Comparative anatomy of the equine hock and distal hindlimb
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What arteries supply the equine hindlimb?
cranial and caudal tibial
What vein is large and palpable in equine?
medial saphenous
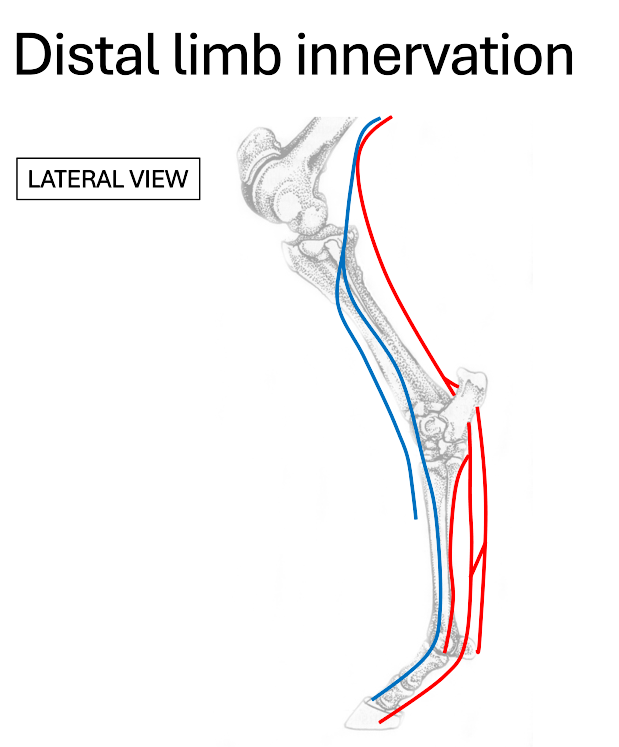
red
tibial nerve
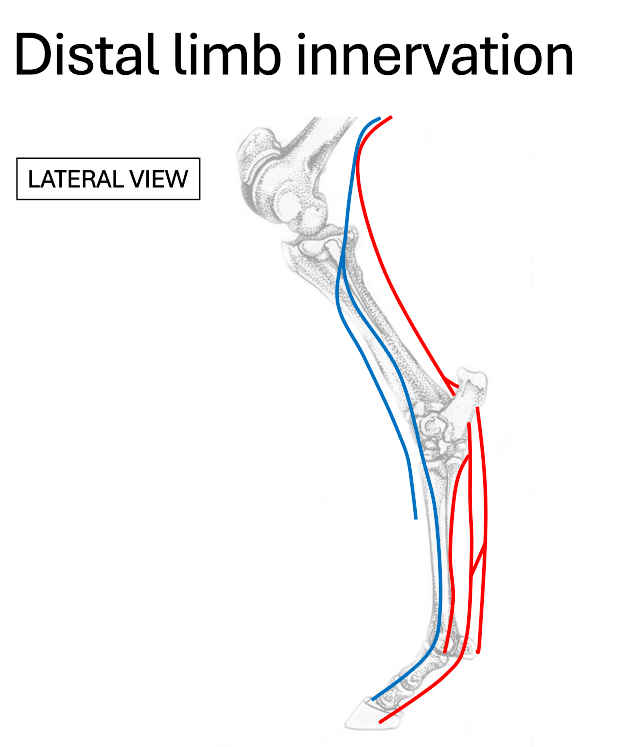
blue
deep fibular (peroneal) nerve
Where do the dorsal metatarsal nerves run?
medial & lateral to extensor tendons
What nerve provides the majority of sensory innervation to the distal limb?
tibial nerve
What does the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve branch into?
dorsal metatarsal nerves
What does the tibial nerve branch into?
plantar nerves
plantar metatarsal nerves
In the hindlimb, what do muscles caudal to the distal limb tend to do?
flex stifle
extend hock
flex digit
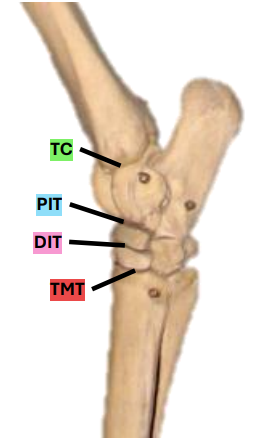
What are the 4 levels of the tarsal joint?
tarsocrural
proximal intertarsal
distal intertarsal
tarsometatarsal
What levels of the equine tarsal joint communicate?
capsule for TC & PIT
Which levels of the equine tarsal joint occasionally communicate?
DIT & TMT
What ligaments support the tarsus?
collateral ligaments
long plantar ligament
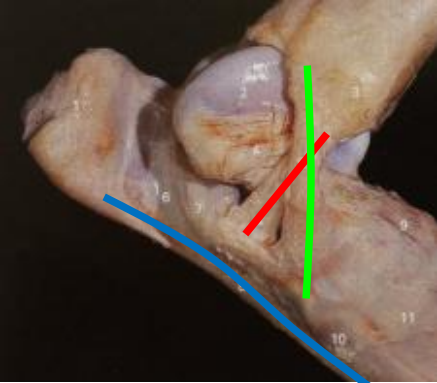
red
medial collateral ligament
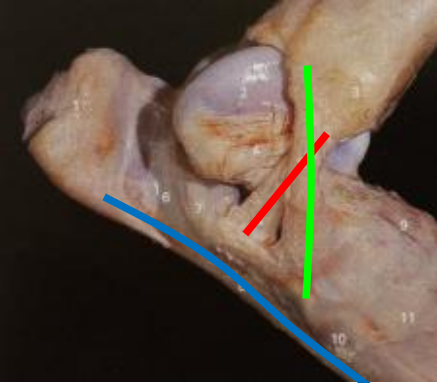
green
lateral collateral ligament
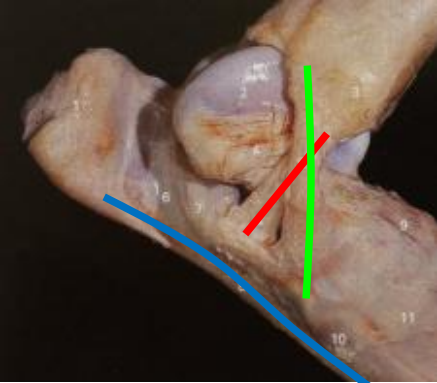
blue
long plantar ligament
What is the role of the collateral ligaments?
ensure joint doesn’t move side to side
What is the role of the long plantar ligament?
resist hyperextension of foot and digit
Where are the hock flexors located?
cranial to hock joint
What hock flexor do equine species NOT have?
fibularis longus
Name the equine hock flexors
fibularis (peroneus) tertius
cranial tibial
long digital extensors
lateral digital extensors
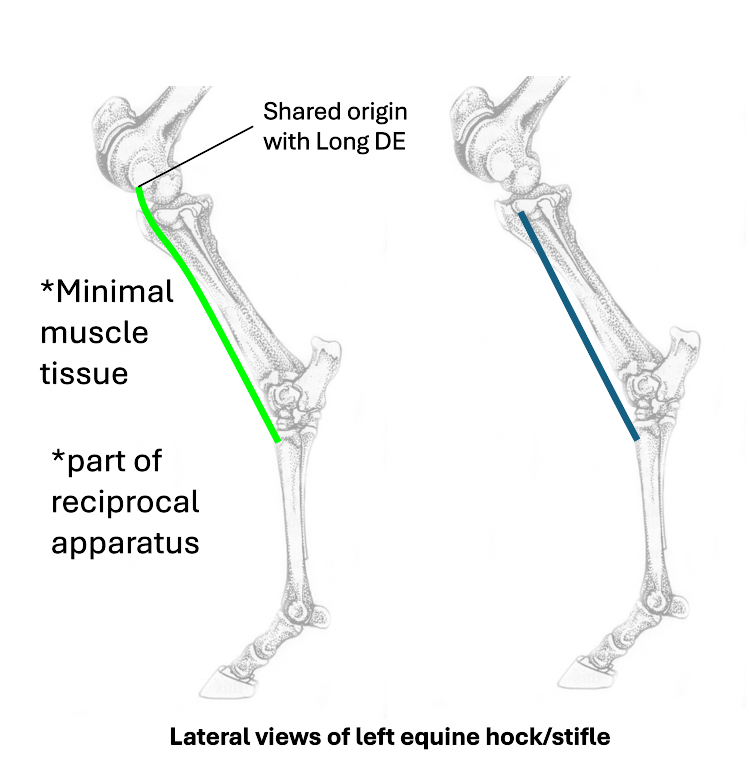
green
fibularis (peroneus) tertius
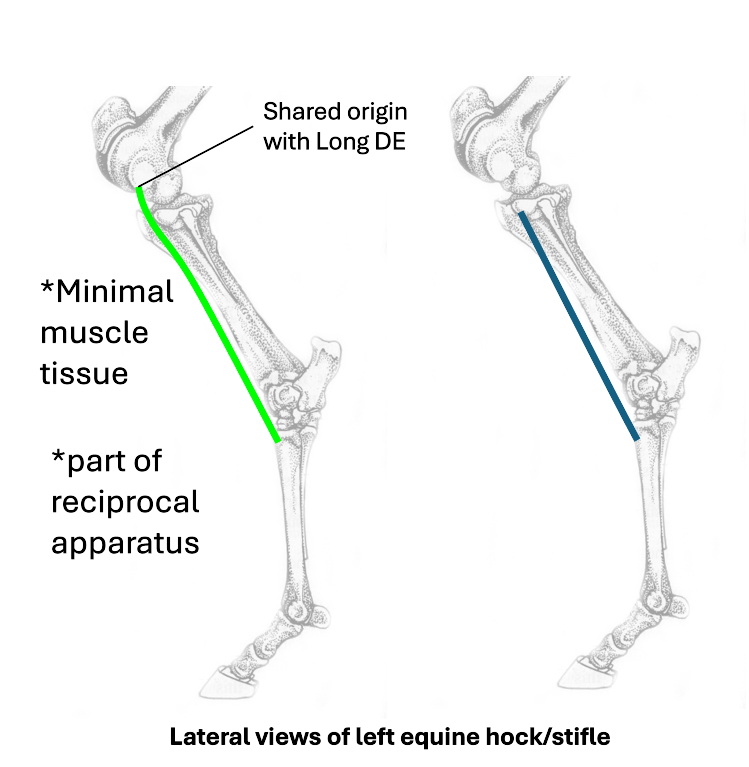
blue
cranial tibial
What does fibularis (peroneus) tertius have a shared origin with?
