Endo/Repro Exam 1: Other Pancreatic Hormones (Dr. Leavis)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
T/F: The pancreas is an exocrine and endocrine organ
true
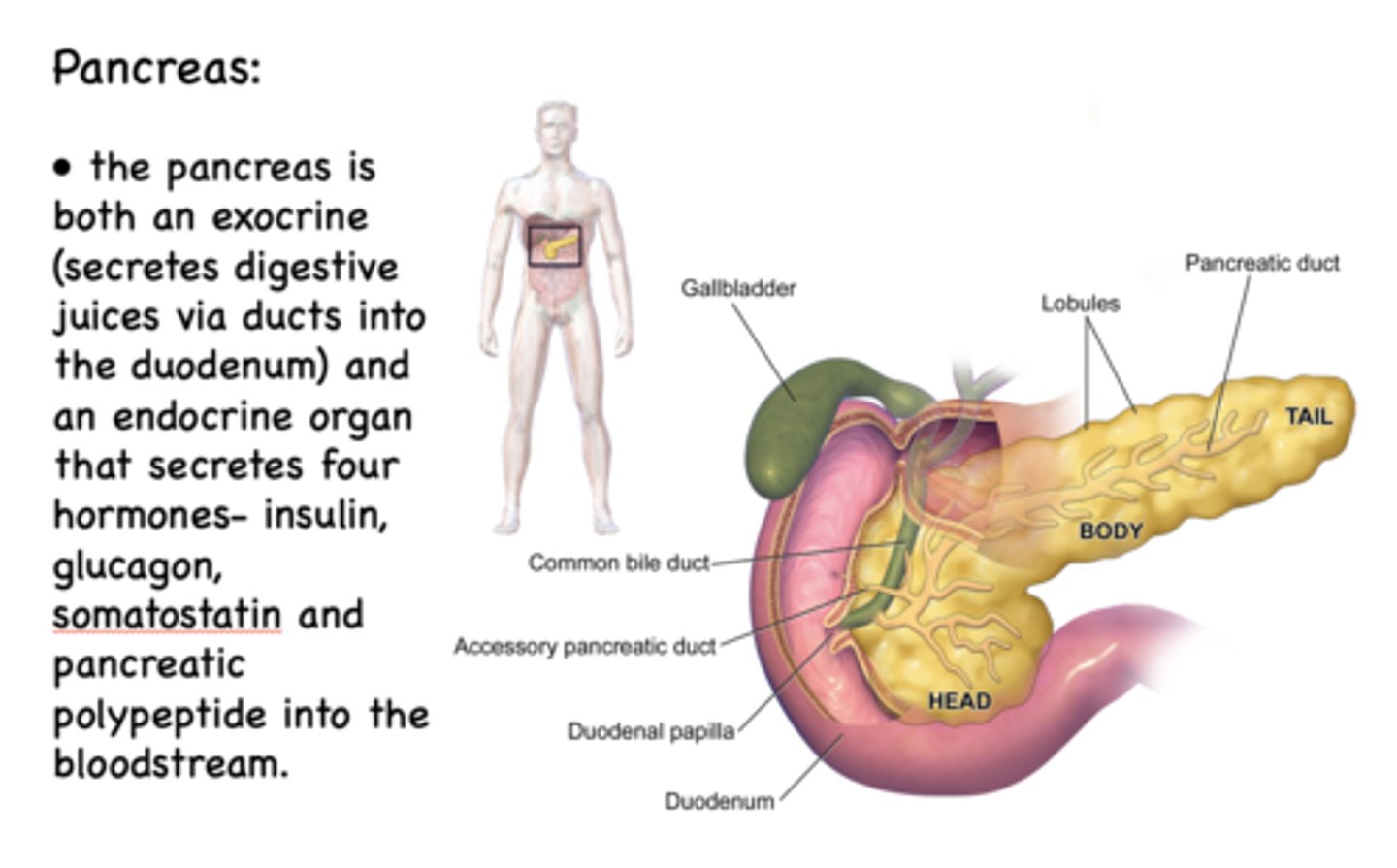
What 4 hormones does the endocrine pancreas secrete?
- Insulin
- Glucagon
- Somatostatin
- Pancreatic polypeptide
What is the functional unit of the pancreas?
Islets of Langerhans
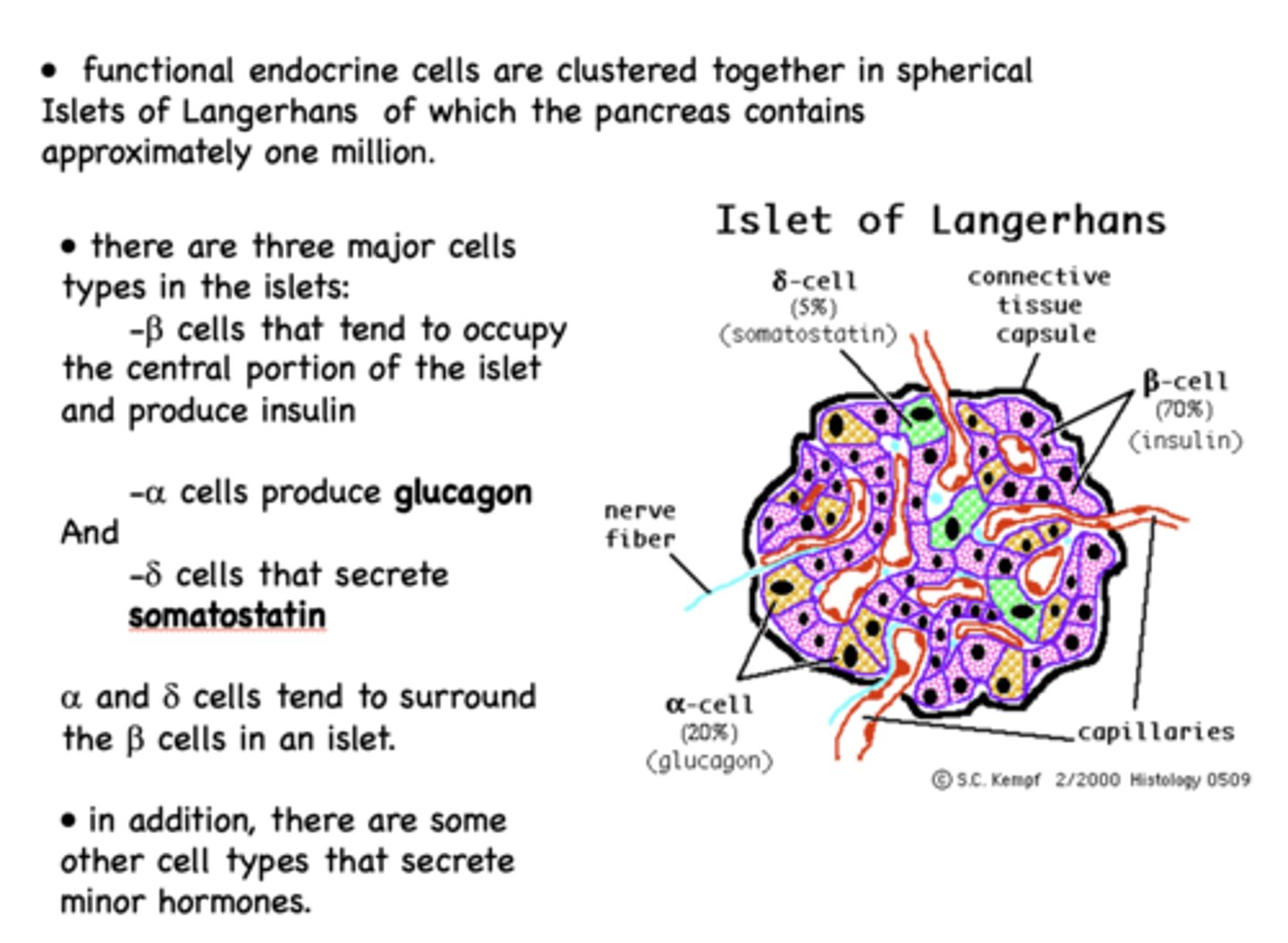
What are the three major cell types in the Islets of Langerhans?
- Beta cells
- Alpha cells
- Delta cells
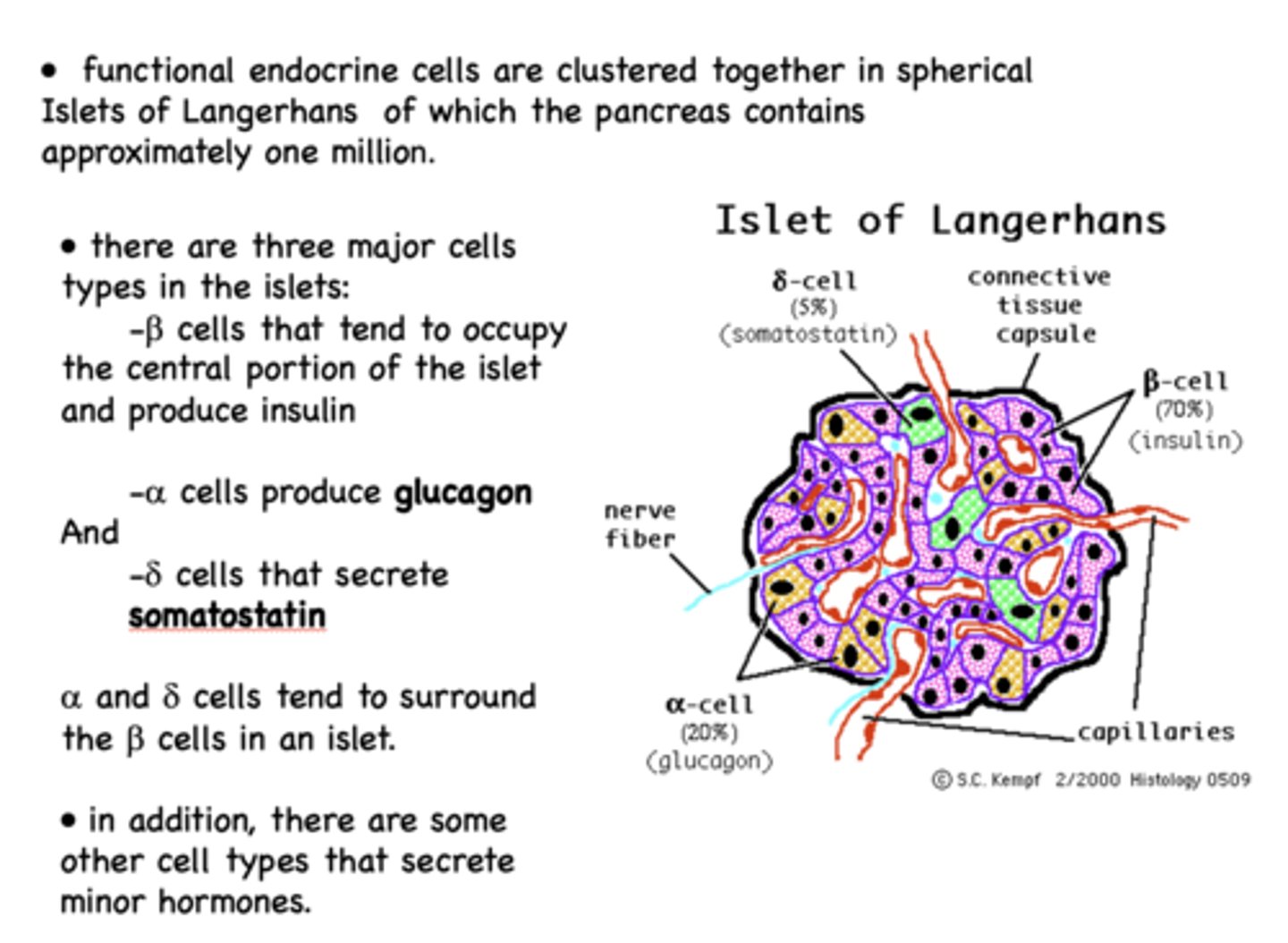
