AP Psychology: Topic 3.7 - Classical Conditioning
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Behavioral perspective
a theory suggesting that behavior is learned and is shaped by observable, environmental factors

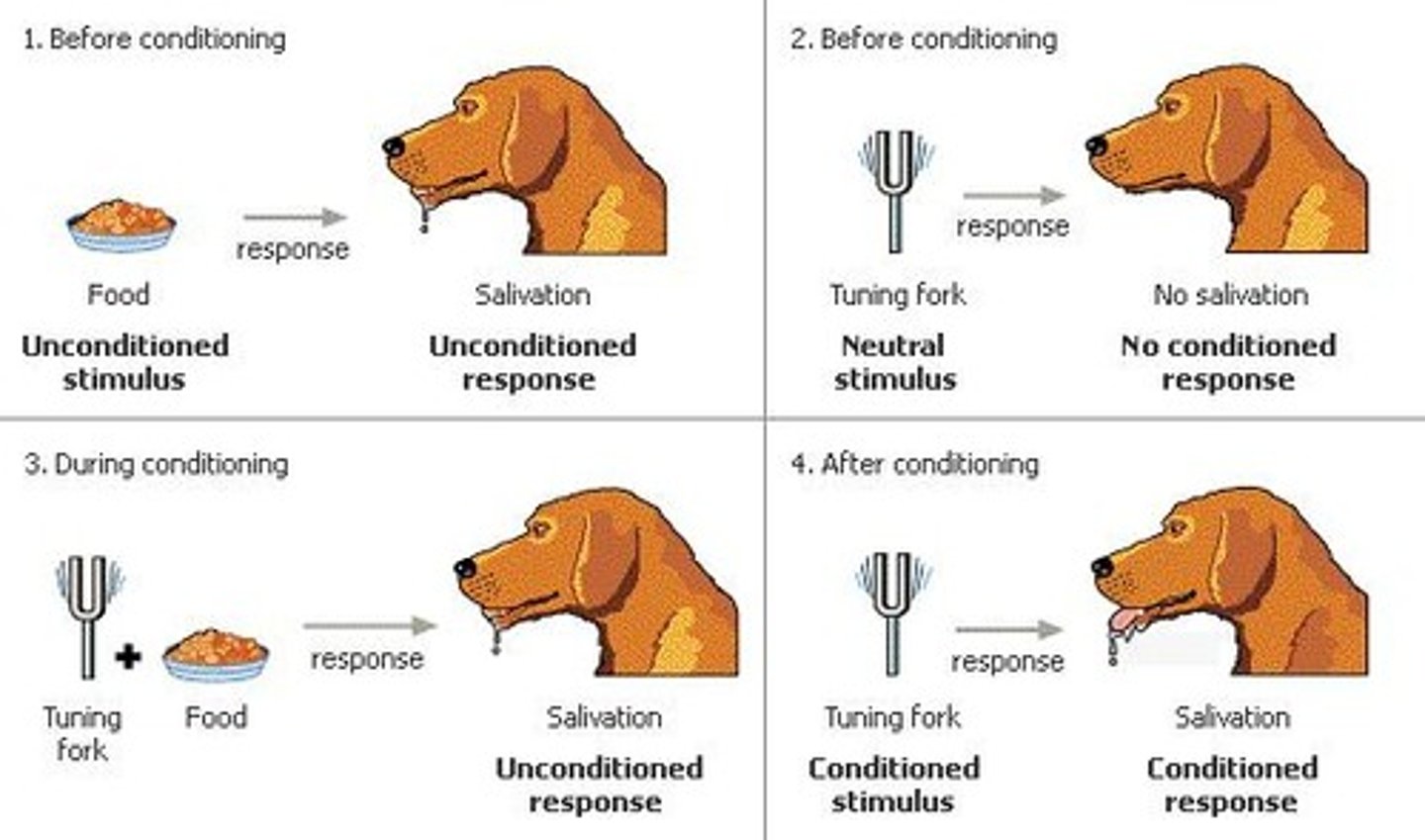
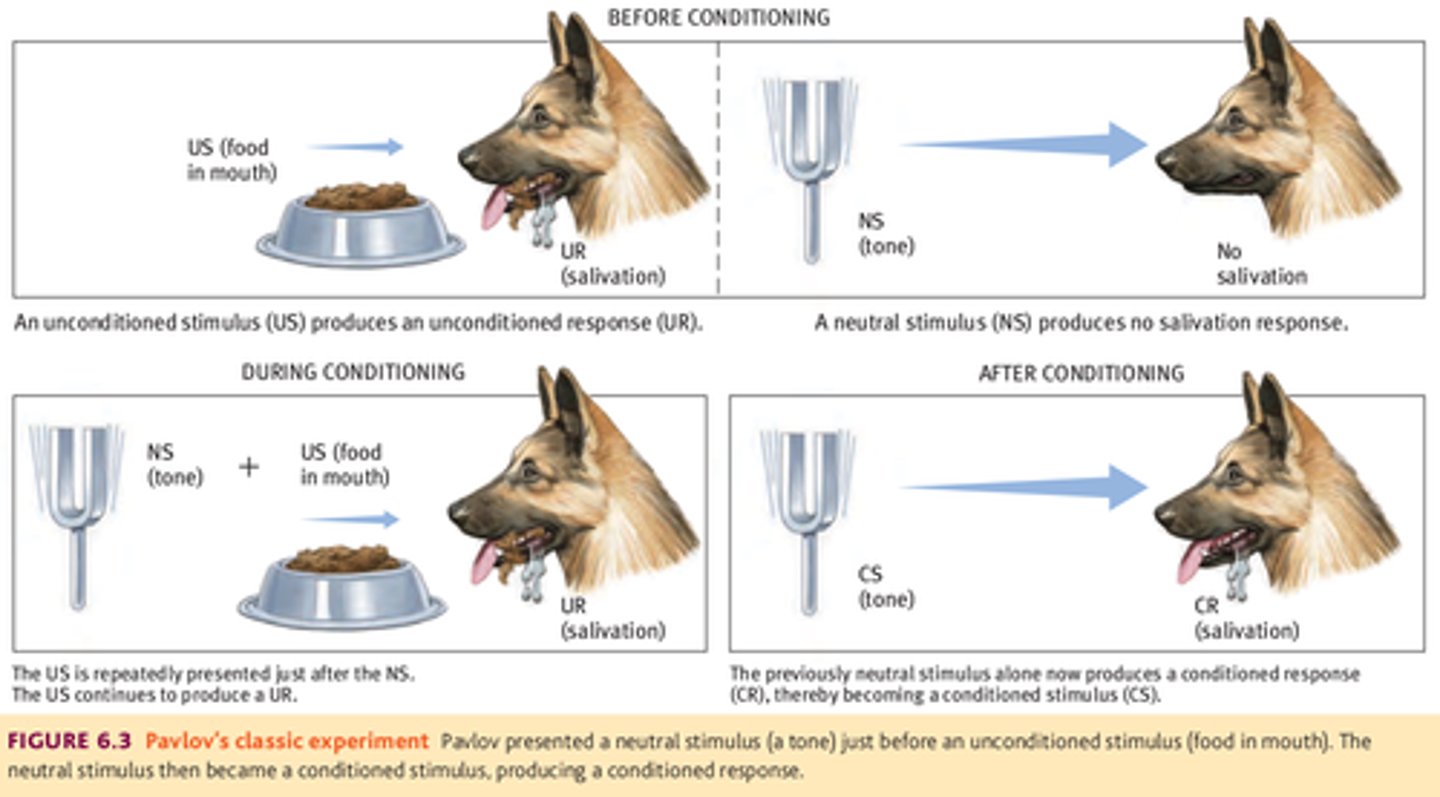
Classical conditioning
a learning process that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a behavior (e.g., salivation)
