Neuroanatomy Exam 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Brodmann areas 1,2 and 3 collectively form what type of functional cortex?
Somatosensory cortex
Do areas 1,2, and 3 receive the same level of thalamic input?
No
Information to parvocellular cells comes from which retinal cells?
Cones
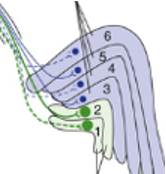
Which layers contain input from parvocellular cells and which from magnocellular cells?
Parvocellular = 3 - 6
Magnocellular = 1 & 2
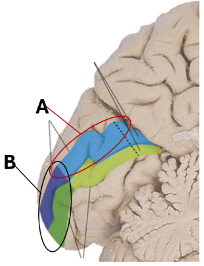
Which fibers terminate in A and B?
A = inferior visual field
B = macula
What is another name for optic radiations?
Geniculocalcarine fibers
The phenomenon whereby people with damage to the primary visual cortex (and so, cannot see) yet can indicate the direction of a moving object is known as what?
Blindsight
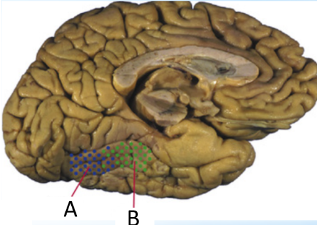
Damage to which region shown in the figure to the right would result in the patient having difficulty recognizing faces?
B
What pathway is increased in people who, when presented photographs, have an enhanced ability to distinguish fearful from angry faces?
Afferent Amygdala-Pulvinar path
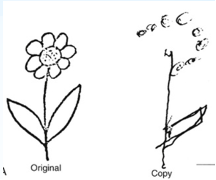
The figure to the right shows the drawing a patient made (“copy”) when they were asked to copy the drawing (“original”).
What neurological disorder is this patient demonstrating?
Contralateral neglect
What specific region of the brain is most likely damaged when contralateral neglect is present?
Right Parietal Lobe/ Right intra-parietal sulcus
A patient is unable to touch her nose with her index finger when asked to imitate the examiner's movement but is capable of doing so spontaneously if her nose itched. What specific region of the brain is most likely damaged that can explain this peculiar disability?
Left Parietal Lobe/ Left Intra-parietal sulcus
What is the main function of the corpus callosum?
Connects the two halves of the hemispheres together allowing for sharing of information between them
In the Ultimatum game, people tend to turn down offers of money that do not seem fair.
By inhibiting what region of the brain do people accept offers of money that they know are not fair?
Dorsolateral Pre Frontal Cortex
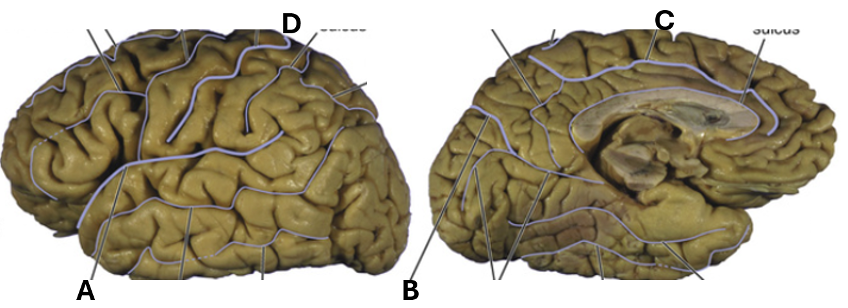
What is shown by “A”?
Lateral sulcus
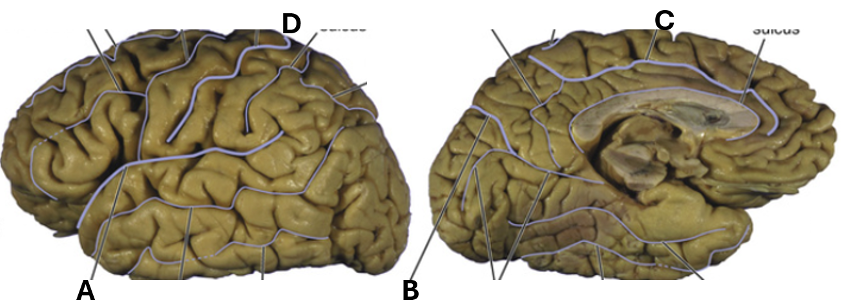
What is shown by “B”?
Parietoocciptal sulcus
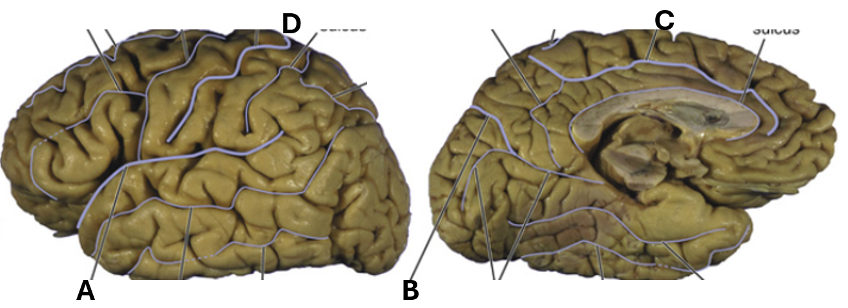
What is shown by “C”?