Beta cells of the islet of langerhans are the most prominent cell type and are responsible for producing what?
insulin
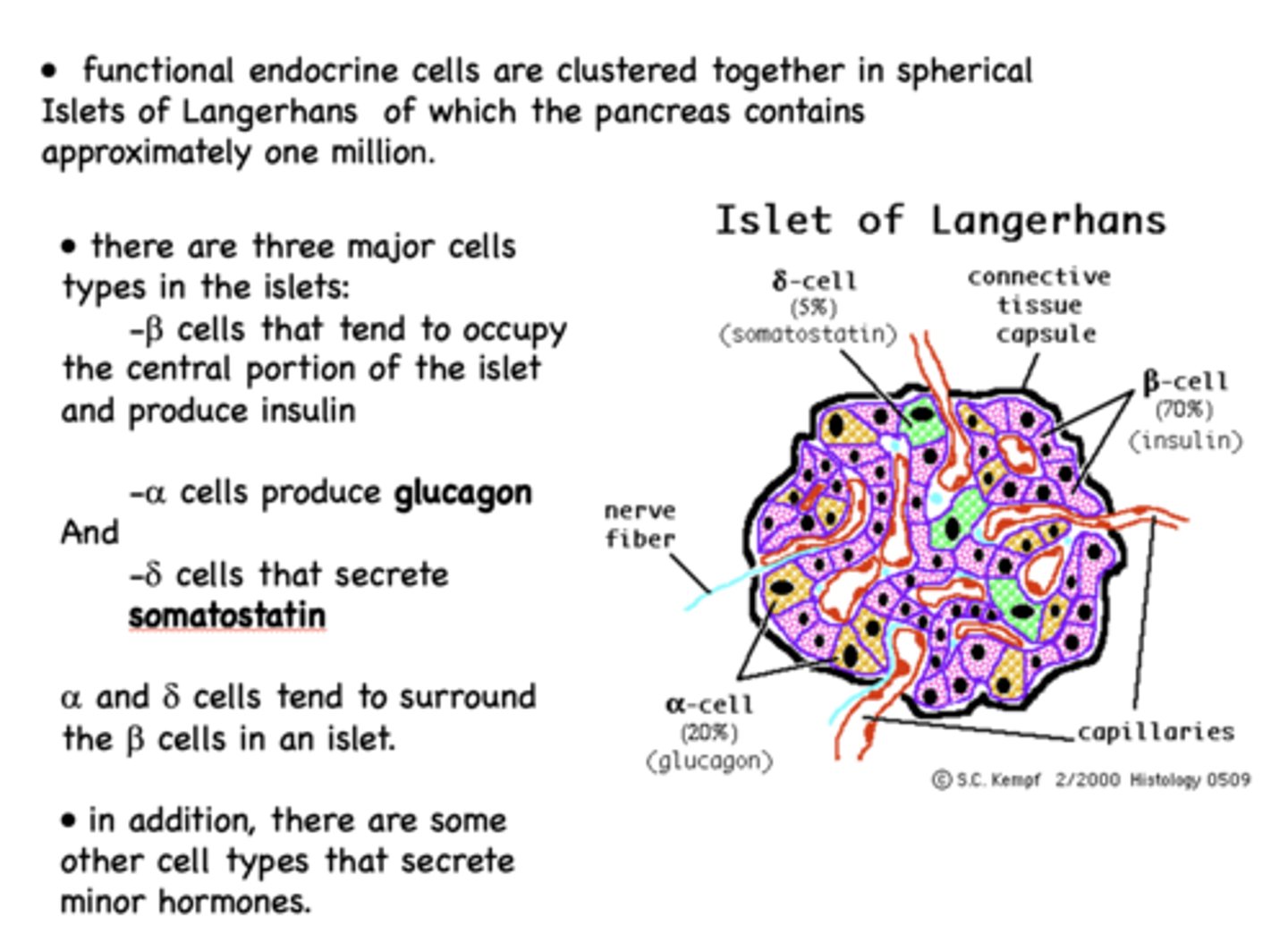
Alpha cells of the islet of langerhans are the second most prominent cell type and are responsible for producing what?
glucagon
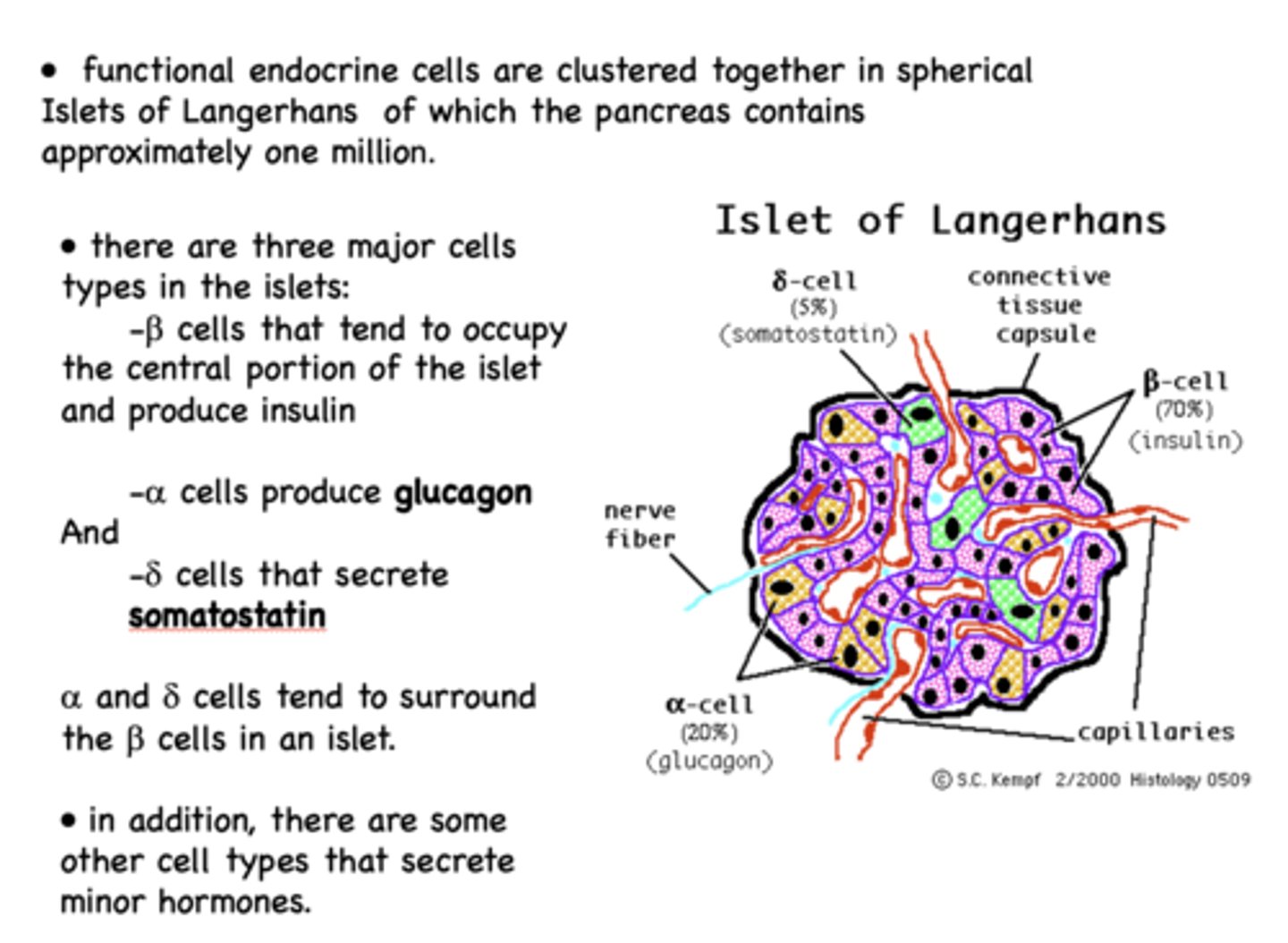
Delta cells of the islet of langerhans are the least prominent cell type and are responsible for producing what?
somatostatin
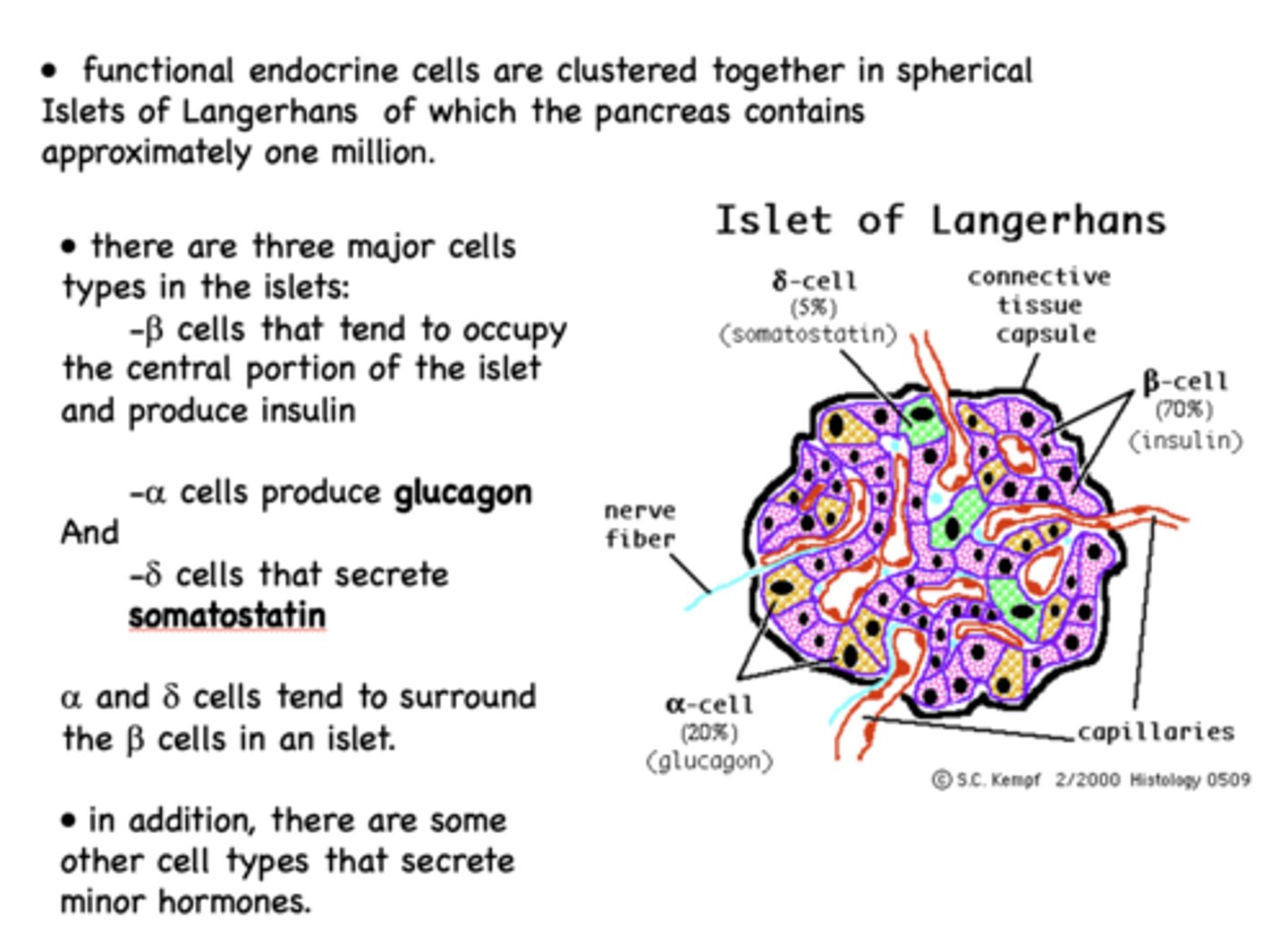
What is secreted by a cells when insulin levels fall -during fasting between meals?
glucagon

