B2.2 Organelles and Cell Compartmentalisation
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
draw and label a mitochondria
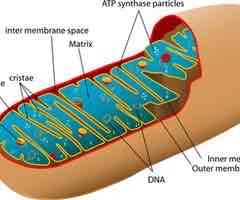
intermembrane space
a spall space that allows a concentration gradient to develop which drives ATP synthesis
matrix
allows for compartmentalization of enzymes and substrates needed for Krebs cycle
cristae
foldings of inner membrane of mitochondria
what is the function of cristae
increase surface area to accommodate the enzymes and proteins needed for ATP synthesis
what is the function of mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration to produce ATP
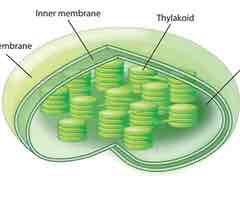
what is the function of chloroplast
site of photosynthesis
stroma
contains all the substrates and enzymes for Calvin cycle
thylakoids
small fluid volume that allows for concentration gradient to develop to drive ATP synthesis
thylakoid membrane
contain light absorbing pigments and enzymes organized in photosynthesis
draw and label a chloroplast
what is the function of the nucleus
contains almost all of the cells' genetic material
what is the function of the membrane of the nucleus
protect the DNA from the rest of the cell
what does the membrane of the nucleus contribute to the gene expression
the membranes allow for the regulation of gene expression in the cell in response to the environment
what is the function of the nuclear pore
allows transport of molecules to and from cytoplasm
how are the nuclear pores lined
they are lined with integral proteins which control whether or not a substance can pass through
what is the function of the nuclear envelope
breaks down during mitosis and meiosis and reassembles after
what can nuclear envelope break down into
vesicle during cell division and reassemble around the two new nuclei after
what is the function of ribosomes
make polypeptides using mRNA (build proteins)
what are the two types of ribosomes
free ribosomes and bound ribosomes
where are bound ribosomes found
RER
where are free ribosomes found
cytoplasm
how do bound ribosomes make protein
mRNA contains a signal sequence that designates it to be translated into polypeptides at the RER and then exported outside of the cell
how do free ribosomes make protein
proteins produced remain inside the cell's cytoplasm and are used in the cell
what is the function of the golgi apparatus
it processes and secretes protein
how are proteins transported
proteins made in RER are transported via vesicles to the golgi apparatus
how are proteins sorted
enzymes in the cristernae modify and sort the proteins to their final destination
what are the main functions of vesicles
transport and storage of materials
what is the main function of transport vesicle
move substances from one part of the cell to another
what is the function of secretory vesicles
store or transport molecules to be secreated out of the cell
what is the function of lysosome
contain hydrolytic enzymes to break down macromolecules
what is the function of peroxisomes
detoxification of harmful compounds
what are the four types of vesicles
secretory, transport, peroxisomes, lysosomes
what is clathrin
a protein that aids in the formation of vesicles
what is the function of clathrin
it brings together the cytoskeleton and other proteins needed to create from the plasma membrane or membranes of intercellular organelles