Cingulate sulcus
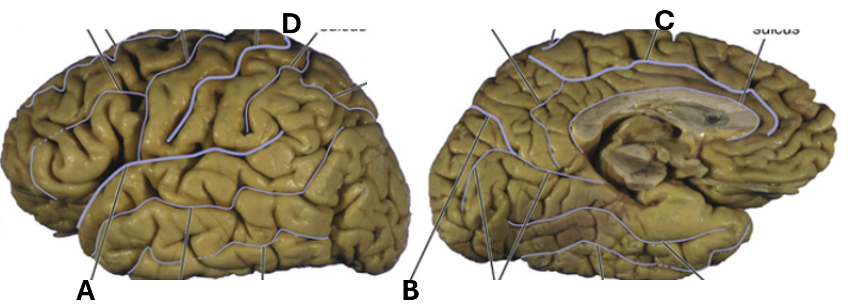
What is shown by “D”?
central sulcus
What are the primary functions of the frontal lobe?
short term memory, motor planning, speech generation, executive functioning
What are the primary functions of the parietal lobe?
perception of touch/pressure, speech comprehension (incomplete)
What are the primary functions of the temporal lobe?
speech comprehension, processing auditory information, long term memory formation, object recognition
What are the primary functions of the occipital lobe?
visual processing
Define the sensory homunculus in terms of cortical representation
Areas of the body with more sensory fibers occupy more cortical space.
Who was the first to map out the sensory homunculus on the cortex?
Wilder Penfield
Put the following in order in terms of auditory transduction in the brain starting at the ear (1):
a) medial geniculate body
b) trapezoid body
c) organ of Corti
d) primary auditory cortex
e) auditory nuclei
f) auditory nerve
C---F---B---E---A---D (incomplete, need to confirm)
Where does an earworm reside?
Anterior Superior Temporal Gyrus (aSTG)
What fissure (seen on the lateral surface of the whole brain) separates paleocortex from the neocortex?
The Rhinal fissure
How is paleocortex different from neocortex?
Paleocortex has 3-5 layers while neocortex has 6 layers
Name one cortical structure that is composed of archicortex
Hippocampus
Lorente de No, proposed that neurons in a cortical column are not simply linked linearly but possess one other feature. What is this feature?
Feedback loop
Who discovered that cells in different layers of the same column respond to the same stimuli?
Vernon Mountcastle
In the visual cortex, to what stimulus do neurons in an orientation column respond?
A particular orientation of a black bar on a white background (or a white bar on a black background)
Put the following in order in terms of light transduction in the brain starting at the eye.
a) lateral geniculate body b) retina c) primary visual cortex d) optic chiasm
B---D---A---C
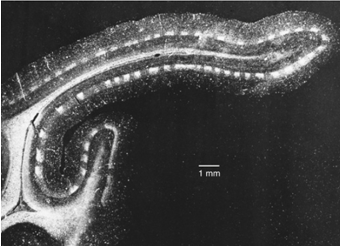
An autoradiograph of a section through the visual cortex of a monkey whose ipsilateral eye had been injected with a radioactive amino acid 2 weeks before sectioning is shown to the right. Explain why there are white and dark bands present.
Ocular dominance columns
Explain why, if one optic nerve is severed rostral to the chiasm, you will have impairment in one eye, but you will still be able to see the full visual field from the other eye.
The left visual field will still be able to send signal ipsilaterally (for the right visual hemi-field) and contralaterally (for the left visual hemi-field)
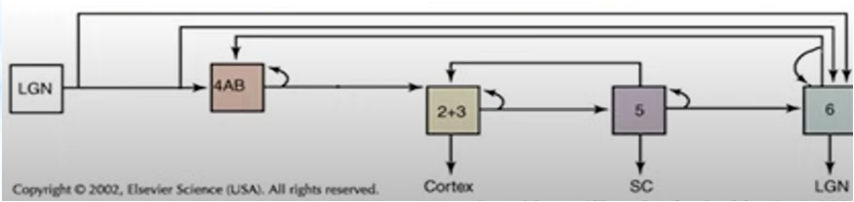
Explain this image.
LGN of thalamus sends info to layer 4, layer 4 sends info to layers 2&3, layers 2&3 send information to the cortex and layer 5, layer 5 sends information to layer 6 and back to layers 2&3, layer 6 sends information back to the LGN and layer 4.
How do association cortices receive input?
Serially and in parallel
Which cortical layer contains multiple sized pyramidal cells and loosely packed stellate cells?
VI (polymorphous)
Which cortical layer contains densely packed stellate cells only?
IV (inner granule)
Which cortical layer contains axons and dendrites and very few cell bodies?
I (molecular)
Which cortical layer contains large pyramidal cells only?
