Temporal & Infratemporal Regions (4/15)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
the infratemporal fossa (ITF) is a deep facial region that contains how many muscles of mastication?
2 out of 4
what more medial space does the ITF communicate with?
pterygopalatine fossa
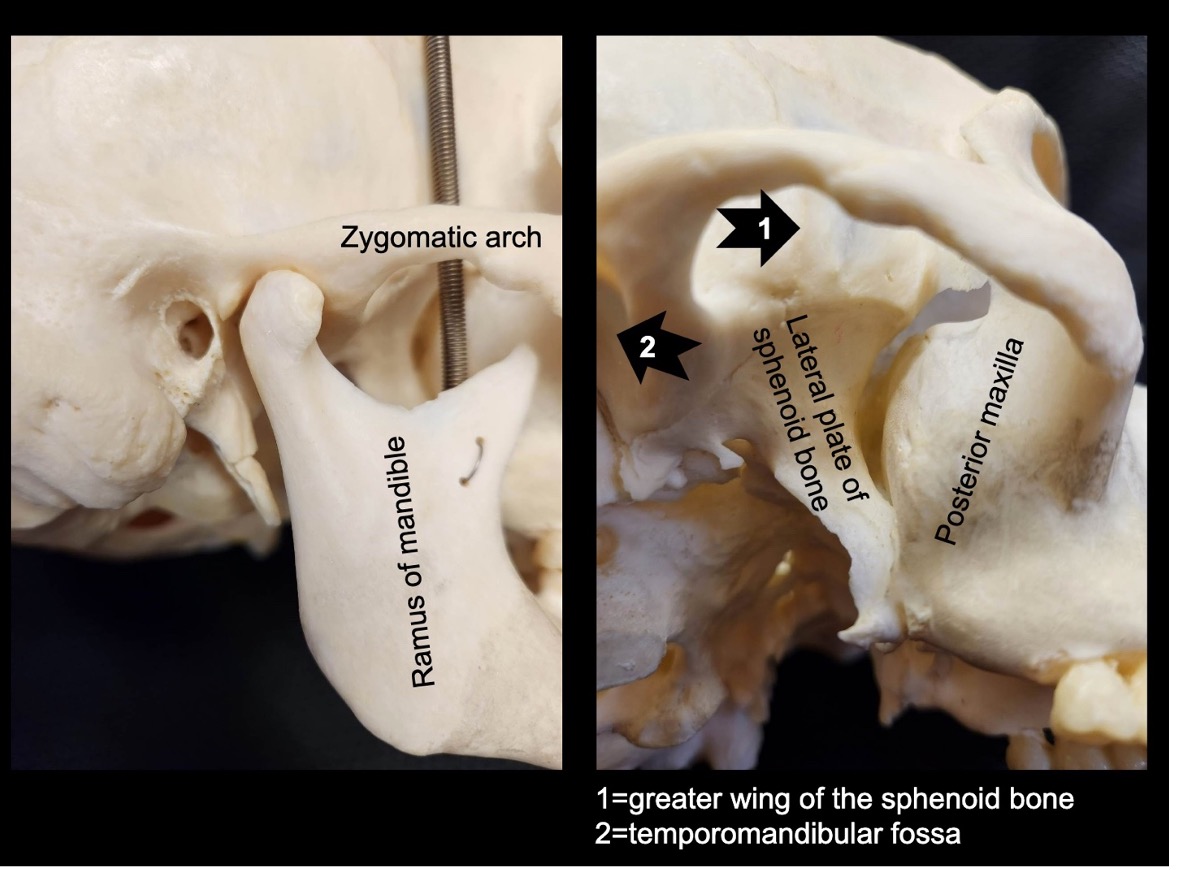
what is the lateral boundary of the ITF?
ramus of mandible
zygomatic arch
what is the medial boundary of the ITF?
lateral pterygoid plate
what is the anterior boundary of the ITF?
posterior aspect of maxilla
what is the posterior boundary of the ITF?
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
what is the superior boundary of the ITF?
greater wing of sphenoid
(not a Q) ITF
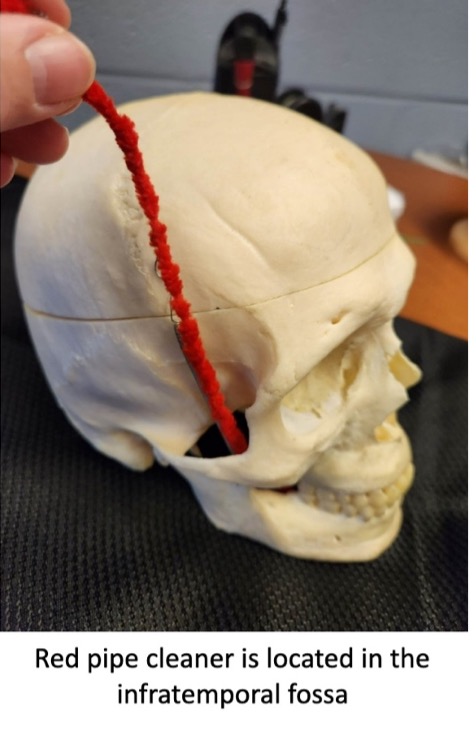
(not a Q) boundaries of ITF
*mandible removed in this image
*note the external auditory meatus (hole posterior to ramus of mandible)
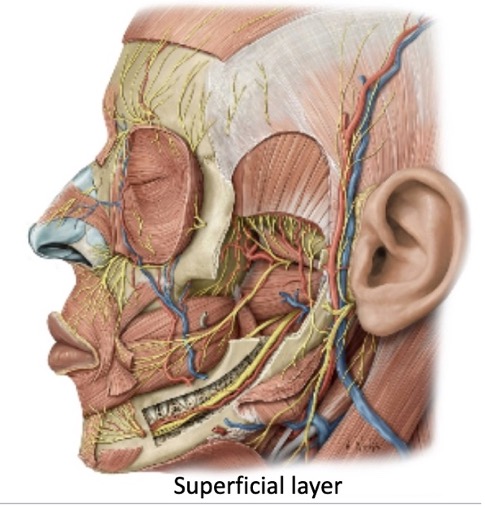
name the contents of the ITF
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
maxillary artery
pterygoid plexus of veins
mandibular division (V₃)
otic ganglion (a PSNS ganglion)
(not a Q) ITF superficial contents
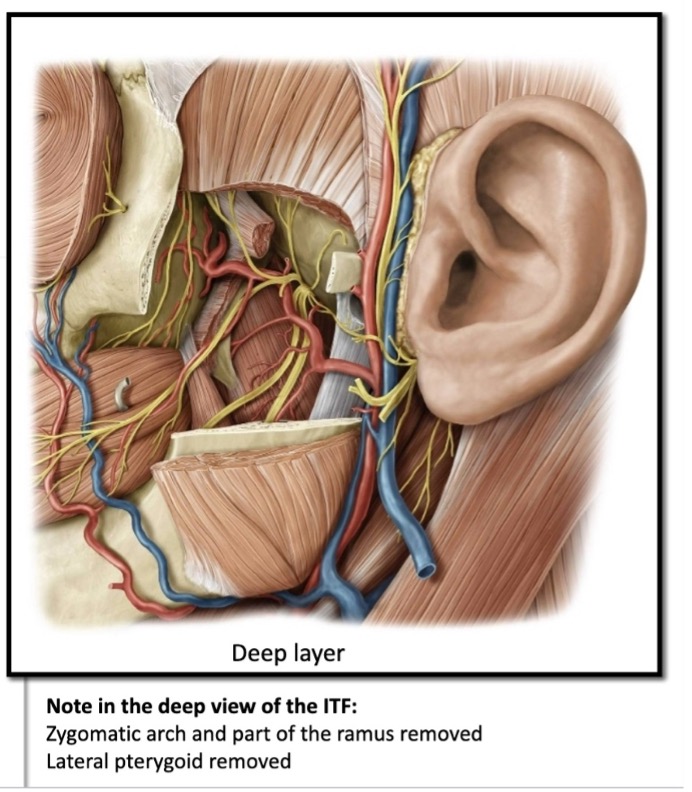
(not a Q) ITF deep contents
name the muscles that act on the mandible
temporalis
masseter
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
what does it mean to protract/retract the jaw?