long digital extensor
What nerve innervates fibularis (peroneus) tertius and cranial tibial?
fibular (peroneal) nerve
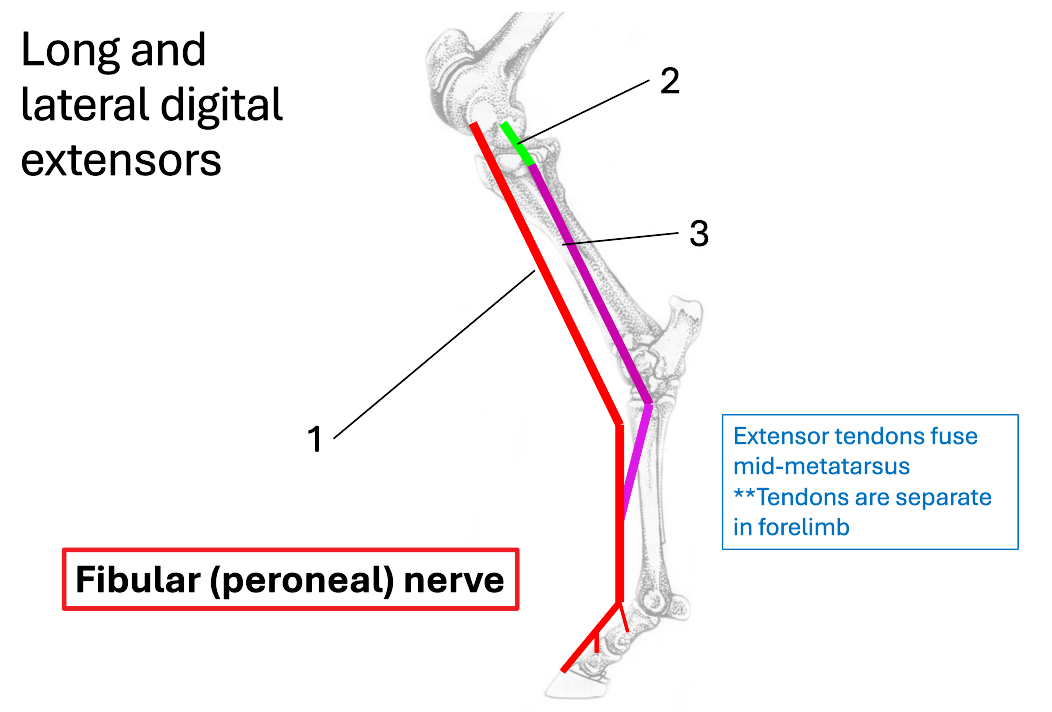
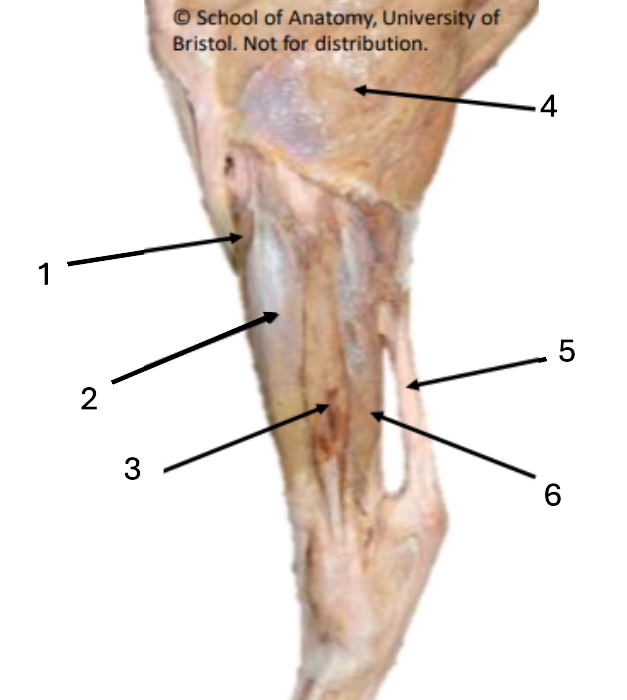
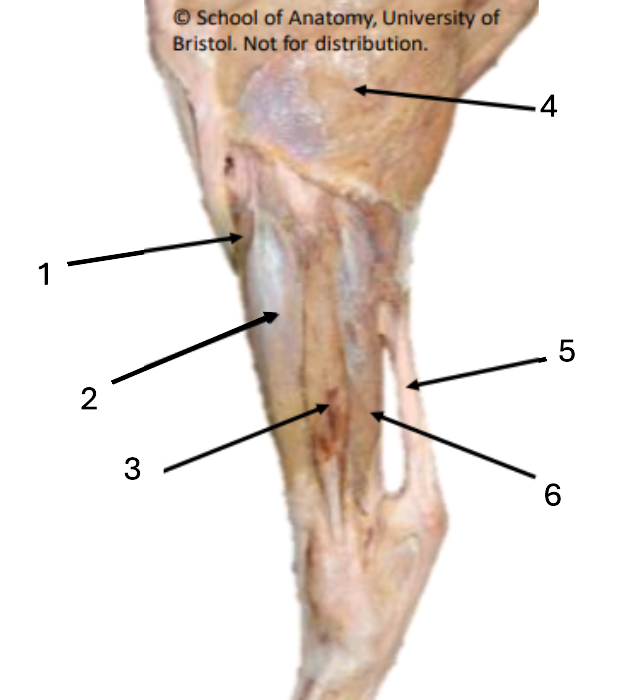
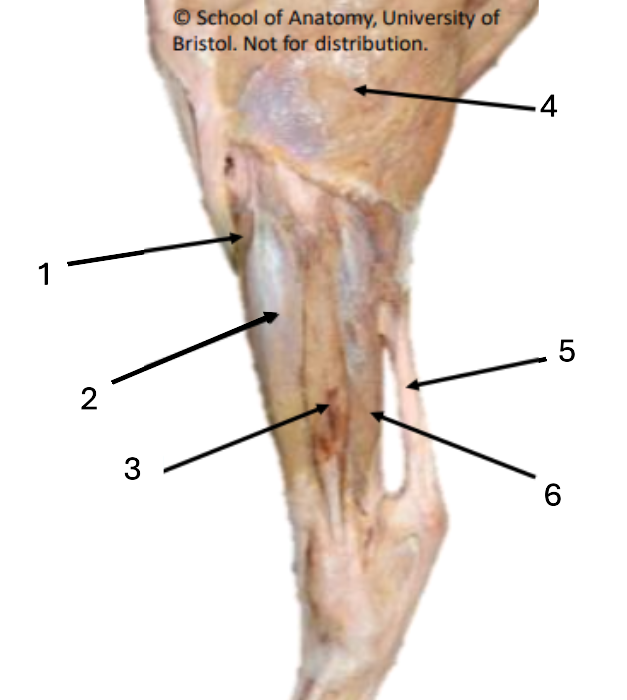
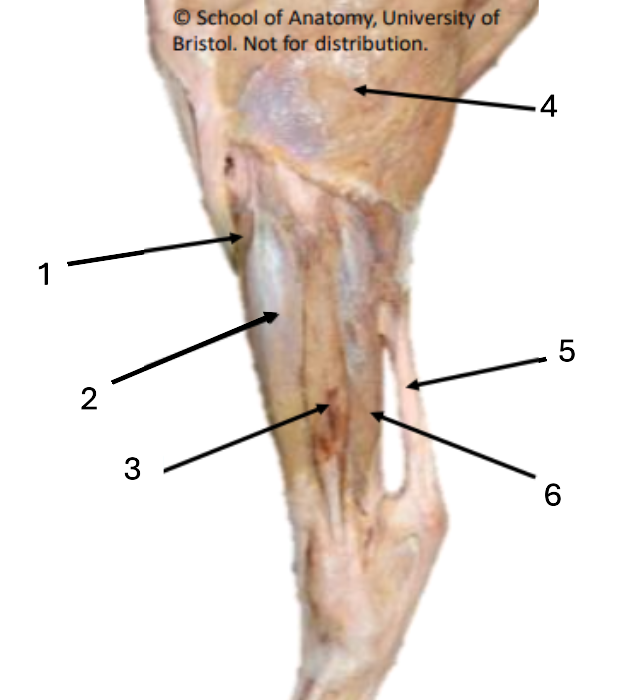
1 (red)
long digital extensor
2 (green)
lateral collateral ligament of stifle
3 (purple)
lateral digital extensor
Where do extensor tendons fuse?
