yr 10 bio- Genetics and evolution
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Where is genetic information stored?
Genetic information is stored inside the nucleus of an organism’s cells
Genetic information is found in a molecule - DNA
DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid
The structure of DNA
Structure is known as a double helix.
A DNA molecule is like a ladder. Each "rung" of the ladder is made up of two smaller molecules, known as bases.
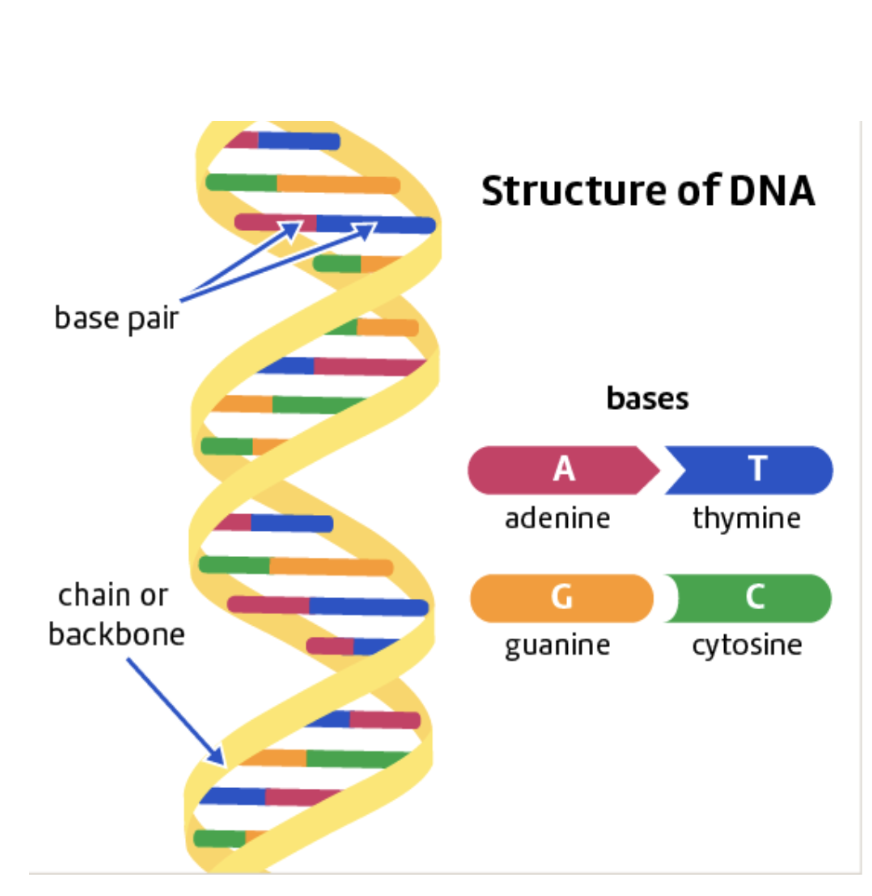
DNA bases
adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
DNA base pairing rule
Each base can only join with one other type of base to form a rung of the ladder:
adenine (A) and thymine (T) join together – A–T
guanine (G) and cytosine (C) join together – G–C
Each A-T or G-C combination is known as a base pair.
The two bases in a base pair are complementary.
What is a gene
A gene is a section of a DNA molecule
It provides instructions for building a specific protein.
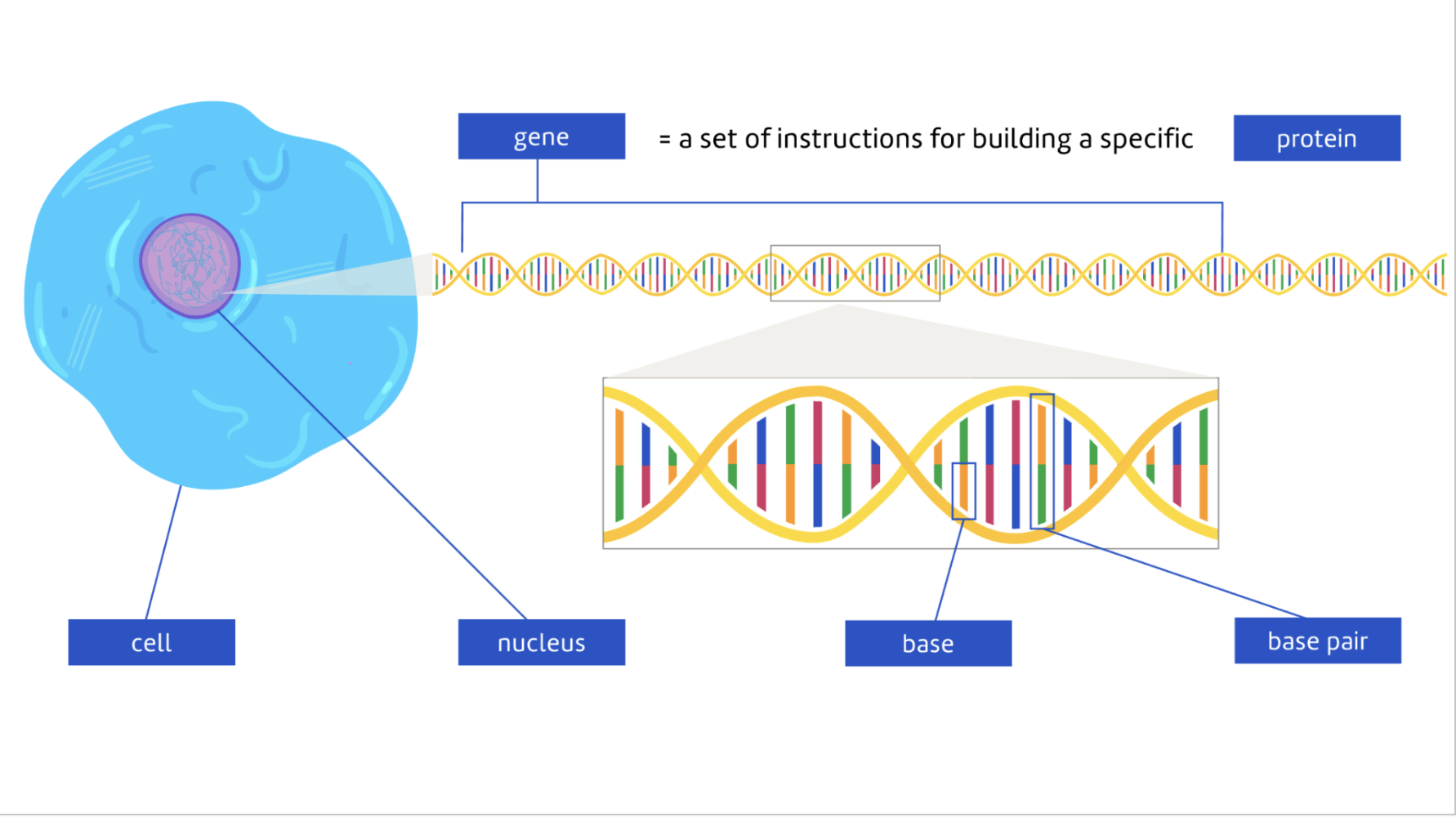
How information is passed down from parent to offspring
Genetic information is passed down from one generation to the next in packets or units. These are known as genes.
