Anatomy Quiz 5
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
Olfactory Nerve
What is the Anatomical Name of CN I?
Function of Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
smells
loss of smell
What is Anosmia?
anosmia
What are the clinical applications of Olfactory nerve (CN I)?
Sensory
What is the Nervous Function of Olfactory Nerve (CN I)?
Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
Which cranial nervous passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone?
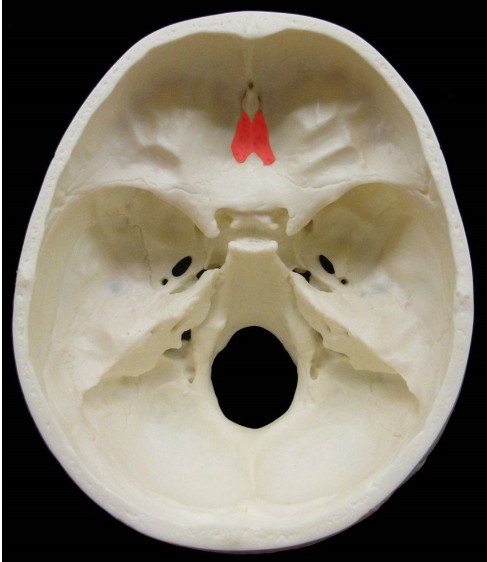
Olfactory Bulb
ID Structure
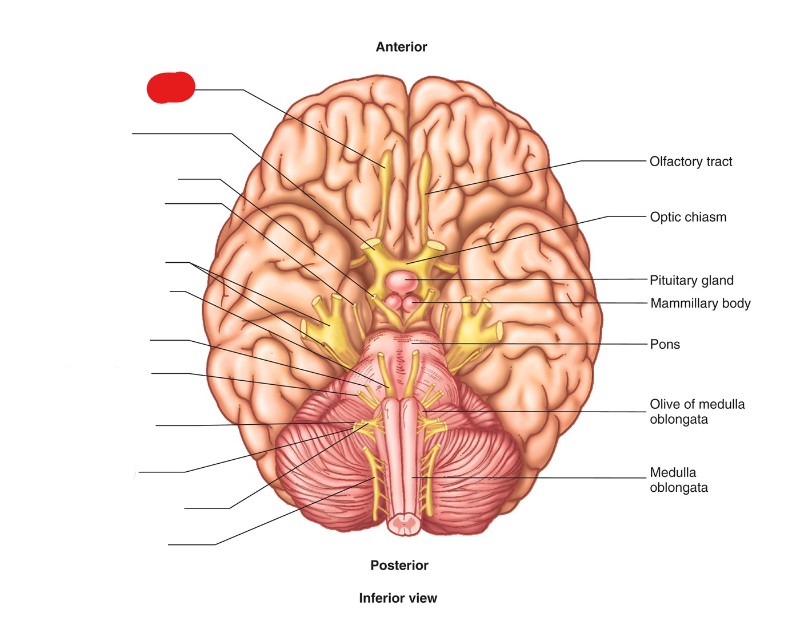
Optic Nerve
What is the Anatomical Name of CN II?
Functions of Optical Nerve (CN II)
vision
sensory
What is the Nervous Function of Optic Nerve (CN II)?
loss of sight
What is Anopsia?
anopsia
What are the clinical applications of Optic Nerve (CN II)?
Optic Nerves (CN II)
What nerve does Anosmia affect?
Optic Nerve (CN II)
Which Cranial Nerve passes through the optical canal of the sphenoid bone?
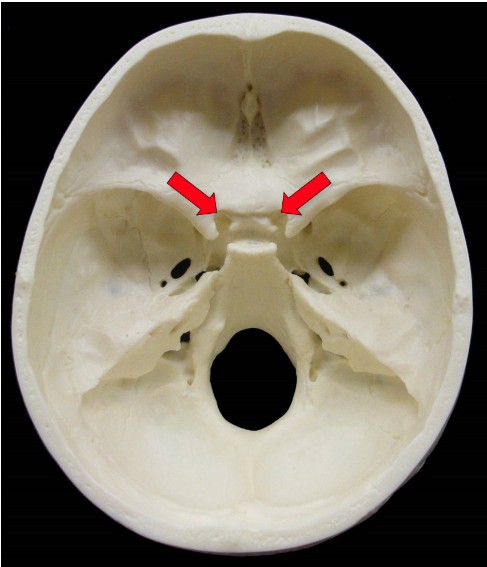
Optic Nerve (CN II)
ID Structure
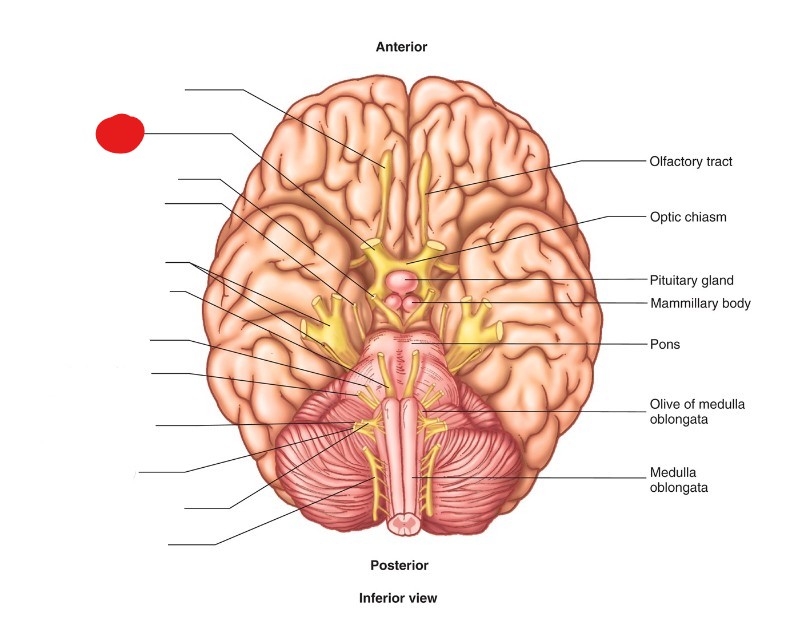
Oculomotor Nerve
What is the Anatomical Name of CN III?
