Histology of Pituitary Gland
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Pituitary Gland (aka hypophysis)
What
Encapsulated with
Vascularised?
Regulated by
What: Master gland
Encapsulated with: Irregular, dense connective tissue
Vascularised: Highly vascularised
Regulated by: Hypothalamus
How is the hypopthalamus connected to the pituitary gland?
Through the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system:
Hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract (axons) → connects to neurophypophysis (posterior pituitary)
Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system (capillaries) → connects to adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
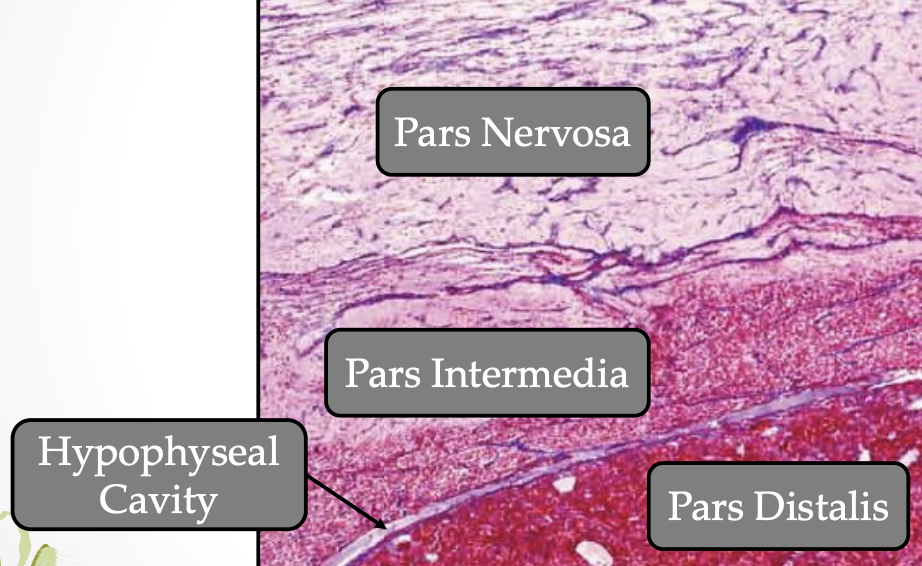
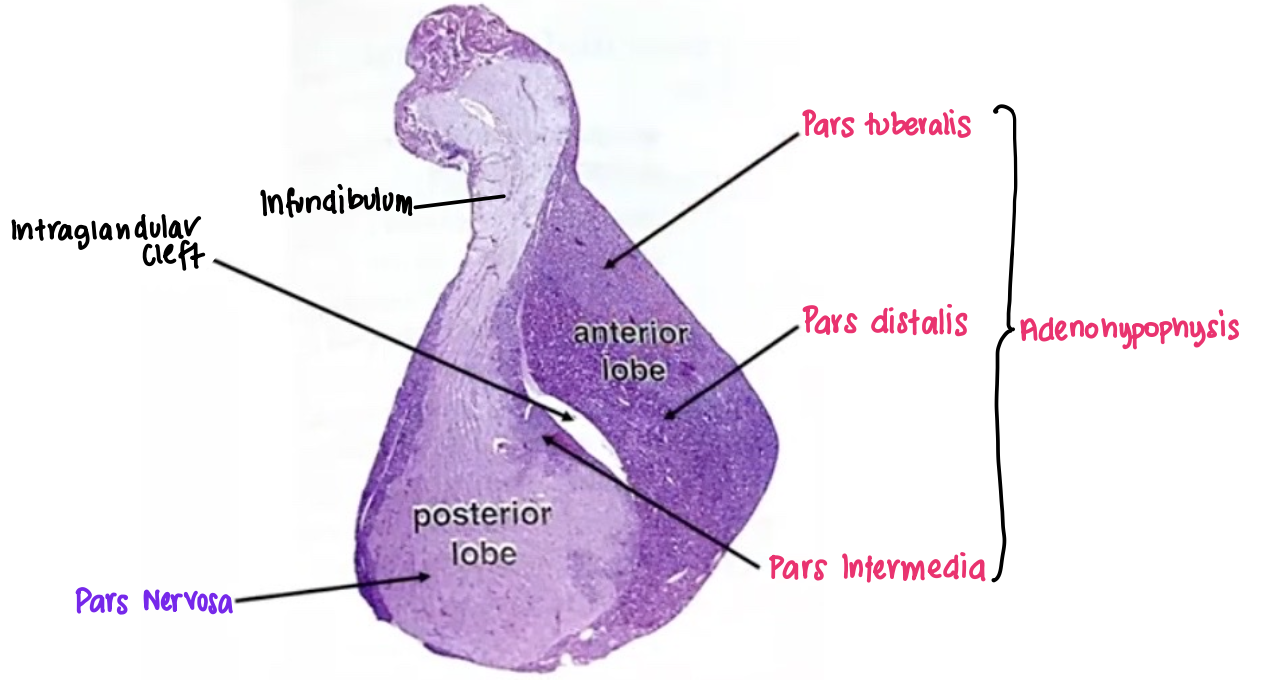
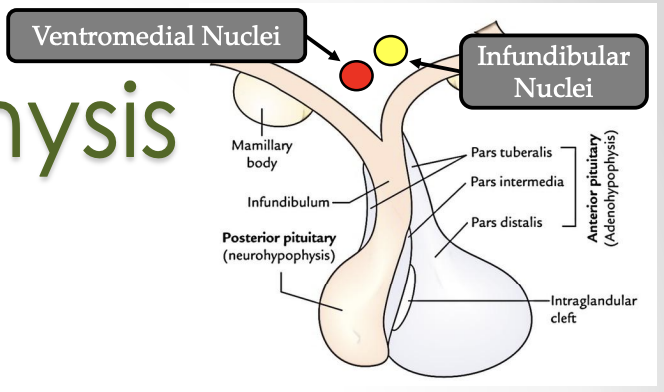
The pituitary gland consist of what 2 components?
Neurohypophysis (diencephalan floor)
Adenohypophysis (Rathke’s pouch)
Pituitary Gland: Neurohypophysis
What
Function
Where and what are the cell bodies of neurohypophyseal hormones located
Which hormones are associated with neurohypophysis
Are they produced in the neurohypophysis
Where are these hormones stored
What is pars nervosa
Contains
In which animals is the neurohypophysis larger than adenohypophysis
What: The posterior pituitary
Function: Stores and releases hormones made in the hypothalamus
Where and what are the cell bodies of neurohypophyseal hormones located:
Where: In the hypothalamus
What:
Supraoptic nuclei
Paraventricular nuclei