The passing down of traits via genes from one generation to the next is called inheritance.
Proteins
Proteins are molecules
The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid
Amino acids bond together → proteins
Proteins make up most of the cells & tissues of an organism’s body
How does DNA build proteins
DNA is stored in a cell's nucleus.
Each gene in a strand of DNA is a recipe for making a specific protein.
Proteins are built out of amino acids outside the nucleus, in the cell's cytoplasm.
What’s the role of RNA
Transcription is the process where a cell creates a RNA copy of a DNA sequence.
This RNA molecule is single stranded.
The RNA carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where proteins are made.
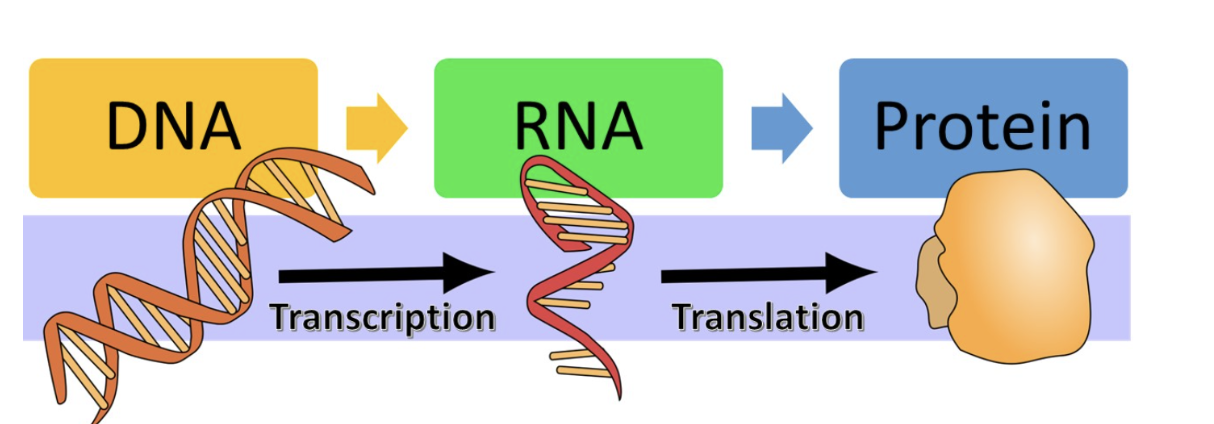
RNA bases
RNA contains a base that's not found in DNA.
In place of thymine (T), RNA uses the base uracil (U).
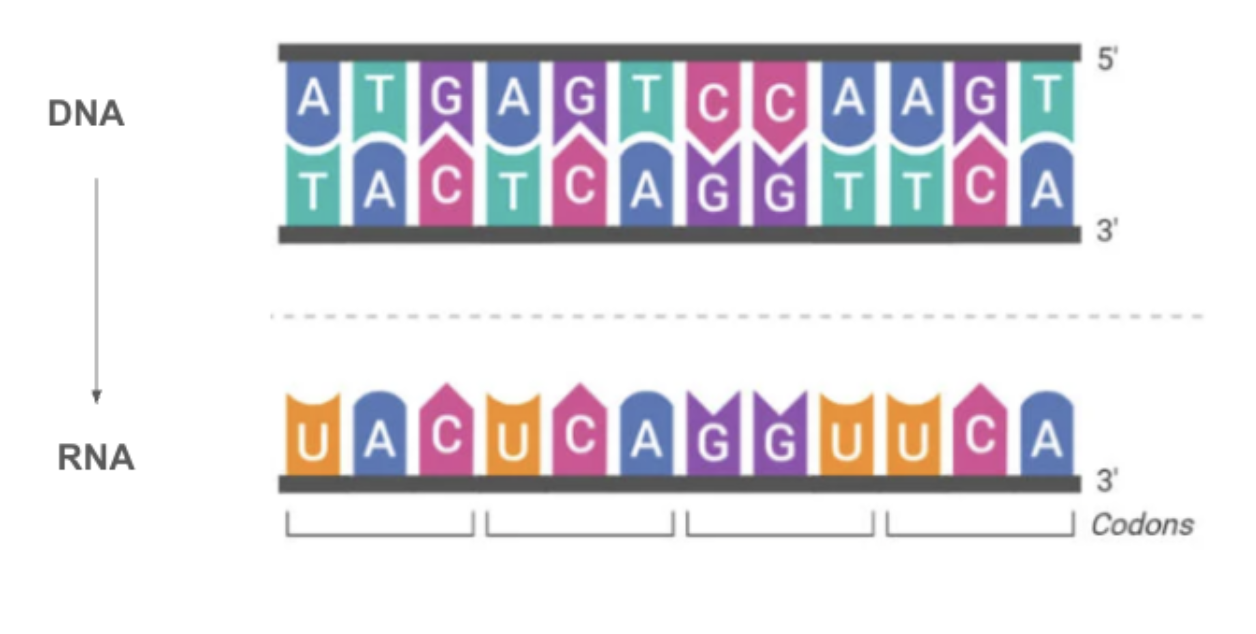
Codons
The bases in the RNA strand provide instructions for building a specific protein
The cell "reads" the bases of the RNA in groups of three.
Each group of three bases is called a codon.
Codons "code" for amino acids.