V (inner pyramidal)
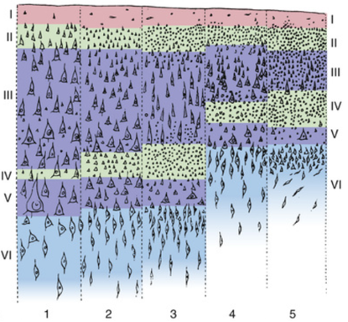
Which layer is Homotypical Cortex?
2,3, & 4
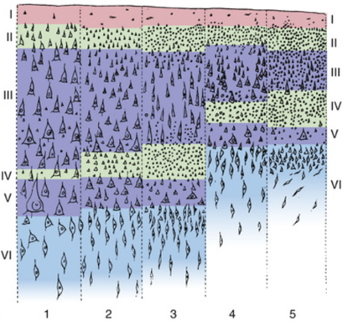
Which layer is Granular Cortex?
5
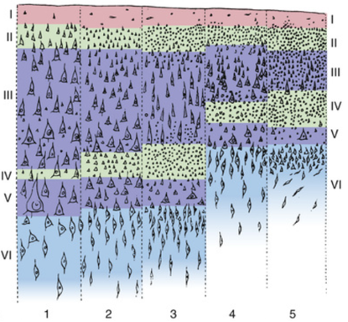
Which layer is found primarily in Sensory areas?
5
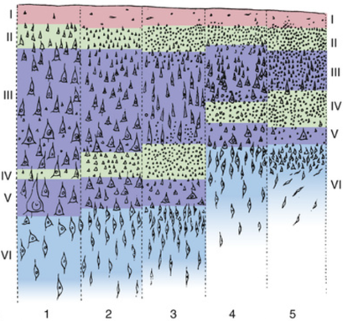
Which layer is found primarily in Motor areas?
1
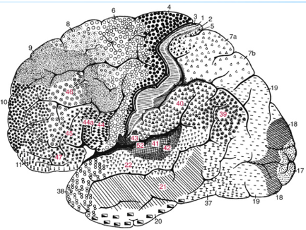
What was the staining technique used to generate the cortical map shown?
Nissl
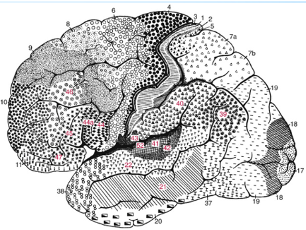
Who constructed this map?
Brodmann
Afferent and efferent connections in the cortex may be examined by using what staining technique?
Myelin/ Weigert stain
Name one structure to which efferents from layer VI project.
Thalamus
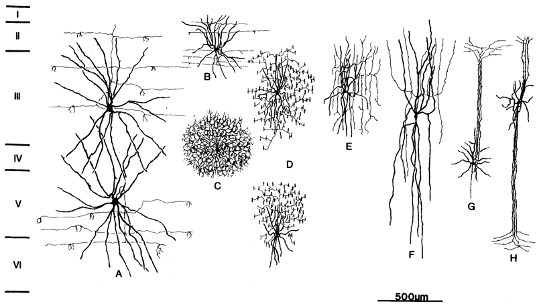
Which of these are projection neurons?
None
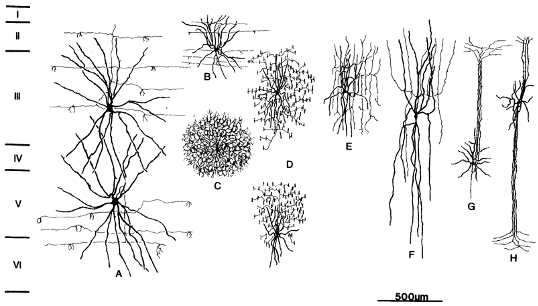
Which of these is a multi-polar neuron?
C/E/G
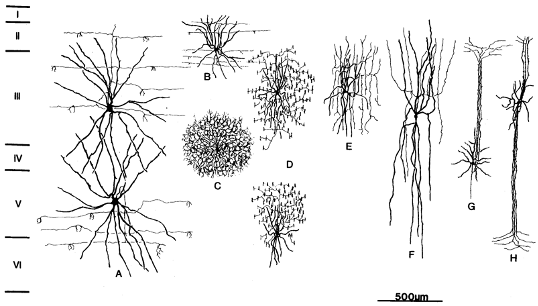
Which of these are known as chandelier neurons?
D
In addition to morphology, what two other pieces of information does the Patch-Seq technique provide to aid in elucidating neuronal function?
Electrophysiological data and proteomics
In a SLAM presentation, microglia were shown to have three major roles in shaping the post-natal brain. Name one of these processes.
Synaptogenesis (sculpting and pruning); synaptic plasticity; myelination
In a SLAM presentation, what tissue was shown to primary express SARS-CoV-2 entry factors?
Choroid plexus/ choroid epithelial cells
What cortical layer was affected and what process was disrupted in the COVID SLAM?
Layer 2/3; association fibers were disrupted leading to compromise of cognitive function.