positioning ch2
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
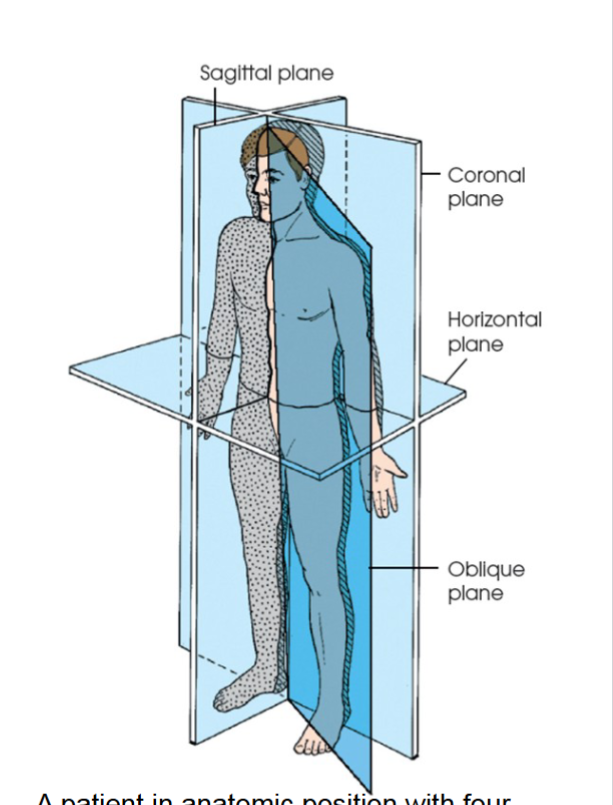
sagittal plane
divides the body or body part into right and left segments. passes through the body vertically from front to back. fig 2.1 a
midsagittal passes through the midline divides into equal right and left halves.
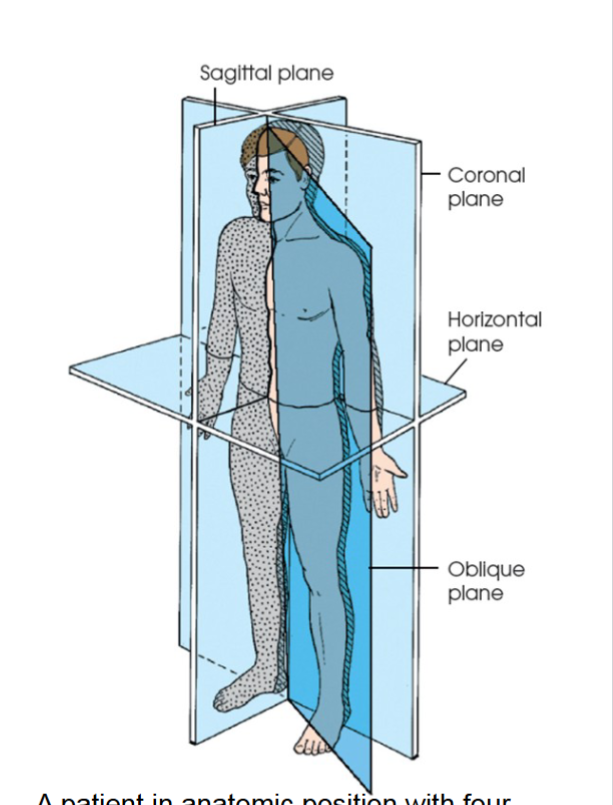
coronal plane
divides the body or body part into anterior and posterior segments . passes through the body vertically from one side to the other.
midcoronal plane passes through the midline dividing anterior and posterior segments into equal halves.
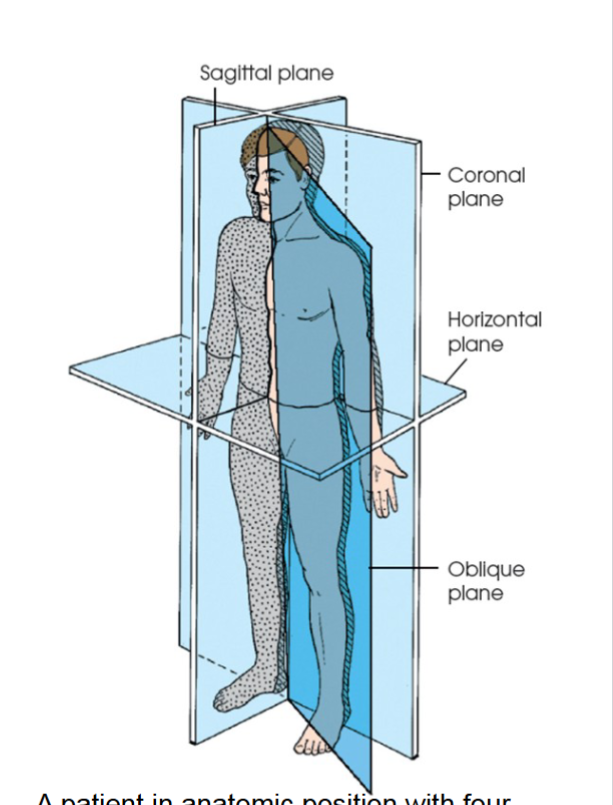
horizontal plane
passes crosswise through the body or body part at right angles to the longitudinal axis. positioned at a right angle to sagittal and coronal planes. divides body into superior and inferior portions. axial, transverse, or cross sectional plane also
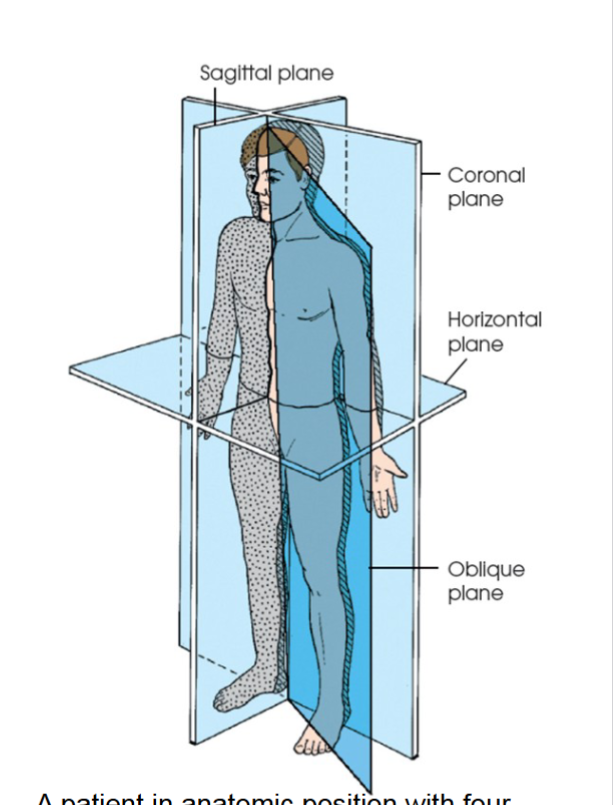
oblique plane
can pass through a body part at any angle among the three previous planes. (fig 2.1)
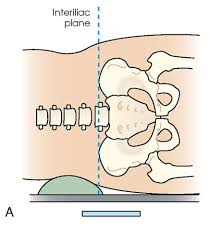
interiliac plane
special plane. transects the pelvis at the top of the iliac crests at level of fourth lumbar spinous process. used in positioning lumbar spine, sacrum, and coccyx. (fig 2.4 a)
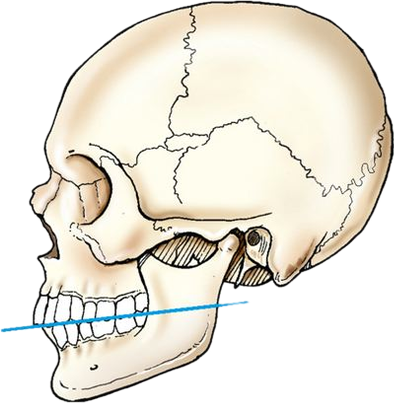
occlusal plane
special plane. formed by the biting surfaces of the upper and lower teeth with the jaws closed. used in positioning the odontoid process and some head projections. fig 2.4 b
body cavities
two great cavities of the torso are the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
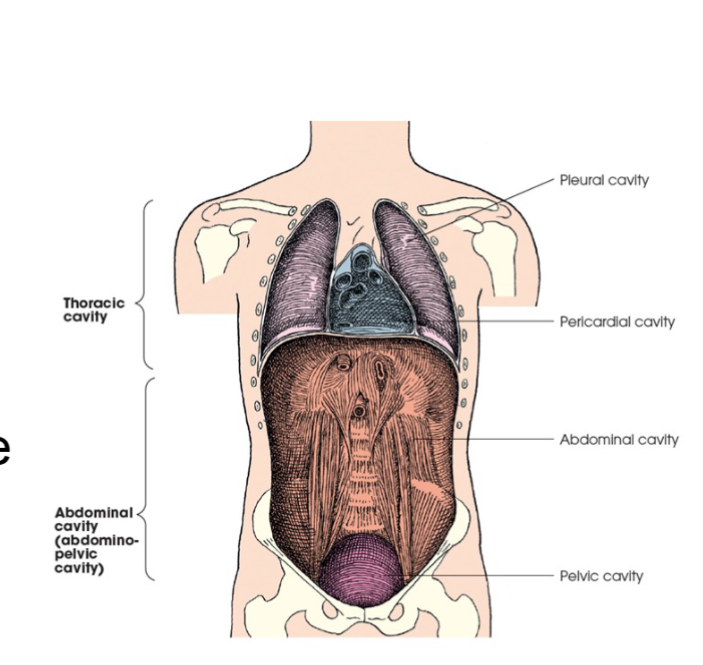
thoracic cavity
subdivided into pericardial segment and two pleural portions fig. 2.5
principal structures
pleural membranes
lungs
trachea
esophagus
pericardium
heart and great vessels
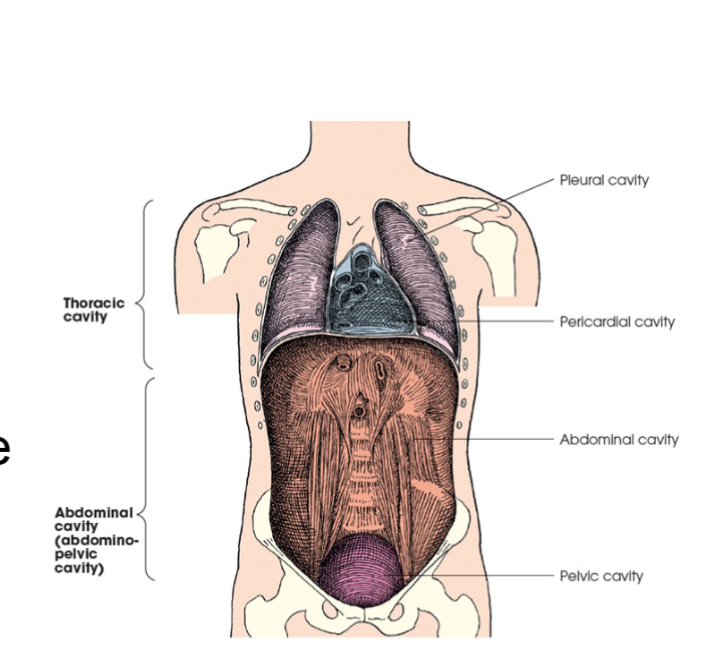
abdominal cavity
this cavity has no intervening partition the lower portion is called the pelvic cavity. fig 2.5
principle structures
peritoneum
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
spleen
stomach
intestines
kidneys
ureters
major blood vessels
pelvic portion- rectum, urinary bladder, parts of reproductive system
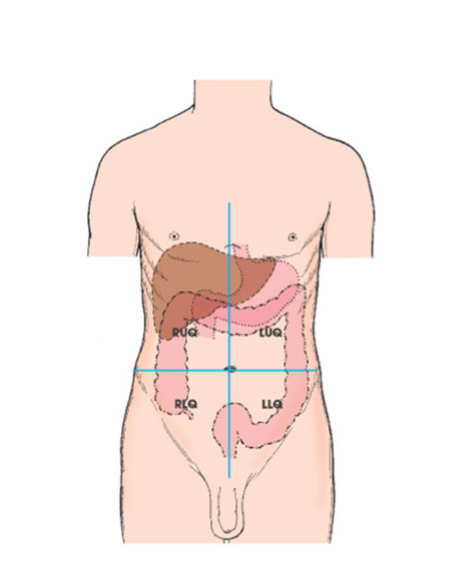
abdomen
portion of trunk bordered superiorly by diaphragm, and inferiorly by pelvic aperture (inlet) can be divided in four quadrants or nine regions.