Association
when a subject is conditioned to connect a stimuli with another stimuli, and this results in a specific behavior

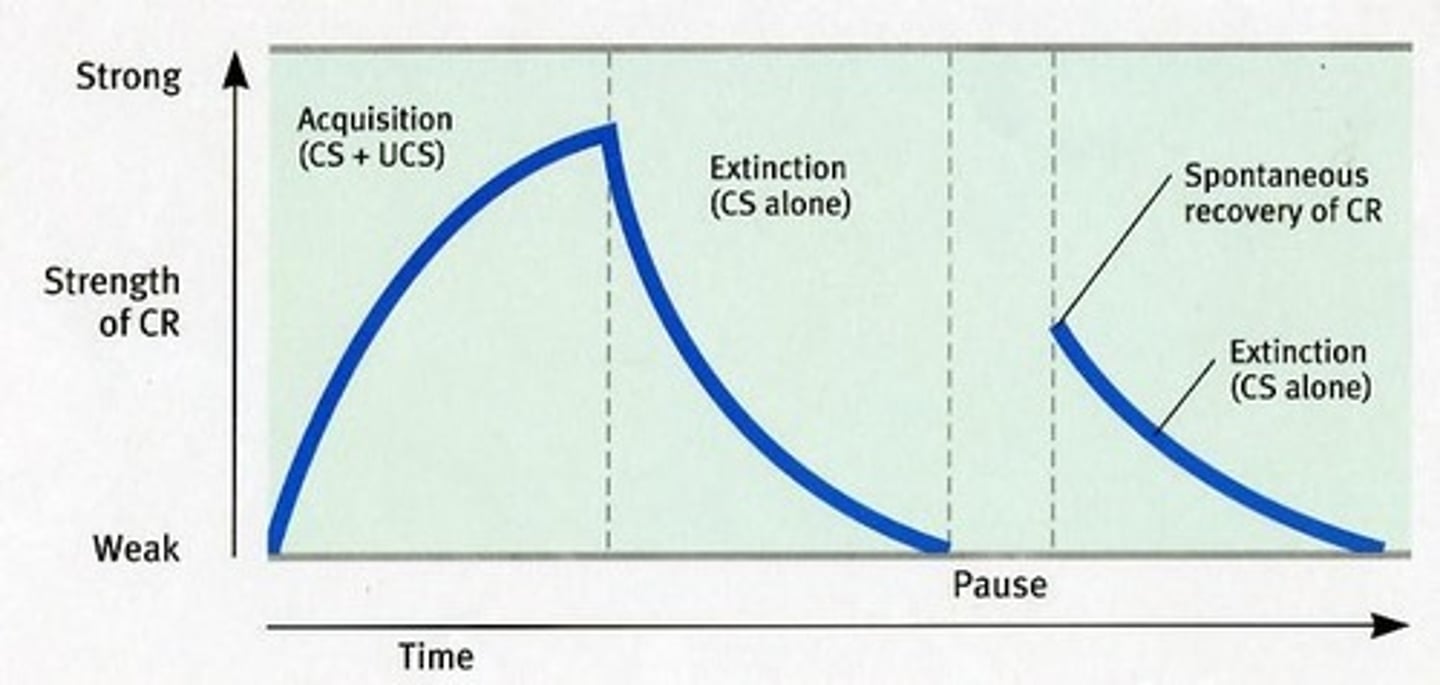
Acquisition
the period of initial learning in classical conditioning in which a human or an animal begins to connect a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus will begin to elicit the conditioned response
