health beliefs
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
block three week 1 socpop
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
lay health beliefs
beliefs are things we believe to be true
perspectives of ordinary people
often complex and sophisticated
may be sensible or irrational
lay health belief example
a person believing they’re not at risk of heart disease because they’re thin
antibiotics will help cold symptoms
where health beliefs come from
rooted in socio-cultural contexts in which we live
shaped by people’s
place in society
culture
personal biography
social identity
can be informed by medical and health knowledge or can contradict it
culture
values, norms and traditions that affect how individuals of a particular group perceive, think, interact and behave and make judgements about their world
importance of culture
shapes the way we think, feel and experience our lives
we all have multiple cultures
why lay health beliefs are importance to doctors
insight into needs of your pts
info and support
influence health seeking behaviour
how people respond to symptoms
decisions about consulting
expectations about treatment
concordance with treatment plans
therefore important to explore your pts health beliefs in order to understand, assess and provide appropriate care and treatment
why people decide to consult a doctor
perception of symptoms
explanation of symptoms
evaluation of symptoms
health beliefs and behaviours: predicting COVID 19 vaccine hesitancy
gender was most common influence on health behaviour- followed by education, age, geographical location, occupation, income
other factors: COVID knowledge, prior COVID diagnosis, flu vaccination history
health behaviours defined
behaviours relayed to the health status of the individual
good health behaviours: sleeping (7-8 hours), regular exercise, healthy eating, breakfast
health protective behaviors: wearing a seatbelt, regular health checkups, health screening
health impairing habits: smoking, high fat diet, alcohol abuse
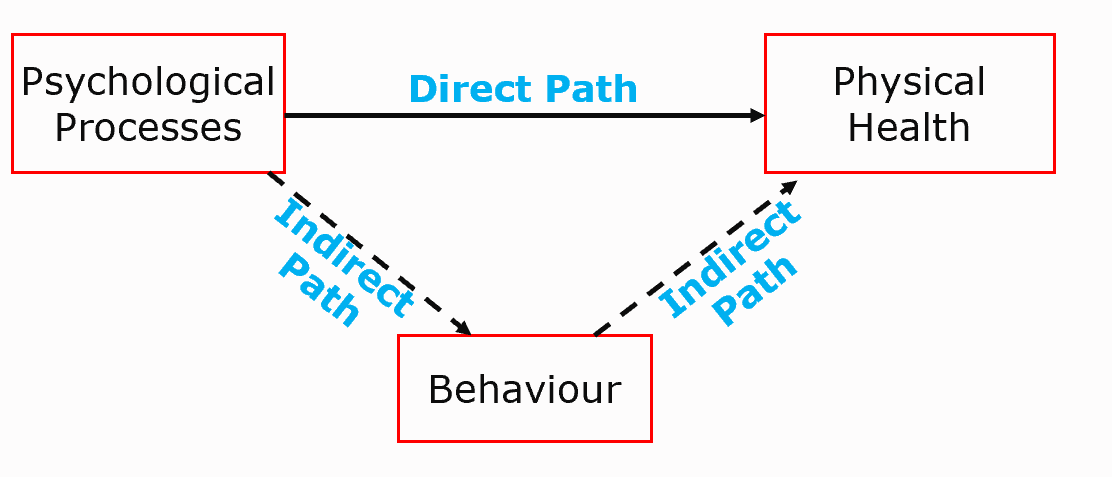
dual pathway model