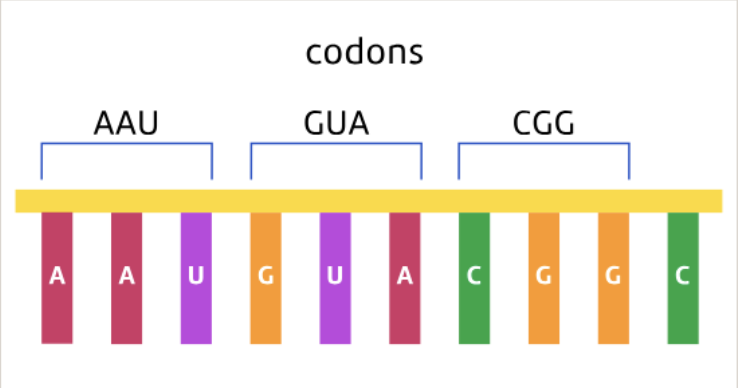
How codons determine amino acids
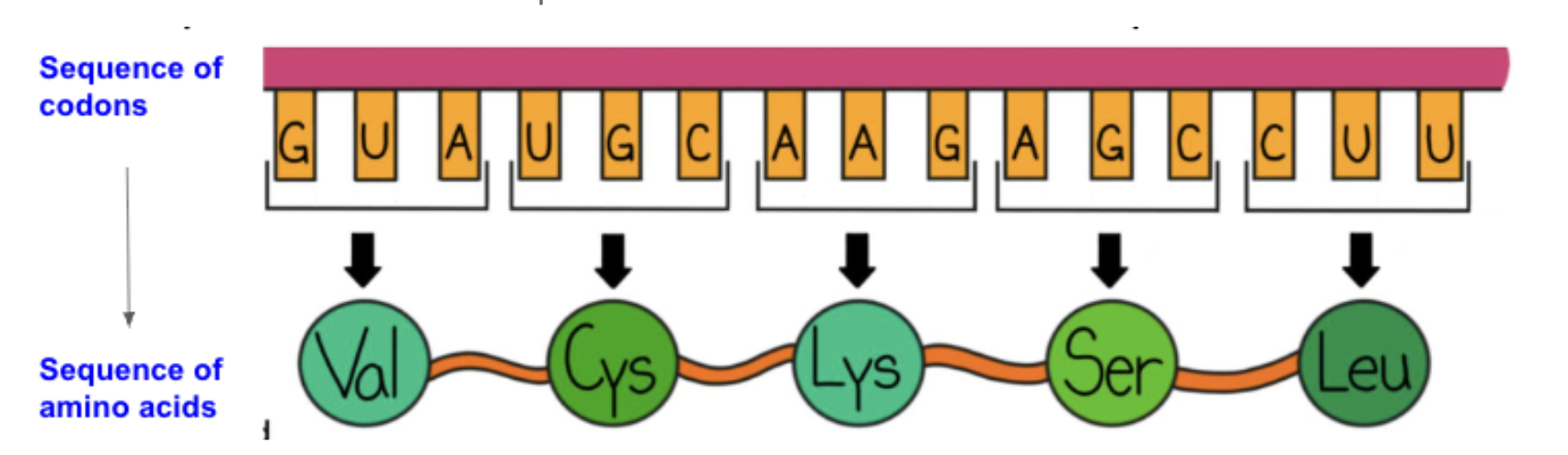
The set of bases in a gene make up the code for that gene.
These are used to create an RNA molecule, made up of a sequence of codons.
The codons that make up the RNA molecule determine the sequence of amino acids needed to build a protein.
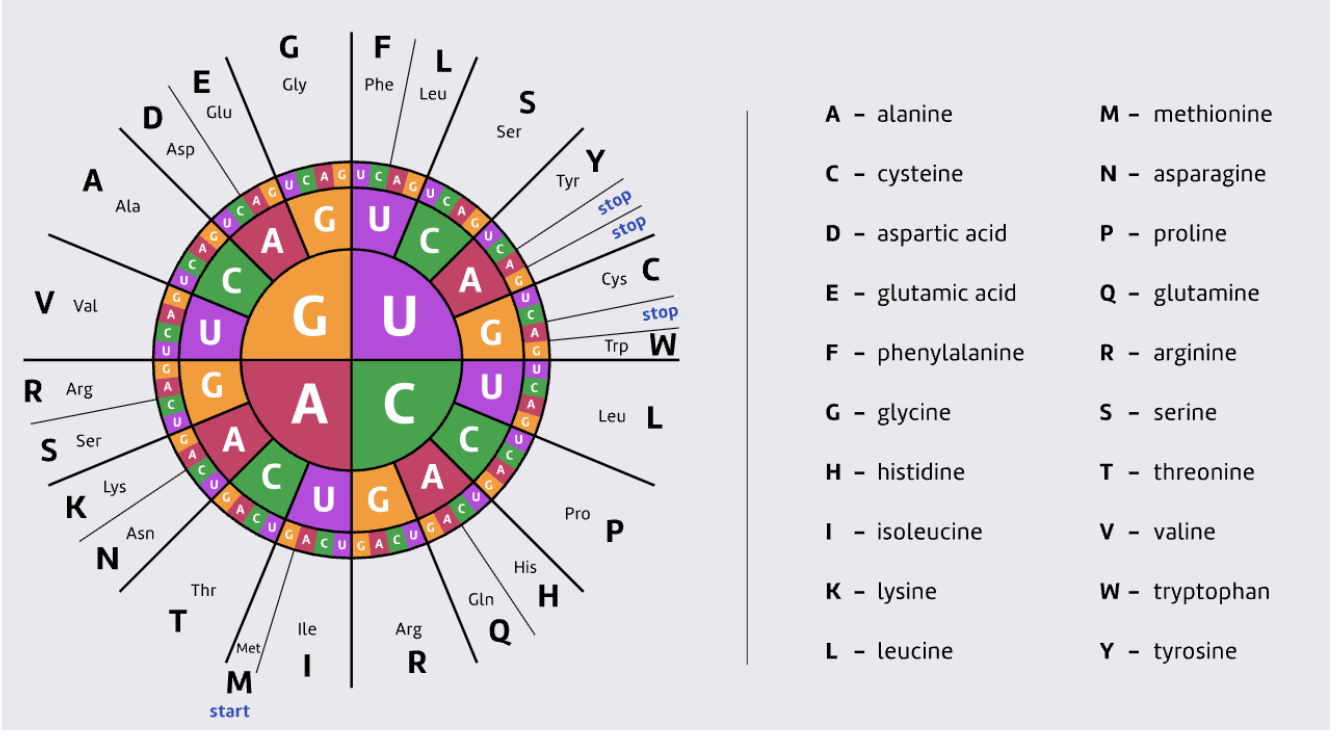
The codon wheel
There are 20 amino acids found in human proteins
Which codons code for which amino acids can be shown in the codon wheel.
Work from the inner circle outwards to determine the 3 letter sequence of the amino acid
AUG = Met
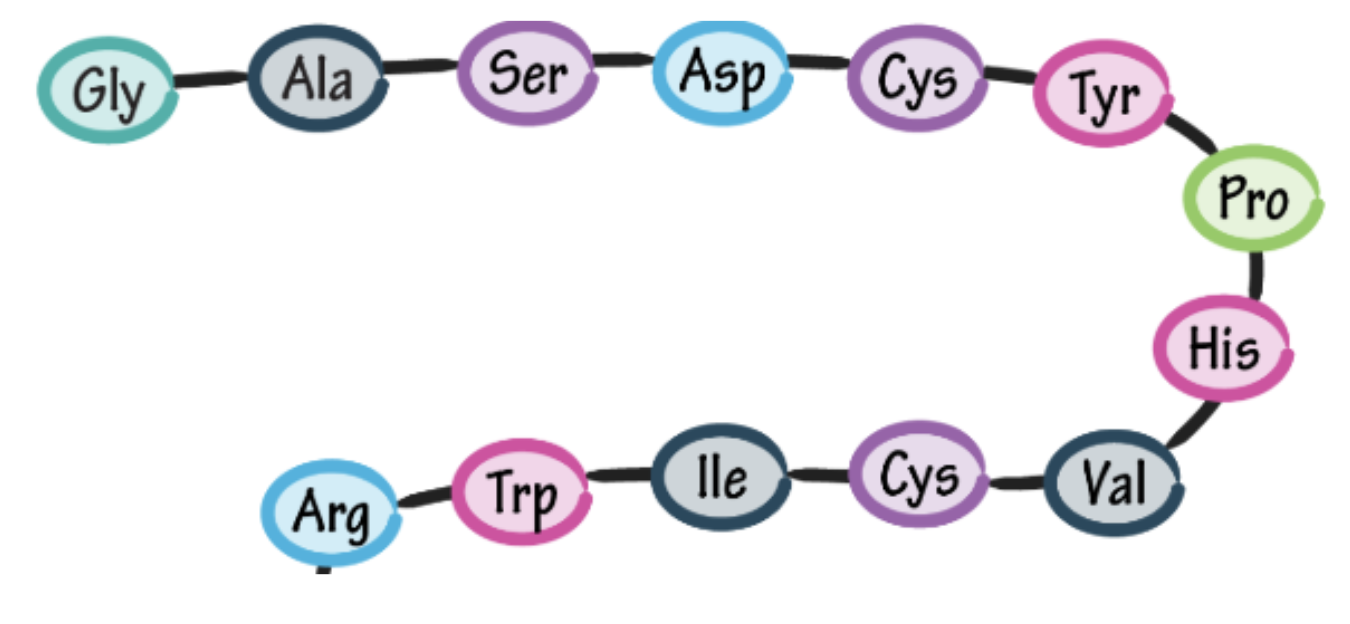
Building a protein
A sequence of codons determines the order in which amino acids are strung together to build a protein.