Functions of Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
controls a group of muscles responsible for movement of the eyeball and eyelid (m)
accommodation of lens for near vision (ps)
constriction of the pupil (ps)
clinical applications of Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
strabismus, diplopia, and ptosis
Strabismus
a condition in which the eyes are not properly aligned with each other
diplopia
creates double vision
ptosis
having droopy eyelids
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
ID Structure
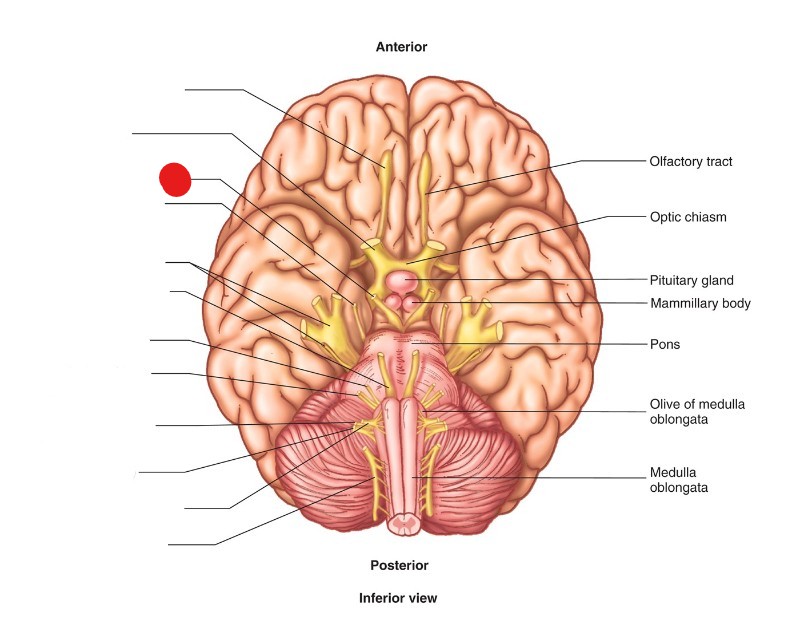
motor and parasympathetic
What are the Nervous Functions of Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)?
Trochlear Nerve
What is the Anatomical Name of the CN IV?
Functions of Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
controls the superior oblique muscle (involved with movement of the eyeball) (m)
clinical applications of the Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
strabismus and diplopia
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
ID Structure
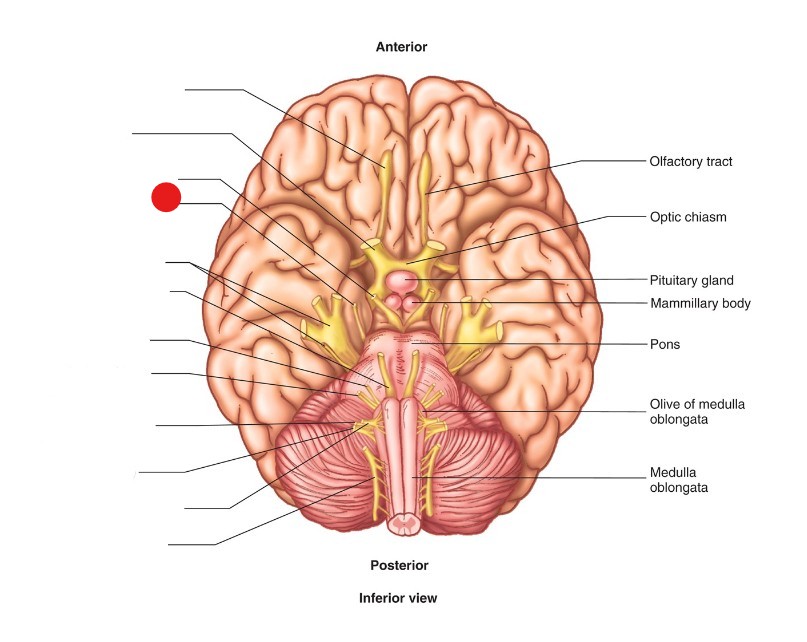
motor
What are the Nervous Functions of the Trochlear Nerve?
Trigeminal Nerve
What is the Anatomical Term for CN V?
