Early Christian and Byzantine History: Edicts, Church Structure, and Empire Fall
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Who ended Christian persecution in 311 AD?
Emperor Galerius

What was the Edict of Milan (313 AD)?
A joint declaration by Constantine and Licinius granting religious freedom throughout the Roman Empire

When did Constantine become sole emperor?
324 AD
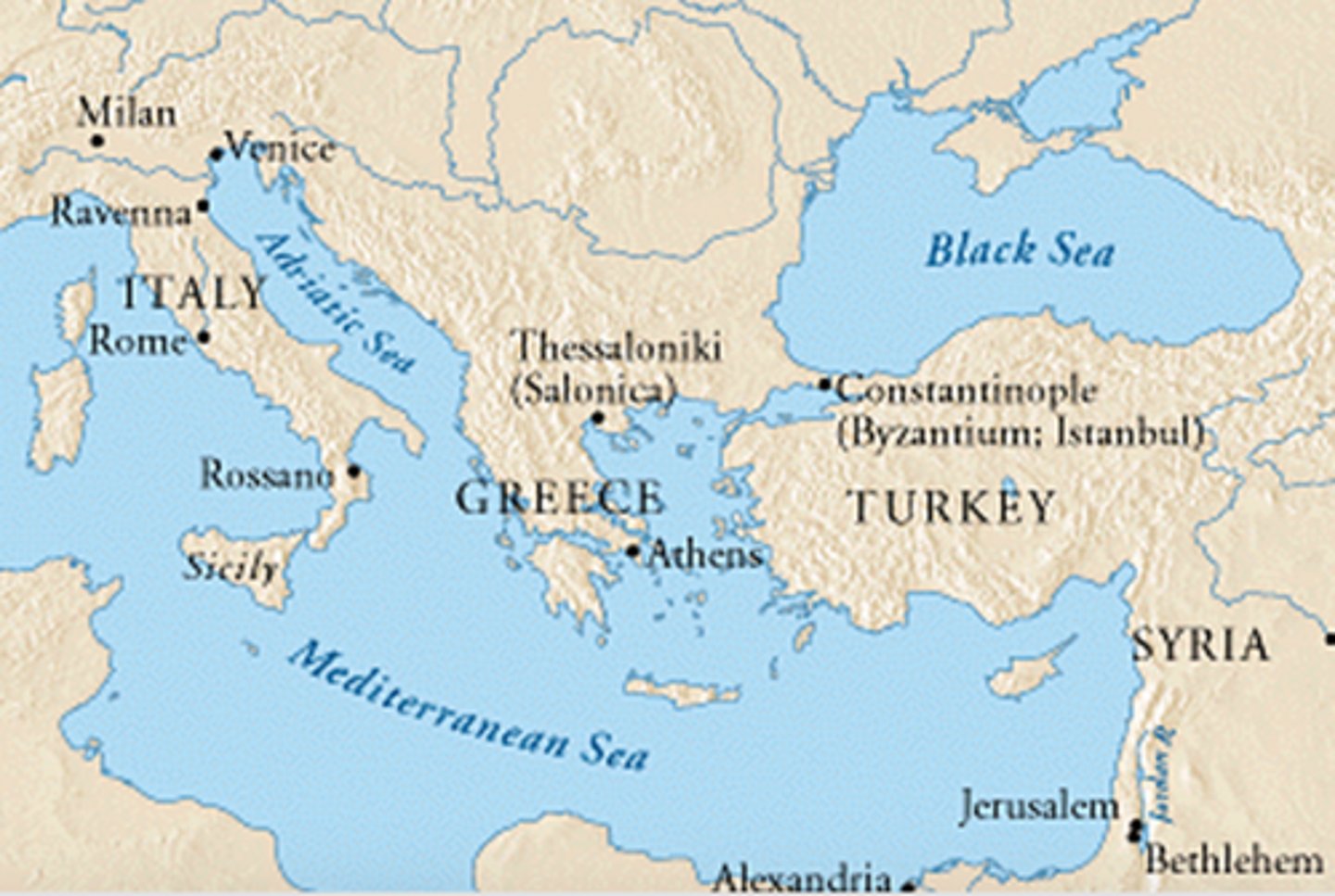
What major change did Constantine make to the capital of the empire?
He moved it to Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul)
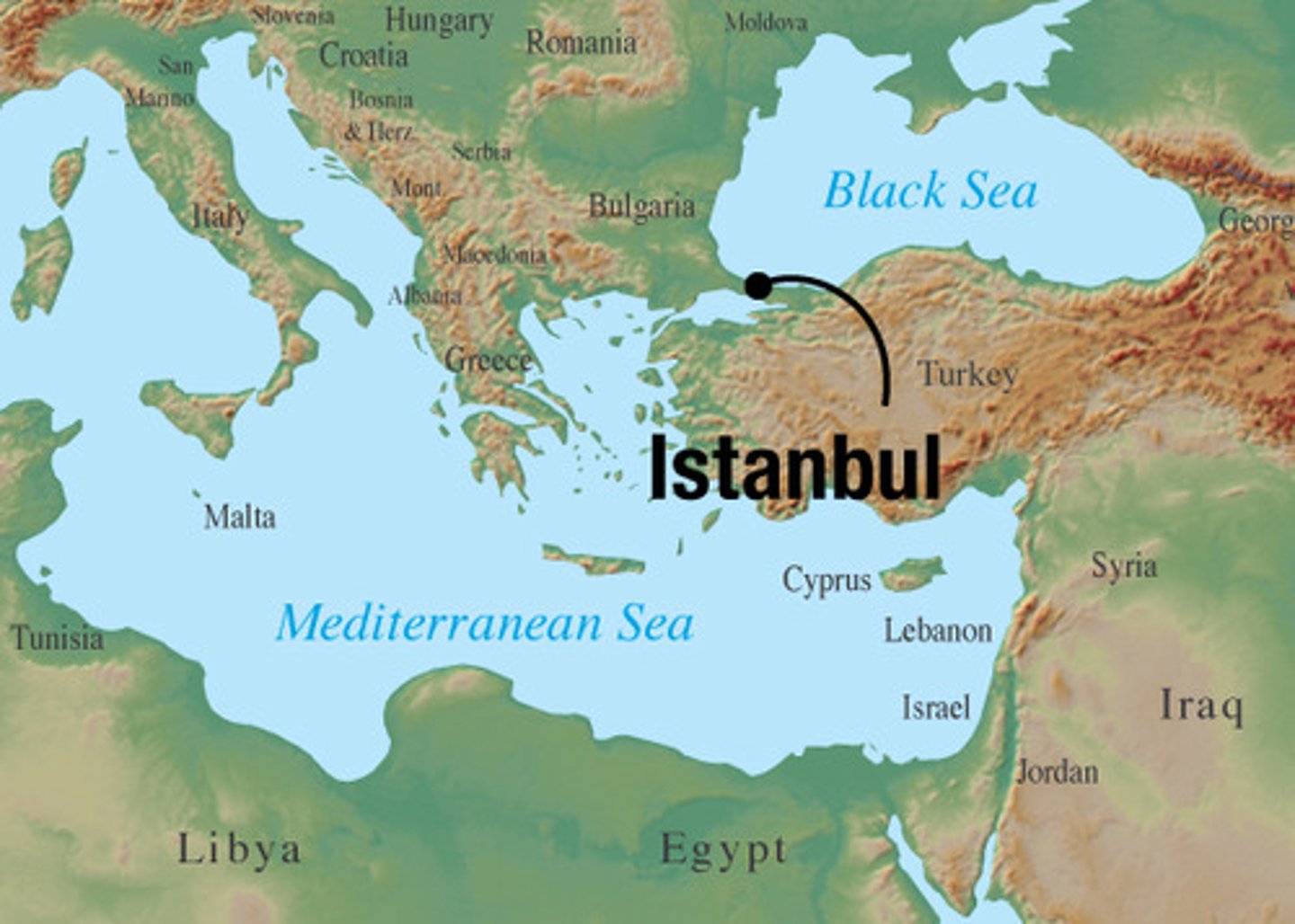
What new religious freedom did Christians gain after legalization?
Public worship was permitted
What major church-building project symbolized Christianity's new status?
The Archbasilica of St. John Lateran
How did legalization affect Church leaders politically?
They gained political influence
What happened to Christian property after legalization?
Confiscated property was returned
How did legalization affect evangelization?
Christians were free to spread the faith openly
How did Constantine support Church unity?
He supported ecumenical councils

What is Caesaropapism?
Government interference in Church affairs

How did legalization increase social inequality?
The gap between rich and poor became more pronounced

Who were 'convenience Christians'?
People who became Christian for political or social advantage

