MIS Final
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lord help me
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
database
collection of data that is self-described
deletion anomaly
deleting in one file, but not others
insertion anomaly
inserting data in one file, but not others
update anomaly
only updating in one location
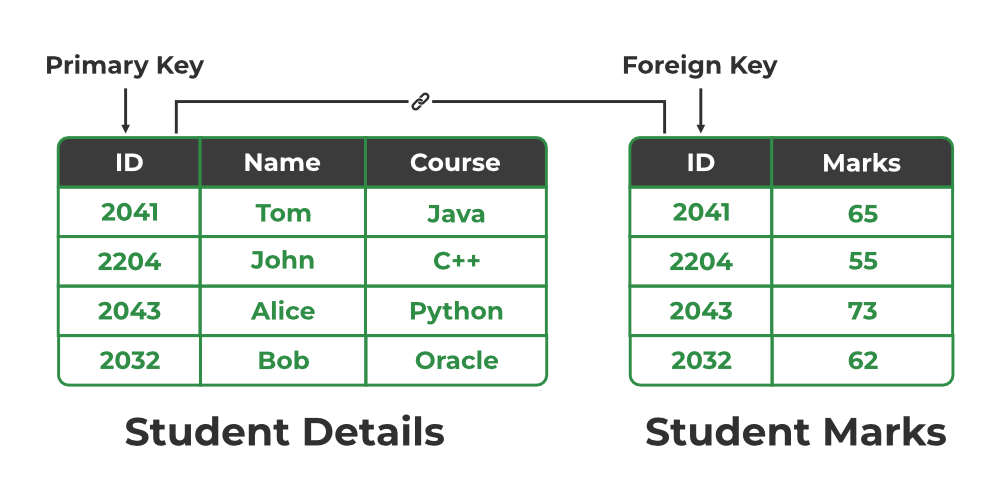
primary key
unique identifier, doesn’t change, defined within table
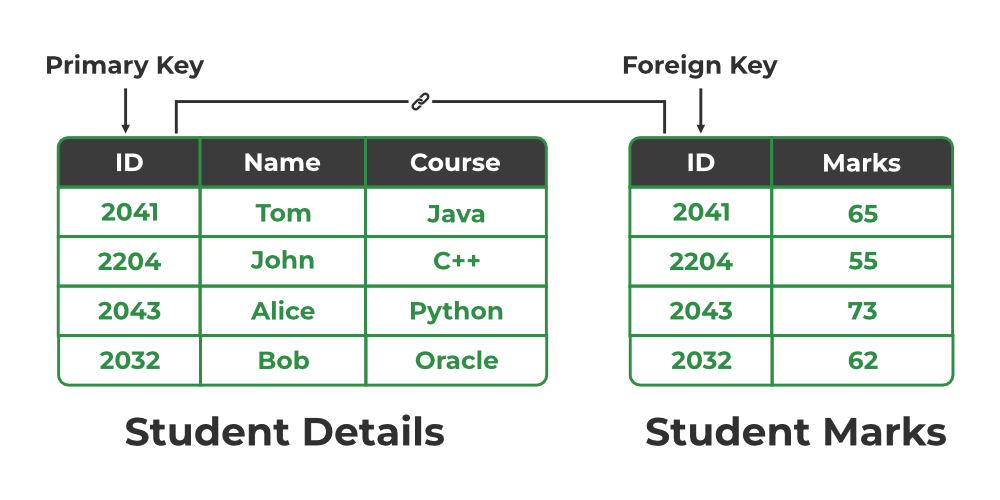
foreign key
column or set of columns in a table that refers to the primary key of another table, creates relationships between tables, maintains referential integrity, and data consistency
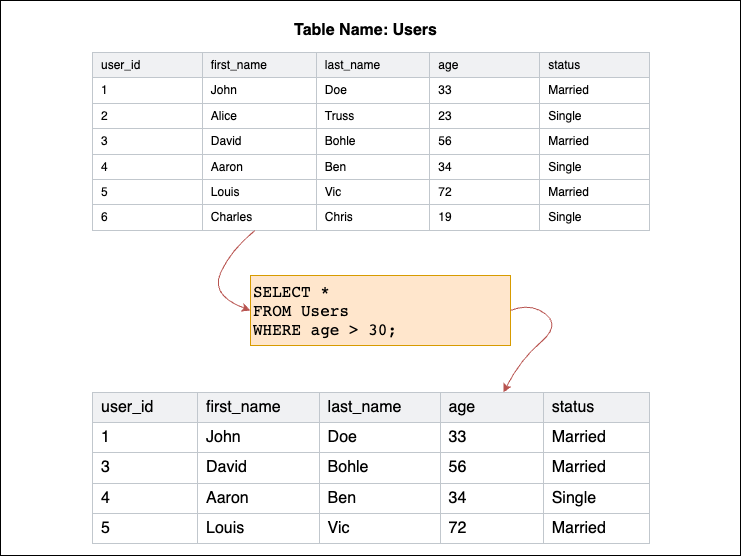
Structured Query Language
standardized language to manage and manipulate databases and extracting data (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE)
table
one sheet of data- group of related records/rows
row (record)
one complete set of related data about a single item
column (field)
category or attribute (eg. FirstName, LastName, PhoneNumber)
character
single letter, number, or symbol
byte
unit of storage for one character
tables/files
where data is stored
metadata
data about data (file creation/modification date. who modified, owner, data type)
user
people interacting with system
Database management system
software that creates, manages, and provides access to the database (Oracle, Access)
DBMS operations
read, insert, modify, delete

entity relationship model
visually represent data structure
entity
things we store data about
relationships
how entities are connected
crow foot diagram
shows ER between tables
cardinality
how many of one entity relates to another -
Zero or One (Optional One): O| (Ring and Dash) - Minimum zero, maximum one.