protract = move forward
retract = move backward
what are the attachments of temporalis?
temporal fossa
coronoid process
what is the action of temporalis on mandible?
elevate
retract
(not a Q) temporalis
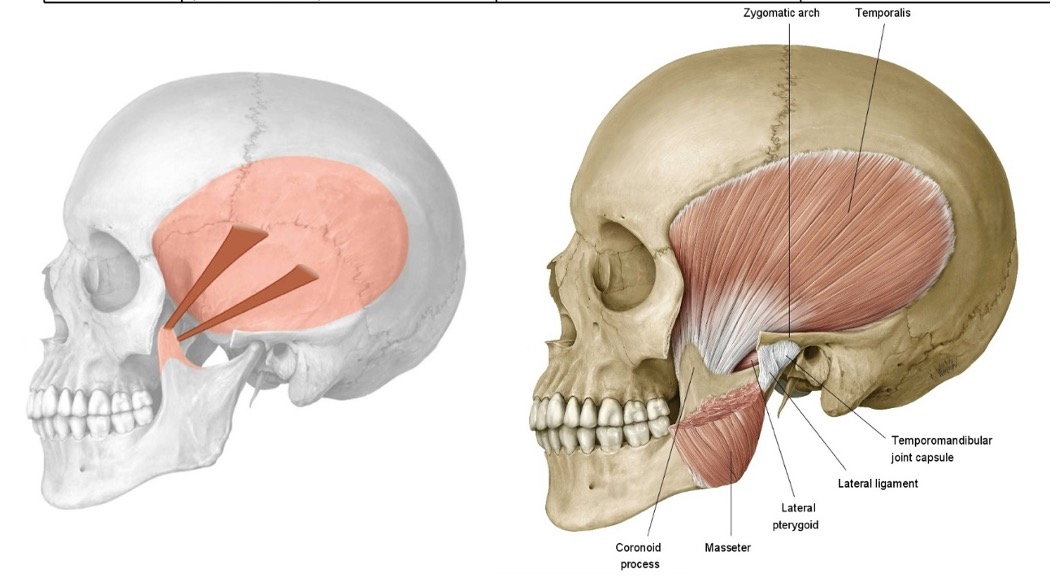
what are the attachments of masseter?
zygomatic arch
superficial side of angle of mandible
what is the action of masseter on mandible?
elevate
(not a Q) masseter
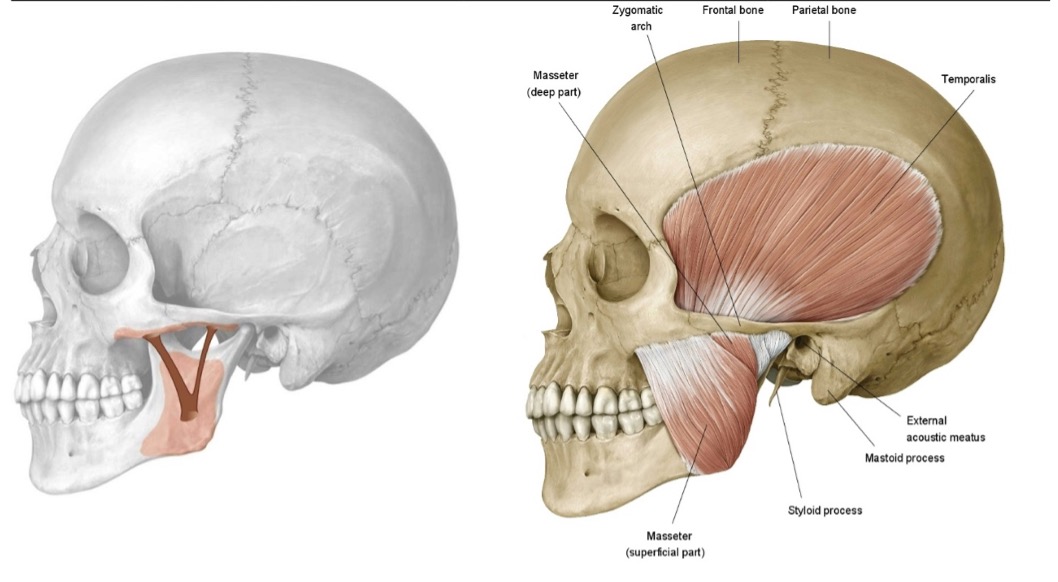
name the heads of medial pterygoid
superficial head
deep head
name the heads of lateral pterygoid
superior head
inferior head
what are the attachments of medial pterygoid?
maxilla (superficial head) and medial part of lateral pterygoid plate (deep head)
deep side of mandibular angle
what is the action of medial pterygoid on mandible?