Which hormones are associated with neurohypophysis: ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin
Are they produced in the neurohypophysis: No,
They are produced in the hypothalamus and
Stored and released from the neurohypophysis
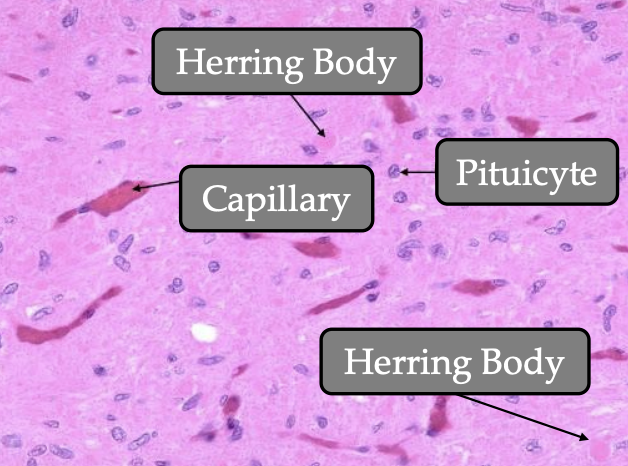
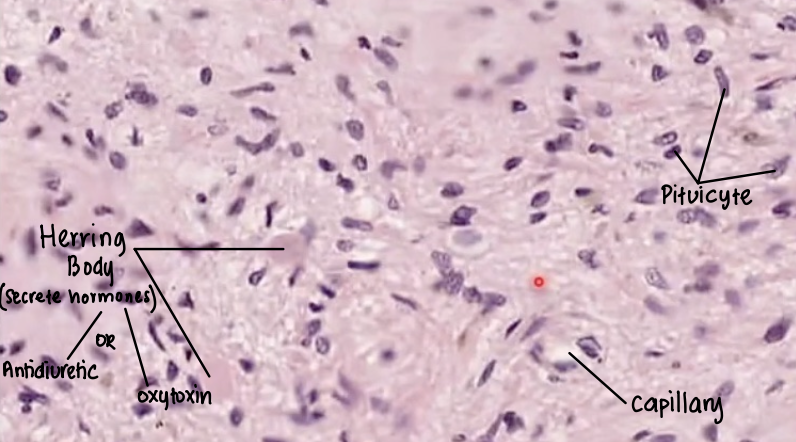
Where are these hormones stored: Neurosecretory granules called Herring bodies
What is pars nervosa: The main part of the neurohypophysis contain
Contains:
Terminal axons
Surrounding pituicytes (support cells with lipid droplets & cytoplasmic projections)
In which animals is the neurohypophysis larger than adenohypophysis: Feline and porcine
Pituitary Gland: Neurohypophysis
What is the pathway of signals from hypothalamus → neurohypophysis to release ADH and oxytocin
Signals start in the cell bodies of the hypothalamus and they produce ADH and oxytocin
Supraoptic nucleus
Paraventricular nucleus
Then nerve impulses travel along the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract which consist of axons
Axons terminate at the pars nervosa of the neurohypophysis
Hormones are then stored in Herrring bodies
They are released in the bloodstream response to nerve impulses
Pituitary Gland: Neurohypophysis
Describe the histology cytoplasm staining of pituicytes and Herring bodies
Pituicytes: Lightly stained but has dark elongated nucleus
Herring bodies: Esoinophilic (pink/red)
Pituitary Gland: Adenohypophysis
What
Function
Where and what are the cell bodies of adenohypophysis hormones located
Function
How do hypothalamic hormones reach the anterior pituitary
