nuclear structure and organization
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
How do nuclear compartments differ from cytoplasmic compartments?
They are not surrounded by other membranes
Translation happens in the ___ and DNA rep. Transcription and RNA processing happens in ___
cytoplasm
nucleus
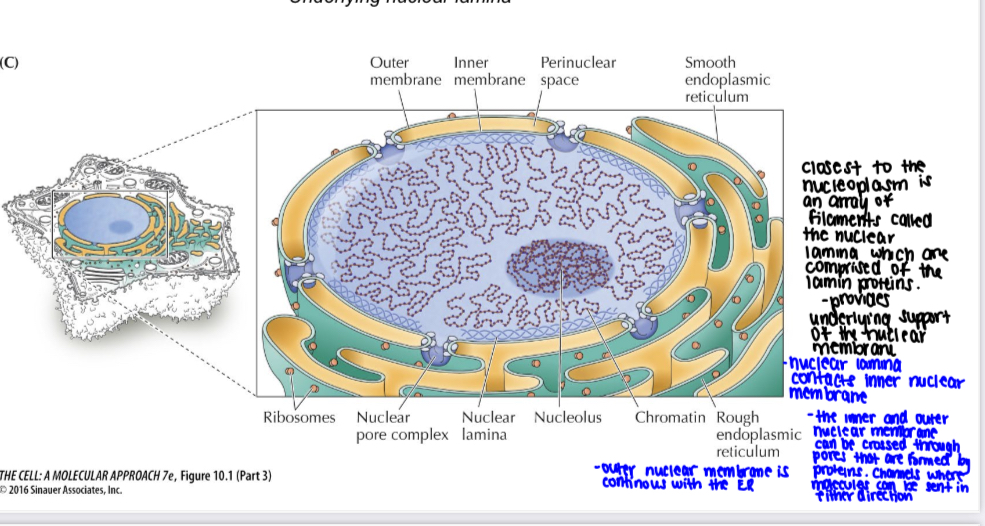
The nuclear envelope comprised of
2 nuclear membranes
nuclear pore complexes
Underlying nuclear lamina (lamin proteins providing support of the nuclear mem)
The outer nuclear membrane (ONM) is continuous with the ___, and the peri-nuclear space between inner and outer nuclear membranes is connected to the ___
rER
ER lumen
The inner nuclear membrane (INM) is distinct from the ONM, and contains proteins that connect to the nuclear lamina
nuclear lamina
Nuclear pores form between ?
inner and outer nuclear membranes
The nuclear envelop controls traffic of proteins and RNAs through What?
through nuclear pore complexes to regulate gene expression
e.g. import of transcription factors export of mRNAs and ribosome components
8 subunits surrounding a central channel Is called
“Nucleoporins” (NUPs)
Describe Euchromatin
is decondensed and transcriptionally active. It is distributed throughout the nucleoplasm.
Describe heterochromatin
is highly condensed and not transcribed. It is often associated with nucleoli and the nuclear lamina
Lamina-associated domains (LADs):
heterochromatin associates with nuclear lamina.
Nucleolus-associated domains (NADs)
heterochromatin associates with periphery of nucleoli.
The genes within LADs and NADs are generally transcriptionally
repressed.
The Nucleolus: a ribosome factory For
rRNA transcription and processing, ribosome assembly

Tandem repeats of rRNA genes, very ___ transcription gives the tree-like appearance, which are made of ___
active
RNAs
RNA polymerase I what?
The most important
5S rRNA is *produced Where and by what?
outside nucleolus by RNA Pol III
Svedberg unit -
a unit of sedimentation coefficient, a measure of a particle's size, shape, and mass as it settles in a solution under centrifugal force
Newly transcribed 45S pre-rRNA acts as an organizing site for formation of new ?
nucleoli after mitosis
Internal transcribed spacers has to be___ and external transcribed spacer are regions btwn
Spliced out
repeats
Series of cleavages by proteins guided to pre-rRNA by small nucleolar ____and ___Followed by ~100 ribose methylations.