elevate
(not a Q) medial pterygoid
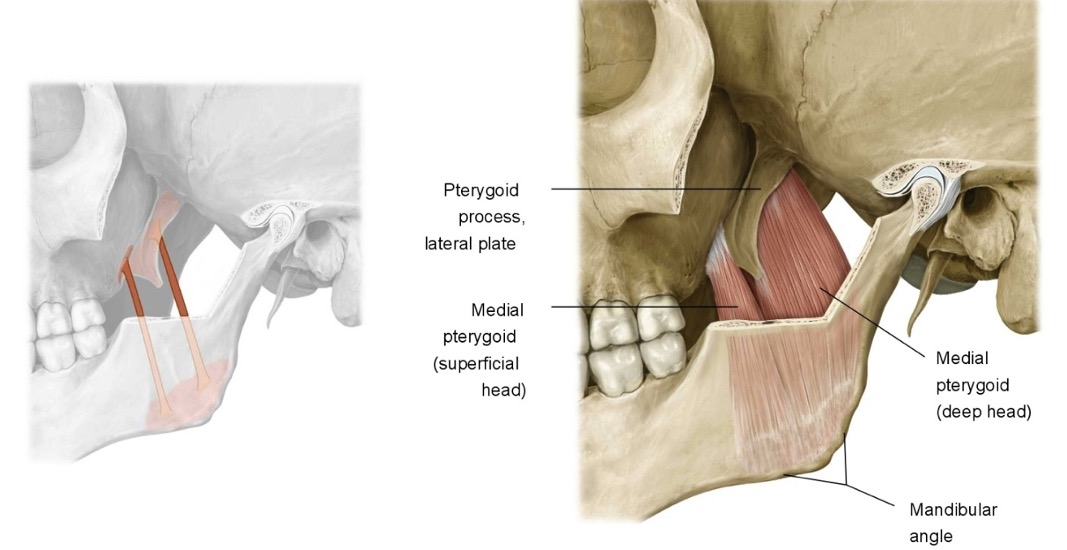
what are the attachments of lateral pterygoid?
greater wing of sphenoid (superior head) and lateral part of lateral pterygoid plate (inferior head)
condyloid process at TMJ
what is the action of lateral pterygoid on mandible?
protract
depress chin
(not a Q) lateral pterygoid
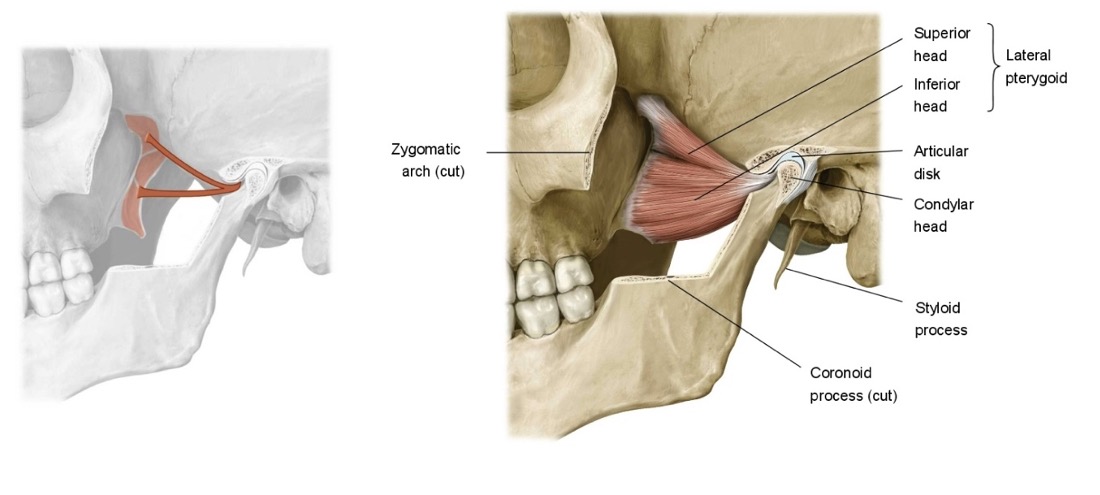
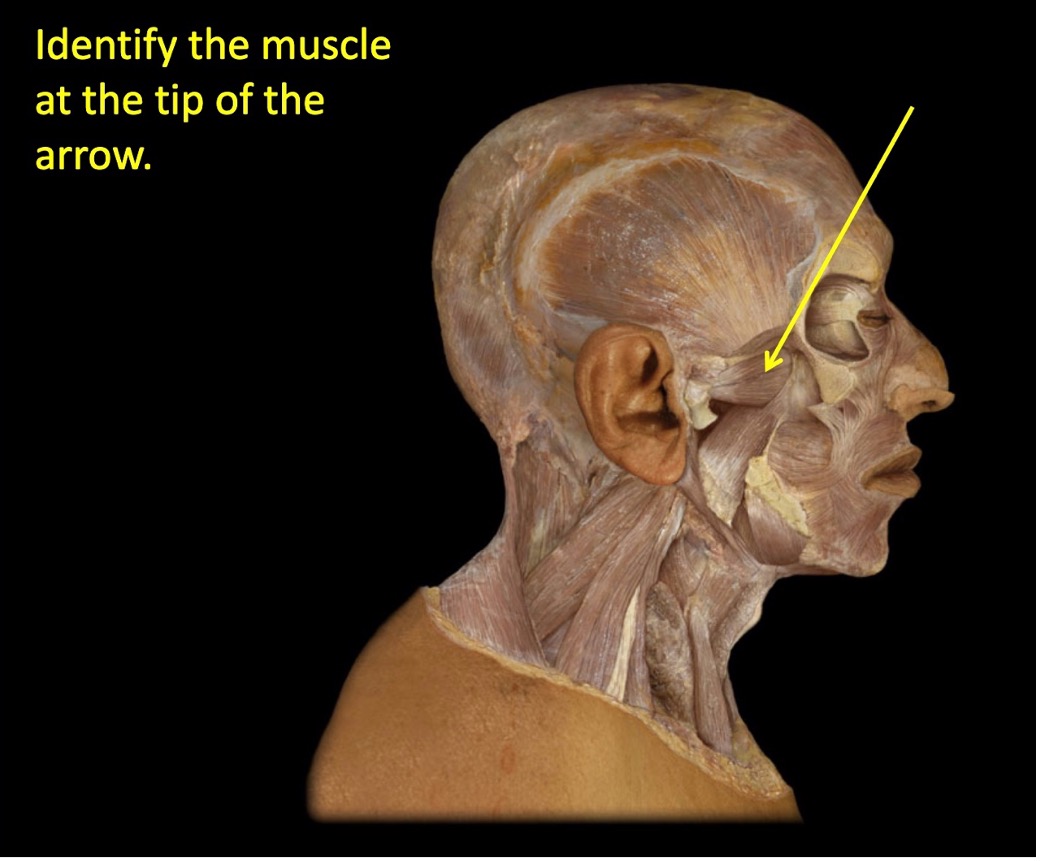
(review) identify the muscle at the tip of the arrow
lateral pterygoid
(medial pterygoid runs more obliquely, lateral pterygoid runs horizontal)
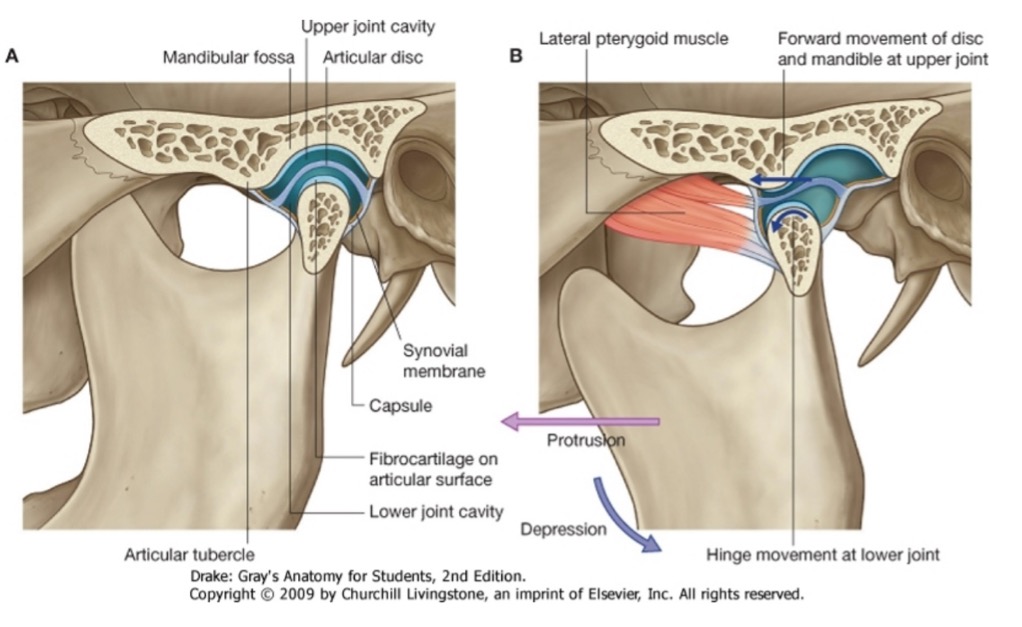
what articulates in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
mandibular fossa and articular tubercle of the temporal bone
head of the mandible (condylar process)
what type of joint is the TMJ?
modified hinge joint
what divides the TMJ into superior and inferior joint cavities?
an articular disc that separates the bony articular surfaces
what action occurs between what 2 structures at the superior joint cavity?