mid-metatarsus
What nerve innervates the long and lateral digital extensors?
fibular (peroneal) nerve
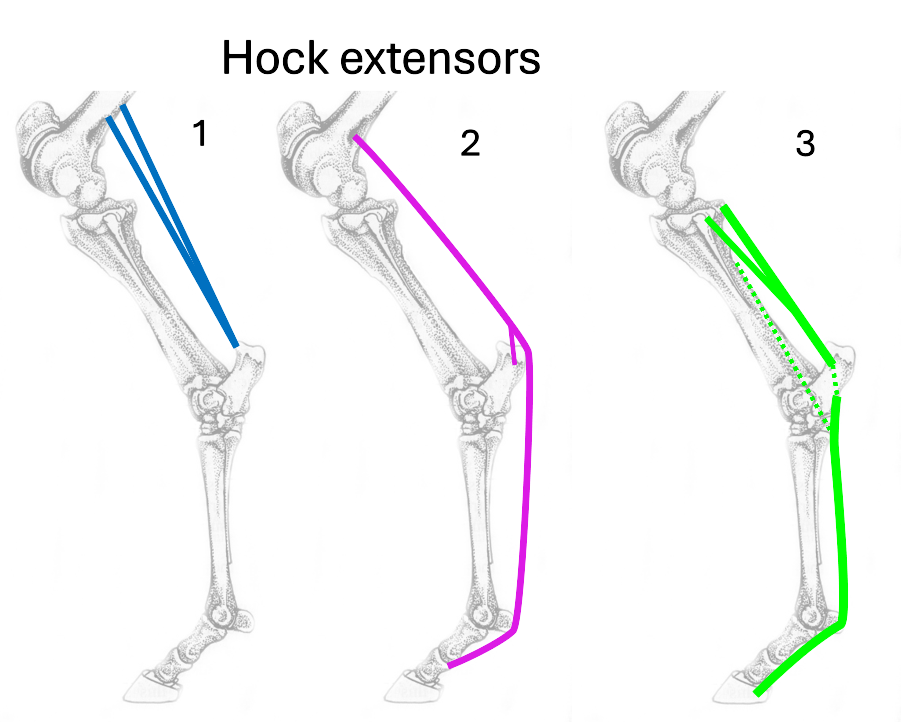
1 (blue)
gastrocnemius
2 (purple)
superficial digital flexor
3 (green)
deep digital flexor
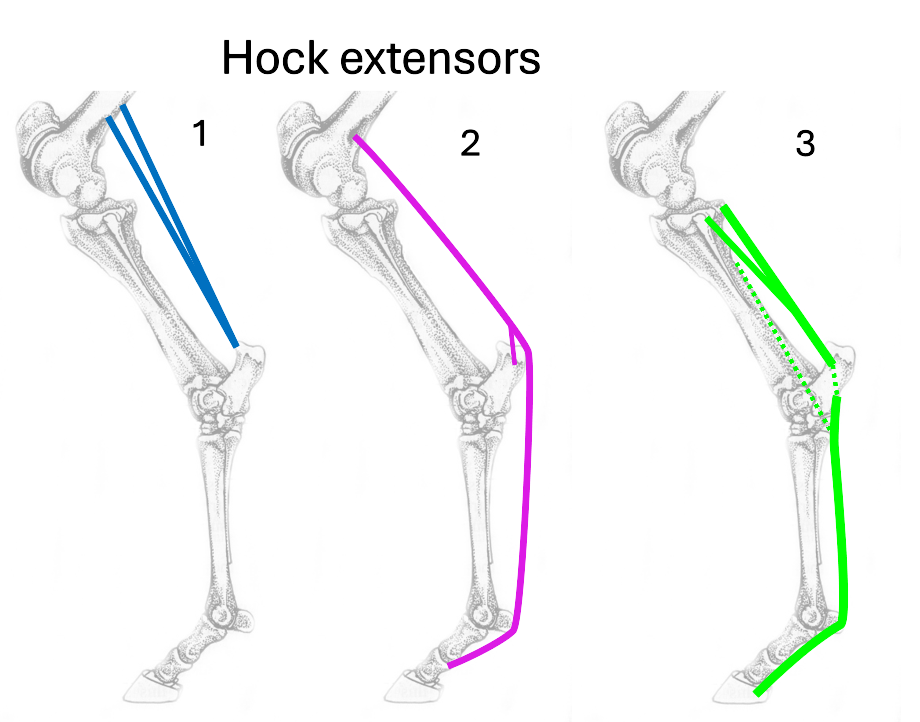
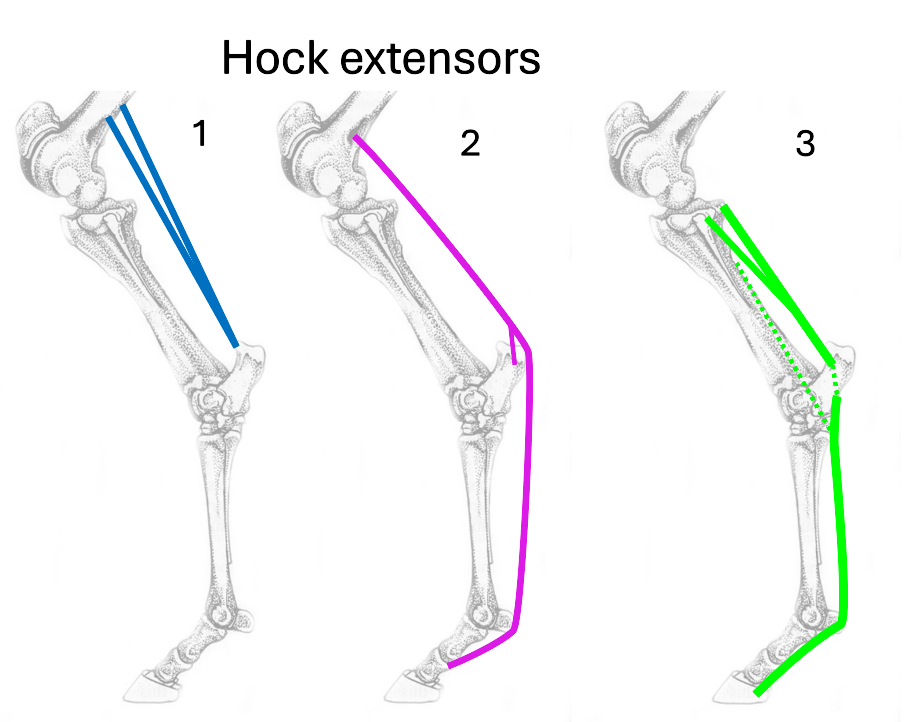
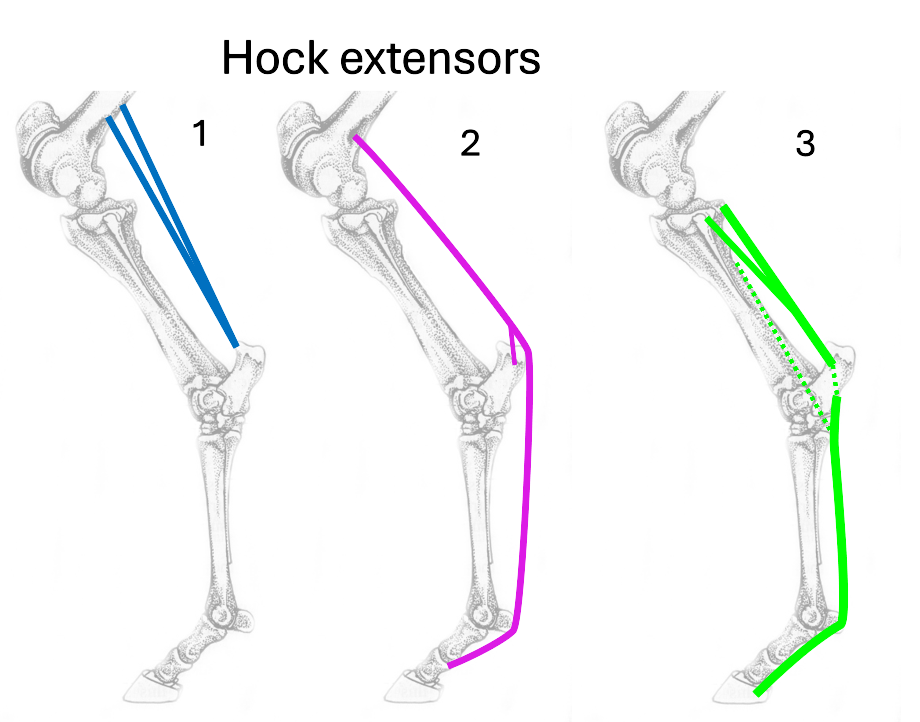
Name the 3 hock extensors
gastrocnemius
superficial digital flexor
deep digital flexor
Where is the origin and insertion of gastrocnemius?
origin = femur
insertion = calcaneus
What is the origin and insertion of superficial digital flexor?
origin = femur
insertion = calcaneus & P1&P2
What is the origin & insertion of deep digital flexor?
origin = tibia
insertion = P3
How many bellies does deep digital flexor originate as?