RUQ
RLQ
LLQ
LUQ- spleen is here fig 2.6
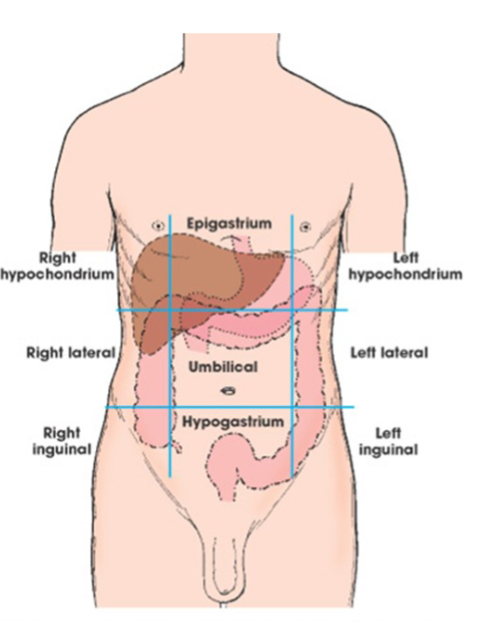
regions of abdomen
not as used as quadrants but some divide the abdomen into nine regions.
superior- right hypochondrium, epigastrium, left hypochondrium
middle- right lateral, umbilical, left lateral
inferior- right inguinal, hypogastrium, left inguinal
osteology
the detailed study of the body of knowledge relating to bones of the body .
206 primary bones in adult human skeleton
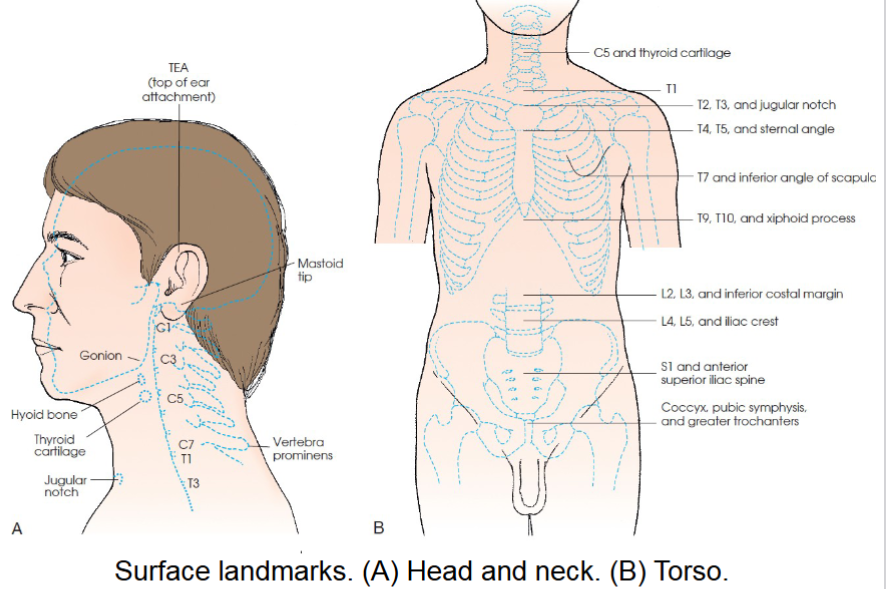
cervical area landmarks
C1- mastoid tip
C2, C3- ganion (angle of mandible)
c3,c4- hyoid bone
c5-thyroid cartilage
c7, T1- vertebrae prominens
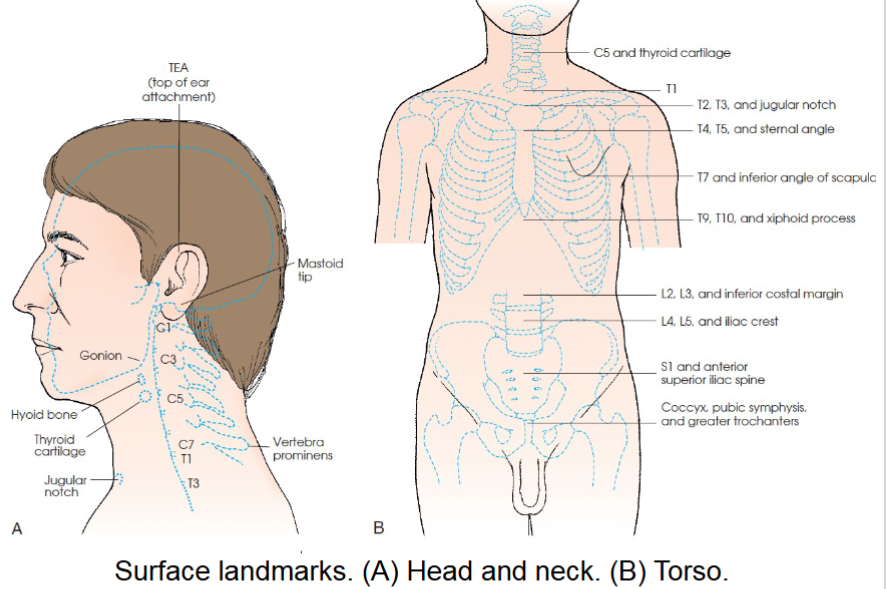
thoracic area landmarks
T1- approx 2 in above level of jugular notch
T2, T3- level of jugular notch
T4, T5- level of sternal angle
T7- level of inferior angles of scapulae
T9,T10- level of xiphoid process
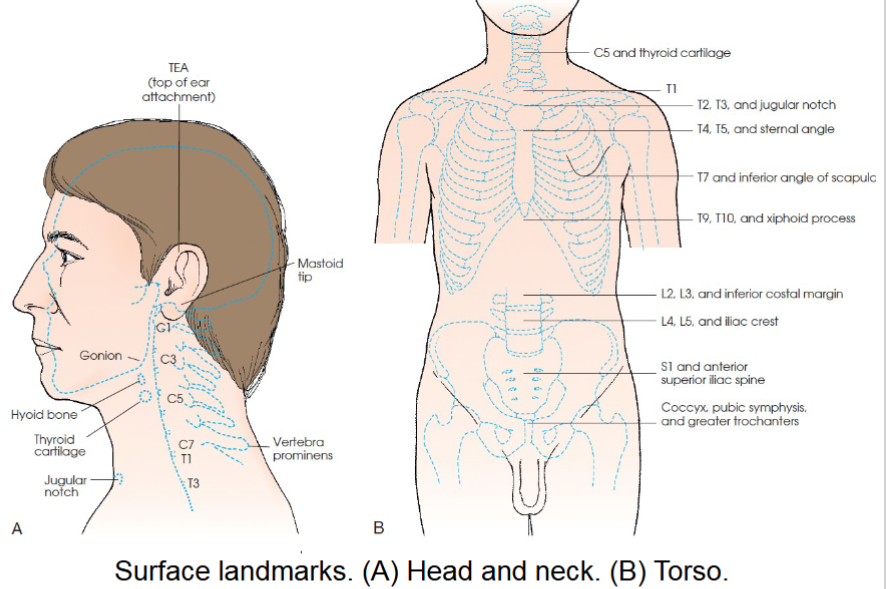
lumbar area landmarks
L2, L3- inferior costal margin
L4,L5- level of superior most aspect of iliac crests
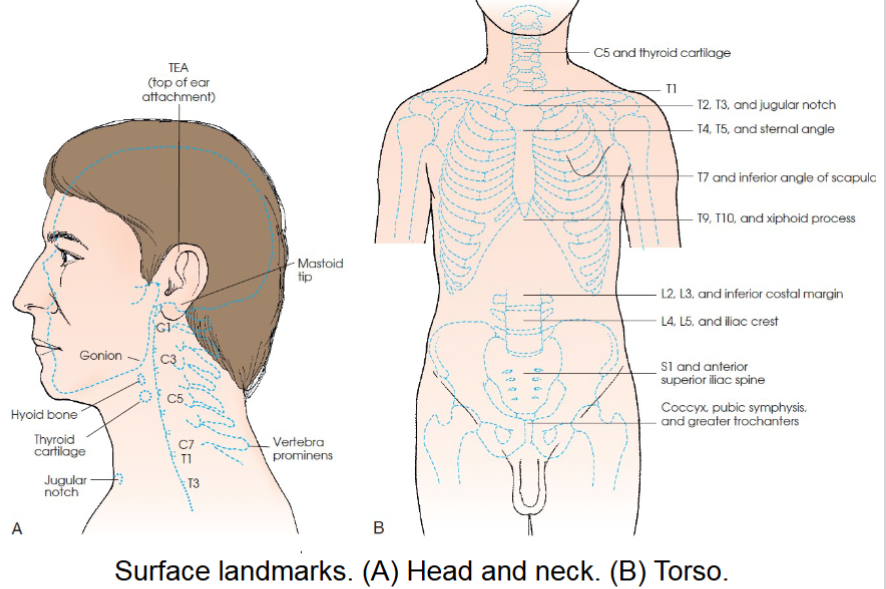
