Central and Peripheral Nervous System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
astrocyte
Anchor neurons and blood vessels
Transport nutrients between blood vessels and neurons
Form the blood-brain barrier
Repair damaged tissue
CNS
oligodendrocytes
Myelinate certain axons in the CNS
microglial
Act as phagocytes (engulf and destroy pathogens, debris); assists with immune response
CNS
ependymal
Line ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord
Produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
CNS
schwann cell
Myelinate certain axons in the PNS
satellite cell
Wraps/surrounds neuron cell bodies (somas) in the PNS for support and protection
Brain tumors are usually gliomas because
glial cells divide. Neurons do NOT.
Sympathetic division of autonomic nervous system
mobilizes body systems during activity
“Fight-or-flight" (stress, danger) – speeds things up
Paraympathetic division of autonomic nervous system
promotes housekeeping functions during rest
"Rest-and-digest" (relaxation) – slows things down, conserves energy
white matter
made out of groups of myelinated axons
grey matter
made out of groups of cell bodies (somas)
nuclei
grey matter (cell bodies/somas) in the CNS
ganglion
grey matter (cell bodies/somas) in the PNS
tract
white matter (myelinated axons) in the CNS
nerve
white matter (myelinated axons) in the PNS
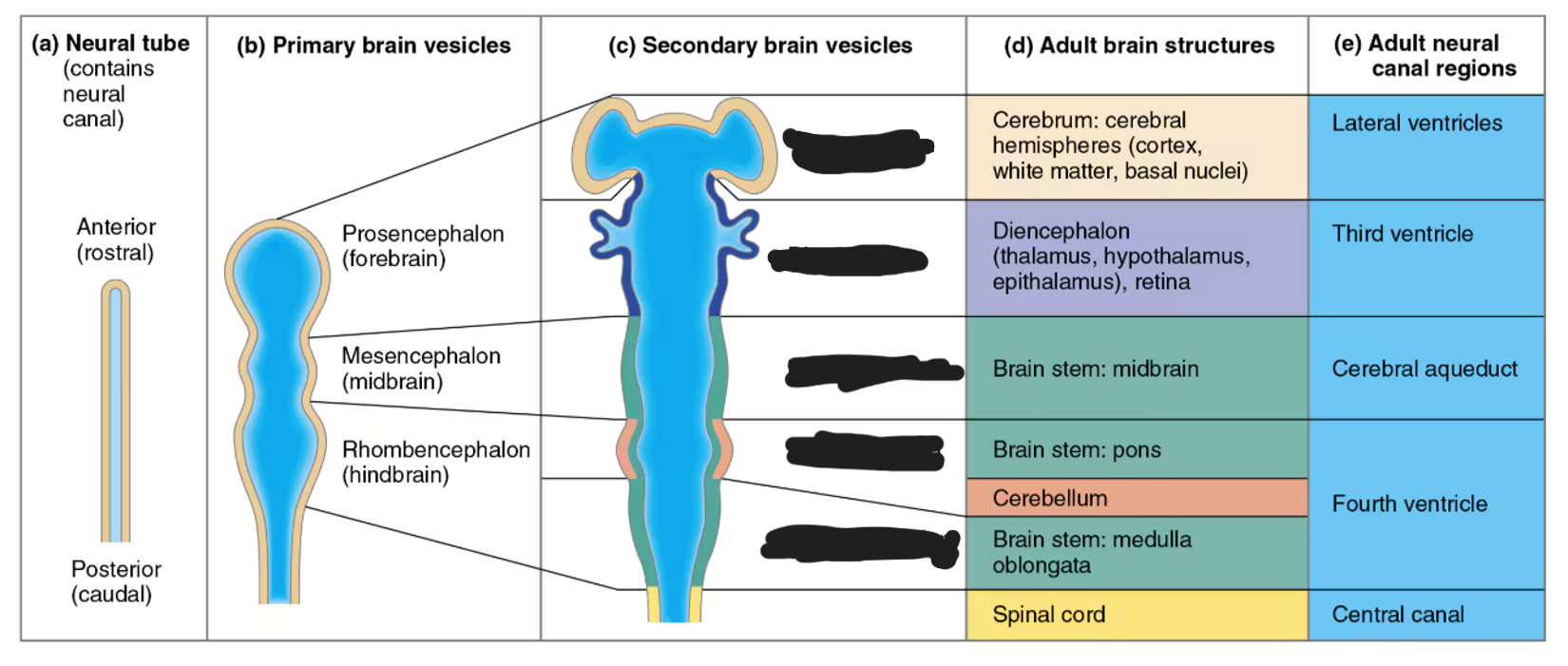