Functions of Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
supplies “chewing muscles” (muscle of mastication) (m)
sensation to the face (s)
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
ID Structure
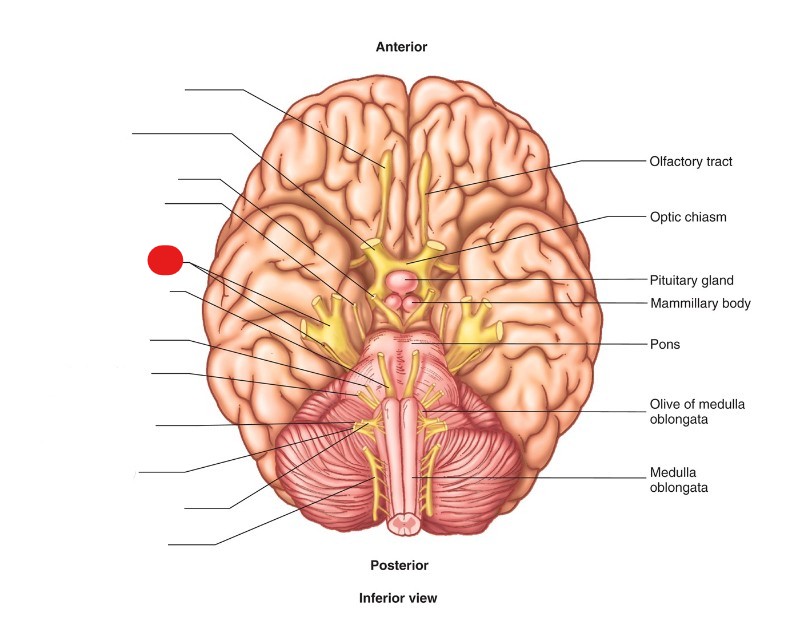
Clinical Applications of Trigeminal Nerves (CN V)
loss of muscle function and loss of facial sensation
motor and sensory
What is the Nervous Function of Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)?
Abducent Nerve
What is the Anatomical Name of CN VI?
Functions of the Abducent Nerve (CN VI)
controls the lateral rector muscle (involved with movement of the eyeball) (m)
clinical applications of aducent Nerve (CN VI)
strabismus and diplopia
abducent nerve (CN VI)
ID Structure
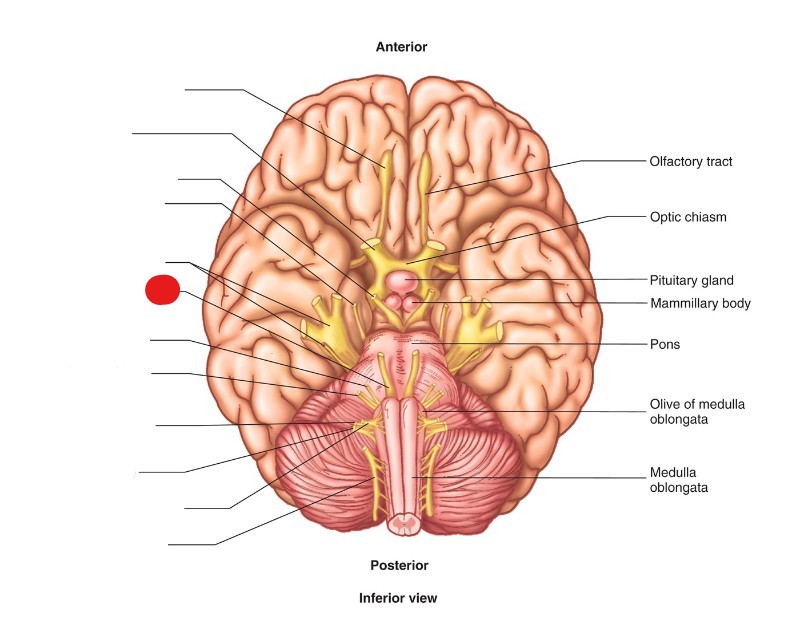
motor
What are the Nervous Functions of abducent nerve (CN VI)?
facial nerve
What is the Anatomical name of CN VII?
Functions of facial nerve (CN VII)
supplies muscles of “facial expression” (m)
supplies taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue (s)
clinical applications of facial nerve (CN VII)
facial (Bell’s palsy) (m)
loss of taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue (s)
weakness or paralysis to one side of the face
What is Bell’s palsy?
facial nerve (CN VII)
ID Structure
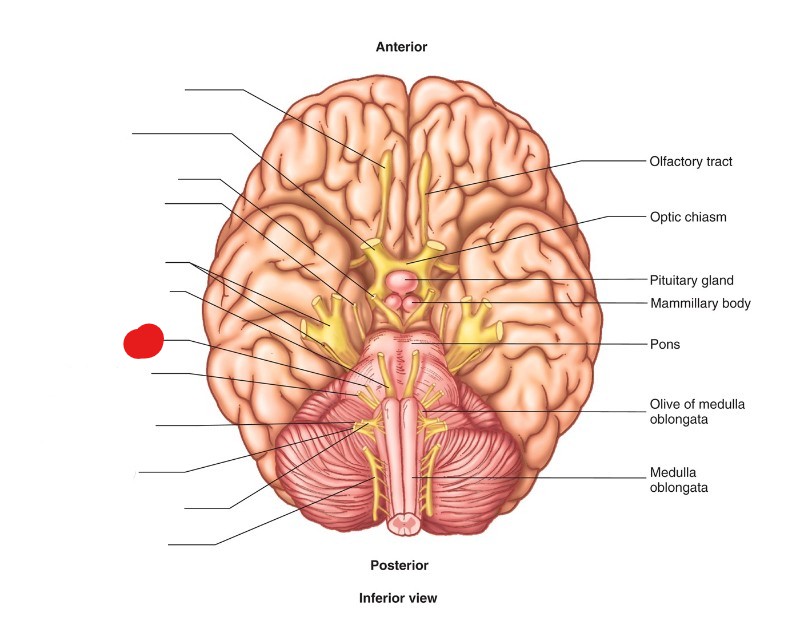
motor and sensory
What are the Nervous Functions of facial nerve (CN VII)?