What new social class emerged among clergy?
A clerical aristocracy

Who were the Desert Fathers?
Christians who withdrew from society to seek a more authentic faith
Why did some Romans convert to Christianity?
To keep Roman citizenship

What were the five major patriarchates?
Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, Jerusalem
Why did Rome have primary authority?
Because of St. Peter's legacy
How did Church administration change after legalization?
It began to mirror Roman political systems
What local Church units developed?
Parishes and dioceses
What was the long-term result for Church hierarchy?
A more formal and organized structure

Who ruled the Eastern Empire after Constantine's death?
Constantius, who supported Arianism

Who ruled the Western Empire after Constantine's death?
Constans, who supported Orthodox Christianity

What percentage of the population was Christian by 350 AD?
57%
Which emperor made Christianity the official religion of the empire?
Theodosius I

Why did Constantinople weaken the Western Empire?
It became the new capital, shifting power eastward

What were the barbarian migrations?
Large east-to-west population movements

Who were the Huns?
A group from Asia seeking fertile land

Which Germanic tribe invaded Gaul and Rome?
The Visigoths

What happened in 410 AD?
The Visigoths sacked Rome
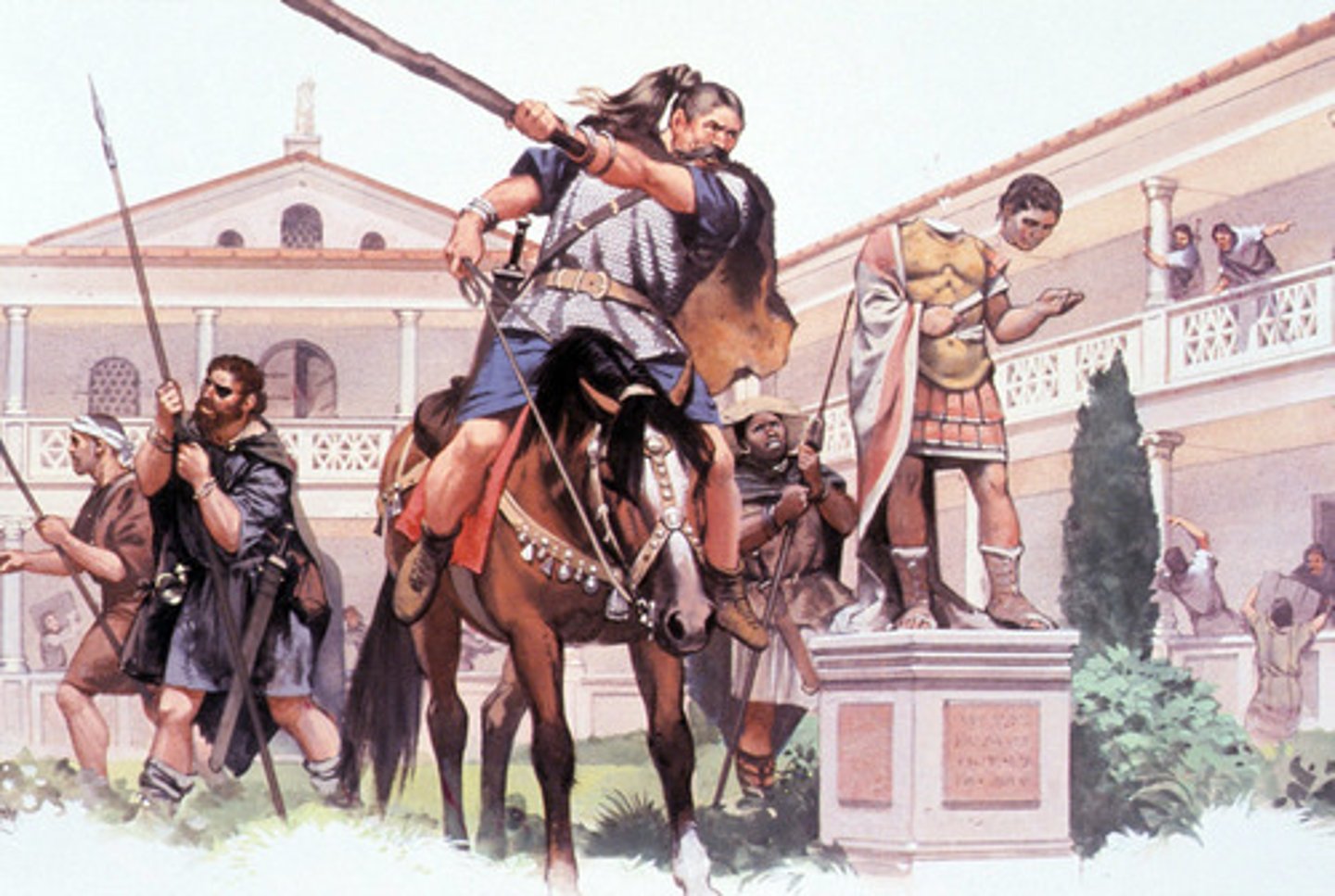