3
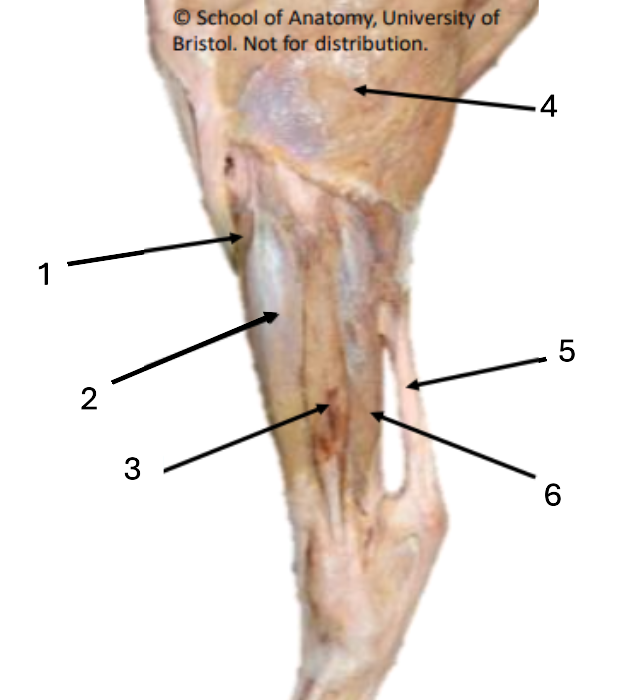
1
cranial tibial
2
long digital extensor
3
lateral digital extensor
4
biceps femoris
5
common calcaneal tendon
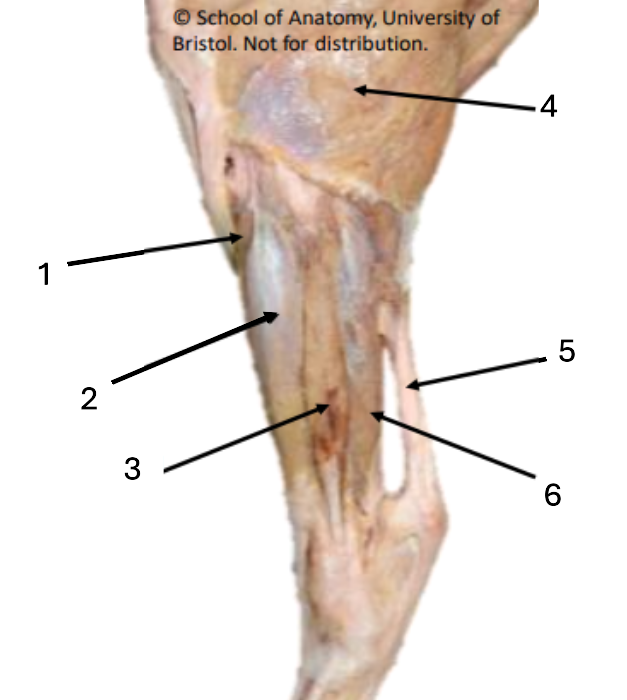
6
deep digital flexor
What do the hip, stifle & hock all tend to do with weight bearing?
flex
What does the passive stay apparatus do?
prevents the hip, stifle & hock from flexing with weight bearing
What does the hindlimb passive stay apparatus comprise of?
patella locking mechanism
reciprocal apparatus proximally
plantar support structures
How is the SDF involved in the stay apparatus?
flexion of hock limited by proximal portion of SDF when stifle locked
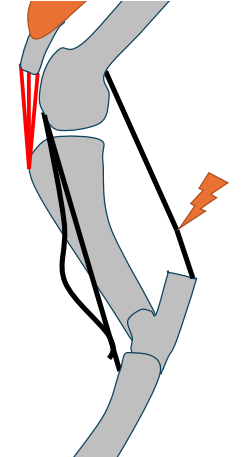
What affect does the SDF rupturing have?
hock can flex even with locked stifle - problem for weightbearing
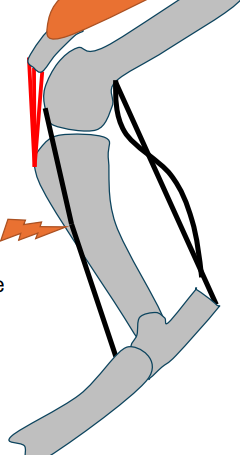
What happens when the fibularis (peroneus) tertius ruptures?
can extend hock despite stifle remaining flexed (DOES NOT AFFECT WEIGHTBEARING)
What is the role of the long plantar ligament?
resist hyperextension of the foot and digit
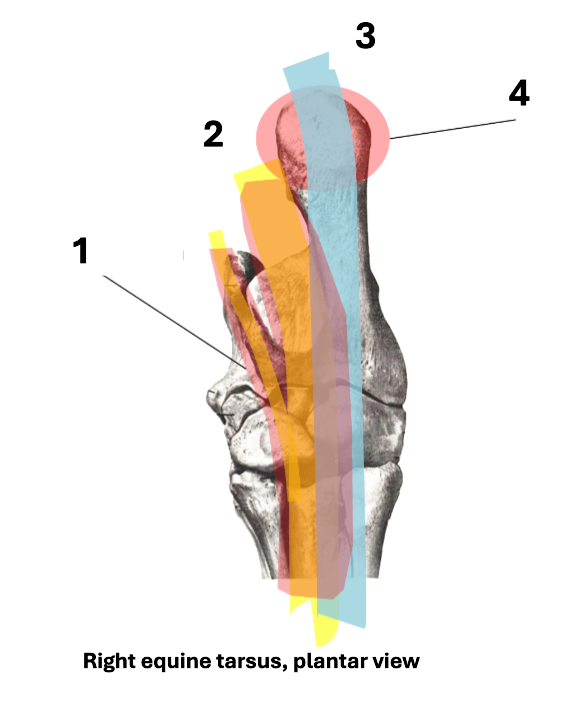
1
tarsal flexor sheath
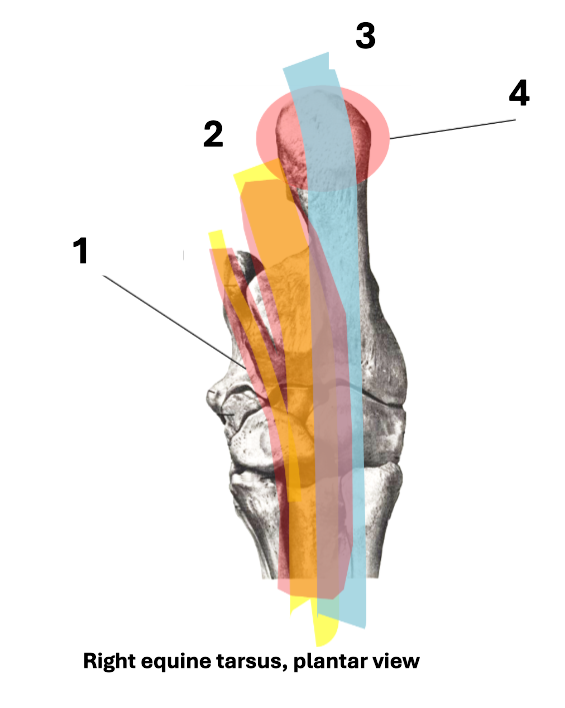
2
DDFT
3
SDFT
4
calcaneal bursa
What is the DDFT in?
tarsal sheath (runs in sustentacular groove of talus)
What can swelling of the DDFT in tarsal sheath be confused with?
tarsocrural compartment (between tibia and tarsus)
What protects the SDFT?
calcaneal bursa
What does the calcaneal bursa do?
protect SDFT as it runs over calcaneus
What is the function of the SDFT attachment to calcaneus?