sacrum and pelvic area landmarks
S1, S2- level of anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Coccyx- level of pubic symphysis and greater trochanters
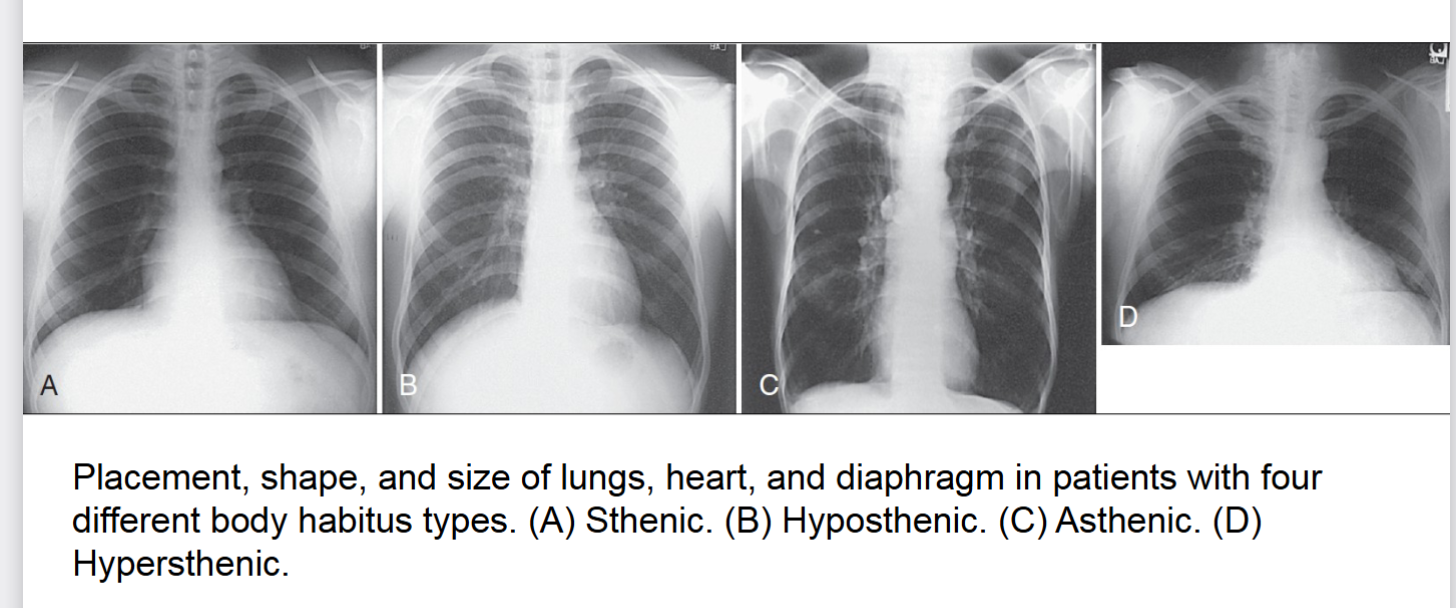
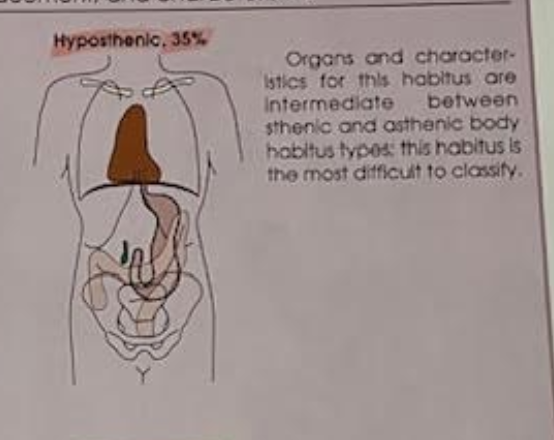
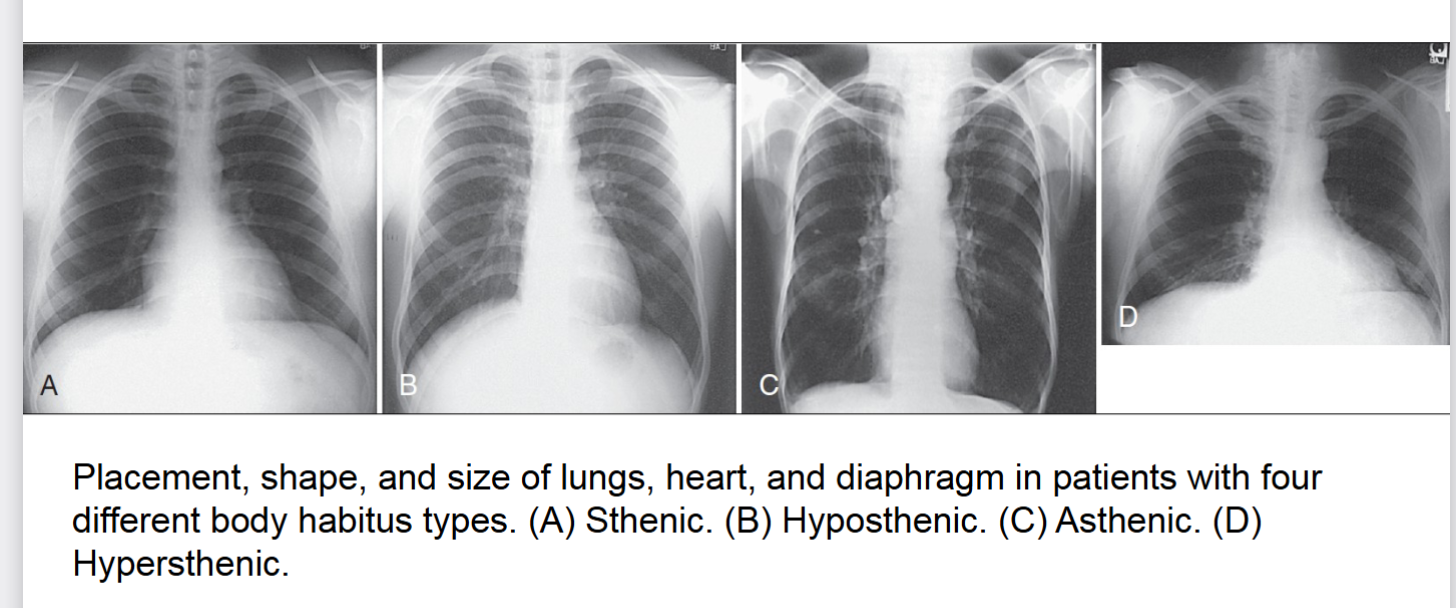
body habitus
common variations in the shape of the human body, affects locations of the heart lungs diaphragm stomach colon and gallbladder. 4 types of ____ ____
sthenic (average)
hyposthenic (AVERAGE)
asthenic (extreme)
hypersthenic (extreme)
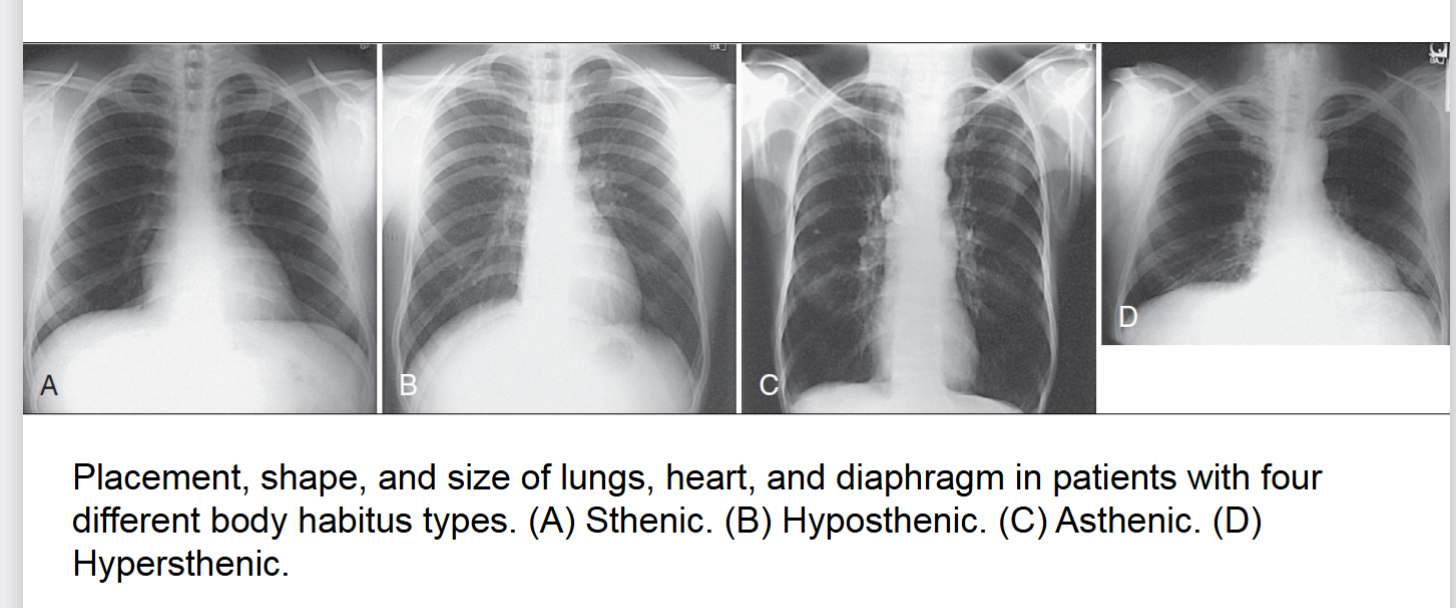
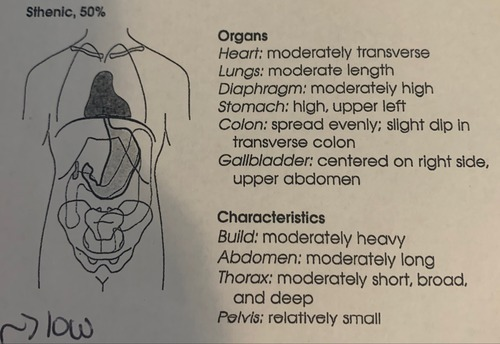
sthenic
one of four body habitus. 50% frequency in population. avg .more than 85% of population has this or hyposthenic. (box 2.1)
heart- moderatly transverse
lungs- moderate length
diaphragm- moderately high
stomach- high upper left
colon- spread evenly slight dip in transverse colon
gallbladder- centered on right side upper abdomen
hyposthenic
one of four body habitus 35% frequency more than 85% of population has this or sthenic.