anterior gliding occurs between the articular disc and the mandibular fossa at the superior joint cavity
what action occurs between what 2 structures at the inferior joint cavity?
rotation between the mandibular condyle and the articular disc occurs at the inferior joint cavity
(not a Q) TMJ
which of the 2 terminal arteries of the external carotid artery takes a serpentine course through the ITF?
maxillary artery
the maxillary artery can be divided into 3 portions during its course through the ITF; list where each is located
1st: lies deep to the ramus of the mandible
2nd: lies anterior to the ramus of the mandible (location of muscular branches)
3rd: begins at the entrance of the pterygopalatine fossa and continues into the fossa
(not a Q) arteries of ITF
*memorize middle meningeal a, inferior alveolar a, and sphenopalatine a
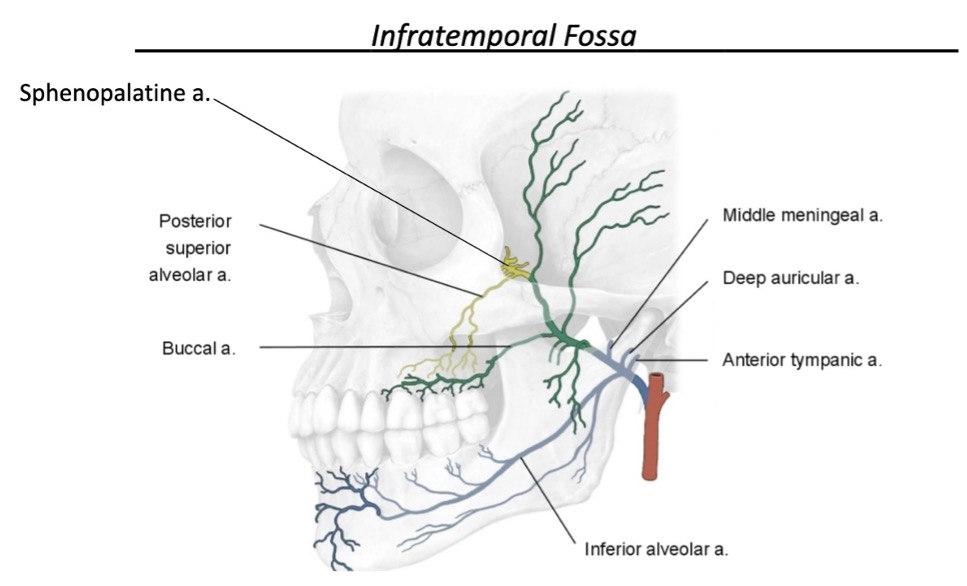
name the branches of the maxillary artery that perfuse the ITF
middle meningeal artery
inferior alveolar artery
sphenopalatine artery
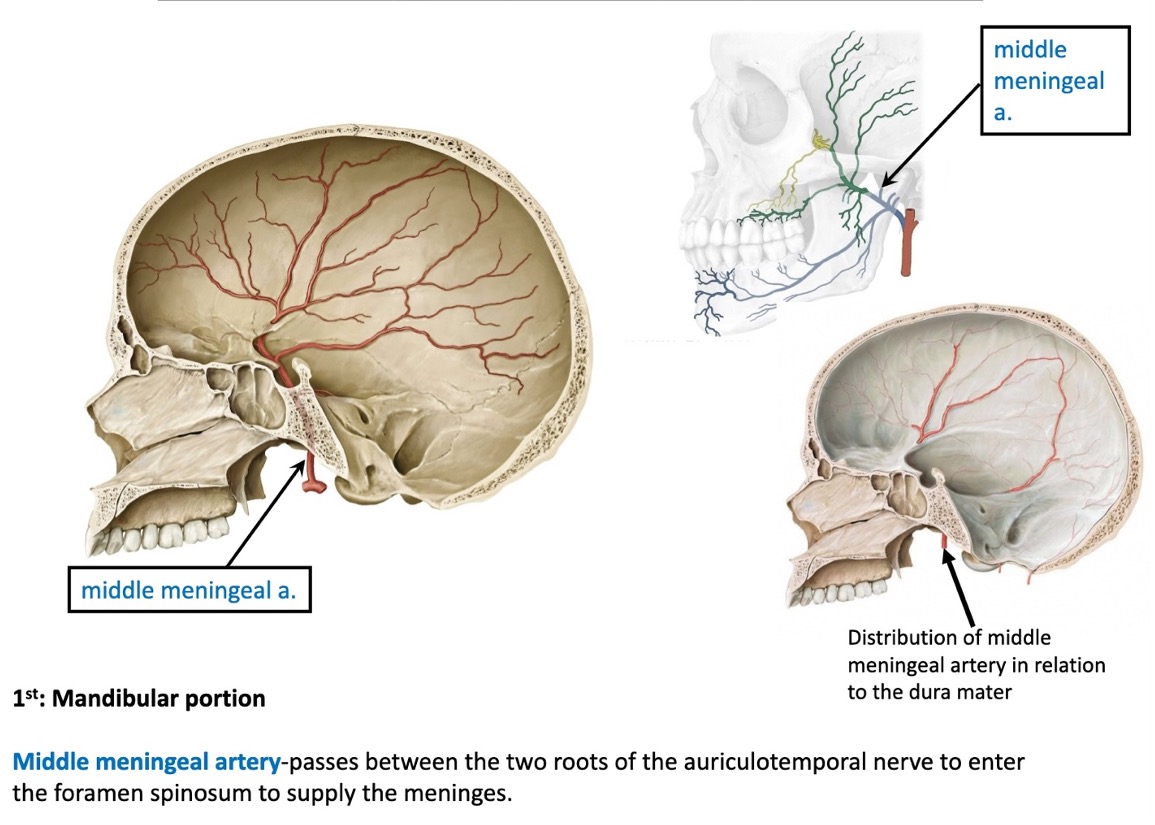
what does the middle meningeal artery supply?