vestibulocochlear nerve
What is the anatomical name of CN VIII?
Functions of vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
vestibular branch: equilibrium (s)
cochlear branch: hearing (s)
clinical applications of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
vestibular branch: vertigo
cochlear branch: tinnitus
vertigo
a sensation of spinning or whirling, where the person or their surroundings appear to be moving
tinnitus
hearing noises like ringing, buzzing, or roaring in your ears when there is no external sound source
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
ID Structure
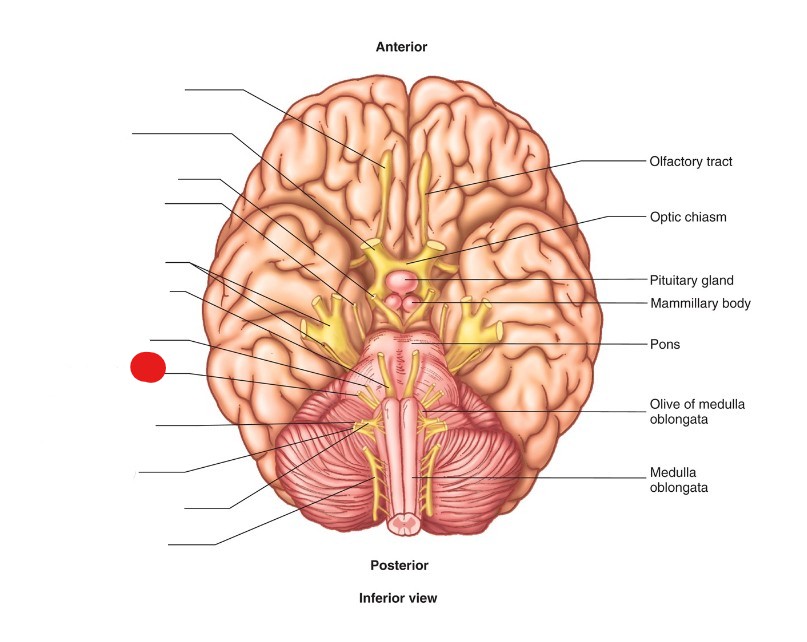
sensory
What are the nervous functions of vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)?
glossopharyngeal nerve
What is the anatomical name of CN IX?
Functions of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
taste on posterior 1/3 tongue (s)
sensation to throat (s)
supplies muscles involved with swallowing (m)
clinical applications of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
loss of taste on posterior 1/3 of tongue
decreased sensation to throat
difficulty swallowing
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
ID Structure
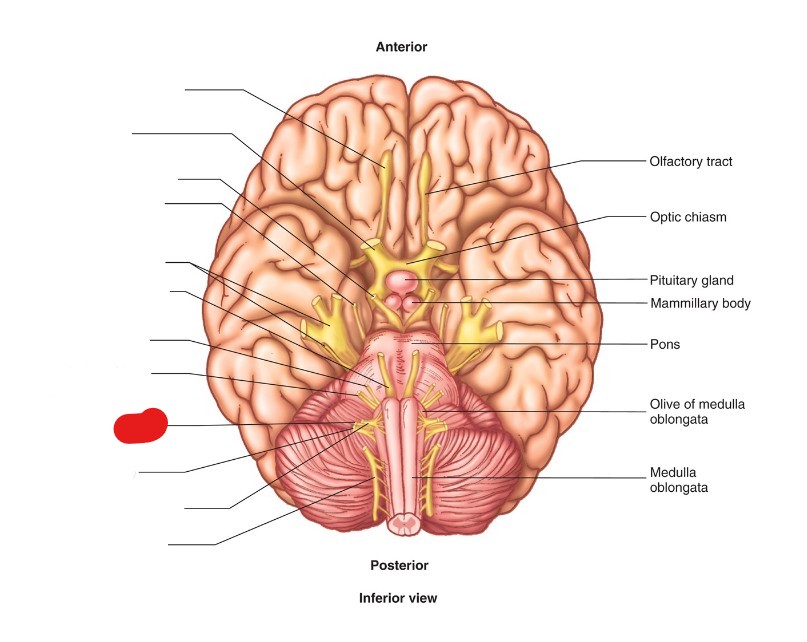
motor and sensory
what is the nervous functions of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II)
which cranial nerves are in the cerebrum?
oculomotor nerve (CN III) and trochlear nerve (CN IV)
which cranial nerves are in the midbrain?
trigeminal nerve (CN V), abducent nerve (CN VI), facial nerve (CN VII), and vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
which cranial nerves are in the pons?
