Rome Unit
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
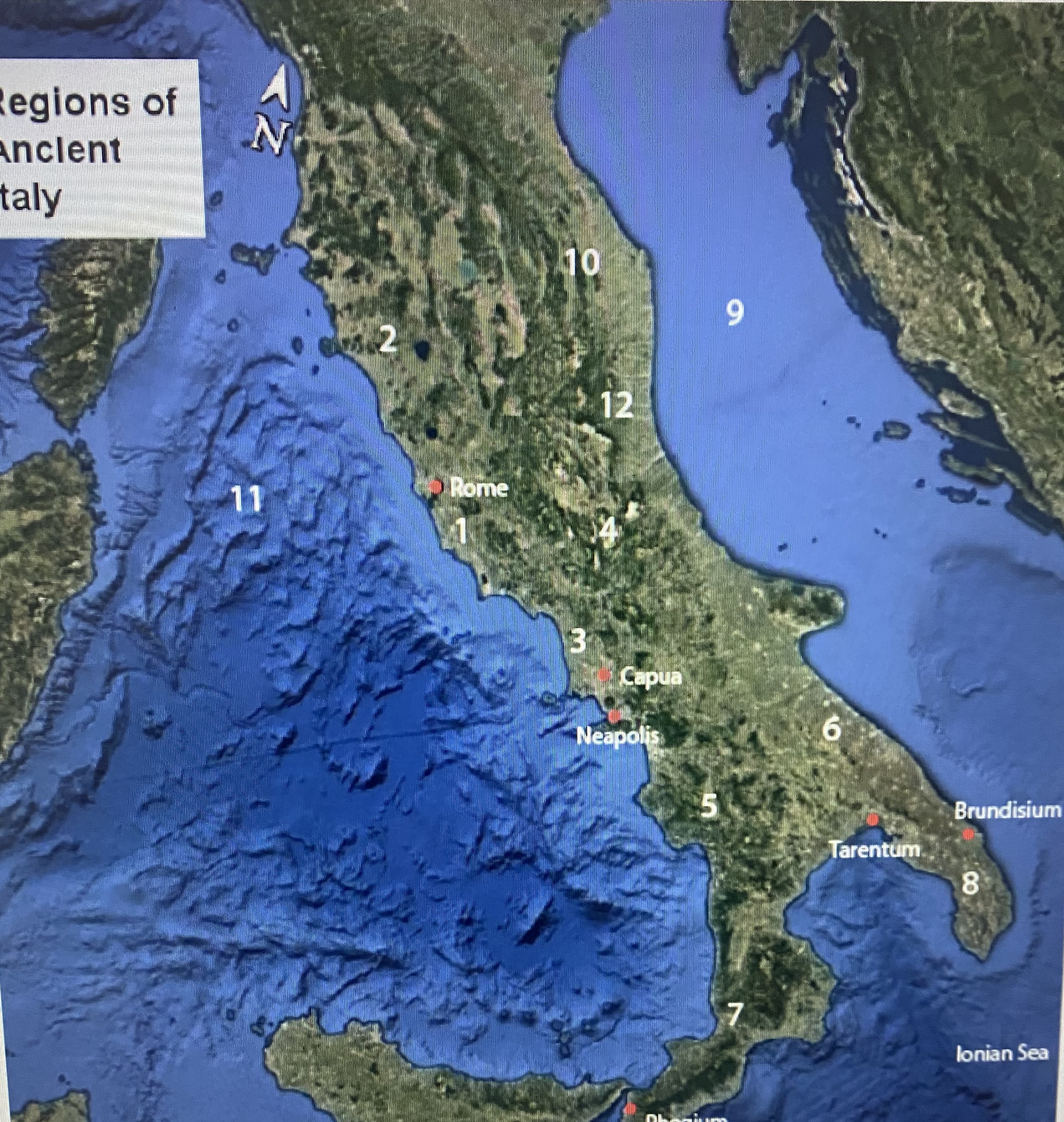
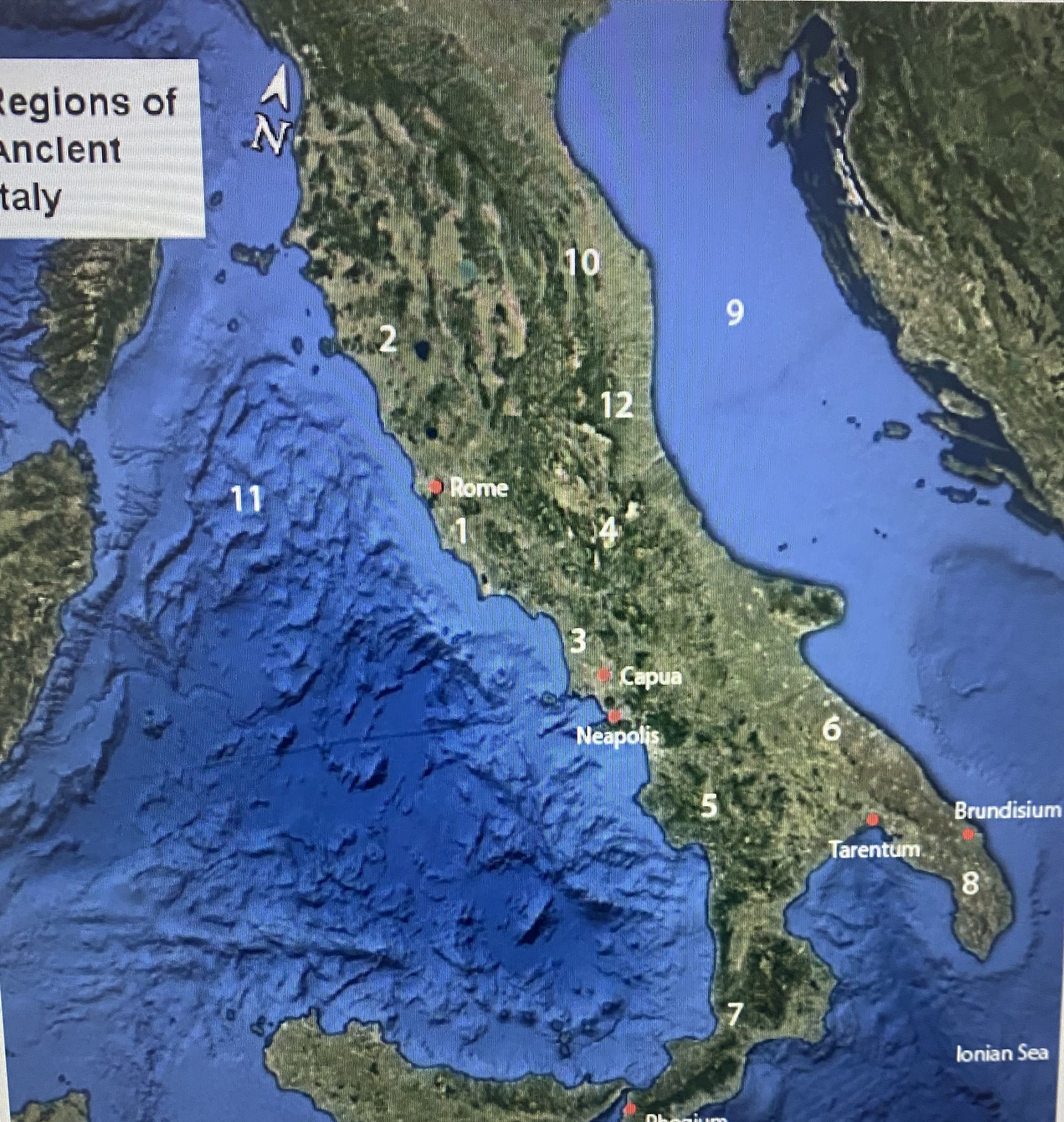
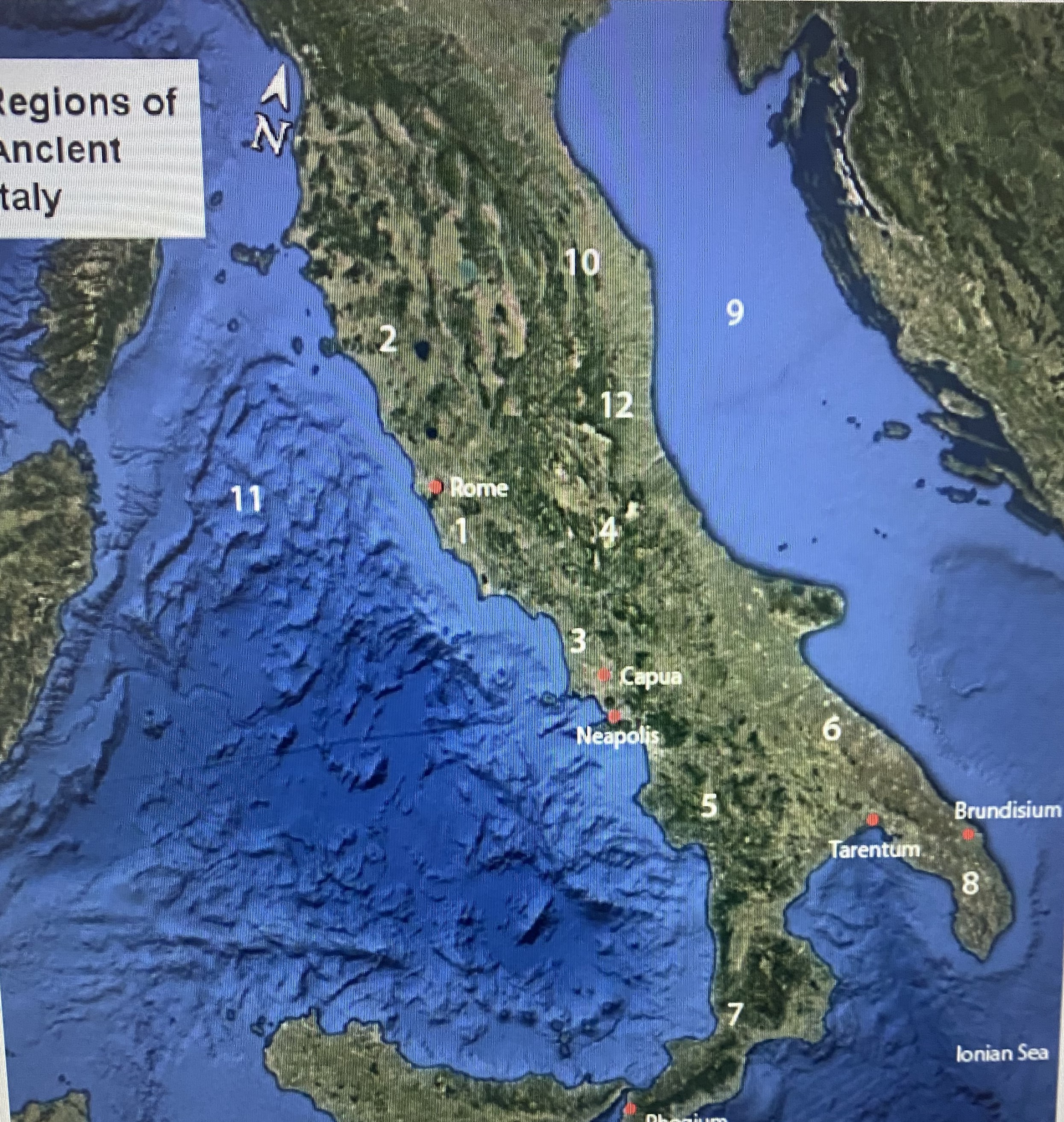
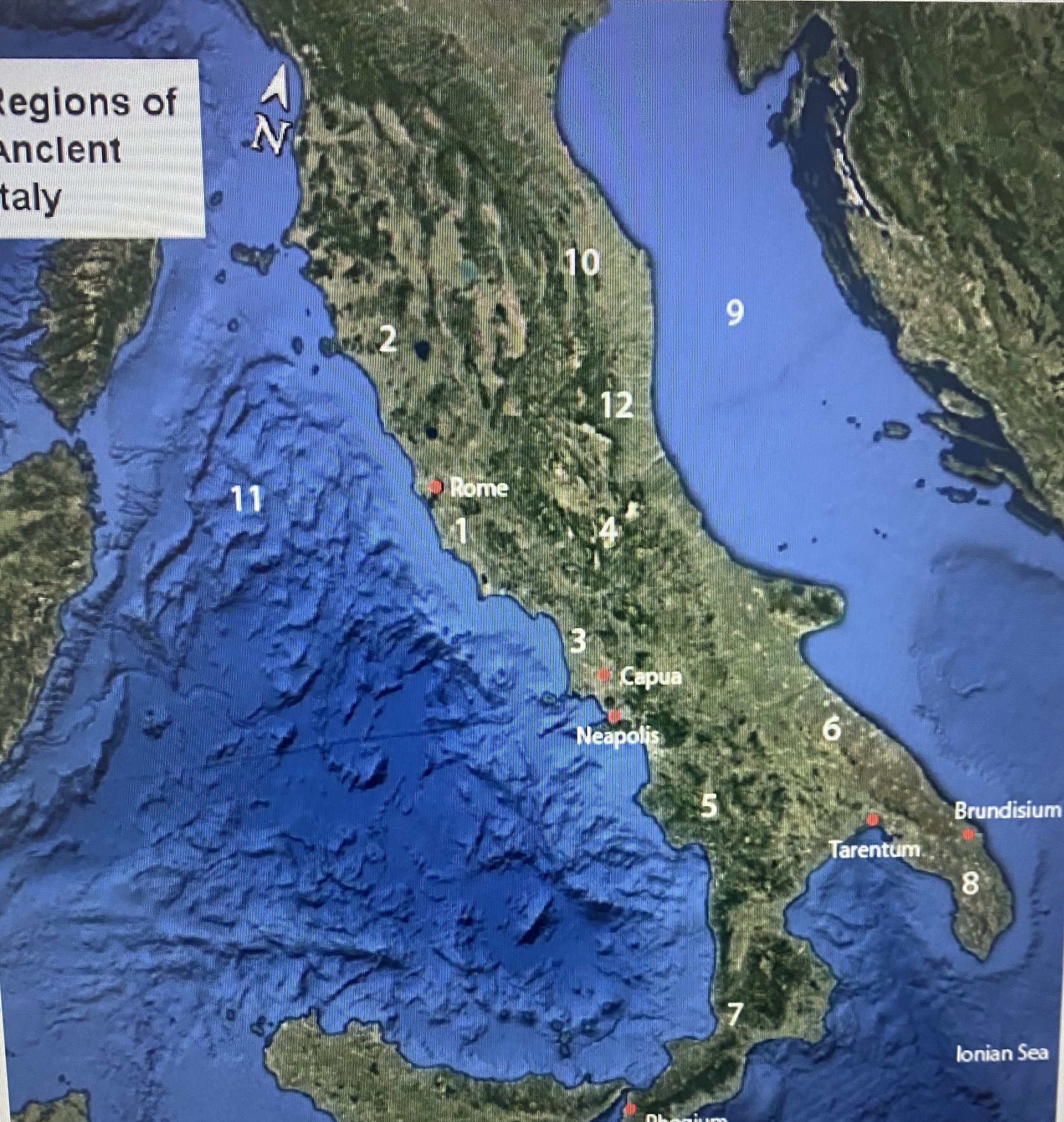
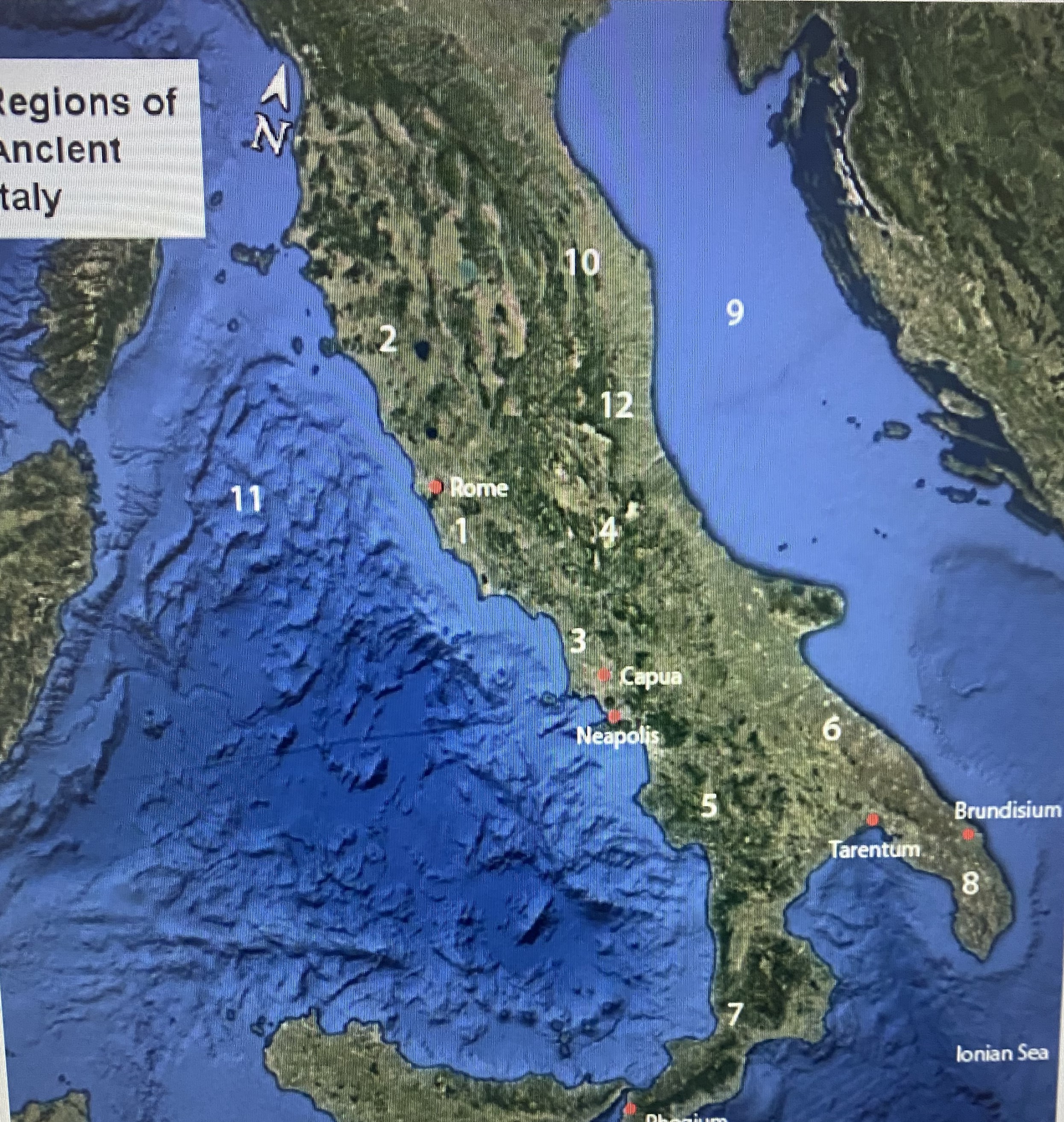
#1
Latium
#2
Etruria
#3
Campania
#4
Samnium
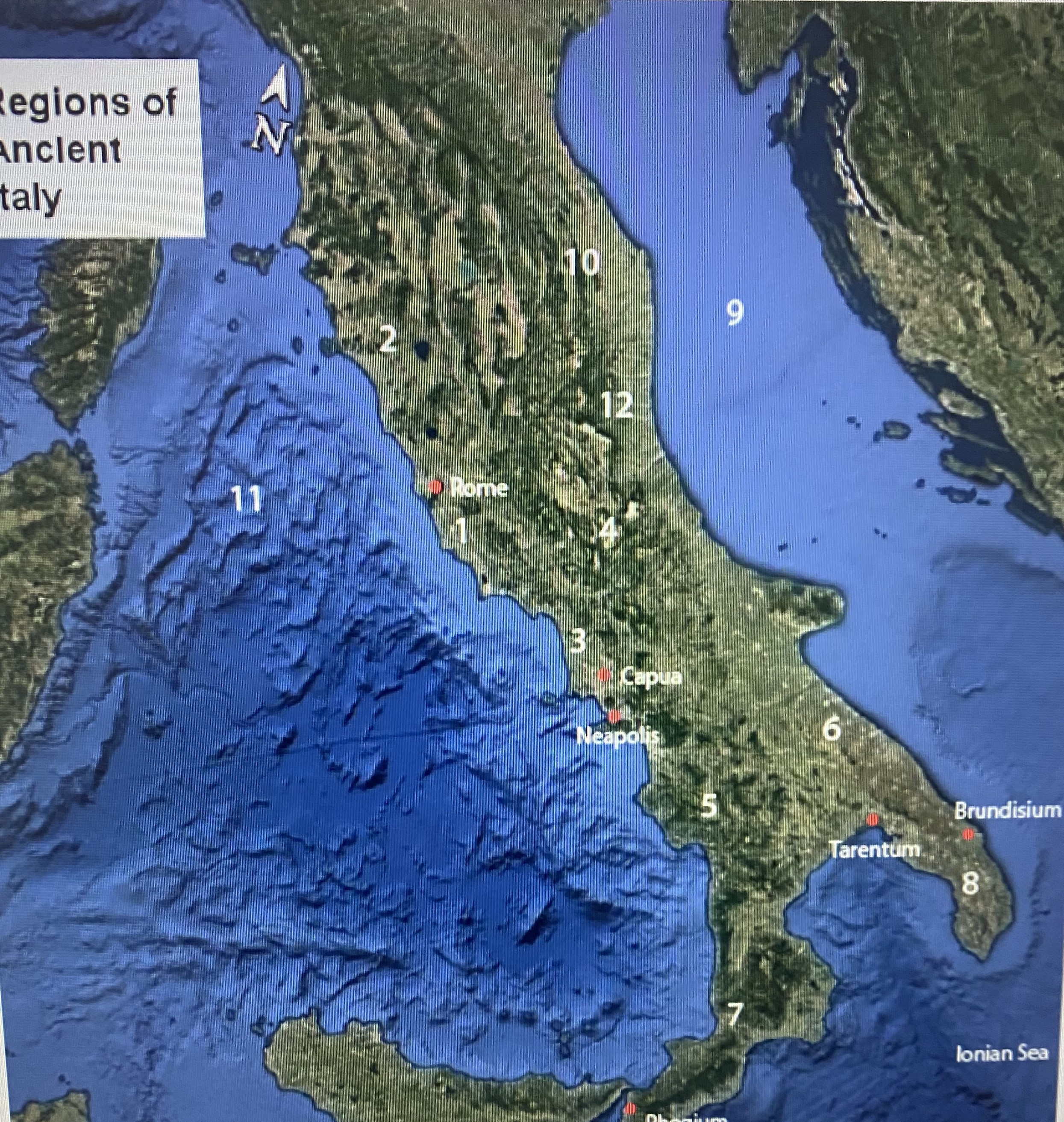
#5
Lucania
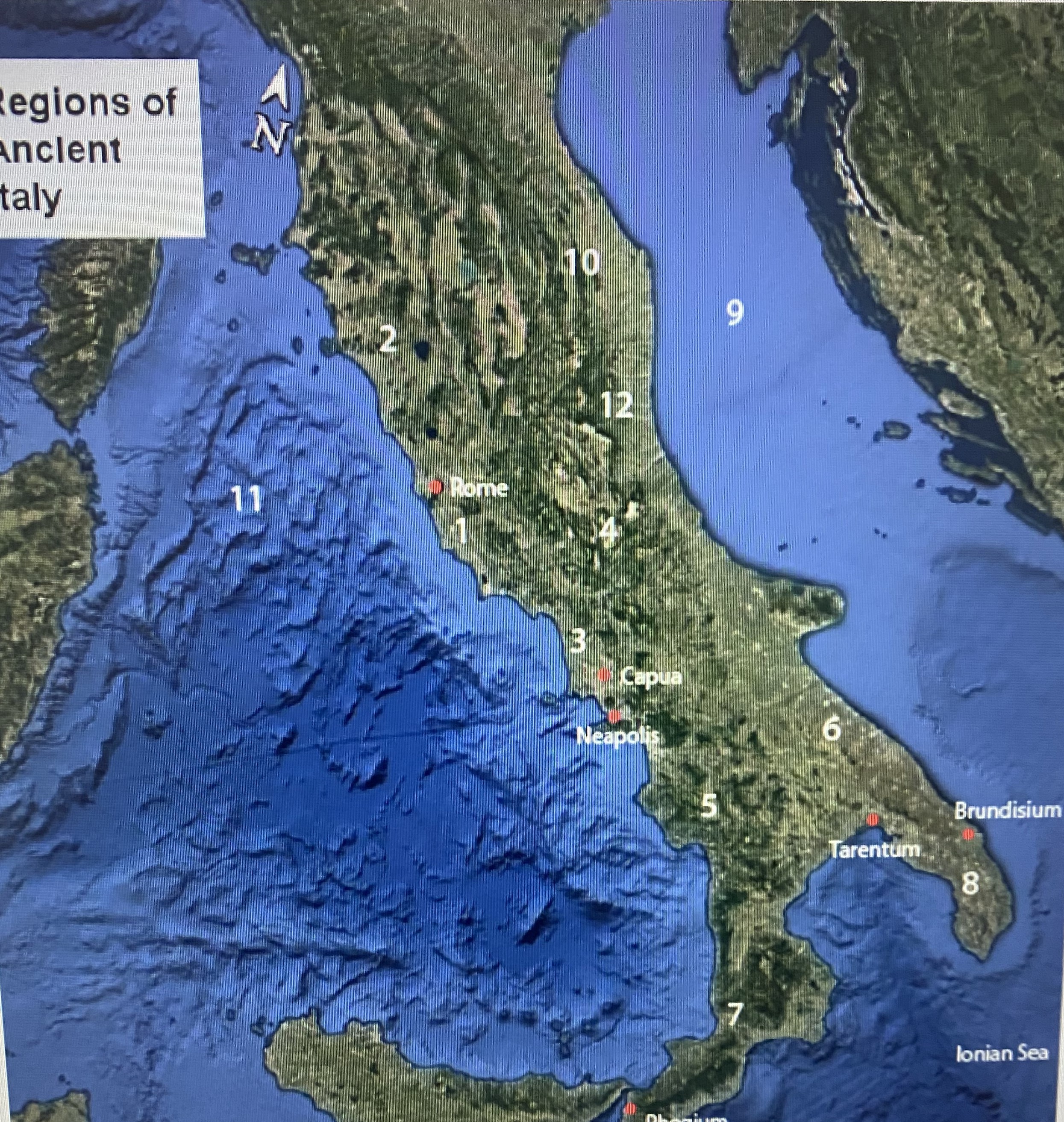
#6
Apulia
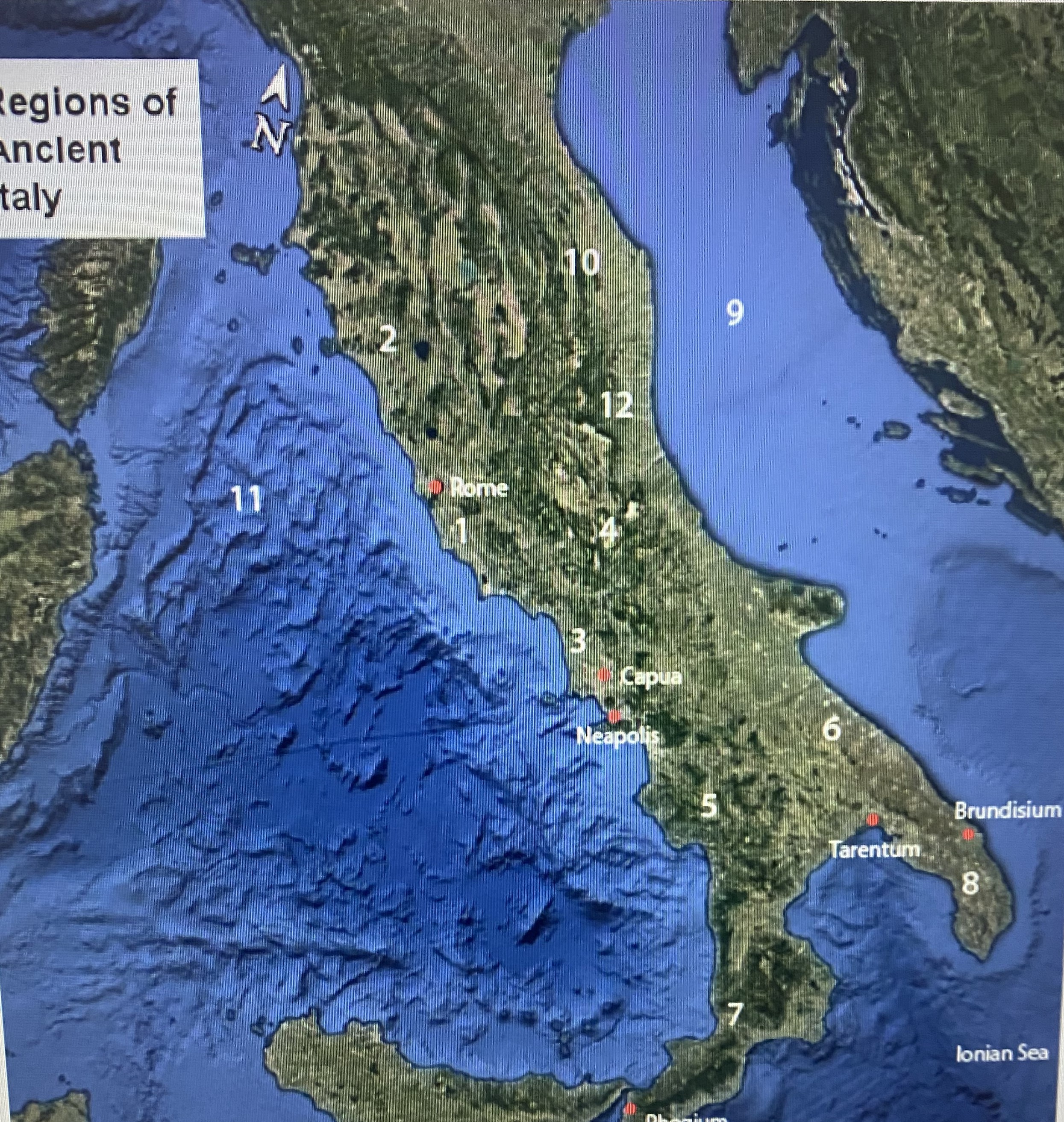
#7
Brutium
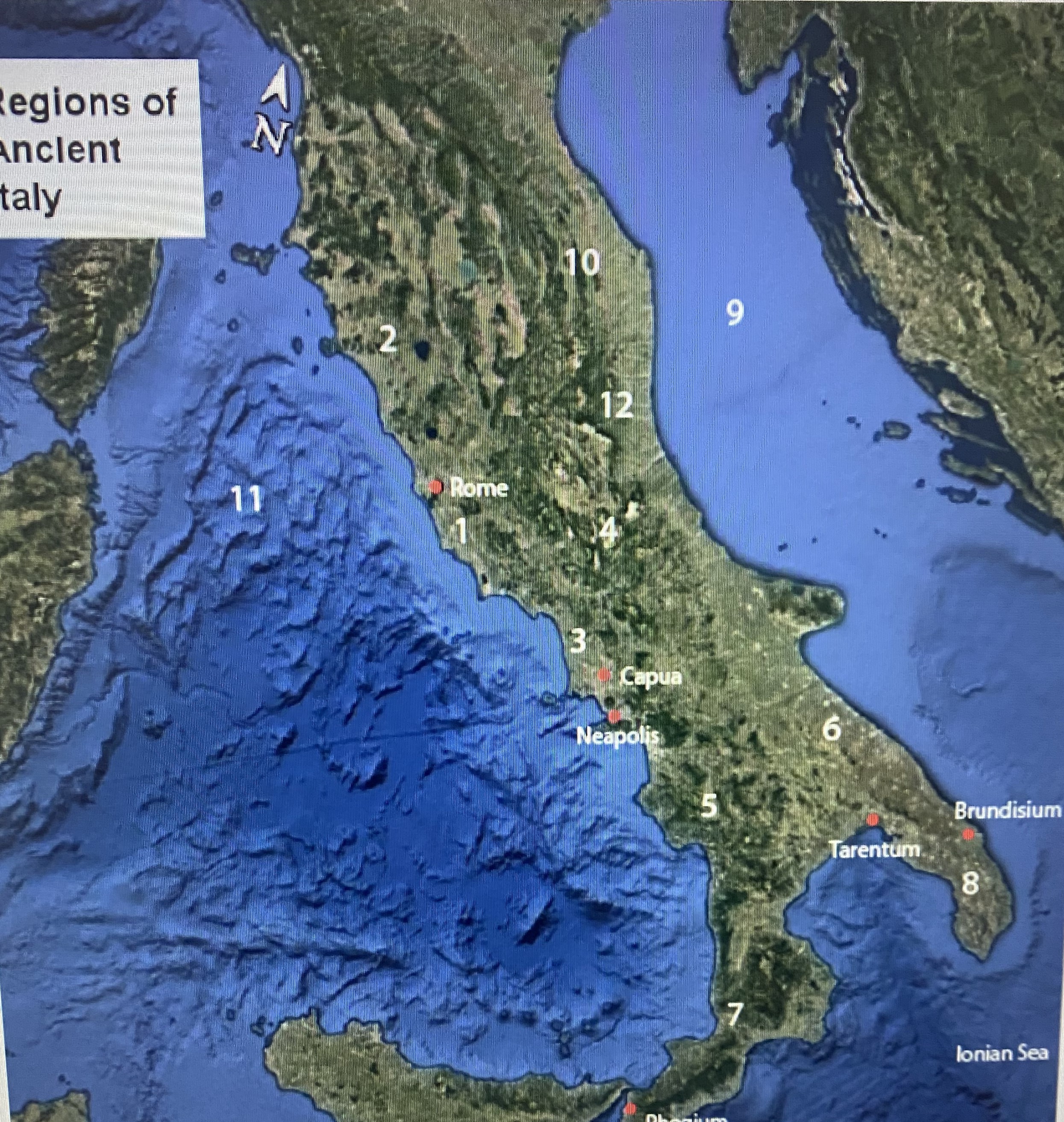
#8
Calabria
#9
Adriatic Sea
#10
Umbria
#11
Tynhenian sea
#12
Picenum
Aedile
Funded public works such as roads, organized festivals, and ran the public grain supply
Military Tribune
6 officers attached to a legion that served as military aides to generals of the Roman army
Tribune of Plebs
Was meant to protect the commoners from the nobles, could veto any law
Quaestor
Lowest office of the cursus honorum, served as aides to higher officials, and as quartermasters
Praetor