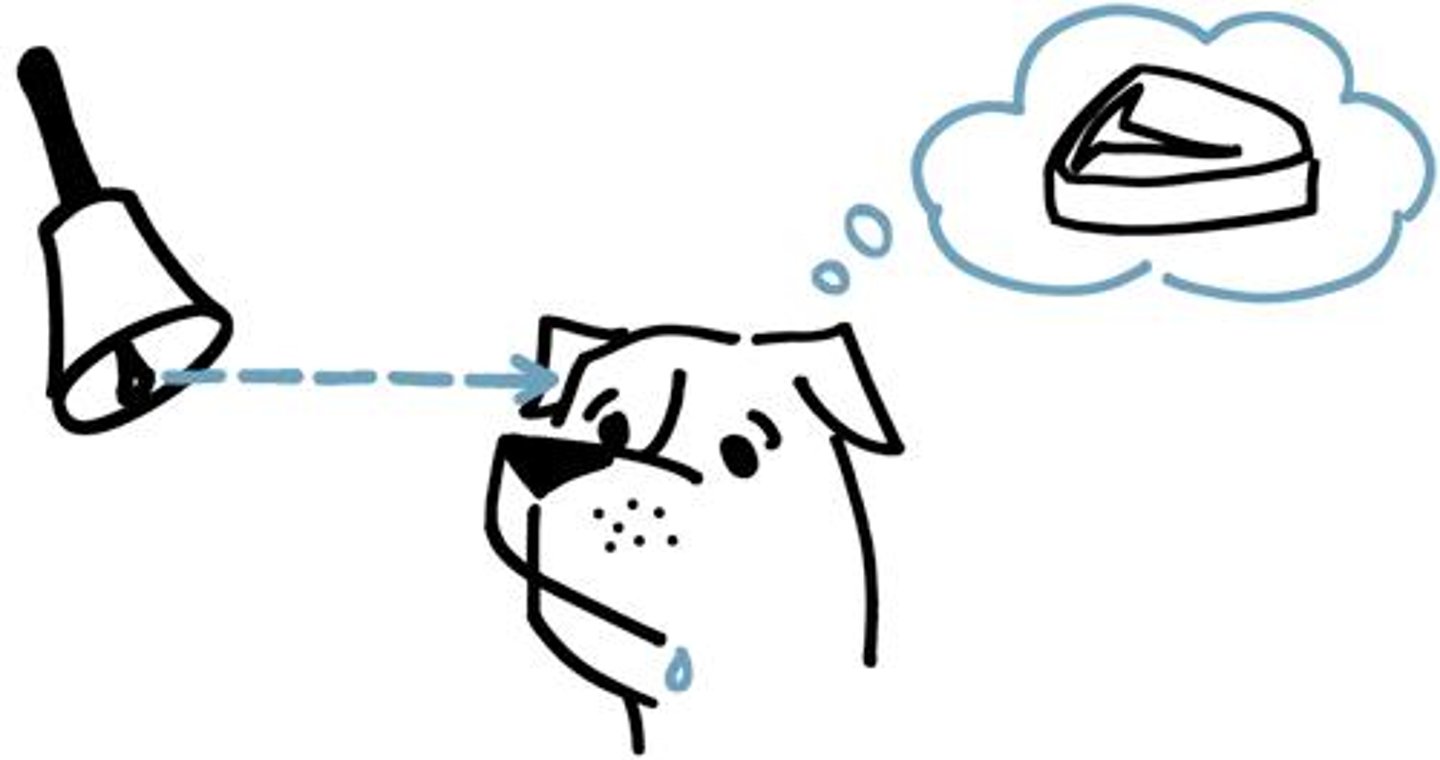
Associative learning
learning that two things occur together (e.g., a dog learns that it will get a treat when it obeys a command)

Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
a stimulus that unconditionally—naturally and automatically—triggers a response
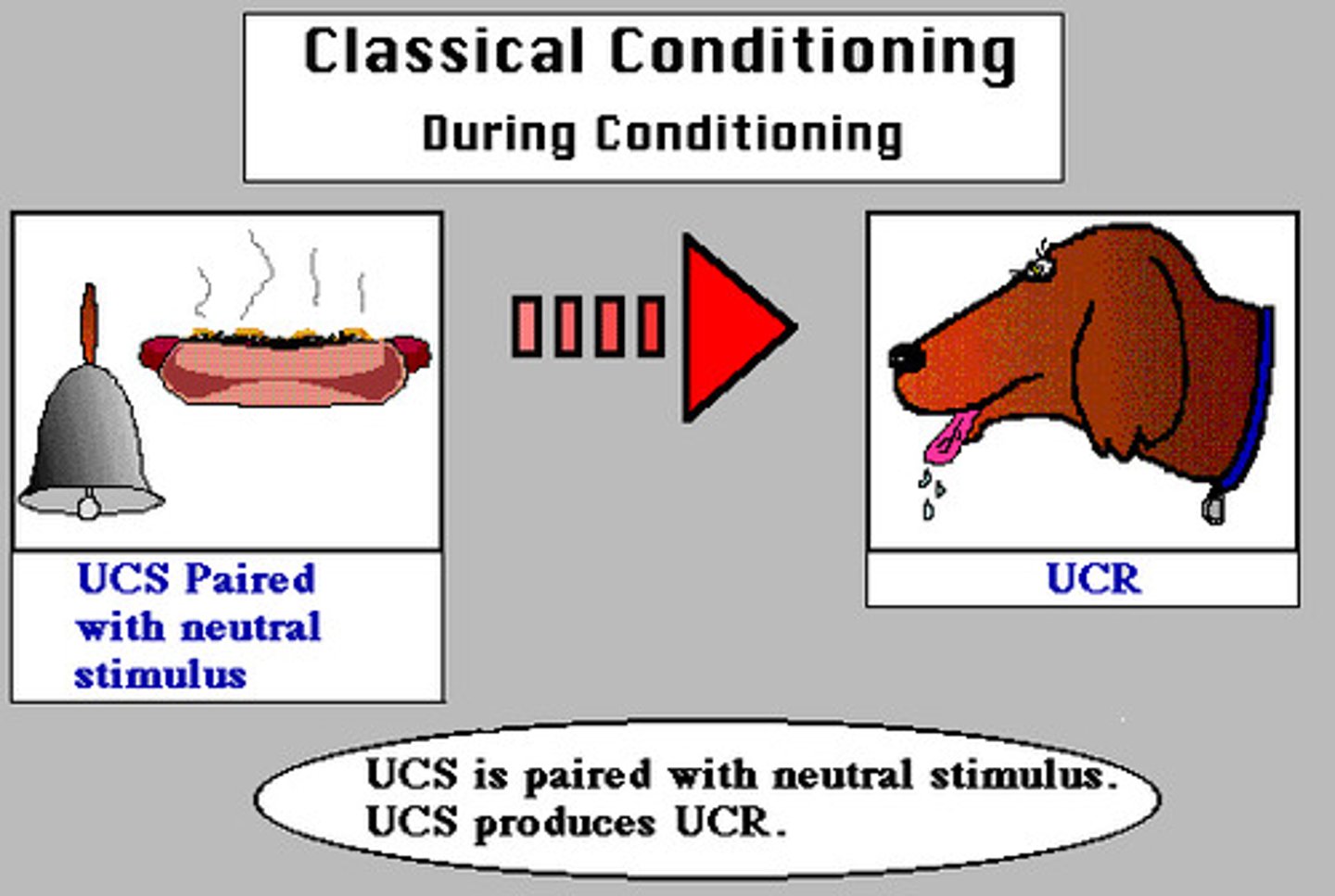
Unconditioned response (UCR)
an unlearned, naturally occurring response to an unconditioned stimulus