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), accessory nerve (CN XI), and hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
which cranial nerves are in the medulla oblongata?
vagus nerve
what is the anatomical name of CN X?
functions of vagus nerve (CN X)
sensation to throat (s)
supplies muscles involved with swallowing (m)
carries parasympathetic information to thorax and abdomen (ps)
clinical applications of vagus nerve (CN X)
decreases sensation to throat
difficulty swallowing
loss of parasympathetic information in thorax and abdomen
vagus nerve (CN X)
ID Structure
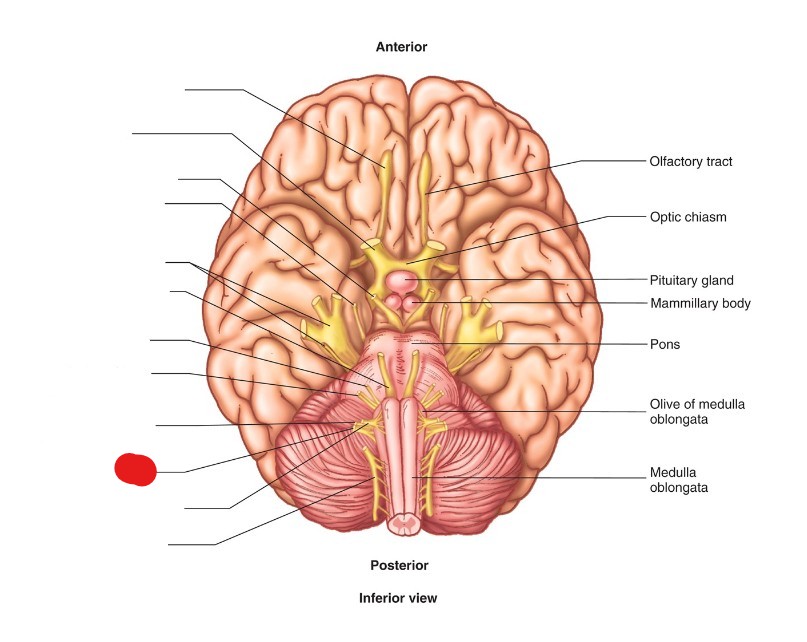
sensory, motor, and parasympathetic
what is the nervous functions of vagus nerve (CN X)?
accessory nerve
what is the anatomical name of CN XI?
functions of accessory nerve (CN XI)
supplies the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles (m)
clinical application of accessory nerve (CN XI)
loss of muscle function
accessory nerve (CN XI)
ID Structure
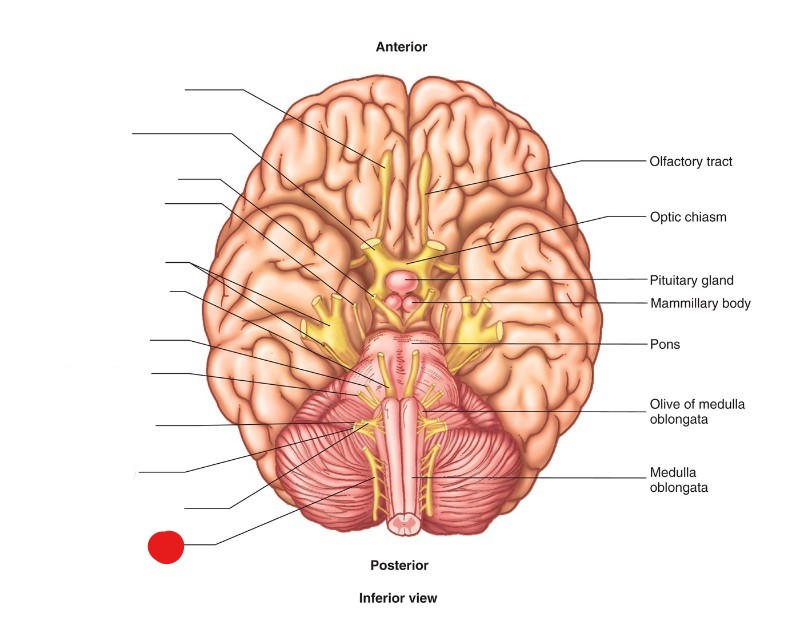
motor
what are the nervous functions of accessory nerve (CN XI)?
hypoglossal nerve
What is the anatomical term for CN XII?
