salts?
* Emulsify lipids to form tiny droplets and micelles
* increases surface area for lipase action - faster hydrolysis
* increases surface area for lipase action - faster hydrolysis
30
New cards
What are Micelles?
Water soluble vesicles formed from fatty acids, glycerol, monoglycerides and bile salts
31
New cards
Describe the process of Lipid absorption:
* Micelles deliver fatty acids, glycerol and monoglycerides to epithelial cells of ileum for absorption
* cross via simple diffusion as lipid-soluble and non-polar
* cross via simple diffusion as lipid-soluble and non-polar
32
New cards
What is Lipid modification?
* Smooth ER reforms monoglycerides / fatty acids into tryglycerides
* golgi apparatus combines tryglycerides with proteins to form vesicles called chylomicrons
* golgi apparatus combines tryglycerides with proteins to form vesicles called chylomicrons
33
New cards
How do lipids enter blood after modification?
* Chylomicrons move out of cell via exocytosis and enter lacteal
* lymphatic vessels carry chylomicrons and deposit them in bloodstream
* lymphatic vessels carry chylomicrons and deposit them in bloodstream
34
New cards
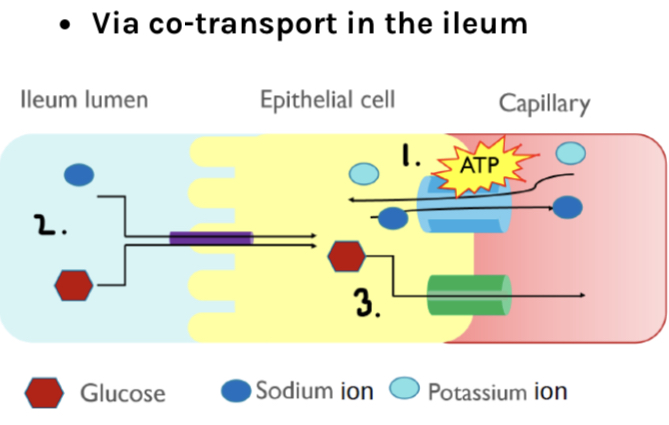
How are glucose and amino acids absorbed?
Via co-transport in the ileum
35
New cards
Describe the structure of Haemoglobin (Hb) and its role:
* Quaternary structure protein
* 2 alpha chains
* 2 beta chains
* 4 associated haem groups in each chain containing Fe2+
* transports oxygen
* 2 alpha chains
* 2 beta chains
* 4 associated haem groups in each chain containing Fe2+
* transports oxygen
36
New cards
Affinity of haemoglobin
The ability of haemoglobin to attract / bind to oxygen
37
New cards
Saturation of haemoglobin
When haemoglobin is holding the maximum amount of oxygen it can hold
38
New cards
Loading / unloading of haemoglobin
* Binding/detachment of oxygen to haemoglobin
* also known as association and disassociation
* also known as association and disassociation
39
New cards
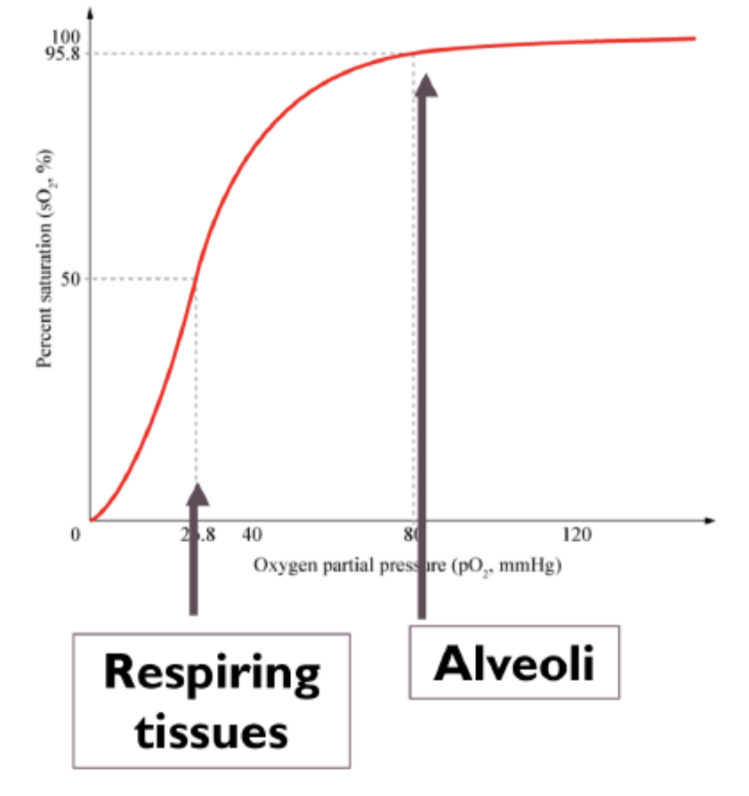
Oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
* oxygen is loaded in regions with high partial pressures (alveoli)
* unloaded in regions of low partial pressure (respiring tissue)
* unloaded in regions of low partial pressure (respiring tissue)
40
New cards
Oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve shifting left
Hb would have a higher affinity for oxygen
load more at the same partial pressure
becomes more saturated adaptation in low-oxygen environments
e.g. llamas/ in foetuses
load more at the same partial pressure
becomes more saturated adaptation in low-oxygen environments
e.g. llamas/ in foetuses
41
New cards
Cooperative binding
* Hb's affinity for oxygen increases as more oxygen molecules are associated with it
* when one binds, Hb changes shape meaning others bind more easily
* explaining S shape of curve
* when one binds, Hb changes shape meaning others bind more easily
* explaining S shape of curve