Served as judges in the law courts and commanded provinces
Consul
Ran the government, had imperium
Imperium
Power to raise armies, punish citizens, consult omens; held by consuls and praetors
Censor
Determined the social position of the Roman people and position in Senate, leased public lands
Dictator
Emergency office with absolute power, appointed by Consul or Senate
Master of the horse
Second in command to the dictator, appointed by the dictator
Interrex
Selected in the event of both consuls’ death while in office
Curiate Assembly
Patrician population divided by family clans; ratified elections of consuls and praetors
Centuriate Assembly
People divided into centuries by wealth; declared war; elected consuls, praetors, censors; passed laws
Tribal Assembly
people divided into tribes by residence; elected quaestors, curule aediles, and military tribunes; tried judicial cases
Plebian council
plebian population; elected tribunes of plebs & plebian aediles; passed laws
Augurs
Priests who interpret signs
Aquilifer
Standard bearer for a legion
Auspices
Natural phenomena thought to reveal signs from the gods
Century
group of approximately 90 soldiers; 2 to a maniple
Cohort
Group of approximately 400 soldiers; 10 to a legion
Legion
main unit of the Roman army; approximately 4000 to 6000 soldiers; 2 Roman legions and 2 auxiliary legions
Pontifex Maximus
Most important position in religion, chief high priest
Flamen Dialis
High priest of Jupiter
Talent
Weight of measurement for precious metals of 55-60 pounds
Patrician
Member of one of the descendants of the original Senators of Rome
Maniple
Unit of the army consisting of 2 legions; 3 to a cohort
Ovation
lesser triumph; general parades through city on horseback with his army
Triumph
highest ceremonial parade of Roman general leading army on a 4-horse chariot, only given to the emperor and his family
Corona Muralis
‘wall crown’ award for first soldier over an enemy wall
Auctoritas
Influence or prestige