2 broad ways in which psychological processes may influence physical health
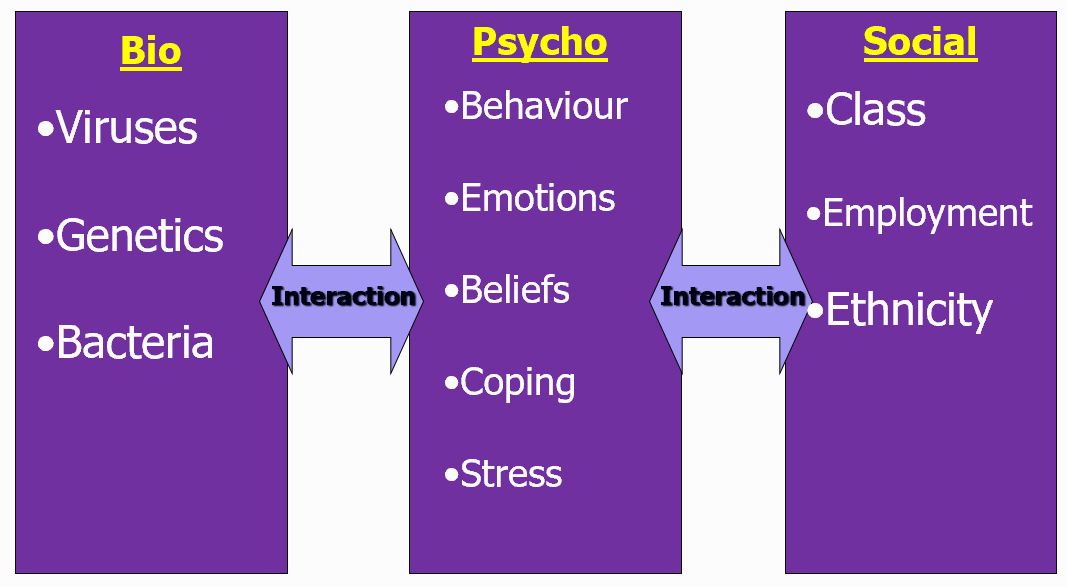
bio-psycho-social model
determinants of health behaviour
background factors: characteristics that define the context in which people live their lives
stable factors: individual differences (personality) in psychological activity that are stable over time and context
social factors: social connections in the immediate environment
situational factors: appraisal of personal relevance that shape responses in a specific situation
stable factors
e.g individual differences, personality
refer to variations between people in psychological activities that produce repsonses stable across time and context
stable factors influence appraisal in 3 keyways
determine if an event is salient (e.g sensitivity towards particular types of event)
provide a generalised framework for understanding and evalutating the event (e.g as threat or challenge)
make available or suggest potential responses (e.g intitial response options)
individual differences and health
3 broad types of individual differents
emotional dispositions (psychological processes involved in both the experience and expression)
generalised expectancies (psychological processes involved in formulating expectations in relation to future outcomes)
explanatory styles (psychological processes involved in explaining causes of -ve events)
5 personality traits: emotional dispositions (OCEAN)
Openness to new experiences
Conscientiousness
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Openness to new experiences
Intellect and interest in culture; artistic, curious, imaginative, wide range of interest.
Conscientiousness
The will to achieve; self disciplined, efficient, organised, reliable, thorough.
Extroversion
Outgoing; talkative, enthusiastic, seeking excitement, assertive and active.
Agreeableness
Loving, friendly and compliant; sympathetic, appreciative, trusting, kind, forgiving, generous.
Neuroticism
Experience more negative emotions; anxious, tense, worried, hostile, self-pitying, vulnerable.