42
New cards
How carbon dioxide affects haemoglobin
* When carbon dioxide dissolves in liquid, carbonic acid forms
* decreases pH causing Hb to change shape
* affinity decreases at respiring tissues
* more oxygen is unloaded
* decreases pH causing Hb to change shape
* affinity decreases at respiring tissues
* more oxygen is unloaded
43
New cards
Bohr effect
* High carbon dioxide partial pressure
* causes oxyhaemoglobin curve to shift to the right
* causes oxyhaemoglobin curve to shift to the right
44
New cards
Oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve shifting right
* Hb has lower affinity for oxygen
* unloads more at the same partial pressures
* less saturated
* present in animals with faster metabolisms that need more oxygen for respiration
* e.g. birds/rodents
* unloads more at the same partial pressures
* less saturated
* present in animals with faster metabolisms that need more oxygen for respiration
* e.g. birds/rodents
45
New cards
Closed circulatory
system
system
Blood remains within blood vessels
46
New cards
Name different types of blood vessels
Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins
47
New cards
Structure of arteries
* Thick muscular layer
* thick elastic layer
* thick outer layer
* small luman
* no valves
* thick elastic layer
* thick outer layer
* small luman
* no valves
48
New cards
Capillary endothelium
* Extremely thin
* one cell thick
* contains small gaps for small molecules to pass through (e.g. glucose, oxygen)
* one cell thick
* contains small gaps for small molecules to pass through (e.g. glucose, oxygen)
49
New cards
Capillaries
* Form capillary beds
* narrow diameter (1 cell thick) to slow blood flow
* red blood cells squashed against walls shortens diffusion pathway
* small gaps for liquid / small molecules to be forced out
* narrow diameter (1 cell thick) to slow blood flow
* red blood cells squashed against walls shortens diffusion pathway
* small gaps for liquid / small molecules to be forced out
50
New cards
Arterioles
* Branch off arteries
* thickest muscle layer to restrict blood flow
* thinner elastic layer and outer layer than arteries as pressure lower
* thickest muscle layer to restrict blood flow
* thinner elastic layer and outer layer than arteries as pressure lower
51
New cards
Tissue fluid
* Liquid bathing all cells
* contains water, glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, ions and oxygen
* enables delivery of useful molecules to cells and removal of waste
* contains water, glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, ions and oxygen
* enables delivery of useful molecules to cells and removal of waste
52
New cards
Tissue fluid formation
* At arteriole end, the smaller diameter results in high hydrostatic pressure
* small molecules forced out (ultrafiltration)
* red blood cells / large proteins too big to fit through capillary gaps so remain
* small molecules forced out (ultrafiltration)