What is a mutation?
A change in the DNA sequence of an organism
Changes can then be passed down to new generations
There are many types of mutations
Small changes in the DNA sequence can have big consequences
Types of mutations
Point mutation- a single base is changed
The three point mutations are:
Insertion
Deletion
Substitution
Insertion
The addition of one or more bases, this causes a frameshift to occur - a change in the amino acid sequence.
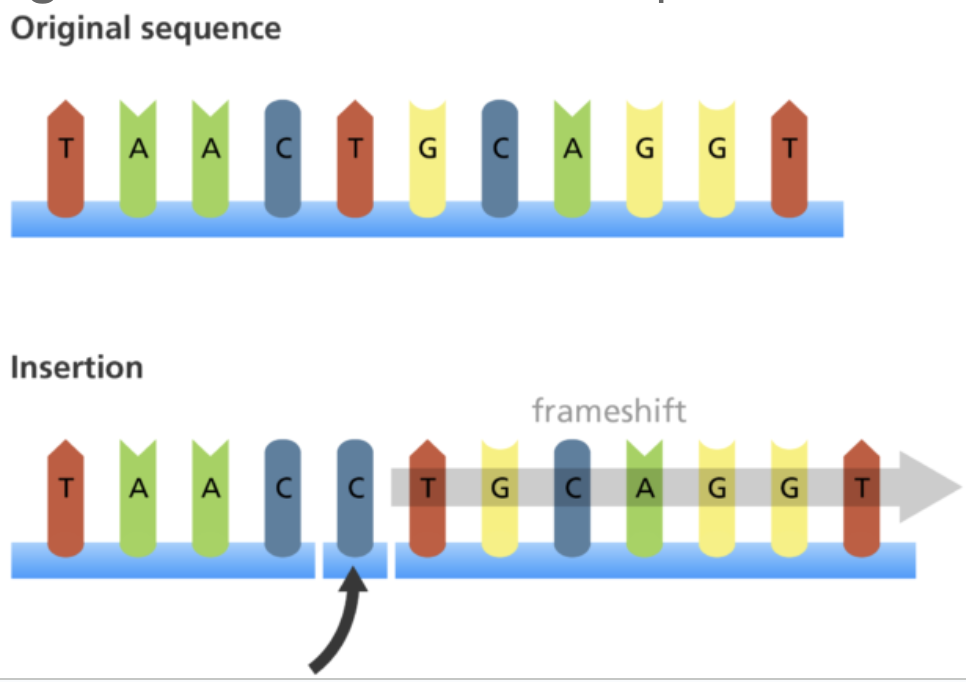
Deletion
When one or more bases are removed from the sequence, this causes a frameshift to occur.
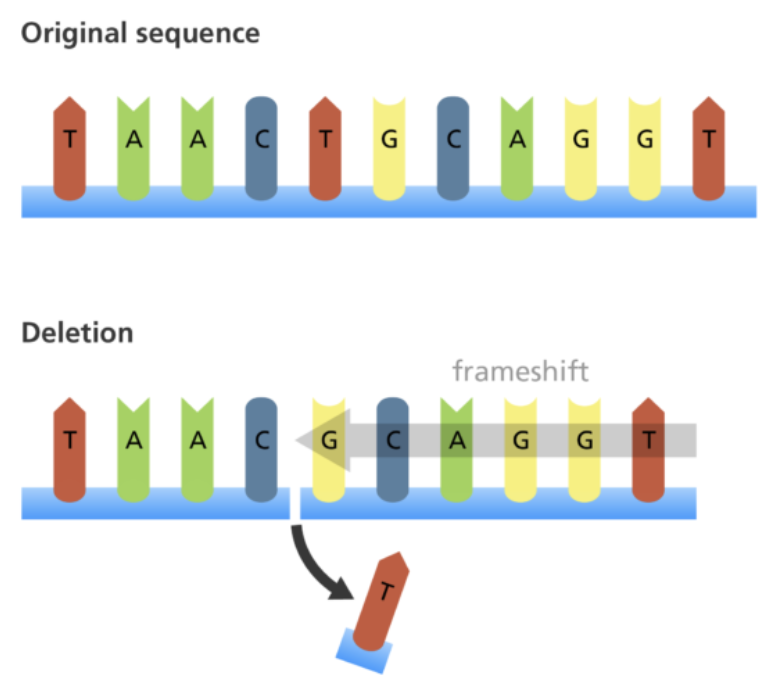
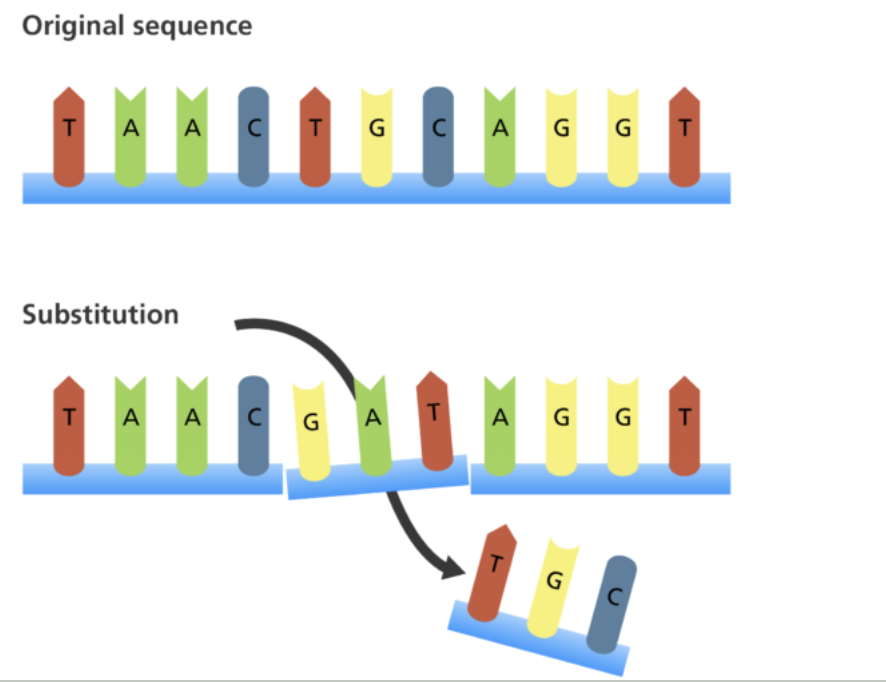
Substitution
When one or more bases in a sequence is replaced by the same number of bases. No frameshift occurs.