What is the most potent stimulus for secretion of glucagon?
hypoglycemia (blood sugar < 1mg/ml)

what are stimuli of glucagon?
- Decreasing insulin
- Amino acids
- Sympathetic stimulation

What inhibits glucagon?
- Somatostatin
- Fatty acids

What acts primarily on the liver to increase and maintain blood glucose during times of fasting ?
glucagon

Glucagon is an antagonist of what?
insulin

how is glucagon synthesized?
Glucagon is a peptide hormone synthesized as proglucagon and then processed into the 29-residue glucagon in alpha cells

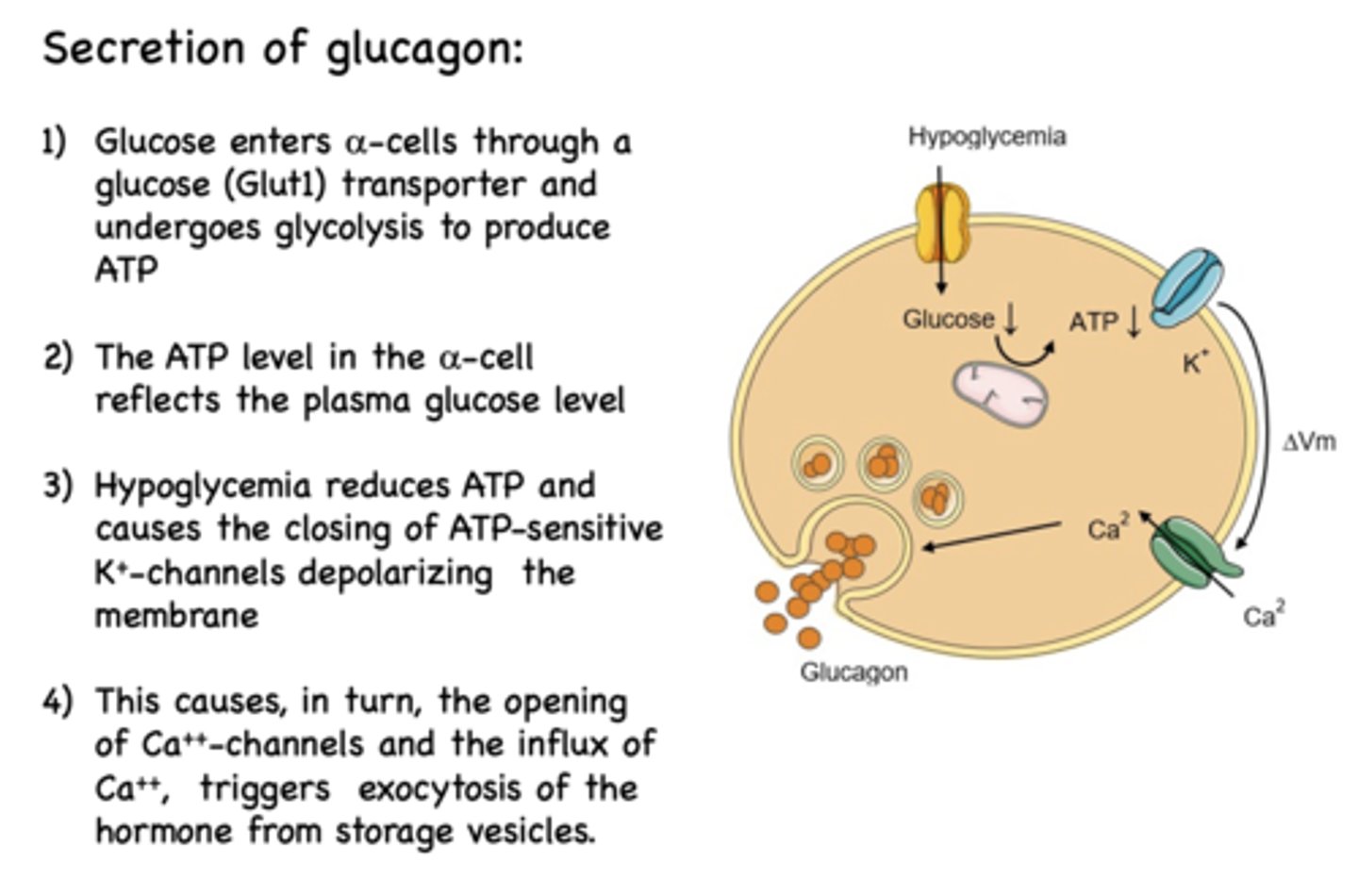
The first step of the secretion of glucagon is that is enters alpha cells through a ______ transporter and undergoes glycolysis to produce ATP
Glut1 (glucose transporter)
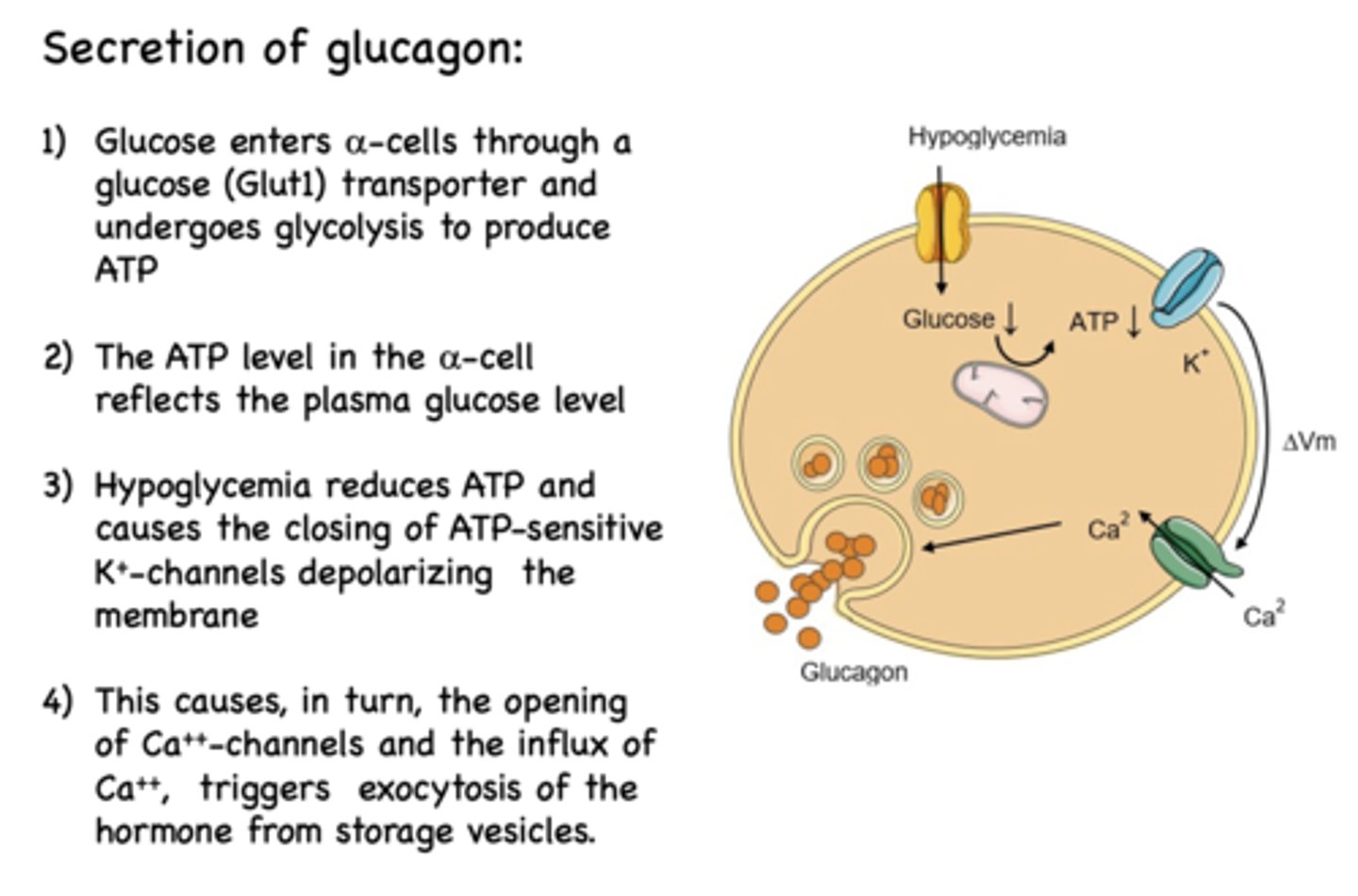
The ATP level in the alpha cells reflects what?
plasma glucose level
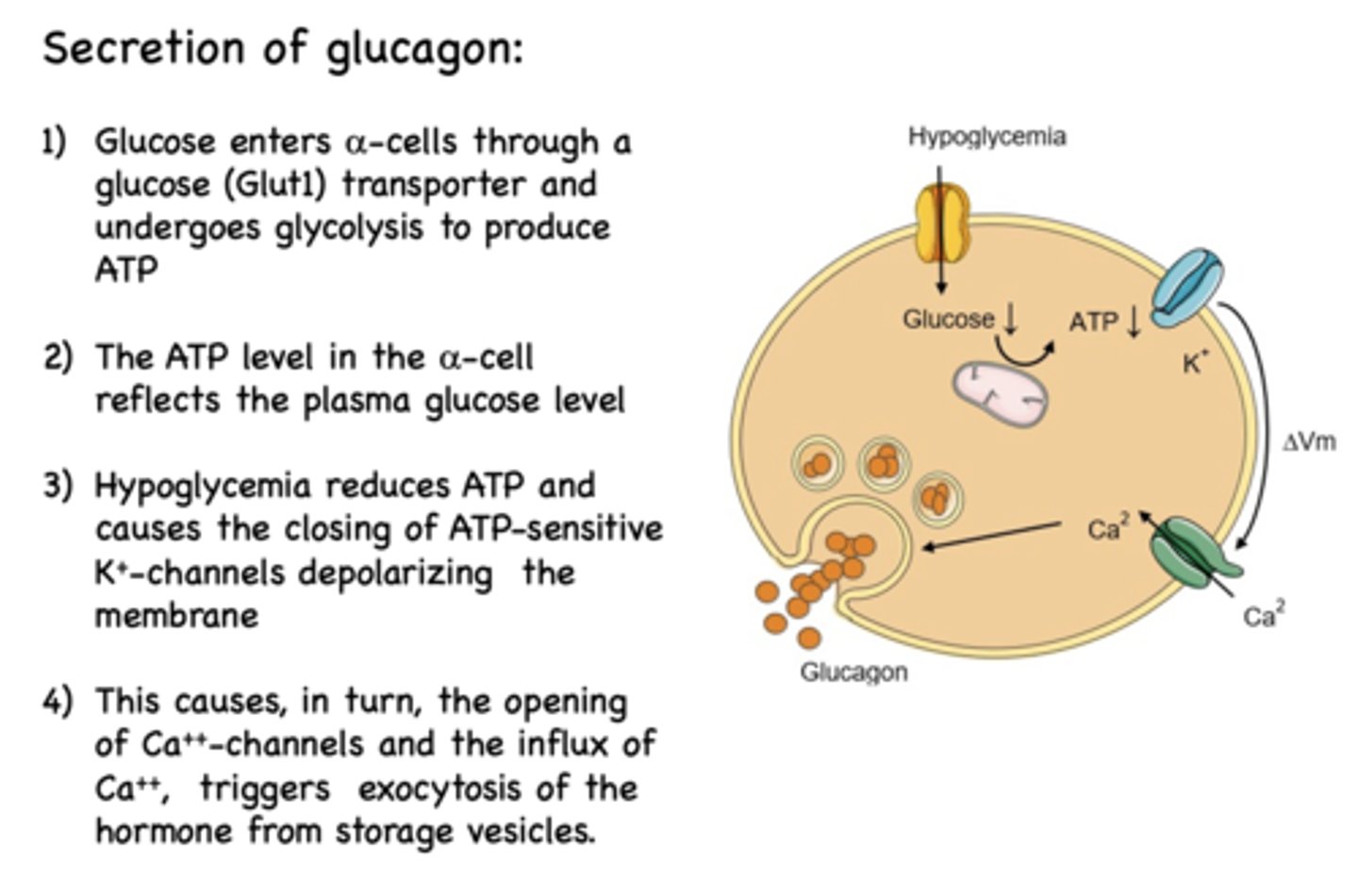
_______________ reduces ATP and causes the closing of ATP-sensitive K+-channels depolarizing the membrane
Hypoglycemia
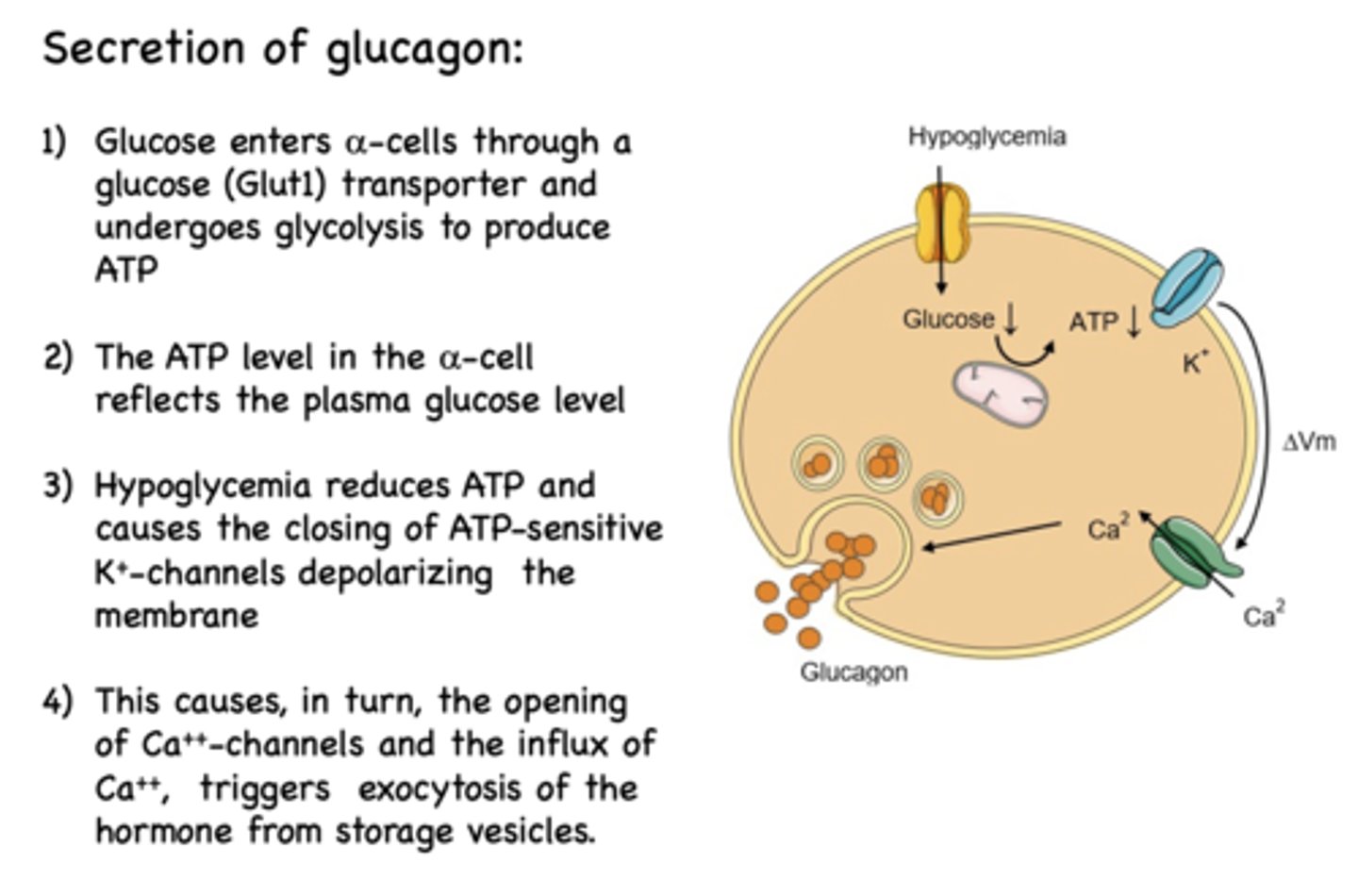
Depolarization of alpha cells causes the influx of what?
Ca2+
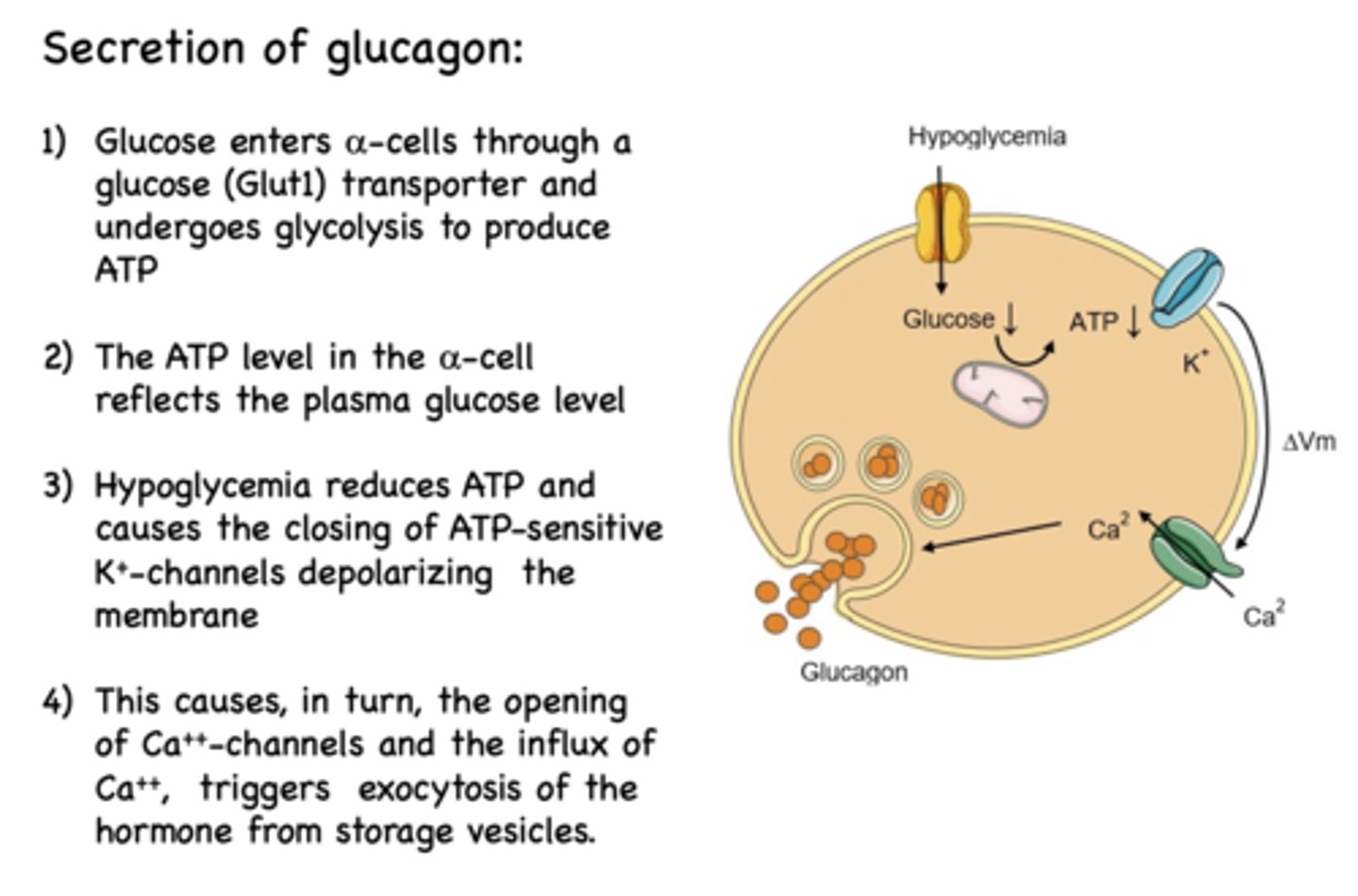
Calcium influx into alpha cells triggers what?
exocytosis of glucagon from storage vescicles
Where are glucagon receptors located primarily?
liver (also found in kidneys, heart, adrenal glands, GI tract, pancreas in small amounts)