asthenic
one of four body habitus only 10% of population has this habitus. heart is nearly vertical at midline lungs are apices above clavicles diaphragm is low stomach is low and medial. usually frail build with a short abdomen and small pelvis
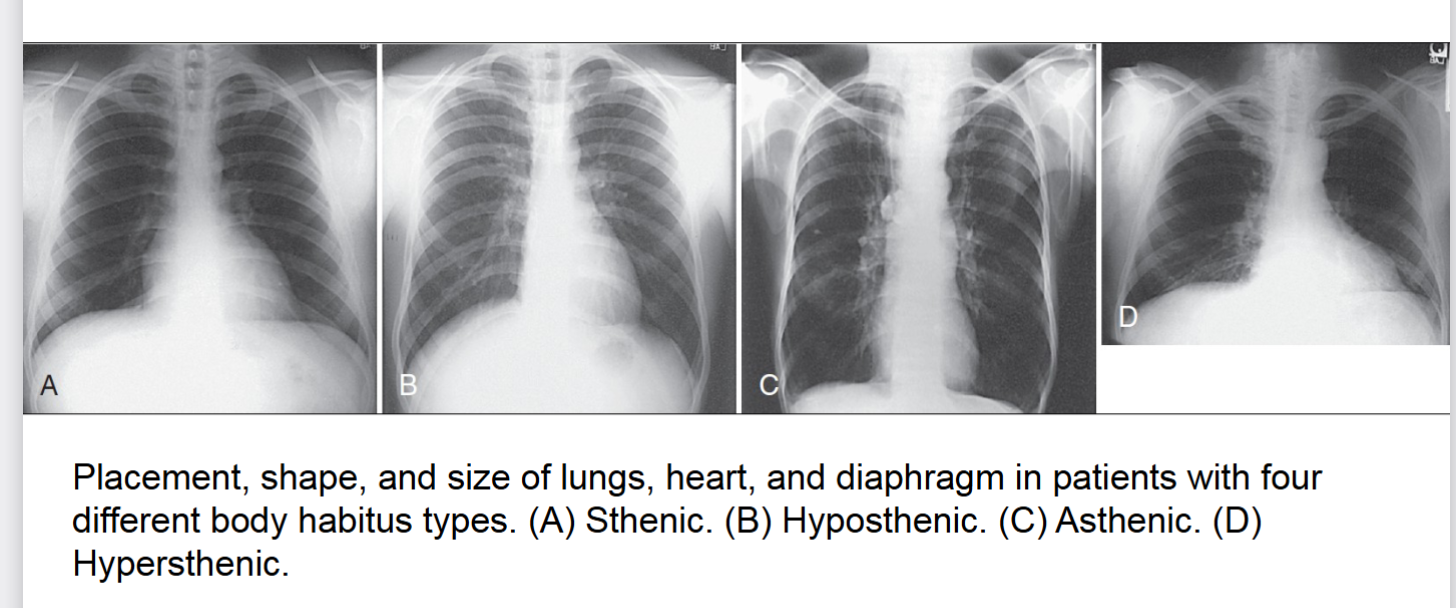
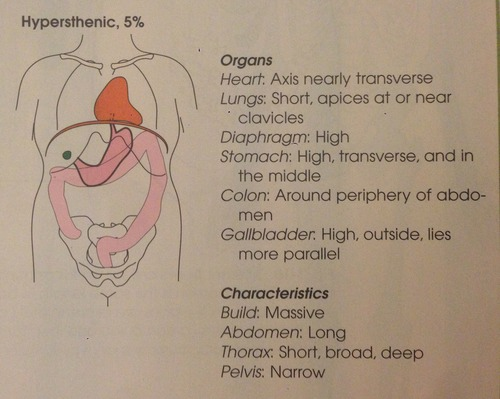
hypersthenic
one of four body habitus only 5% of population has this habitus. heart axis nearly transverse lungs short apices at or near clavicles stomach is high transverse and in the middle. diaphragm is high
build is usually massive abdomen is long pelvis is narrow
skeleton functions
adult human skeleton has 206 primary bones. bones provide the following
attachment for muscles
mechanical basis for movement
protection of internal organs
a frame to support the body
storage for calcium phosphorous and other salts
production of red and white blood cells
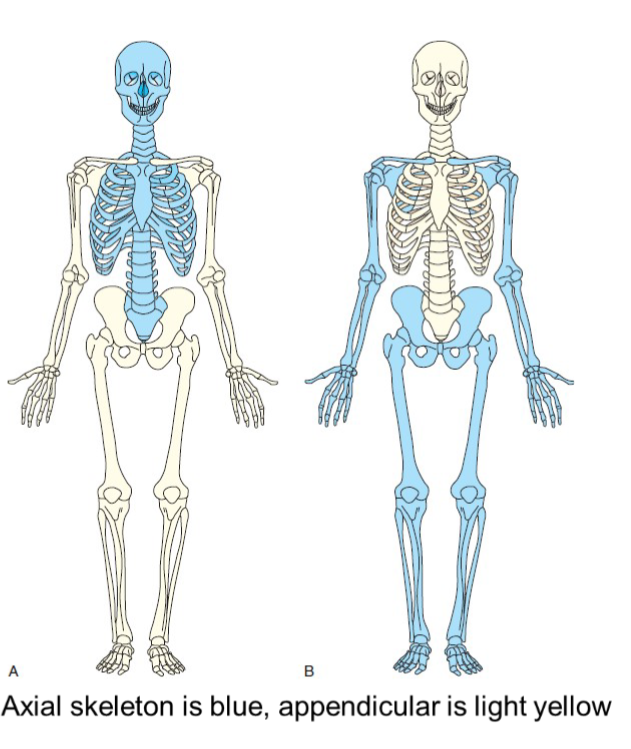
axial skeleton
supports and protects the head a trunk with 80 bones
skull
cranial 8
facial 14
auditory 6 (ossicles are small bones in ear not official bones)
neck
hyoid- 1
thorax
sternum 1
ribs 24
vertebral column
cervical 7
thoracic 12
lumbar 5
sacrum 1
coccyx 1
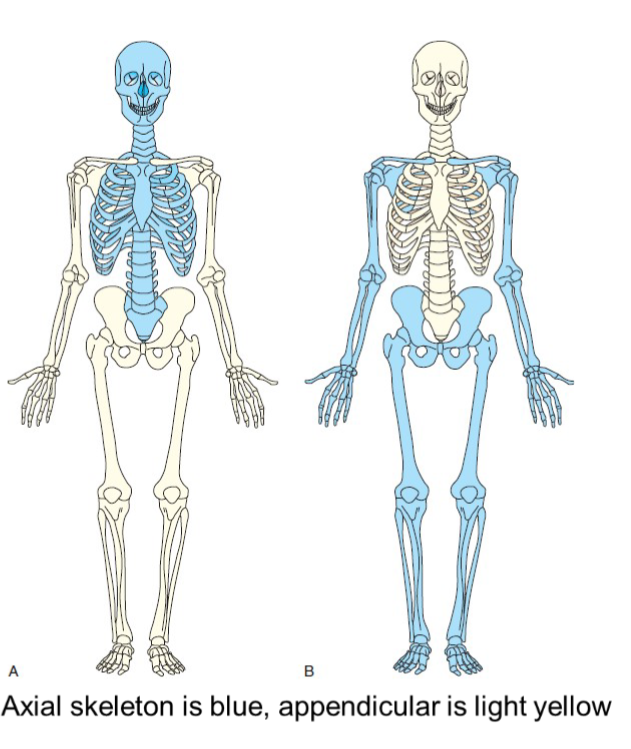
appendicular skeleton
allows body to move in various positions and from place to place. 126 bones
shoulder girdle
clavicles 2
scapulae 2
upper limbs
humeri 2
ulnae 2
radii 2
carpals 16
metacarpals 10
phalanges 28
lower limbs
femora 2
tibias 2
fibulae 2
patellae 2
tarsals 14
metatarsals 10
phalanges 28
pelvic girdle
hip bones 2
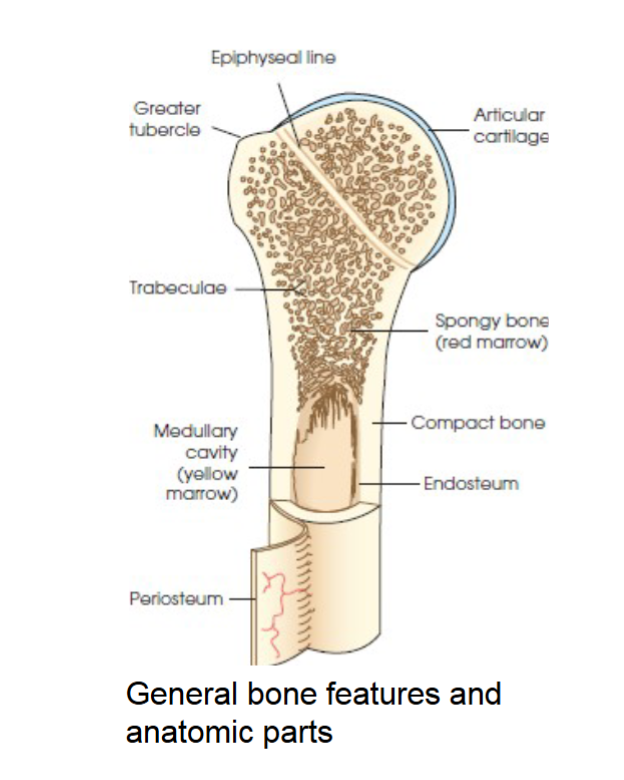
compact bone
general bone feature. strong dense outer layer. protects the bone and gives it strength for supporting the body.
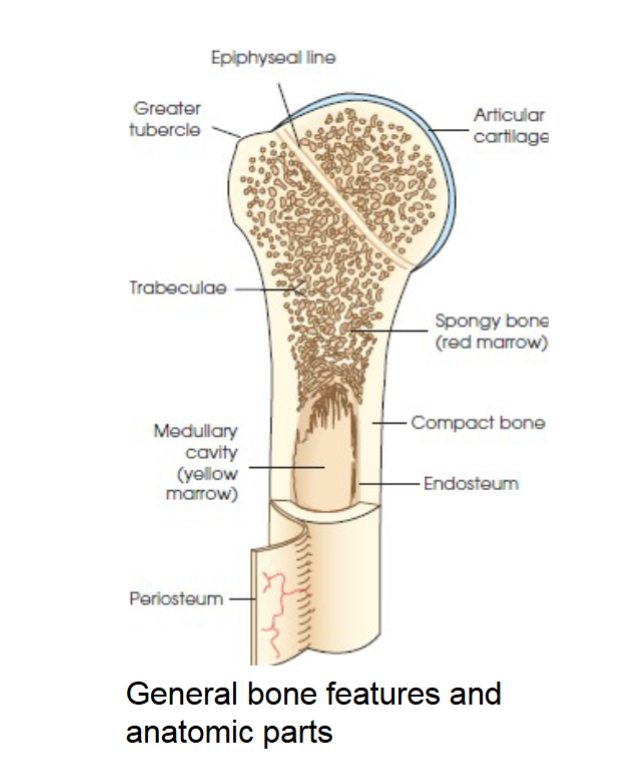
spongy bone
general bone feature. inner less dense layer. contains spiculated network called trabeculae. trabeculae filled with red and yellow marrow. red marrow produces red and white blood cells, yellow stores adipose fat cells.
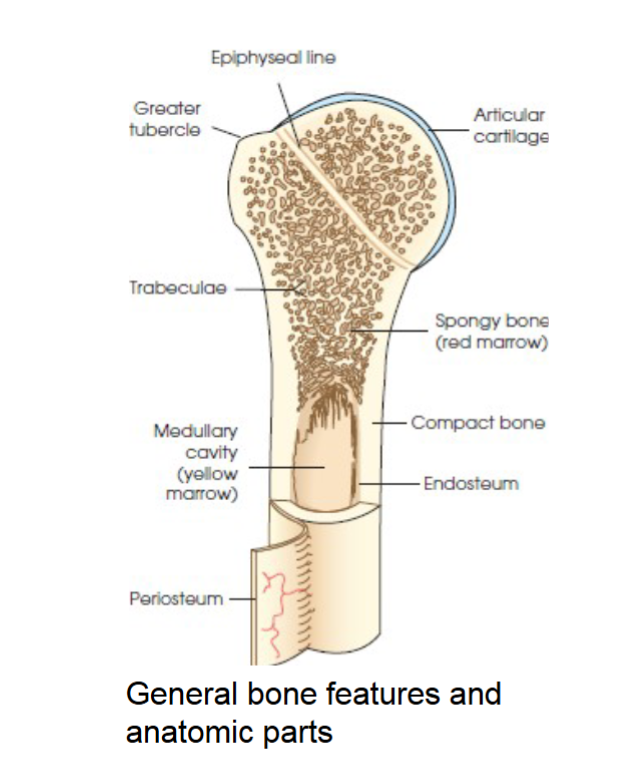
medullary cavity
long bones have a central cavity contains trabeculae filled with yellow marrow. in long bones red marrow is concentrated at ends of bone not in this cavity.