What year traditionally marks the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
476 AD
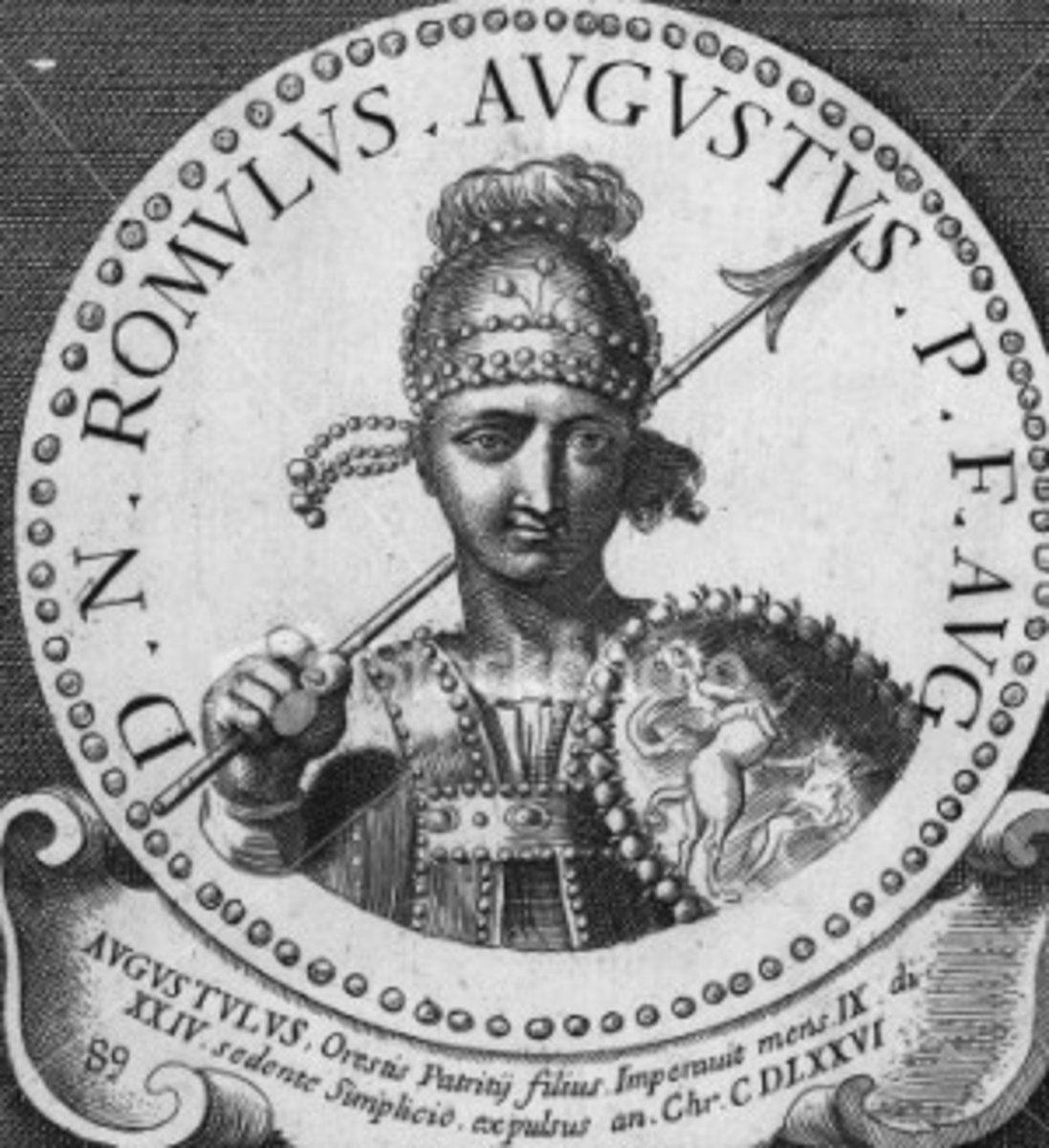