The main signaling of glucagon involves _____________ activation which activates _____________ to produce _____________ and _____________, which activate downstream enzymes
Main signaling of glucagon involves G-protein activation which activates adenylyl cyclase to produce cAMP and protein kinase C, which activate downstream enzymes

What is glucagon signaling inactivated by?
receptor-mediated endocytosis and proteolysis by enzymes

What is the circulating half-life of glucagon?
4-7 min

Does glucagon increases or decreases hepatic glucose production and release?
increases
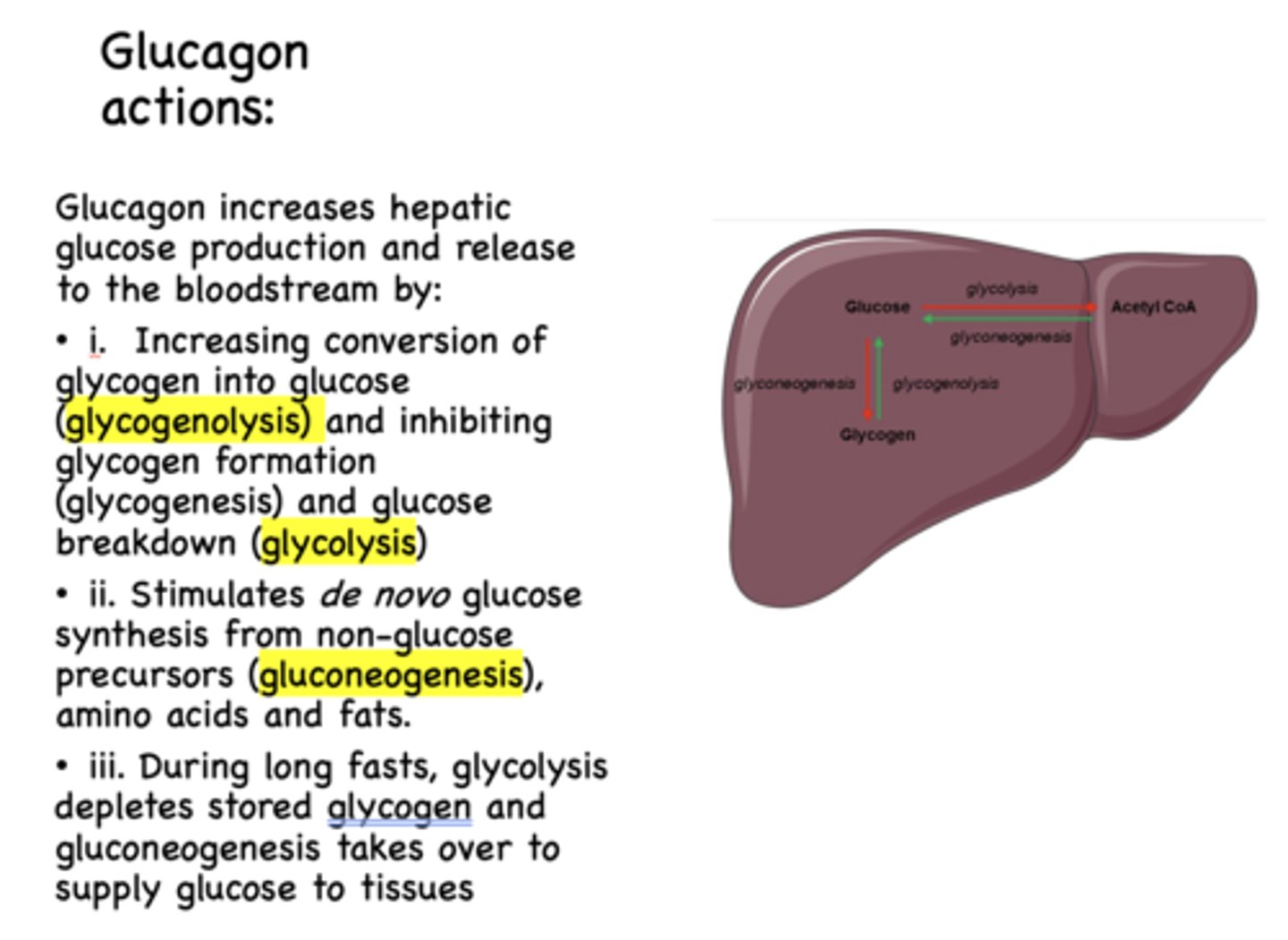
glycogen to glucose is known as ______________
glycogenolysis
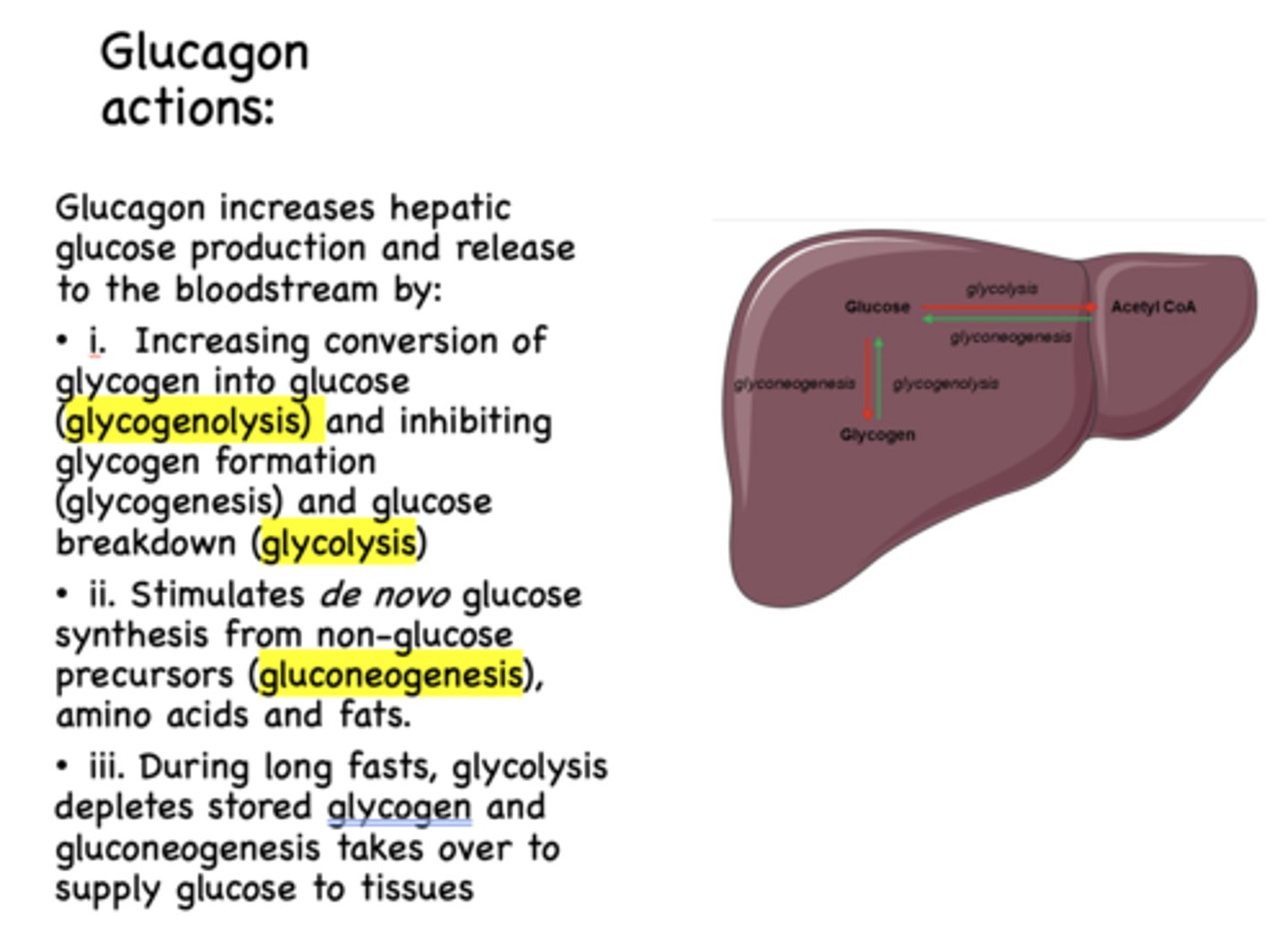
glycogen formation is known as ______________
glycogenesis
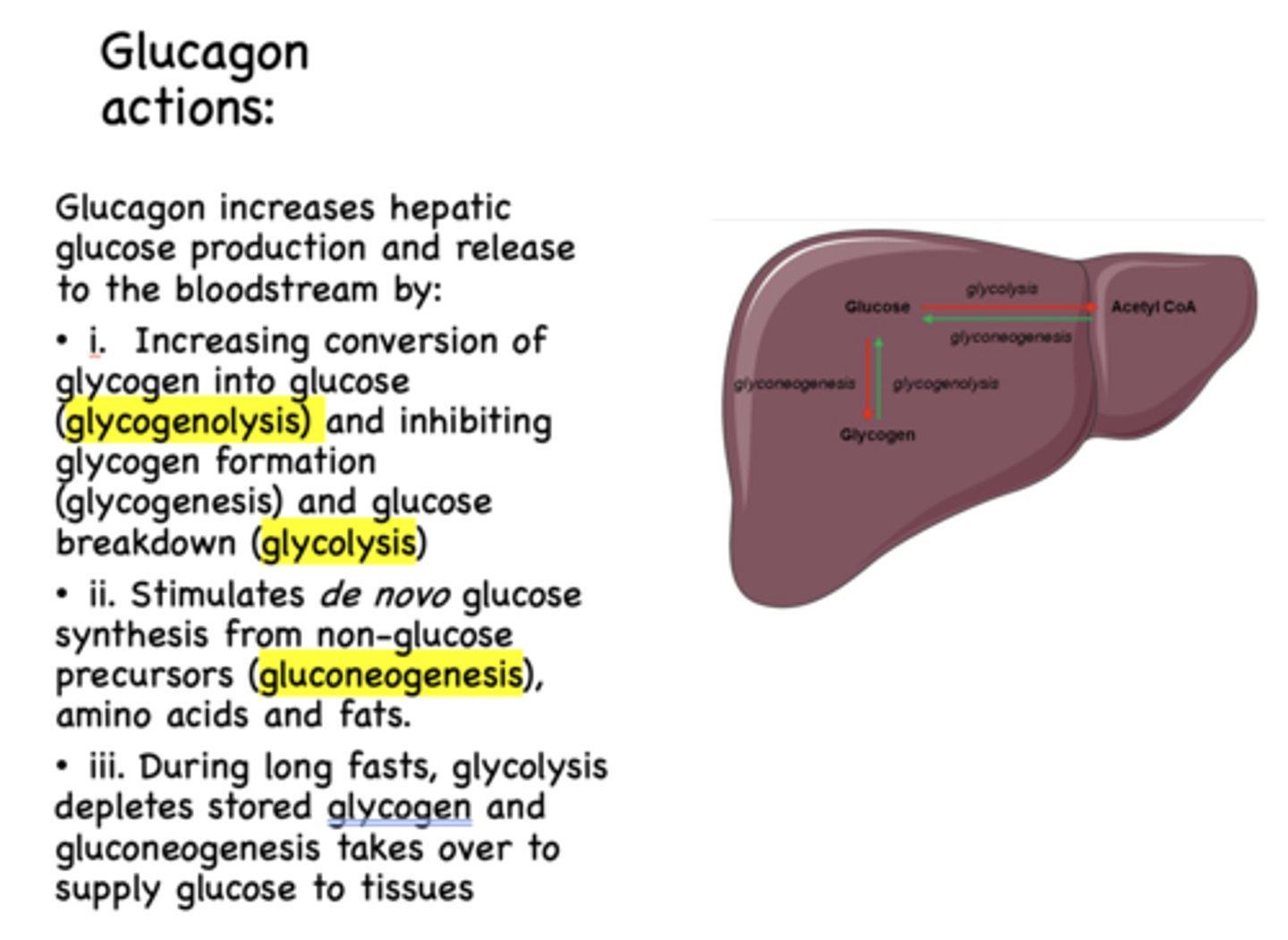