Genetic traits
Traits are features of an organism determined by your genes
Genes are inherited from your parents
E.g. eye colour, skin colour, hair colour
Simple inheritance patterns diagram
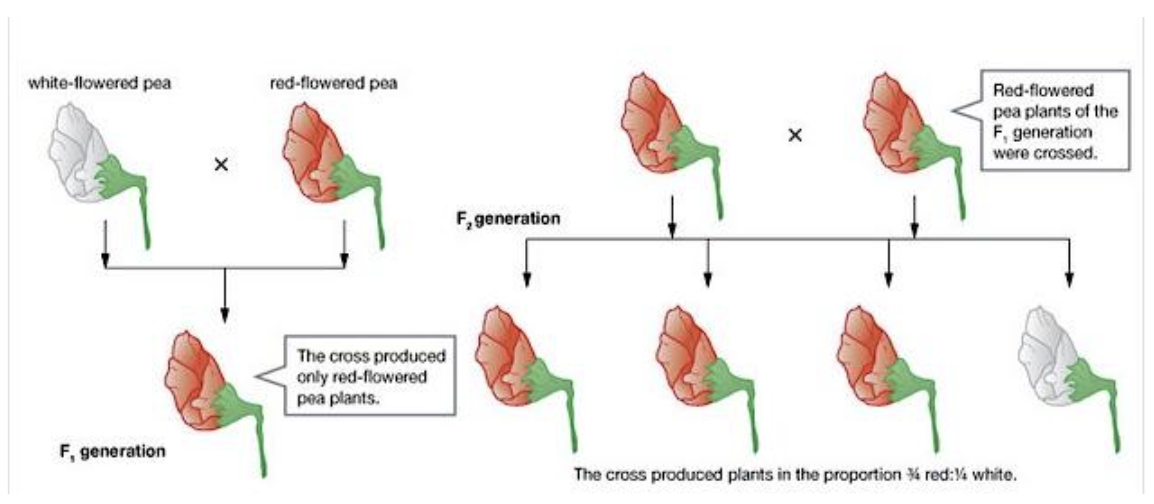
Dominant and recessive traits- pure breeding red and white pea plants
In pure-breeding lines, only the characteristics of the parents will be shown in the offspring.
Red-flowered will produce red-flowered
White-flowered will produce white-flowered
However, when a red-flowered pea plant and a white-flowered pea plant were crossed, all the offspring had red flowers.
This means that the red characteristic is dominant and the white characteristic is recessive.
Genes and alleles
When there is more than one possible characteristic for a particular gene, the different possibilities are called alleles.
Alleles are variations of genes.
In Mendel’s work it showed that pea plants have two alleles for flower colour, the red dominant allele and the white recessive allele.
Using alleles
Using our knowledge of alleles and which is dominant and which is recessive, we are able to predict the characteristics of offspring for particular genes.
For example:
A red pure-bred flower would be written as: RR
