RAD 230: Bontrager Ch 11 Workbook - Skull
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Which one of the following bones is not part of the floor of the cranium...
A. Temporal..
B. Ethmoid...
C. Occipital...
D. Sphenoid
Occipital
Which aspect of the frontal bone is thin-walled and forms the forehead
squamous
What four cranial bones articulate with the frontal bone
right parietal, left parietal, sphenoid, and ethmoid
Which structures are found at the widest aspect of the skull
parietal tubercles of two parietal bones
What is the name of a prominent landmark (or bump) found on the external surface of the occipital bone
external occipital protuberance (inion)
List the number of individual bones that articulate with the following cranial bones...
Parietal bone...
Occipital bone...
Temporal bone..
Sphenoid...and
Ethmoid
5 for parietal..
6 for occipital..
3 for temporal..
7 for sphenoid..and
2 for ethmoid
What is the thickest and densest structure in the cranium
petrous portion
True or False: The hypophysis is another term for the pituitary gland
True, hypophysis cerebri
True or False: The sphenoid bone articulates with all the other cranial bones
true
The shallow depression just posterior to the base of the dorsum sellae and anterior to the foramen magnum is the
clivus
Which small section of the bone is located superior to the cribiform plate
crista galli
What is the formal term for the left sphenoid fontanel in the adult
left pterion
What is the name of the cranial suture formed by the inferior junction of the parietals to the temporal bones
squamosal suture
What are the two terms for the small, irregular bones found in the adult skull sutures
