Computer Networks Midterm
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Processing Delay
checking of packet data by the device. it checks for forwarding and data integrity. Usually the smallest, after propagation
Queueing delay
this delay happens on the router. If the delay is less than 0, there is little to no queueing delay. If the delay = 1, we at max cap. for the queue. If the delay is greater than 1, there is more packets arriving than can be serviced.
Transmission delay
the time it takes for the device to get the packet ONTO the link. measured in L/R
Propagation delay
the time it takes for the packet to travel OVER the link. measured in d/s (where d is the length of the link and s is the speed of propagation)
Application layer
for supporting network applications - HTTP, IMAP, SMTP, DNS
Transport layer
for process to process data transfer - TCP, UDP. provides transmit instructions
Network layer
for forwarding and routing of datagrams for source to destination - IP, routing protocols
Link layer
for data transfer between neighboring network elements - Ethernet, WiFi (802.11), PPP
Physical Layer
bits on the wire/ signals in the air
Packet sniffing
reading the packets that are in the air that are transmitted from a device via wifi.
IP spoofing
getting the traffic that is intended for one receiver to be sent somewhere else
DDoS
distributed denial of service attack is swarming a server with so many requests that it cannot function
client-to-server architecture
where clients are communicating with servers either as a medium or as a ricochet.
servers are always on
clients can connect intermittenly
clients do not connect to each other, only through the server
peer-to-peer architecture
there is no central server that is always on, instead peers request data from other peers.
this architecture is self-scalable
there might be a small server to start connection between devices
socket
combination of IP address and port number to designate specific request in a specific spot in memory.
stateless (for HTTP)
either side of the HTTP connection is not keeping tabs on what is going on
web cache
backup servers that get data from origin server updates and keep frequently requested websites/data. web caches turn over data pretty quickly to keep up with demand.
