Opportunistic Yeasts in Clinical Microbiology II
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Opportunistic Yeasts
Common fungi causing infections in immunocompromised individuals: C. neoformans and C. albicans
Part of normal flora of mucus membraines
Candida albicans
Major pathogen causing various infections, part of normal flora.
Cryptococcus neoformans
Pathogen associated with pulmonary infections and immunosuppression.
Blastoconidia
Asexual reproduction form produced by budding yeasts.
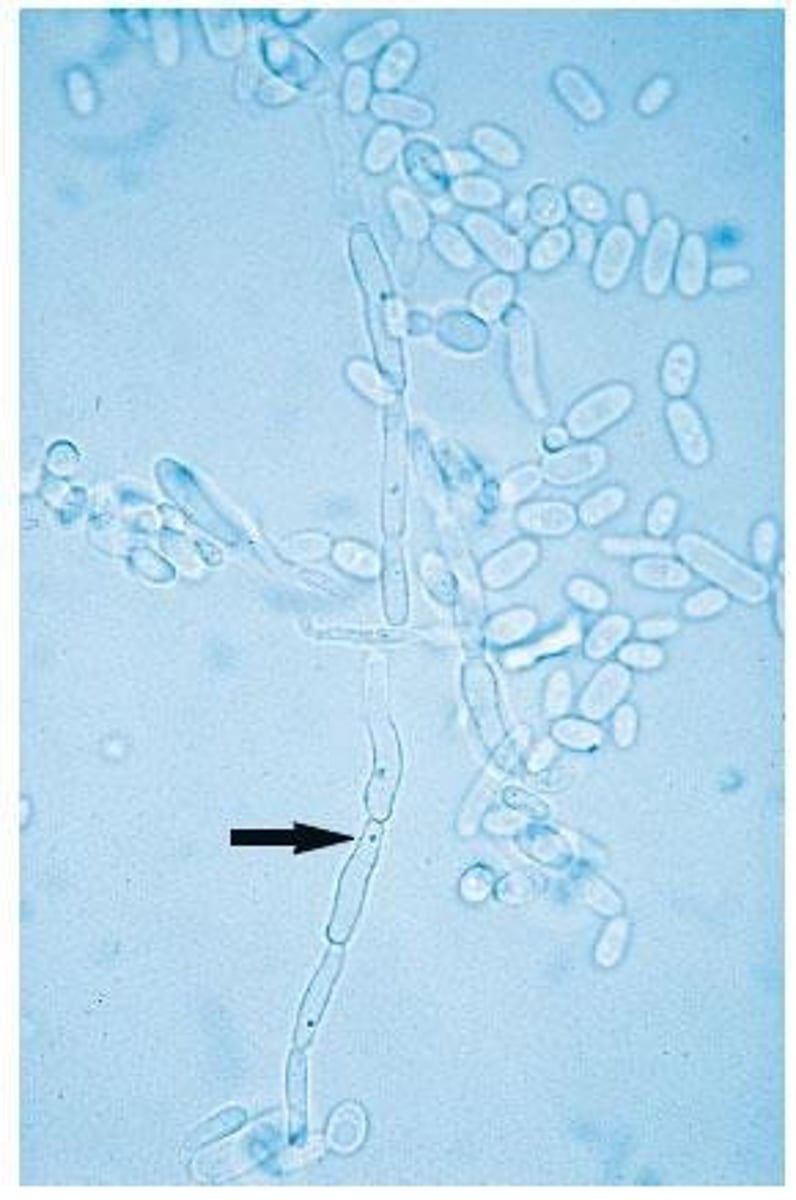
Pseudohyphae
Tubular structures without septa just contstriction, seen in some yeasts.
Hyphae
Filamentous structures formed by some yeast species.
Germ Tube
Tubular out-pouching used for yeast species identification. C. albicans is positive
Candidiasis
Infection caused by Candida species; opportunistic in immunocompromised pts., diabetics, and antibiotics
Azoles
Class of antifungal drugs effective against yeast infections.
Amphotericin B
Potent antifungal used for severe fungal infections.
Cornmeal Agar
Medium enhancing conidia formation for Candida differentiation.
CHROMagar
Differential media showing color changes for Candida species.
Birdseed Agar
Medium for Cryptococcus neoformans, produces dark colonies.