What was the Eastern Roman Empire later called?
The Byzantine Empire

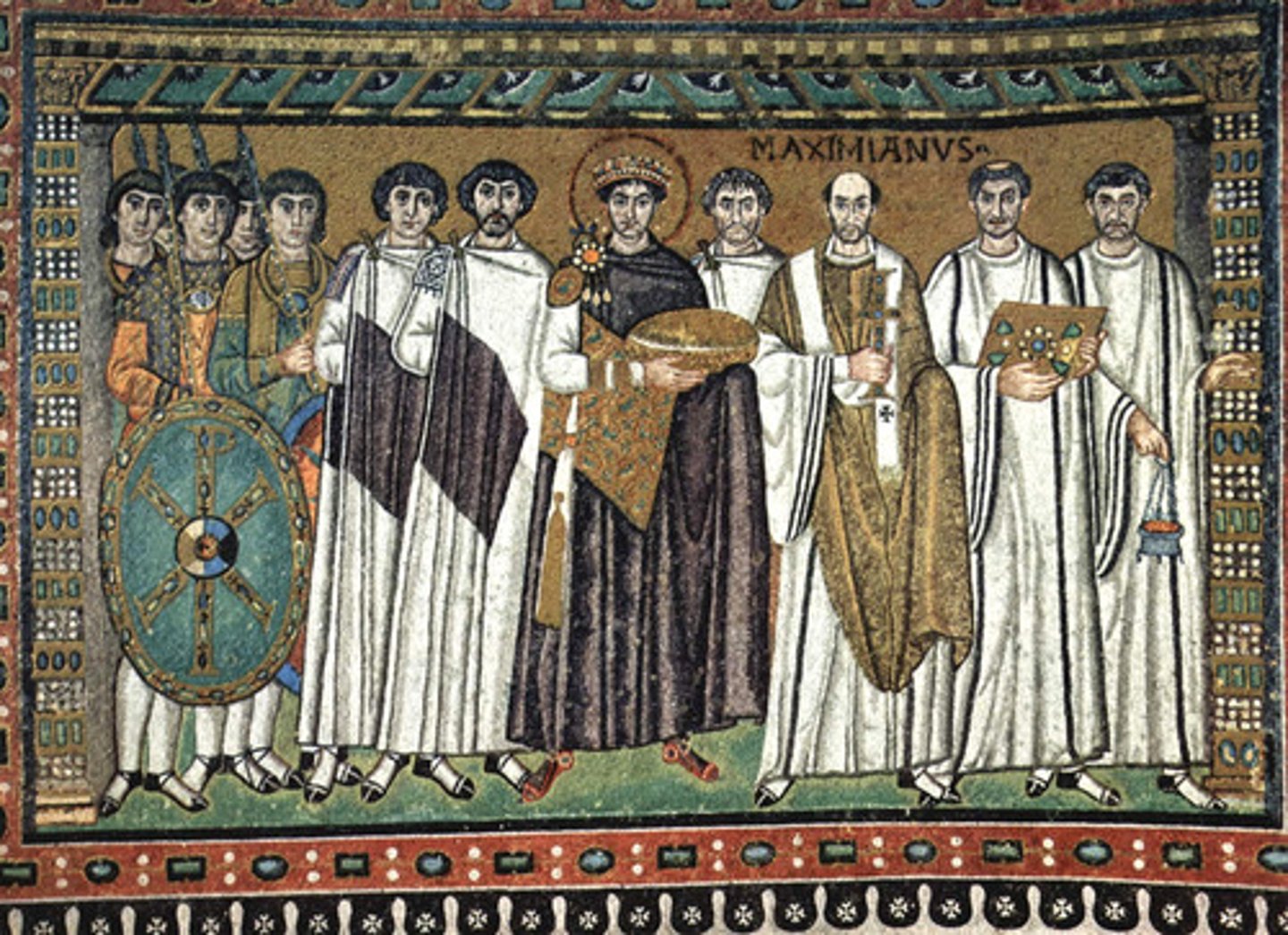
Who was Justinian I?
A Byzantine emperor who ruled from 527-565