Generalised Expectancies
locus of control: expectations that future outcomes will be determined by factors that are either internal (self) or external (powerful others and chance)
internal locus of control is generally associated with more favourable outcomes and performance of health behaviours but is dependent on situational factors
people with internal locus of control believe:
they are responsible for their own health
illness can be avoided by taking care of themselves
ill health results in part from not eating correctly or not getting enough exercise
self efficacy
belief in one’s own ability to organise and execute a course of action and the expectation that the action will result in, or lead to, a desired outcome
explanatory styles
optimism
attributional style
optimism (pessimism)
expectation of a positive future outcome (however achieved) despite a current -ve event
low levels of physiological reactivity in mild/moderate levels of stress and promotes active coping responses
associated with better physical health, illness recovery and health behaviour performance
attributional style
casual explanations of -ve events as internal (self), permanent (time) and global (situation)
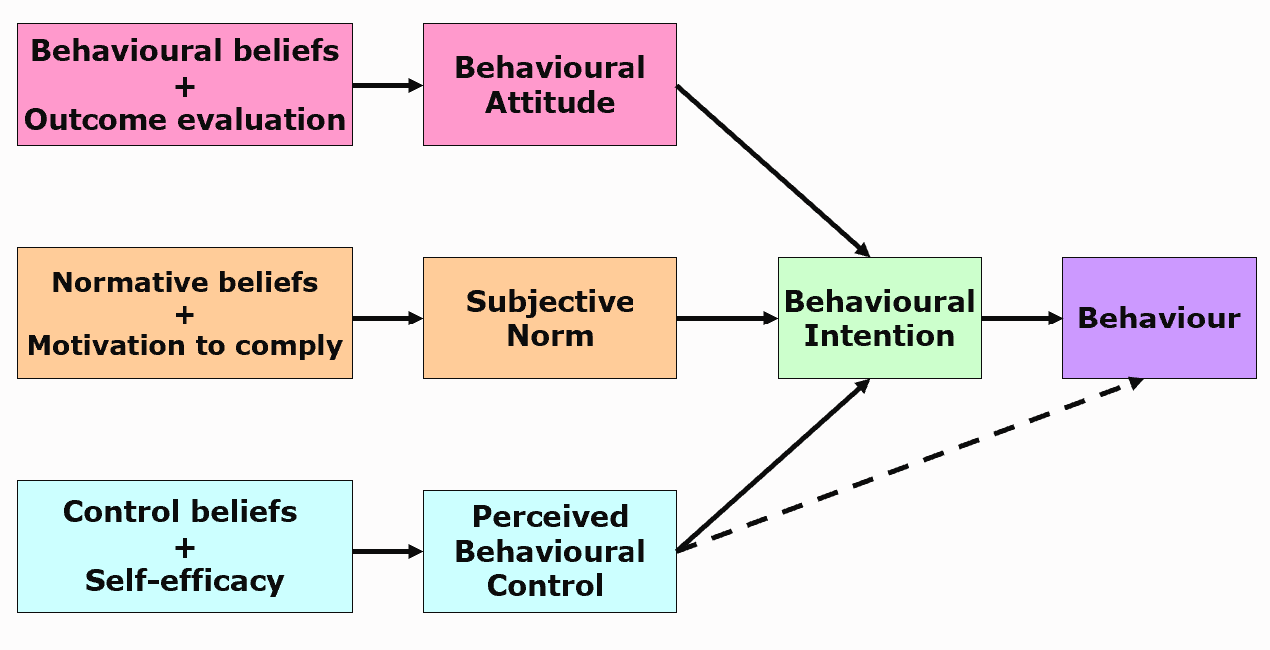
social cognition theories
attempt to explain the relationship between social cognitions (beliefs, attitudes, goals) and behaviour
e.g:
Health Belief Model (Rosenstock, 1966)
Theory of Planned Behaviour (Ajzen, 1988)
Transtheoretical Model (1983)
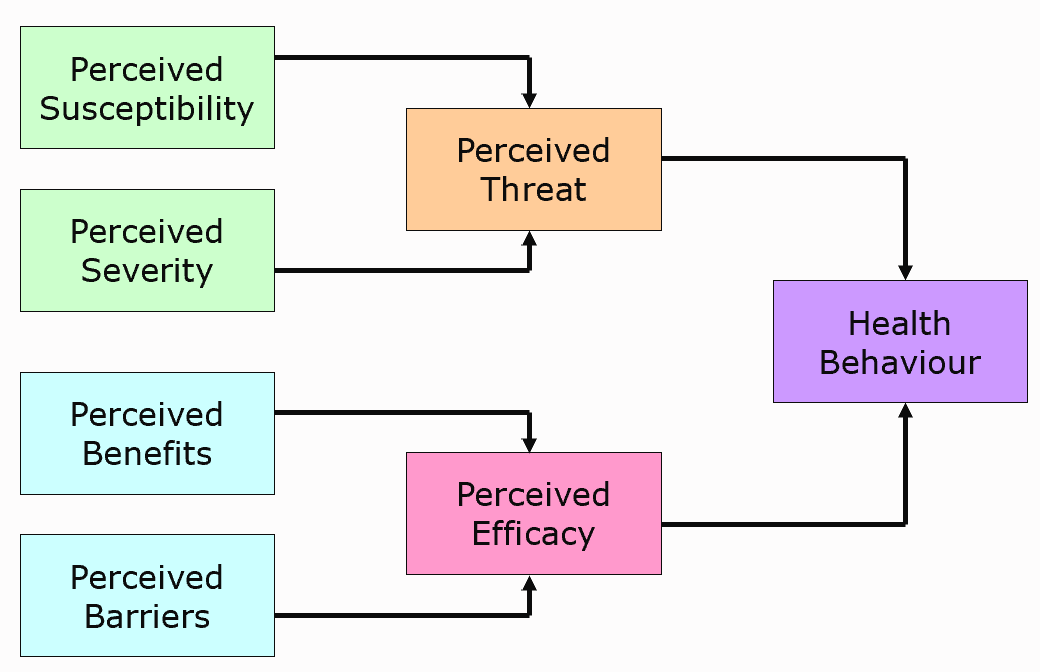
Health Belief Model
Theory of Planned Behaviour
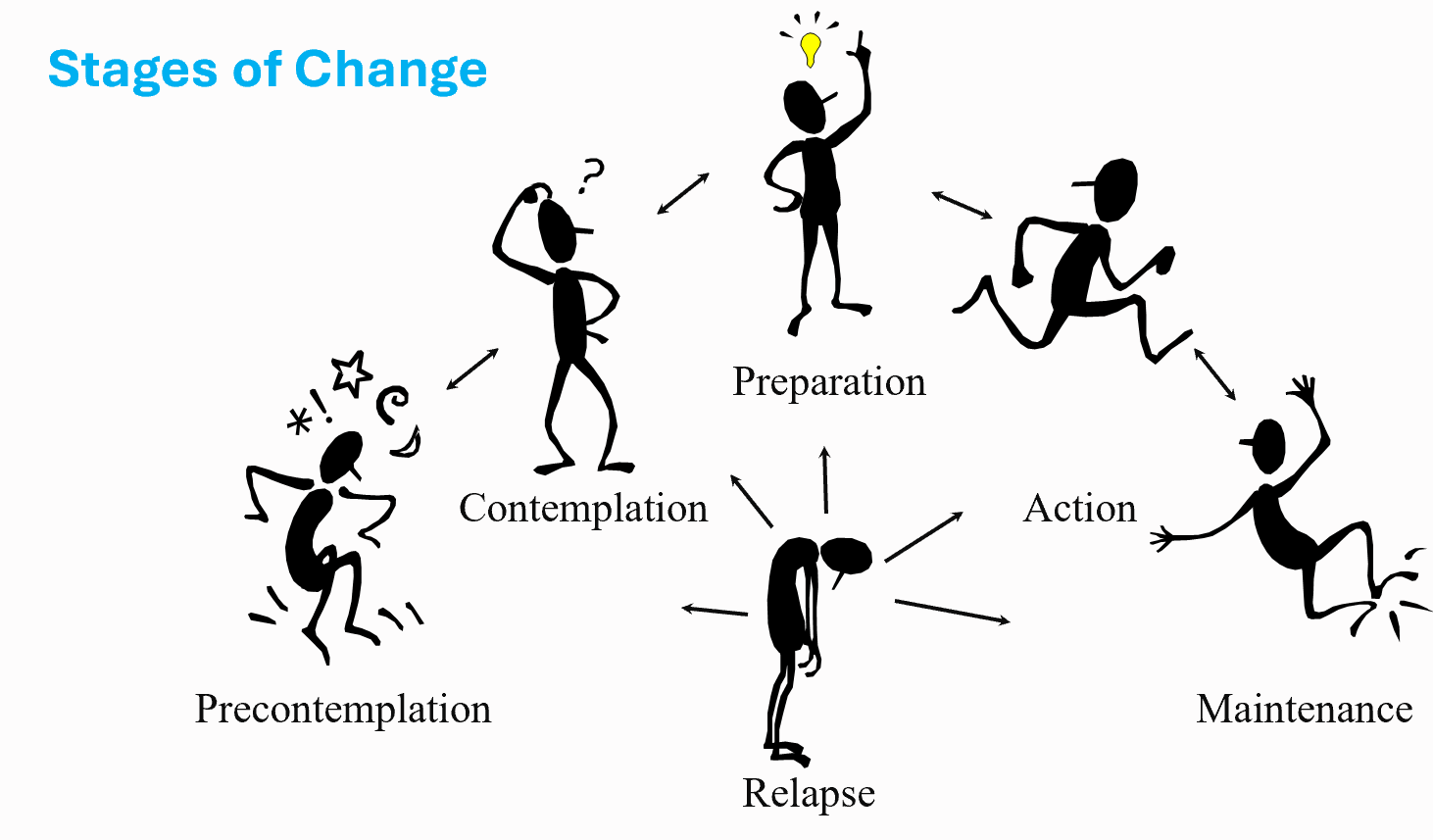
Stages of Change in Transtheoretical Model
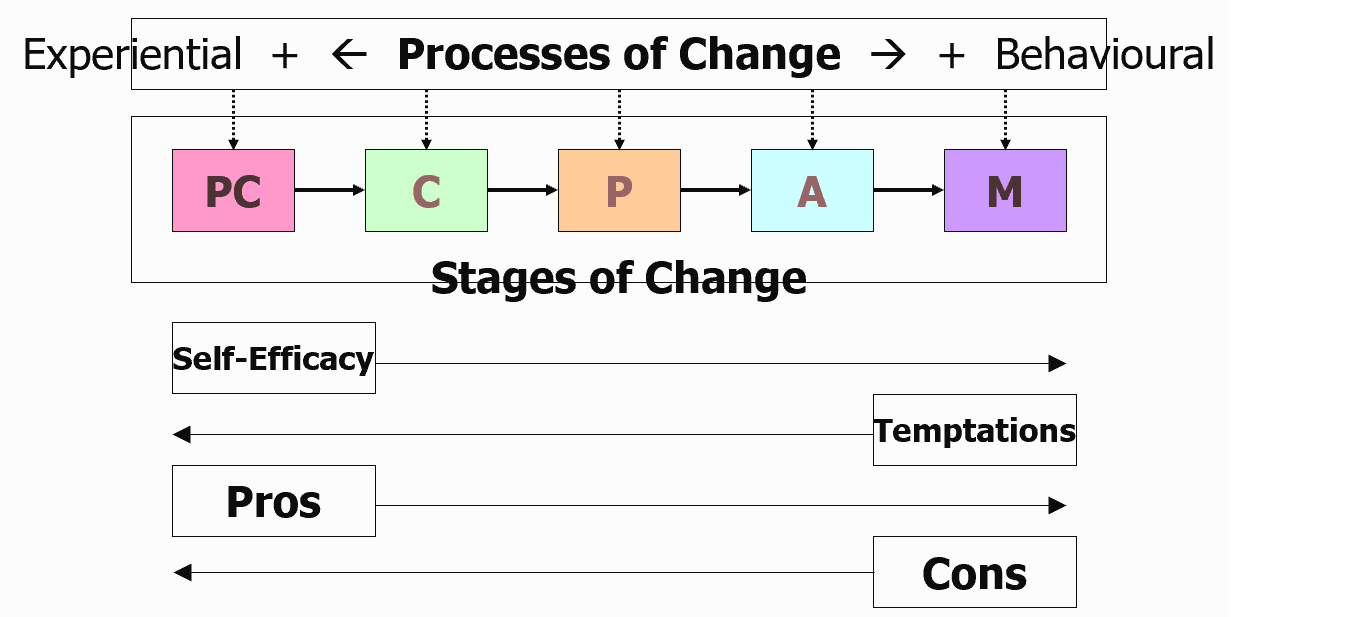
Stages of Change
precontemplation
contemplation
preparation
action
maintenance