AP2 Practical 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
hypothalamus
major controller of endocrine glands; secretes releasing & inhibiting hormones to control activity of anterior pituitary; produces ADH & oxytocin to be released by posterior pituitary
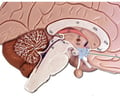
pituitary gland
also called the hypophysis; located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone; connected to the hypothalamus via the infundibulum; consists of two lobes
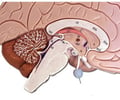
anterior pituitary
lobe of the pituitary also called the adenohypophysis; consists of 3 divisions
posterior pituitary
lobe of the pituitary also called the neurohypophysis; consists of the pars nervosa
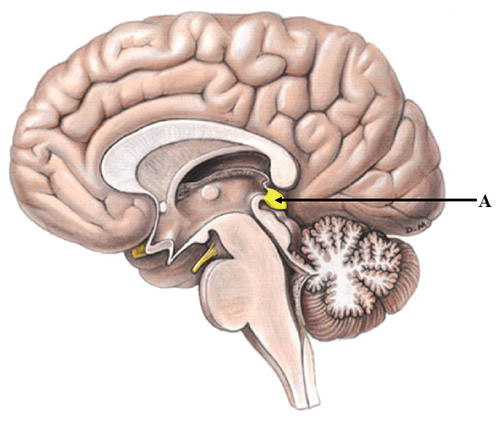
pineal gland
gland which lies in the posterior portion of the roof of the third ventricle; produces melatonin
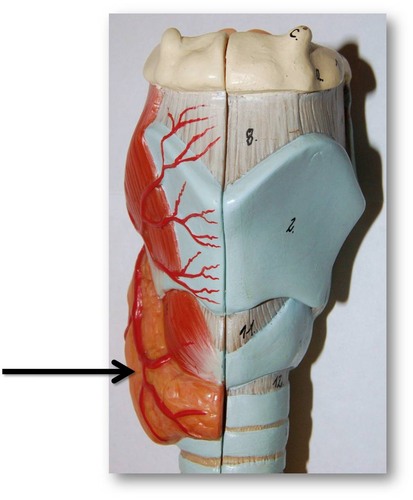
thyroid gland
gland which lies anterior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx; consists of two lobes connected by isthmus; produces T3, T4 hormones
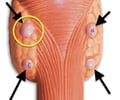
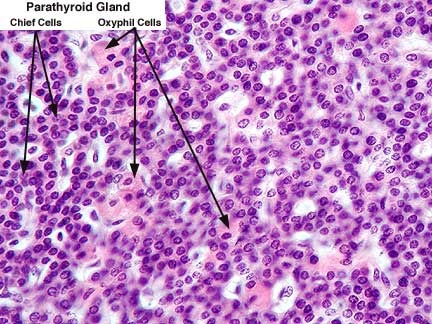
parathyroid glands
4 glands embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland; produces PTH
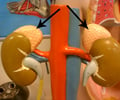
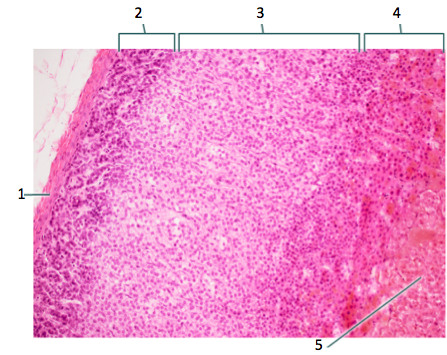
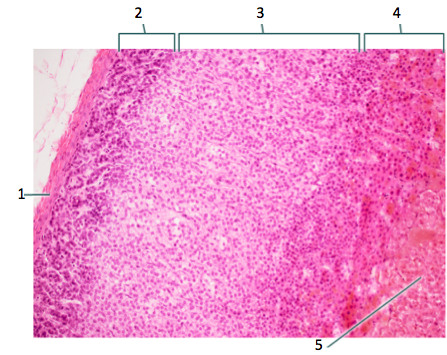
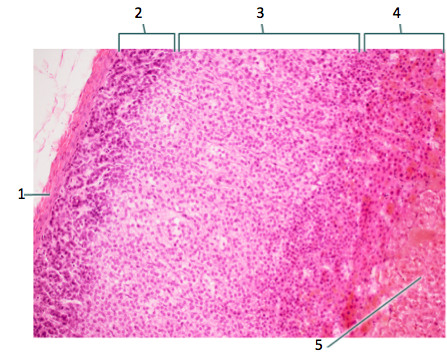
adrenal glands
glands which lie along the superior border of each kidney; consists of the cortex & medulla
pancreas