sutral, or wormian
These following bones are within what structure....
pterygoid hamulus, anterior clinoid processes, foramen ovale, and sella turcica
sphenoid
These following bones are within what structure....
glabella and supercilliary arch
frontal
These following bones are within what structure....
perpendicular plate, superior nasal conchae, and cribiform plate
ethmoid
These following bones are within what structure....
foramen magnum, lateral condylar portions, and inion
occipital
These following bones are within what structure....
zygomatic proces, EAM, and petrous ridge
temporal
Which one of the following skull classifications applies to a skull with an angle of 54° between the midsagittal plane and the long axis of the pars petrous
brachycephalic
Which of the preceding classifications is considered the average-shaped skull
mesocephalic
What landmark corresponds to the highest level of the petrous ridge
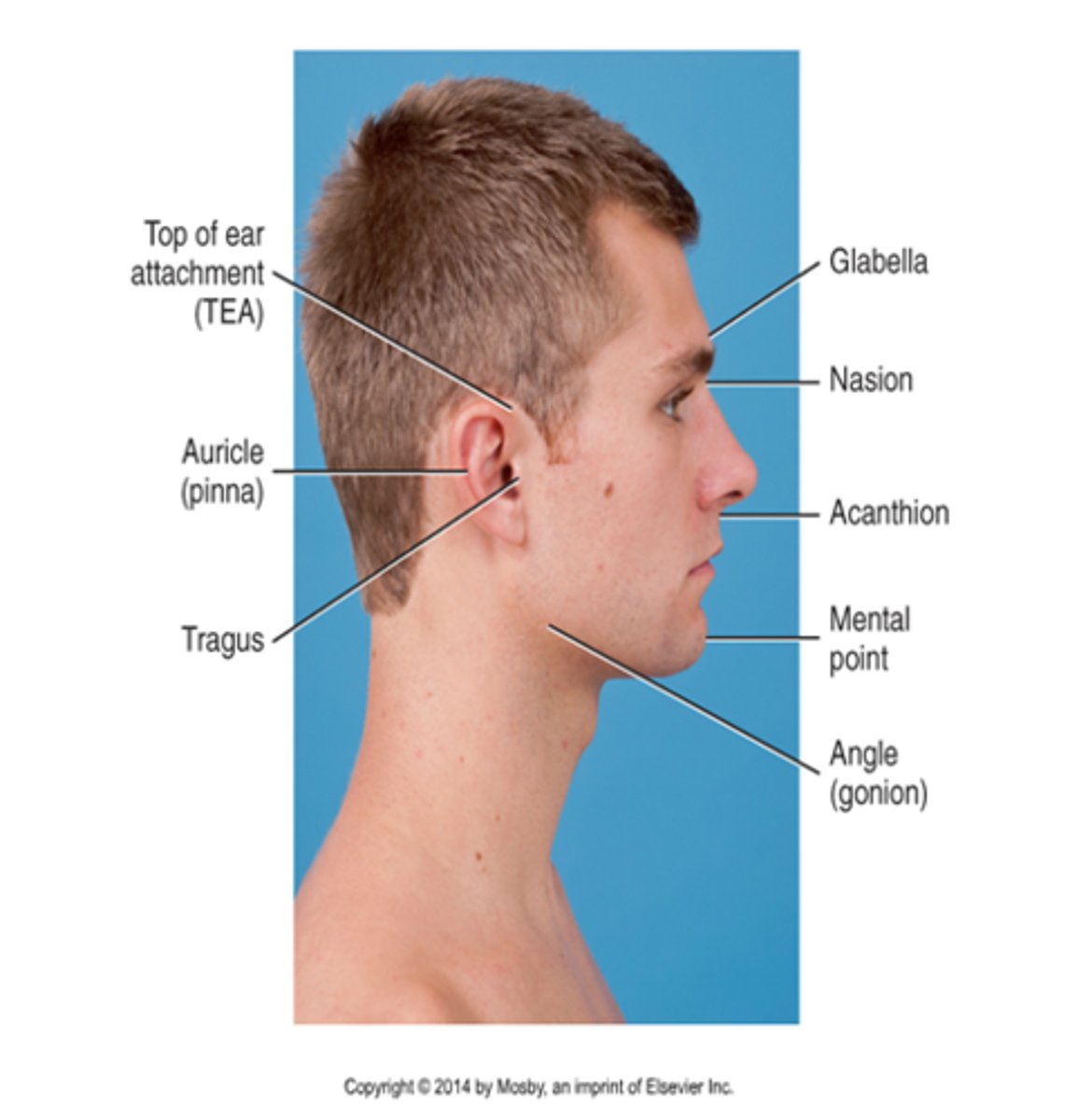
TEA
Reid's base line is an older term for
IOML
How much of a difference in degrees is there between the OML and IOML
7 to 8 degree difference
Which one of the following positioning errors frequently results in a repeat exposure of a cranial position...
A. Rotation..
B. Incorrect CR placement..
C. Slight flexion..
D. Slight extension
rotation
Condition that begins with bony destruction followed by bony repair
Paget's disease
Tangential view may be helpful to determine extent or degree of this fracture
depressed fracture
What clinical indication may require a decrease in manual exposure factors
multiple myeloma
Which aspect of the temporal bone is considered to be the thinnest