glucose breakdown is known as ______________
glycolysis
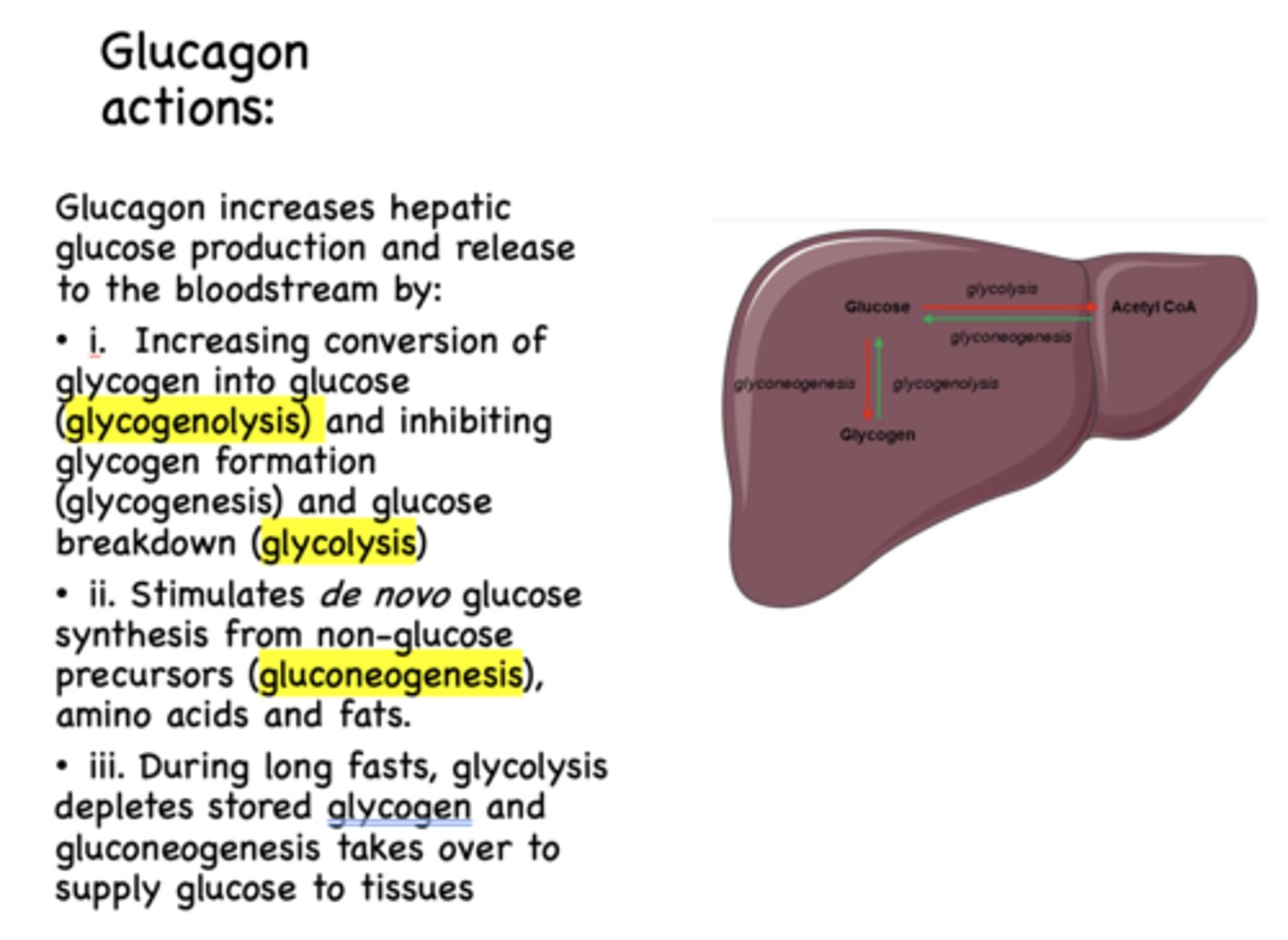
Glucagon has what effect on glycogenolysis?
increases
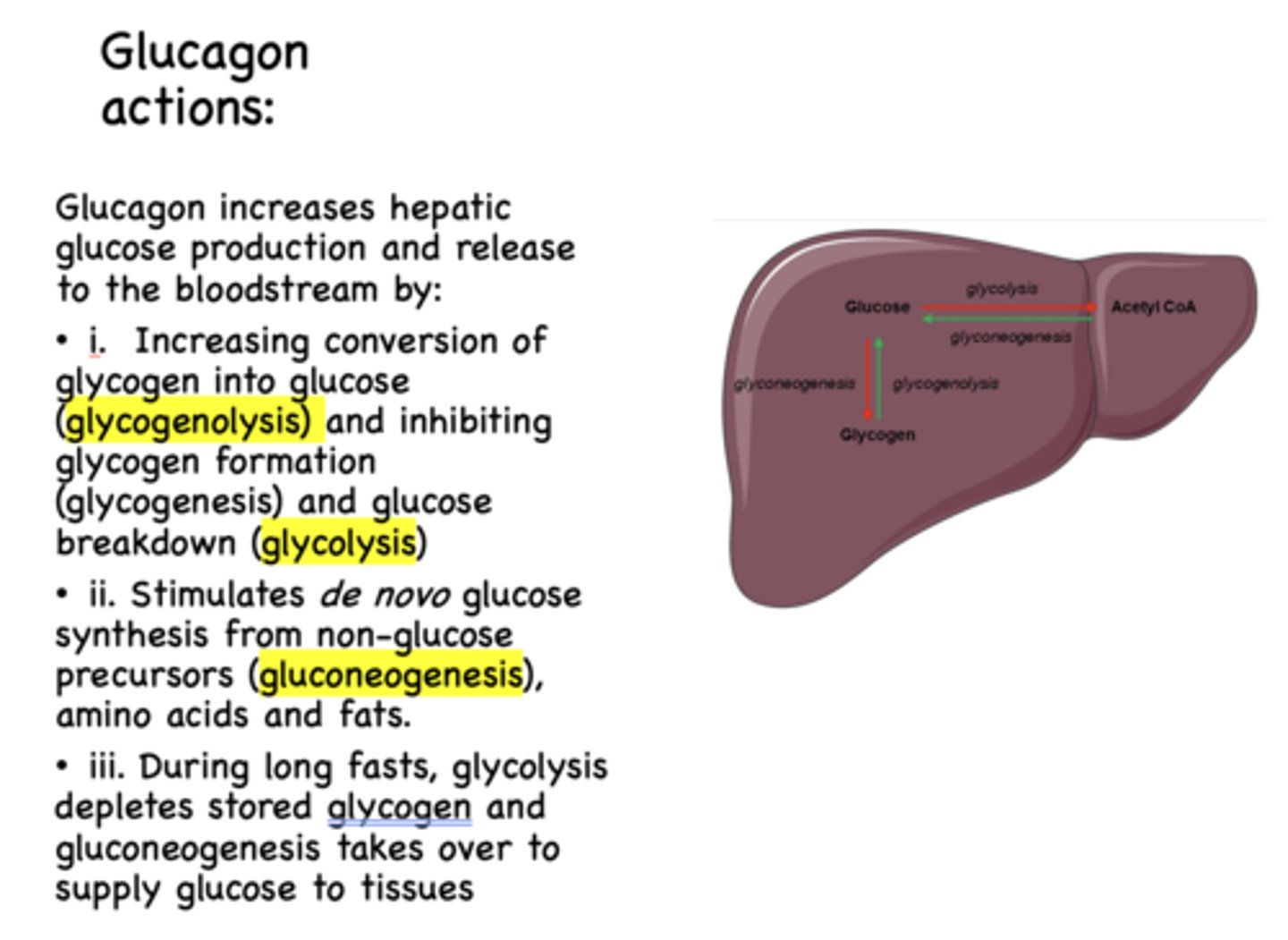
Glucagon has what effect on glycogenesis?
inhibits
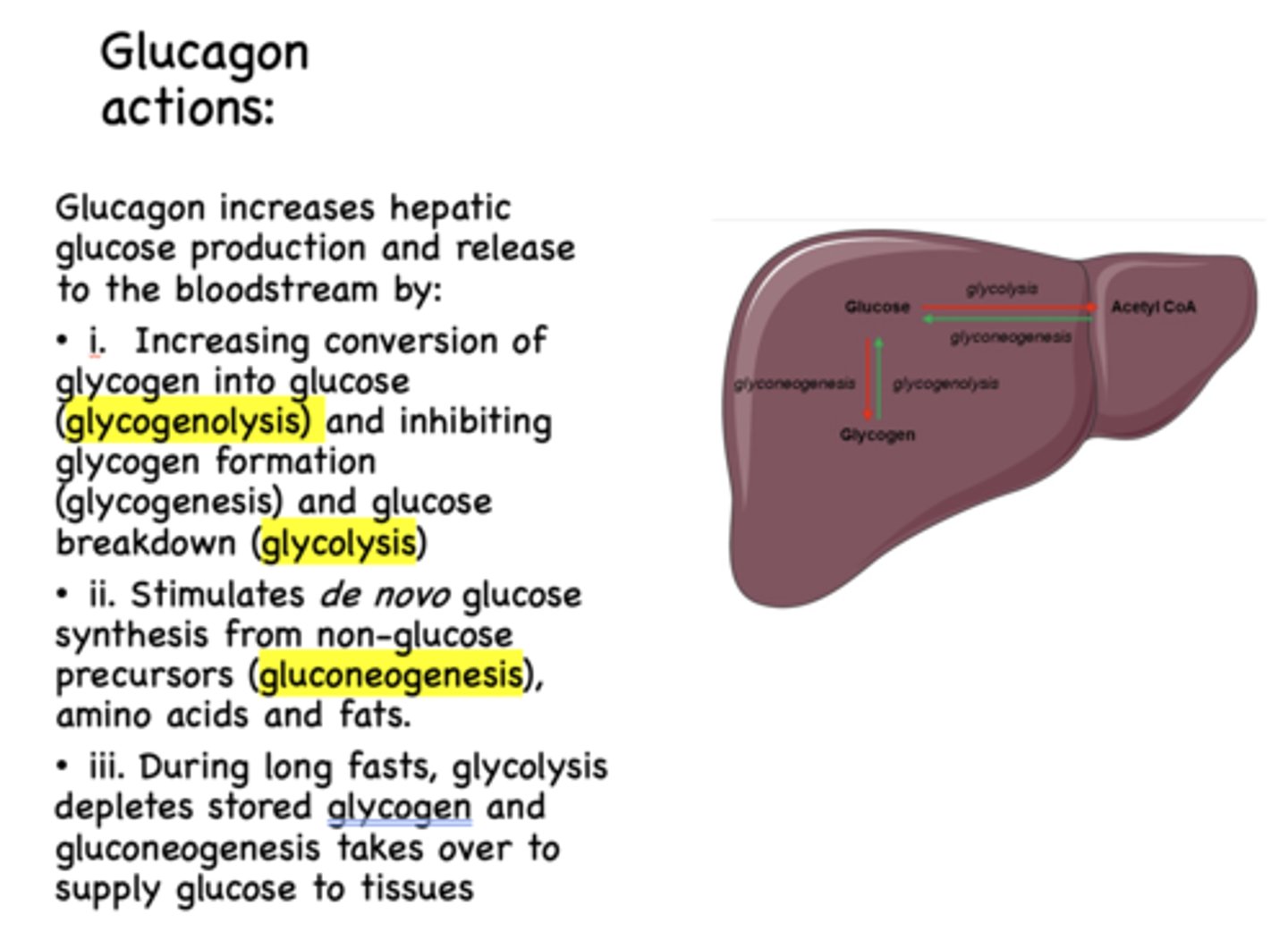
Glucagon has what effect on glycolysis?
inhibits
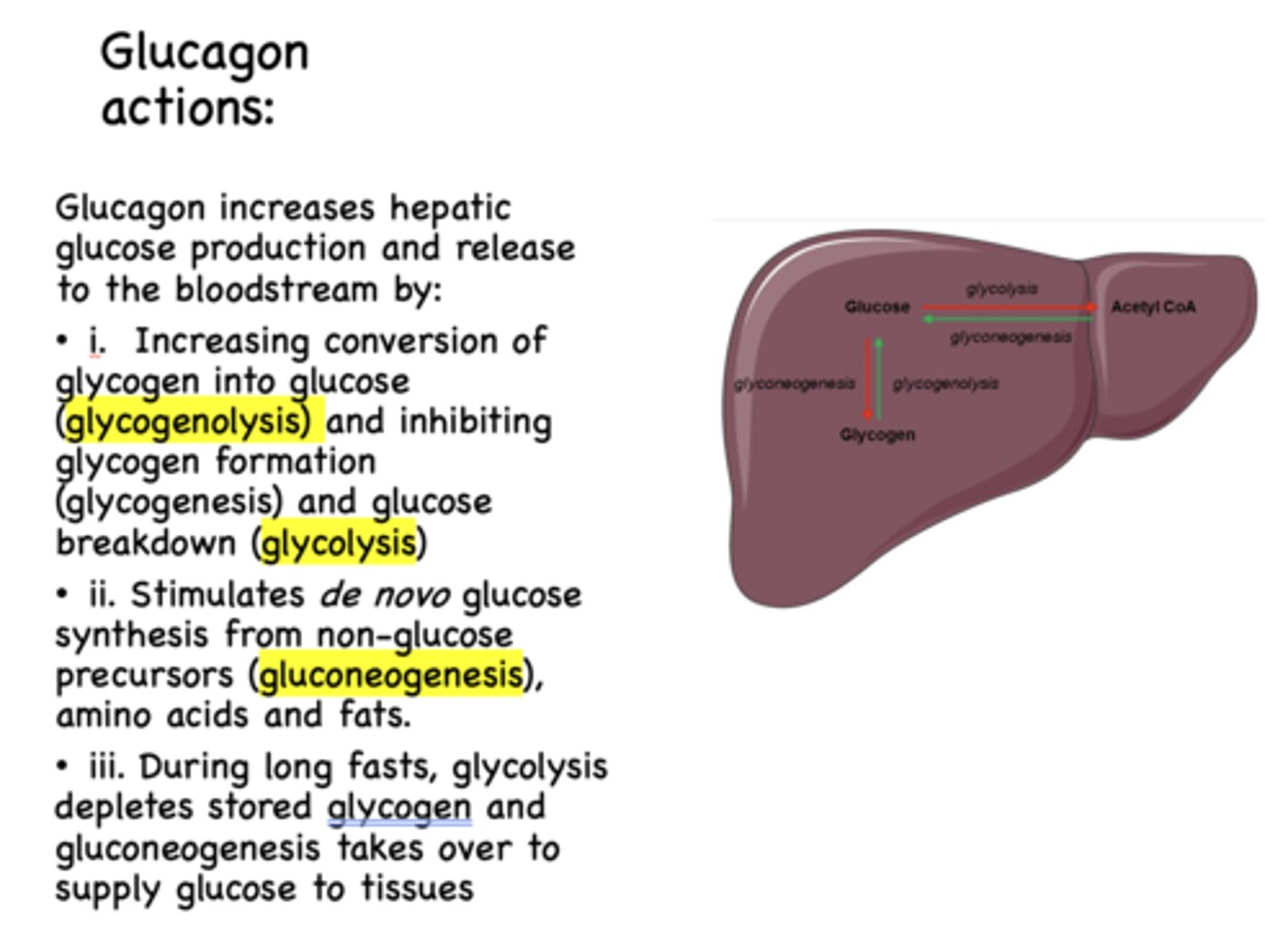
de novo glucose synthesis form non-glucose precursors (amino acids, fats) which is known as _____________
gluconeogenesis
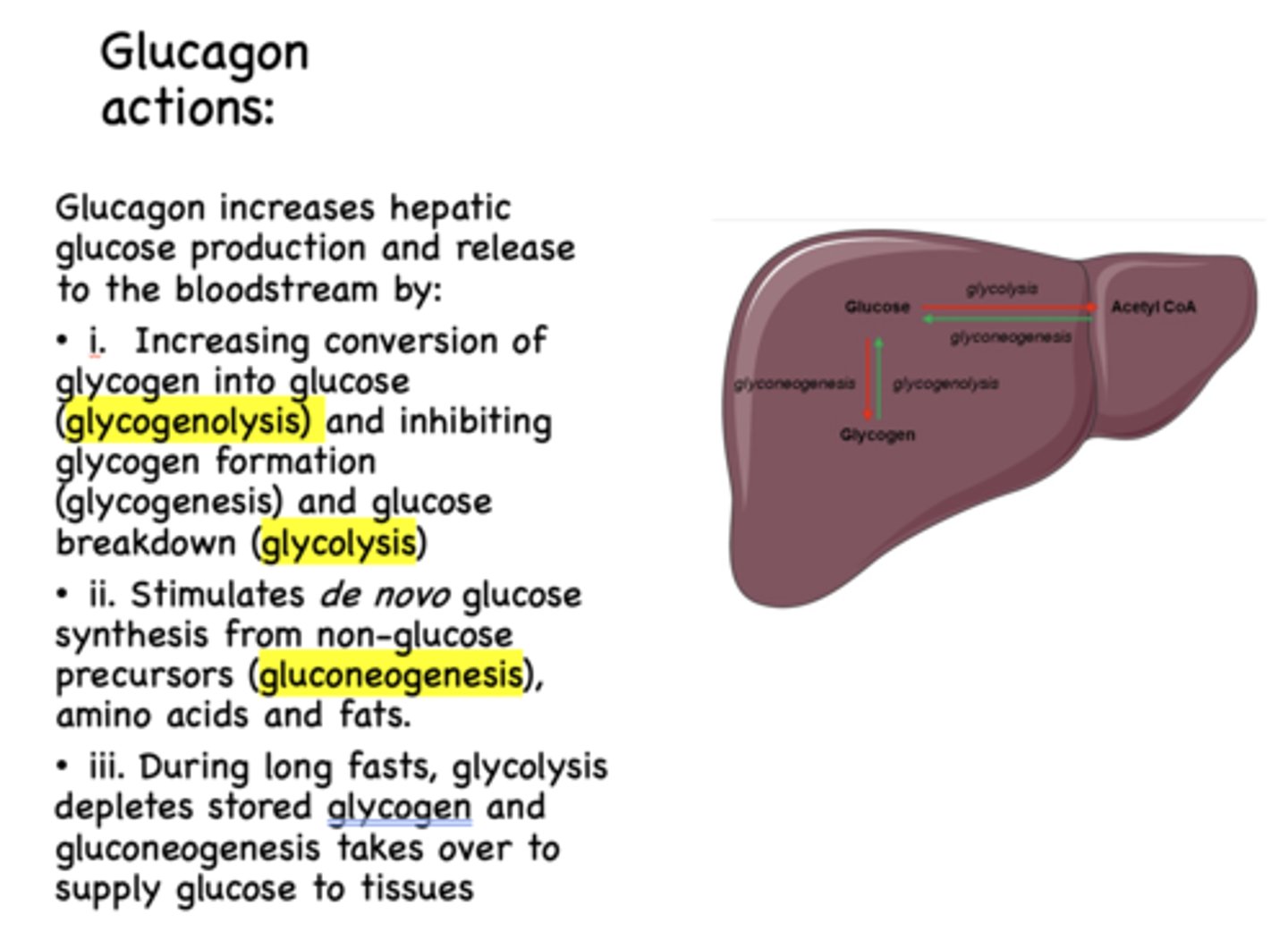
Glucagon has what effect on gluconeogenesis?
stimulates
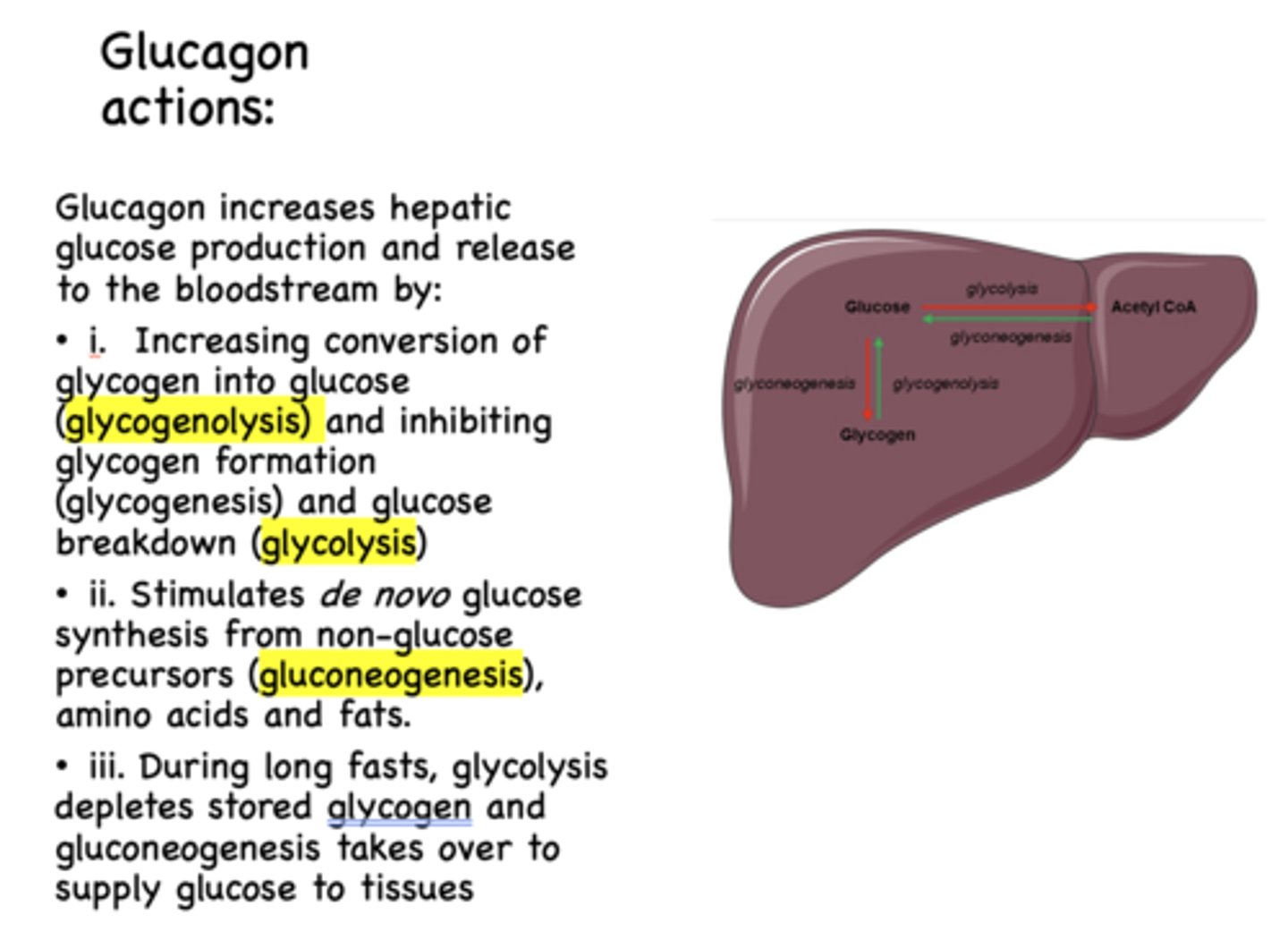
When does glycolysis deplete stored glycogen and gluconeogenesis takes over to supply glucose to tissues?
during long fasts
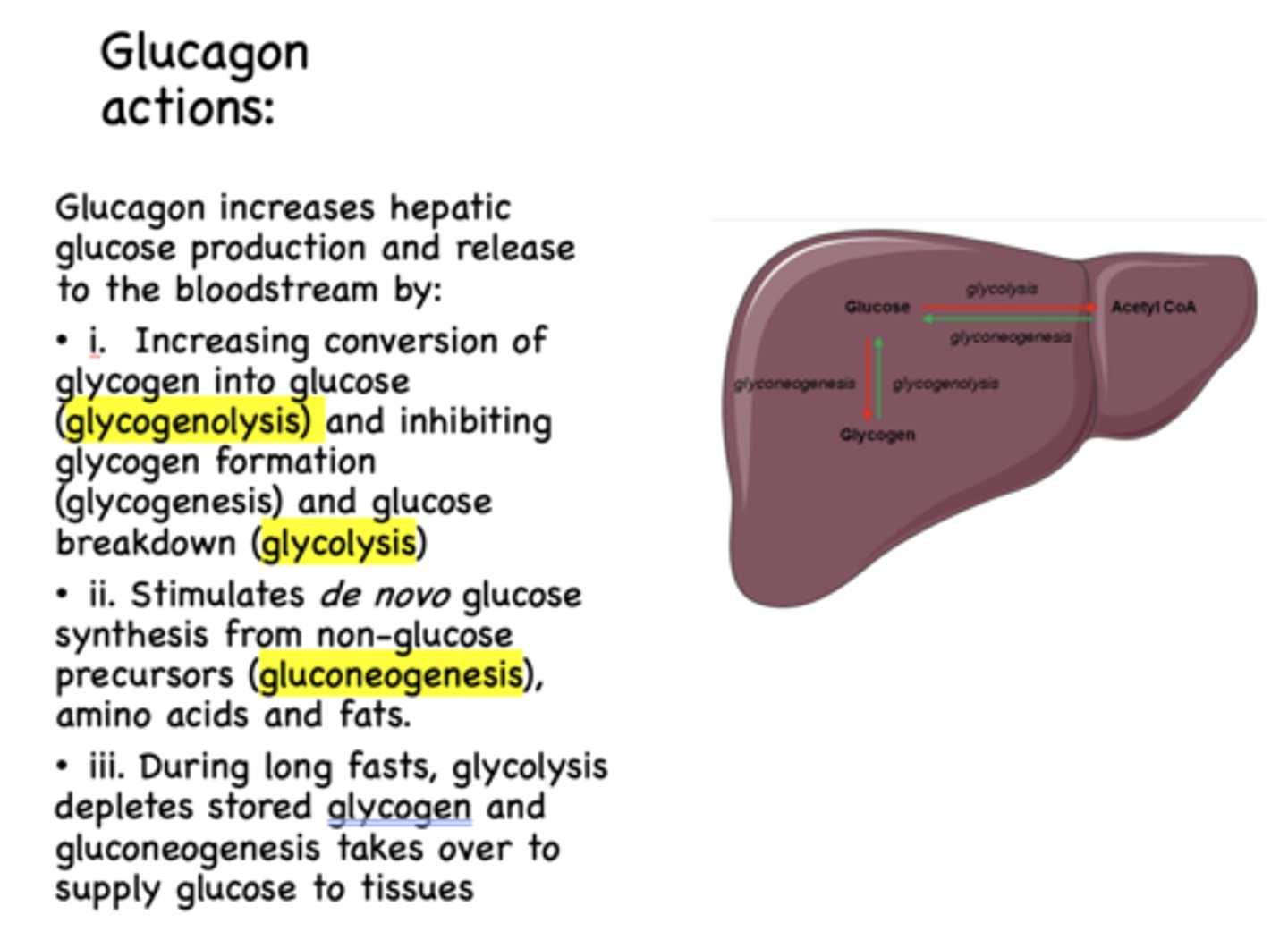
___________ promotes glycogen breakdown to release glucose (glycogenolysis) from liver
Glucagon