RNAs (snoRNAs) and snoRNPs.
Analogous to formation of spliceosomes on pre-mRNA by
small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs).
Conversion of uridine to pseudouridine (Ψ), sometimes called the 5th nucleotide.
Ψ =
methylated uridine.
ribosome assembly
1)rRNA associated with ribosomal proteins in the nucleolus (imported from cytoplasm)
2)40S and 60S subunits are exported separately to cytoplasm using exportin Crm1
ribosomal protein mRNAs are transcribed outside the nucleolus by RNA Pol II and exported to cytoplasm for translation.
Polycomb Bodies
Centers of transcriptional repression via methylation of histone H3, Lys27. Frequently associated heterochromatin.
Cajal Bodies
Assembly and storage of snRNPs involved in pre-mRNA splicing, other RNA-protein complexes. Also play a role in assembly of telomerase.
Speckles
storage of snRNPs and splicing factors. These are recruited to actively transcribed genes for pre-mRNA processing. Different Types of Nuclear
Nuclear Bodies: Nuclear Sub-Compartments with Distinct Functions
Chromatin domains
• Nucleolus
• Polycomb bodies
• Cajal bodies
• SpecklesMED204 – review hist
LAMINOPATHIES
Diseases resulting from mutations in nuclear lamins or in lamina-associated proteins
Removes the laminA cleavage site, so it remains anchored to the nuclear membrane. Causes problems with nuclear structure and the transcription of genes. May also cause problems with DNA repair
examples of laminopatheies
• Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (LMNA)
• Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
X-linked (emerin)
autosomal dominant (LMNA)
• Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2B1 (LMNA)
• Dilated Cardiomyopathy (LMNA)
• Dunnigan-type Familial Partial Lipodystrophy (LMNA)
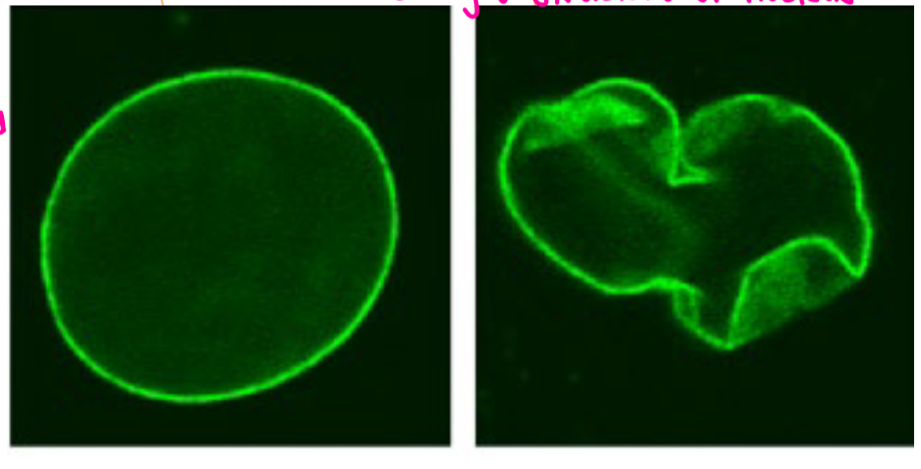
How is a progeria cell different than a normal cell
The structure of the nucleus changes
Abnormal splicing and removal of 50 amino acids from Lamin A protein results in loss of ___ cleavage site – ___cannot be removed
Zmpste24
Lipid Anchor
Explain progeria mutation
Mutation in gene for laminate A , farnesyl isn’t cleaved be no binding site for Zmpste so it can aggregate near the membrane
Lamin A:
Expression is regulated during development
Lamin C:
Alternatively spliced form of lamin A
Lamin B:
Expressed in virtually all somatic cells
Isoprenylation means what ?
diff length carbon chains that are added
phosphorylation means what?
important during onset of mitosis ; induces them to fall apart and allow nuclear membrane to dissolve
CaaX motif:
Cysteine, Aliphatic, Aliphatic, X
What does farnesyl = 15 Carbon create ?