squamous portion
Which aspect of the temporal bone contains the organs of hearing and balance
petrous pyramid or pars petrous
Which two projections of the cranium project the dorsum sellae within the foramen magnum
AP axial Towne and PA axial Haas
How much central ray angle is required for the AP axial projection Towne method for skill with the IOML perpendicular to the image receptor.....
What is the central ray angle for this same projection with a perpendicular OML
37 degree caudad...
30 degree caudad
Where is the central ray centered for a lateral projection of the cranium
2 inches superior to EAM
To prevent tilting of the skull for the lateral projection of the cranium, the _________ line is placed perpendicular to the IR
interpupillary
Where should the petrous ridges be located (on the image) for a well-positioned, 25 degree caudad PA axial Haas projection
superior to mastoid processes and symmetrical
Where is the central ray centered for an SMV projection of the skull
1 1/2 inch inferior to mandibular symphysis
Which positioning line is parallel to the IR for the SMV projection of the skull
IOML
SITUATION: A radiograph of an AP axial projection for the cranium reveals that the dorsum sellae is projected superior to the foramen magnum. What must be modified during the repeat exposure to correct this problem
increase CR angle approximately 7 degree caudad
SITUATION: A radiograph of a lateral projection of the cranium reveals that the greater wings of sphenoid are not superimposed. What type of positioning error is present on this radiograph
rotation