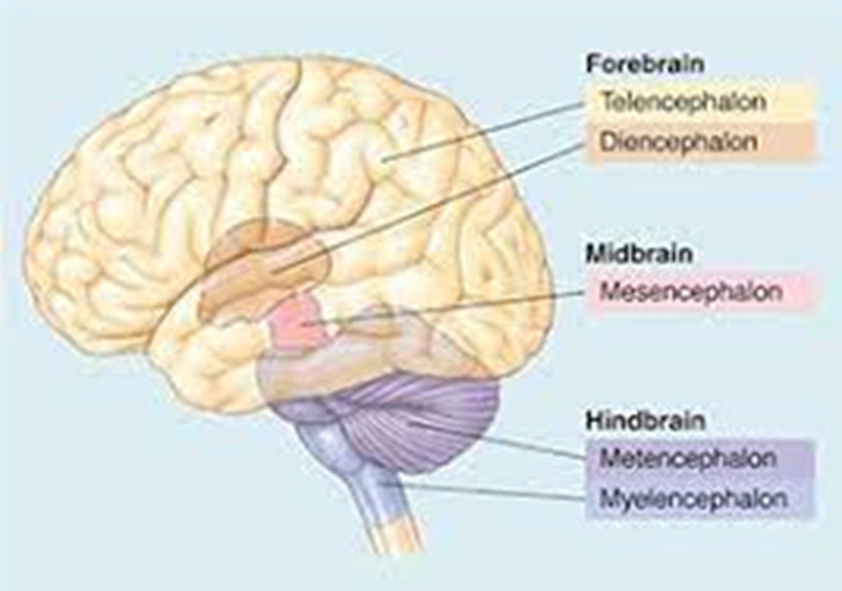
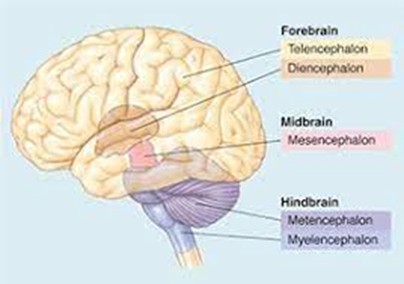
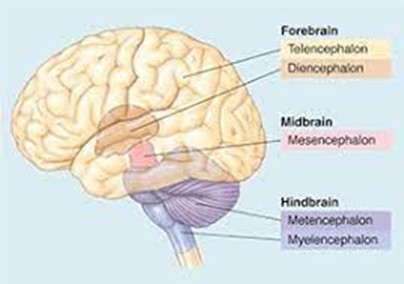
forebrain secondary brain vesicles
telencephalon and diencephalon
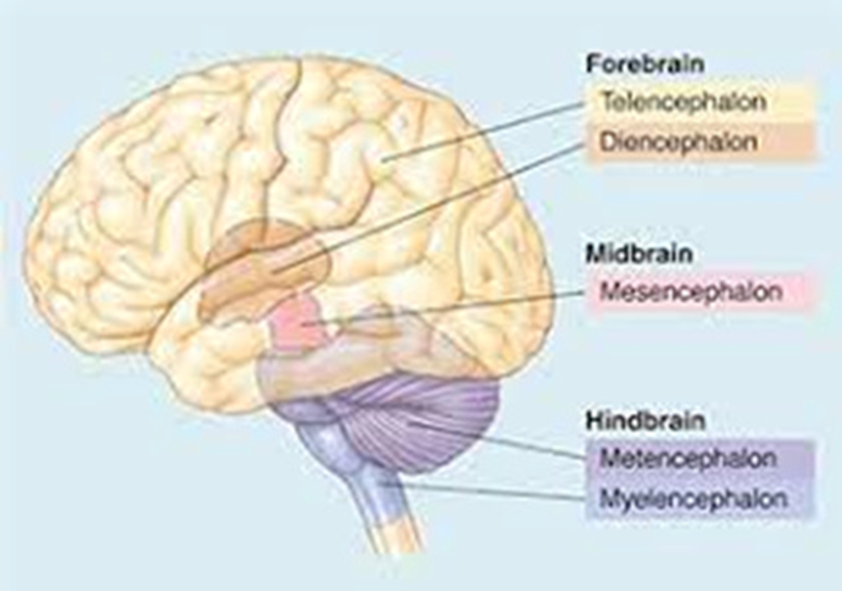
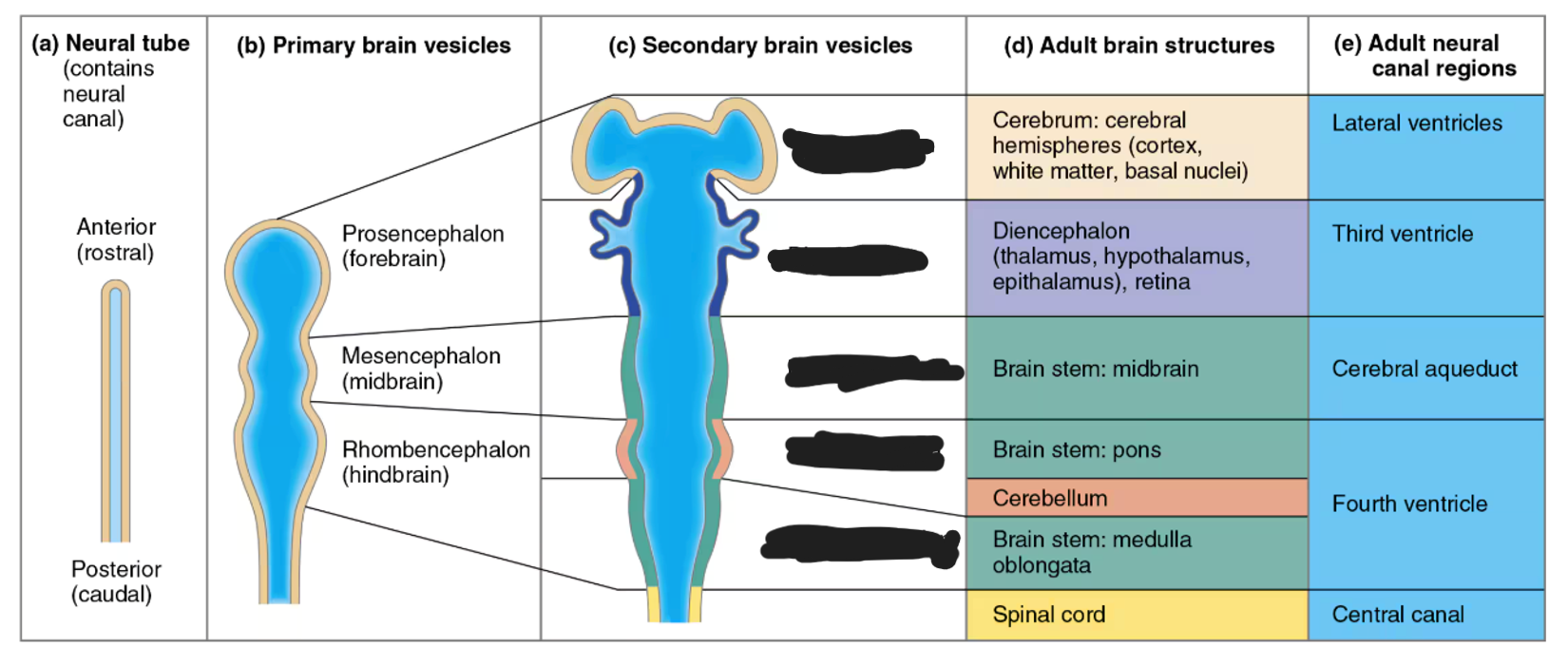
midbrain secondary brain vesicles
mesencephalon
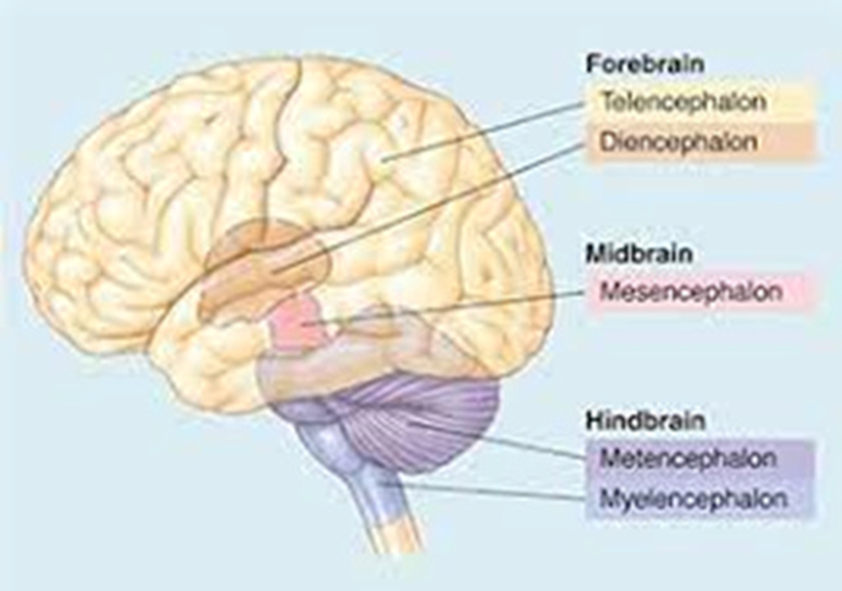
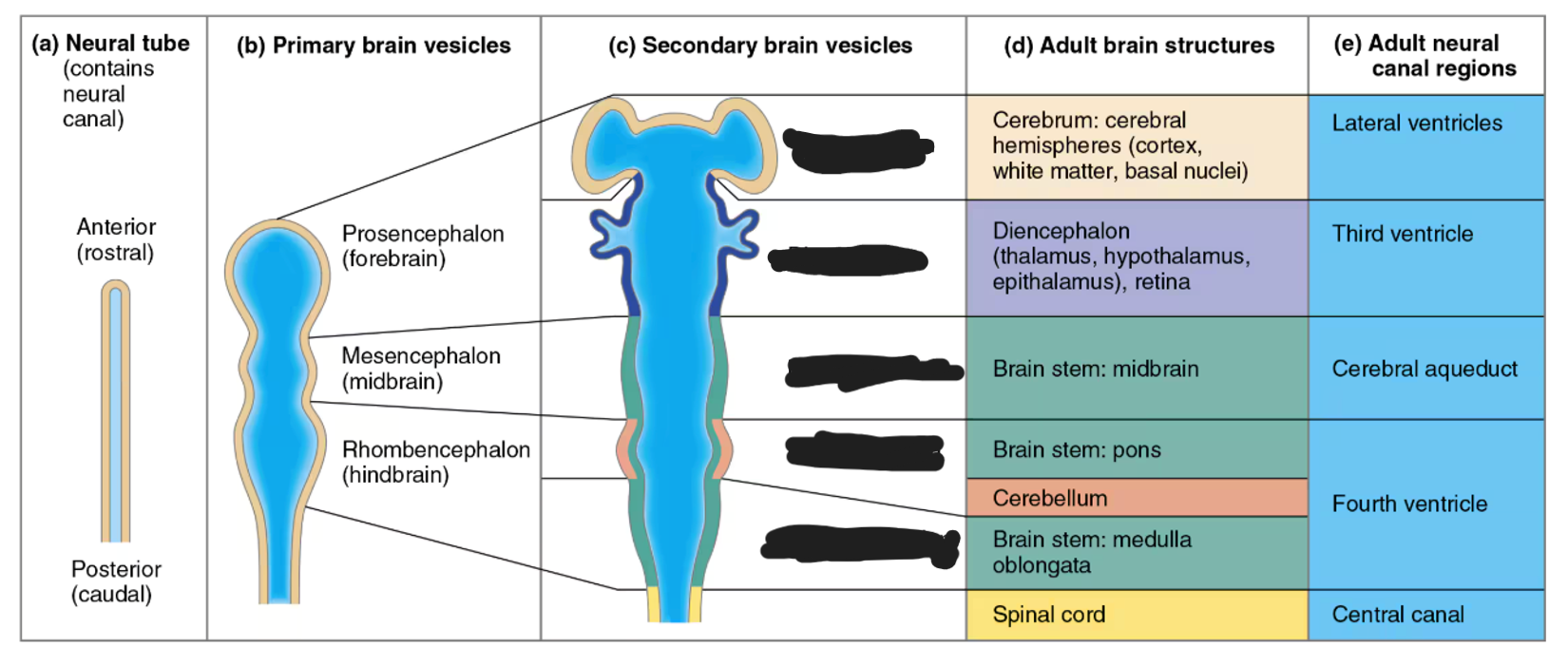
hindbrain secondary brain vesicles
metencephalon and myelencephalon
telencephalon adult brain structures
cerebrum (outer shell of brain): cerebral cortex (grey matter), fibers (white matter), and basal nuclei
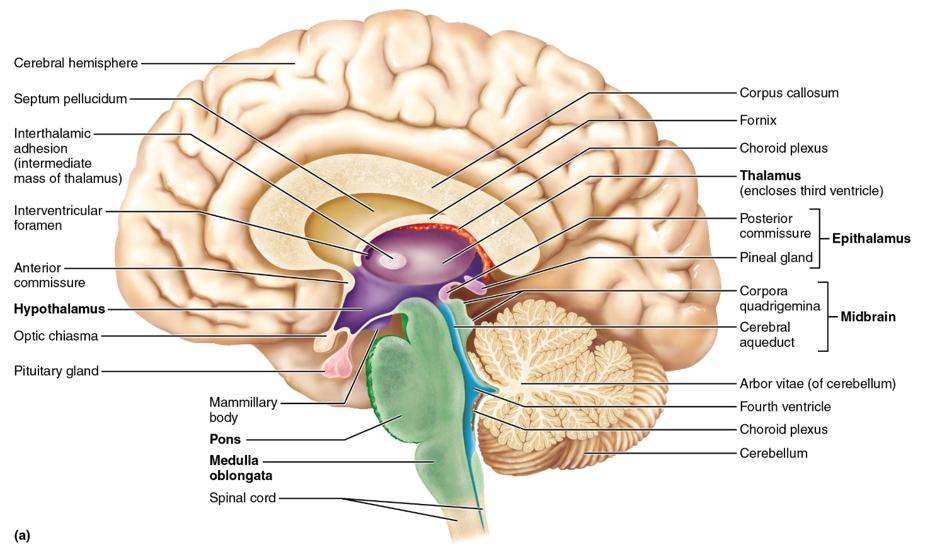
diencephalon adult brain structures
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus (and retina)
mesencephalon adult brain structures
midbrain portion of the brainstem
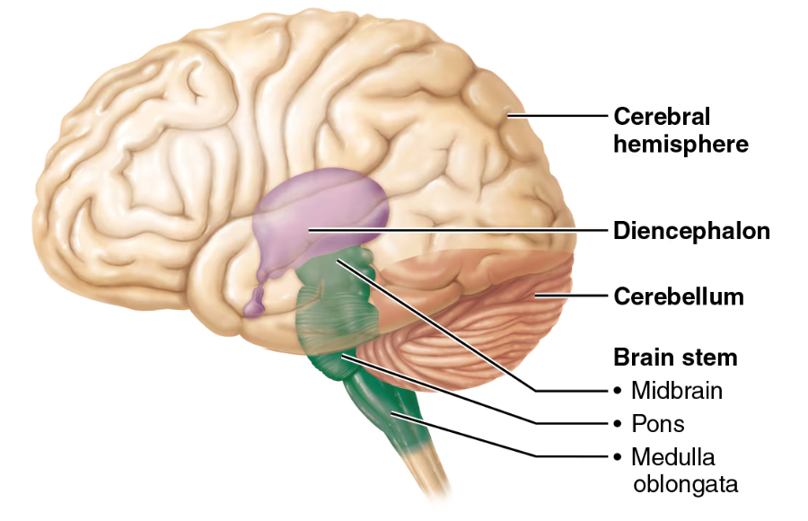
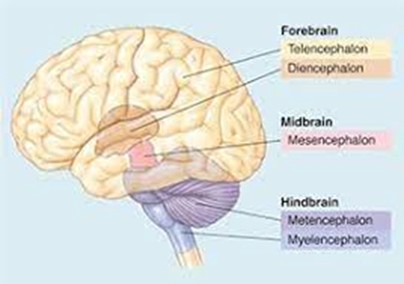
metencephalon adult brain structures
pons portion of the brainstem and the cerebellum
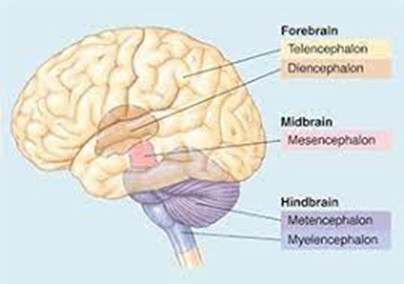
myelencephalon adult brain structures
medulla oblongata portion of the brainstem

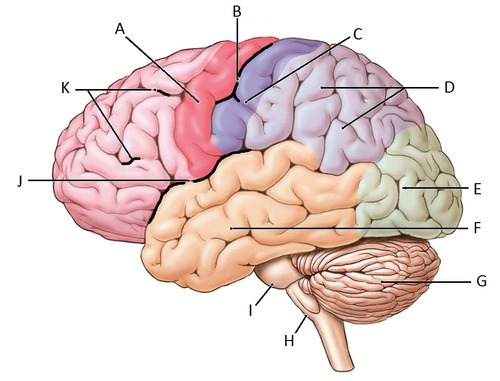
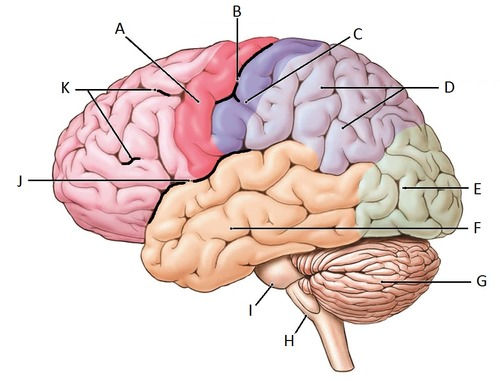
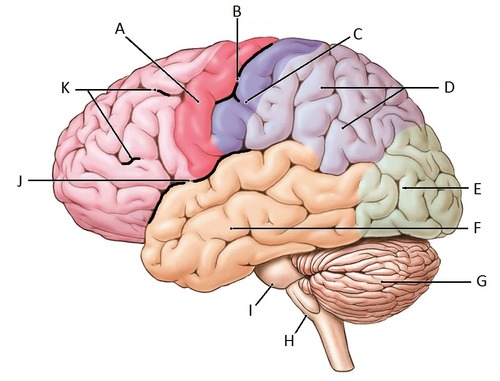
j
find the Lateral Sulcus/Fissure
-
find the Longitudinal Fissure
b
find the central sulcus
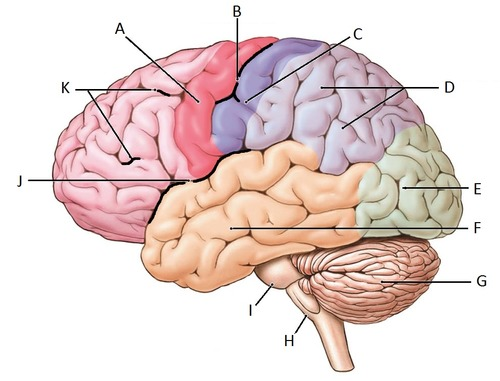
yellow and blue gyri between central sulcus