Species where adenohypophysis is histologically prominent
3 components
What: Anterior pituitary
Function: Produce and secrete hormones
Where and what are the cell bodies of adenohypophysis hormones located:
Located: In the hypothalamus
What:
Infundibular nucleus
Ventromedial nucleus
Function of these cells: Produce releasing or inhibiting hormones that regulate the anterior pituitary
How do hypothalamic hormones reach the anterior pituitary:
After the hypothalamic production of releasing/inhibiting hormones
Hormones enter primary capillary plexus (median eminence)
Which is at the base of hypothalamus
Then they are carried by the portal veins to the secondary capillary plexus
Which is in the adenohypophysis
Hormones diffuse to pituitary cells → stimulate or inhibit hormone secretion
Species where adenohypophysis is histologically prominent:
Equine
Canine
Ruminant
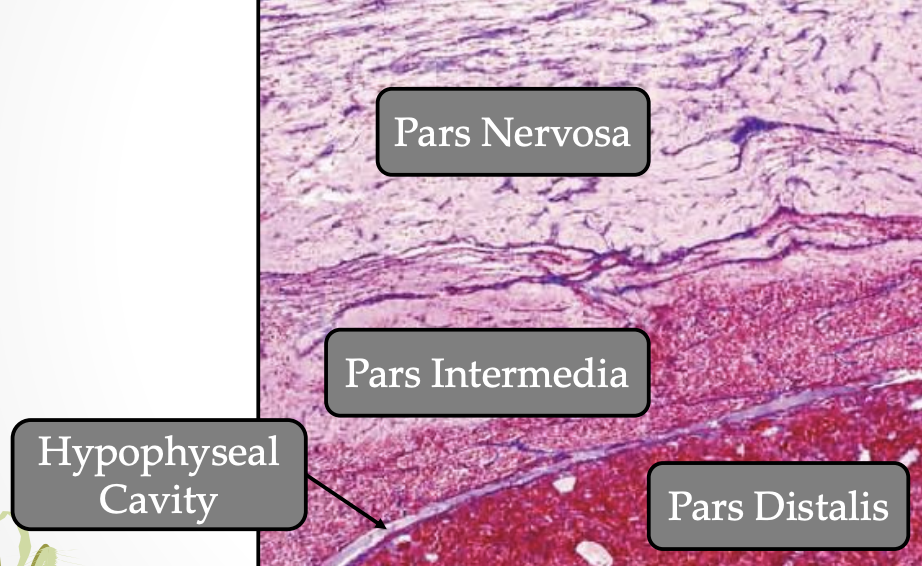
3 components:
Pars distalis (biggest, main part that secretes anterior pituitary hormones) #c9184a
Pars tuberalis (tip that wraps around pituitary stalk) #f7aef8
Pars intermedia (between anterior and posterior pituitary) #db00b6
Adenohypophysis: Pars Distalis #c9184a
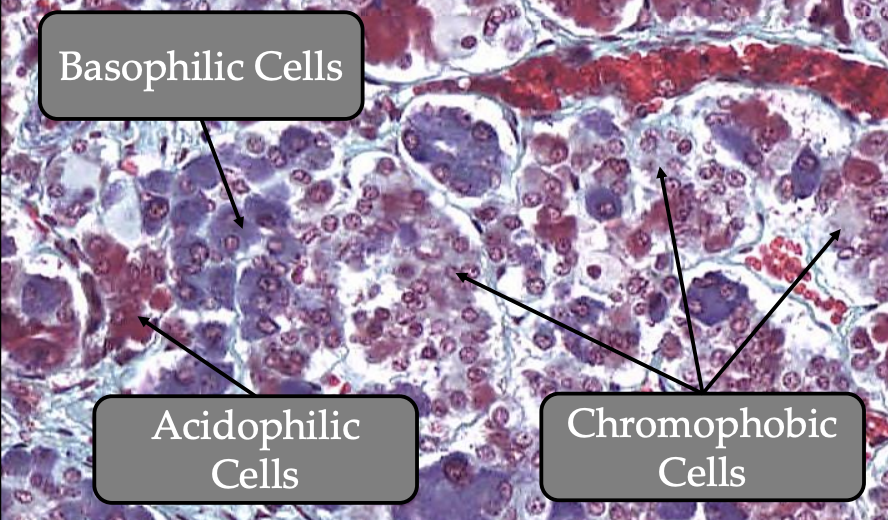
What are the 2 types of cells in Pars Distalis
Chromophobic cells
Chromphilic cells
Adenohypophysis: Pars Distalis —> Chromophobic Cells #c9184a
What
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
What: Undifferentiated, non secretory stem cells
Cytoplasm: Light colored homogenous
Nucleus: Large
Adenohypophysis: Pars Distalis —> Chromophlic Cells #c9184a