* red blood cells / large proteins too big to fit through capillary gaps so remain
53
New cards
Reabsorption of tissue fluid
* Large molecules remaining in capillary lower its water potential
* towards venule end there is lower hydrostatic pressure due to loss of liquid
* water reabsorbed back into capillaries by osmosis
* towards venule end there is lower hydrostatic pressure due to loss of liquid
* water reabsorbed back into capillaries by osmosis
54
New cards
Role of the lymph in tissue fluid reabsorption
* Not all liquid will be reabsorbed by osmosis as equilibrium will be reached
* excess tissue fluid (lymph) is absorbed into lymphatic system and drains back into bloodstream and deposited near heart
* excess tissue fluid (lymph) is absorbed into lymphatic system and drains back into bloodstream and deposited near heart
55
New cards
Cardiac muscle
* Walls of heart having thick muscular layer
* unique because it is:
* myogenic - can contract and relax without nervous or hormonal stimulation
* never fatigues so long as adequate oxygen supply
* unique because it is:
* myogenic - can contract and relax without nervous or hormonal stimulation
* never fatigues so long as adequate oxygen supply
56
New cards
Coronary arteries
* Blood vessels supplying cardiac muscle with oxygenated blood
* branch off from aorta
* if blocked, cardiac muscle will not be able to respire, leading to myocardial infarction (heart attack)
* branch off from aorta
* if blocked, cardiac muscle will not be able to respire, leading to myocardial infarction (heart attack)
57
New cards
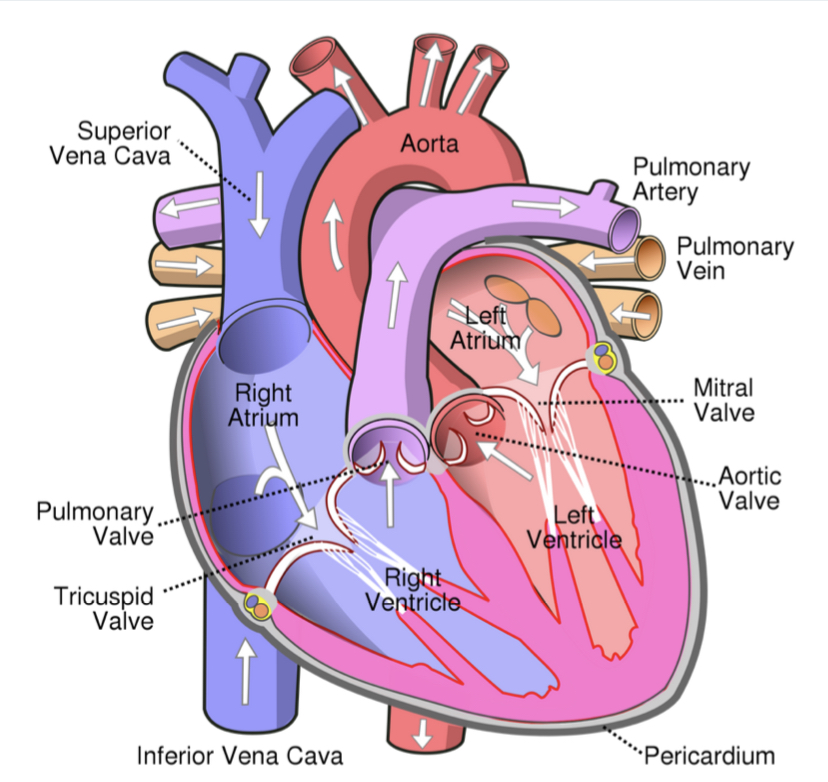
Structure of the heart
58
New cards
Adaptation of left ventricle
* Has a thick muscular wall in comparison to right ventricle
* enables larger contractions of muscle to create higher pressure
* ensures blood reaches all body cells
* enables larger contractions of muscle to create higher pressure
* ensures blood reaches all body cells
59
New cards
Veins connect to the heart
* Vena cava - carries deoxygenated blood from body to right atrium
* Pulmonary vein - carries oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium
* Pulmonary vein - carries oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium
60
New cards
Arteries connected to the heart
* Pulmonary artery - carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs
* Aorta - carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to rest of the body
* Aorta - carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to rest of the body
61
New cards
Valves within the heart
* Ensure unidirectional blood flow
* semilunar valves are located in aorta and pulmonary artery near the ventricles
* atrioventricular valves between atria and ventricles
* semilunar valves are located in aorta and pulmonary artery near the ventricles
* atrioventricular valves between atria and ventricles
62
New cards
Opening and closing of valves
* Valves open if the pressure is higher behind them compared to in front of them.
* AV valves open when pressure in atria > pressure in ventricles
* SL valves open when pressure in ventricles > pressure in arteries
* AV valves open when pressure in atria > pressure in ventricles
* SL valves open when pressure in ventricles > pressure in arteries
63
New cards
The Septum
* Muscle that runs down the middle of the heart
* separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
* maintains high concentration of oxygen in oxygenated blood
* maintaining concentration gradient to enable diffusion to respiring cells
* separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
* maintains high concentration of oxygen in oxygenated blood
* maintaining concentration gradient to enable diffusion to respiring cells
64
New cards
Cardiac output
* Volume of blood which leaves one ventricle in one minute.
* heart rate = beats per minute
* Cardiac output = heart rate\* stroke volume
* heart rate = beats per minute
* Cardiac output = heart rate\* stroke volume
65
New cards
Stroke volume
* Volume of blood that leaves the heart each beat
* measured in dm^3
* measured in dm^3
66
New cards
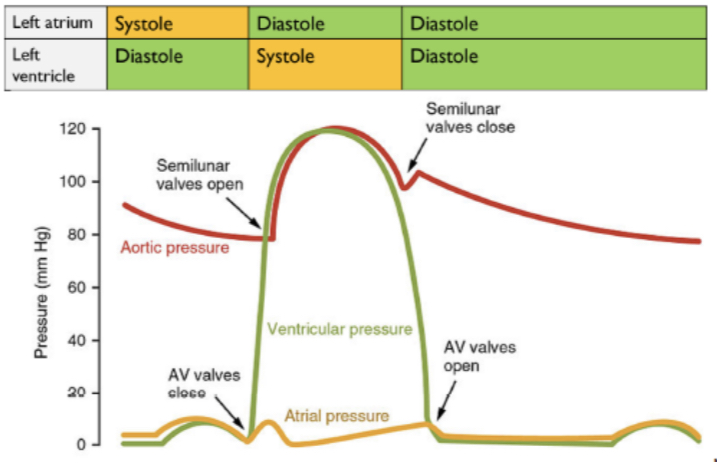
Cardiac cycle
Consists of diastole, atrial systole and ventricular systole
67
New cards
Diastole
* Atria and ventricular muscles are relaxed
* when blood enters atria via vena cava and pulmonary vein
* increasing pressure in atria
* when blood enters atria via vena cava and pulmonary vein
* increasing pressure in atria
68
New cards
Atrial systole
* Atria muscular walls contract, increasing pressure further.
* pressure atria > pressure ventricles
* atrioventricular valves open and blood flows into ventricles
* ventricular muscle relaxed
* pressure atria > pressure ventricles
* atrioventricular valves open and blood flows into ventricles
* ventricular muscle relaxed
69
New cards
Ventricular systole
* After a short delay (so ventricles fill), ventricular muscular walls contract
* pressure ventricle > atria pressure and artery pressure
* atrioventricular valves close and semi-lunar valves open
* blood pushed into artery
* pressure ventricle > atria pressure and artery pressure
* atrioventricular valves close and semi-lunar valves open
* blood pushed into artery
70
New cards
Transpiration
* Loss of water vapour from stomata by evaporation
* affected by:
* light intensity
* temperature
* humidity
* wind
* can be measured in a lab using a potometer
* affected by:
* light intensity
* temperature
* humidity
* wind
* can be measured in a lab using a potometer
71
New cards
How light intensity affects transpiration
* As light intensity increases, rate of transpiration increases
* more light means more stomata open
* larger surface area for evaporation
* more light means more stomata open
* larger surface area for evaporation
72
New cards
How temperature affects transpiration
* As temperature increases, rate of transpiration increases
* the more heat there is, the more kinetic energy molecules have
* faster moving molecules increases evaporation
* the more heat there is, the more kinetic energy molecules have
* faster moving molecules increases evaporation
73
New cards
How humidity affects transpiration
* As humidity increases, transpiration decreases
* the more water vapour in the air, the greater the water potential outside the leaf