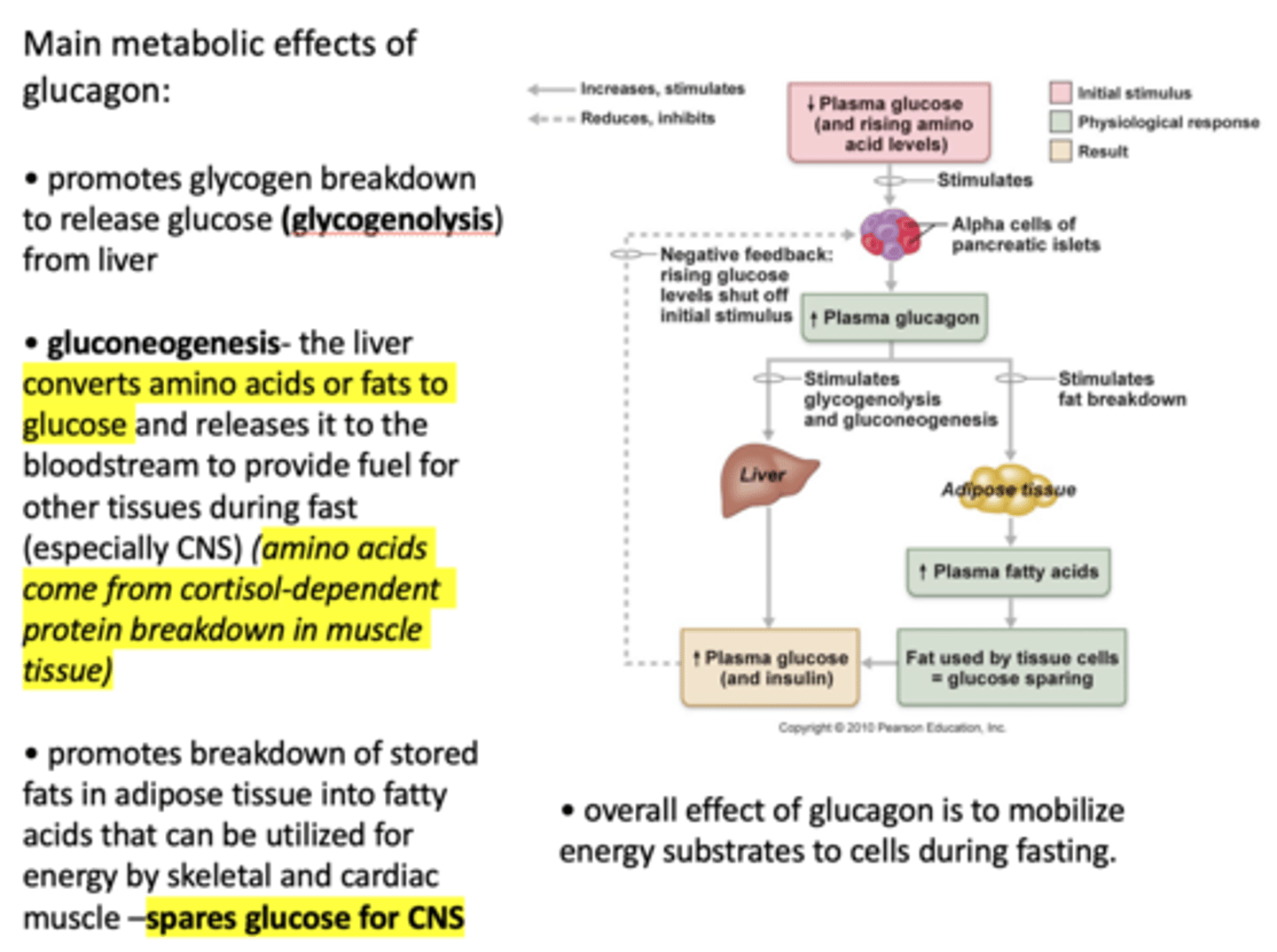
Define the following:
The liver converts amino acids or fats to glucose and releases it to the bloodstream to provide fuel for other tissues during fast (especially CNS)
Gluconeogenesis
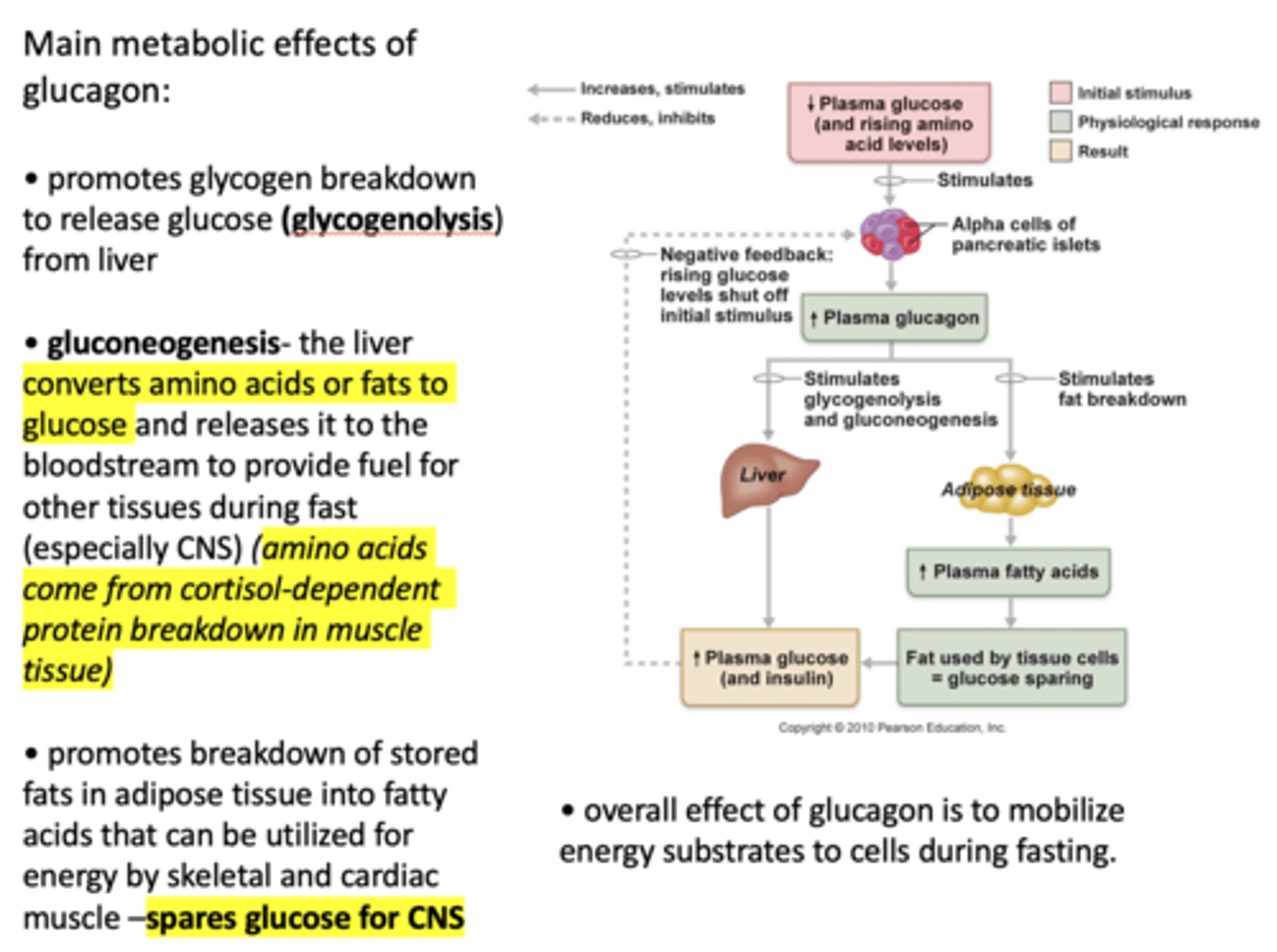
Where do amino acids come from in gluconeogenesis?
Cortisol-dependent protein breakdown in muscle tissue
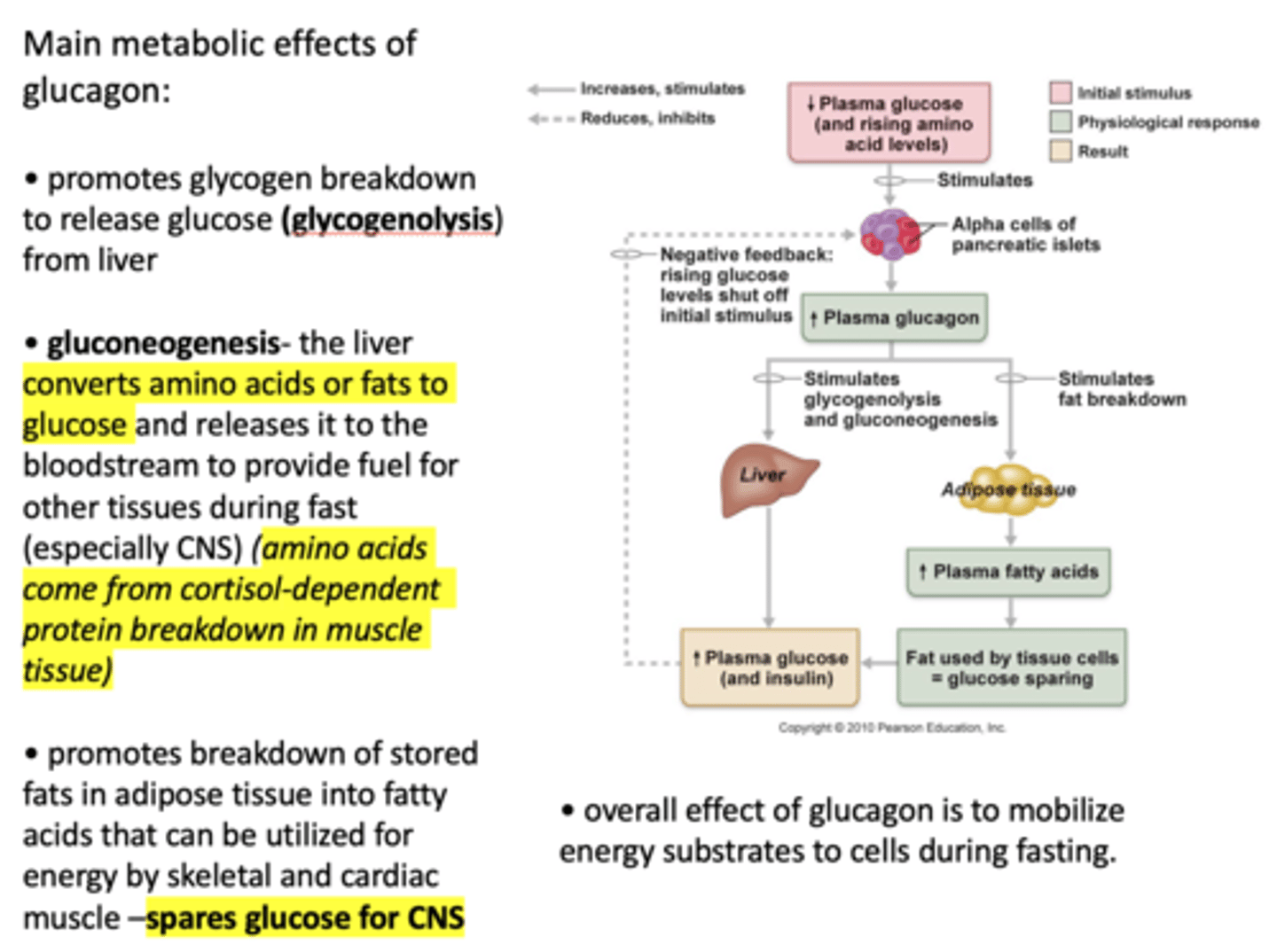
Why does glucagon promotes breakdown of stored fats in adipose tissue into fatty acids that can be utilized for energy by skeletal and cardiac muscle?
Spares glucose for CNS
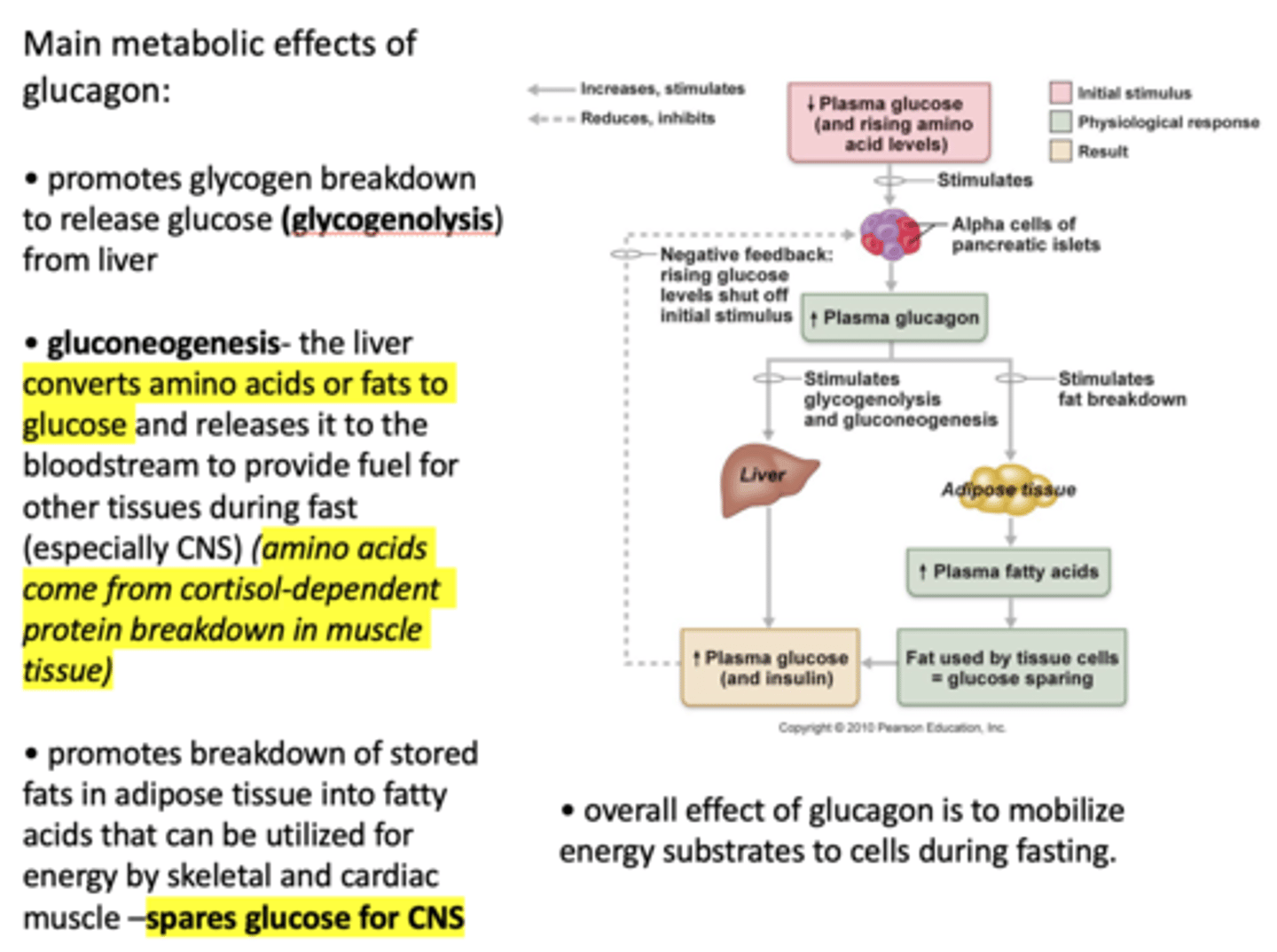
Overall, when plasma glucose decreases, plasma glucagon ___________
increases
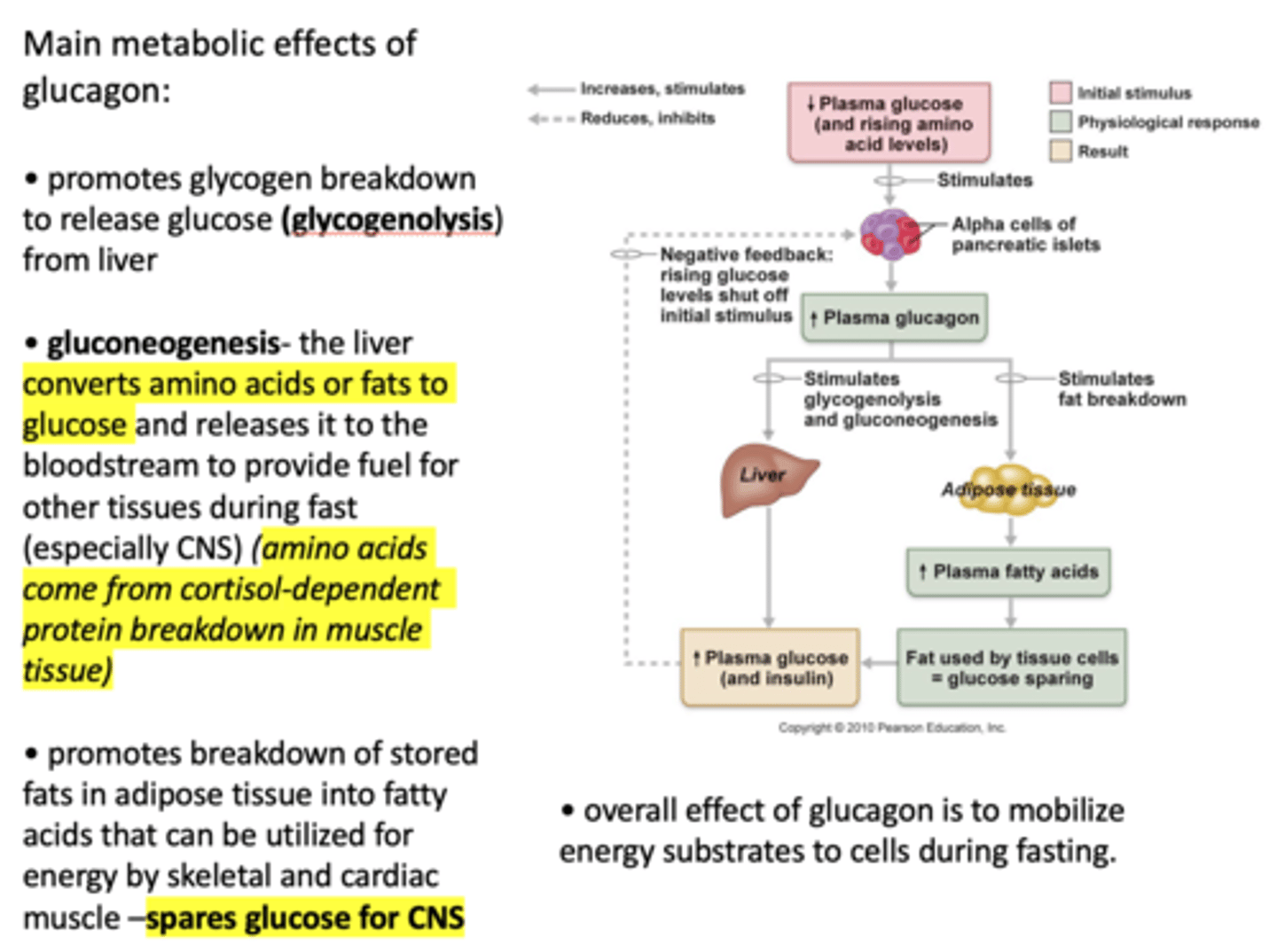
When plasma glucagon increases, what three process are stimulated?