SITUATION: A radiograph of a 15 degree caudad PA axial projection of the cranium reveals that the petrous ridge are at the level of the supraorbital margin. Without changing the central ray angle, how must the head position be modified during the repeat exposure to produce a more acceptable image
increase extension of the skull to place the OML perpendicular to the IR (will project ridges into lower 1/3 of orbits)
SITUATION: A patient with a possible basilar skull fracture enters the emergency room. The physician wants a projection to demonstrate a possible sphenoid sinus effusion. Which projection of the cranium is best for this situation
Horizontal beam (dorsal decubitus) lateral skull projection
SITUATION: The same patient with the possible basilar skull fracture requires a frontal projection of the skull. The physician wants the projection to demonstrate the frontal bone and place the petrous ridges in the lower 1/3 of the orbits, but it has not been determined whether the patient's cervical spine has been fractured, so the patient cannot be moved from a supine position. What should the technologist do
perform the AP projection with a 15 degree cephalad CR angle to the OML
SITUATION: A patient comes to the radiology department for a skull series. Because of the size of the patient's shoulders, he is unable to flex his neck sufficiently to place the OML perpendicular to the IR for the AP axial projection. His head cannot be raised because of possible cervical trauma. What other options does the technologist have to obtain an acceptable AP axial projection
use IOML instead and increase CR angle to an additional 7 degree caudad