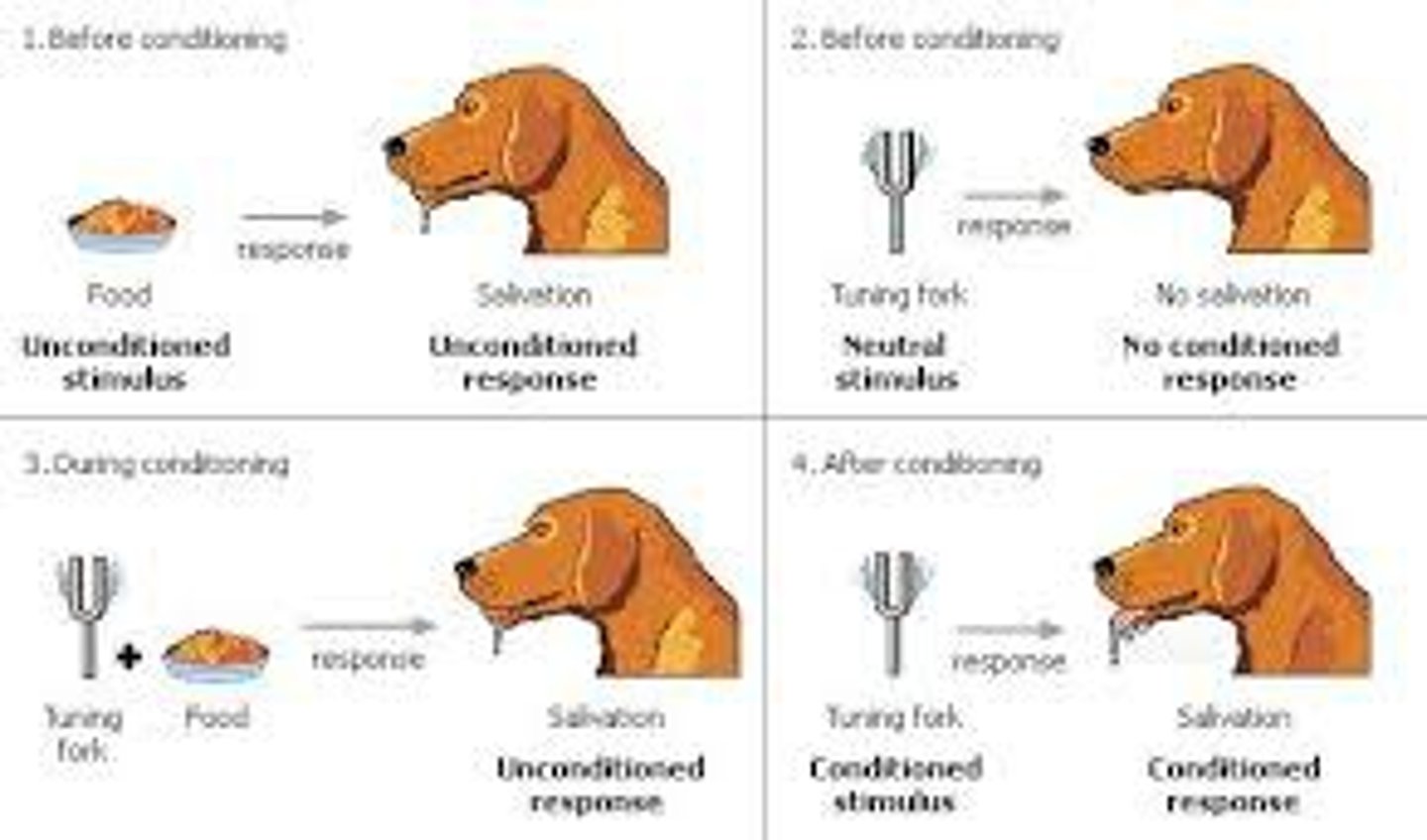
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
a neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, triggers a conditioned response
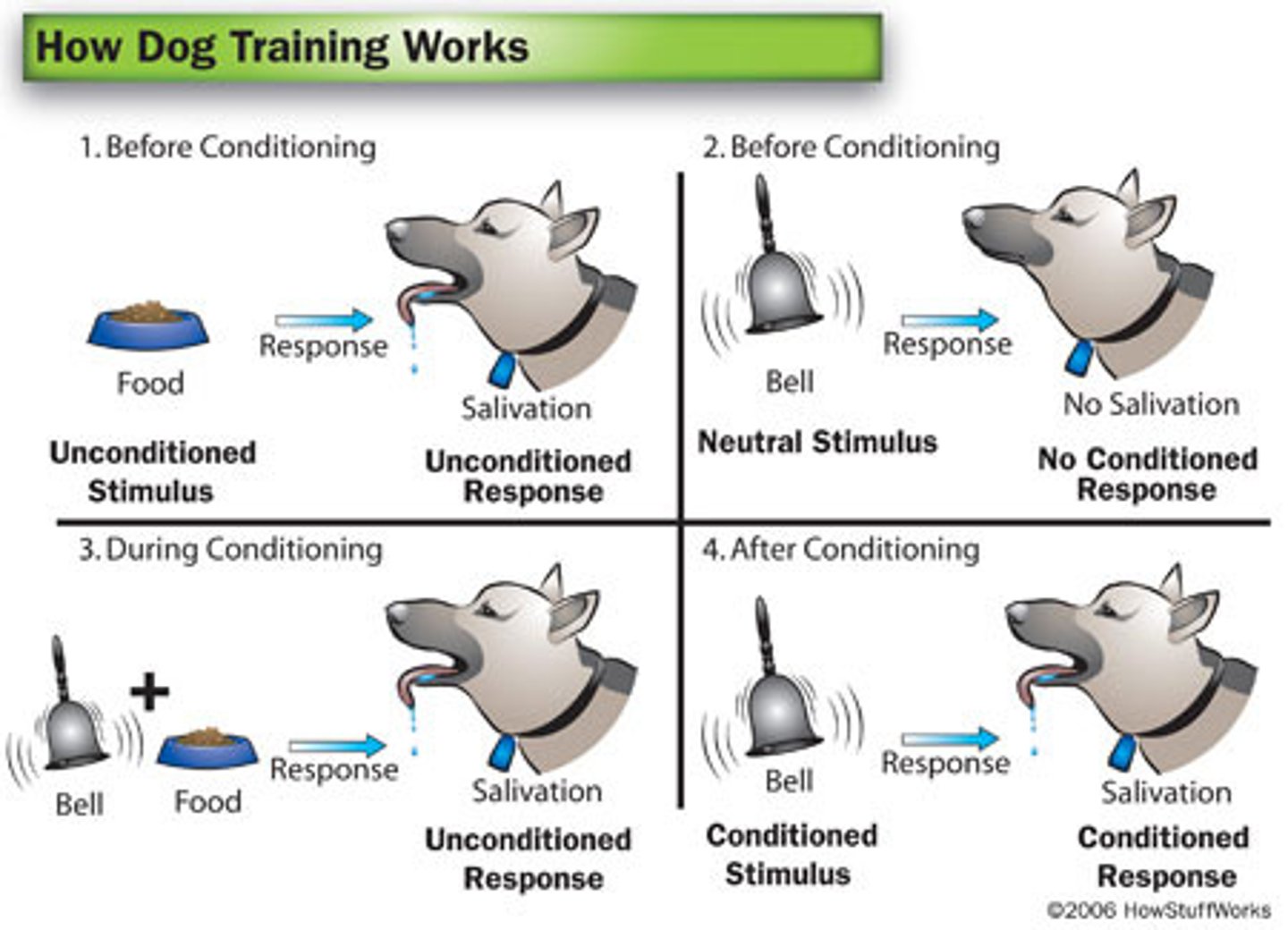
Conditioned response (CR)
the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus
Extinction
the gradual weakening of a conditioned response that results in the behavior decreasing or disappearing

