Mutations and Synthetic Biology
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Mutation
Any mistake or change in the DNA sequence/order
What causes a mutation to occur?
When a mistake is made in mitosis or meiosis- the DNA polymerase misses the mutation while checking the DNA for mistakes during DNA replication. A mutation can also happen during lifetime, via chemicals or radiation.
Point Mutation
A change in a base pair in DNA. It changes that particular amino acid (called substitution; the amino acid is changed).
Ex. Sickle cell anemia
ABCDEFG → ABCDRFG
Frameshift Mutation
When a single base is added or deleted. This causes the rest of the bases to shift over. This is also called a base insertion/addition or deletion.
ABC DEF GHI →ACD EFG HI
Substitution Mutation
A nitrogenous base replaces another.
Types: Silent, missense, nonsense
Silent Mutation
If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT mutation.
Missense Mutation
If a substitution changes the amino acid to another amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE mutation.
Nonsense Mutation
If a substitution changes the amino acid to a “stop,” it’s called a NONSENSE mutation.
Chromosomal Mutations
Mutations dealing with parts of a chromosome instead of nitrogenous bases
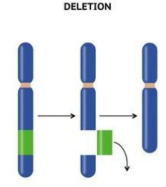
Deletion (chromosomal)
When part of a chromosome or allele is left out.
Ex. Prader-Willi Syndrome and Cri du’ Chat Syndrome
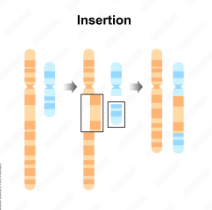
Insertion (chromosomal)
When a part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches itself to a sister chromatid (a copy of your original chromosome after DNA replication during cell division). WITHIN CHROMOSOME PAIRS.
Inversion
When a part of a chromosome breaks off and is put back in backwards. Inversions typically don’t affect the individual.
Ex. Leukemia
ABCDEFG → ABEDCFG
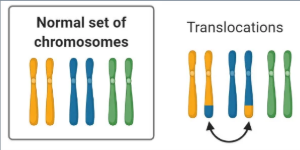
Translocation
When a part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome (not its copy/sister chromatid). WITHIN DIFFERENT CHROMSOME PAIRS.
Ex. Blaschko Linear Hypopigmentation
Errors in Chromosome Separation
Nondisjunction - when a homologous (same structure) chromosome fails to separate properly during meiosis cell division (production of sperm and eggs).
One cell might get more chromosomes or less chromosomes.
Trisomy (an example of nondisjunction)
Extra chromosome in the gametes
Ex. Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome
Synthetic Biology
Designing and engineering the genetic material of organisms to give them new abilities or functions.
Why do we use genetic engineering?
Improve agriculture
GMO’s - can improve the food product
Pest or insect resistance
Medical improvements - such as human growth hormones, insulin production, cancer therapy, vaccines and other medicines.
Other research purposes
CRISPR
CRISPR is a technology that allows scientists to modify the DNA in living organisms
It is being researched to treat diseases such as sickle cell disease and cancer
Sickle cell trials had positive outcomes
This is a very new technology