Chapter 1 - Intro to the Human Body
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Anatomy definition
the science of what body structures are & the relationships among them (structure)
Physiology definition
the science of the body functions and how the body works (function)
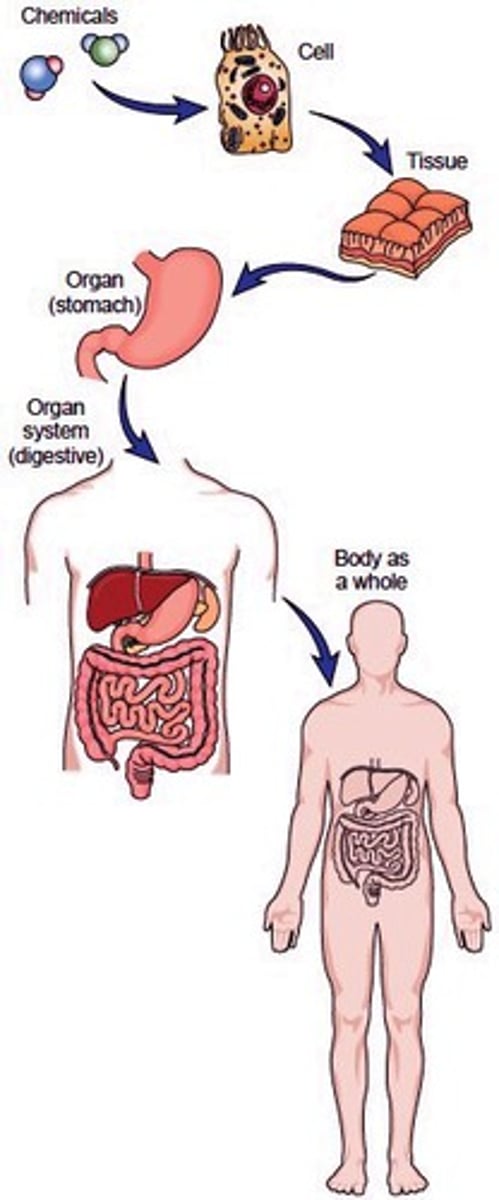
Levels of organization (smallest to largest)
atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations of one species, ecosystem of different species, biosphere
integumentary system functions
protection, water retention, thermoregulation, makes vitamin D, detects sensations, stores fat/provides insulation
skeletal system functions
support/protection, provides SA for muscle attachments, aids body movements, stem cells that produce blood cells, stores minerals and lipids
muscular system function
participates in movements, maintains posture, produces heat
nervous system functions
nerve impulses reg. body activities, detects changes in the body's internal and external environments, interprets changes, & responds by causing contractions or glandular secretions
endocrine system functions
regs. body activities by releasing hormones (chem messengers transported in blood from endocrine gland or tissue to target organ)
cardiovascular system functions
heart pumps blood through vessels, blood carries nutrients & O2 to cells & CO2 & wastes away from cells & helps reg. acid-base balance, temp., & water content of body fluids, blood components help defend against disease & repair damaged vessels
lymphatic system functions
Returns proteins and fluid to blood, carries lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood, contains sites of maturation and proliferation of B cells and T cells that protect against disease-causing microbes
respiratory system functions
Transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air; helps regulate acid-base balance of body fluids; air flowing out of lungs through vocal cords produces sounds
digestive system functions
physical and chemical breakdown of food, absorbs nutrients, eliminates solid wastes
urinary system functions
Produces, stores, and eliminates urine; eliminates wastes and regulates volume and chemical composition of blood; helps maintain the acid-base balance of body fluids; maintains body's mineral balance; helps regulate production of red blood cells
reproductive system functions
gonads (testes/ovaries) & associated organs...
females - fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, & mammary glands
males - epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, & penis
Characteristics of living organisms
- metabolism
- responsiveness
- movement
- growth
- differentiation
- reproduction
metabolism
the sum of all chemical processes that occur in an organism (catabolism/anabolism)
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy
Ex: digestive tract catabolizes proteins from food into amino acids
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Ex: amino acids are used to anabolize new proteins that make up body structures (muscle, bone, etc.)
responsiveness
the body's ability to detect and respond to changes
movement
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, and even tiny structures inside cells
growth
an increase in body size that results from an increase in the size of existing cells, an increase in the number of cells, or both
differentiation
the development of a cell from an unspecialized to a specialized state
reproduction
refers to either the formation of new cells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement or the production of a new individual
Homeostasis
The maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions
- dynamic condition
- conditions can shift within normal ranges
relationship between structure and function
structure determines function
why do living organisms need energy?
chemical processes, growth, movement, etc.