* reduces water potential gradient and evaporation
* the more water vapour in the air, the greater the water potential outside the leaf
* reduces water potential gradient and evaporation
74
New cards
How wind affects transpiration
* As wind increases, rate of transpiration increases
* the more air movement, the more humid areas are blown away
* maintains water potential gradient, increasing evaporation
* the more air movement, the more humid areas are blown away
* maintains water potential gradient, increasing evaporation
75
New cards
Cohesion in plant transport
* Because of the dipolar nature of water, hydrogen bonds can form - cohesion
* water can travel up xylem as a continuous column
* water can travel up xylem as a continuous column
76
New cards
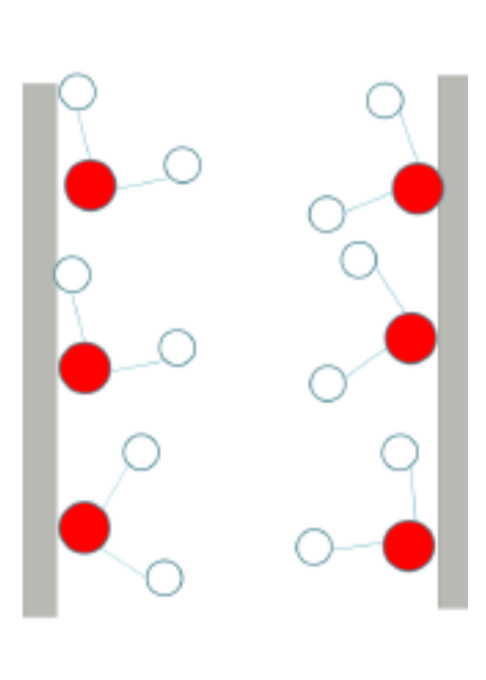
Adhesion in plant transport
* Water can stick to other molecules (xylem walls) by forming H-bonds
* helps hold water column up against gravity
* helps hold water column up against gravity
77
New cards
Root pressure in plant transport
* As water moves into roots by osmosis, the volume of liquid inside the root increases
* therefore the pressure inside the root increases
* this forces water upwards
* therefore the pressure inside the root increases
* this forces water upwards
78
New cards
Cohesion- tension theory
* As water evaporates out the stomata, this lowers pressure
* water is pulled up xylem (due to negative pressure)
* cohesive water molecules creates a column of water
* water molecules adhere to walls of xylem pulling it upwards
* this column creates tension, pulling xylem inwards
* water is pulled up xylem (due to negative pressure)
* cohesive water molecules creates a column of water
* water molecules adhere to walls of xylem pulling it upwards
* this column creates tension, pulling xylem inwards
79
New cards
Translocation
* Occurs in phloem
* explained by mass flow hypothesis
* transport of organic substances through plant
* explained by mass flow hypothesis
* transport of organic substances through plant
80
New cards
Sieve tube elements
* Living cells
* contain no nucleus
* few organelles
* this makes cell hollow
* allowing reduced resistance to flow of sugars
* contain no nucleus
* few organelles
* this makes cell hollow
* allowing reduced resistance to flow of sugars
81
New cards
Companion cell
* Provide ATP required for active transport of organic substances
* contains many mitochondria
* contains many mitochondria
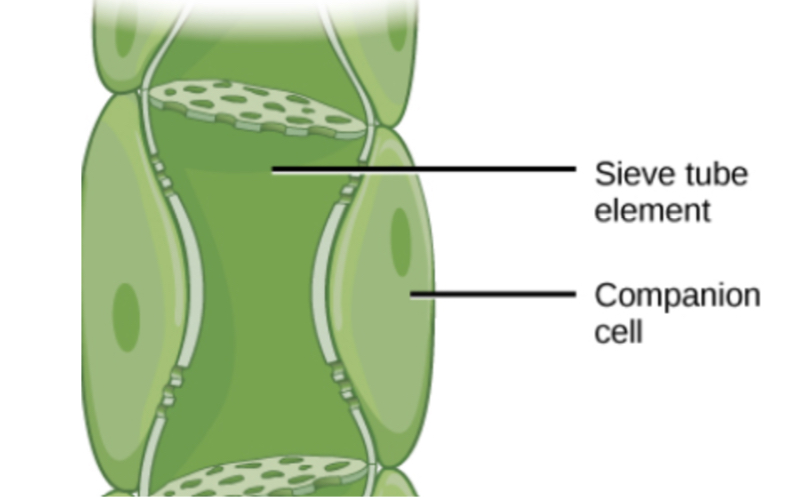
82
New cards
Mass flow hypothesis
* Organic substances, sucrose, move in solution from leaves (after photosynthesis) to respiring cells
* source -> sink direction
* source -> sink direction
83
New cards
How is pressure generated for translocation
* Photosynthesising cells produce glucose which diffuses into companion cell
* companion cell actively transports glucose into phloem
* this lowers water potential of phloem so water moves in from xylem via osmosis
* hydrostatic pressure gradient generated
* companion cell actively transports glucose into phloem
* this lowers water potential of phloem so water moves in from xylem via osmosis
* hydrostatic pressure gradient generated
84
New cards
What happens to sucrose after translocation?