A and AAAA record
A record name: host name, value: IPv4. AAAA record name: host name, value: IPv6
NS record
name: domain, value: host name of authoritative server. sends back the A record because authoritative servers hold all the IP addresses
C NAME record
name: domain/hostname(ibm.com), value: canonical name(testserver2.ibm.com)
MX record
name: domain, value: mail server for indicated domain
iterative request
when each step/request is returned to the requesting server. "I don't know, here is the info for who to ask next"
recursive request
"I don't know, let me find out for you"
DASH
stands for dynamically adaptive streaming over HTTP.
used by server to reprocess uploaded video to other resolutions
used by device/client to monitor internet speeds and request the video quality the device can handle
CDN
content distribution networks store/serve multiple copies of videos at multiple geographically distributed sites
enter deep (CDN)
entering deep into local ISP networks which have copies of servers
closer to users means faster downloads
individual servers are vulnerable to attacks and harder to maintain
bring home (CDN)
puts copies of servers at IXPs which are at the heart of the Internet
simpler distribution and more security for servers
access is farther meaning slower downloads
multiplexing
TCP collecting packets and weaving them together to be sent out
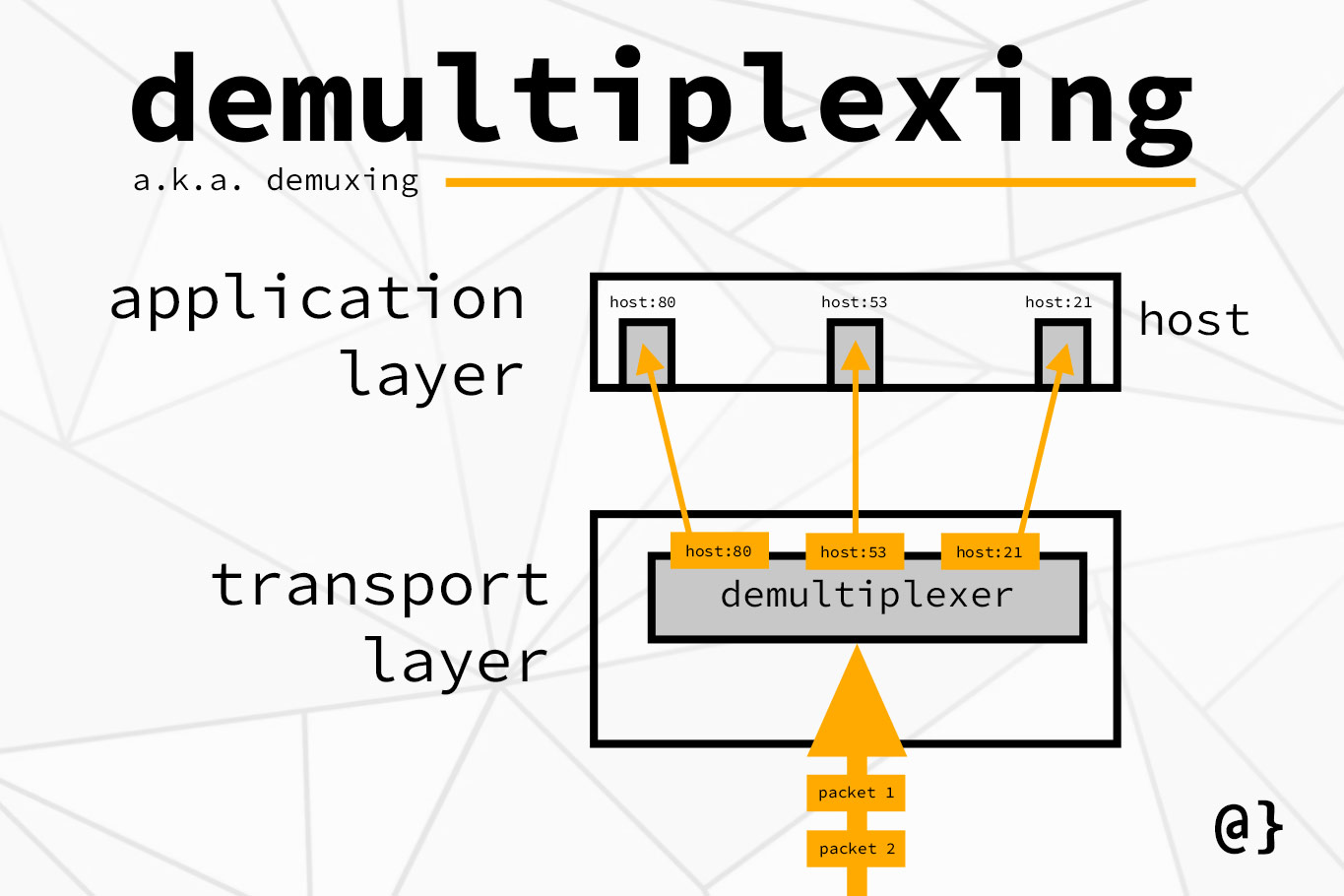
demultiplexing
TCP taking the packets from the Internet and distributing them to their sockets
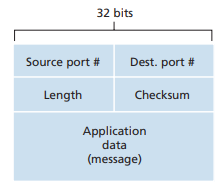
UDP header
checksum is the sum of all of the words(16 bit phrases) in a segment using binary arithmetic with overflow wrap-around and transforms to the 1’s complement.
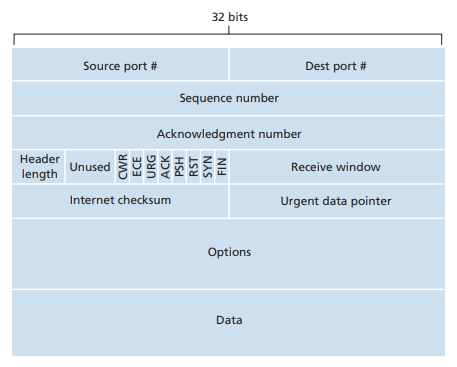
TCP header
flow control: receive window field which has the # of bytes the receiver is willing to accept.
congestion notification: CWR and ECE fields
connection management: RST, SYN, and FIN fields
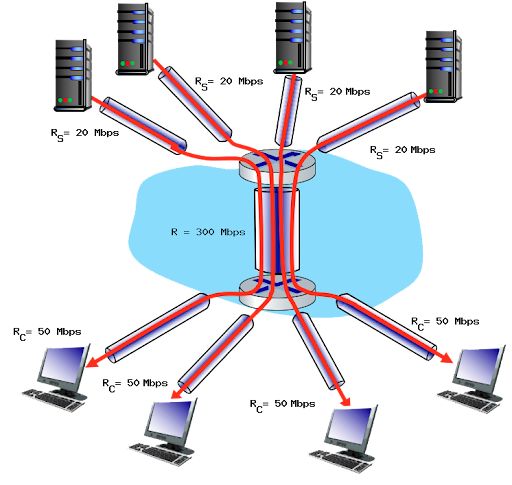
bottleneck
Ways to add reliability (building blocks of TCP)
numbering packets
establish 2-way communication
timing: TTL and RTT and determining if a packet is missing or just taking a long time
ensure that all of the packets were received (ACK and NAK)