Quiz 3/4 BIO190A
1/42
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does free-energy change tell us?
Whether or not a reaction occurred spontaneously?
Catabolic Pathways
Release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds, “downhill reactions”
Anabolic Pathways
Consume energy the build complex molecules from simpler ones, “uphill reactions”
Bioenergenetics
The study of how organisms manage their energy resources.
Draw Private
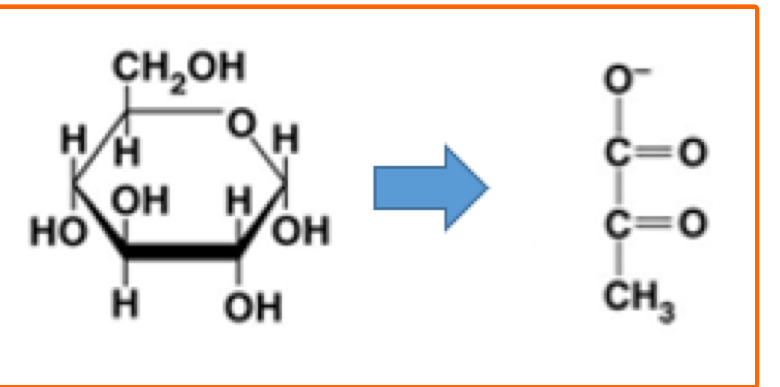
Free Energy Change Equation
Delta G= Gfinalstate- Ginitialstate
Spontaneous Reactions
Releases energy that can perform that can work; is exergonic and has a negative delta G
Non spontaneous reactions
Require energetic to preform work, are endergonic and have a positive delta G.
How do cells mange energy resources, and what is the mechanism by which they do it
Energy coupling- uses an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one.
What is the cells energy shuttle
The ATP Cycle
What makes up ATP
Triphosphate group, ribose, and a nitrogenous base
How much free energy is released with one catabolism of ATP
7.3 kcal/mol
What provides energy to phosphorylation ADP.
Catabolic reactions in the cell- especially cellular respiration and light reactions
Three forms of Work that ATP powers
Mechanical work, transport work, and chemical work
Mechanical work is
Movement of cell or structures- ATP binds noncovalently to motor proteins and is then hydrolyzed
Transport Work is..
Movement across a membrane across a concentration gradient. Works through ATP phosphorylation of membrane proteins.
Chemical Work is…
Pushing an endergonic reaction that cannot happen spontaneously. Usually uses a phosphorylation intermediate and requires very specific enzymes.
Definition of a Catalyst
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
Enzymes work by…
Lowering the activation energy barrier
Definition of a Substrate
The molecule that undergoes a chemical reaction
What does an enzyme do to a substrate?
Binds to a substrate to form an enzyme-substrate complex.
What is an induced fit?
Brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the chemical reactions.
How does an active site lower EA and speed up a reaction?
Orienting substrates correctly, straining substrate bonds, providing a favorable environment, covalently bonding to substrate (those that participate).
What are the steps in the catalytic cycle of an enzyme?
1)Substrates enter active site
2)Substrates are held in active site by weak interactions
3)Substrates are converted into products.
4)Products are released
5)Active site is available for new substrates
An enzymes activity can be affected by…
Temp, pH, and cofactors
In what ways are enzymes regulated
Competitive inhibition, non-competitive inhibition, feedback regulation, and allosteric competition
Energy flows into an ecosystem as _ and leaves as -.
Sunlight, heat
Equation for Celluar Respiration
C6H1206+6O2= 6H2O+6CO2+Energy (ATP AND HEAT)
The purpose of Cellular Respiration is to
Create a specific series of catabolic reactions, breaking down organic molecules to produce ATP.
In Cellular respiration __ is reduced and —- is oxidized.
Oxygen, fuel. (Which creates an electrochemical gradient)
If no oxygen is available for Cell. Reps., then what is done?
The cell switches to fermentation, which produces only a low level of ATP.
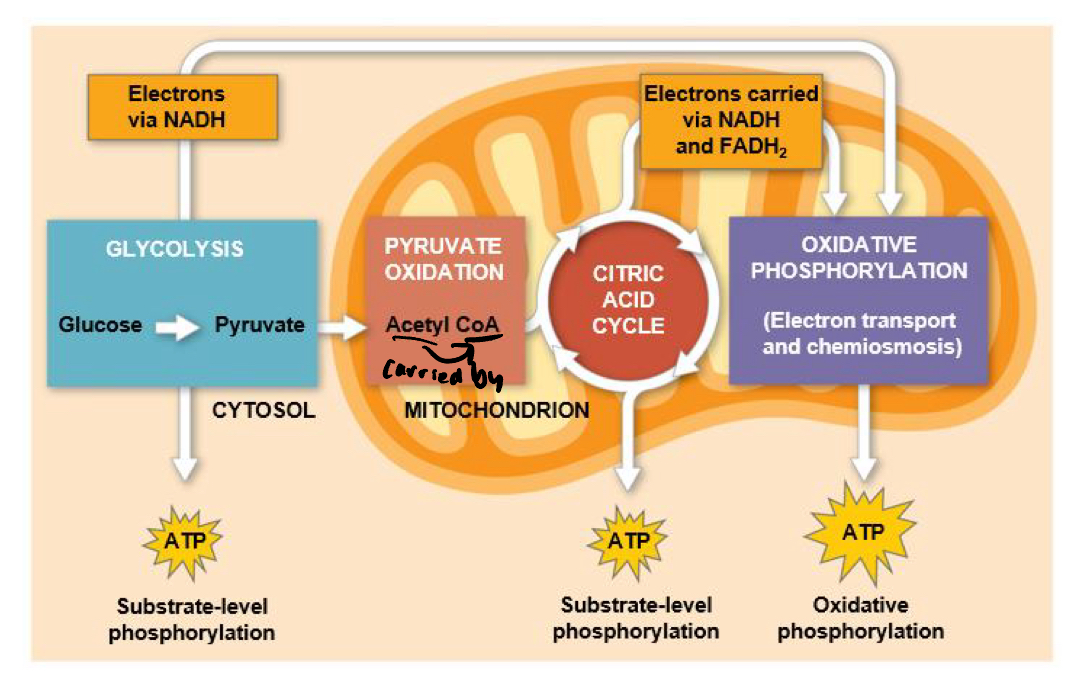
General Overview of Glycolysis
Breaks down glucose to produce two pyruvate molecules.
General Overview of Pyruvate oxidation And CAC
Oxidizes pyruvate(removes electrons), becomes acetyl, enters citric acid cycle with CoA, and completes breakdown of glucose.
General overview of oxidative phosphorylation
Redox reactions from electron transport chain drives production of ATP via chemiosmosis.
Draw Cellular Respiration diagram
What are the two electron carriers in electron transport chain.
NADH (coenzyme) and FADH2
Definition of Electron Transport Chain
Series of protein complexes that accept then release an electrons. Accepts from NADH and FADH2. Creates a concentration gradient
Two main ways of producing ATP are called…
Substrate-level phosphorylation, and Oxidative phosphorylation.
By which mechanism does oxidative phosphorylation work..
ATP Synthase uses energy harvested by oxidation of glucose and stored by electron transport chain. Accounts for 90% of ATP generated by Cell. Resp.
Function of Kinase
Adds a phosphate
Function of Phosphatase
Removes a phosphate
In prokaryotic cells, where does the steps of Cell. Resp. take place?
CAC in cytosol and ETC in plasma membrane
Glycolysis consists of what phases?
Energy Investment and Energy Payoff