find the precentral gyrus and the postcentral gyrus
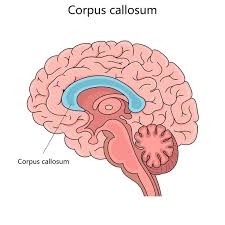
corpus callosum
The cerebral hemispheres are the two halves (left and right) of the cerebrum, connected by the
decussation
The crossing of nerve fibers or tracts from one hemisphere of the central nervous system to the other, resulting in contralateral control of the body
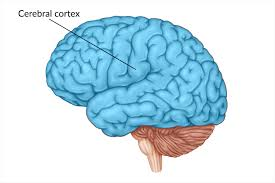
cerebral cortex
superficial grey matter that has specialized sensory, motor, and association areas separated by different lobes
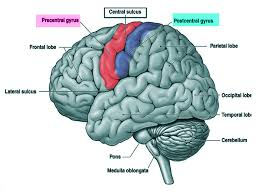
precentral gyrus
this is the primary motor cortex; damage to this structure may cause loss or impairment of voluntary movement on the contralateral side of the body
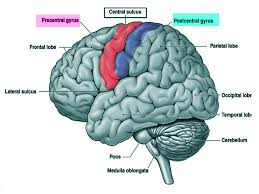
postcentral gyrus
this is the primary somatosensory cortex; damage to this may cause loss or impairment of somatic sensation (touch, pain, temperature, proprioception) on the contralateral side of the body.
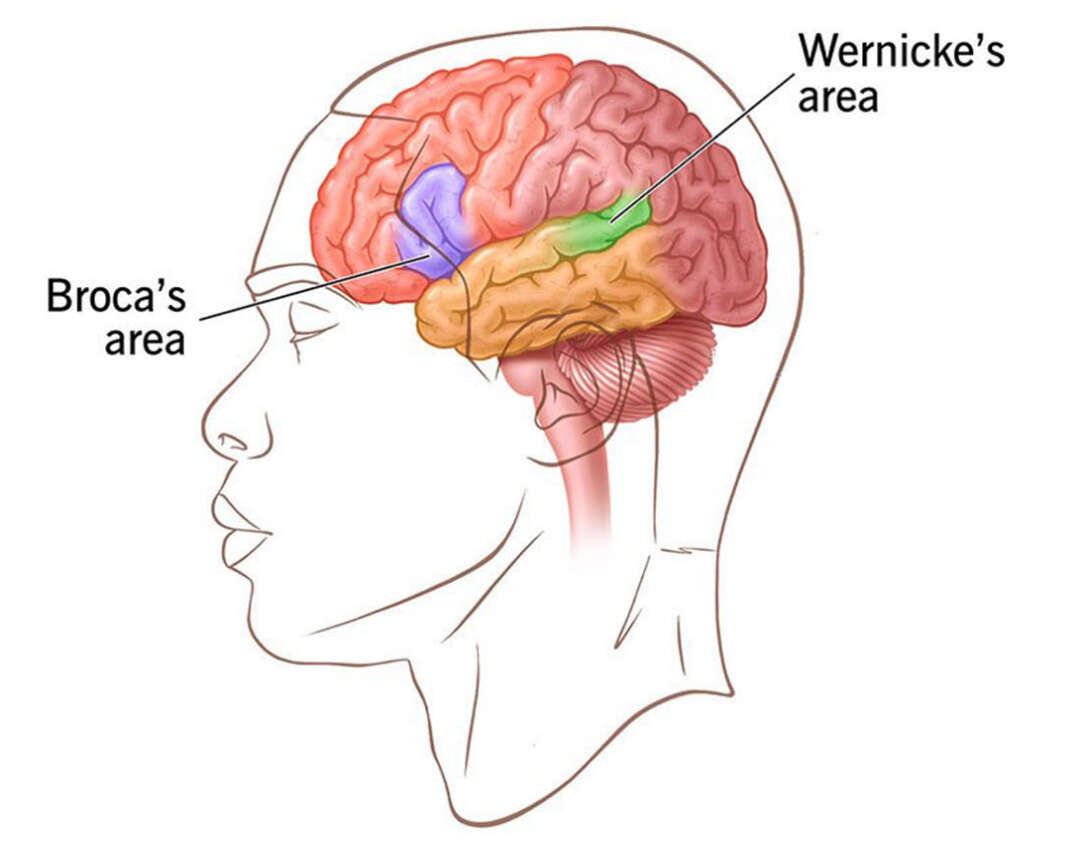
Broca’s Area
Motor speech area responsible for speech production; damage makes it hard to form words and sentences, though comprehension often remains intact

Wernicke’s Area
Language/speech comprehension area; damage may lead to fluent but meaningless speech and difficulty comprehending others
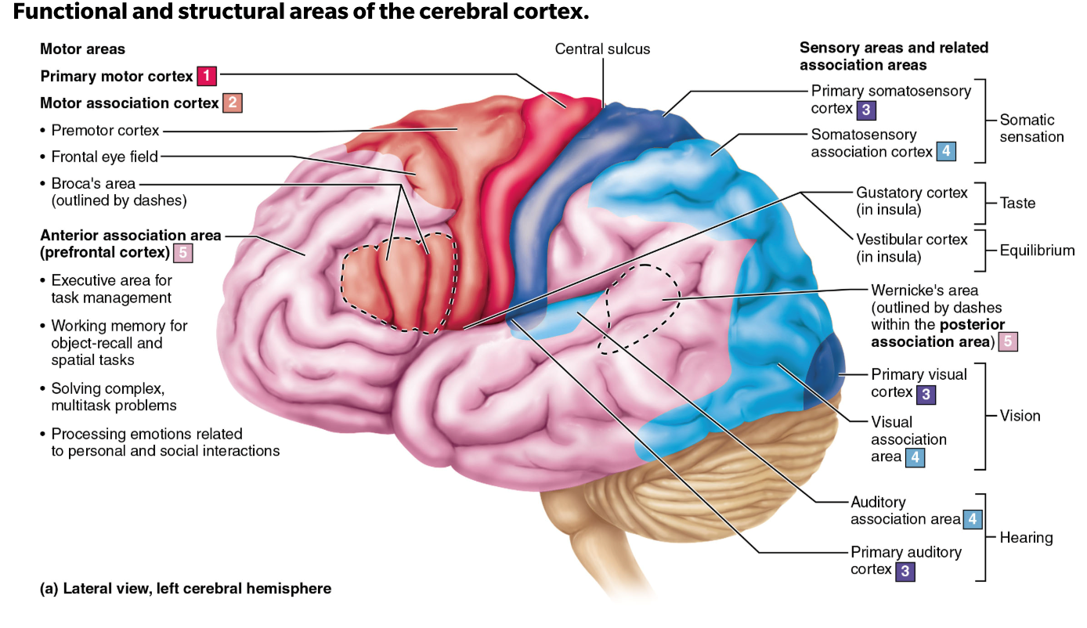
occipital lobe
the primary visual cortex is located in the..
