Wk 5 pt1 - Cardiopulmonary responses to submaximal, incremental and maximal aerobic exercise
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is cardiopulmonary responses?
These are mechanisms in the body that occur to meet the body’s requirements when we exercise. (e.g., ATP requirements, and Production of lactate and CO2.
What is VO2?
It is a description of O2 utilisation by the body. It increases in proportion to exercise intensity.
How is VO2 measured?
In either absolute terms (litres per minute) or relative to body mass (ml/kg/min)
What is the body’s VO2 at rest?
It is around 0.2-0.3L/min (or 3.5-5.0 ml/kg/min)
What are some changes associated with VO2?
Some things include ventilation, cardiac output (L/min), heart rate, redistribution of blood flow to exercising muscle, and extraction of oxygen from the blood into the muscle and mitochondria.
What is the Fick equation?
VO2 represents oxygen consumption (mL/min)
Q represents cardiac output (L/min)
a - vo2 diff represents the arteriovenous oxygen difference (mL/dL)
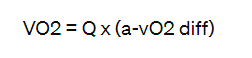
What is VO2 max?
The description of the maximal rate at which O2 can be utilised.
What is VO2 max limited by?
The rate of delivery and the rate of consumption within the muscle.
What is VO2 max associated with?
The capacity to do long periods of exercise and the intensity of maintaining this form of exercise. It is a determining factor in endurance performance.
What are some key factors in VO2 max?
Maximal oxygen delivery (Q max, HR max, SV max), O2 carrying capacity of the blood (Hb, HCt), capillarisation of muscle, a - vo2 diff, and maximum capacity of the muscle to utilise oxygen.
VO2 responses during exercise
At the 4 minute mark, the individual has achieved VO2 corresponding to moderate intensities of exercise. As exercise intensities increase beyond moderate levels, VO2 will increase gradually, indicating a higher metabolic demand on the body.
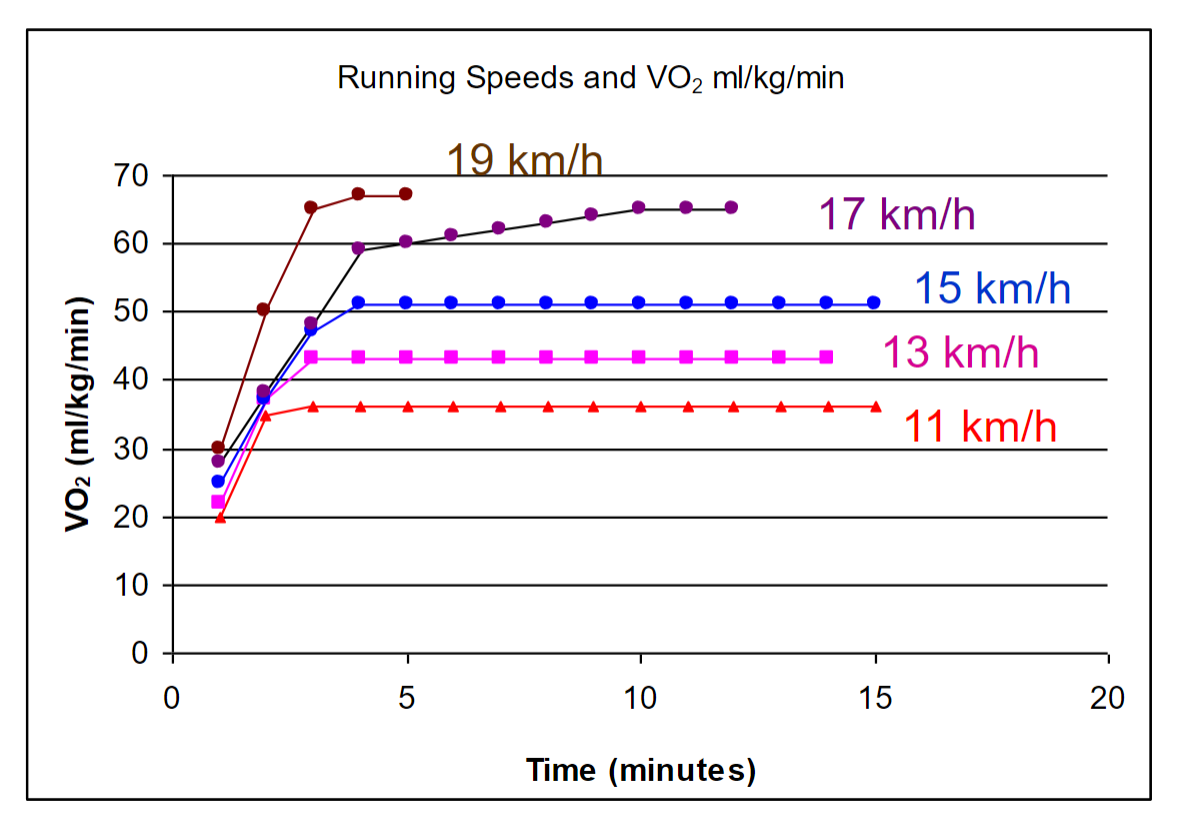
What are some other responses you can use to estimate O2 consumption and VO2 max?
Exercise intensity (e.g., running speed, or cycling watts), heart rate, and perceived exertion.
