Biochemistry Exam 1 Review 2
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Function of Globular Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Binding: Interaction strength can be expressed by:
Association (binding) constant: Ka, units M^-1
Dissocation constant: Kd, units M, Kd = 1/Ka
Ka = [PL]/[P][L]
Kd = [P][L]/[PL]
Binding: Magnitudes - strong and weak
Strong binding: Kd < 10nM
Weak binding: Kd > 10 uM
Proteins typically have high specificity: only certain ligands ___.
bind
High specificity can be explained by the ____ of the binding site and the ligand.
Complementary
Complementary of the binding site and the ligand in ….
size
shape
charge
hydrophobic/hydrophilic character
What is induced fit? Induced fit allows for ____ binding of the ligand. Induced fit allows for ___ affinity of different glands.
the adaptation where conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding.
tighter
high
T/F? Both the ligand and the protein can change their conformations.
TRUE
_____ is a special case of allosteric regulation.
Cooperativity
Allosteric Proteins:
Binding of a ____ to one site affects the binding
Can they be positive? negative? both?
What is it called when a normal ligand of the protein is the allosteric regulator?
What is it called when a different ligand affects binding of the normal ligand?
ligand
both
homotropic
heterotropic
Cooperativity = ?
positive homotropic regulation
Hemoglobin binds O2 _____.
cooperatively
Hemoglobin is a ___ of two subunits.
Each subunit is similar to ____.
tetramer
myoglobin
Are the sequences of hemoglobin and myoglobin similar?
They are not very similar.
Subunit interactions of Hemoglobin:
What molecule is in the T state?
deoxyhemoglobin - hemoglobin without oxygen bound.
Define R and T states of hemoglobin.
Do they have more or less interactions?
Are they more stable or flexible?
Low or high affinity for O2?
T = tense state
more interactions
more stable
Lower affinity
R = relaxed state
fewer interactions
more flexible
higher affinity
O2 binding triggers a ___ → ___ conformational change.
T → R
Conformational change from the T state to the R state involves breaking ____ ___ between the a1-B2 interface.
ion pairs
Hemoglobin (Hb) affinity for O2 depends on __.
H+ binds to Hb and stabilizes the __ state.
Protonates His146 which then forms a ____ _____ with Asp94.
Leads to release of ___.
pH
T
salt bridge
O2
The pH differences between ____ and ____ _____ increases efficiency of the O2 transport.
lungs
metabolic tissues
pH effect on O2 Binding to Hemoglobin is known as the ____ ____.
Bohr Effect
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate regulates O2 binding:
_____ heterotrophic regulator of Hb function.
Present at mM concentrations in _____.
Produced from an intermediate in ____.
Small ____ charged molecule, binds to the ____ charged central cavity of Hb.
Stabilizes the ___ states.
Negative
erythrocytes
glycolysis
negatively
positively
T
2,3-BPG binds to the …
central cavity of Hb
2,3-BPG allows for ___ release in the tissues and adaptation to changes in altitude:
Hemoglobin binds to O2 quite tightly when ___ is entirely absent.
At high altitudes, O2 delivery _____ by about ¼ to 30% of max.
Increase in BPG concentration _____ affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
O2
BPG
declines
decreases
Sickle-Cell anemia is due to a mutation in ____.
Hemoglobin
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are catalysts that increase rates without being used up.
Most enzymes are ____ proteins and ____.