meninges
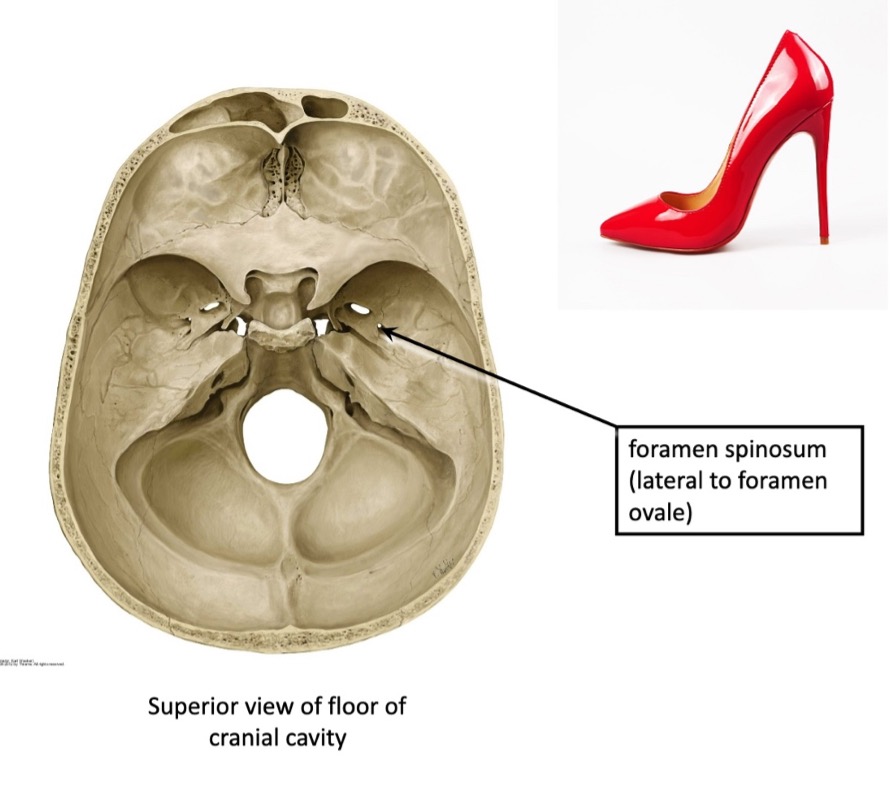
the middle meningeal artery passes between what structure to enter the foramen spinosum to supply the meninges?
passes between the 2 roots of the auriculotemporal nerve to enter the foramen spinosum to supply the meninges
(not a Q) middle meningeal artery
what foramen is foramen spinosum lateral to?
foramen ovale
(not a Q) superior view of floor of cranial cavity
*note foramen spinosum, where the middle meningeal artery enters
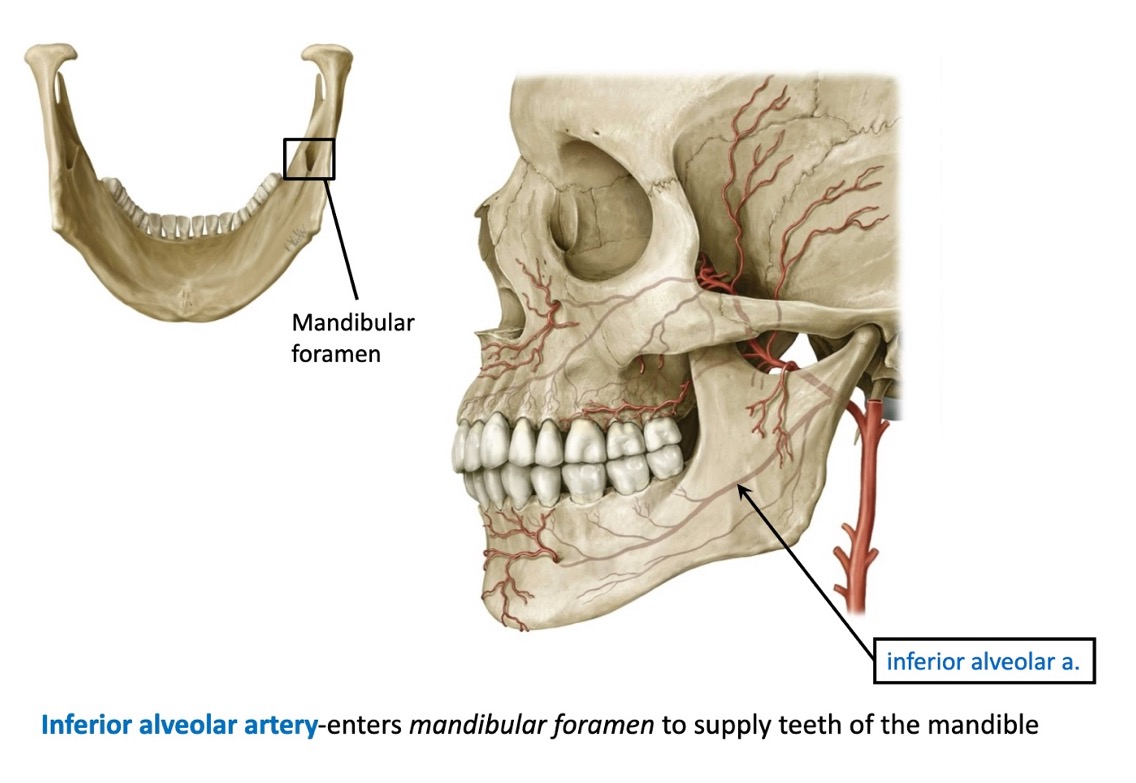
what does the inferior alveolar artery supply?