Census
Assigned men to their social class and century in comitia centuriata and tribe in comitia tributa; determined membership in the Senate
Consul Suffectus
elected to serve out the term of a consul who dies in office (unless both die)
Curia
Senate’s meeting place; not a particular location
Cursus Honorum
‘path of the offices’; sequence of offices held by Roman politician; quaestor to praetor to consul
Fasti
Calendar or poem by Ovid, showing festivals and other events and magistrate
Imperator
victorious Roman leader; declared by soldiers; only available to princeps, also declared by soldiers proclaiming their leader emperor
Imperium Maius
emperor’s imperium, also sometimes granted to his successor, supersedes that of any other holder
Imperium pro consule/praetore
consular or praetorian imperium held by someone not in office
Legate
envoy or commissioner appointed by the princeps or army staff officer
Magistrate
State official
Pontifex
Member of a college of priests
Prefect
Roman officers in command of auxiliary troops and certain areas of the empire
Princeps
Unofficial title of emporer
Principate
term for the Roman Empire from Augustus to Diocletian
Privatus
a man not holding a magistracy
Prorogue
prolonging imperium of consul or praetor after end of term
Province
sphere in which a magistrate holds imperium
Senate
Advisory body made up of former consuls, praetors, and quaestors; determined domestic and foreign policy, province allocation
Senatus consultum
Decree of the senate
Tribunicia potestas
‘power of the tribune’, the power of tribunes exercised by the emperor and sometimes his successor
Parentalia
9 day festival in February celebrating deceased family members
Conubium
legal right to marry. Only marriages between citizens were legal. Members of senatorial class could not marry freed slaves
Affectio Maritalis
'marital affection'; desire to live together as husband and wife
Grammaticus
First stage teacher
Rhetor