Spontaneous recovery
when a learned behavior recovers from extinction after a rest period
Stimulus discrimination
when a subject demonstrates the conditioned response only to the conditioned stimulus and not to stimuli that are similar to the CS
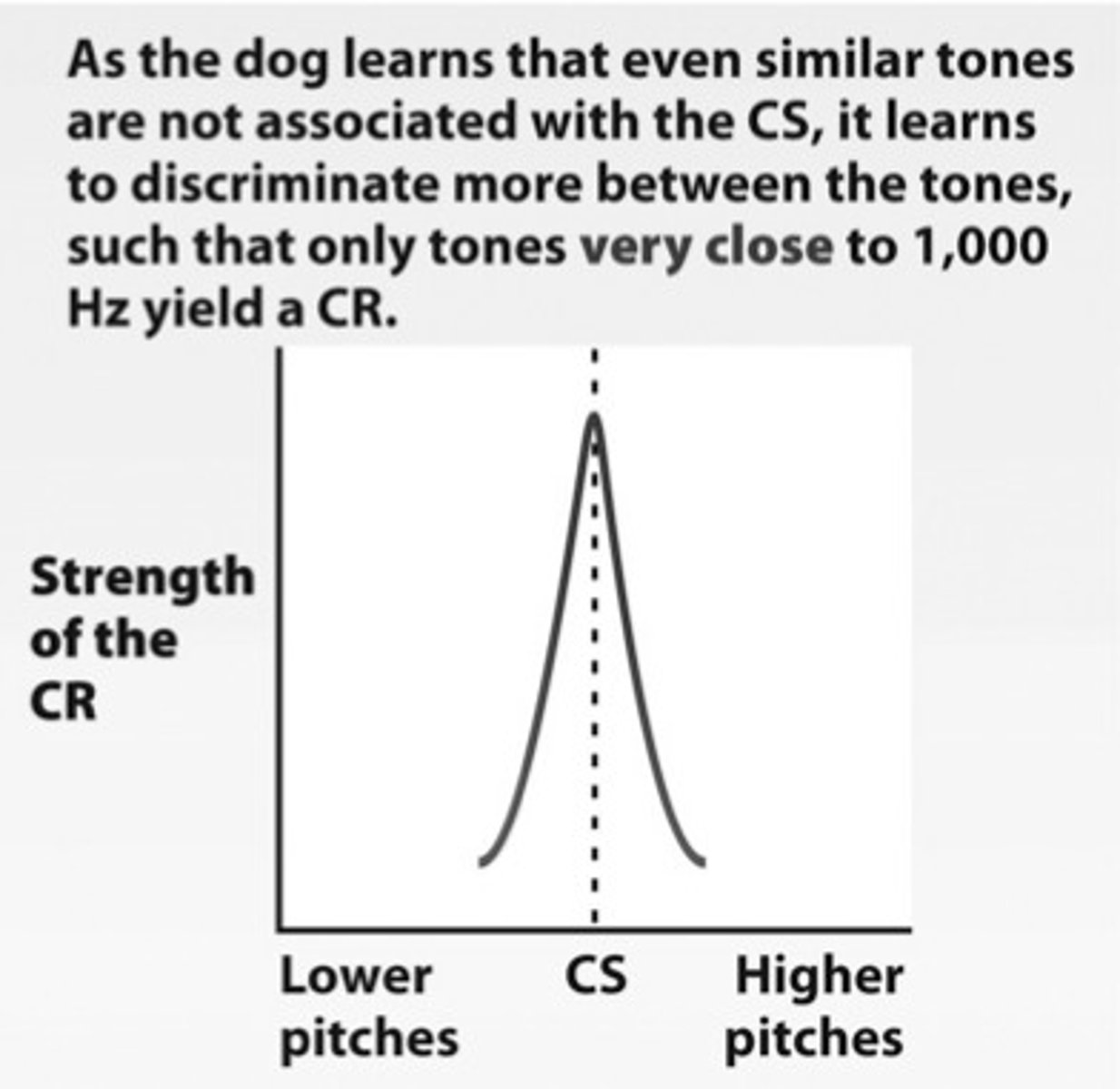
Stimulus generalization