functions of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
supplies muscles responsible for movement of tongue (m)
clinical applications of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
difficulty chewing, speaking, and swallowing
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
ID Structure
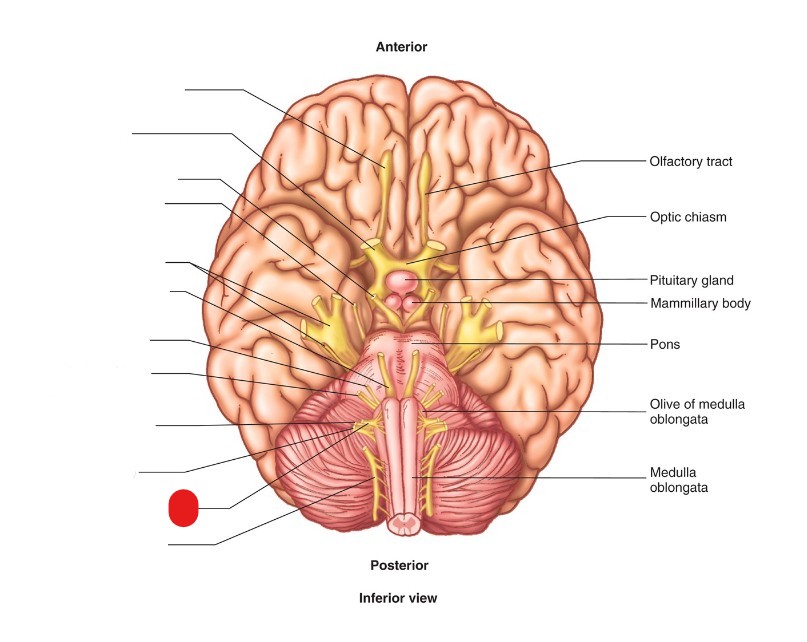
motor
what is the nervous function of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)?
gustatory (taste) pathway
when food chemicals (dissolved by saliva) come into contact with taste buds, action potentials are generated
facial nerves (CN VII) and glossopharyngeal nerves (CN IX)
name all the nerves that detect taste on tongue
accessory structures of the eye
the eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, and extrinsic eye muscles
functions of eyelids (palpebrae)