reciprocal apparatus function
some check-ligament-like function
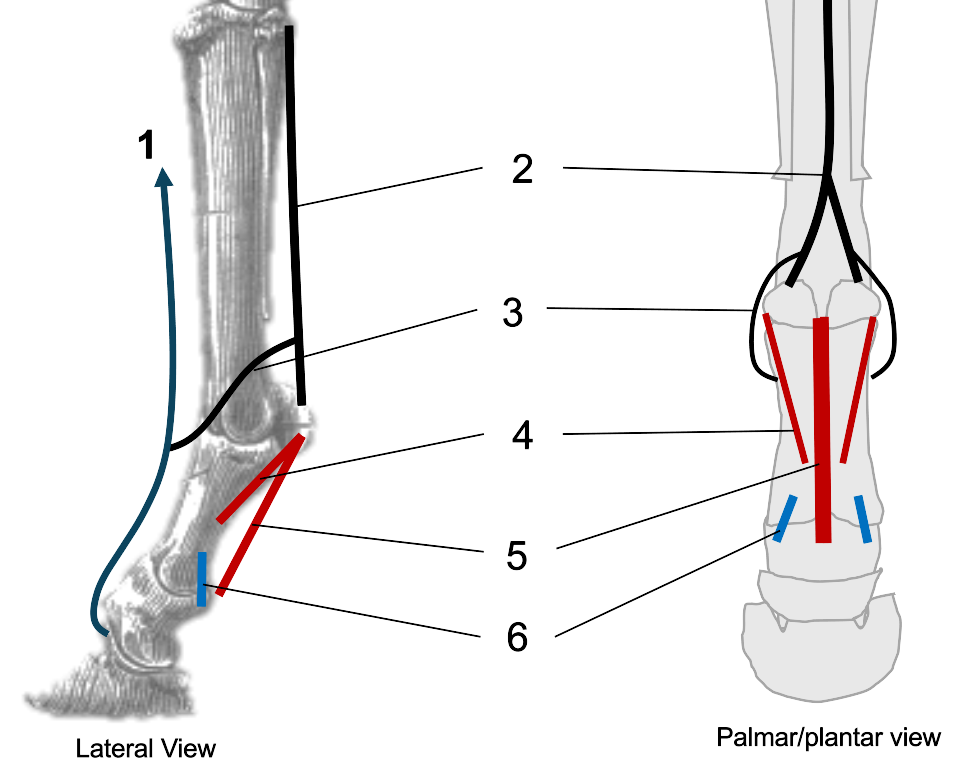
1
CDE/LatDE
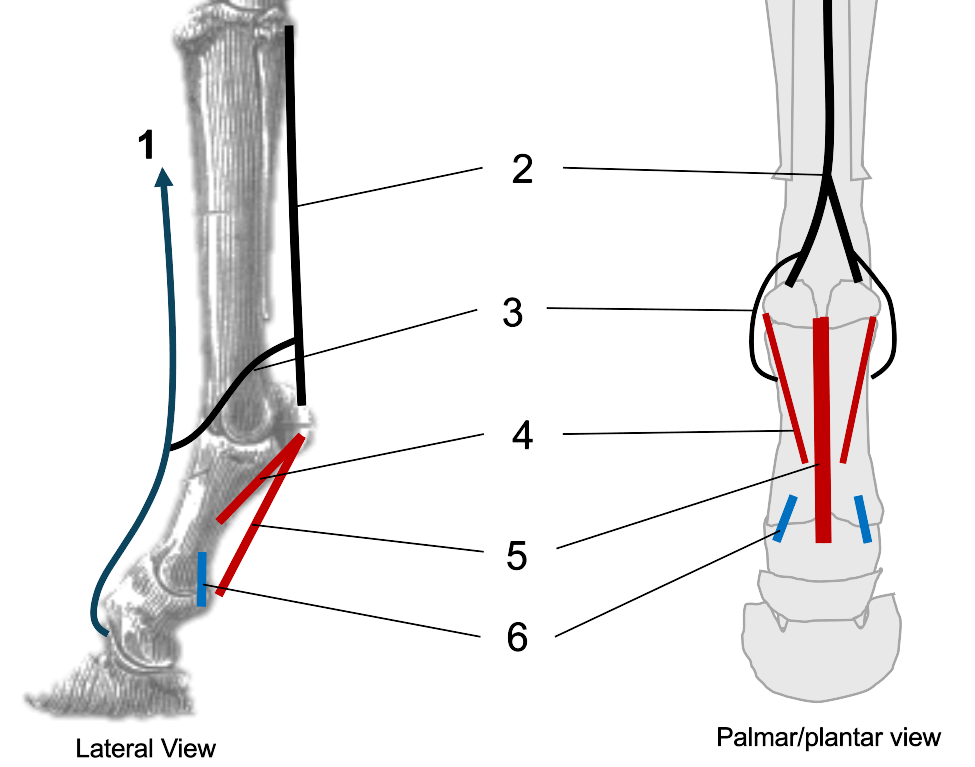
2
interosseous (suspensory ligament)
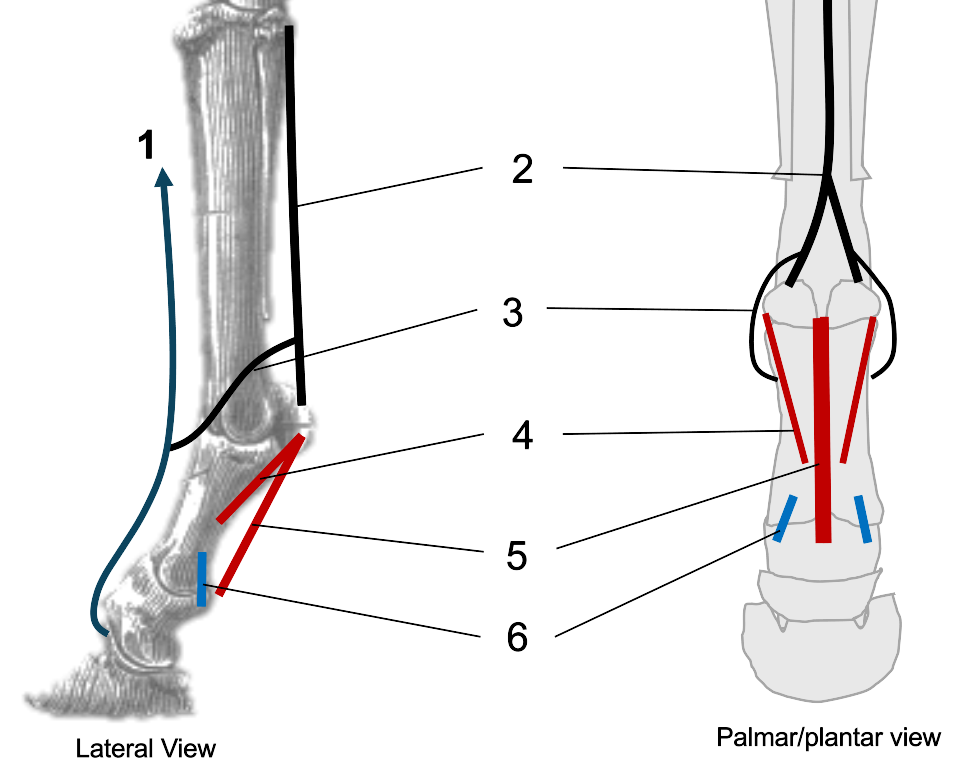
3
extensor branches of interosseous
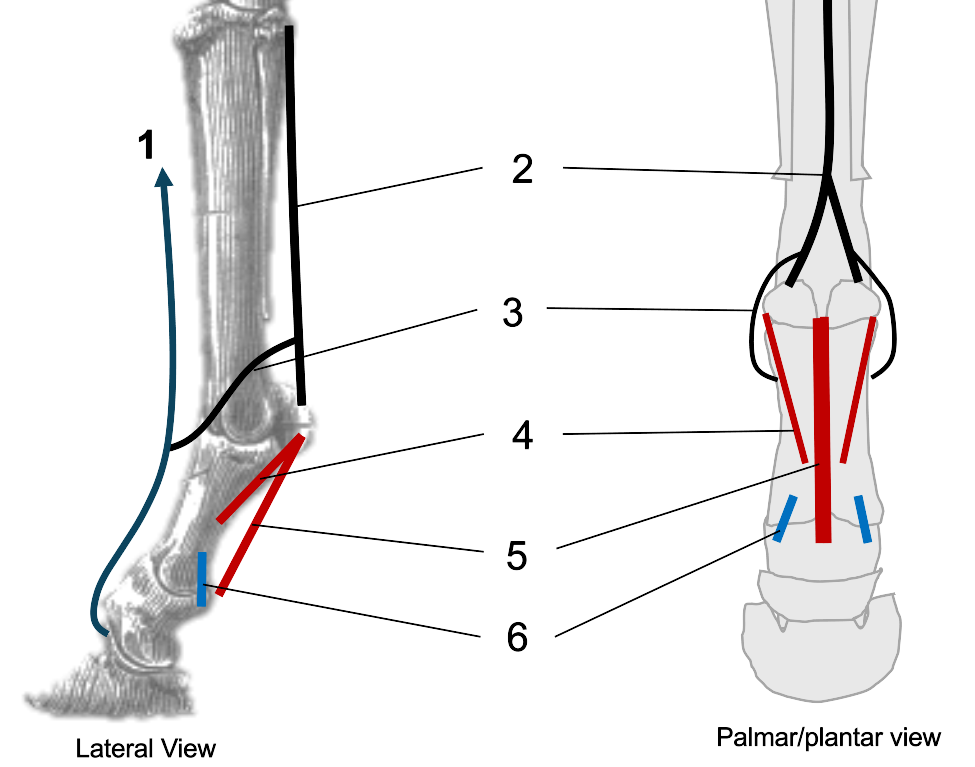
4
oblique sesamoidean ligaments
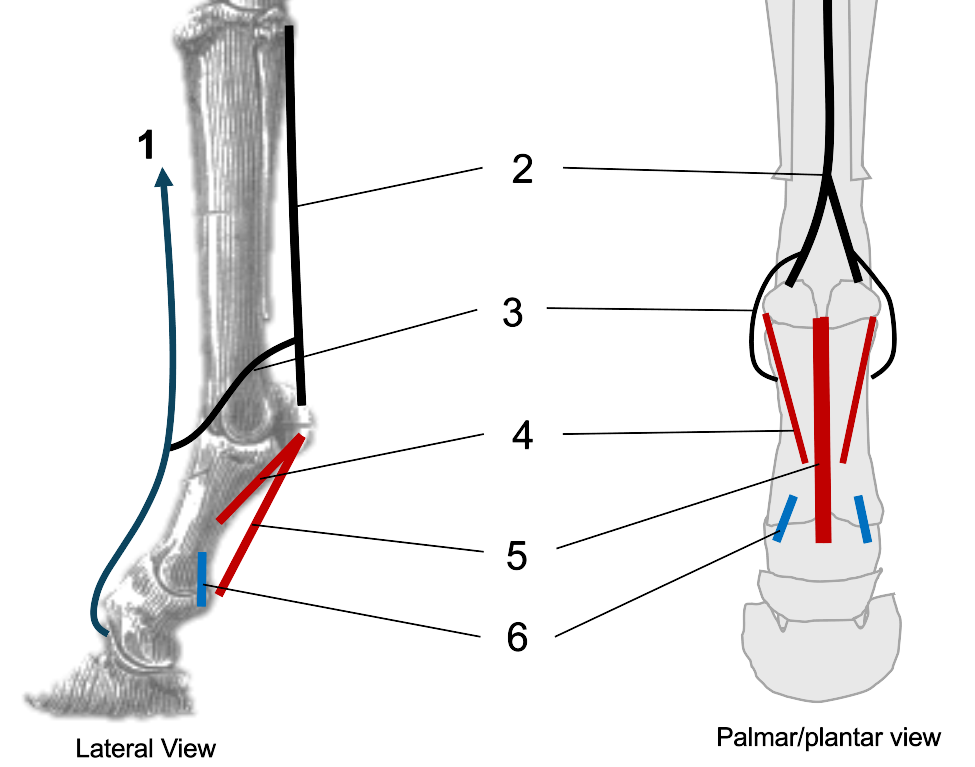
5
straight sesamoidean ligament
6
palmar ligaments of the pastern
What are the species differences to consider in the bovine hindlimb?
less covering over rump (no vertebral heads of hamstrings)