SITUATION: A radiograph of an AP axial Towne projection for cranium reveals that the posterior arch of C1 and dorsum sellae are superimposed. Both are projected into the foramen magnum. What modification is needed to correct this error present on the initial radiograph
decrease CR angle based on the skull line used, OML 30 degree; IOML 37 degree
SITUATION: A radiograph of a lateral skull demonstrates that the orbital plates (roof) of the frontal bone are not superimposed. What is the positioning error present on this radiograph
tilt of the skull
SITUATION: A radiograph of an AP axial Townes for cranium reveals that the left petrous portion of the temporal bone is wider than the right. What is the specific positioning error present on this radiograph
rotation to the right
SITUATION: A radiograph of a SMV projection of the cranium demonstrates that mandibular condyles are projected into the petrous portion (pyramids) of the temporal bone. How must the position be altered during the repeat exposure to correct this error
extend the skull further to place the IOML parallel to the IR
True or False: In general, all the paranasal sinuses are fully developed by the age of 6 or 7 years
False, fully developed in late teens (ethmoid develops last)
The sphenoid sinus lies directly inferior to the
sella turcica
Which single projection of the facial bones best demonstrates any possible air-fluid levels in the sinuses if the patient cannot stand or sit erect
horizontal beam lateral projection
Shape description for the classification of the skull:
Mesocephalic
Width between 75% & 80% of length
Shape description for the classification of the skull:
Brachycephalic
Width ≥80% of length