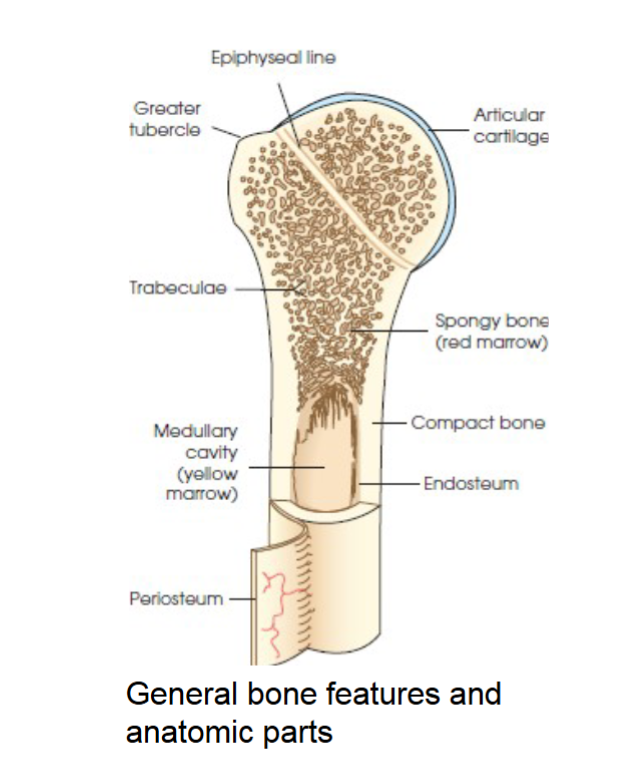
periosteum
tough fibrous connective tissue covers all bony surfaces except articular surfaces which are covered by articular cartilage.
blood vessels and nerves exit bone through this
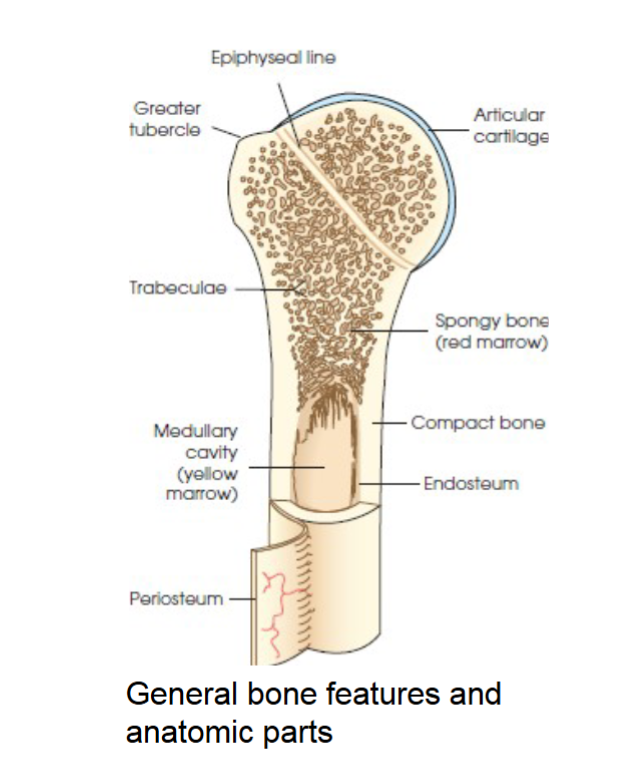
endosteum
the tissue lining the medullary cavities of bones. lines marrow cavity.
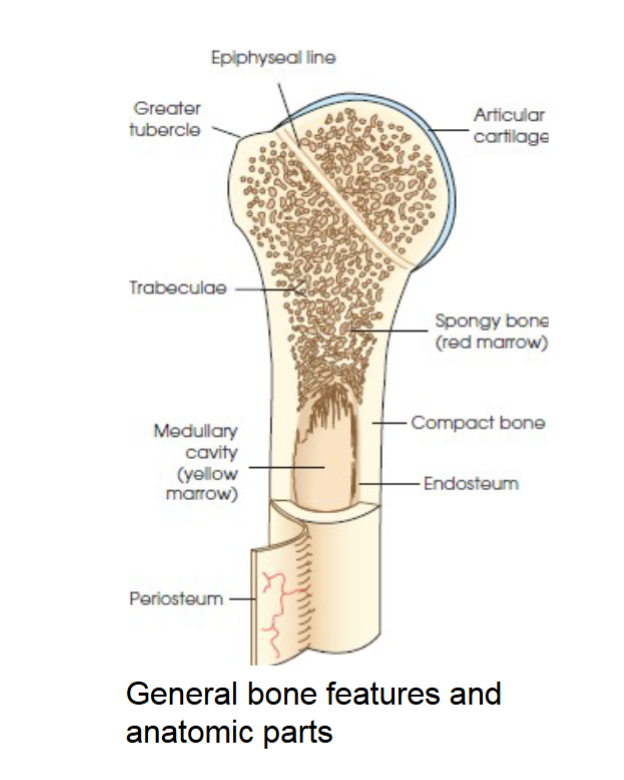
tubercles and tuberosities
knob like projections on bones covered by periosteum, muscles, tendons, and ligaments attach to the periosteum at these projections.
foramina
bones are live organs that need a blood supply and they also contain nerves. vessels and nerves enter and exit the bones through opening called the ______
nutrient foramen
near the center of all long bones is this opening in the periosteum. the nutrient artery of the bone passes into this opening and supplies the cancellous bone and marrow. fig 2.14
ossification
term that applies to the development and formation of bones. begins in second month of embryonic life.
two process- intermembranous and endochondral
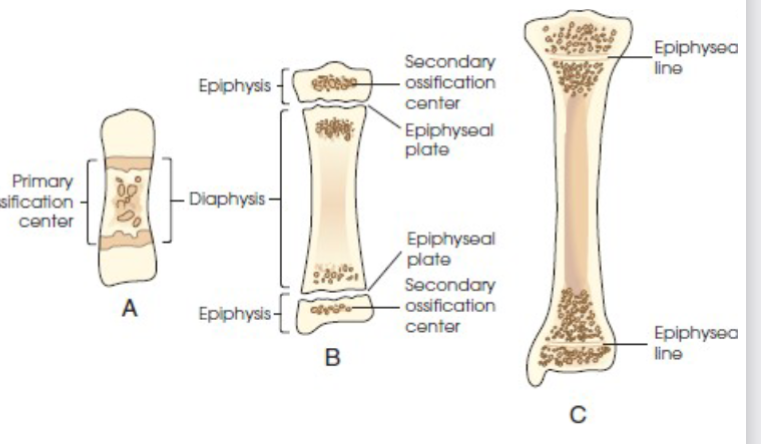
intramembranous ossification
bones that develop from fibrous membranes in the embryo produce flat bones (bones of skull, clavicles, mandible, and sternum.)
before birth these bones are not joined as flat bones they grow after birth then join and form sutures. other bones in this category merge and create joints of the skeleton.
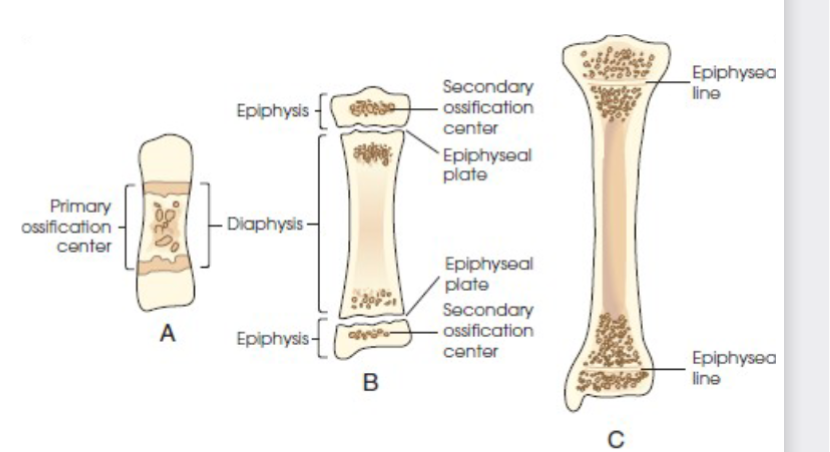
endochondral ossification
bones created by this develop from hyaline cartilage in the embryo and produce short, irregular, and long bones. occurs from two distinct centers of development
Primary
Secondary centers of ossification.
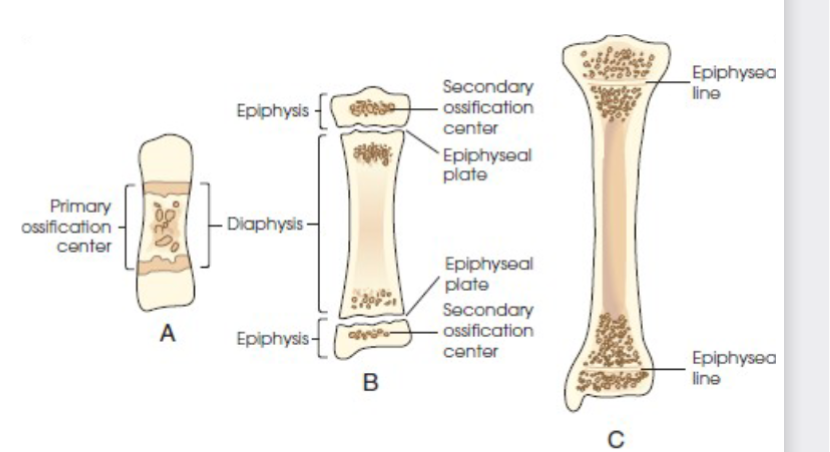
primary ossification
begins before birth and forms long central shaft in long bones. and forms entire bulk of short and irregular bones.
during development only the long shaft of bone is called diaphysis.
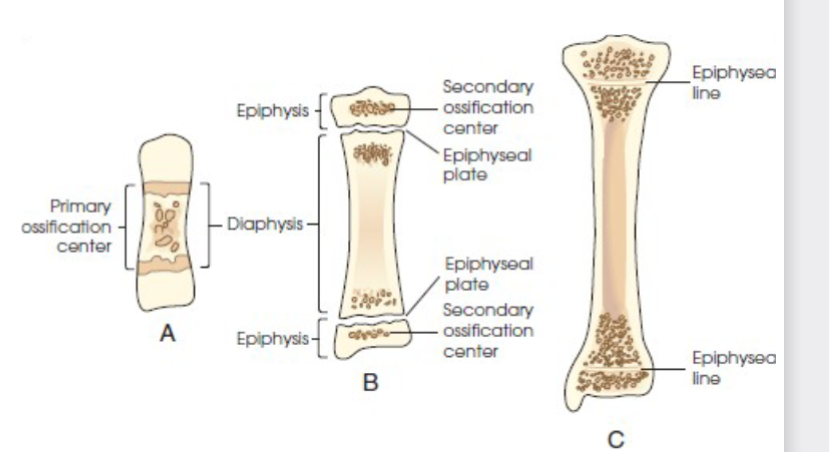
secondary ossification
occurs after birth. when separate bones begin to develop at both ends of long bones. each end is called epiphysis.