fibularis (peroneus) tertius more muscular/fleshy than horse
has fibularis (peroneus) longus
What are the features of the bovine distal limb?
metapodials III & IV fused
fetlock joint duplicated
What are the extensor tendons in the bovine distal limb?
common/long digital extensor (2 bellies - lateral=both digits, medial=medial digit)
lateral digital extensor (goes to lateral digit)
Why is the bovine foot clinically relevant?
claw amputation
salvage surgery
understanding neurovascular arrangement of foot to apply local anaesthetic for surgery
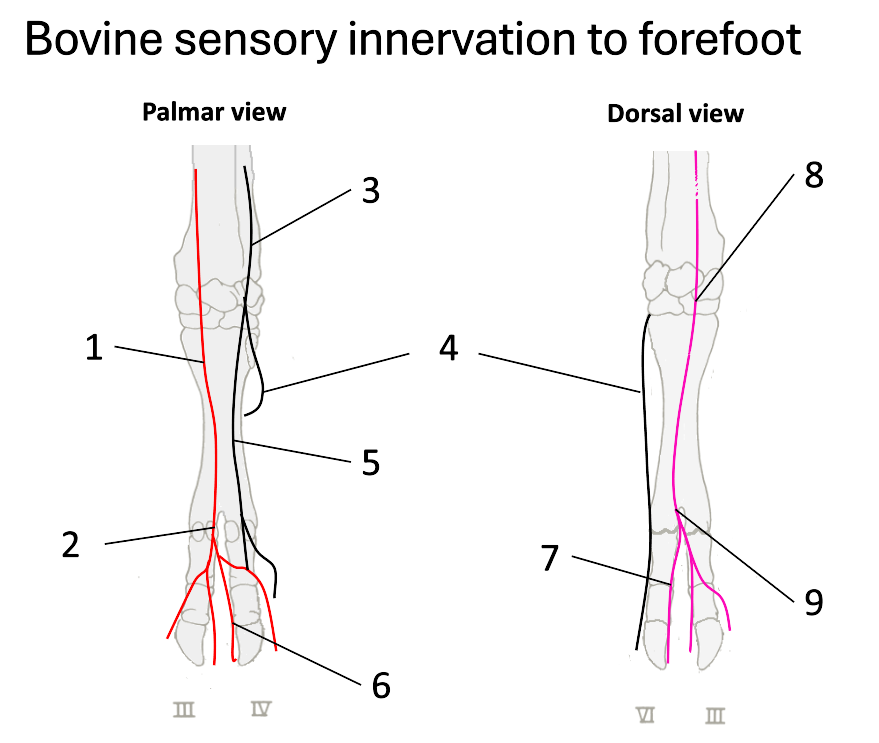