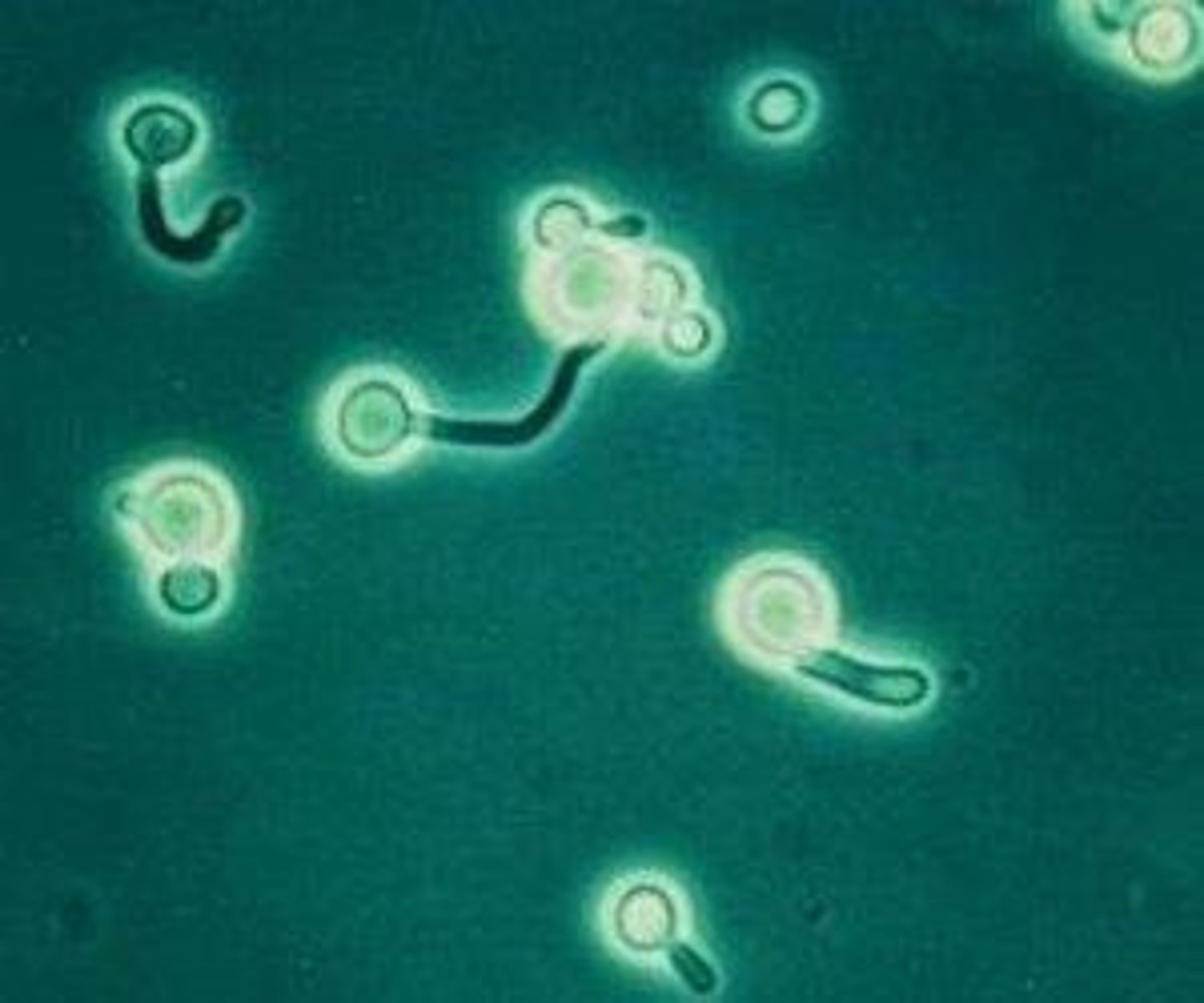
India Ink
Staining method to visualize capsules around yeasts, especially C. neoformans which makes black colonies
Serological Tests
Detect capsule antigen in body fluids for diagnosis.
Latex Agglutination
Test indicating infection via detectable capsule antigen.
Phenol Oxidase
Enzyme converting phenolic compounds to melanin in Cryptococcus.
Geotrichum candidum
Causes geotrichosis, wound infections, skin lesions, and thrush; part of normal flora and produces arthroconidia.
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Yeast causing Interstitial Plasma Cell Peumonia, especially in immunocompromised patients; cannot be cultured
Carbohydrate Utilization
Testing method to differentiate yeast species based on growth.
Rapid Urease Test
Identifies urease production to differentiate yeast species.
C. albicans
NF of mouth, GI, and urogenital tract
Diseases: thrush, UTI, vaginitis, diarrhea
C. albicans colonies
white to cream colored, smooth, creamy, extensions or "feet" around perimeter
C. albicans Microscopic Morphology
Blastoconidia, pseudohyphae, true hyphae, chlamydoconidia, germ tubes
C. glabrata
UTIs commonly in the immunocompromised but also NF
C. glabrata colonies
Pinpoint, white, smooth colonies showing growth in 72 hrs
C. tropicalis
Long pseudohyphae with blastoconidia causing candidemia and fungal sepsis
C. dubliniensis
Highly associated with HIV+ pts.
Similar to C. albicans but more SEVERE
C. krusei
Long blastoconidia on tree-like branches of pseudohyphae; multidrug resistant in immunocompromised
Crytococcosis
A pulmonary infection that disseminates in the blood
C. neoformans
Present in bat or bird droppings, pigeon poo, decaying plants, and milk
C. neoformans diagnosis
Macroscopic: large, tan, mucoid, black on birdseed
Microscopic: large, round, budding yeast