at first diaphysis and epiphysis are separate, as growth occurs plate of cartilage called epiphyseal plate develops between the two areas, common site of fracture in pediatric patients
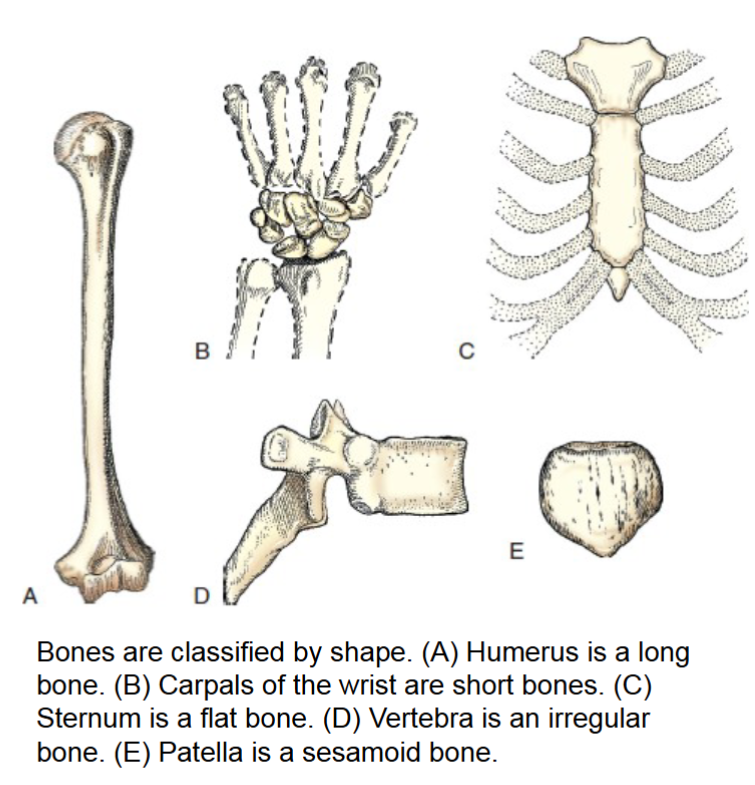
bone classification
bones are classified by shape
long
short
flat
irregular
sesamoid
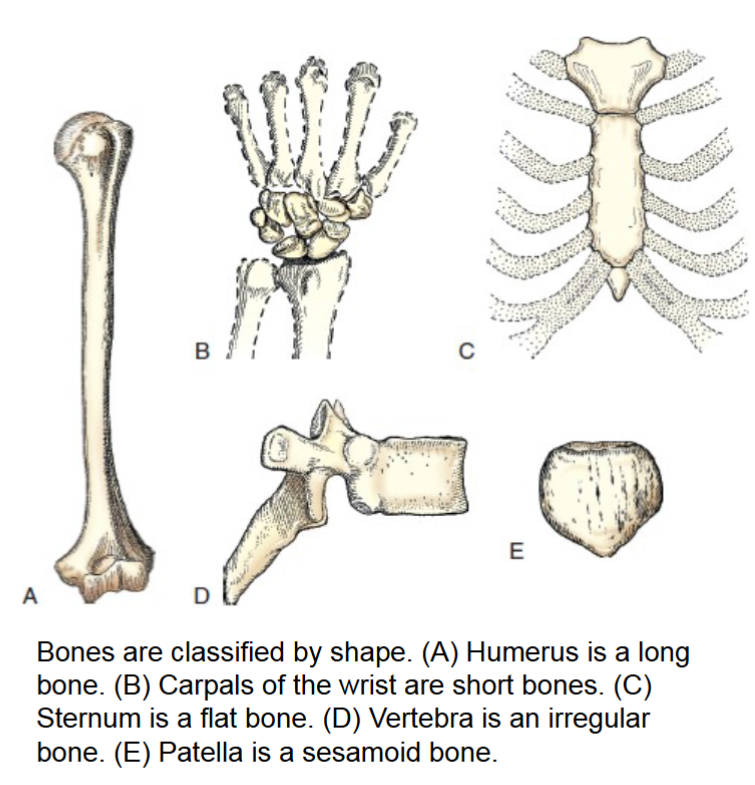
long bones
only found in the limbs. consist primarily of long cylindic shaft called the body, and two large rounded heads that have smooth articular surface covered by articular cartilage.
ends articulate with other long bones. primary function of these bones is to provide support.
(femur, humerus, phalanges)
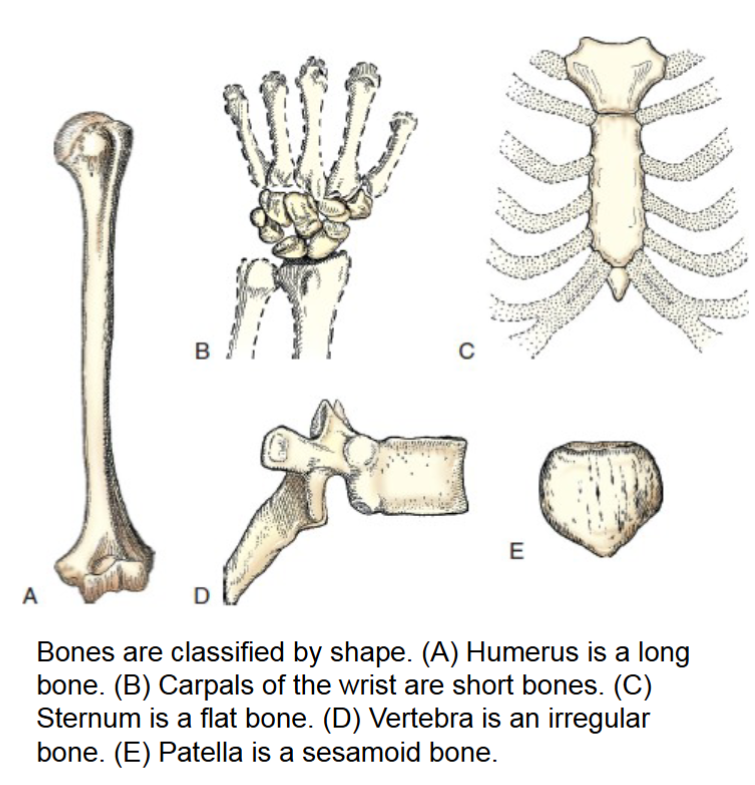
short bones
consist of cancellous bone containing red marrow. have a thin outer layer of compact bone. the carpal bones of the wrist and tarsals of ankles are only type of these bones.
varied in shape and allow minimum flexibility of motion in a short distance.
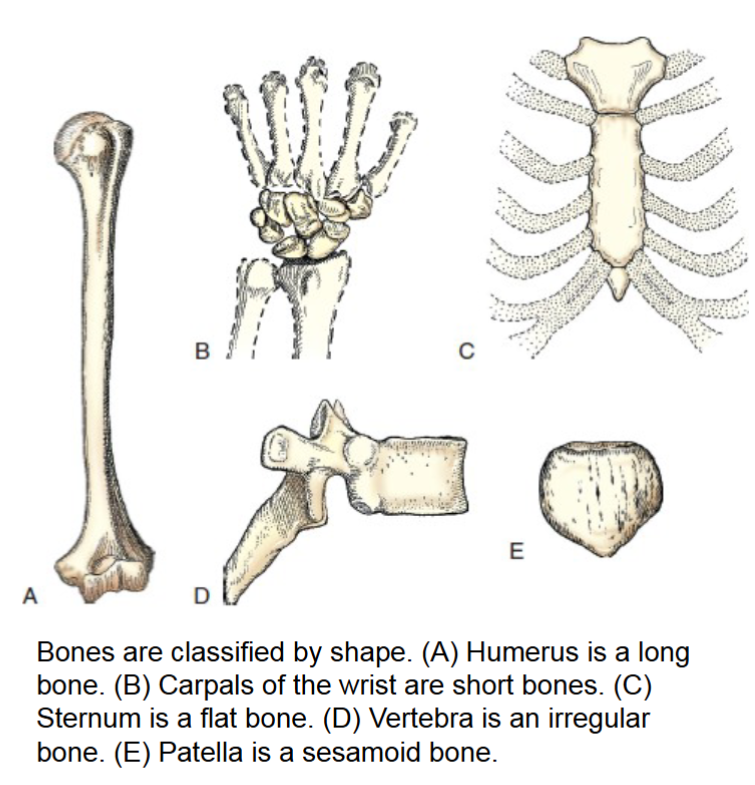
flat bones
consist of two tables of compact bone. the narrow spaces between inner and outer tables contain cancellous bone and red marrow or diploe.
cranium, sternum, and scapula are examples.
surfaces provide protection, and their broad surfaces allow muscle attachment.
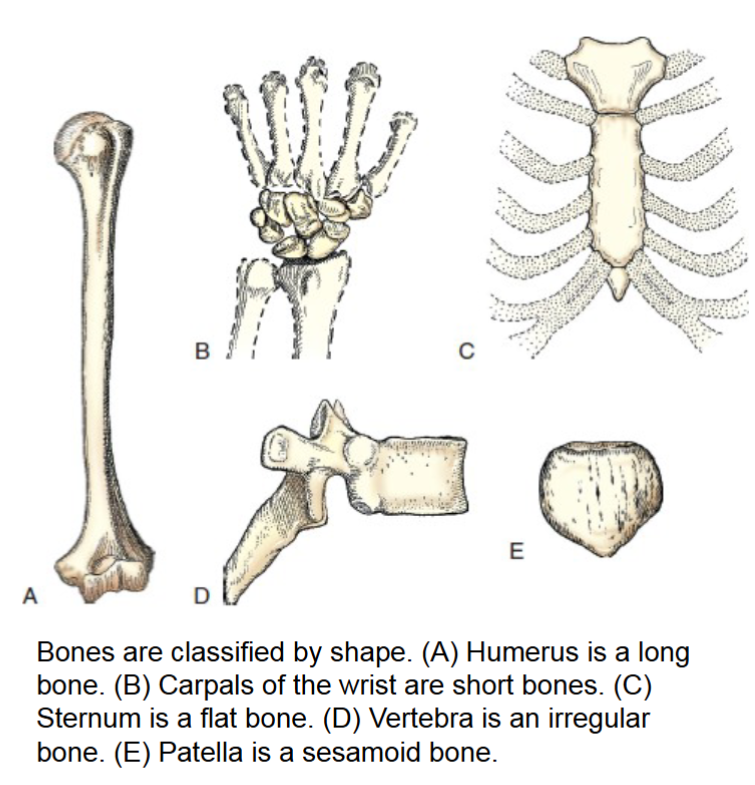
irregular bones
peculiar shapes and variety of forms don’t place them in any other category. vertebrae and bones of pelvis and face fall into this category. have compact bone on exterior and cancellous bone with red marrow on interior.
shape serves as attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments, or they attach to other bones to create joints.
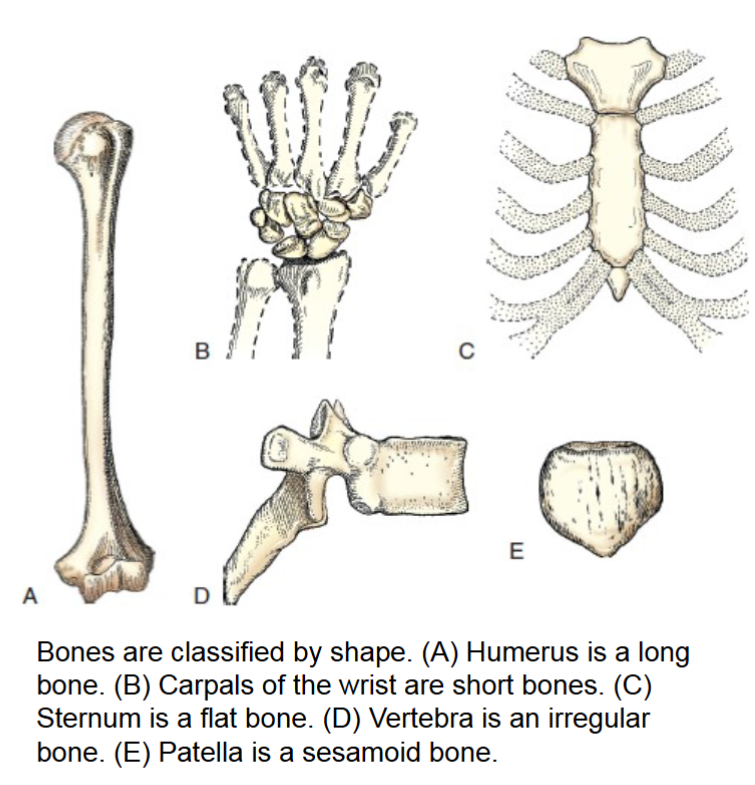
sesamoid bones
small and oval. develop inside and beside tendons.