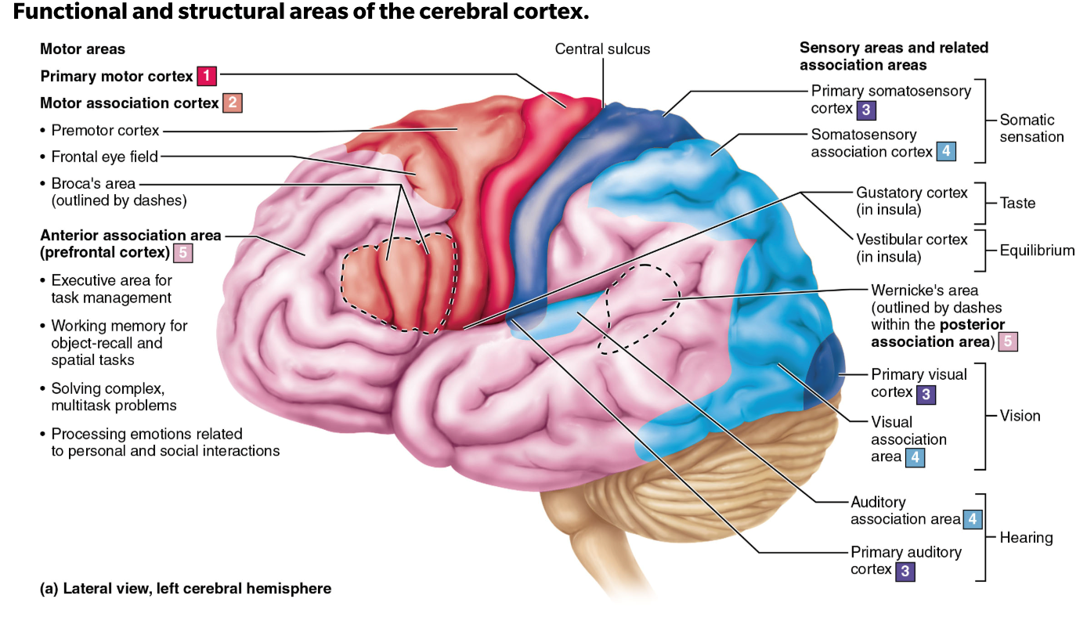
temporal lobe
the primary auditory cortex is located in the..

insula lobe
the vestibular (equilibrium/balance) and gustatory (taste) complex are located in the…
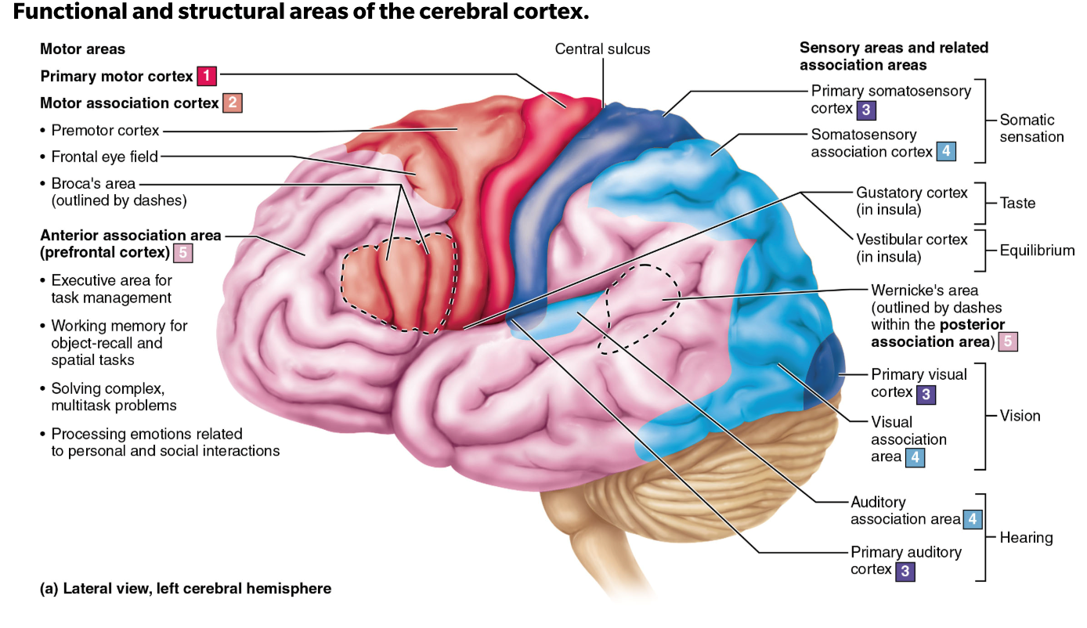
temporal lobe
the olfactory (smell) cortex is located in the inferior…
somas
integrate and process information
axons
transmit information to other neurons or target cells; communication
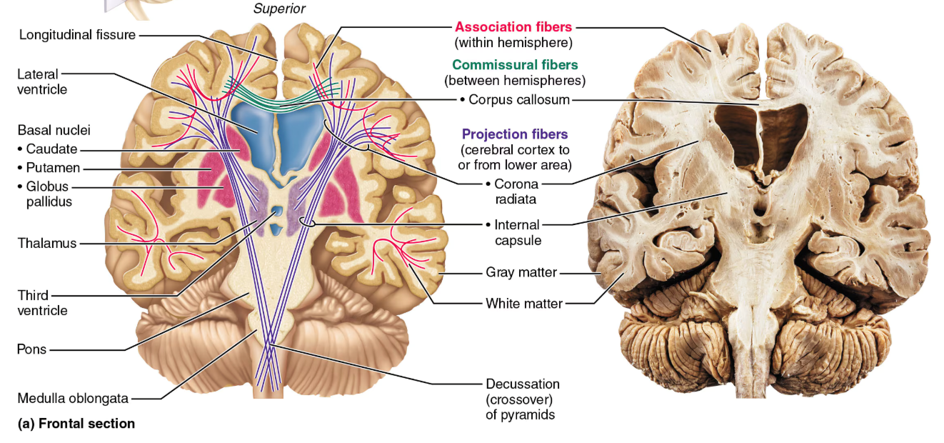
Commissural fibers
axons that connect corresponding regions of the left and right hemispheres; corpus callosum is the largest bundle of this fiber
Association fibers
Axons that connect different regions within the same cerebral hemisphere, allowing communication between cortical areas on the same side of the brain
Projection fibers
Axons that connect the cerebral cortex with lower brain regions and the spinal cord, carrying information to and from the cortex; these fibers go up and down
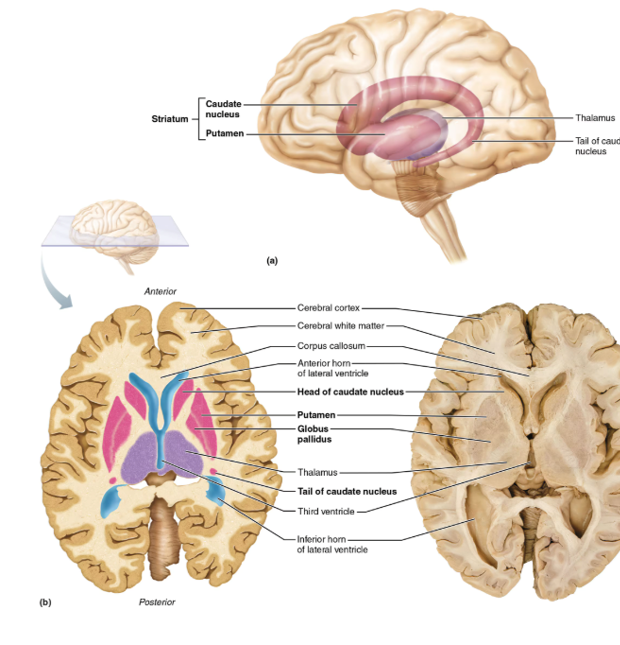
Basal Nuclei
group of somas in the CNS deep to the cerebral cortex that influences skeletal muscle movements (it filters movement patterns); people with Tourette’s Syndrome have something wrong with this part of the brain; this also plays a role in cognition and emotion

thalamus
sensory relay station (except smell/olfaction); the gateway to the cerebral cortex; made of nuclei
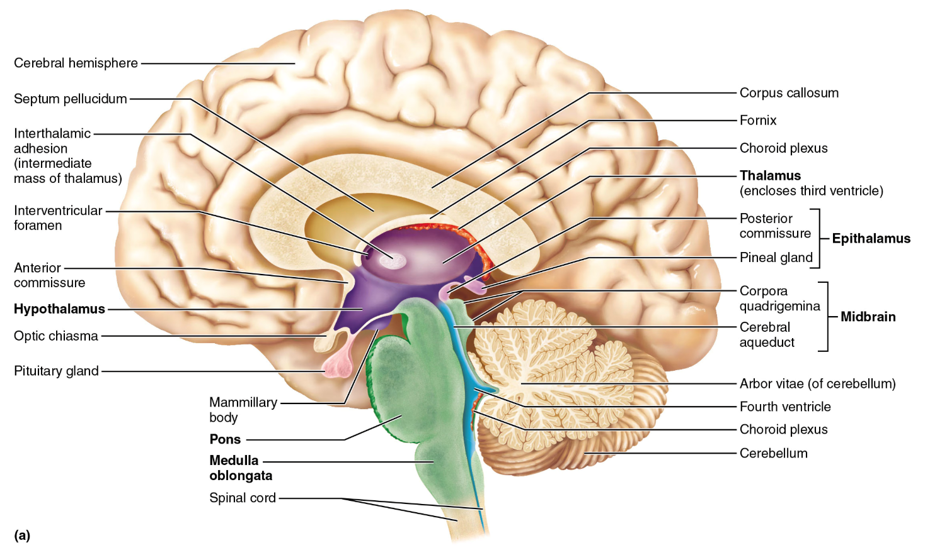
hypothalamus