teeth of the mandible
what foramen does the inferior alveolar artery enter?
enters mandibular foramen to supply teeth of the mandible
(not a Q) inferior alveolar artery
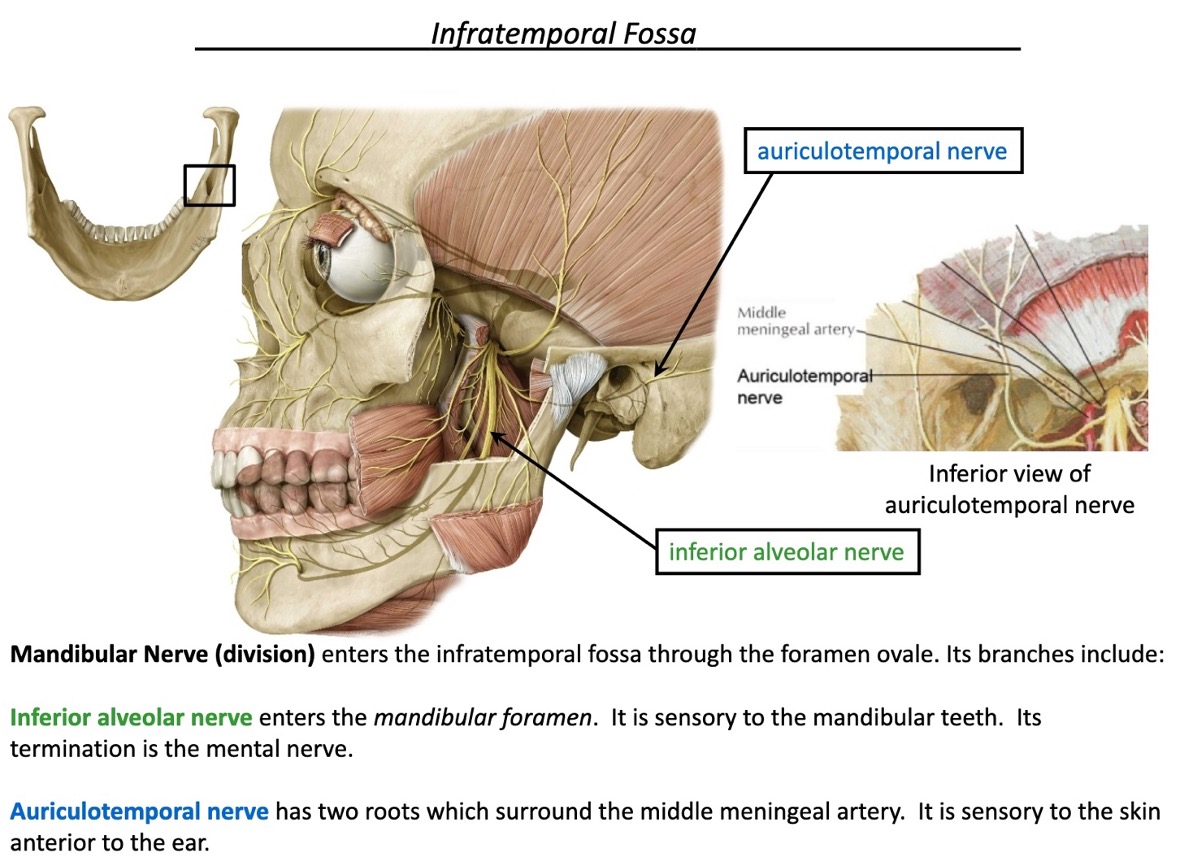
what space is associated with V₃ branches?
ITF
what space is associated with V₂ branches?
pterygopalatine fossa
name the branches of V₃
inferior alveolar nerve
lingual nerve
buccal nerve
auriculotemporal nerve
name the branches of V₂
infraorbital nerve
zygomatic nerve
posterior superior alveolar nerve
sphenopalatine nerves (including posterior nasal branches and nasopalatine nerve)
descending palatine nerves (greater and lesser palatine nerves)
what nerves branch from the infraorbital nerve?
anterior and middle alveolar nerves
through what foramen does the mandibular nerve (V₃) enter the ITF?
foramen ovale
what foramen does the inferior alveolar nerve enter?
mandibular foramen (to dive into the mandible)
what does the inferior alveolar nerve innervate?
sensory to the mandibular teeth
what is the termination of the inferior alveolar nerve?
mental nerve
how many roots does the auriculotemporal nerve have?
2
what do the roots of the auriculotemporal nerve surround?
the middle meningeal artery
what does the auriculotemporal nerve innervate?
sensory innervation to the skin anterior to the ear
(not a Q) inferior alveolar and auriculotemporal nn
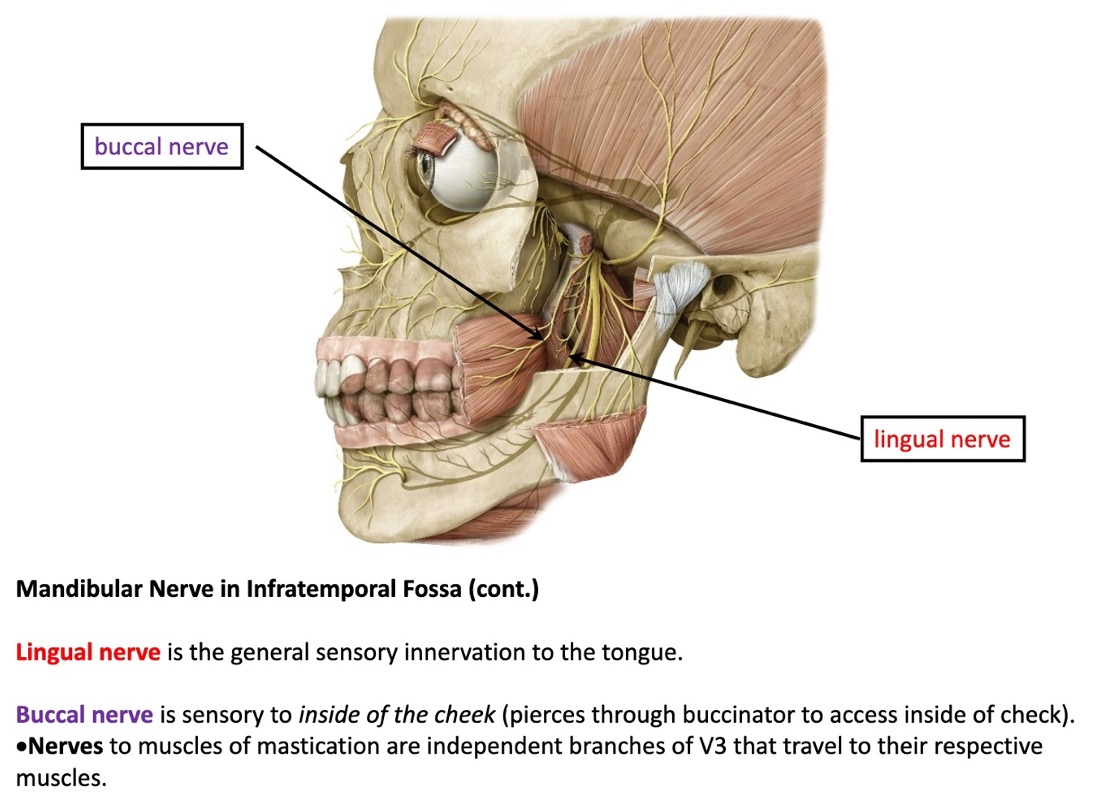
what does the lingual nerve innervate?