globular
soluble
Apoenzyme
protein part of the enzyme
Holoenzyme
complete function including coenzyme and metal ions
In light produced by fireflies:
_____ provides energy
____ is the enzyme
_____ is the cofactor
ATP
luciferase
Mg+2
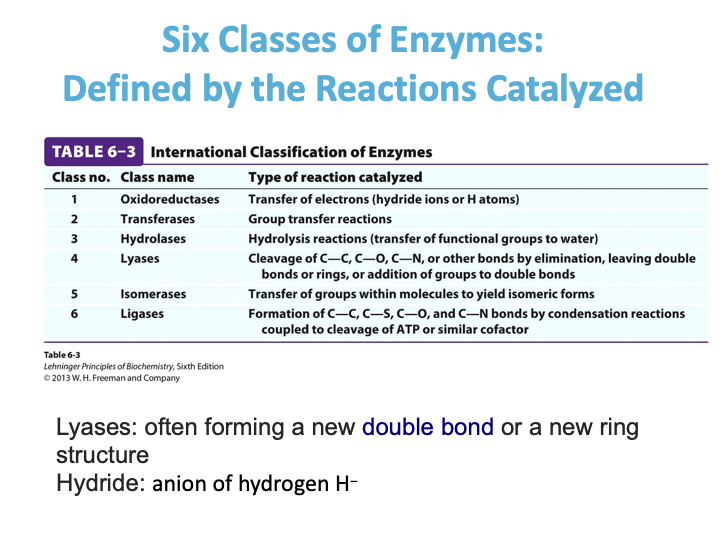
Six Classes of Enzymes:
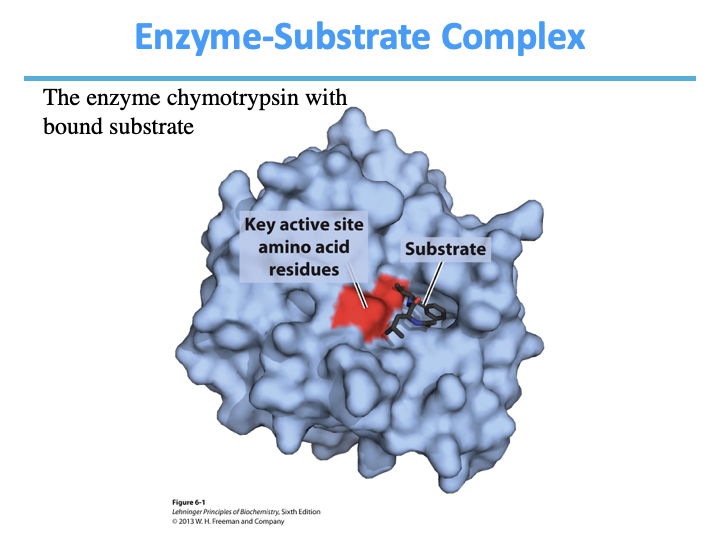
Enzymes act by binding _____.
The non covalent enzyme substrate complex is known as the _____ _____.
substrates
Michaelis complex
Do enzymes affect equilibrium?
_____ reactions face significant activation barriers (delta G++) that must be surmounted during rxn.
Enzymes ____ reaction rates (k) by decreasing deltaG++
No
Slow
Increase
What are inhibitor?
compounds that decrease enzymes activity
Irreversible inhibitors ____ with the enzyme
One inhibitor can permanently ____ ____ one enzyme molecule.
They are often ____ _____ but may be used as drugs.
react
shut off
powerful toxins
Reversible inhibitors ____ to and can ____ from enzyme.
they are often structural analogs of ____ or ____.
They are often used as ____ to slow down a specific enzyme.
bind, dissociate
substrates, products
drugs
Reversible inhibitor can bind to:
to the free enzyme and prevent binding of the substrate
to the enzyme-substrate complex and prevent rxn.
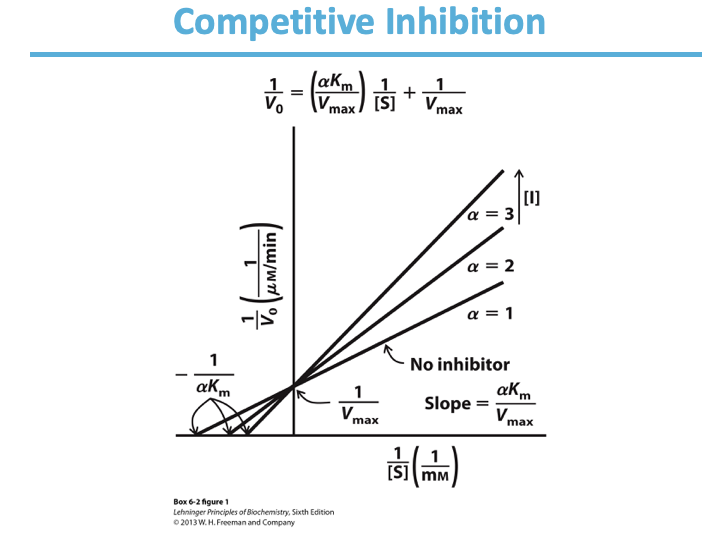
Competitive Inhibition:
Competes with ____ for binding.
Binds ___ site
Does/Doesn’t affect catalysis?
No change in ____ ; apparent increase in ___.