A white pure-bred flower would be written as: rr
A red flower produced by crossing a white and red would be written as: Rr
How alleles represent dominat and recessive genes
The dominant allele is always written with a capital letter. Eg R
The recessive allele is always written with a lower case letter. Eg r
RR or Rr = red flowers because the red is dominant
rr = white flowers because the white is recessive
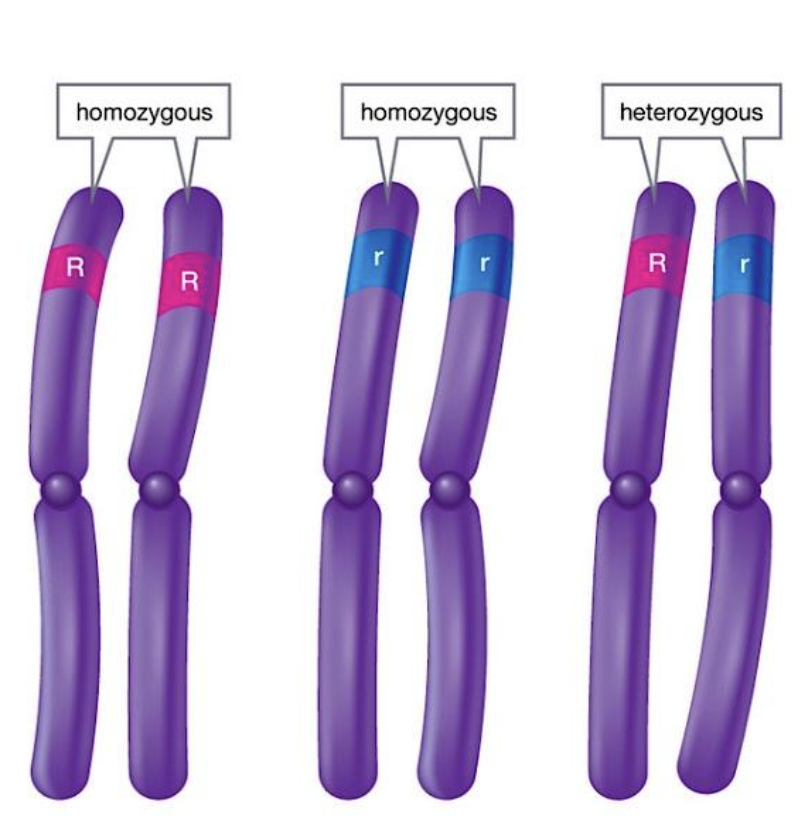
Different types of alleles
If the code has two of the same case letters such as RR or rr = homozygous
If the code has two different case letters such as Rr = heterozygous
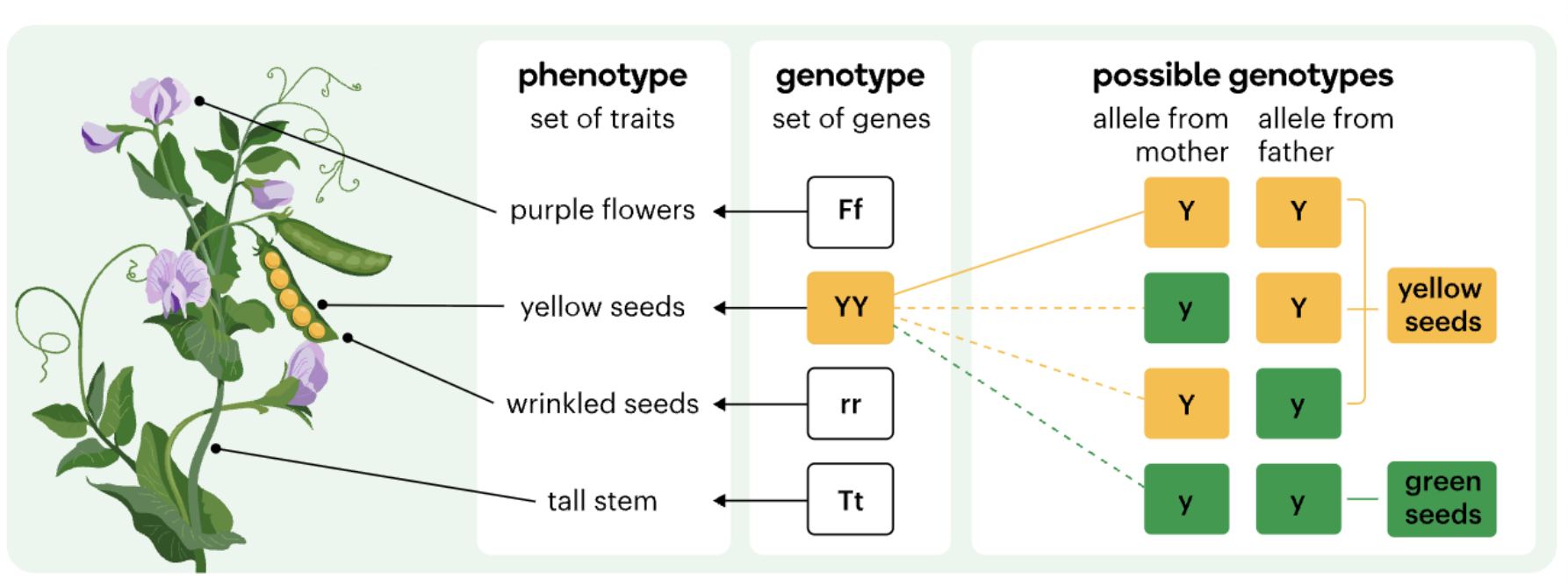
Phenotype vs genotype
A genotype is a genetic code for your characteristics
(invisible code in your DNA)
eg. RR, Rr or rr
A phenotype is the visual appearance or traits produced by the genetic code
(what we can see looking at organisms)
eg red flowers or white flowers.
Phenotype and genotype in pea plants (image)
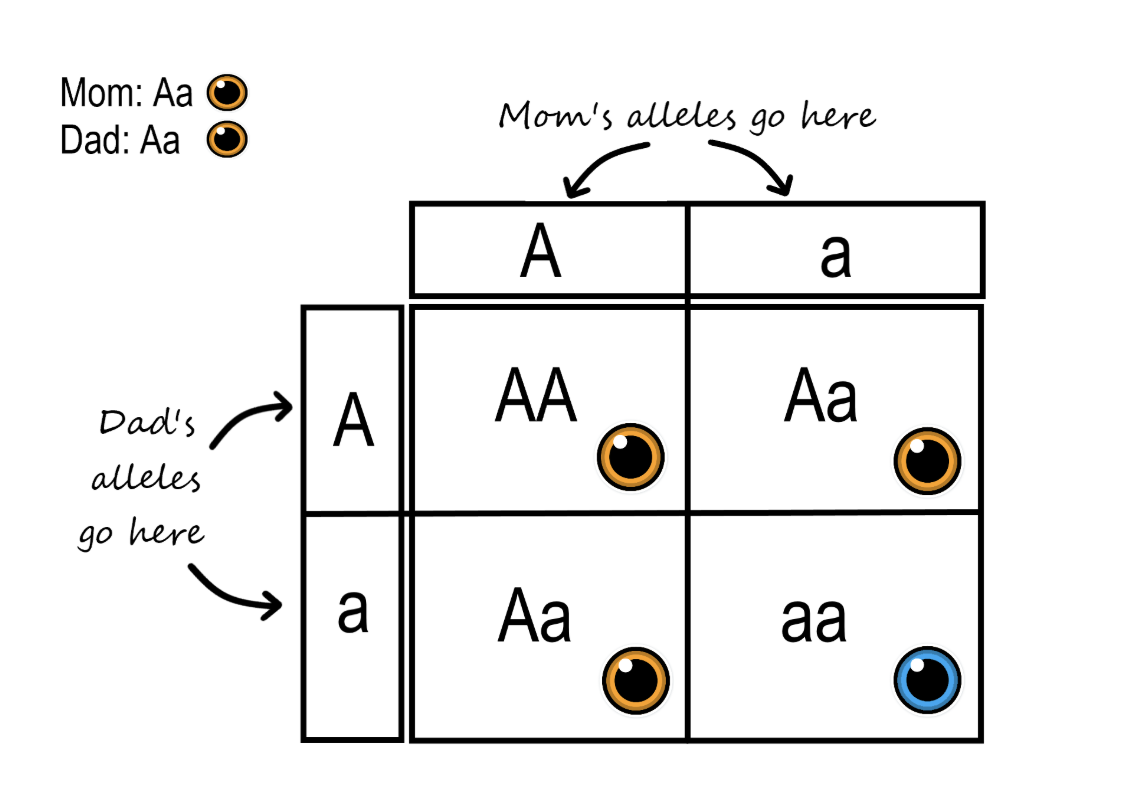
What is used to predict the inheritance of traits
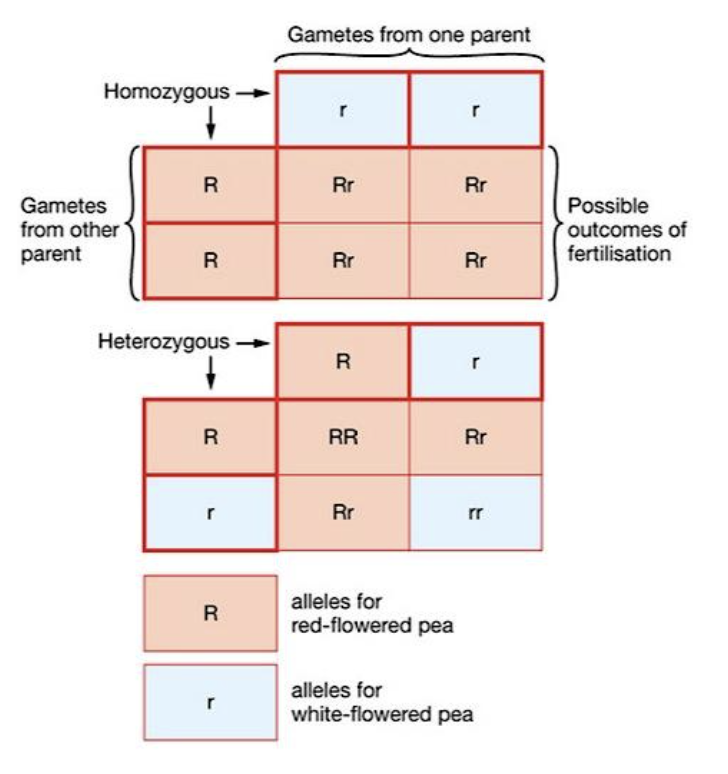
Punnett squares are used to determine the possible types of offspring that could result from a cross.