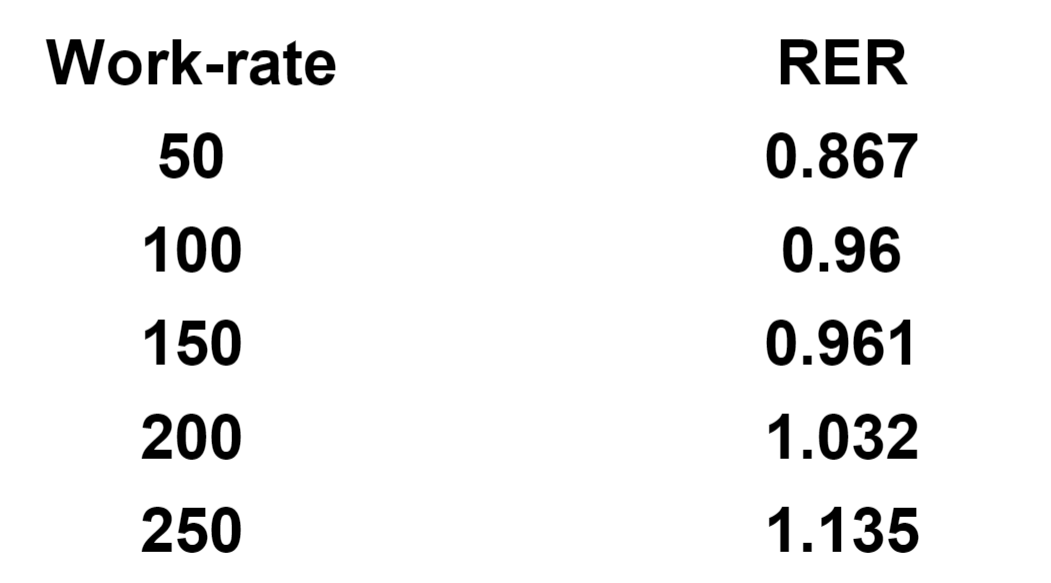
A general guide to responses to increasing work-rate. (VO2 max)
These numbers were on a person weighing 90 kg.

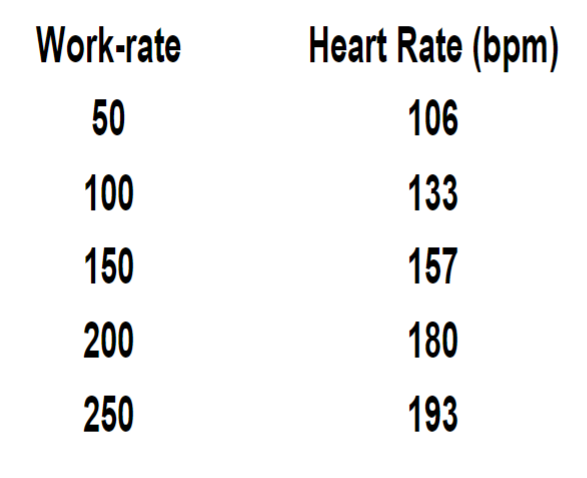
A general guide to responses to increasing work-rate. (Heart rate)
A general guide to responses to increasing work-rate. (Ventilation)

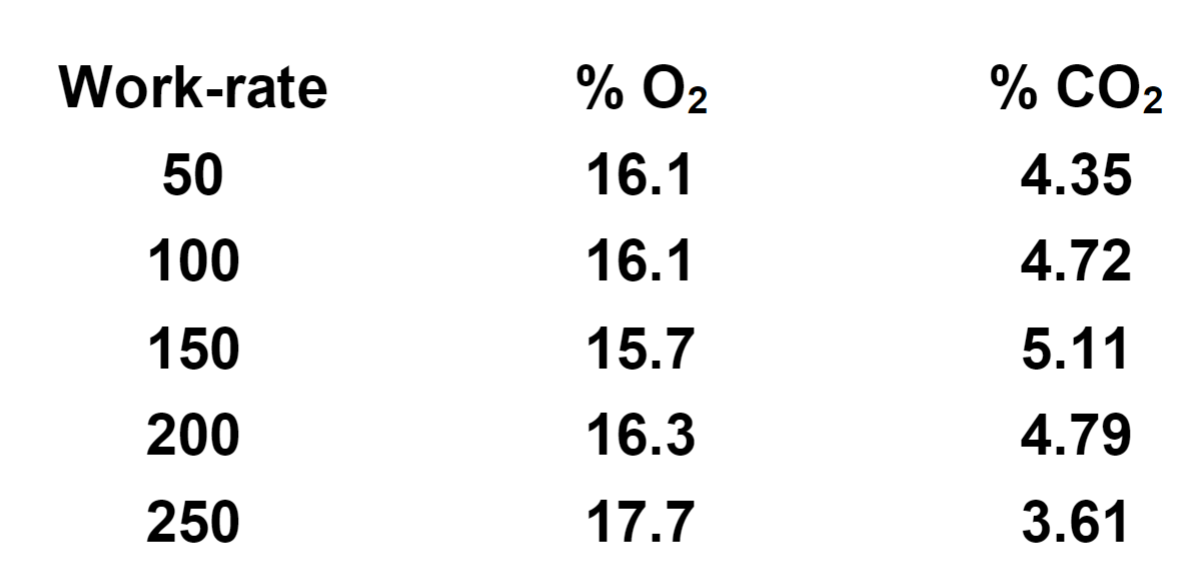
A general guide to responses to increasing work-rate. (O2 and CO2 consumption)
Although % remains consistent, ventilation is increasing in response to increased CO2 production to ensure levels remain in permissible range.
A general guide to responses to increasing work-rate. (Respiratory Exchange Ratio)