- Glycogenolysis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Fat breakdown
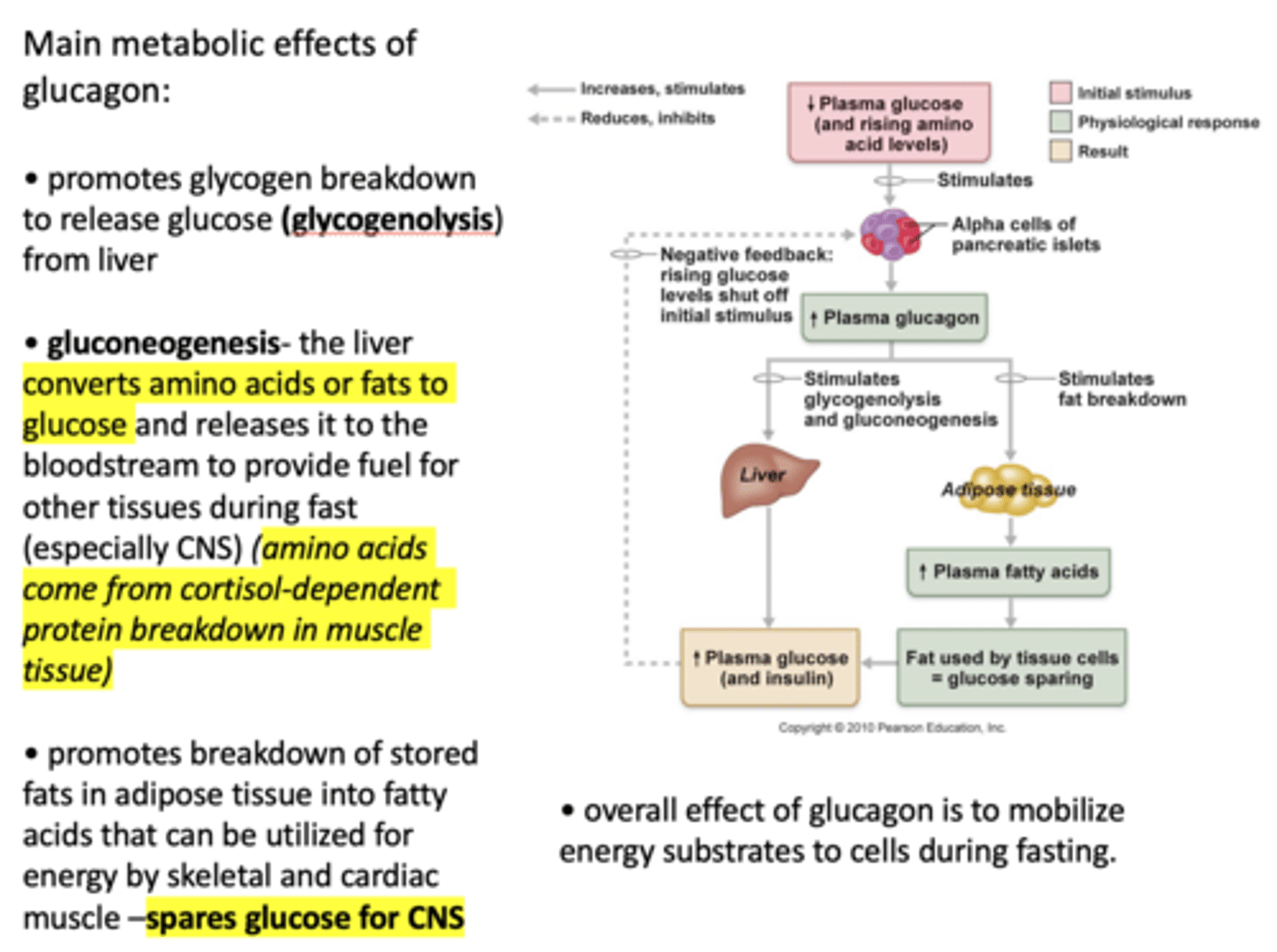
______________ is a cyclic peptide with two isoforms, one with 14 amino acid residues and one with 28.
Somatostatin
What is somatostatin also known as?
growth hormone inhibitory hormone (GHIH)
Where is somatostatin produced?
Delta cells in Islets of Langerhans (also GI tract, hypothalamus, CNS)
______________ acts on target cells by binding to G-protein-coupled receptors to regulate parts of the endocrine system
somatostatin

What is the effect of somatostatin on insulin and glucagon?
inhibits release of both

What is the effect of somatostatin on the hypothalamus?
inhibits release of GH, TSH and Corticotropin (from anterior pituitary)

What is the effect of somatostatin on the GI tract?
inhibits gastrin secretion (from stomach)

What is the effect of somatostatin on the thyroid?
inhibits secretion of T3, T4, calcitonin

What is the effect of somatostatin on the adrenal gland?
inhibits aldosterone release

OVERALL what is the effect of somatostatin?
inhibits hormone and transmitters secretion

Does somatostatin have a short or long half-life?
very short (1-3 min)

Somatostatin can ________ the secretion of other hormones and neurotransmitters due to its short half-life
Fine-tune

What is the clinical use for somatostatins?
antineoplastic effects (tumors)

clinically, somatostatin is effective against …?
acromegaly

Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is secreted by what cells?
F cells
what is the primary role of pancreatic polypeptide (PP)?
to modulate digestion of food by inhibition of gastric emptying as well as biliary secretion