Second stage teacher
First king of Rome
Romulus: Founded Rome and established the Senate
Second king of Rome
Numa Pompilius: Established the vestal virgins, set up the Roman calendar
Third king of Rome:
Tullus Hostilius: Military achievements, killed by lighting due to improper religious rites
Fourth king of Rome
Ancus Martius: Established port of Ostia, first Roman prison
Fifth king of Rome
Tarquinius Priscus: First Etruscan king, construction of first sewer system and race track
Sixth king of Rome
Servius Tullius: Constructed wall around Rome, established census
Seventh king of Rome
Tarquinius Superbus: Tyrannical ruler, sons’ rape of Lucretia led to overthrowing of monarchy
Lupercalia
Festival in honor of Pan and the wolf who raised Romulus and Remus, priests ran through crowds naked and whipped nearby women
Saturnalia
Festival in December where roles between slaves and masters were reversed
Lares
Spirits that protected the house and material items of the household
Penates
Spirits that watched over members of the family
Janus
God of gates, doorways, and time
Quirinus
God that Romulus becomes when he dies, may have been a Sabine war god
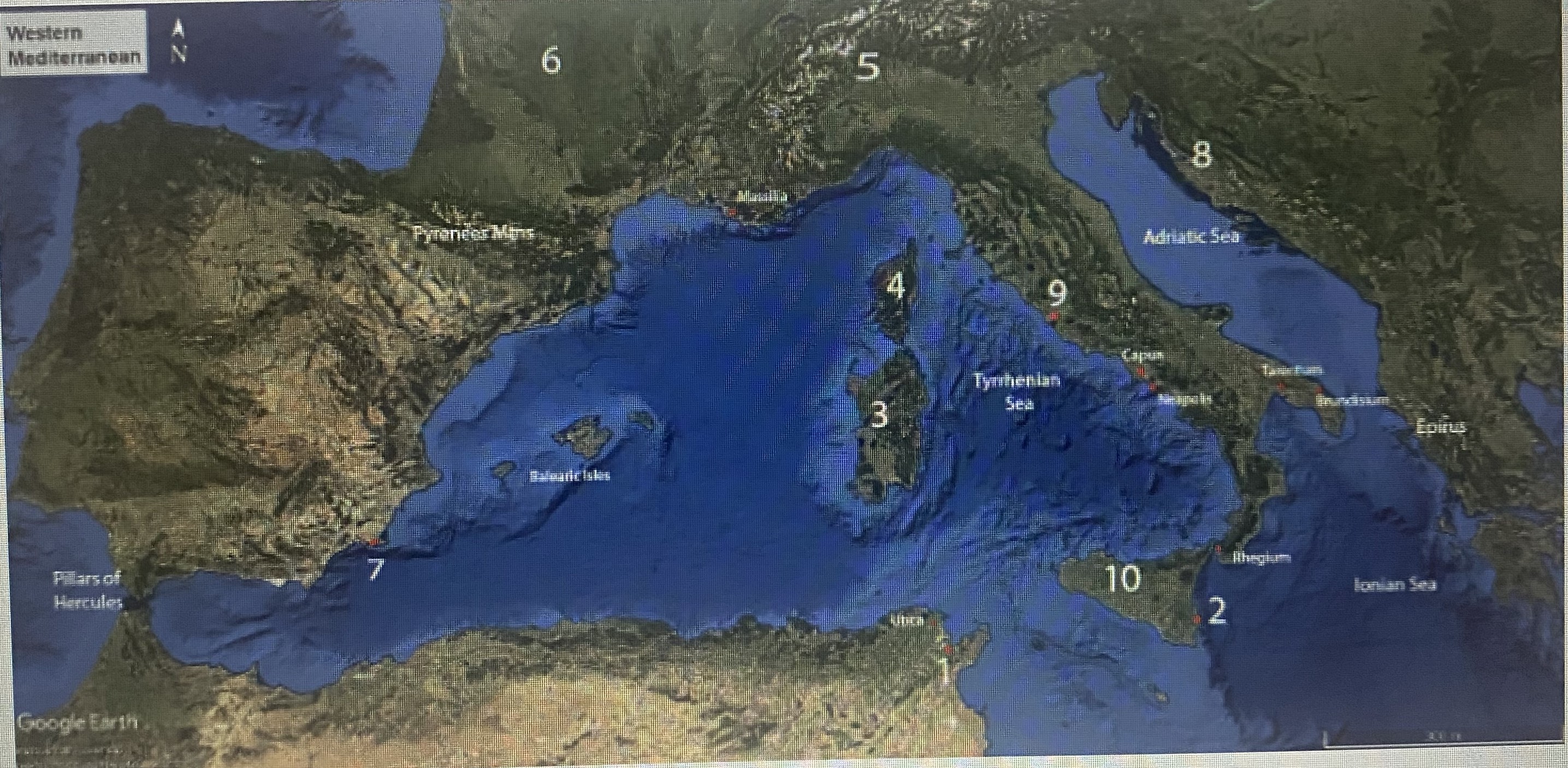
#2
Syracuse
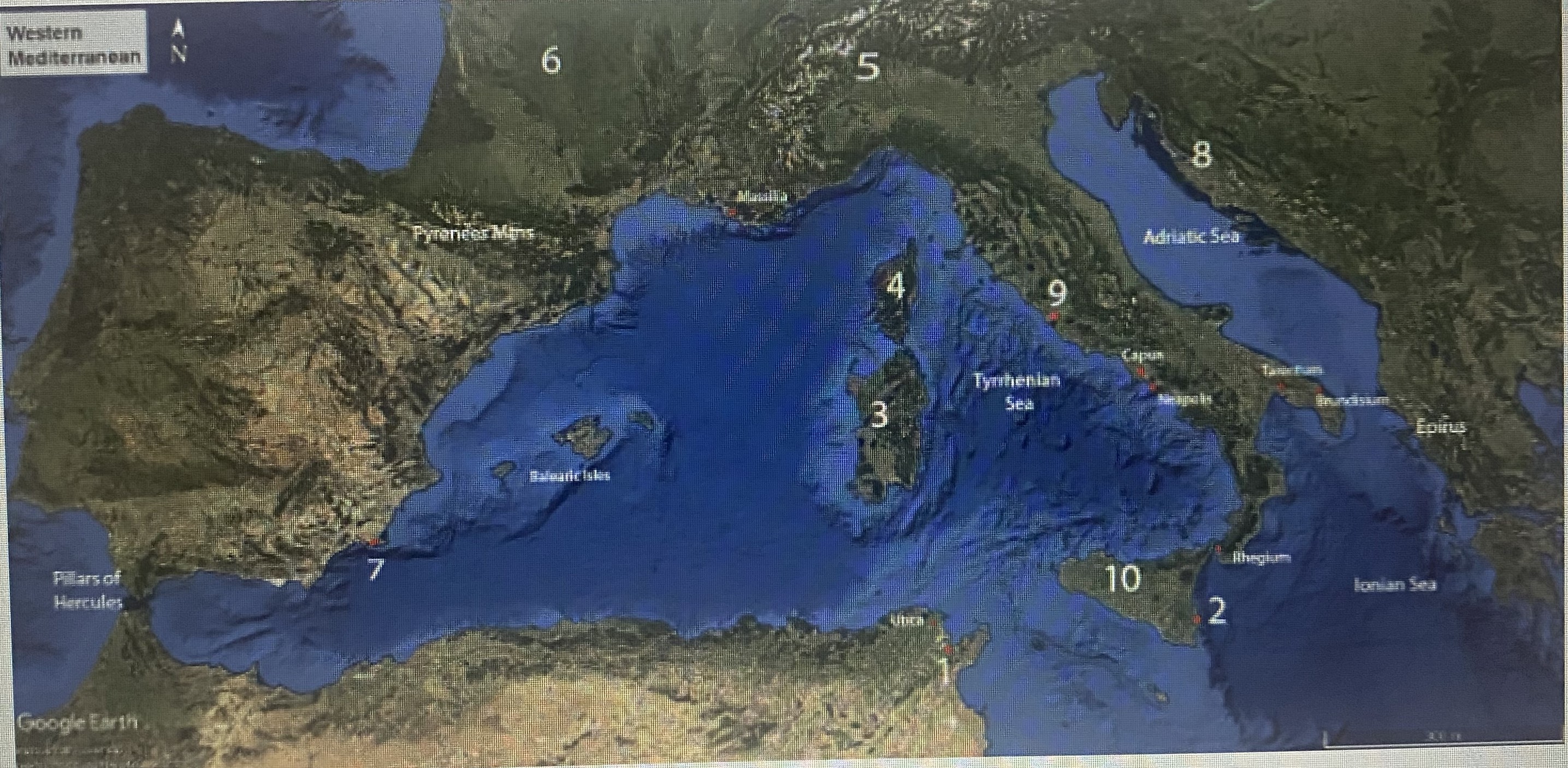
#3
Sardinia
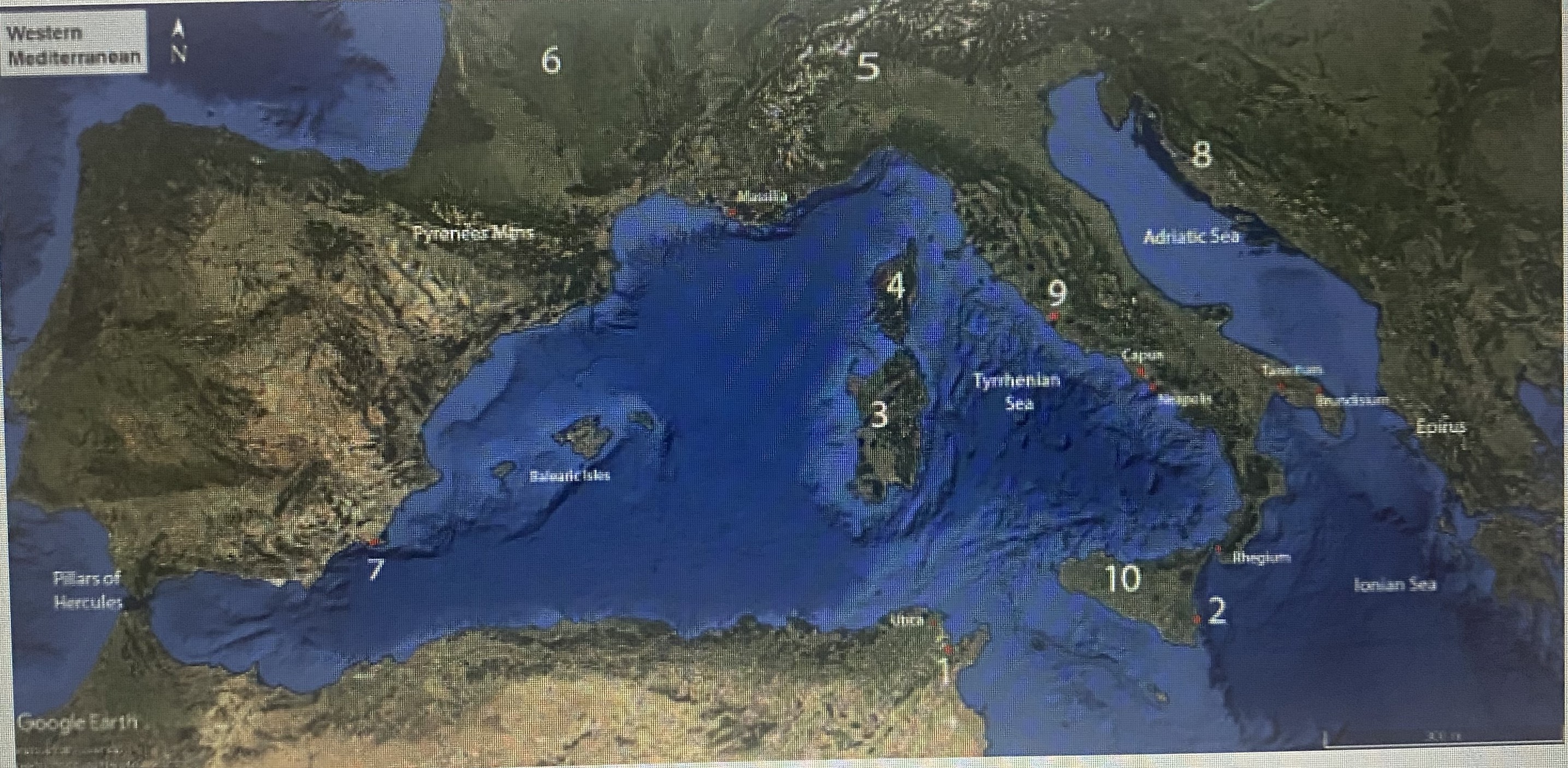
#4
Corsica
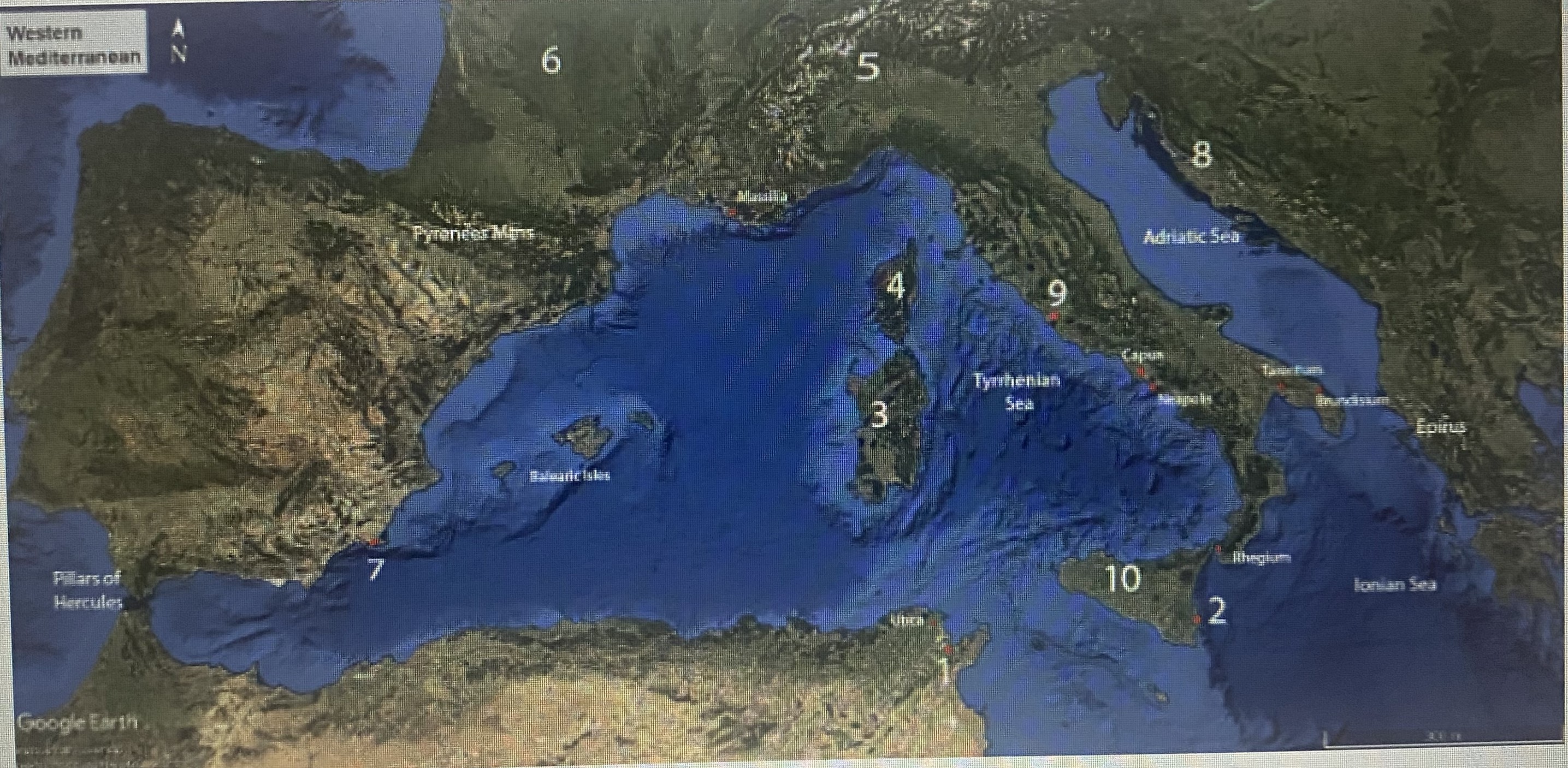
#10
Sicily
Tanaquil
Wife of 5th king of Rome, secured the throne for her son in law by shutting the palace down and summoning him
Sextus Tarquinius
Son of the last king of Rome, assaulted Lucretia who then caused the downfall of the Tarquinius family
Lucius Junius Brutus
Nephew and bodyguard of the last king, led a revolt against the king for his sons assault of Lucretia
Lars Porsena
Etruscan king of the city of Clusium, tried to invade Rome
Horatius Cocles
Was able to hold the Etruscans off long enough to defend the only bridge into Rome, long enough for the Romans to destroy it
Gaius Mucius Scaevola
Because the Etruscans couldn’t get into Rome they pillaged the surrounding countryside, he offered to go and kill Lars Porsena
Aequi
Italian tribe who frequently fought Rome, joined the Etruscans and the Volsci to attack Rome
Which Punic war was fought mostly on water?
First
Which battle ended the second Punic war?
Battle of Zama
Which battle ended the Antigonid dynasty?
Battle of Pydna
How many Punic wars did Carthage win?
None
Which battle did Hasdrubal die in?
Killed by Nero and Livius at the Battle of Metaurus, while bringing reinforcements to Hannibal
Who shadowed Hannibal around Italy?
Quintus Fabius Maximus
Who led the Roman attack on Syracuse during the second Punic war, known as the sword of Rome?
M. Claudius Marcellus
Battle of Trasimene
217 BCE battle in which Hannibal caught a Roman army, led by G. Flaminius, while marching along a lake and annihilated the Roman army
Battle of Zama
202 BCE battle that saw P. Cornelius Scipio defeat Hannibal ending the 2nd Punic War