BFCP1 S13
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
S13: Biological Membranes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
2 key functions of biological membranes
Compartmentation
Potential energy gradient: diff concentrations of solutes inside and outside the cell
Translocases
Transport proteins embedded in the membrane
When does PE spike in a membrane?
When a polar/charged molecule crosses, because it is unstable and unfavorable
Facilitated diffusion
No energy needed, molecule moves with gradient
Primary active vs secondary active diffusion
Primary: compound requires ATP to move against gradient
Secondary: compound moves against gradient powered by another compound moving with its gradient (no ATP required)
Channel proteins
Tunnels to allow molecules to move in
Carrier proteins
Molecules bind and change conformation of carrier proteins to allow movement
Transporters/transporter proteins allow for _______ diffusion.
Primary active diffusion
Integral vs peripheral membrane proteins
Which one can be removed with salt/base without dissolving the bilayer?
Integral: embedded in bilayer, can’t be removed without dissolving membrane
Peripheral: bound to membrane surface, can be removed with salt/base
What does it mean for a lipid to be hydrolyzable?
If you treat that lipid with an enzyme or strong base, the fatty acid will be released
What is the only membrane lipid that is not hydrolyzable?
Cholesterol
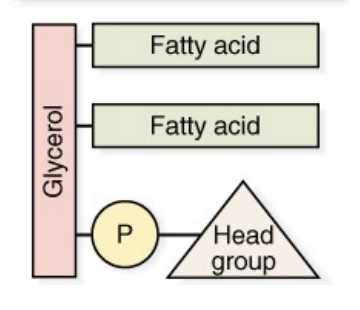
Glycerophospholipid
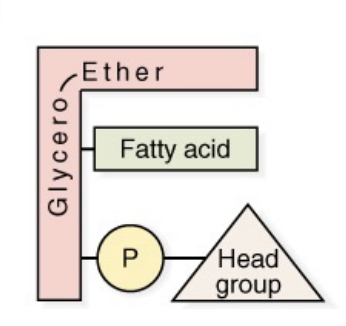
Ether glycerolipid/phospholipid
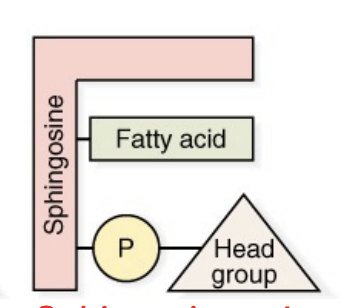
Sphingophospholipid/sphingomyelin
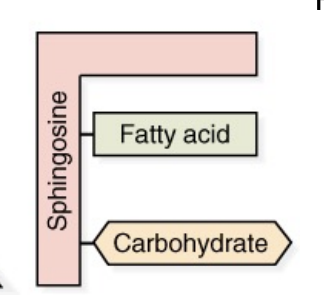
Glycolipid/glycosphingolipid
A lipid is a phospholipid if it contains _______
a phosphate group
A lipid is a glycerolipid if it contains ______
glycerol
A lipid is a sphingolipid if it contains _______
a sphingosine
Glycerophospholipid composition
Glycerol backbone, 2 FAs, 1 phosphate and a head group
Ether glycerolipid composition
Glycerol backbone, 1 ether, 1 FA, phosphate, and head group
Sphingomyelin composition
Sphingosine backbone, 1 FA, phosphate, and head group (choline)
Glycosphingolipid composition
Sphingosine backbone, 1 FA, and 1+ carbs/sugars
FAs are connected to the glycerol backbone via ____ bonds.
ester
Glycerophospholipids are named after their _____. Ex: phosphatidyl_____
head group
Phosphatidic acid
A glycerophospholipid with no head group
Also the precursor for glycerophospholipids
Where does synthesis of glycerophospholipids take place?
ER
Synthesis of _______ requires acyl transferase enzymes and CoA.
glycerophospholipids
Ceramide
Sphingosine + FA
Ceramide + head group =
sphingolipid
Sphingomyelins and glycosphingolipids are examples of _______.
sphingolipids
The head group of sphingomyelin is _____
phosphate + choline
The head group of glycerosphingolipid is ______
1+ sugars/carbs
Ceramides are synthesized in the ______.
Sphingolipids (ceramide + head group) is finished off in the ______.
ER
golgi
Lipid rafts for transportation
Transport of sphingolipids with clusters of cholesterol
A sphingosine is linked to a FA via a _____ bond.
amide
Sphingomyelin is found in which cells? Diseases affecting sphingomyelin will affect what?
Nervous tissue and immune clls
Will affect the brain
What happens if enzymes in the lysosome can’t break down sphingolipids?
Accumulation occurs, especially affecting the brain
Platelet activating factor and plasmalogens are examples of _______
ether phospholipids/glycerolipids
Platelet activating factor vs plasmalogen composition
PAF: glycerol backbone + 1 ester + 1 acetyl group + phosphate + head group
Plasmalogen: glycerol backbone + 1 ester + 1 FA + phosphate + head group
Plasmalogens are synthesized and broken down in ______
peroxisomes
Peroxisomal disorders can lead to (catabolism/anabolism) of _____ lipids and affect synthesis of ______
Peroxisomal disorders can lead to catabolism (aka buildup) of long-chain lipids and affect synthesis of plasmalogens
Zellweger spectrum disorders, RCDP disorders, and refsum disease are all examples of ____
peroxisomal disorders
We ned to have controlled hydrolysis of _______ lipids.
hydrolyzable
Cholesterol is the precursor to _____ and has a characteristic _____ structure.
steroids
4 ring structure
Functions of cholesterol
Regulates fluidity of bilayer
Regulates stability and permeability
Contributes to lipid raft formation
When is cholesterol ester created?
It is acylated: attached to a ____ via a ____ linkage
For storage or transport
Acylated: attached to FA via an ester linkage
ACAT and LCAT enzymes
ACAT: catalyzes the fatty acylation of cholesterol
LCAT: disposes of cholesterol
T/F: membrane lipids are randomly organized
F
In humans, most transmembrane proteins have a ______ shape. This shape requires _______.
alpha helical
a stretch of 20+ consecutive nonpolar AAs
Explain how these components affect fluidity:
Temperature
Lipid composition
Cholesterol
Higher temp = more fluid
More long or saturated FA = less fluid
Cholesterol: acts as a buffer to moderate changes in fluidity
How can fluidity of a membrane be measured?
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP)
Lipid rafts are (thinner/thicker) and (less/more) fluid domains of the lipid bilayer
Thicker, less fluid
T/F: lipid rafts are self-organizing
T
Function of lipid vesicles
Can deliver mRNA or other cargo into the body more stably
Ex: mRNA vaccine for COVID
Glycophorins
In which cells?
Link cytoskeleton to the lipid bilayer
RBCs, notably