provides general sensory innervation to the tongue
(e.g. if you bite or burn your tongue)
what does the buccal nerve innervate?
sensory to inside of the cheek
what muscles does the buccal nerve pierce through to access the inside of the cheek?
buccinator
nerves to muscles of mastication are independent branches of what?
V₃ (mandibular nerve)
*will be tested
(not a Q) lingual and buccal nn
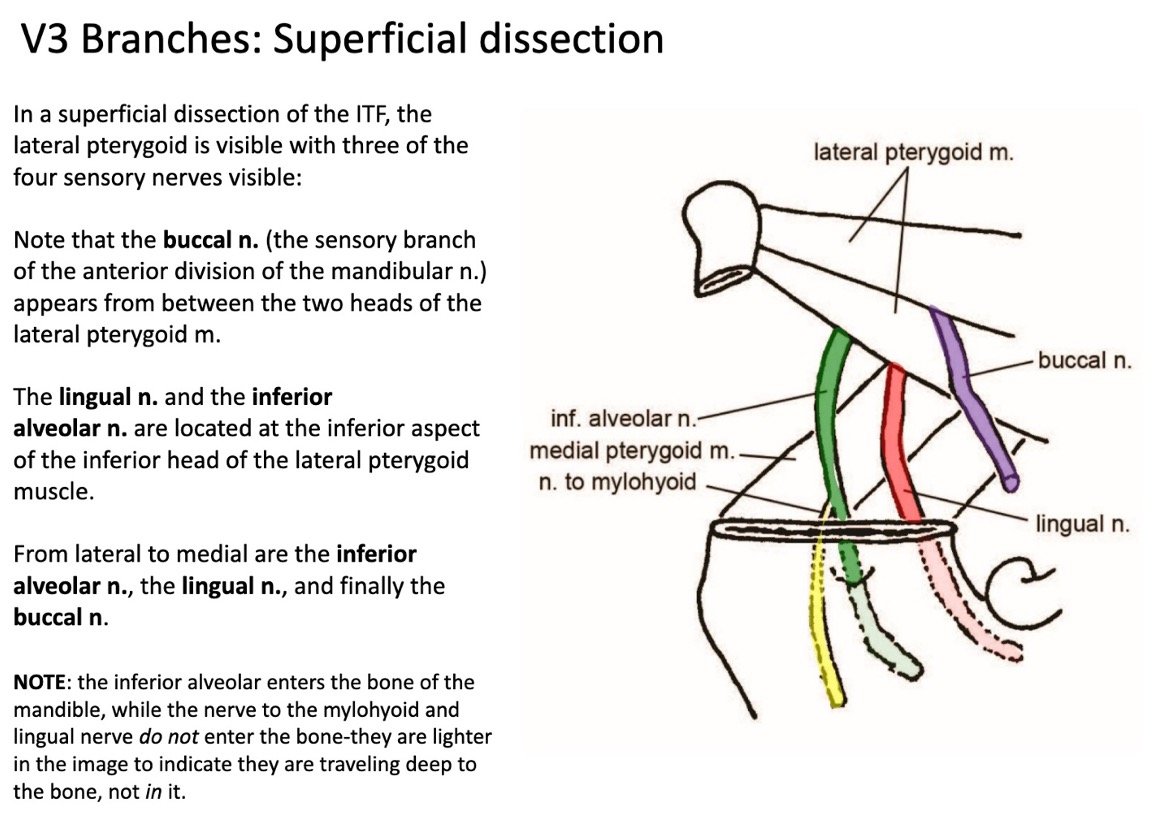
in a superficial dissection of the ITF, the lateral pterygoid is visible with how many of the sensory nerves visible?
3 out of 4
what nerve is the sensory branch of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve?
buccal nerve
between what structures does the buccal nerve appear?
between the 2 heads of the lateral pterygoid m.
where is the lingual nerve located?
at the inferior aspect of the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle
(does not enter here, goes to undersides of tongue to supply sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue)
where is the inferior alveolar nerve located?