controls the autonomic (visceral) nervous system (ex. heart rate, body temperature, hunger and satiety, water balance and thirst); contains nuclei; controls the endocrine system specifically the pituitary gland (anterior)
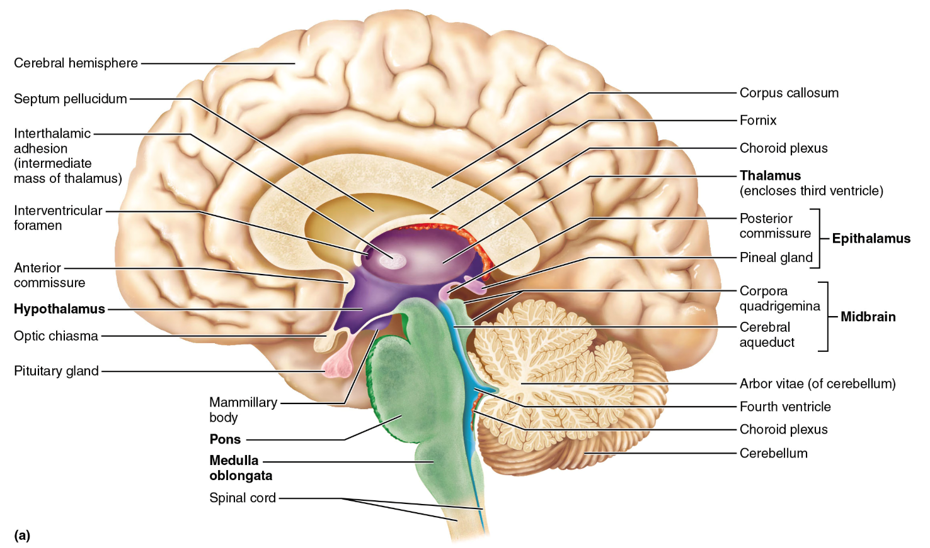
epithalamus
the pineal gland (posterior) is located here; melatonin is secreted from here and this structure controls circadian rhythm
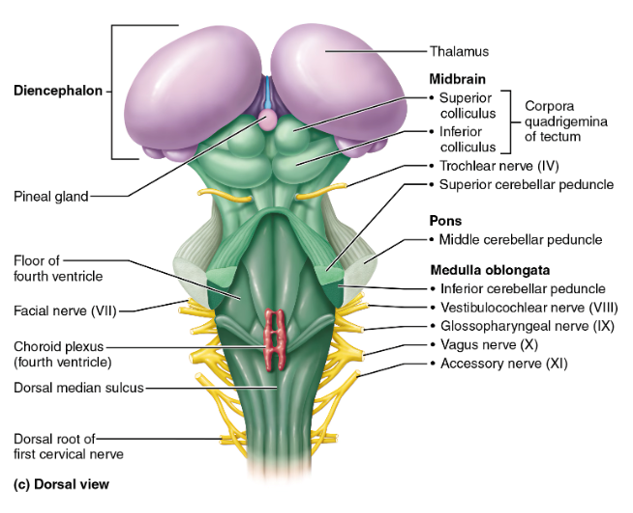
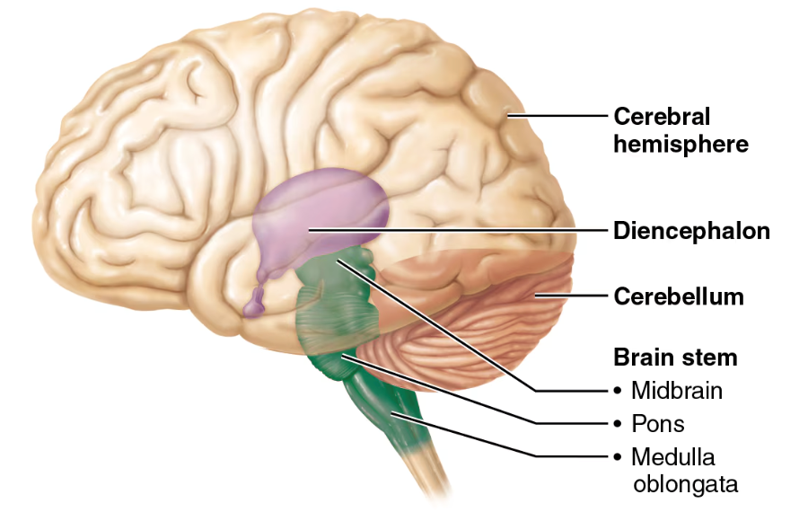
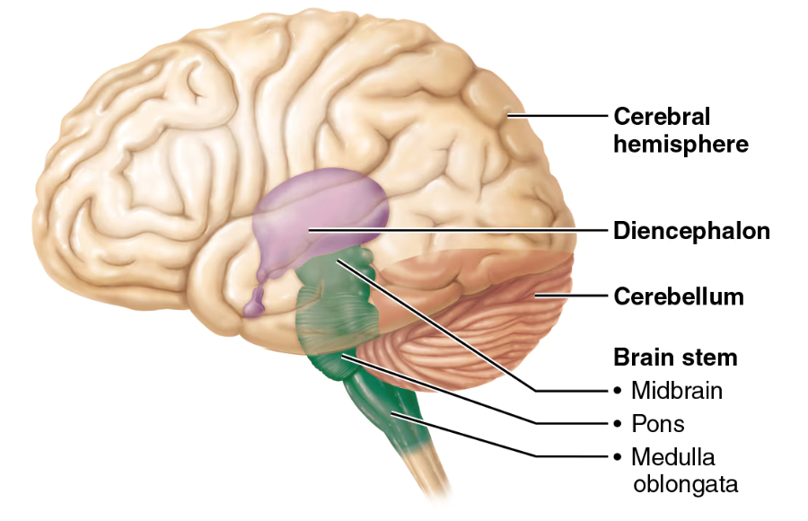
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
the regions of the brainstem
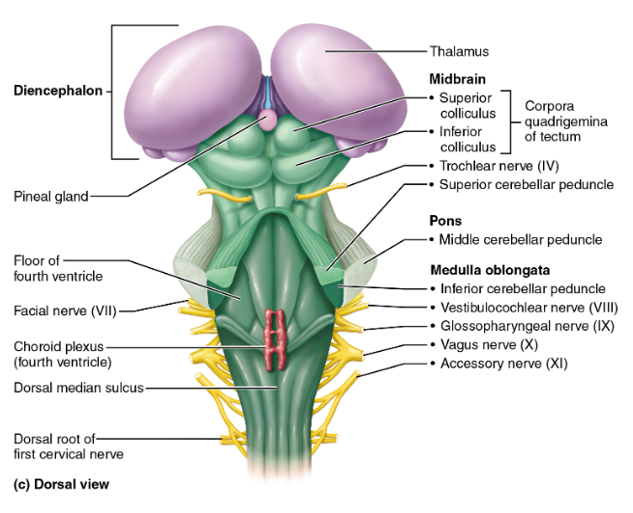
midbrain
contains the superior and inferior colliculi
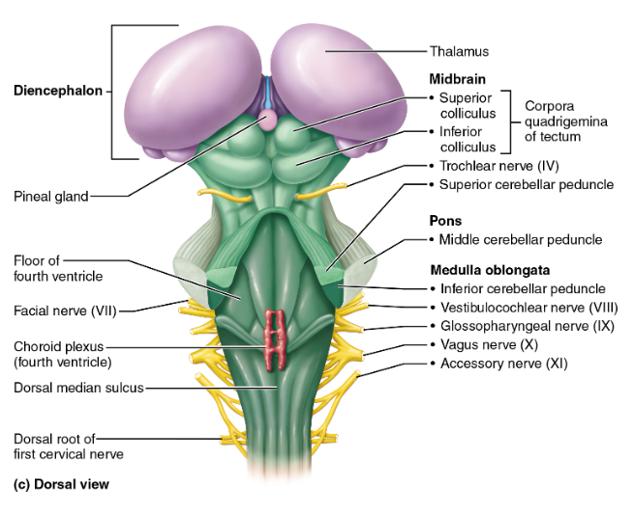
superior colliculi
midbrain structures that act as visual reflex centers, coordinating automatic eye, head, and neck movements in response to visual stimuli; hint: these little balls kinda look like eyes
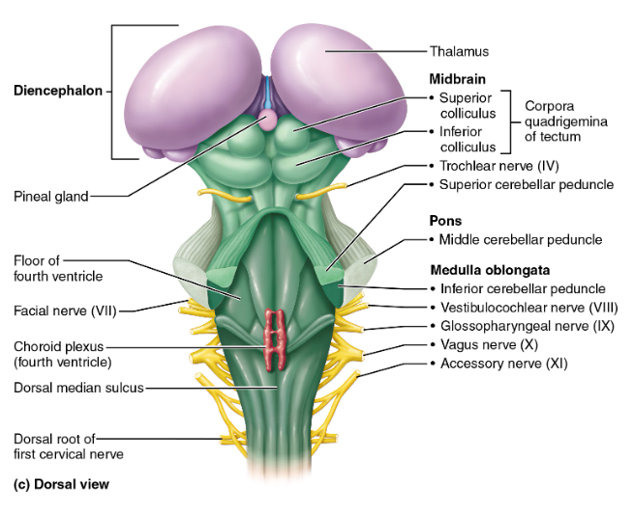
inferior colliculi
midbrain structures that serve as auditory reflex centers, processing sound information and coordinating reflexive responses to auditory stimuli such as turning the head or eyes toward a sound; hint: this structure looks like a hearing aid
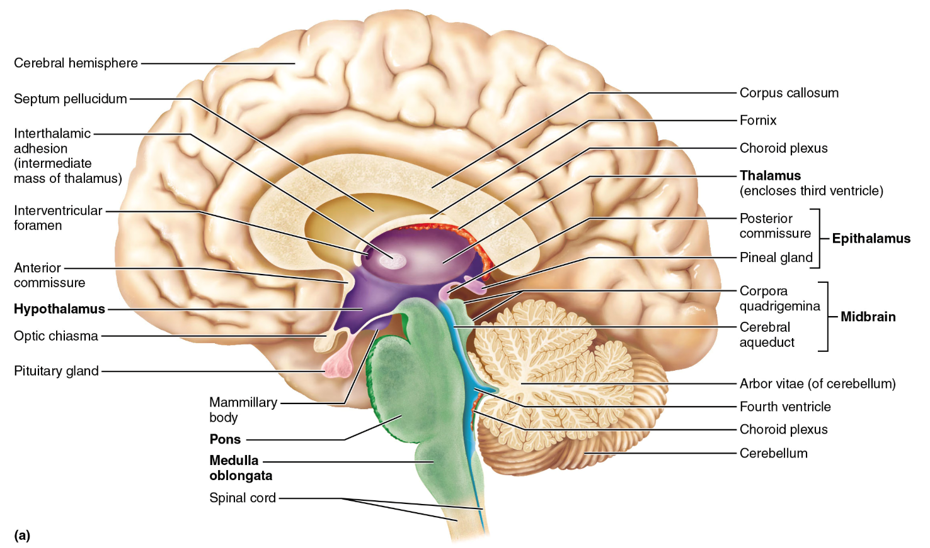
pons
the part of the brainstem below the midbrain; a lot of cranial nerves originate here; it relays impulses between the motor cortex (precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe) and the cerebellum
