Physics - Space, Time and Motion
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Define velocity and acceleration, and how to calculate them (graphically or numerically)?
Velocity is the rate of change of position over time, while acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time. Velocity - dt/ds (or gradient of a displacement/time graph - instantaneous)
Acceleration - dv/dt (or gradient of a velocity/time graph - instantaneous)
Explain the difference between instantaneous and average values of velocity, speed, and acceleration.
Instantaneous values refer to measurements taken at a specific moment, while average values are calculated over a period of time.
E.g. Average Velocity = (u+v)/2
What are the equations of motion for solving problems with uniformly accelerated motion?
s=ut+1/2at²
𝑣=u+at
𝑠=(u+v)t/2
𝑣²=u²+2as
What is the trajectory of projectile motion in the absence of fluid resistance and how does it affect it?
The trajectory is parabolic without fluid resistance. Fluid resistance will decrease tht time of flight, velocity and range of a projectile.
What are conditions to keep in mind while solving projectile problems?
At maximum height Vv = 0
If time taken to reach maxima is t the whole flight will take 2t seconds.
Velocity in the horizontal direction stays constant.
Acceleration stays constant in the vertical direction (g)
Calculate vertical and horizontal components seperately.
What is the optimal angle for firing a projectile in terms of range?
45 degrees
How to seperate horizontal and vertical components?
Horizontal - cosx
Vertical - sinx
What happens at termial velocity?
Acceleration = 0 as Net force = 0
Newton’s First Law
An object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force (Law of Inertia). - Questions asked around translational equilibrium.
Newton’s Second Law
The force acting on an object is directly proportional to its acceleration (provided mass stays constant)
(F = ma)
Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. - Identification of force pairs.
Equation for static friction
Ff ≤ μsFn
FN - Normal reaction force
Equation for dynamic friction
Ff = μdFn
where
FN - Normal reaction force
Hooke’s Law
The extension of a material is directly proportional to the applied load. Fh = -kx
(Gradient of a force-extension gives you the spring constant)
Stoke’s Law
Viscous Drag Force - The frictional force between a spherical object and a fluid which opposed its motion.
Fd = 6πηrv where;
eta - fluid viscosity (PaS)
r - radius
v- velocity (ms^-1)
Buoyancy definition and formula
Upthrust force is experienced by a body partially or fully immersed in a fluid.
Fb=ρVg where;
V - Volume of fluid displaced (m³)
g - gravitational field strength
ρ - density of fluid
Density volume mass formula
Density = Mass / volume
What forces would be acting on a spherical object falling at terminal velocity in a fluid?
Weight = viscous drag force + upthrust/buoyancy
Describe linear momentum (p) and impulse (J) + equations + relevant conditions.
p=mv - Stays constant in a system until an external force is applied.
J (Δp) = FΔt where; F- average resultant force
or (mv-mu)
Only applied when F is constant - allows for changing mass
Differentiate between elastic and non-elastic collisions and explosions in terms of energy.
Elastic/explosions - Momentum and K.E. conserved
Non-elastic - Momentum conserved, K.E. not conserved (generally when object stick together after collision)
Explosions - generally to do with recoil
What is centripetal acceleration and how is it directed?
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration experienced by a body moving at a constant speed along a circular path. It is directed radially towards the center of the circle.
What is angular velocity and how do you calculate it?
The rate of change in angular displacement with respect to time
Write the formula for centripetal acceleration in terms of linear speed (v) and radius (r).
a=v²/r
Express centripetal acceleration using angular velocity (ω) and radius (r).
𝑎=𝜔²r
How can centripetal acceleration be expressed using the period (T) of the motion?
4π²r/T²
What causes circular motion?
Circular motion is caused by a centripetal force acting perpendicular to the velocity of the moving body.
How does a centripetal force affect a body moving along a circular path?
A centripetal force causes the body to change direction continuously, meaning the velocity is constantly changing, even if the magnitude of its velocity remains constant therefore there is an acceleration (centripetal).
angular velocity (ω) and its relationship to linear speed (v).
𝑣=ωr
Linear speed
2πr/T
Centripetal force
mv²/r
Tension at the top of a circle
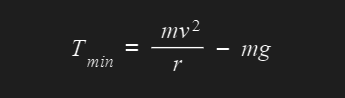
Tension at the bottom of a circle
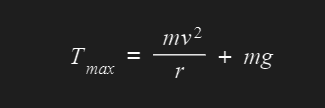
What is the principle of the conservation of energy
The principle of the conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred or transformed from one form to another.
Write the formula for work done (W) by a constant force (F) along the line of displacement (s) with angle θ.
W=Fscosθ
Define mechanical energy.
Mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, and elastic potential energy.
How is work related to energy transformation in a system where mechanical energy is conserved?
When mechanical energy is conserved, work is the amount of energy transformed between different forms of mechanical energy in a system.
Write the formula for the kinetic energy (Ek) of translational motion.
Ek=1/2mv² or p²/2m
What happens to the total mechanical energy of a system in the absence of frictional and resistive forces?
In the absence of frictional and resistive forces, the total mechanical energy of a system is conserved.
Define power (P) and write the formula relating it to work done.
ΔtΔW
What is energy density?
Energy per unit volume of a fuel (J/m³)
What is moment and what is its formula
A moment is the turning effect of a force around a particular point
Moment (N m) = Force (N) × perpendicular distance from the pivot (m)
Or Fdcosθ if it is not perpendicular - Theta (angle between perpendicular and r)
What are couples
A couple is a pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces that act to produce rotation only
A couple consists of a pair of forces that are:
Equal in magnitude
Opposite in direction
Perpendicular to the distance between them
Moment = F(of one couple)*distance between them
Write the formula for the torque (τ) of a force (F) about an axis.
Frsinθ where;
θ = angle between the force and the axis of rotation
What is the condition for rotational equilibrium in terms of torque?
Bodies in rotational equilibrium have a resultant torque of zero.
What happens to an extended, rigid body when an unbalanced torque is applied?
An unbalanced torque applied to an extended, rigid body will cause angular acceleration.
What are the three quantities used to describe the rotation of a body?
Angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration.
List the equations of motion for uniform angular acceleration
Δθ=(ωf+ωi)t
ωf = ωi + αt
Δθ = ωit + 1/2 αt²
ωf²= ωi² + 2αΔθ
Define Moment of inertia and its formula
The resistance to a change of rotational motion, depending on the distribution of mass around a chosen axis of rotation
I = Σmr² - of a non-point mass as it is a sum of all the points in the arrangement.
Derive and show Newton’s 2nd law of rotation
τ = Iα where τ is the average torque
Formula for angular momentum (L) and its conservation conditions.
L = Iω
angular momentum remains constant unless the body is acted upon by a resultant torque
What does an angular impulse (ΔL) represent and write its formula?
An angular impulse represents the change in angular momentum.
ΔL = τΔt = Δ(Iω)
Kinetic energy of rotational motion
1/2 Iω² = L²/ 2I