Shape description for the classification of the skull:
Dolichocephalic
Width <75% of length
CR angles & degree of rotation stated for basic skull positions are based on the ________ (average) skull, which has an approximate angle of _______ between the midsagittal plane & the long axis of the petrous bone
Mesocephalic, 47 degrees
The long, narrow-shaped skull has an angle of approximately _______ degrees between the midsagittal plane & the long axis of the petrous bone
+/- 40
True/False: 2 older terms for the orbitomeatal line (OML) are Reid's base line & the anthropologic base line
False (There are other terms for the infraorbitomeatal line)
There is a _____-degree difference between the orbitomeatal & infraorbitomeatal lines, & _____ degrees between the orbitomeatal & glabellomeatal lines
7-8 degrees for both
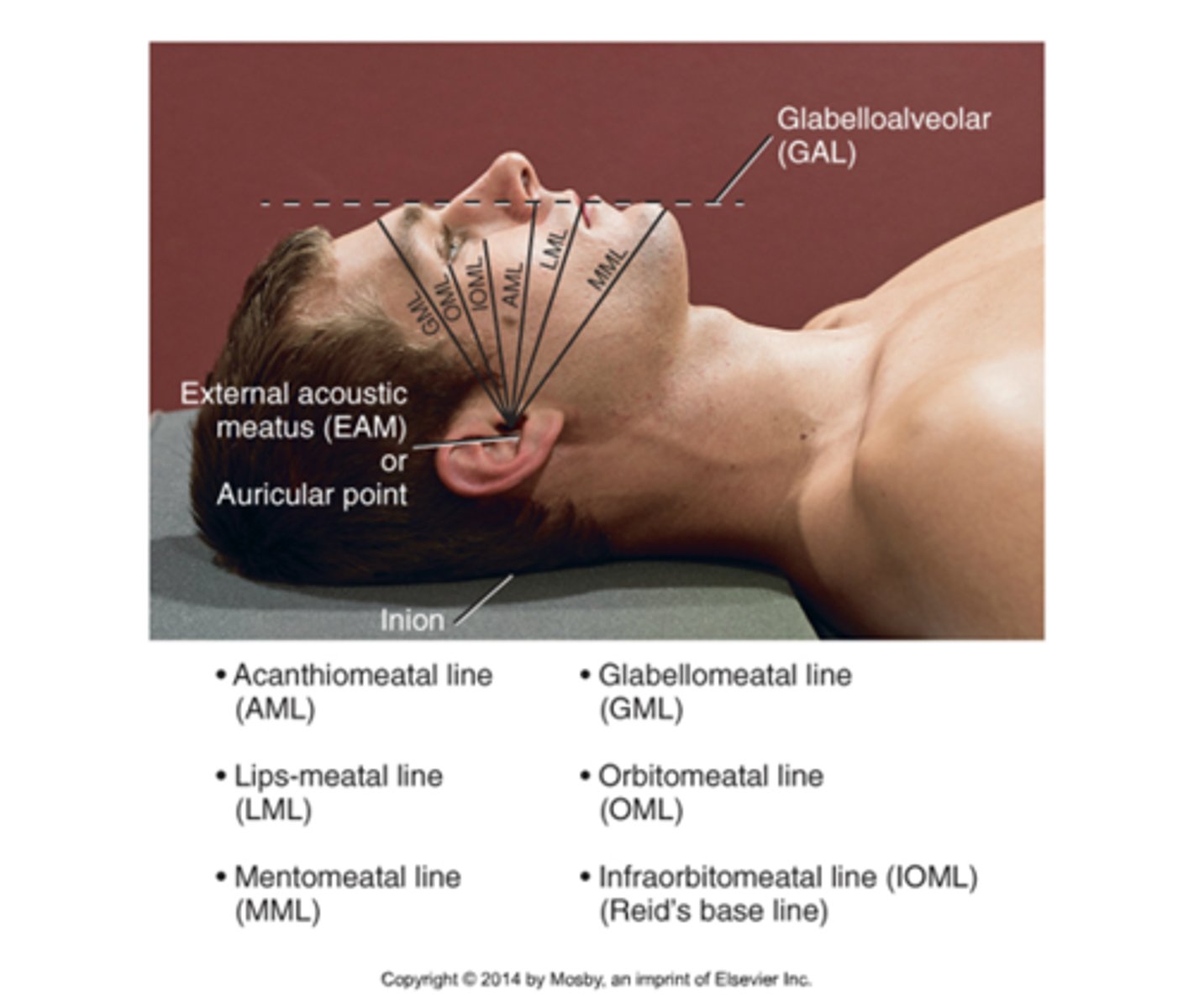
A line between the infraorbital margin and EAM
IOML
Corresponds to the highest "nuchal" line of the occipital bone
Inion
A line between the glabella & alveolar process of the maxilla
Glabelloalveolar line
A line between the mental point and EAM
mentomeatal line
Located at the junction of the 2 nasal bones & the frontal bone
Nasion
Corresponds to the highest level of the facial bone mass
Supraorbital groove
A line between the midlateral orbital margin and the EAM
OML
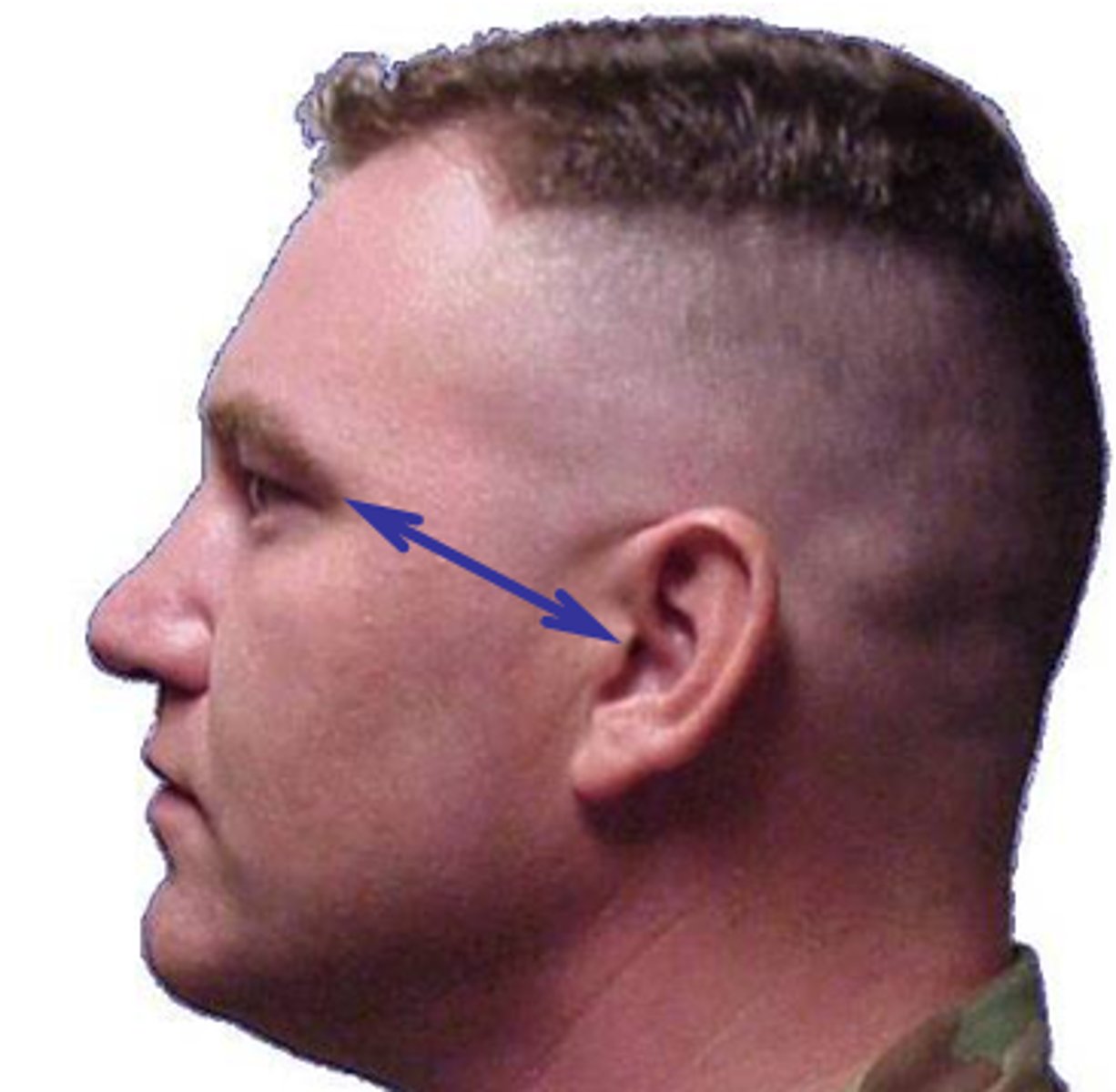
The center point of the EAM
Auricular point
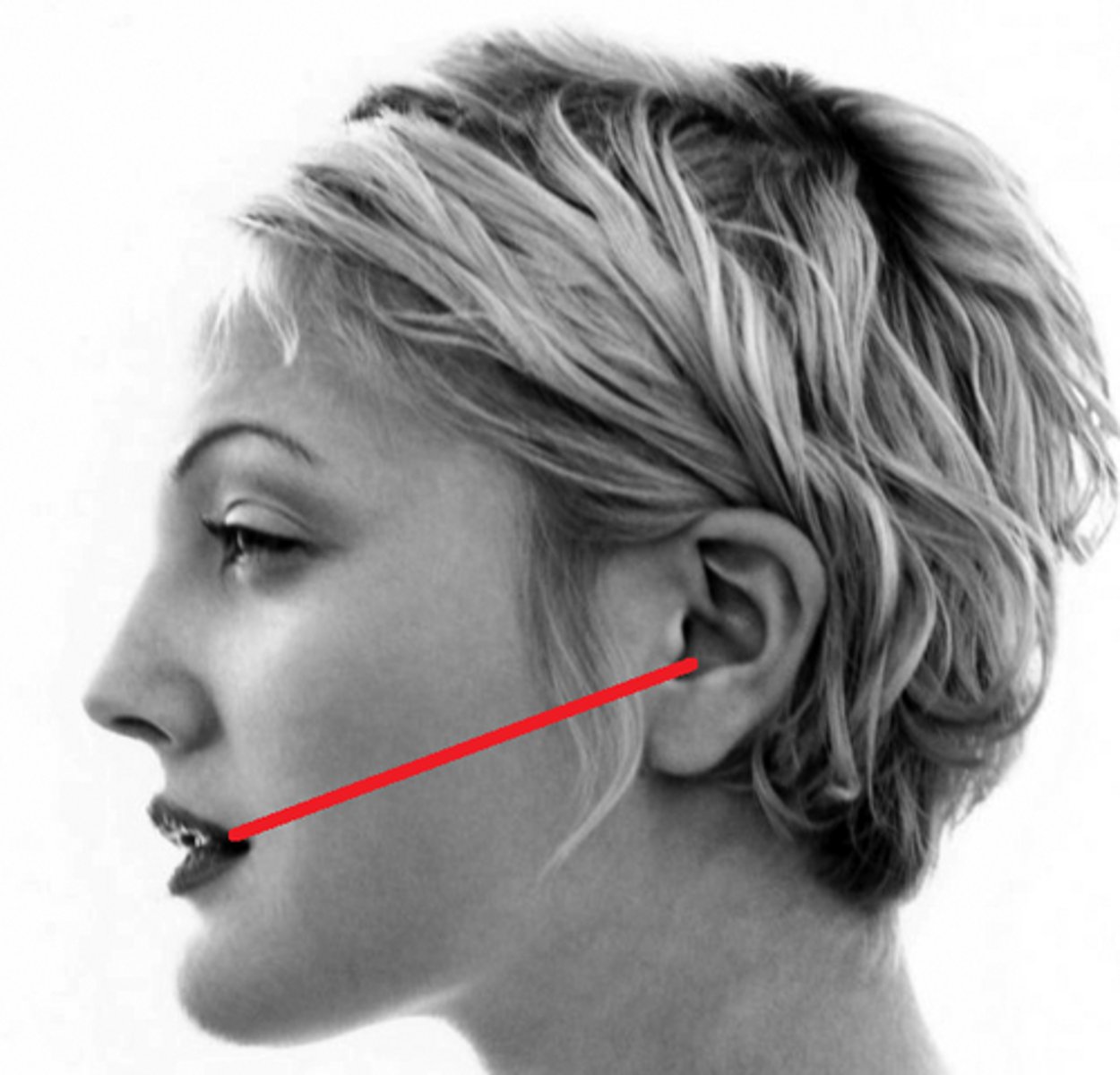
A positioning line that is primarily used for the modified Waters projection
Lips-meatal line
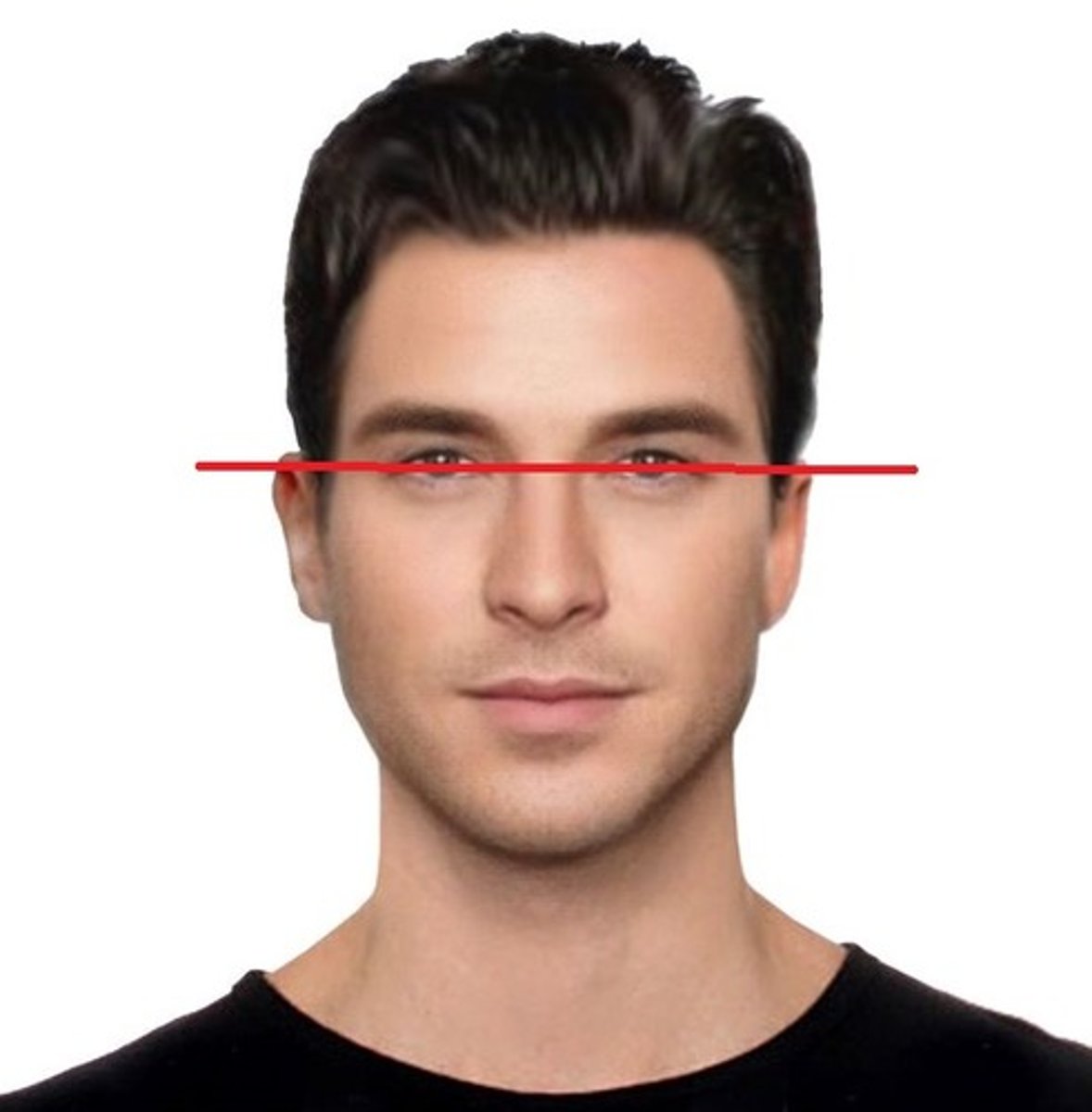
A line used in positioning to ensure that the skull is in a true lateral position?