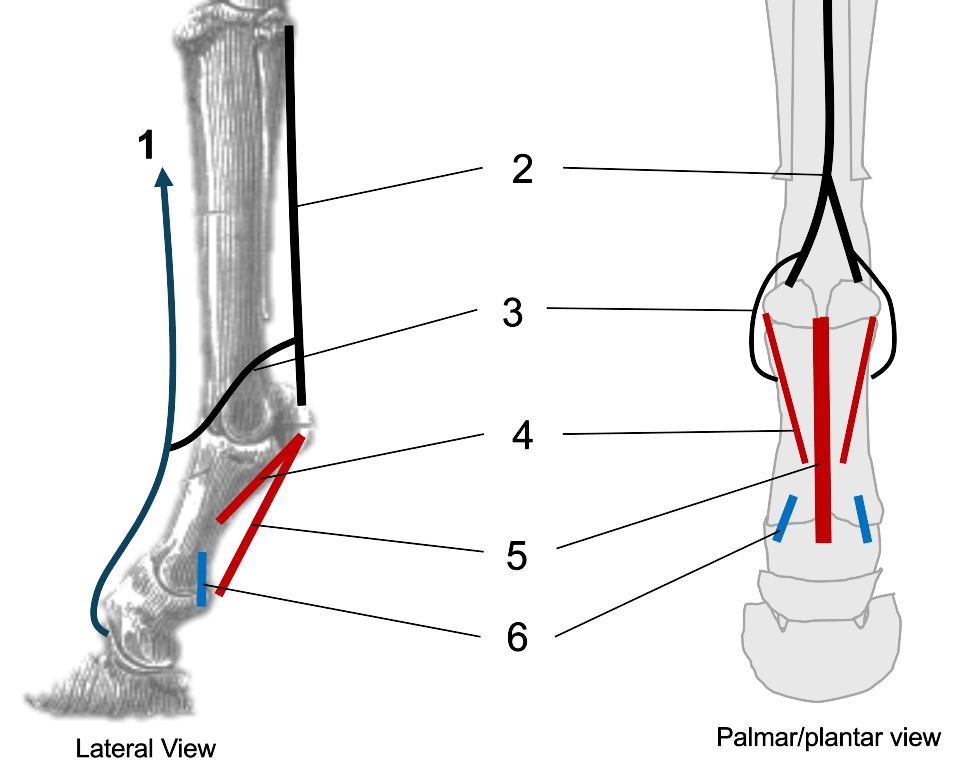
1
median nerve
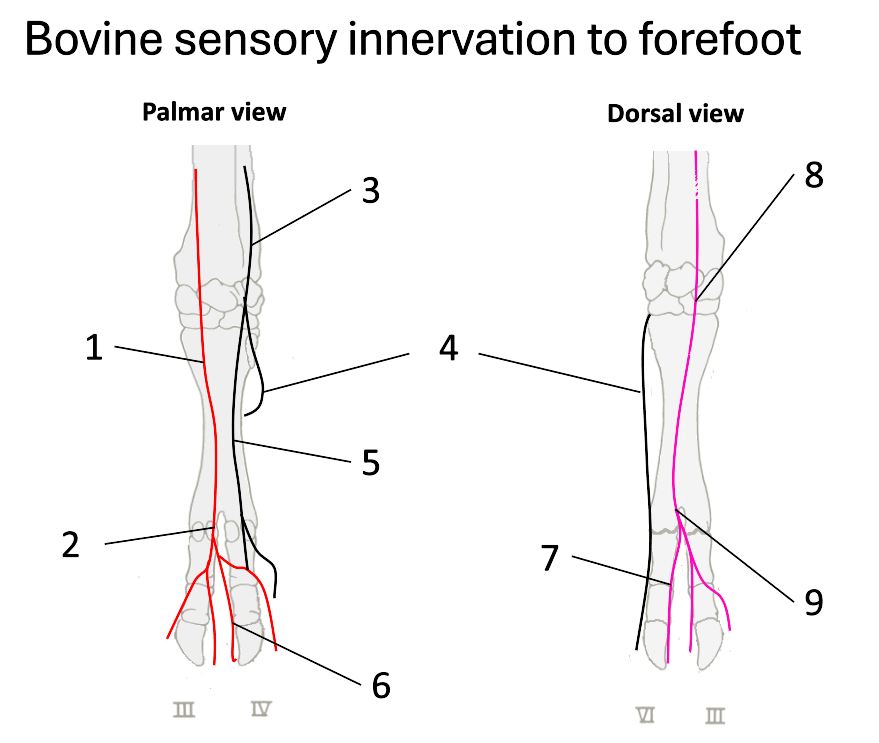
2
palmar common digital
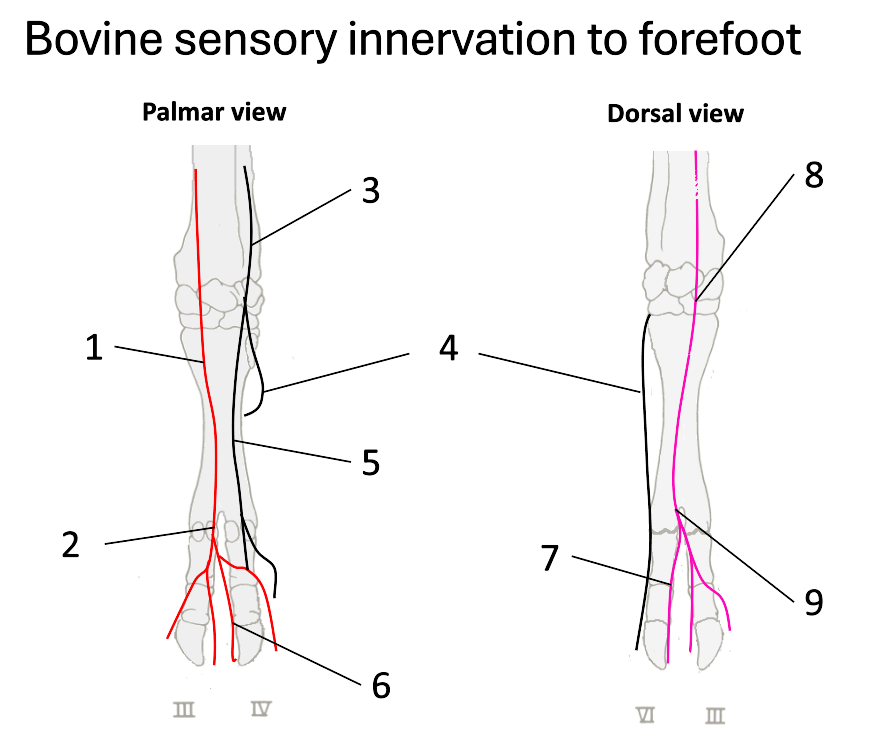
3
ulnar nerve
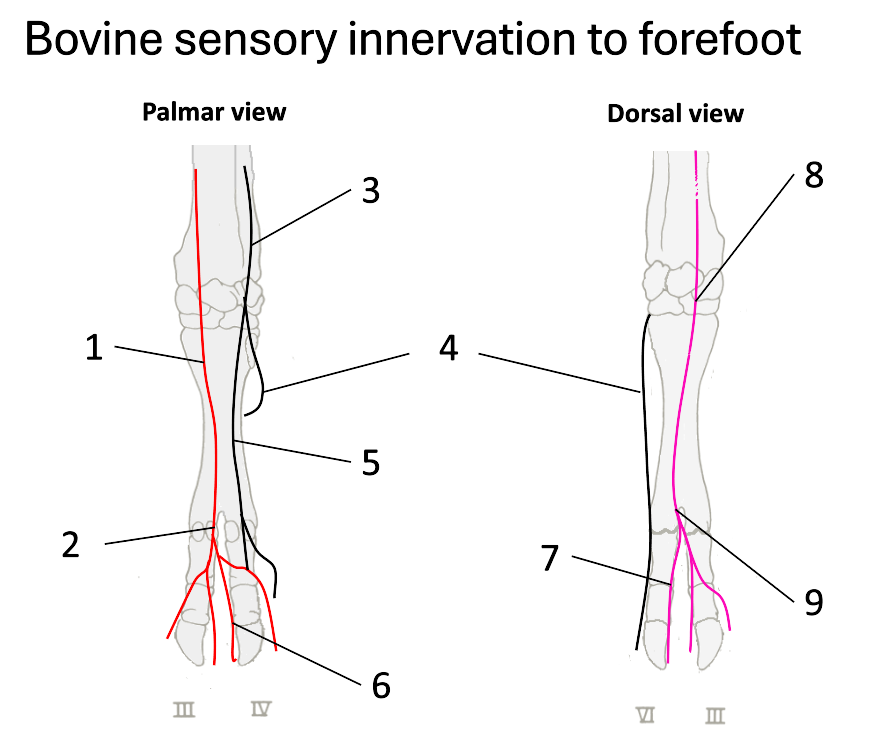
4
dorsal branch of ulnar
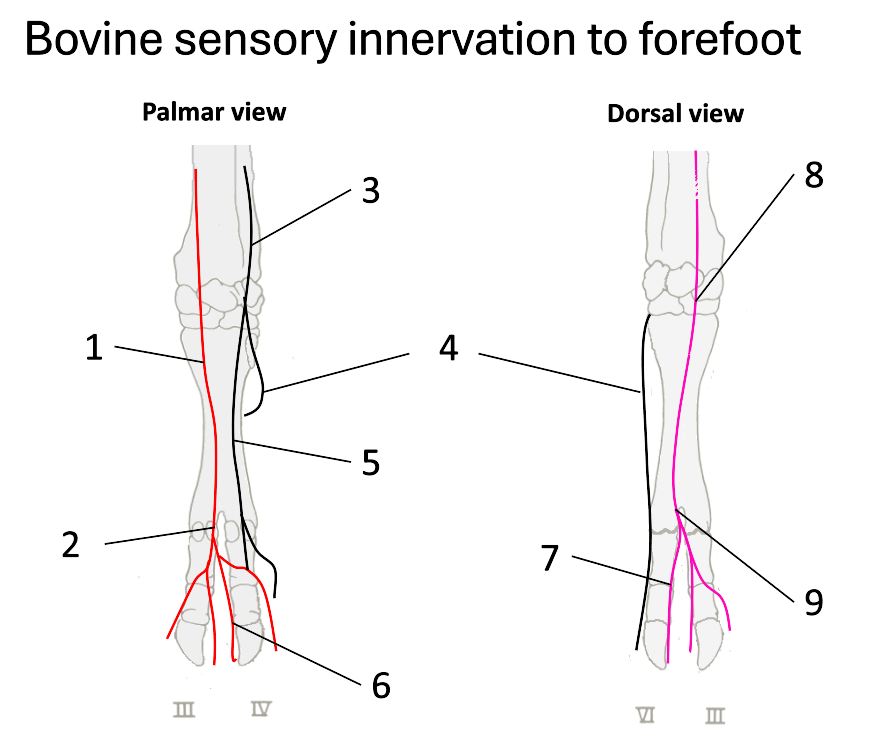
5
palmar branch of ulnar
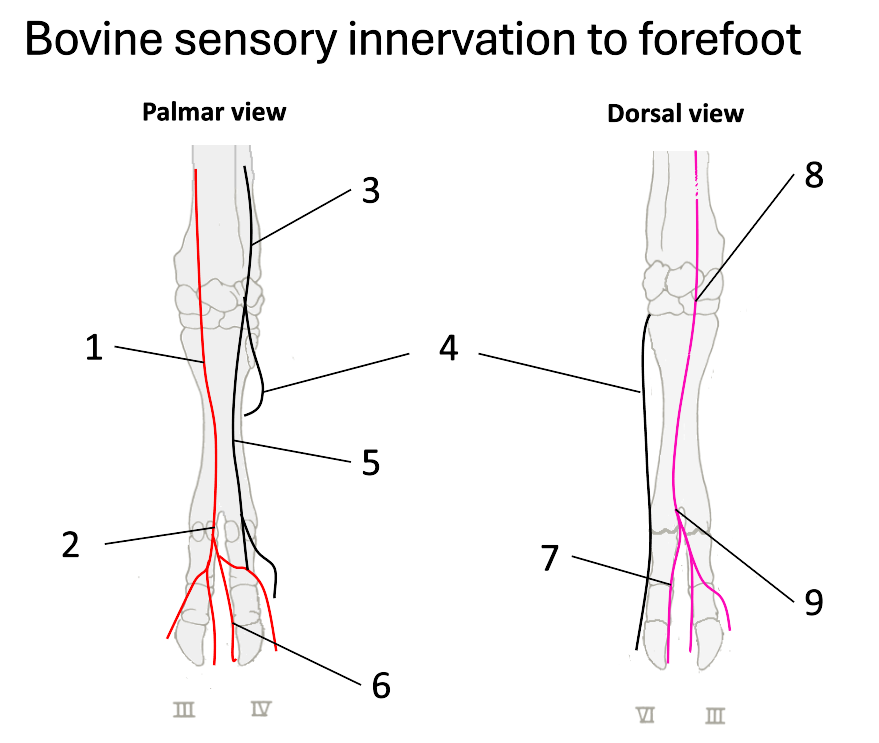
6
axial palmar digit (IV)
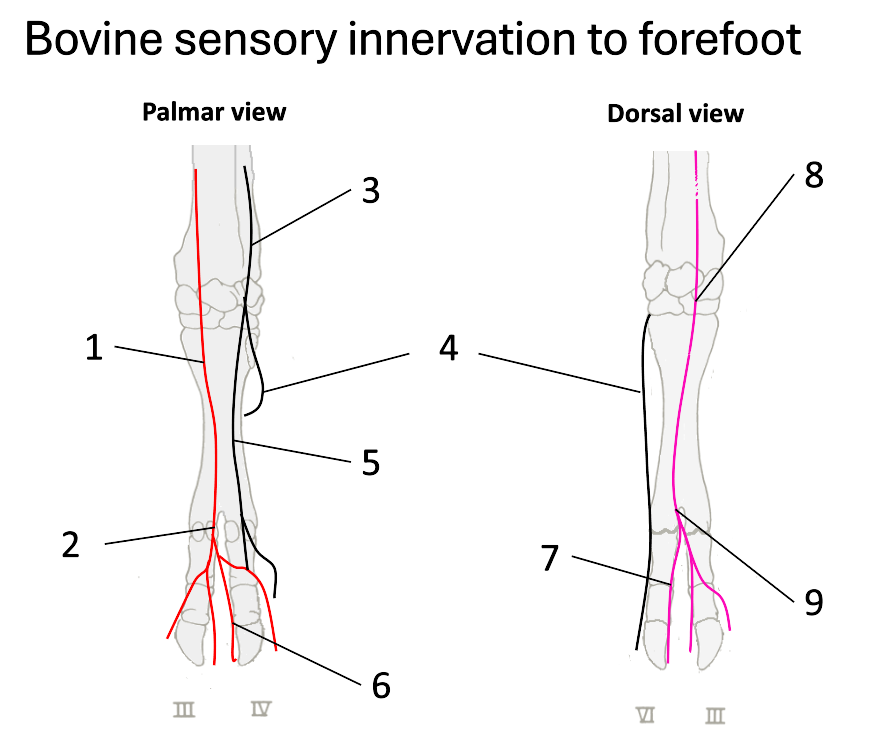
7
dorsal axial digital (IV)
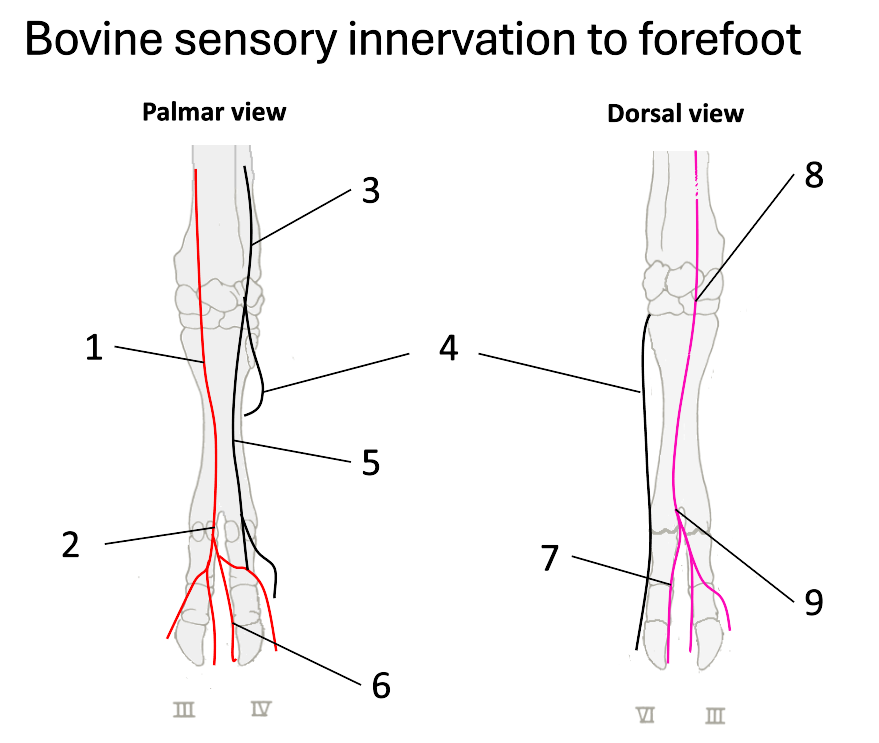
8
superficial branch of radial
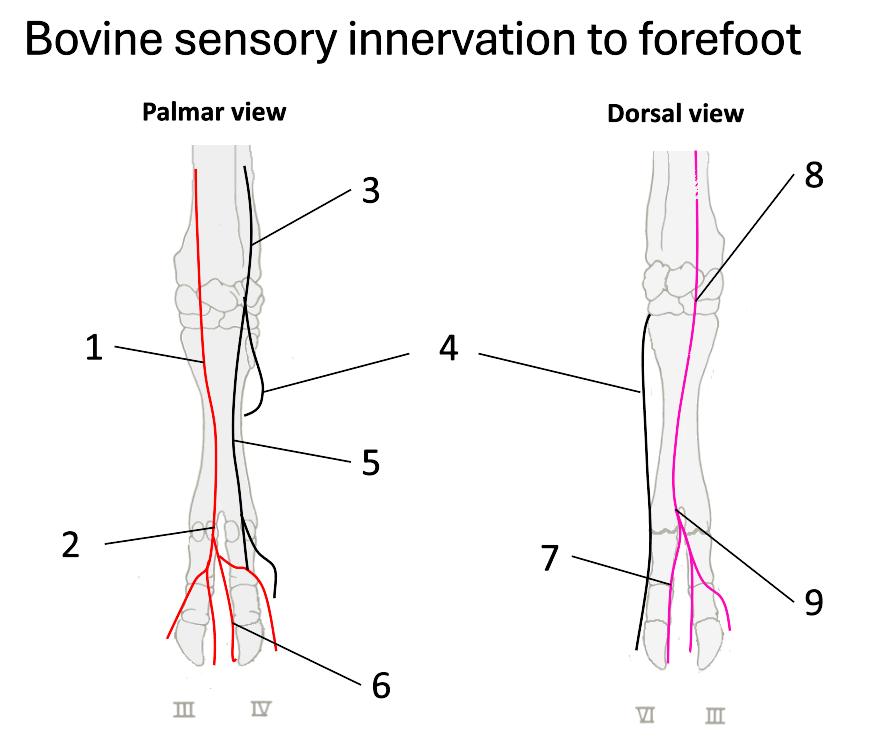
9
dorsal common digital
What do the fibular (peroneal) nerves (deep & superficial) supply?
dorsal surface of both claws
What does the tibial nerve supply?
plantar surfaces
What nerves are there once on the digits?
nerves at each of the 4 aspects of the digits (axial, abaxial, plantar & dorsal digital nerves)
What veins drain the bovine foot?
palmar
plantar
lateral saphenous
What do the palmar and plantar veins run with?
flexor tendons
Why is the ovine foot clinically relevant?
digital dermatitis (e.g. scald, footrot)
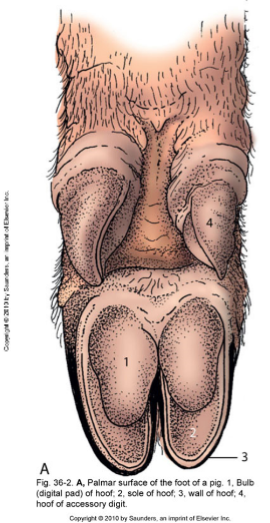
What does this image show?
porcine foot