One and Only One (Mandatory One): || (Dash and Dash) - Minimum one, maximum one.
Zero or Many (Optional Many): O< (Ring and Crow's Foot) - Minimum zero, maximum many.
One or Many (Mandatory Many): |< (Dash and Crow's Foot) - Minimum one, maximum many.
query
requests information
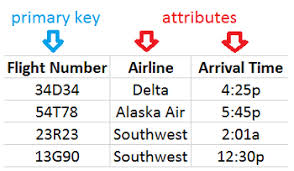
attribute
either primary or foreign key
normalization/centralization
put data into related tables
denormalization
combining into one table
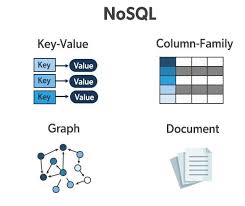
NoSQL
nonrelational databases-manage large data sets between platforms
big data
tools for working with large data
volume
scale of data
variety
different forms of data
veracity
uncertainty of data
velocity
analysis of streaming data
CISO Role (Chief Information Security Officer)
develop policies, minimize risk, handle incidents
gen AI
double-edged sword- used for defense simulations and creating sophisticated attacks
threat
event with potential for asset loss (phishing, malware)
vulnerability
weaknesses in design or control (weak passwords, unpatched software)
exploit
technique used to compromise vulnerability (SQL injections)
social engineering definition
manipulating people into divulging confidential info
tactics of social engineering
phishing emails, pretexting, & baiting
mitigation for social engineering attacks
education and “zero trust” policies
malware: ransomware
encrypts data and demands payment for the key
keyloggers
records keystrokes to steal passwords and data
rootkits
hides in OS to allow remote control and bypass security
bots & botnets
compromised computers controlled centrally for attacks (DDoS)
virus
self-replicating programs that infect a host to cause damage
trojan horses
disguised as legitimate software but performs malicious activity
man-in-the-middle (MitM) & MitMo
intercept communication on web & mobile
SQL injection
inserting malicious code into database queries via web forms
kerberoasting
brute-forcing service account passwords in active directory
supply chain attacks
infiltrating a system through a third-party vendor
CIA triad: confidentiality
prevent unauthorized access (encryption, access controls)
CIA triad: integrity
ensure data accuracy and consistency (checksums, backups)
CIA triad: availability
ensuring data is accessible when needed (redundancy, DRP)
data in transit
move across networks (protected by Transport Layer Security/Secure Socket Layer
data at rest
stored on disk/servers (protected by disk encryption)
data in process
currently in RAM/CPU (most vulnerable)
nist framework: identify
asset management & risk assessment
nist framework: protect
access control & training
nist framework: detect
monitoring & anomaly detection
nist framework: respond
mitigation & communication
nist framework: recover
restoration & improvement
risk analysis steps
value assets
est. loss
est. likelihood
calc costs
decide countermeasures
probable maximum loss (pml)
worse-case scenario cost
identity verification
multi-factor authentication, biometrics, token-based authentication
plan, protect, respond
cycle of continuous security improvement
identity first security
focus on user identity as the perimeter
security culture
moving beyond tools to behavioral change
hybrid environment
securing both on-prem and cloud resources
physical controls
fence, gate, camera
technical controls
firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, network segmentation, antivirus
administrative controls
hiring & termination policies, data classification, separation of duties
types of security controls
preventative
deterrent
detective
corrective
compensating
directive
7-step cybersecurity plan
risk assessment,
define goals & policies,
identify & enact defenses,
create response & recovery plans,
address legal & compliance,
train personnel,
continuous monitoring
software acquisition
needs assessment
budget analysis,
research & selection
evaluate vendors
deployment
database hierarchy
table/file
record within a table
field within a record
characters within a field
components of a database
tables
relationships between rows
metadata
enterprise database
100+ users
personal database
less than 100 users
threat actor
cyberattack
cybercriminal
attack for money
script kiddie
automated attack
broker
sells knowledge
cyberterrorist
causes disruption and panic
hacktivist
targets specific organizations they disagree with
state actor
government-led attacks against people
types of NoSQL
key-value stores
document databases
wide-column (column family) stores
graph databases
data warehouse
large enterprise wide, integrate data from multiple sources
data mart
smaller subset of a warehouse, focused on one single department or function
web mining
for unstructured data online, analyze web pages, user behavior, and the structure of hyperlinks
data mining
finding patterns and relationships with structured data
online analytical processing data cube
organizes business data (like sales, inventory) by categories (dimensions like time, product, region) to allow for fast, flexible analysis, letting users quickly "slice, dice, drill down, and roll up" data to see trends, not just rows and columns.
database administrator role
maintains and manages the performance and availability of database systems
data scientist
analyze data, discover trends, and relationships
committing data
permanently saves all changes made
rollback data
undoes all changes made within a transaction since the last commit
data auditing
review data
data scrubbing
finding and fixing inaccurate data
prescriptive analytics
recommending a course of action for the predictive outcome
data project life cycle
sensing- identify meaningful data
collection- gather data
wrangling- convert to user-friendly format
analysis
storage
data-driven decision making
ask
prepare
process
analysis
share
act