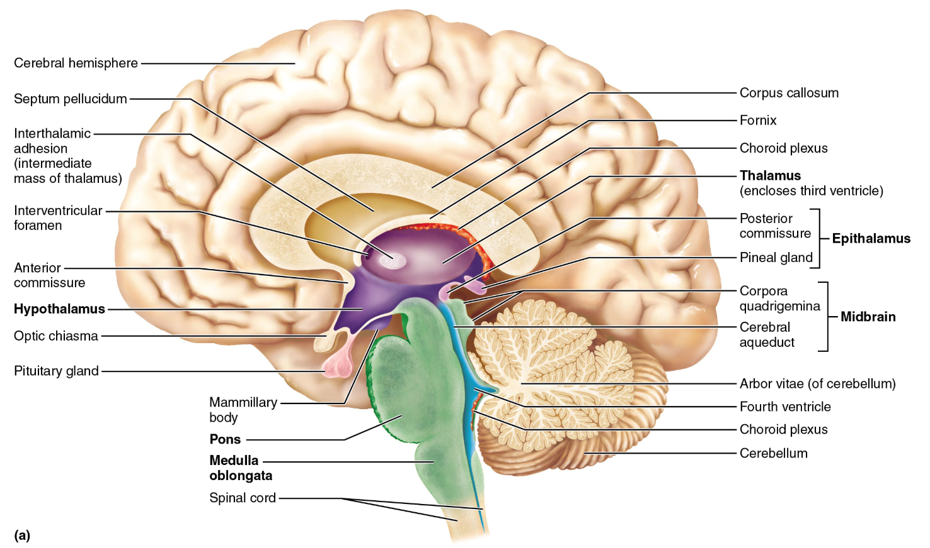
medulla oblongata
cardiovascular center (controls HR) and respiratory center (controls breathing); this is and area of decussation (crossing over of nerve fibers—specifically corticospinal tracts); hint: “______ = Makes you live (HR, breathing)”
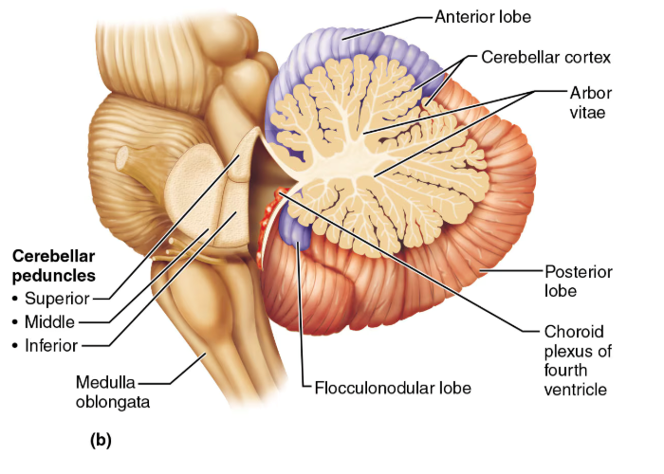
cerebellum
associated with movement patterns; allows smooth, coordinated movements
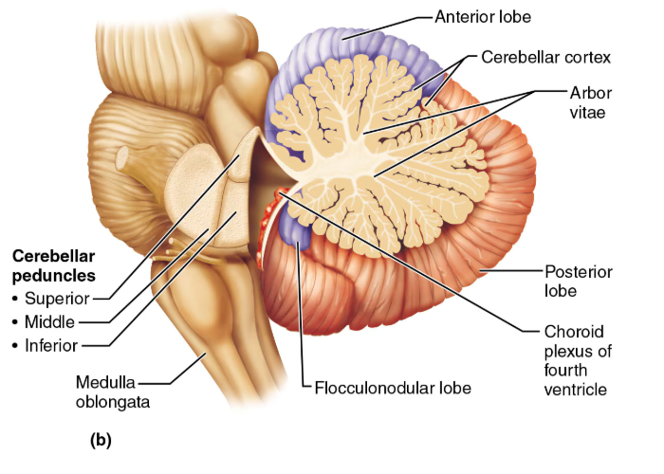
arbor vitae
white matter in the middle of the cerebellum used for communication; looks like the veins of a leaf

the limbic system
controls emotional response and memory; houses the hippocampus and amygdala
hippocampus
part of the limbic system associated with long-term memory
amygdala
part of the limbic system that processes emotion
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Maintains cerebral cortical alertness AKA consciousness
reticular formation
filters sensory information
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
Measures electrical activity of the brain
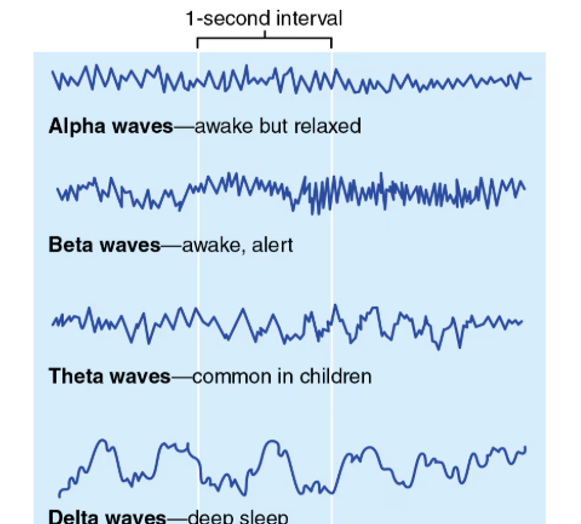
Alpha Waves represent
calm and relaxed; eyes probably closed
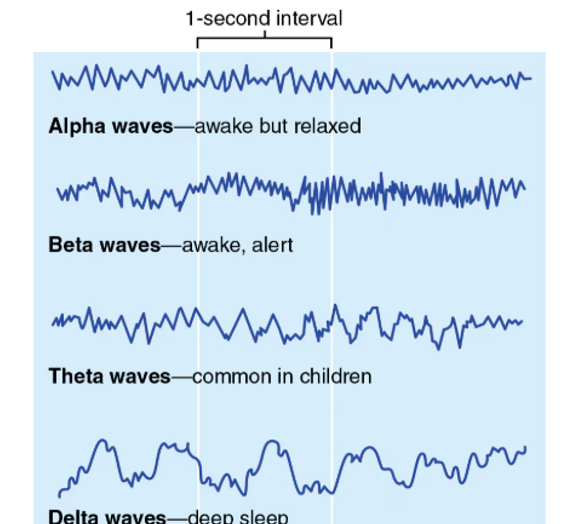
Beta Waves represent
awake and alert; eyes open and mentally stimulated
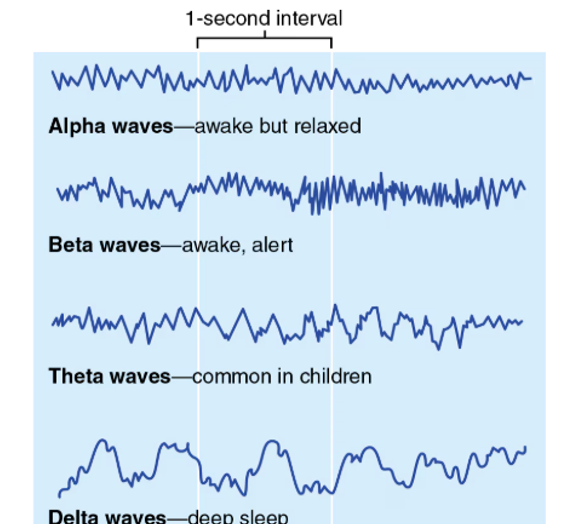
Theta Waves represent
children, more irregular wave pattern