* Used in respiration at the sink
* stored as insoluble starch
* stored as insoluble starch
85
New cards
Investigating translocation
* Can be investigated using tracer and ringing experiments
* proves phloem transports sugars not xylem
* proves phloem transports sugars not xylem
86
New cards
Tracing
* Involves radioactively labelling carbon - used in photosynthesis
* create sugars with this carbon
* thin slices from stems are cut and placed on X-ray film which turns black when exposed to radioactive material
* stems will turn black as that is where phloem are
* create sugars with this carbon
* thin slices from stems are cut and placed on X-ray film which turns black when exposed to radioactive material
* stems will turn black as that is where phloem are
87
New cards
Ringing experiments
* Ring of bark (and phloem) is peeled and removed off a trunk
* consequently, the trunk swells above the removed section
* analysis will show it contains sugar
* when phloem removed, sugar cannot be transported
* consequently, the trunk swells above the removed section
* analysis will show it contains sugar
* when phloem removed, sugar cannot be transported
88
New cards
How do small organisms exchange gases
* Simple diffusion
* across their surface
* across their surface
89
New cards
Why don't small organisms need breathing systems
* They have a large surface area to volume ratio
* no cells far from the surface
* no cells far from the surface
90
New cards
How alveoli structure relates to its function
* Round shape & large number in - large surface area for gas exchange (diffusion)
* epithelial cells are flat and very thin to minimise diffusion distance
* capillary network maintains concentration gradient
* epithelial cells are flat and very thin to minimise diffusion distance
* capillary network maintains concentration gradient
91
New cards
How fish gas exchange surface provides a short diffusion distance
* Thin lamellae epithelium means short distance between water and blood
* capillary network in every lamella
* capillary network in every lamella
92
New cards
How fish gas exchange surface maintains diffusion gradient
* Counter-current flow mechanism
* circulation replaces blood saturated with oxygen
* Ventilation replaces water with oxygen removed
* circulation replaces blood saturated with oxygen
* Ventilation replaces water with oxygen removed
93
New cards
Name of gas exchange system in terrestrial insects
Tracheal system
94
New cards
Describe structure of spiracles
* Round, valve-like openings
* running along the length of the abdomen
* running along the length of the abdomen
95
New cards
Describe trachea & tracheoles structure
* Network of internal tubes
* have rings of cartilage adding strength and keeping them open
* trachea branch into smaller tubes - tracheoles
* tracheoles extend through all tissues delivering oxygen
* have rings of cartilage adding strength and keeping them open
* trachea branch into smaller tubes - tracheoles
* tracheoles extend through all tissues delivering oxygen
96
New cards
How tracheal system provides short diffusion distance
Tracheoles have thin walls so short diffusion distance to cells
97
New cards
How tracheal system maintains concentration gradient
* Body can be moved by muscles to move air - ventilation
* Use of oxygen in respiration and production of CO2 sets up steep concentration gradients
* Use of oxygen in respiration and production of CO2 sets up steep concentration gradients
98
New cards
Amylase
* Produced in pancreas & salivary gland
* hydrolyses starch into maltose
* hydrolyses starch into maltose
99
New cards
Membrane-bound disaccharidases
* Maltase / sucrase / lactase
* hydrolyse disaccharides into monosaccharides
* hydrolyse disaccharides into monosaccharides
100
New cards
Enzymes involved in protein digestion
* endopeptidases
* exopeptidases
* membrane-bound dipeptidases
* exopeptidases
* membrane-bound dipeptidases