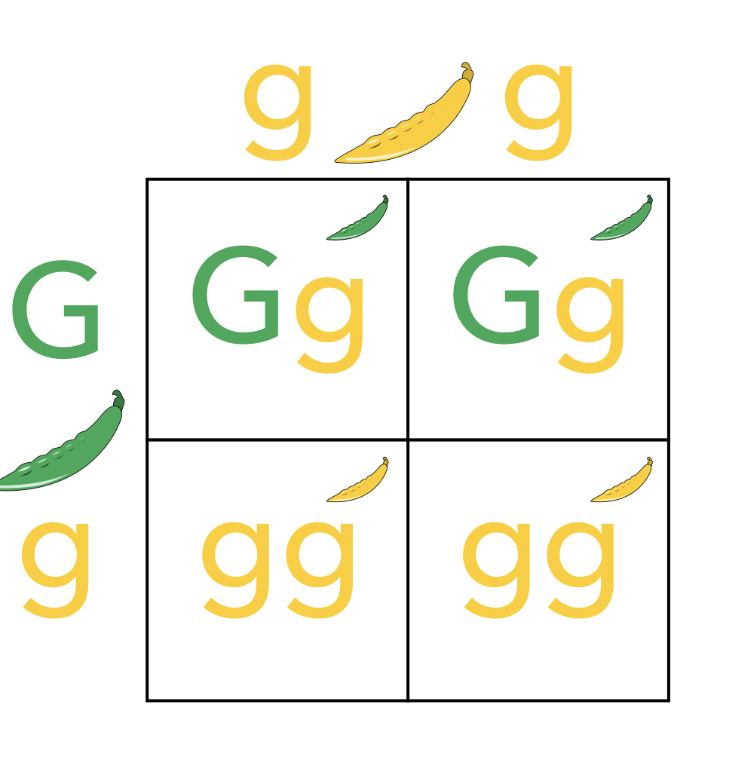
Punnett squares
The top row = possible gametes produced by one of the parents
The side column = possible gametes produced by the other parent
In each square is a possible outcome of fertilisation.
Variation
Differences in traits between individuals of the same species are known as variations.
Variation is produced due to mutation
Genetic trait
A feature that is passed down by genes from one generation to the next.
E.g skin colour
Acquired trait
Gained during an individual's lifetime.
They are not determined by genes in an individual’s DNA.
Random Mutations
Variations in traits can arise from mutations (small random changes) in DNA.
The changes can produce new variations in traits.
They may be harmful, beneficial or have no impact on the organisms survival.
New mutations arise in each generation through reproduction
The evolution of new species needs random mutations to produce genetic variations. For example, variations in three tree frog species.
Evolution
any change in the genetic traits in a population over many generations
Population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same place.
Variation in evolution example
A population of beatles might begin with very little variation in colour.
In each generation, a random mutation can occur to produce a new colour.
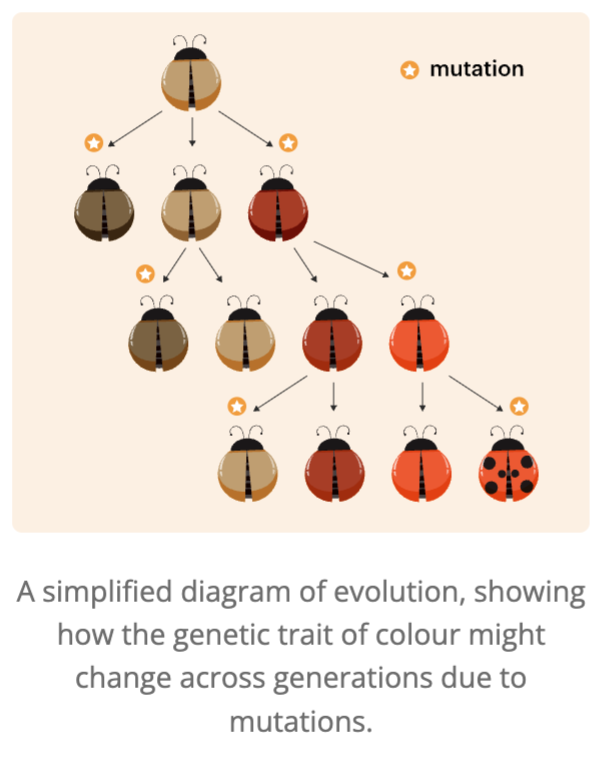
Why is genetic variation important
Because it is needed for a population to evolve.
The amount of variation is genetic diversity
Why is genetic diversity important
Because it helps a species survive when its environment changes.
Scientific theory
A well-supported explanation of a natural phenomenon, developed from
a large body of evidence collected through repeated testing
careful observation
refinement over time.
Fossil records
Show a sequence of gradual changes, showing how complex organisms have evolved from simpler ancestors
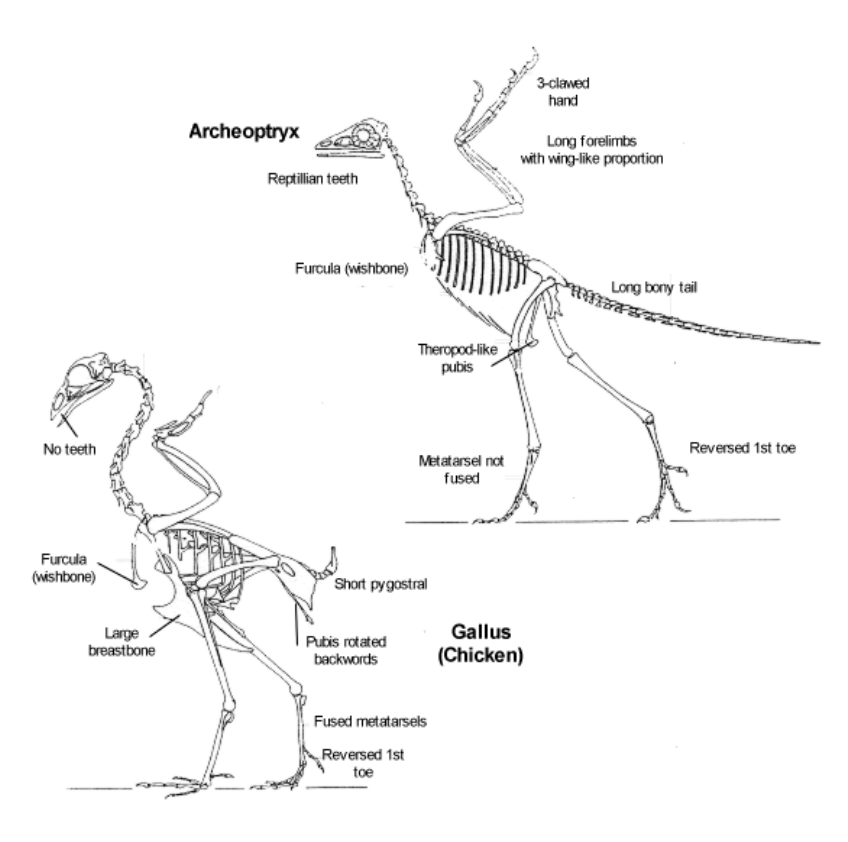
Transitional fossils
display characteristics of two distinct groups and help bridge evolutionary gaps.