gives protection to the eye
spreads tears when we blink
orbicularis oculi and levator palpebrae superioris
what major muscles are associated with moving eyelids?
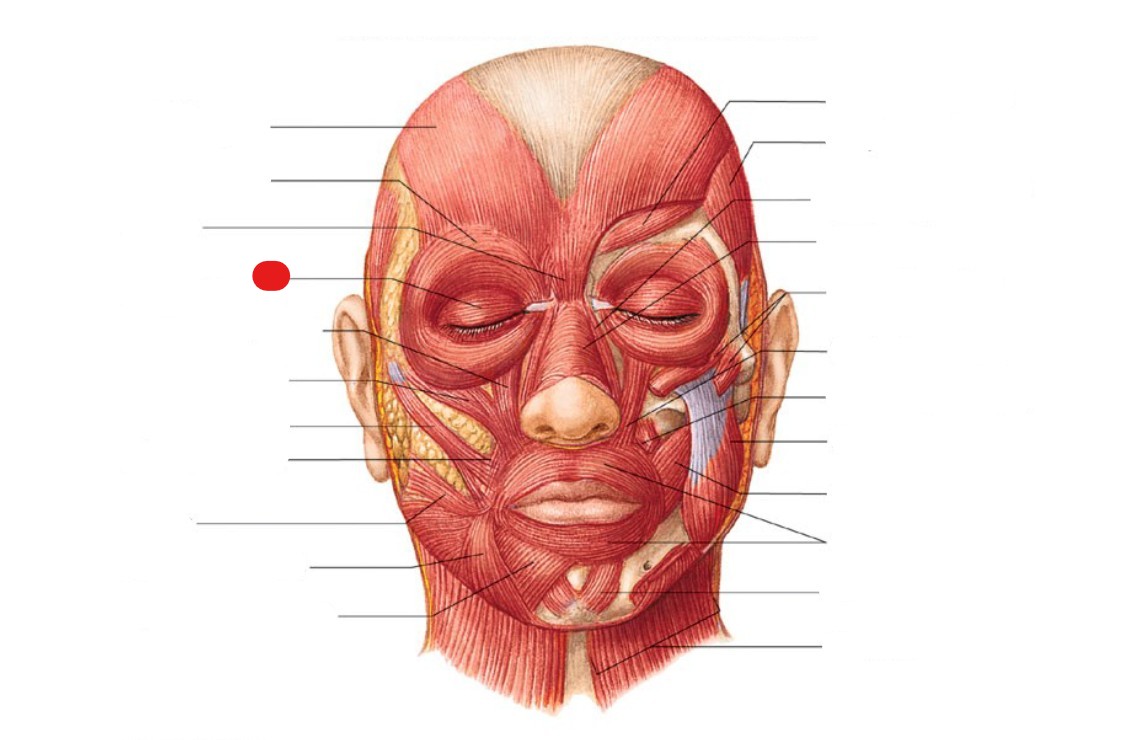
orbicularis oculi
muscle that closes the eyelids
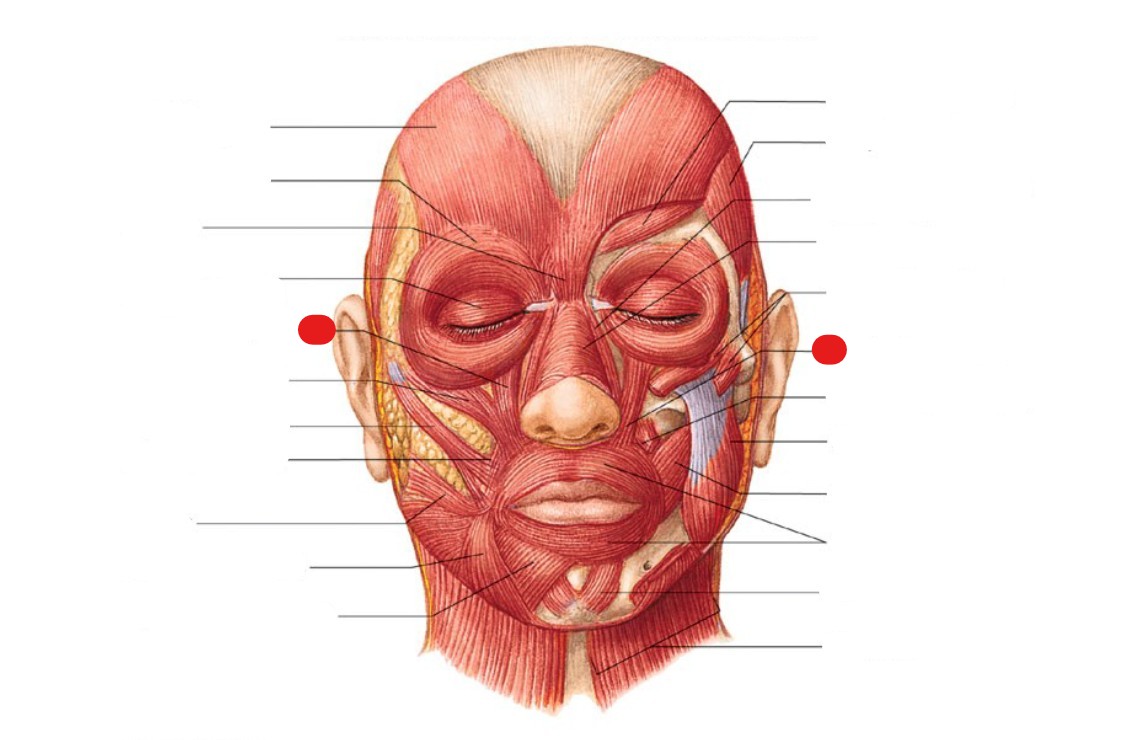
levator palpebrae superioris
muscle that opens upper eyelid
involved with ptosis
orbicularis oculi
ID structure
levator palpebrae superioris
ID Structure
lacrimal glands
produces tears
tears
lubricates and cleans the eye
superior rectus
muscle that elevates the eye
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
which nerve supplies the superior rectus?
superior rectus
ID Structure
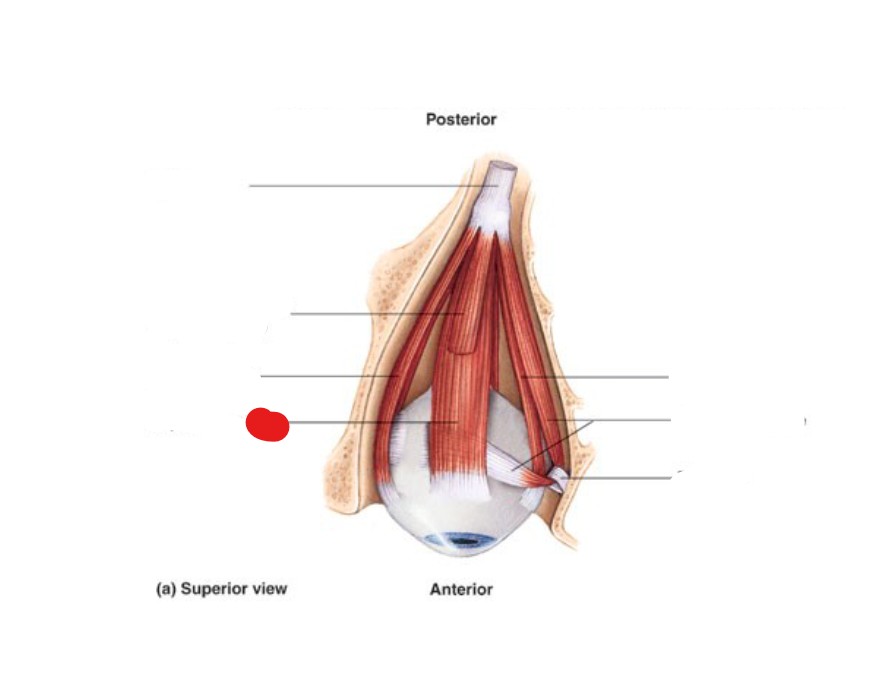
inferior rectus
muscle that depresses eyeball
oculomotor (CN III)
which cranial nerve supplies the inferior rectus?