Interpupillary line or IPL
Corresponds to the level of the petrous ridge
TEA (top of ear attachment)
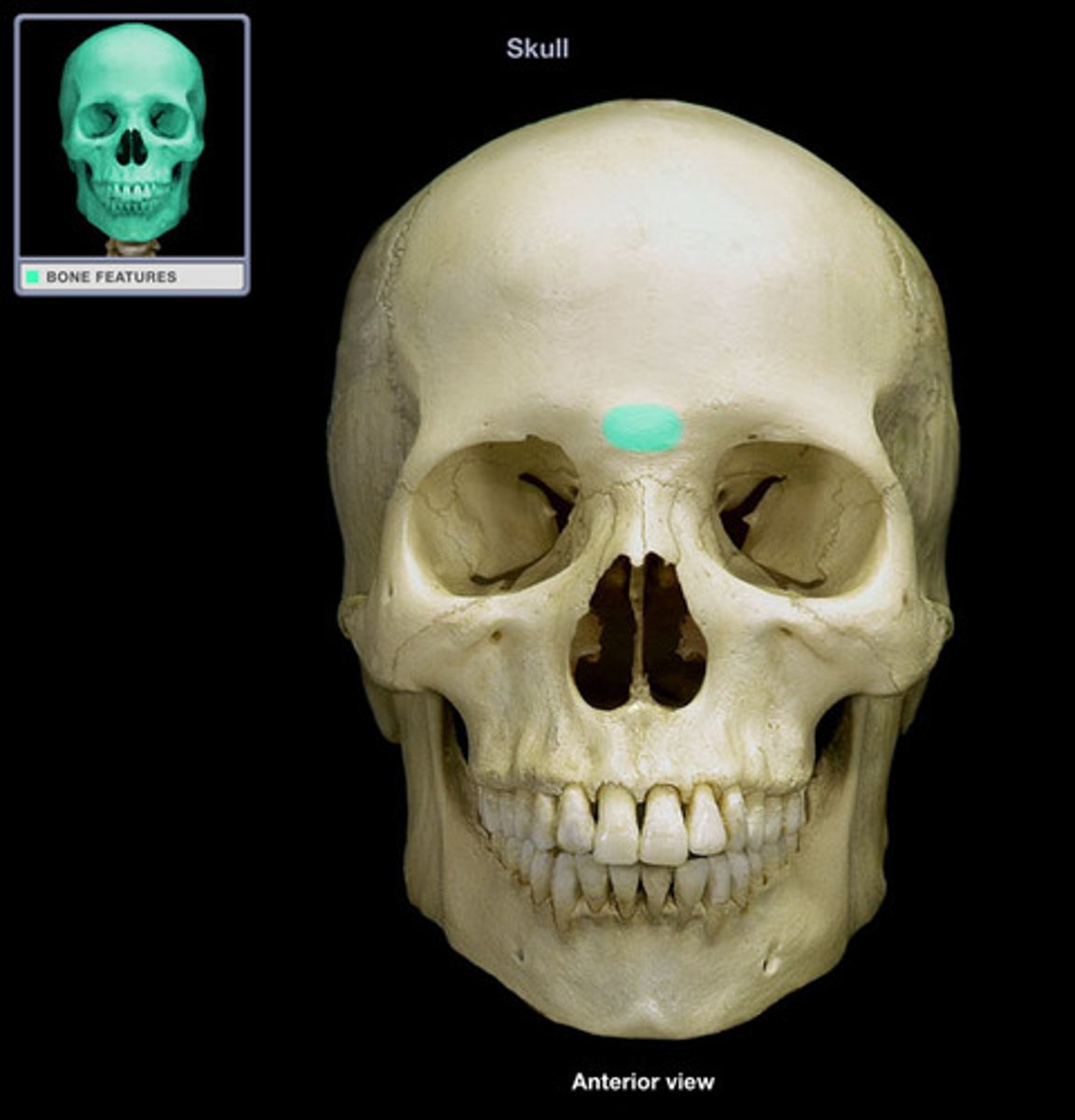
A smooth, slightly depressed area between the eyebrows
Glabella
What is the average kV range for digital skull imaging?