Protect the tendon from excessive wear
Largest is patella
Located:
-Beneath the first metatarsophalangeal articulation of the foot
•-On the palmar aspect of the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint of the hand
- Can be fractured
arthrology
the study of joints or the articulations between bones. joints make it possible for bones to support the body, protect internal organs, and create movement.
two classifications
structural
functional
functional classification
when joints are classified as this they are broken down into three subdivisions
synarthroses- immovable
amphiarthroses- slightly movable
diarthroses- freely movable
(Remember I’m functionally sad)
S > A > D go from immovable to movable
structural classification
classification of joint. based on types of tissue that unite or bind the articulating bones. from there they are put into three groups bases on connective tissue
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
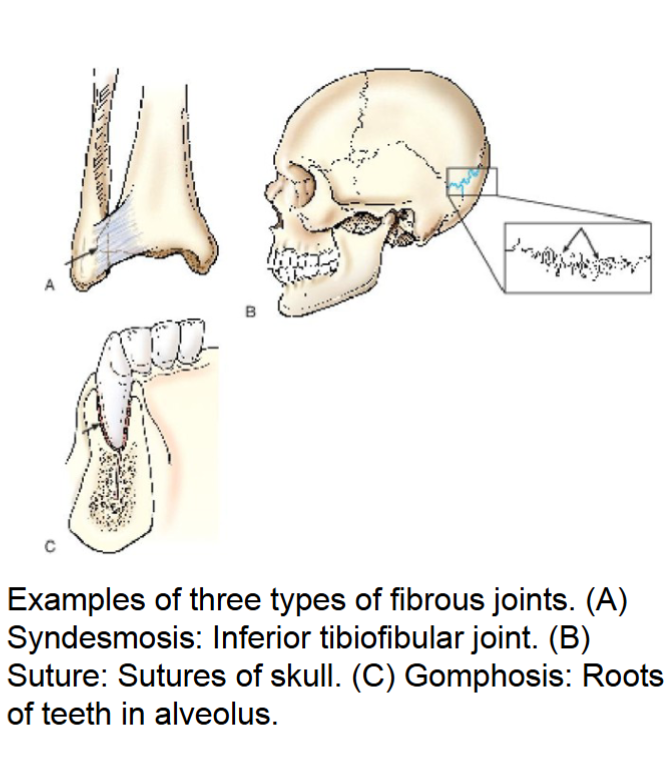
fibrous joints
do not have a joint cavity. united by various fibrous and connective tissues or ligaments.
these are the strongest joints in the body.
three types
syndesmosis- immovable or slightly movable united by sheets of fibrous tissue. (inferior tibiofibular joint)
suture- immovable joint occurring only in skull. interlocking bones are held together with connective tissue (skull sutures)
gomphosis- immovable. only in root of teeth of alveolar socket. held by fibrous periodontal ligaments.
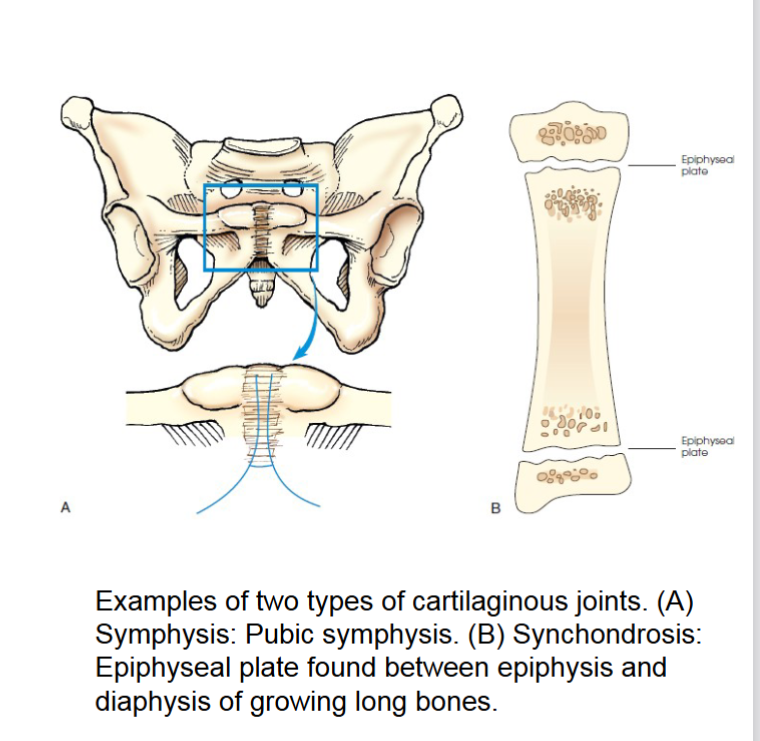
cartilaginous joints
similar to fibrous joints also have no joint cavity and are virtually immovable. hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage unites these joints
symphysis- slightly movable joint. bones in this joint are separated by pad of fibrocartilage. ends of bone contain hyaline cartilage. designed for strength and shock absorption. joint between pubic bones and joints between vertebral body are examples.
synchondrosis- immovable. contains rigid cartilage unites two bones. ex is epiphyseal plate in growing long bone. when growth stops cartilage ossifies making this temporary joint.
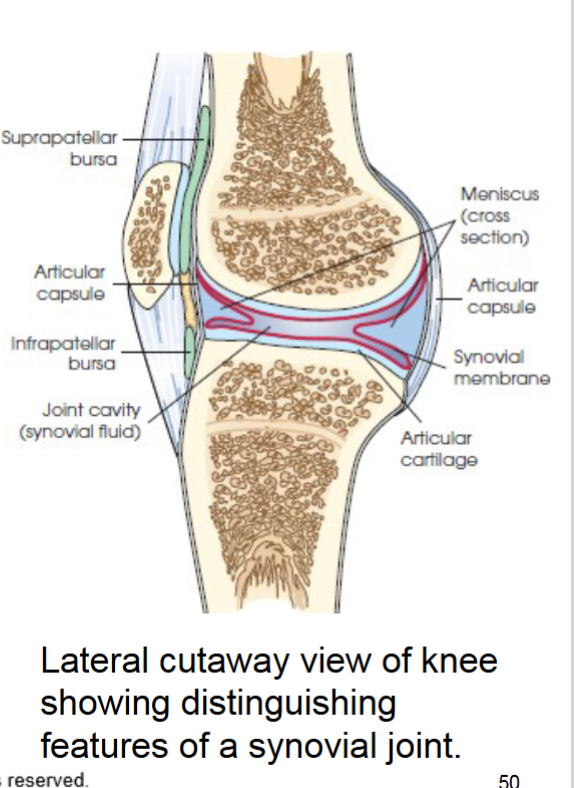
synovial joint
joint permits wide range of motion freely movable. most complex joints in body. they’re enclosed by articular capsule outer layer of this capsule is called fibrous capsule.
have accessory soft tissues
meniscus- act as shock absorbers
bursae- reduce friction between skin and bones tendons and bones and muscles and bones.
six types all freely movable- gliding, hinge, pivot, ellipsoid, saddle, ball and socket (table 2.4 pg 64)
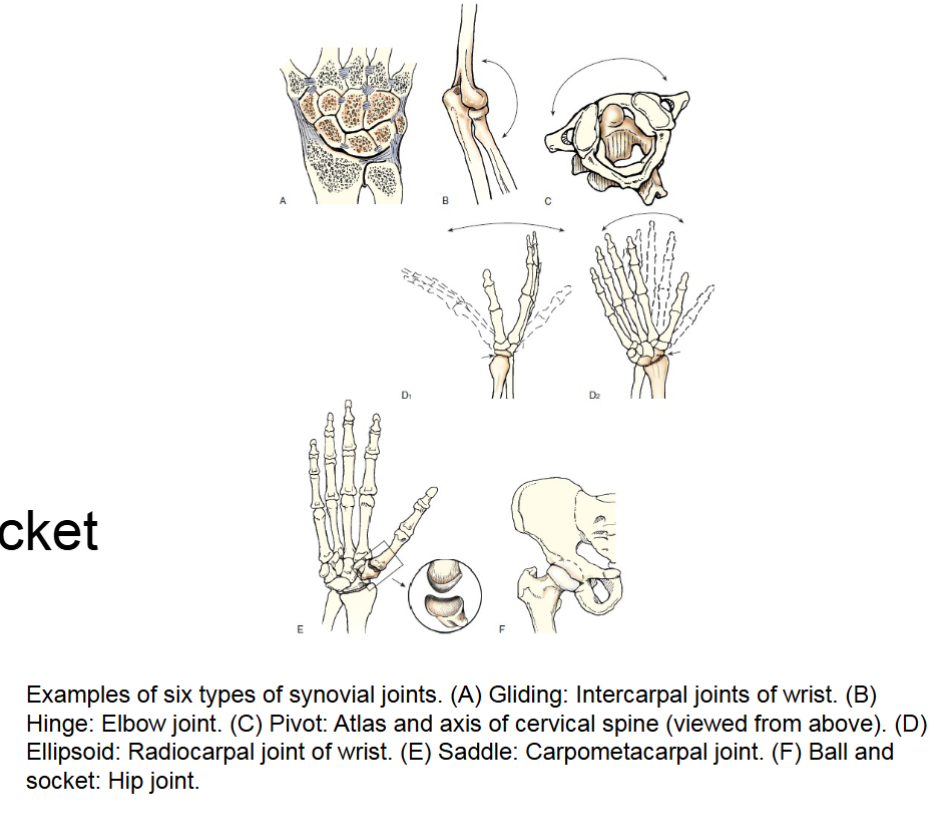
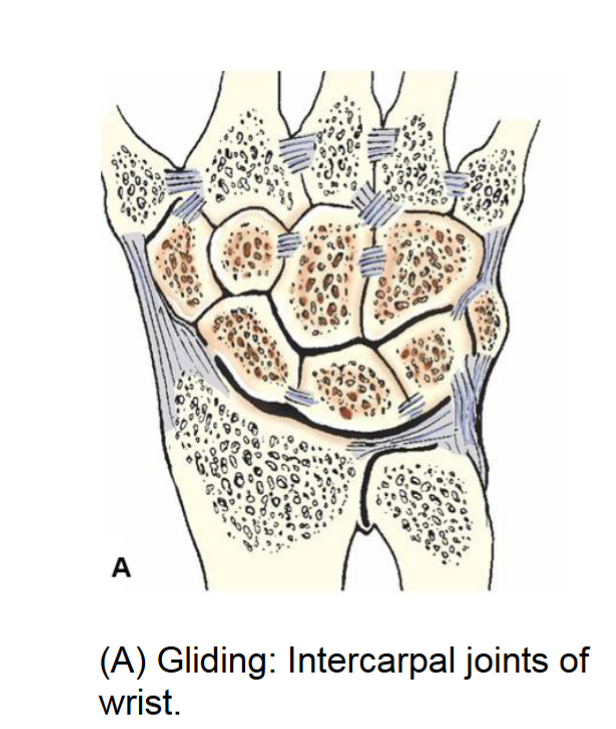
gliding joint
synovial joint. simplest. permits slight movement glide slightly in only one axis uniaxial movement.
intercarpal and intertarsal joints ex.