inferior rectus
ID Structure
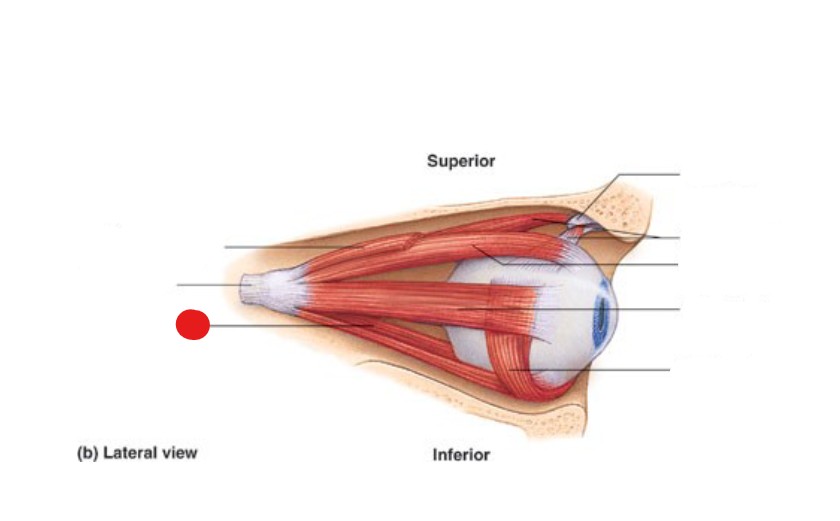
medial rectus
muscle that move eyeball medially
oculomotor (CN III)
which cranial nerve supplies the medial rectus?
medial rectus
ID Structure
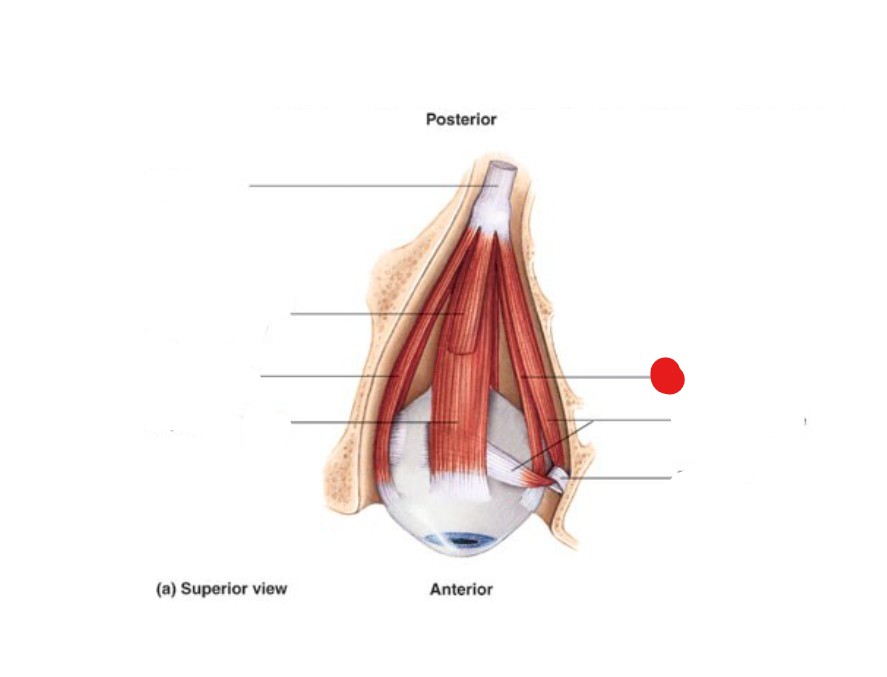
levator palpebrae superioris
muscle that opens upper eyelid
oculomotor (CN III)
which cranial nerve runs to the levator palpebrae superioris?
Levator palpebrae superioris
ID Structure
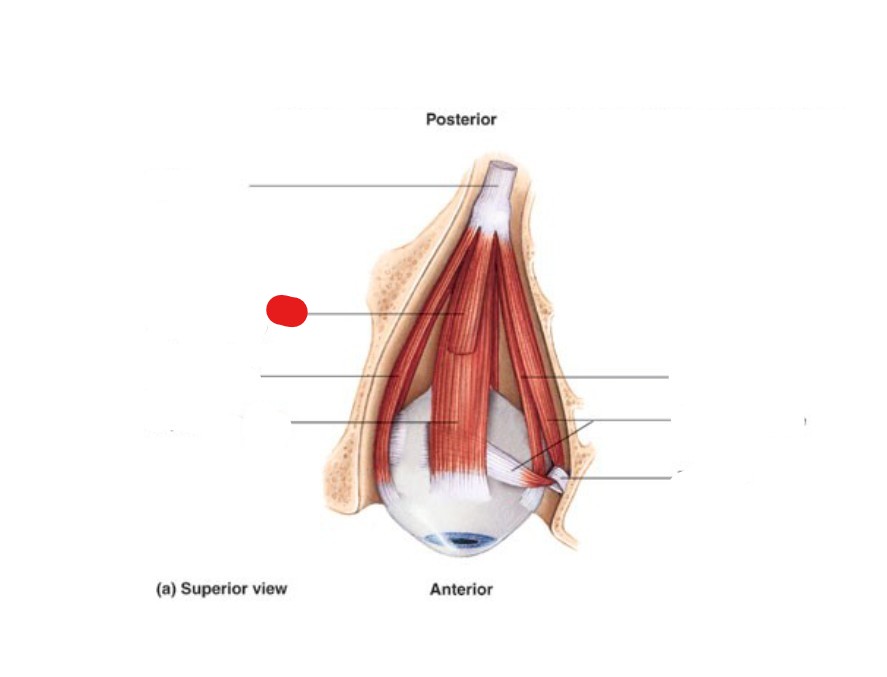
inferior oblique
muscle that elevates and turns eyeball laterally
oculomotor (CN III)
which cranial nerve supplies the inferior oblique?