What was the Justinian Code?
A systematic collection of Roman laws

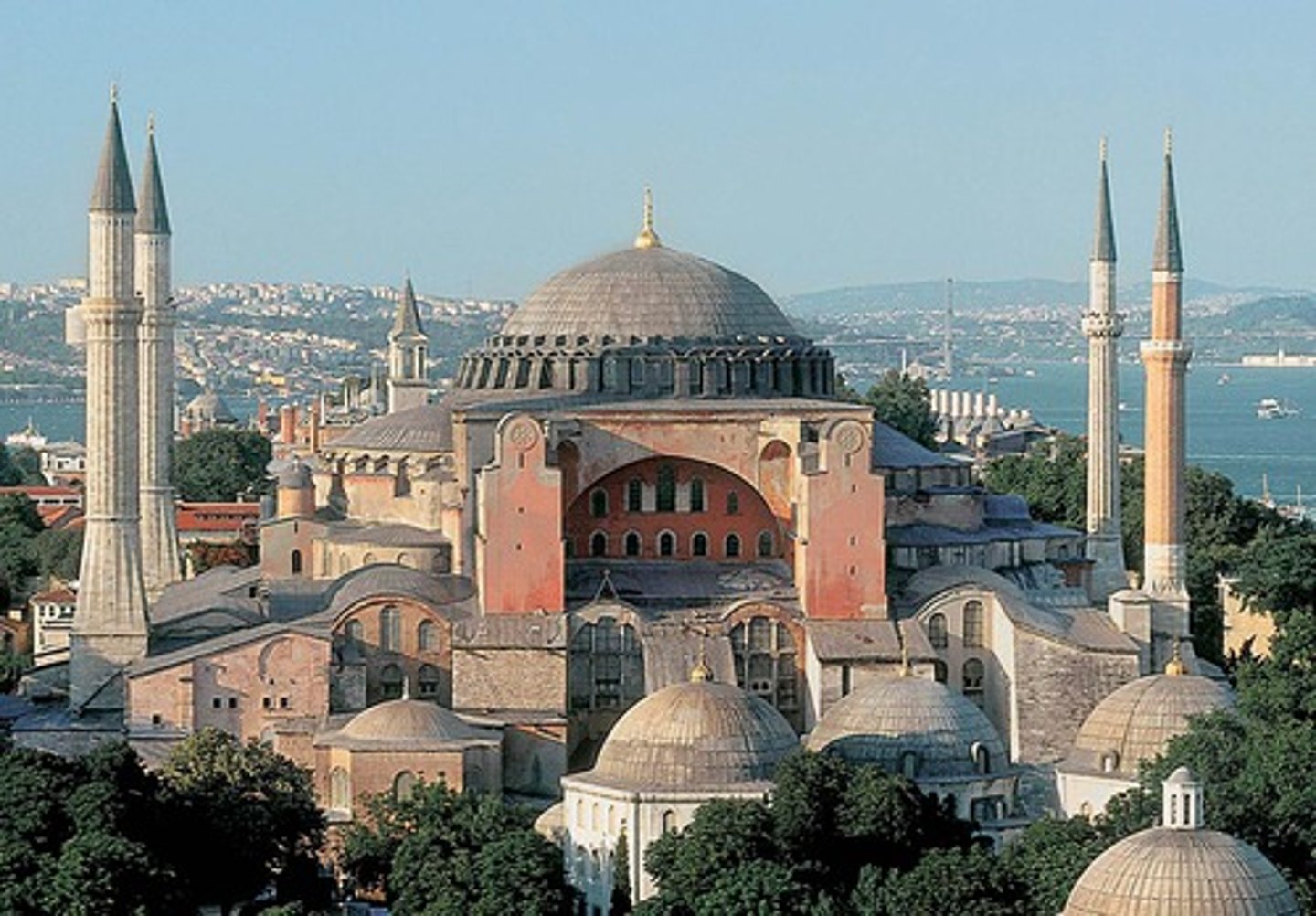
What famous church did Justinian build?
Hagia Sophia

Who was Empress Theodora?
Justinian's influential wife

What military achievement did Justinian attempt?
Reconquering parts of the Western Empire

What problem grew between East and West during this time?
Religious tensions

What language difference divided the Church?
Greek (East) vs. Latin (West)

What major event in 1054 resulted from East-West tensions?
The Great Schism
When did the Byzantine Empire fall?
1453, to the Ottoman Turks