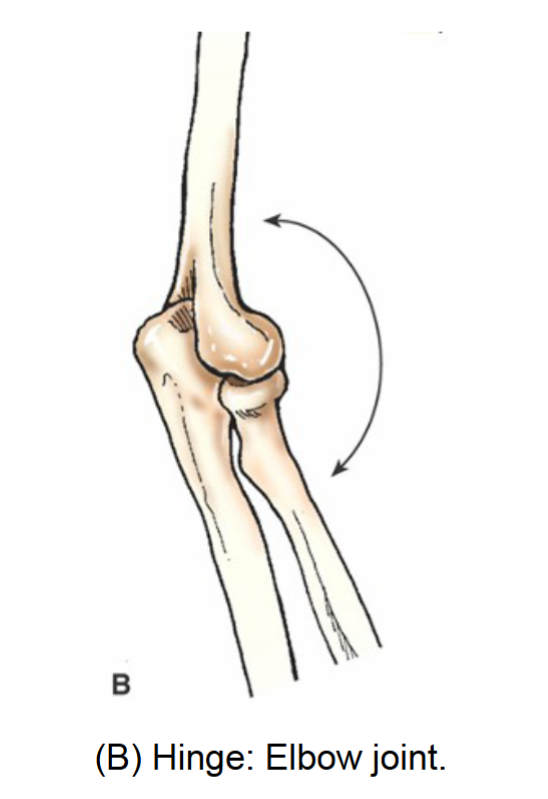
hinge joint
synovial joint. permits flexion and extension. uniaxial movement. moves similar to a door. elbow knee and ankle examples
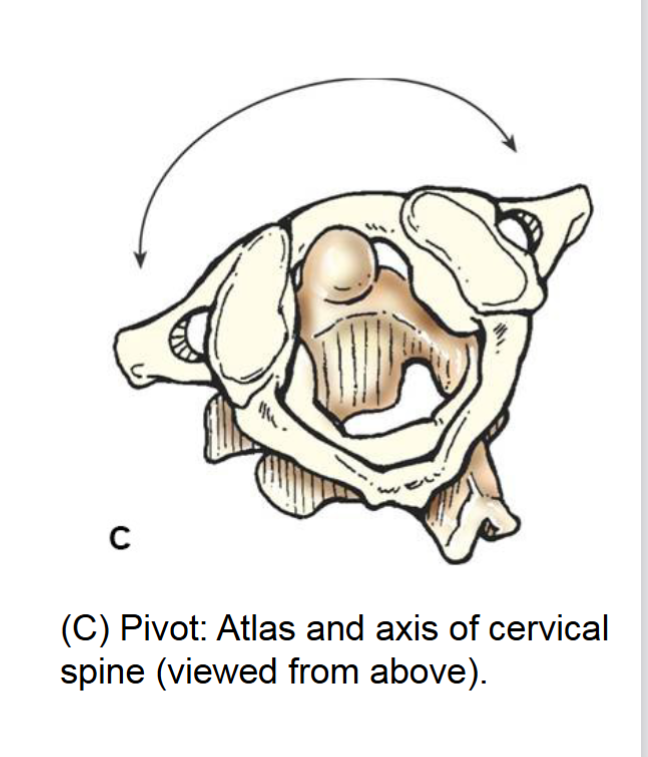
pivot joint
synovial joint. allows rotation around a single axis. uniaxial movement. example anlantoaxial joint (C1-C2) joint
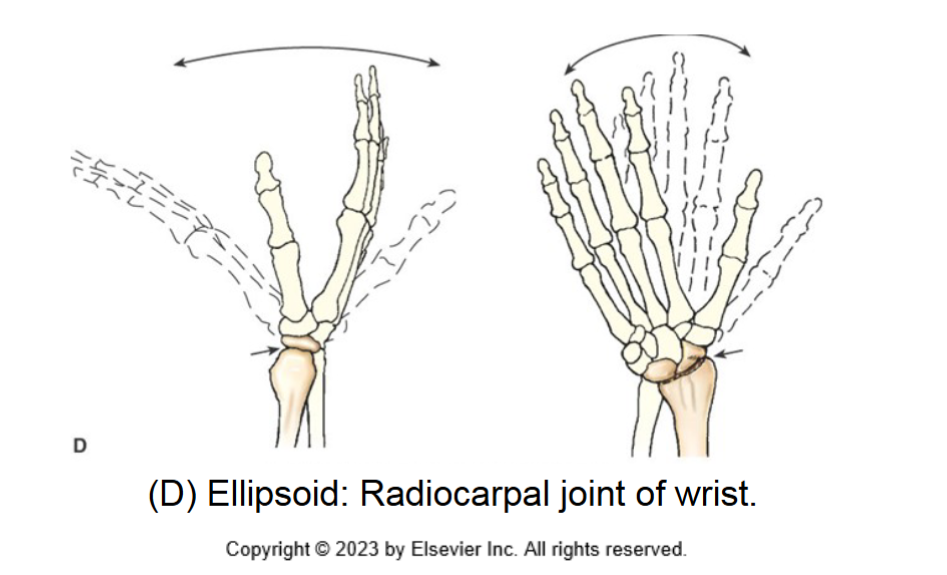
ellipsoid joint
synovial joint. biaxial movement. allows flexion extension abduction adduction and circumduction. allows movement in two directions at right angles of each other.
radiocarpal (wrist joint)
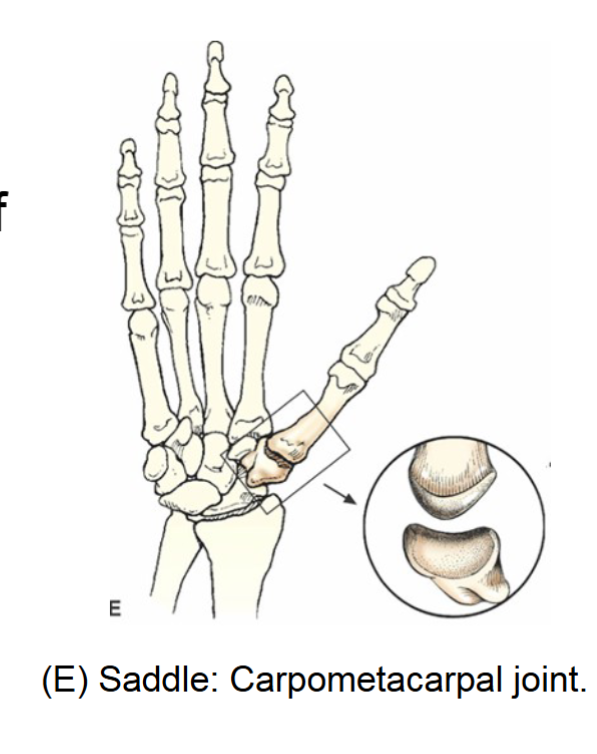
saddle joint
synovial joint. sellar. biaxial movement. similar to movement of ellipsoid, difference is shape of articular surfaces which is saddle shaped while other is shaped like a rider.
carpometacarpal joint between trapezium and first metacarpal
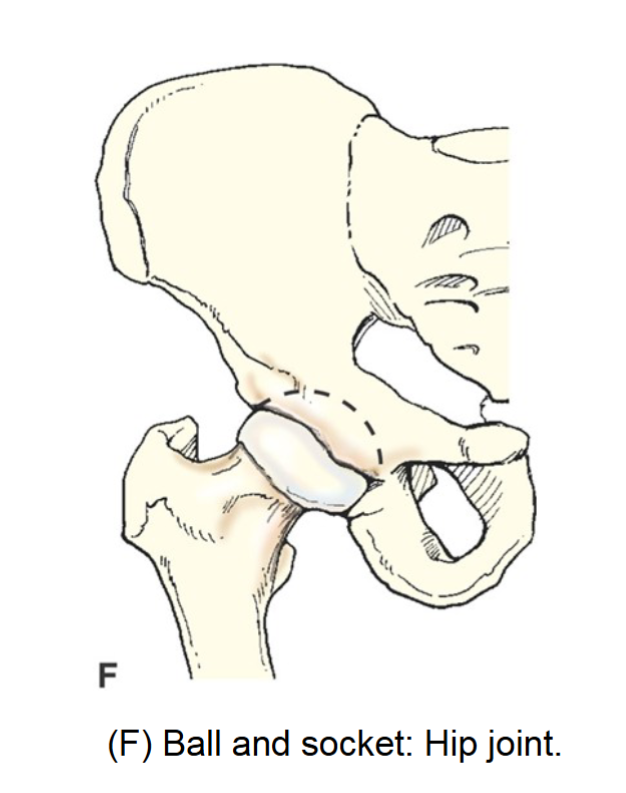
ball and socket joint
spheroid. synovial joint. permits widest range of motion multiaxial movement. flexion extension, abduction adduction circumduction and rotation.
examples hip and shoulder.
processes and projections
processes or projections extend beyond or project out from the main body of a bone.
condyle
rounded process at an articular extremity
coracoid or coronoid
beak like or crown like process
crest
ridgelike process
epicondyle
projection above a condyle
facet
small smooth surfaced articular process
hamulus
hook shaped process
head
expanded end of a long bone (
horn
hornlike process
line
linear elevation not as prominent as a crest
malleolus
club shaped process
protuberance
Projecting prominence
spine
sharp process
styloid
Long, pointed process
trochanter
Either of the two large, rounded, and elevated processes of the proximal femur
tubercle
small round and elevated process
tuberosity
large rounded and elevated process.
depressions
hollow or depressed areas of bone
fissure
cleft or deep groove
foramen
hole in a bone for transmission of vessels and nerves
fossa
pit, fovea or hollow space
groove
shallow linear channel
meatus
tubelike passageway
notch
indentation in the border of a bone
sinus
recess groove cavity or hollow space
sulcus
furrow or trench
fracture
a break in the bone classified according to nature of break
closed fracture
fracture that does not break through the skin
open fracture
serious fracture in which broken bone or bones project through the skin
nondisplaced
fracture in which bone retains its normal alignment
displaced fracture
serious fracture in which bones are not in anatomic alignment
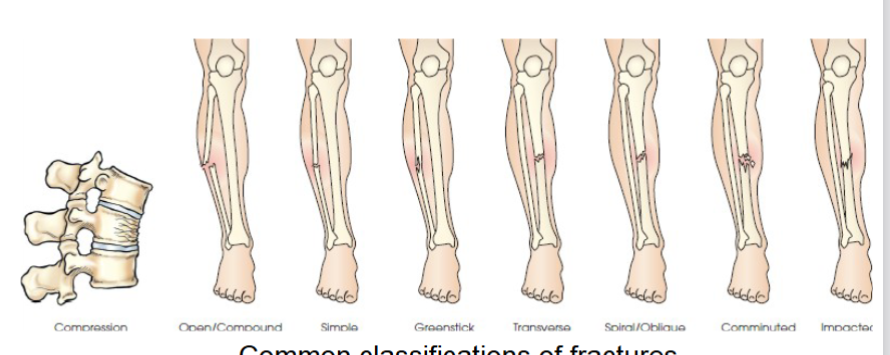
common fracture classifications
-Compression
Compound (open)- broken bone pierces skin
Comminuted- bone breaks into three or more fragments
Greenstick- partial common in children bone bends and cracks one side
Impacted- one bone fragment is driven into other
Transverse- fracture runs horizontally across bones long axis
Spiral or oblique- bone twisted or rotated leading to oblique fracture line
Simple- does not break through skin
Compression- vertebra in spine is crushed or compressed
many fall into more than one category.
anterior (ventral)
forward or front part of the body or of a part
posterior (dorsal)
back part of body or part
caudad
parts away from the head of the body
cephalad
parts towards the head of the body
superior
nearer the head or situated above
inferior
nearer the feet or situated below
central
mid area or main part of an organ
peripheral
at or near the surface, edge or outside of another body part
medial
toward the median plane of the body or toward the middle of a body part
lateral
away from the medial plane of away from the middle of a part
superficial
near the skin or surface
deep
far from surface
distal
farthest from point of attachment or origin