Information flow to coordinate body functions
draw out diagram
ECF
fluid outside the cell
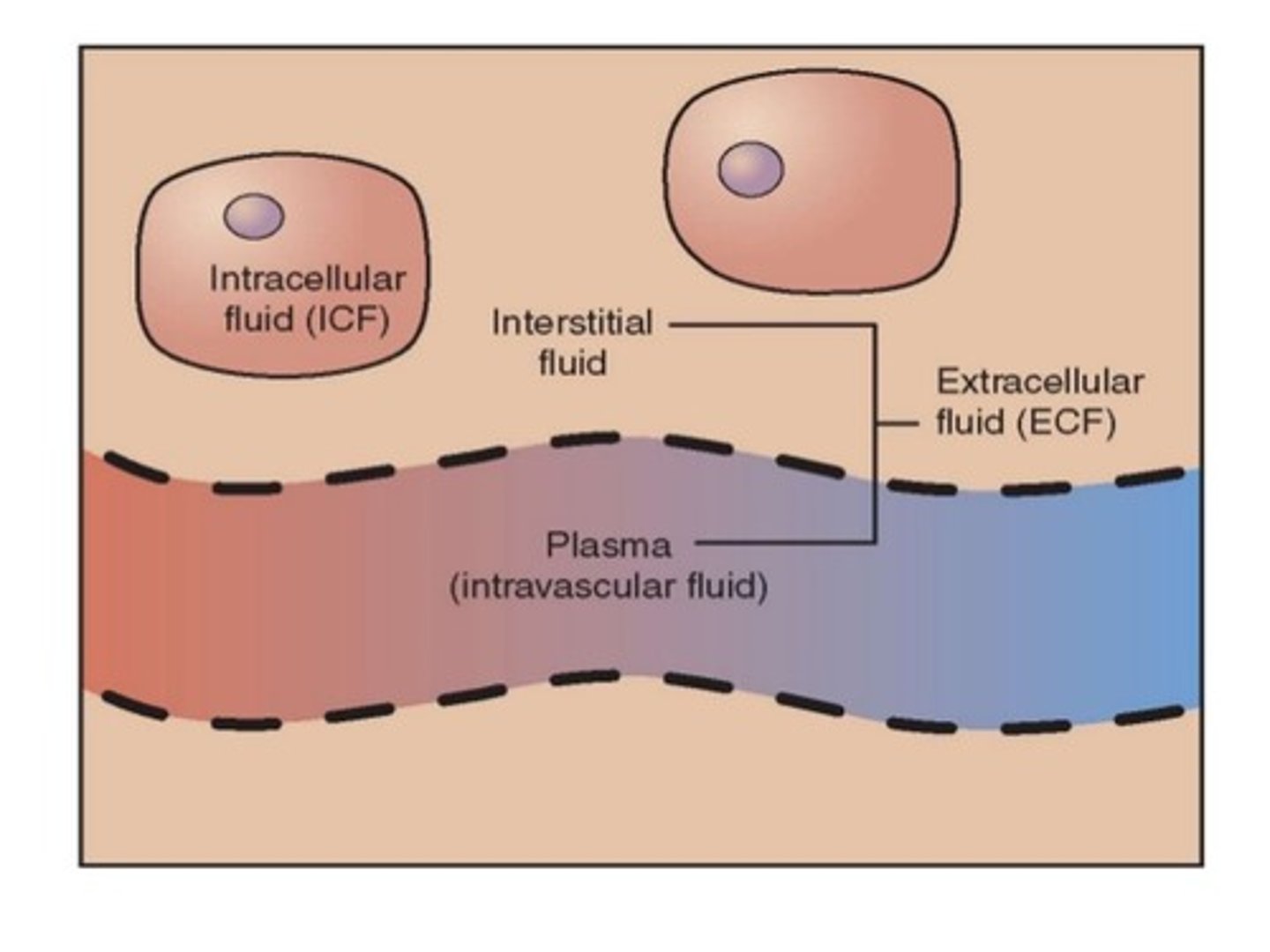
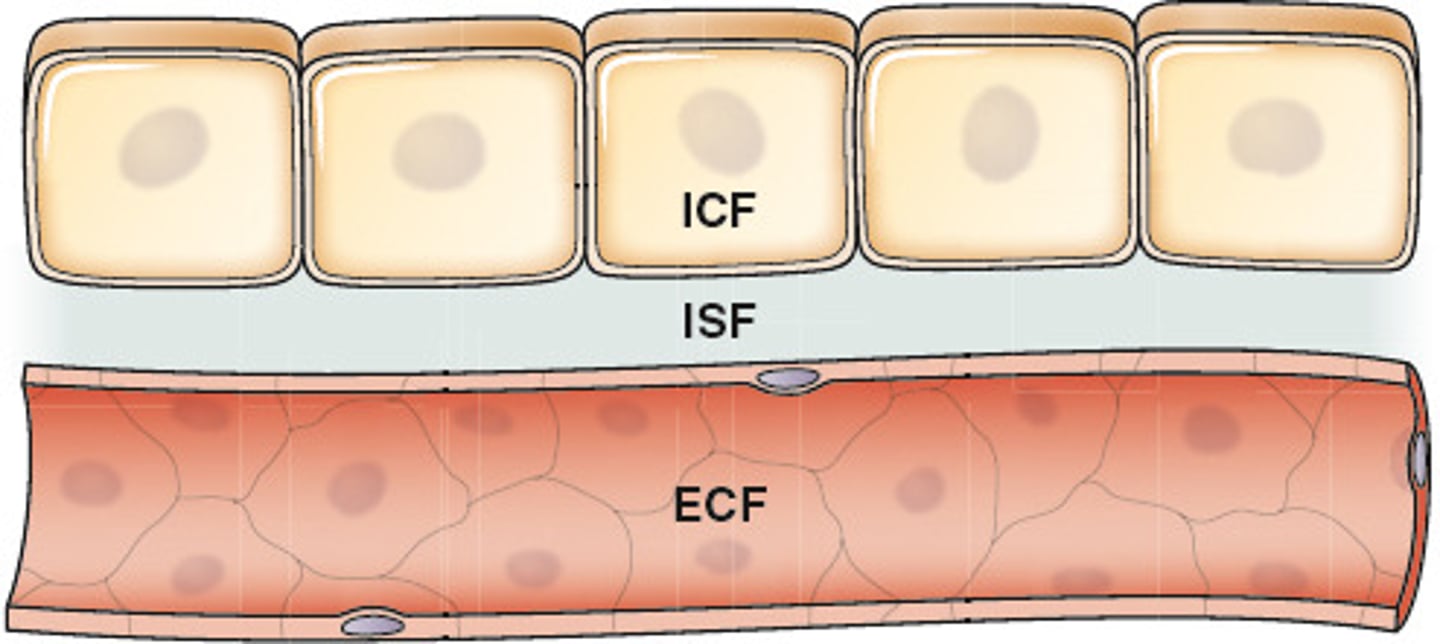
ICF
fluid inside cells
ECF vs. ICF
ECF - more sodium and chloride
ICF - more potassium
interstitial fluid
fluid in the narrow spaces between cells
blood plasma
ECF within blood vessels
lymph
ECF within lymphatic vessels
cerebrospinal fluid
fluid in and around the brain and spinal cord
synovial fluid
ECF within joints
aqueous humor and vitreous body
ECF within the eyes
Internal environment
ECF because it surrounds cells of the body
External environment
the space that surrounds the entire body
Homeostasis vs. Equilibrium
homeostasis - conditions are balanced
equilibrium - conditions are equal
What do control systems do?
keep variables within normal range (maintain homeostasis)
Components of feedback loops
Receptor - body structure that monitors changes and sends input to a control center
Control center - evaluates input from receptors (usually brain/hypothalamus)
Effector - body structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response that changes the controlled condition
Response - alters controlled condition... returns to homeostasis
Positive feedback loop
a feedback loop in which change in a system is amplified
Negative feedback loops
A feedback loop in which a system responds to a change by returning to its original state, or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring.