Module 4: Muscle Phyisology Section 1 Structure of Sketal Muscle
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What NT innervates the muscle at the neuromuscular junction?
NT is acetylcholine (Ach)
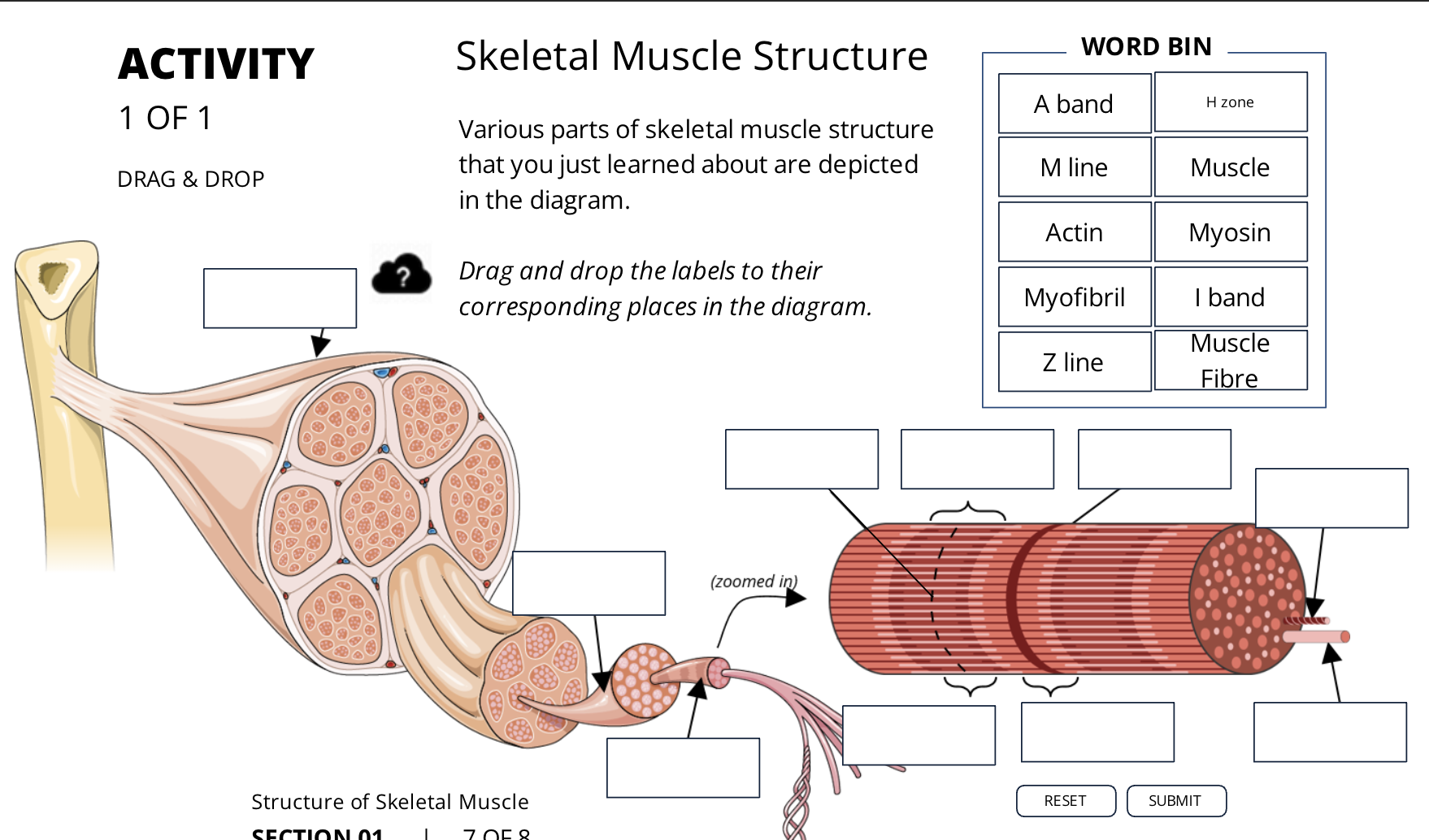
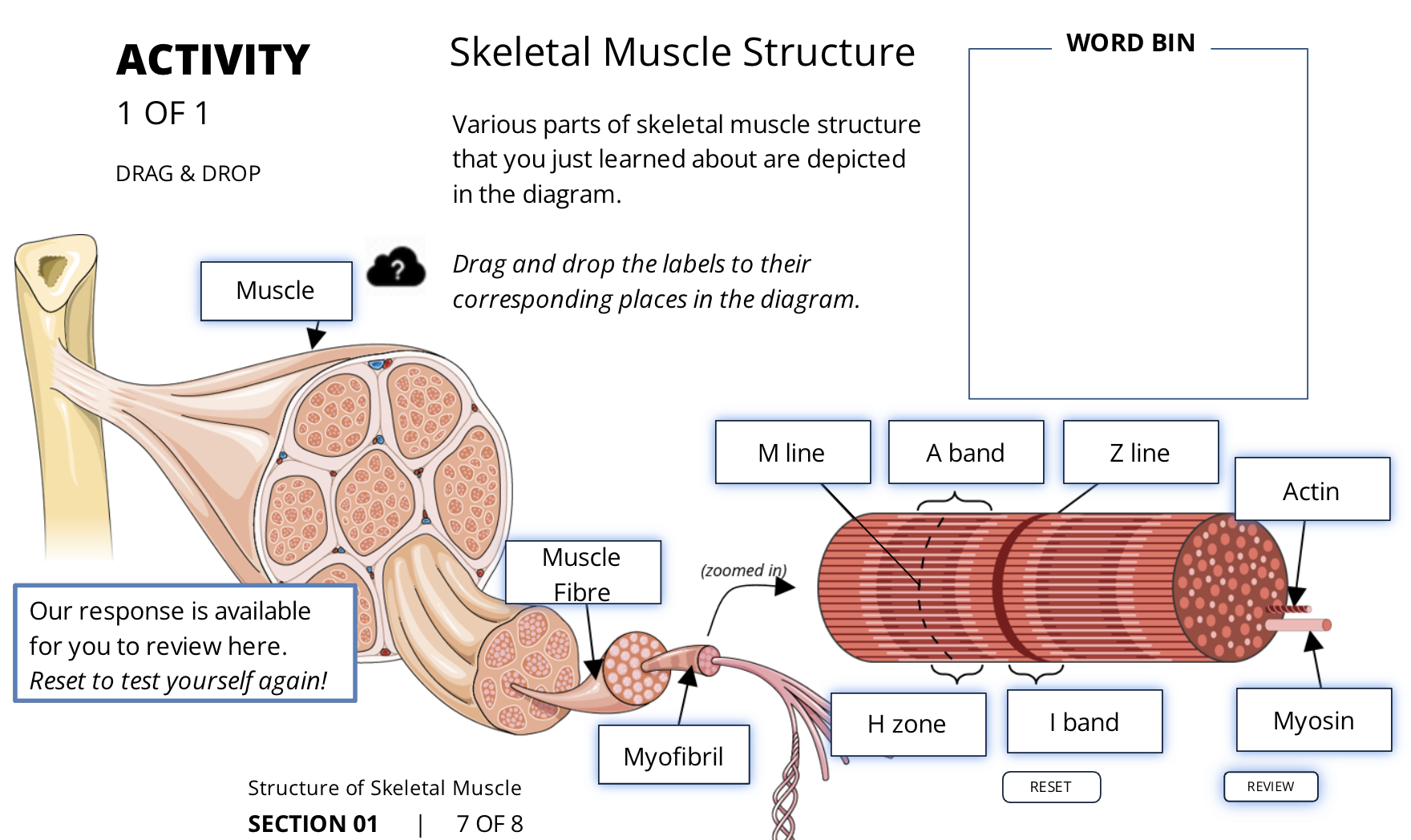
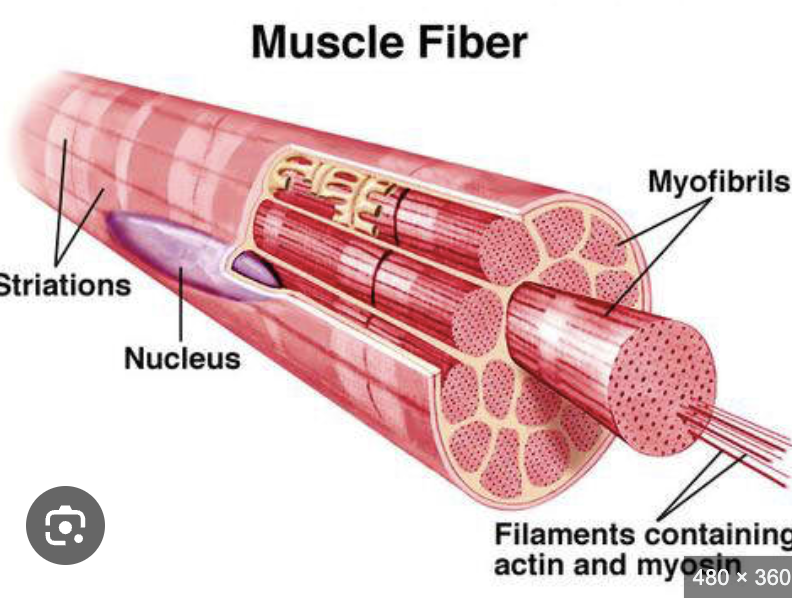
what makes up a skeletal muscle?
individual muscle fibres which each runs the entire length og the muscle
T or F the SK muscle fibres run nonparallel to each other and surrounding connective tissue.
Flase, they run parallel to each other and surronding connective tissue.
what are the 5 levels of organinzation of SKM?
Muscle
Muscle fibre
Myofibrils
Myofibrils - sideview (dark and light straited)
Myofibrils - cross section (myosin and actin)
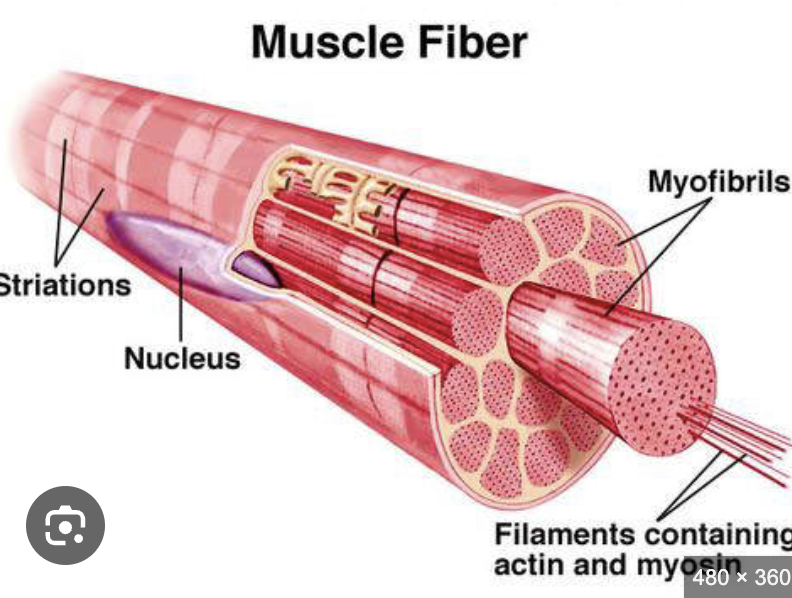
actin is the thick or thin filiement of the myofirbils?
thin filement
myosin is the thick or thin filiement of the myofirbils?
thick filiement
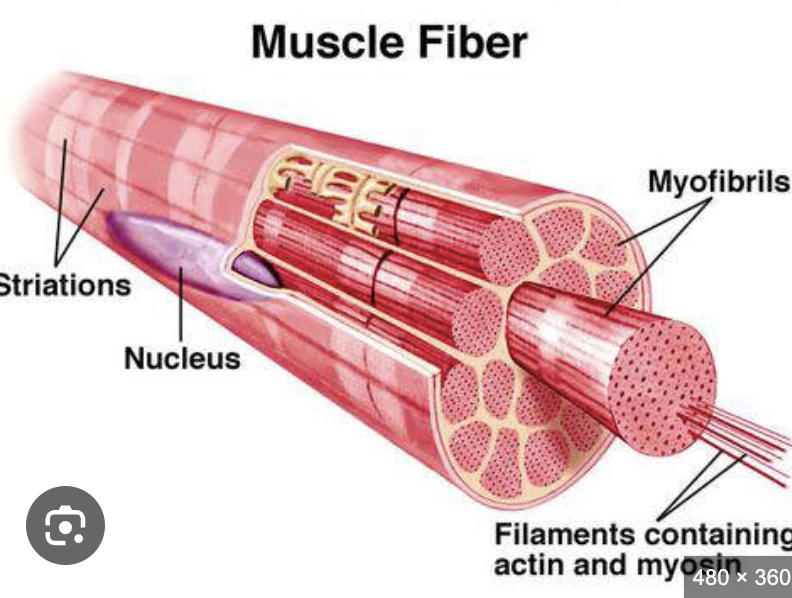
what makes up the muscle fibre?
myofibrils
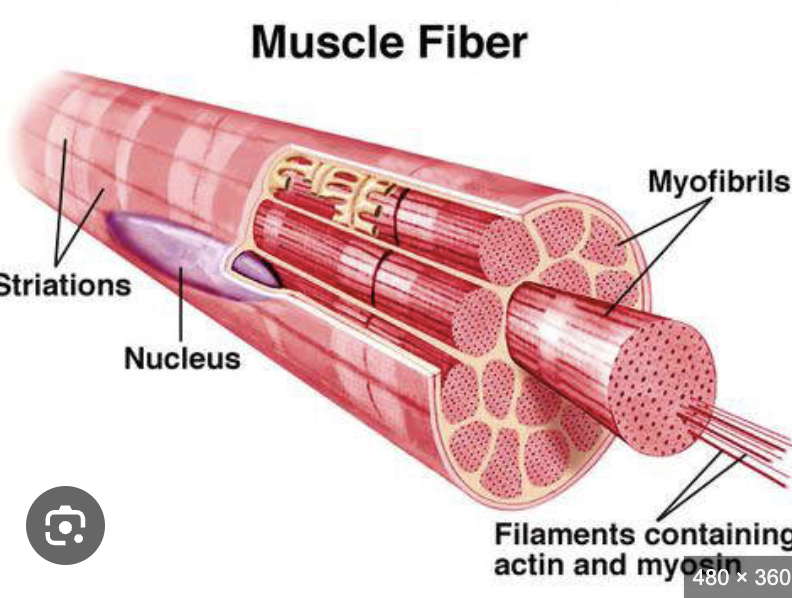
what is the contractile element of the muscle fibre
myofibrils
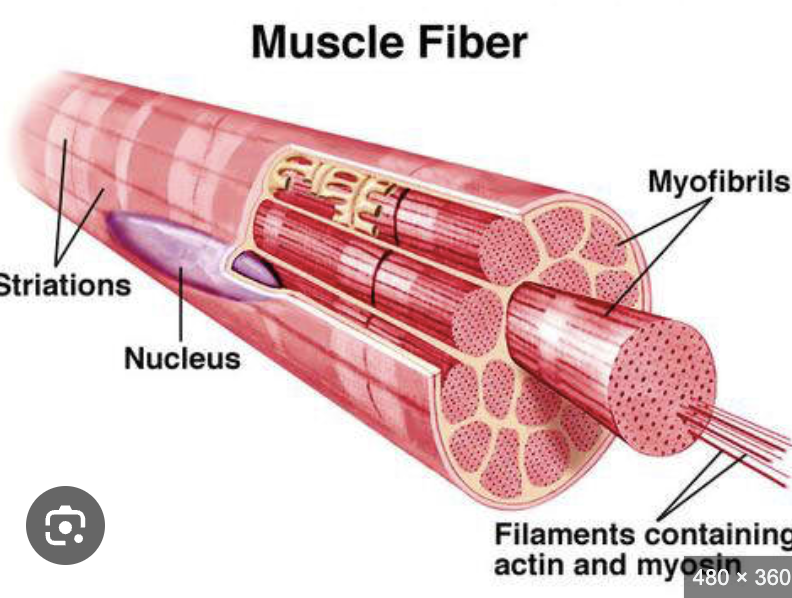
what makes up the side view of the myofibril
light and dark bands “striated pattern = straited msucle”
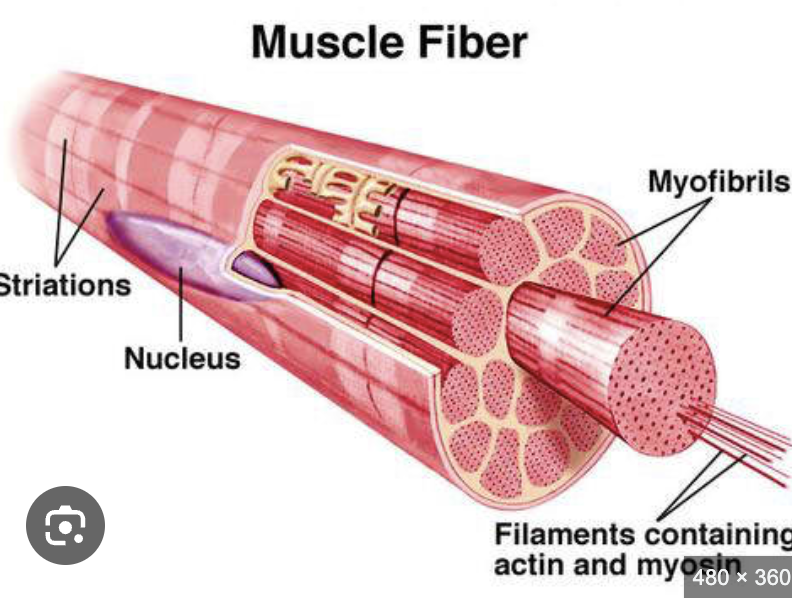
SKM are also called
straited muscle
what is the dark band called on the myofibrils?
A bands
what is the light band called on the myofibrils?
I bands
muscle fibres —— nucleated and have a —— mitochondrias
multinucleated and have a large mitochondires
what is the single muscle cell of the muscle
muscle fibres
the dark band (A band) is made of what?
made of the thick (mysoin / red ) and thin filiments (actin / blue)
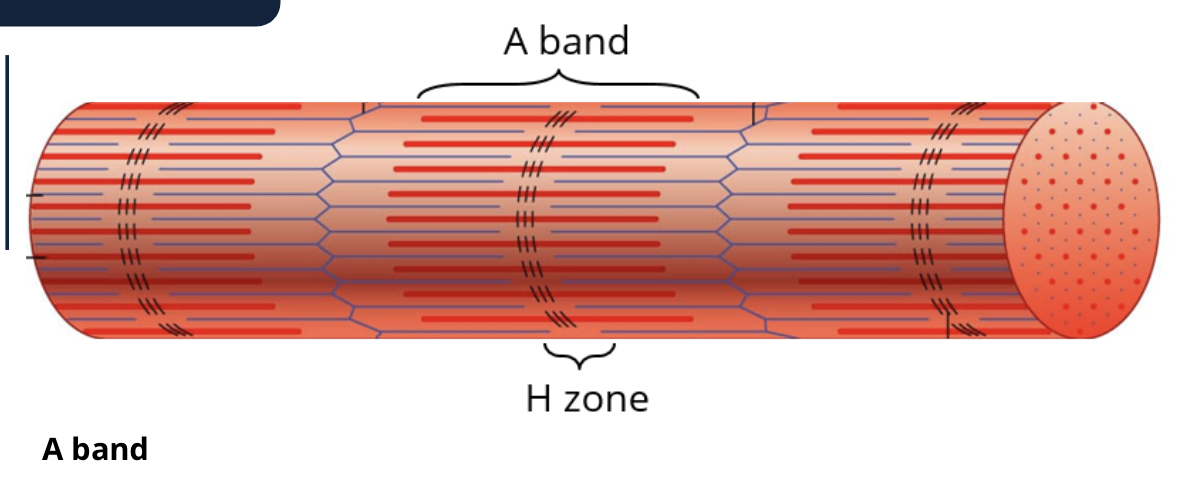
the middle of the A band is lighter or darker. and why and what is it called
the H zone: is lighter bc the thin filimarent (actin) does not reach that far from the end
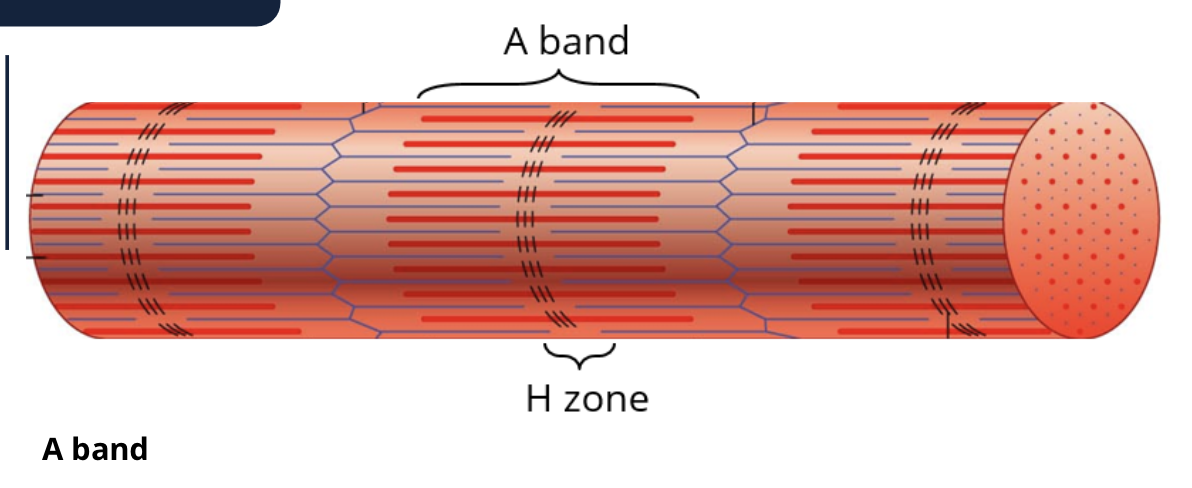
the length of the (dark) A band is determined by what?
the length of thick filement/ myosin
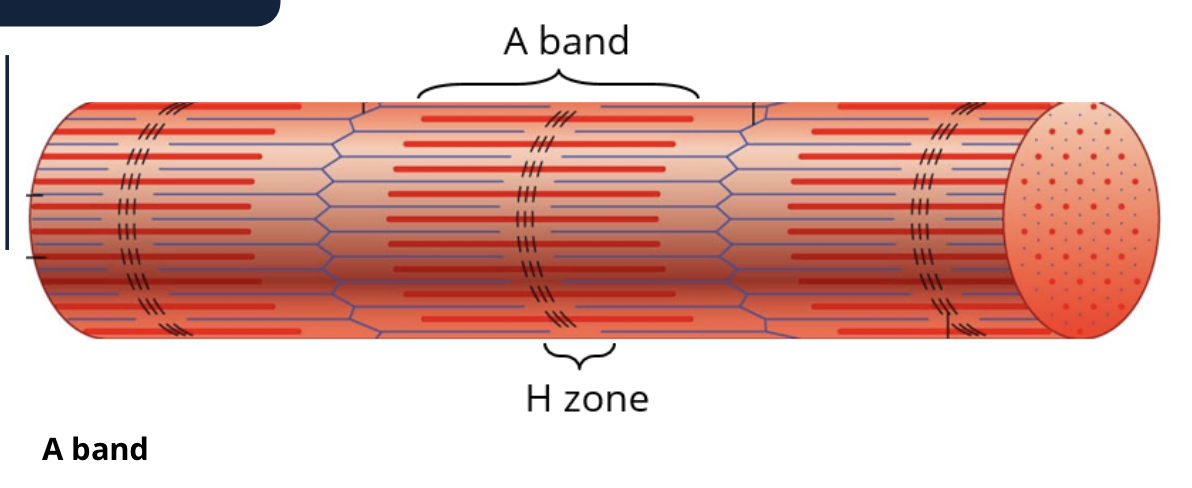
Dark band is the
A band
Light band is the
I band
What makes up the I band
just the thin band (actin)
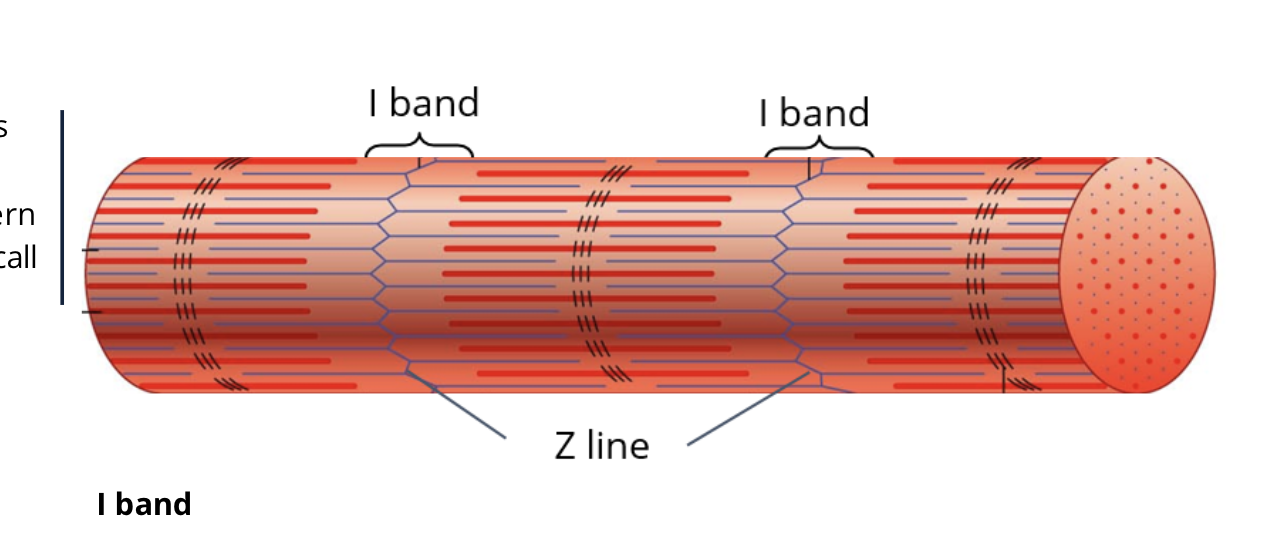
T or F: the A band is made up of only thin filiemtns/actin
F: the A band is made of both actin and myosin but the I band is made up of actin/thin filiments
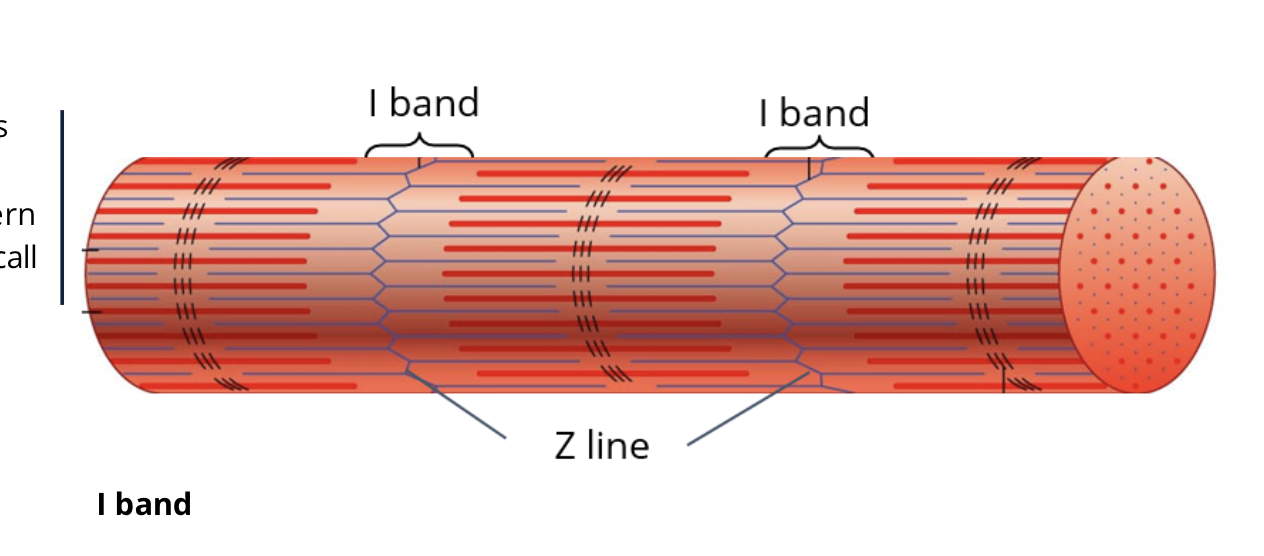
the middle of the I band is called what?
the Z-line and is vertical
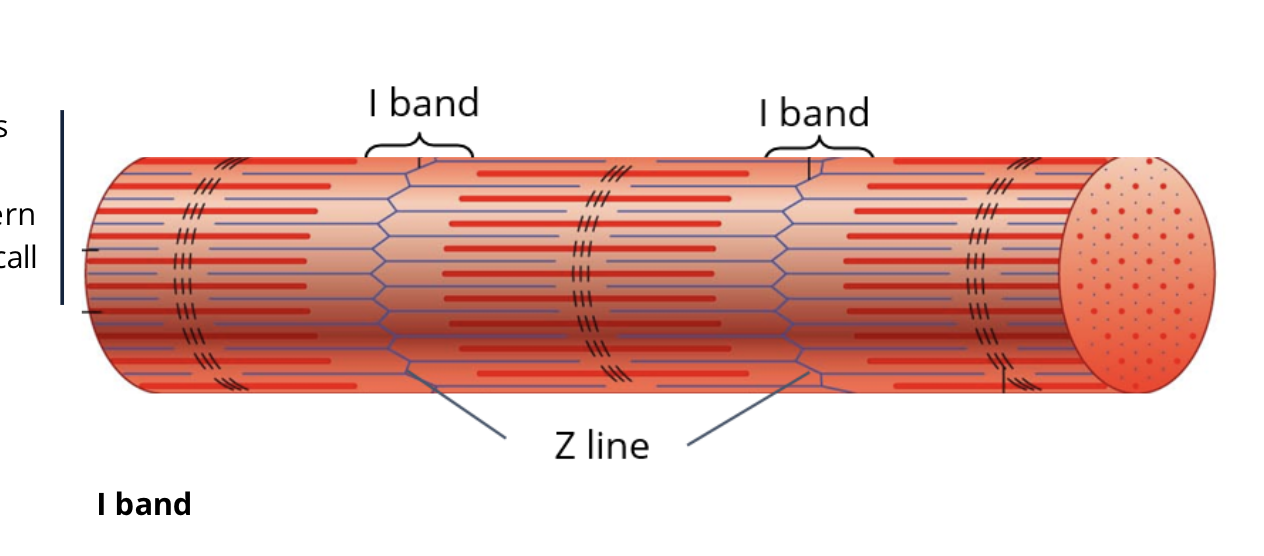
what is the H zone?
slighlty light part of the A band
what makes up the H zone
the protins that hold myosin together in a stack and only contains the heavy chain of myosin
what makes of myosin
2 heavy and 2 light chains
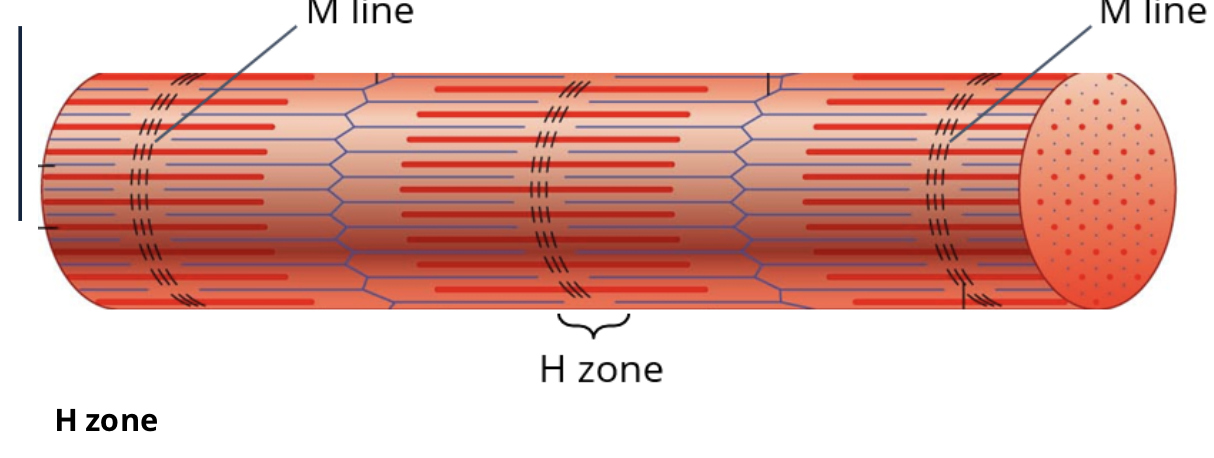
what is the M line running down the center of the H zone?
the protiens that hold the thick filiments together in a stack
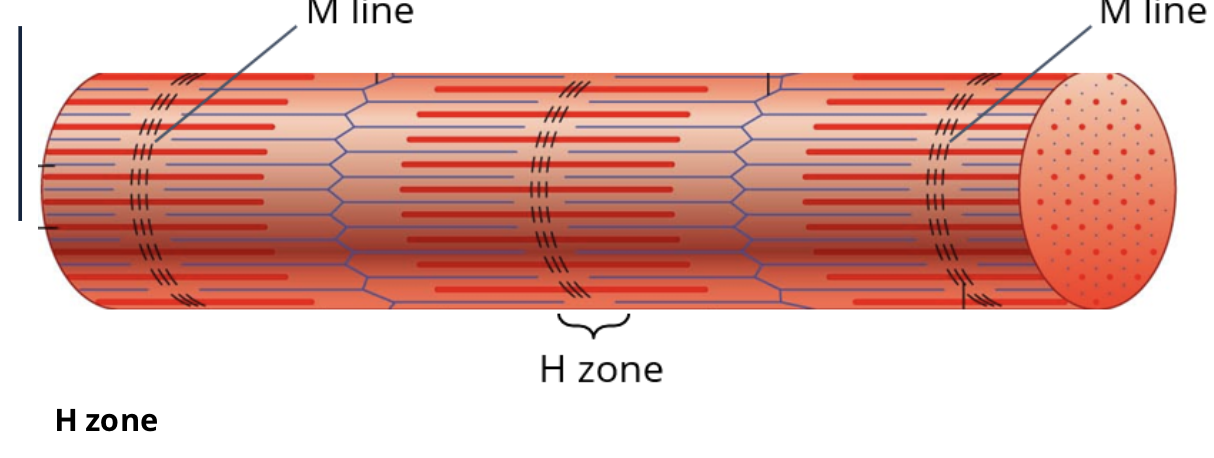
what runs down the center of the H zone
M line
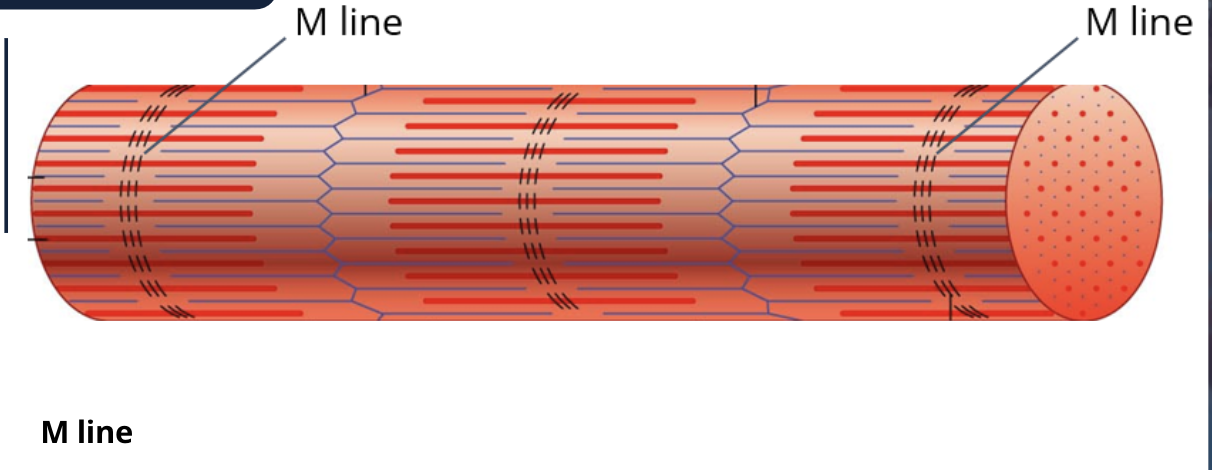
what is the middle part of the I band
the z line
what is the distance from the Z line to Z line called?
the sarcomere
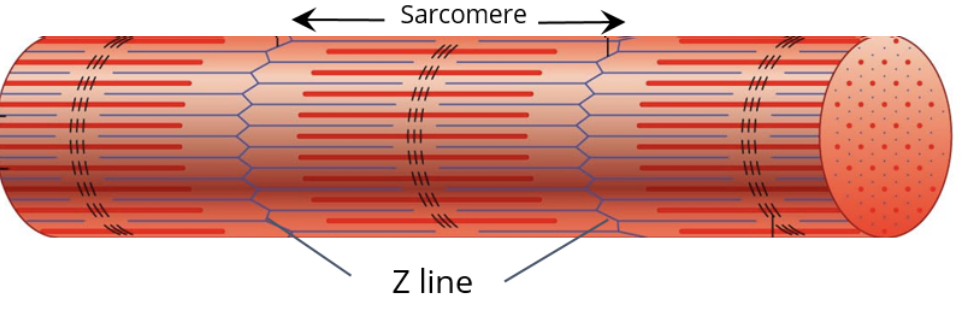
what is the functional unit of the SKM
sacromere
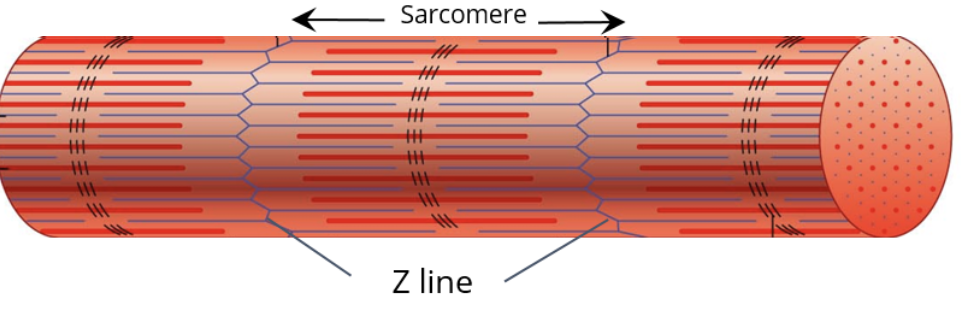
how do muscles grow?
the extend the muscle fibre by adding new sacromeres to the end
Cross-bridges connection form when?
Connection formed when mobile myosin heads bind to actin molecules in muscles.
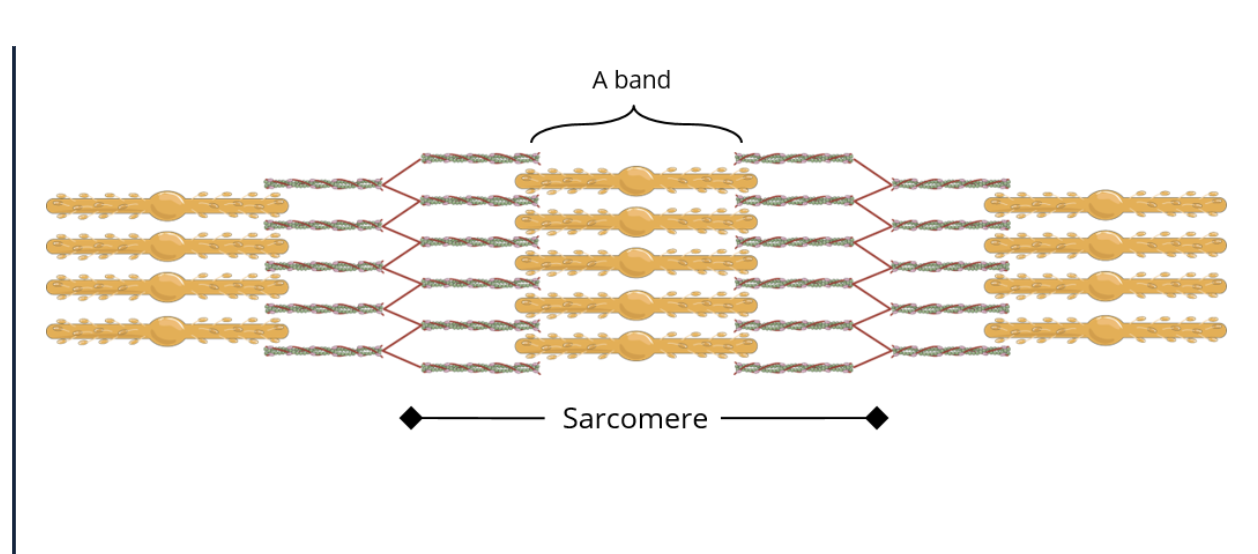
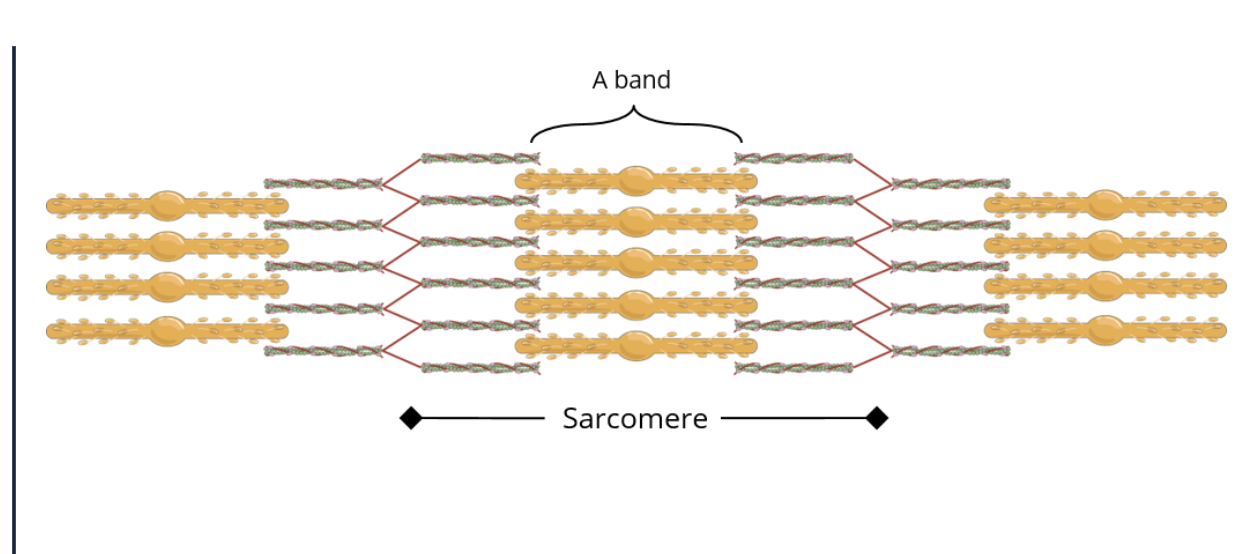
where are crossbridges formed
in the dark band/ A band where the myosin and actin overlap
T or F myosin is a protien
T
what kind of protien myosin
a motor protein
what does myosin walk on using ATP
actin
how many subunits makes up myosin
2
is myosin a dimer
yes it is made of 2 identical subunits
Each subit of myosin looks like what?
a golf club
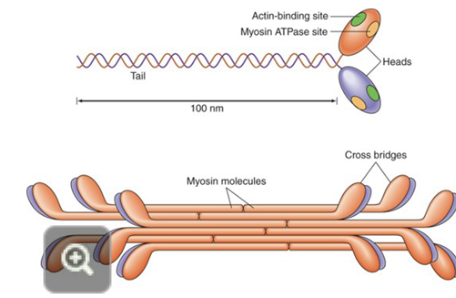
how do the two dimers come together regarding myosin
tail to tail formation with the heads sticking out
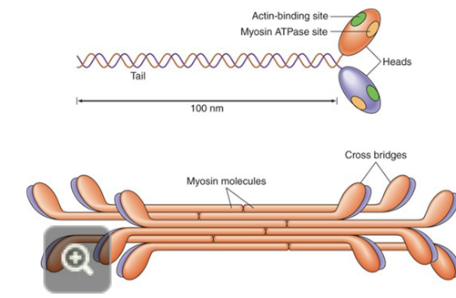
what are the 2 important sites on the myosin head?
the actin binding site and the myosin ATPase site
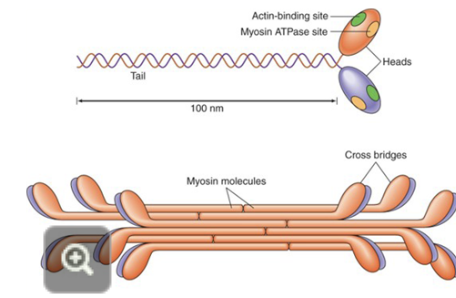
T or false the thick filement is only made of 1 protien type.
T myosin
T or false the thin filement is only made of 1 protien type.
F: actin, tropomyosin, troponin (main structral compenent is actin)
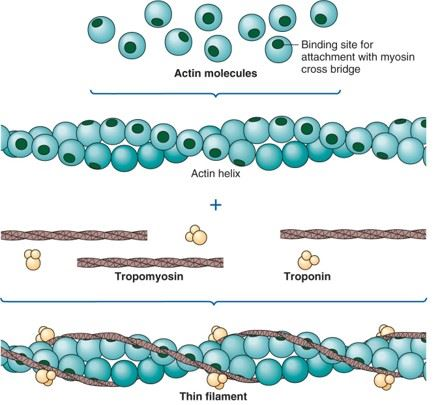
what kind of protien tryopomyosin
regulator protien
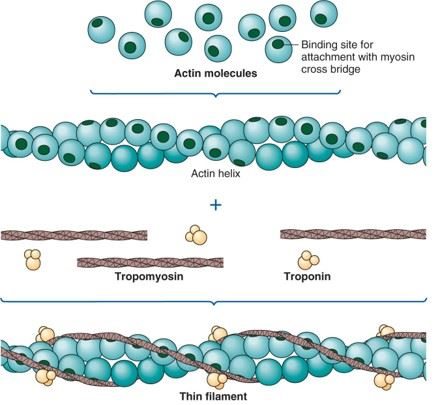
What does tryptomyosin on actin do
is a double helix structure that lies end to end on actin and covers the active bindinding sites that stop the interaction of myosin and actin
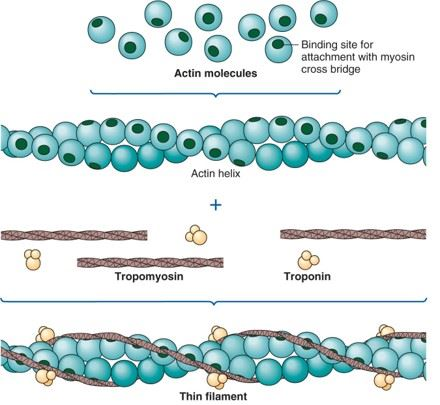
what is tropnin
a regulator protin complex made of 3 polypeptides. one binds to tropomyosin other to actin one to Ca+
what do the 3 polypeptide on troponin bind to?
tropomyosin, troponin, Ca+