In Linweaver-Burk: lines intersect at the _-axis.
substrate
active
doesn’t
Vmax; Km
y
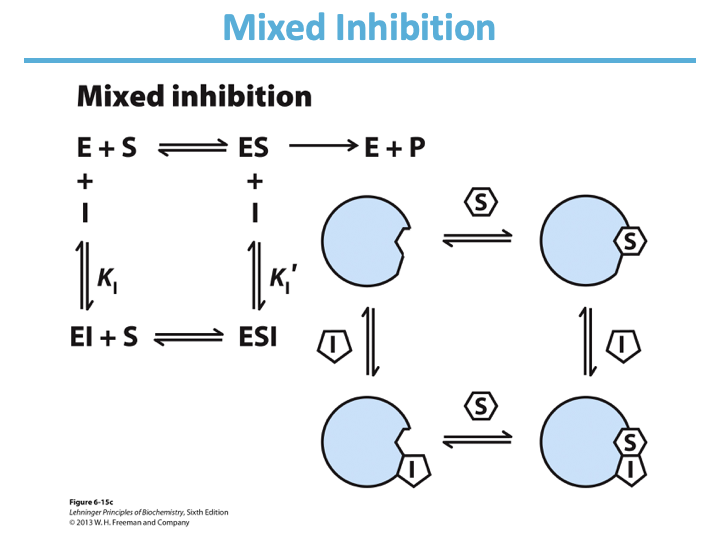
Mixed Inhibition:
Binds enzyme with/without/both substrate?
Inhibits what two things?
Binds to ___ site.
Decrease in ____; apparent change in ____.
In lineweaver-burk: lines intersect ____ from y-axis/
______ inhibitors are mixed inhibitors such that there is no change in Km.
both
catalysis and substrate binding
regulatory
Vmax; Km
left
Noncompetitive
Hexokinase undergoes ____ ____ on substrate binding.
induced fit
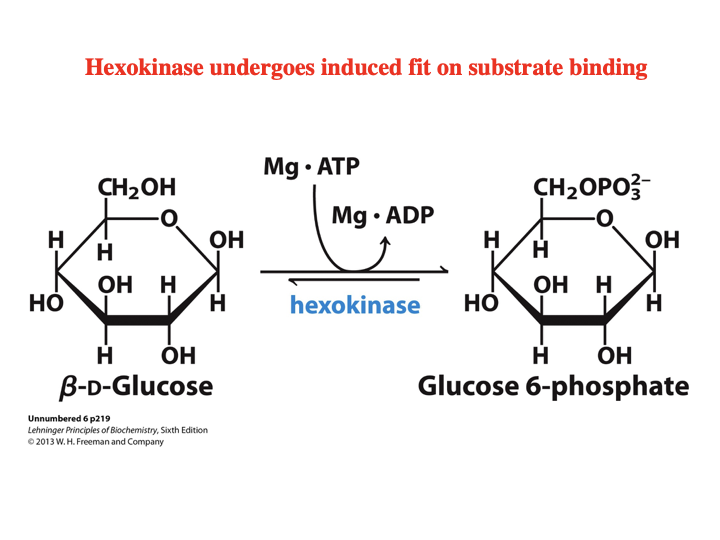
How does hexokinase under induced fit on substrate binding?
Starts in open U-shape and when entering catalytic active form, the ends pinch together after binding of D-glucose.
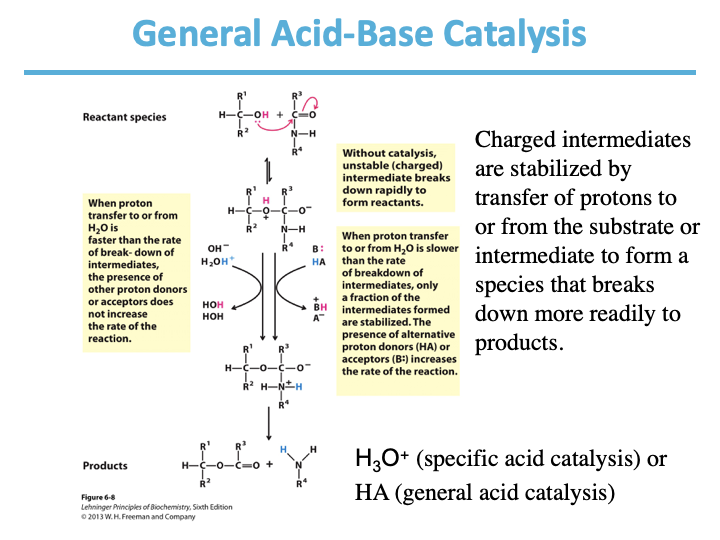
General Acid-Base Catalysis:
Charged intermediates are stabilized by transfer of ____ to or from the substrate or intermediate to form a species that breaks down more readily to products.
protons
Covalent Catalysis:
A transient covalent bond between the ____ and the ____.
Changes the rxn ____
Requires a _____ on the enzyme.
a nucleophile is a chemical species that donates an ____ ____ to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in relation to a rxn.
Can be reactive ___, ___, ___, or ____.
enzyme and the substrate
pathway
nucleophile
electron pair
Serine, thiolate, amine, or carboxylate