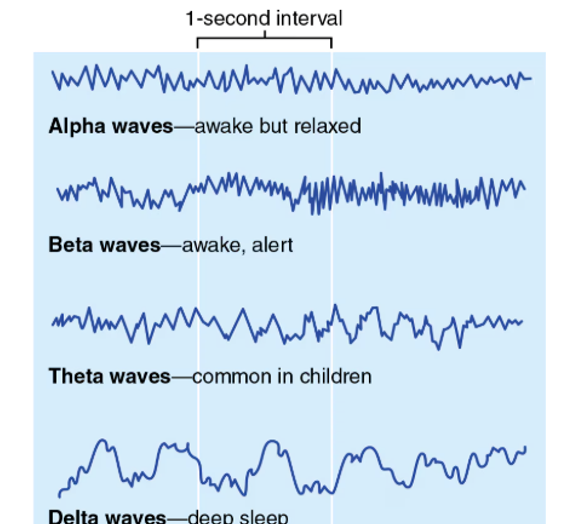
Delta Waves represent
Deep sleep or in awake adults is representative of brain damage
meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater (superficial to deep); these protective layers are deep to the cranium and wrap around the brain and spinal cord
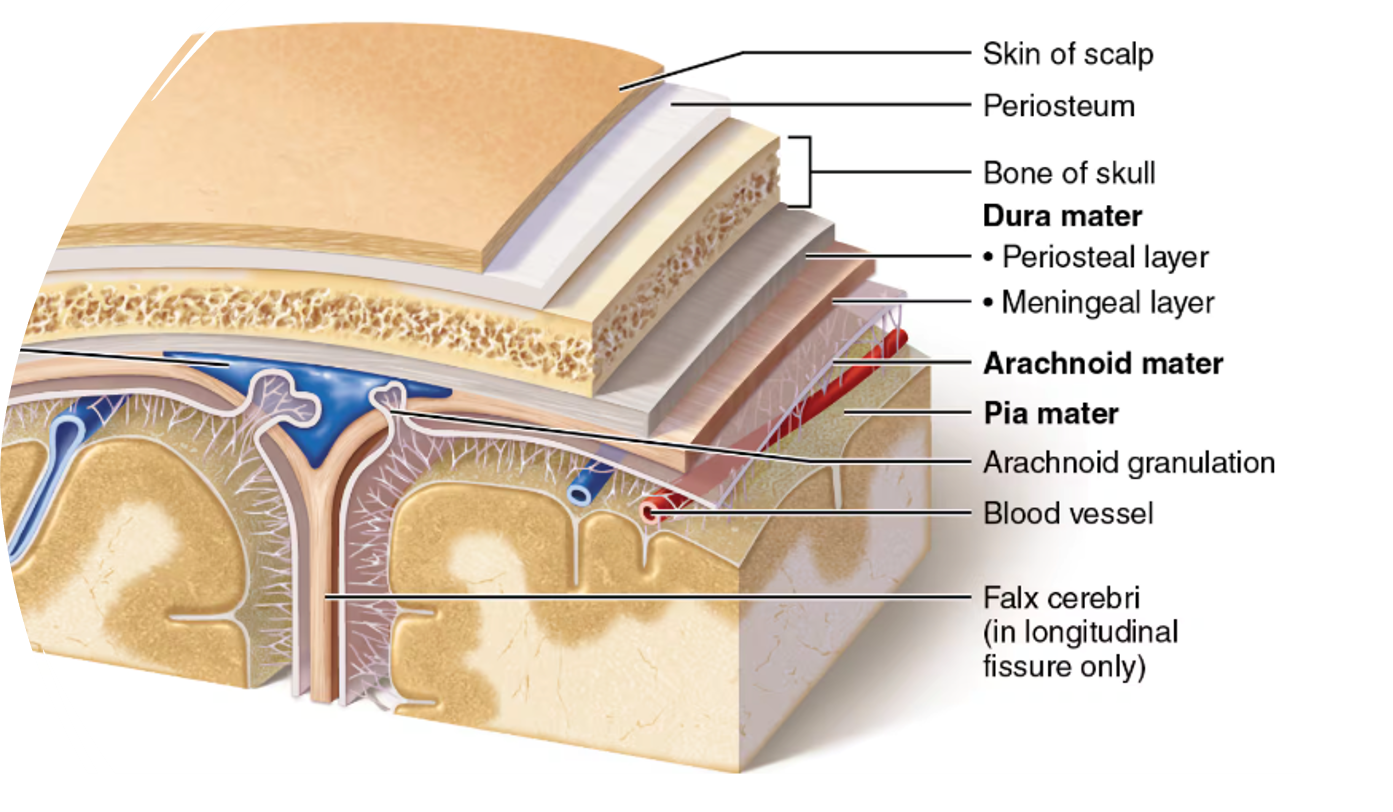
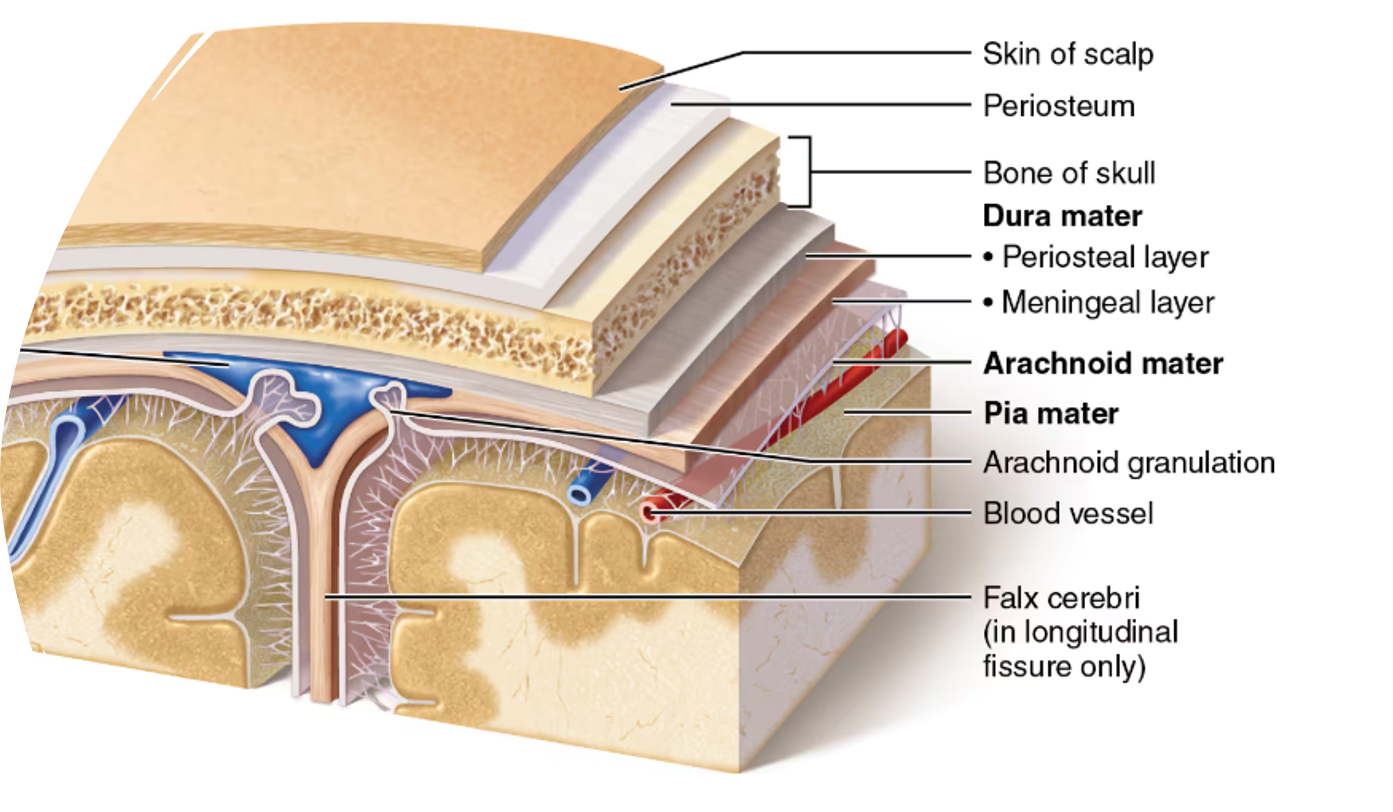
dura mater
most superficial meninges layer; very tough
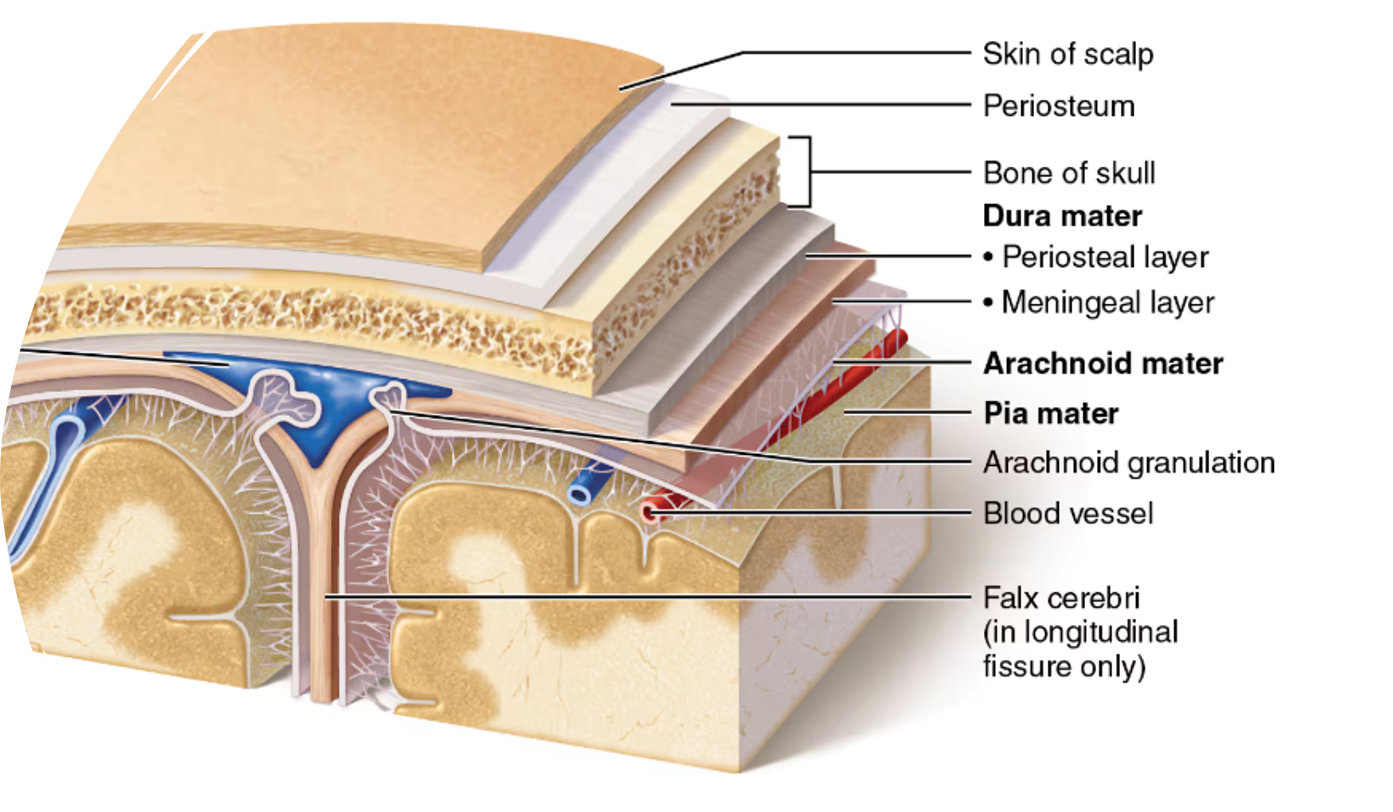
arachnoid mater
thin, web-like middle meninges layer
pia mater
soft, innermost layer of the meninges
Subdural space
space between the dura mater and arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid space
space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater that contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Cerebrospinal Fluid
clear, watery solution formed from blood plasma; produced by the choroid plexus; located in the subarachnoid space and central canal of the spinal cord; constant production/circulation with volume remaining the same
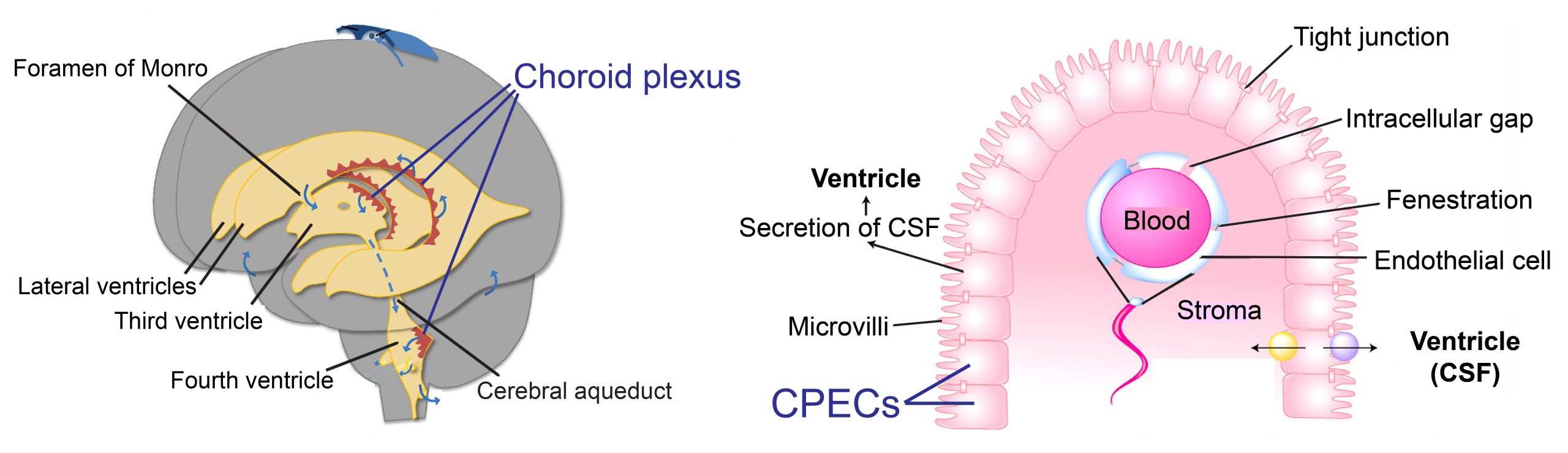
choroid plexus
Clusters of capillaries enclosed by pia mater and layer of ependymal cells; produces CSF from the roof of each ventricle; produced continuously
arachnoid granulations
Projections of the arachnoid mater; CSF drains from the subarachnoid space into the venous system back into the bloodstream
Conus Medullaris
red; end of spinal cord