at the inferior aspect of the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle
order the following nerves from lateral to medial:
lingual nerve
inferior alveolar nerve
buccal nerve
inferior alveolar nerve
lingual nerve
buccal nerve
true or false: the inferior alveolar nerve enters the bone of the mandible
true
(not a Q) superficial dissection of mandibular nerve branches
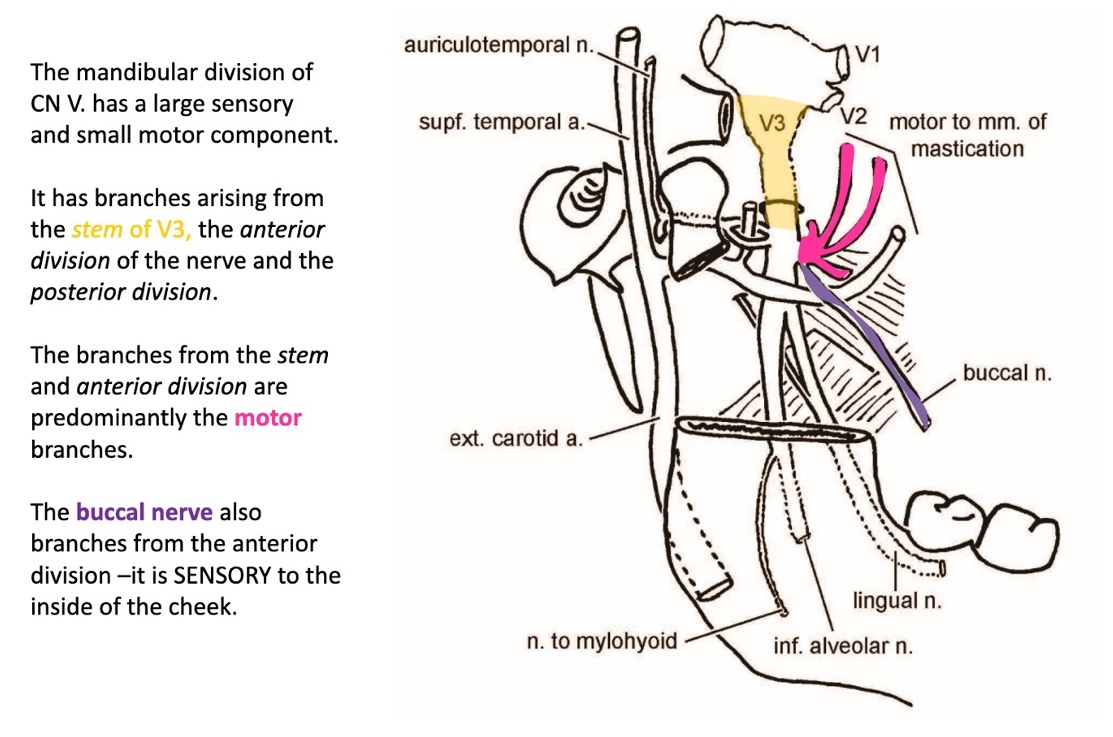
true or false: V₃ has a small sensory and large motor component
false
it has a large sensory and small motor component
V₃ has branches arising from the stem of V₃, the anterior division of the nerve, and the posterior division
which branches are predominantly the motor branches?
the branches from the stem and anterior divisions
from what division of V₃ does the buccal nerve branch?
the anterior division
(not a Q) V₃ branches deep dissection
*note that buccal nerve stays medial to get into cheek
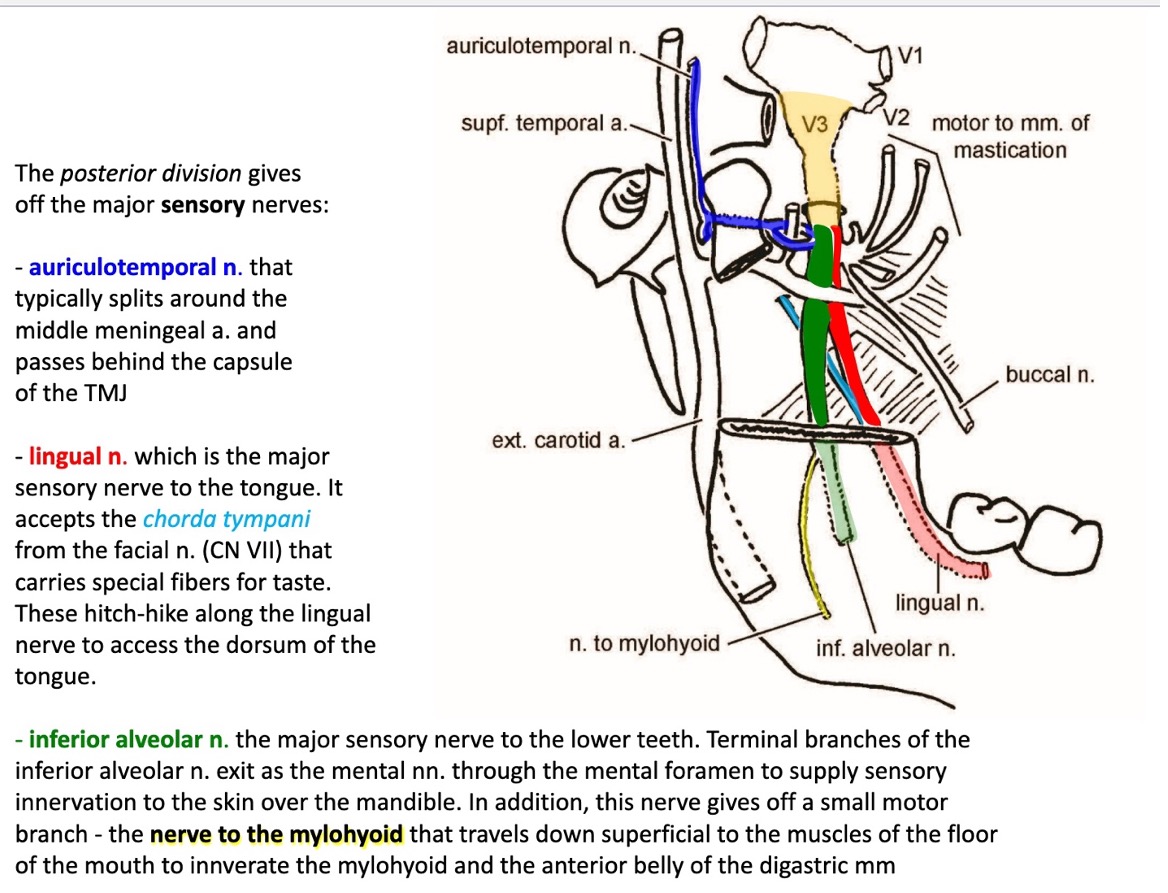
what division of V₃ gives off the major sensory nerves?
the posterior division
the auriculotemporal nerve typically splits around what artery?
the auriculotemporal nerve typically splits around the middle meningeal artery to pass behind the capsule of the TMJ
what is the chorda tympani?
a branch of CN VII that carries special fibers for taste
what nerve accepts the chorda tympani?
lingual nerve
after accepting chorda tympani, where does the lingual nerve travel?
to the dorsum of the tongue
terminal branches of the what nerve become mental nerves as they exit the mental foramen?
inferior alveolar nerve
what do the mental nerves innervate?
sensory innervation to the skin over the mandible
what is the parent nerve of the nerve to the mylohyoid?
inferior alveolar nerve
what does the nerve to the mylohyoid innervate?
travels down superficial to the muscles of the floor of the mouth to innervate the mylohyoid and anterior belly of digastric muscles
(not a Q) V₃ sensory nerves
what nerve innervates the sublingual and submandibular glands?
CN VII
where are the preganglionic PSNS neurons of CN VII located?
superior salivary nucleus
where are the postganglionic PSNS neurons of CN VII located?
submandibular ganglion
what nerve innervates the parotid gland?
CN IX
where are preganglionic PSNS neurons of CN IX located?
inferior salivary nucleus
where are postganglionic PSNS neurons of CN IX located?
otic ganglion
what is trigeminal neuralgia?
damage to CN V → stabbing pain along the path of the nerve, usually on one side of the face
(pain prompted by brushing hand against face, etc.)