80-90
List the 5 common errors made during skull radiography
A. Rotation
B. Tilt
C. Excessive neck flexion
D. Excessive neck extension
E. Incorrect CR angulation
Of the 5 most common error, which 2 are most common?
A. Rotation
B. Tilt
Bilateral horizontal fractures of the maxillae describe a ________ fracture
A. Le Fort
B. Blowout
C. Tripod
D. Contrecoup
A. Le Fort
Which of the following imaging modalities is the most common neuroimaging procedure performed for the cranium?
A. CT
B. Ultrasound
C. MRI
D. Nuclear medicine
A. CT
Which of the following imaging modalities is most commonly performed to evaluate patients for Alzheimer disease?
A. CT
B. Ultrasound
C. MRI
D. Nuclear medicine
D. Nuclear medicine
Fracture that may produce an air-fluid level in the sphenoid sinus
Basal skull fracture

Clinical indication described:
Also called a "ping-pong" fracture
Depressed skull fracture
A tumor that may produce erosion of the sella turcica
Pituitary adenoma
AKA osteitis deformas
Paget's disease
Which of the following clinical indications may require an increase in manual exposure factors?
A. Advanced Paget's disease
B. Metastatic neoplasm
C. Multiple myeloma
D. Basal skull fracture
A. Advanced Paget's disease
Which cranial bone is best demonstrated with an AP axial (Towne method) projection of the skull?
Occipital
When using a 30 degree caudad angle for the AP axial (Towne method) projection of the skull, which positioning line should be perpendicular to the image receptor?
A. OML
B. IOML
C. GAL
D. AML
A. OML
A properly positioned AP axial (Towne method) projection should place the dorsum sellae into the middle aspect of the:
A. Orbits
B. Clivus
C. Foramen magnum
D. Anterior arch of C1
C. Foramen magnum
A lack of symmetry of the petrous ridges indicates which of the following problems with a radiograph of an AP axial projection?
A. Tilt
B. CR angle
C. Flexion or extension
D. Rotation
D. Rotation
If the patient cannot flex the head adequately for the AP axial (Towne method) projection, the technologist could place the ________ perpendicular to the IR & angle the CR _______ degrees caudad
IOML, 37
What evidence on a an AP axial (Towne method) radiograph indicates whether the correct CR angle & correct flexion were used?
Dorsum sellae & posterior clinoids should be projected into the foramen magnum
What CR angle should be used for the PA axial (Haas method) projection of the cranium?
25 degrees cephalad
Where is the CR centered for a lateral projection of the skull?
2 inches above the EAM
Which specific positioning error is present if the mandibular rami are not superimposed on a lateral skull radiograph?
A. Tilt
B. Rotation
C. Overflexion
D. Incorrect CR angle
B. Rotation
Where will the petrous ridges be projected with a 15-degree PA axial (Caldwell) projection of the cranium?
In the lower one-third of the orbits
Which positioning error is present if the petrous ridges are projected higher in the orbits than expected for a 15-degree PA axial projection?
Excessive flexion or insufficient CR angle
Which projection of the cranium produces an image of the frontal bone with little or no distortion?
0 degree PA
For a patient with possible trauma, what must be determined before performing the SMV projection of the skull?
Rule out any possible cervical fractures or subluxation
What positioning error has been committed if the EAMs are not superimposed with one of them more superior than the other on a lateral projection of the cranium?
Tilt of the skull
Which skull positioning line is placed parallel to the plane of the IR for the SMV projection?
A. OML
B. IOML
C. AML
D. GML
B. IOML
Which of the following projections best demonstrates the sella turcica in profile?
A. AP axial
B. SMV
C. 15-degree PA axial
D. Lateral
D. Lateral
Which of the following projections best demonstrates the foramen rotundum?
A. SMV
B. 25 to 30-degree AP axial
C. 25 to 30-degree PA axial
D. Lateral
C. 25 to 30 degree PA axial
Which of the following projections best demonstrates the clivus in profile?
A. AP axial
B. 15-degree PA
C. Lateral
D. SMV
C. Lateral
Where does the CR exit for a PA axial (Haas method) projection of the skull?
A. 1.5 inches superior to the nasion
B. 3/4 inch anterior to the EAM
C. 2.5 inches above the glabella
D. Level of nasion
A. 1.5 inches superior to the nasion
A radiograph of an AP axial (Towne method) projection of the cranium shows that the right petrous ridge is wider than the left side. Which specific positioning error is present on this radiograph?
Rotation of skull present; rotation of patient's face toward left