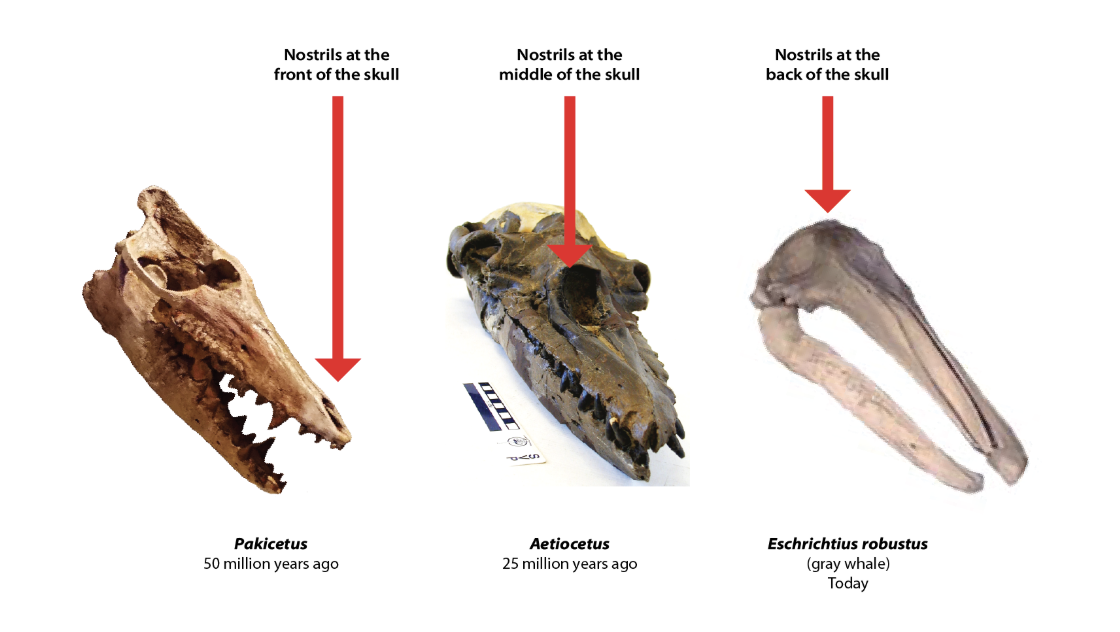
Homologous structures
Body parts that have the same basic structural design but may serve different functions in different organisms.
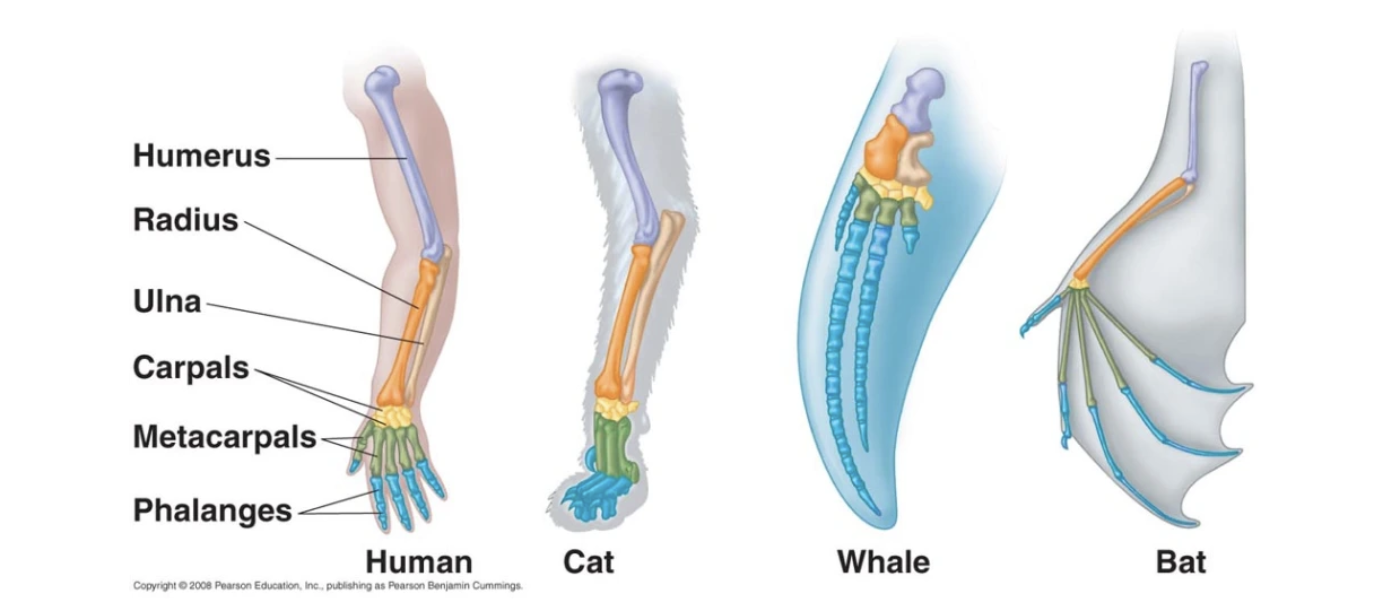
DNA sequences
show the generic similarities between species, which supports evolution.
All living organisms use the same basic genetic code.
More similar genetic material = more recent common ancestor
Natural selection
The survival of organisms that are better adapted to their environment.
This process can result in the evolution of a population.
Better adapted variations survive and reproduce in greater numbers.
So, over many generations, they become more common.
Selection pressure
Any challenges that affects an organism’s ability to survive in a particular environment.
Example of selection pressure
hunting by predators
access to resources, such as food, shelter, territory and mates
human activities, such as hunting and pollution
Selection pressure: frequency
Selection pressures can either increase or decrease the frequency of a genetic trait.
Traits that help organisms survive and reproduce become more frequent.
Traits that make it more difficult for organisms to survive and reproduce become less frequent.
Species
Any group of organisms that can breed to produce fertile offspring. The ability to reproduce allows a species to continue to exist and evolve.
Speciation
The process of forming a new species
Process of speciation
Isolation of a population
Evolution under different selection pressures
Distinct species- can no longer breed to produce fertile offspring
Adaptation
Any genetic trait that helps an organism survive in its environment
structural adaptation
a physical feature of the body
behavioural adaptation
a behaviour or action
a physiological adaptation
an internal body process
Amino acids
Molecules that are the building blocks of proteins
Hypothesis
a testable, proposed explanation for an observation or phenomenon