Lipophillic motif so it can associate with membranes
Describe mechanism of when CAAX box is farnesylated
It allows lamin A to interact with the nuclear membrane on its own and after lamin a Associates with the membrane, It binds to other receptors like emerin and lamin B and farnesyl gets cut off
Nuclear Lamina Is composed of what?
Composed of lamins, intermediate filament proteins which form a cytoskeletal lattice or meshwork associated with the inner nuclear membrane
what is the transmembrane component of the LINC complex
Linker of Nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton interacting with lamina
Architecture of the Nuclear envelope and Organization of its components are dependent on the
Nuclear lamina
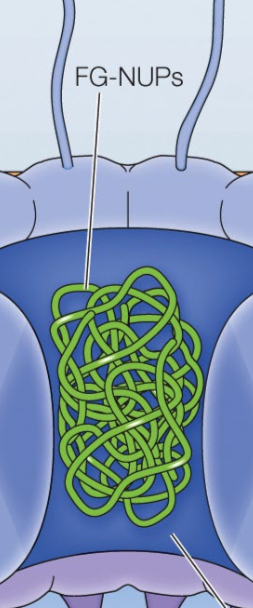
FG-NUPs are the barrier to ___. Contain phe-Gly (F-G) repeats and facilitate ___between cytoplasm and nucleus.
permeability
regulated transport
What are importins
Proteins that enter the nucleus contain nuclear localization signals (NLS) that are recognized by special transport receptors
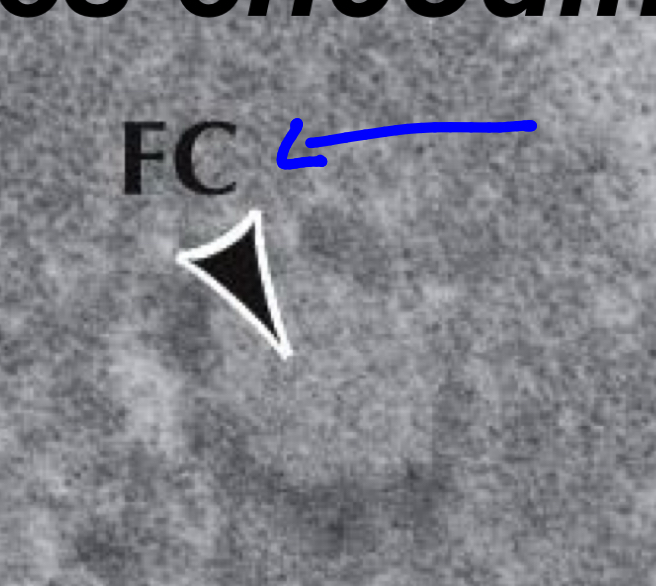

Fibrillation center
Gene encoding rRNA
Clear looking
Granular component
Assembly of ribosomal subunits
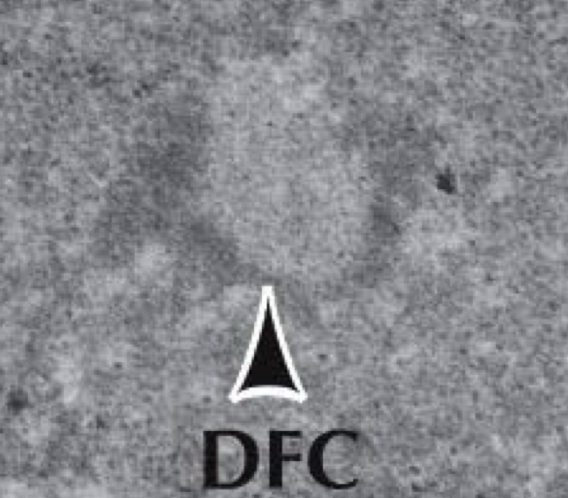

Dwane fibrillation component
Transcription of rRNA genes nucleolus organizing region
Nucleolus functions and number per nucleus
1-4
rRNA transcription, processing and ribosome assembly