when a subject demonstrates a conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the original conditioned stimulus

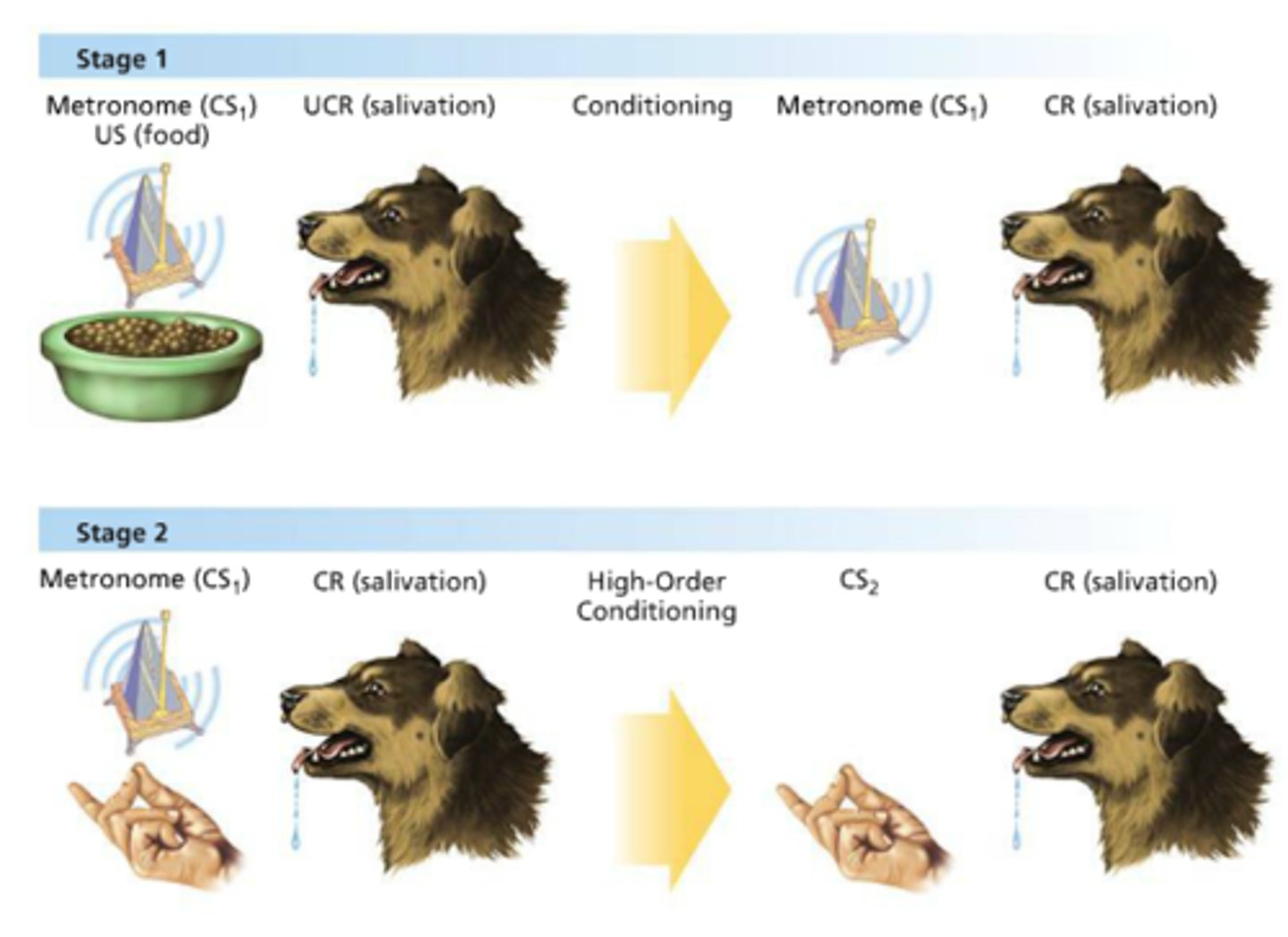
Higher-order conditioning
when a conditioned stimulus becomes associated with a new unconditioned stimulus (e.g., an animal learns that a tone predicts food could then be taught that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone)
Counterconditioning
a behavior modification technique in which a stimulus that creates a negative response is paired with something known to create a positive response
Taste aversion
the avoidance of a certain food following a period of illness after consuming the food

One-trial conditioning
if a condition is powerful or extreme, something can be learned even if the individual is only exposed to the condition once (taste aversion is a common example of this)

Biological preparedness
the natural tendency of animals to learn certain associations (e.g., nausea, fear) with only one or few pairings due to the survival value of the learning

One-trial learning
when conditioning occurs after a single experience involving an intense stimulus (e.g., fear, pain, sickness)

Habituation
the diminished effectiveness of a stimulus in causing a response following repeated exposure to the stimulus