2 types
What do they secrete
Acidophilic cells
Secrete: Somatotropic and lactotropic
Basophilic cells
Secrete: Gonadotropic, thyrotropic and corticotropic
Adenohypophysis: Pars Distalis —> Chromophlic Cells (acidophilic cells) #c9184a
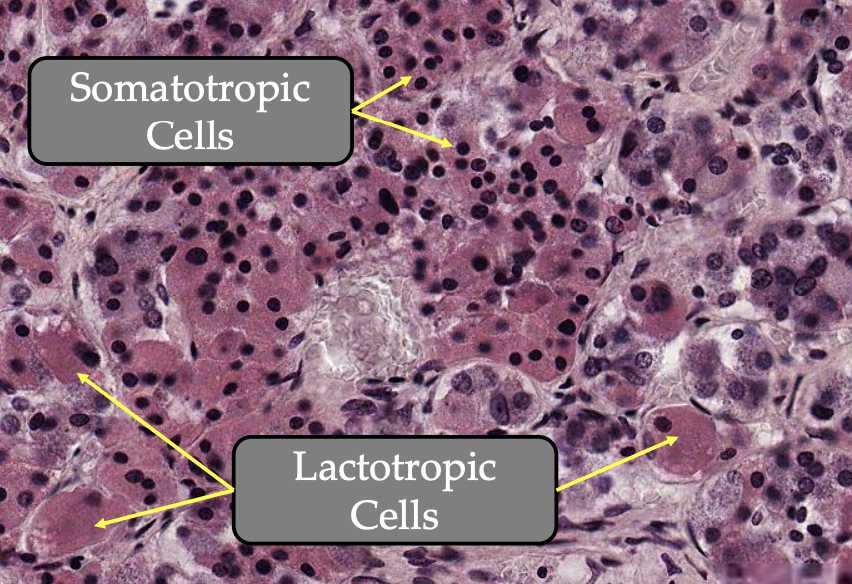
Somatotropic cells
Size
Shape
Consist of
Secrete
Lactotropic cells
Size
Shape
Consist of
Secrete
Prominent during
Somatotropic cells:
Size: Small
Shape: Round
Consist of: Large, densely packed granules
Secrete: Growth hormone
Lactotropic cells:
Size: Large, single
Shape: Polyhedral cells
Consist of: Larger granules
Secrete: Prolactin hormone
Prominent during: Gestation and post partum
Adenohypophysis: Pars Distalis —> Chromophlic Cells (basophilic cells) #c9184a
Gonadotropic cells
Size
Shape
Consist of
Secrete
Thyrotropic cells
Consist of
Secrete
Corticotropic cells
Secrete
Function
Gonadotropic cells:
Size: Small
Shape: Round
Consist of: PAS positive granules
Secrete: FSH and LH
Thyrotropic cells:
Consist of: Smallest granules
Secrete: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Corticotropic cells:
Secrete: Adrenocortoropic hormone
Function: Regulates cortical adrenal gland hormone synthesis
Adenohypophysis: Pars Intermedia #f7aef8
Staining
Secrete
Synthesis
Staining: Basophilic
Secrete: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
Synthesis: Pro-opiomelanocortin → β-endorphin
Adenohypophysis: Pars Tuberalis #db00b6
What
Location
Arrangement
What: Adenohypophysis projection
Location: Partially surrounds anterior aspect of infundibulum
Arrangement: Cluster