Filum Terminale
pink; extension of pia mater to sacrum; helps anchor spinal cord
Cauda Equina
yellow (looks like a horse tail)
how many spinal nerves are there?
31
are the horns white matter or grey matter?
grey matter
These horns receive sensory input
dorsal horns
These horns contain somatic motor neurons for skeletal muscles
ventral horns
These horns contain visceral autonomic motor neurons
lateral horns
types of tracts in columns
ascending (3), descending (2), transverse
First-order neurons
Sensory receptor (ex. hand) to spinal cord or brainstem
Second-order neurons
Spinal cord or brainstem to thalamus or cerebellum
Third-order neurons
Thalamus to somatosensory cortex of cerebrum (post-central gyrus)
Lateral Spinothalamic Tract carries
pain and temperature through the lateral column; this is also an ascending pathway the crosses at the spinal cord level
Upper motor neurons
Cerebral cortex (precentral gyrus) to brainstem or spinal cord
Lower motor neurons
Brainstem or spinal cord to skeletal muscle (skip the thalamus)
Lateral Corticospinal Tract
sends conscious voluntary movement of arms and legs through the lateral column; this is a descending pathway the crosses in the medulla oblongata
Nociceptors are sensory receptors that detect…
pain (damaged cells/tissue)
Proprioceptors are sensory receptors that are located in…
muscles, tendons, and joints; used so the brain knows where limbs are located in space