lies between the inferior border of the stomach & proximal portion of small intestine
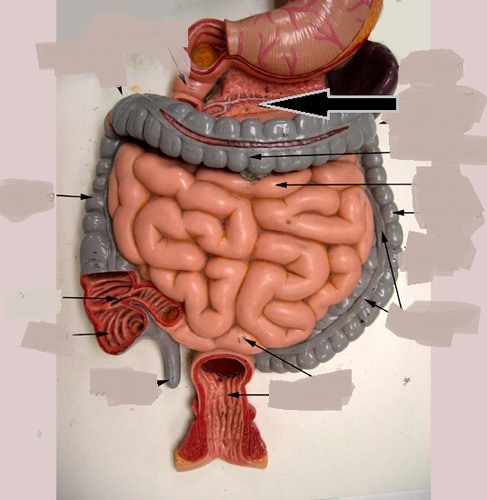
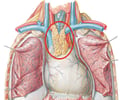
thymus
produces thymosins
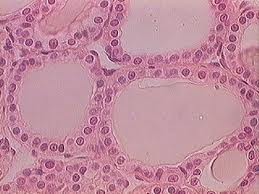
colloid-filled follicles
hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epithelium, containing viscous colloid in cavity
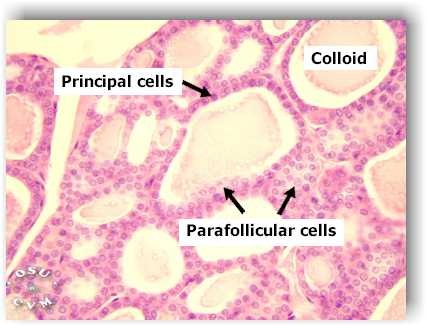
C cells
cells between thyroid follicles which produce calcitonin
Chief (principal) cells
cells of the parathyroid that produce PTH
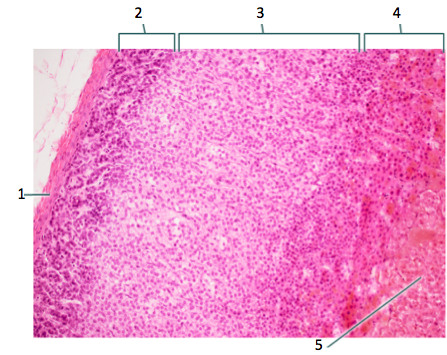
zona glomerulosa
2 in the diagram; outer layer of the adrenal cortex which produces mineralocorticoids AKA aldosterone
zona fasiculata
3 in the diagram; middle layer of the adrenal cortex which makes up 78% of it; produces glucocorticoids AKA cortisol
zona reticularis
4 in the diagram; inner layer of adrenal cortex which produces androgens
adrenal medulla
5 in the diagram; produces epinephrine & norepinephrine
pancreatic acini
#1 in diagram; clusters of exocrine cells which produce digestive enzymes
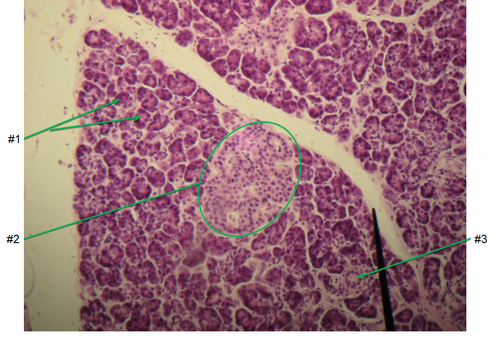
pancreatic islets
2 in the diagram; endocrine cells producing insulin, glucagon, & somatostatin
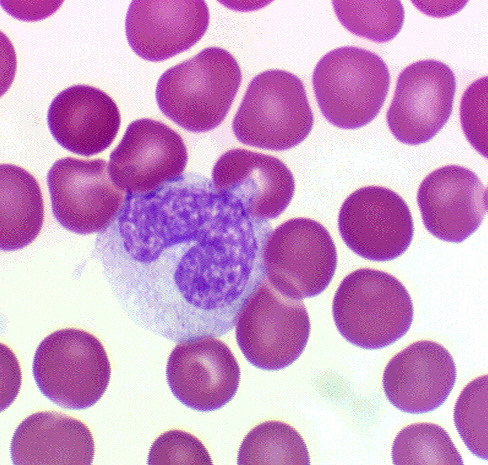
neutrophils
make up 50-70% of WBCs; multilobed nucleus
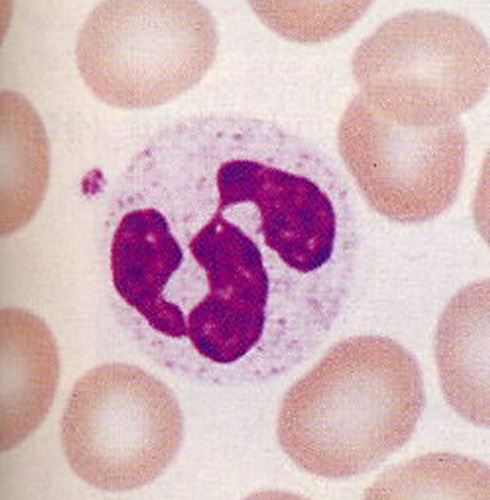
eosinophils
make up 2-4% of WBCs; bilobed nucleus; red cytoplasmic granules
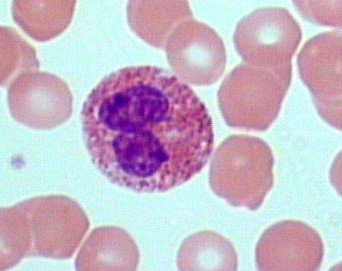
basophils
make up less than 1% of WBCs; bilobed nucleus; purplish-black cytoplasmic granules
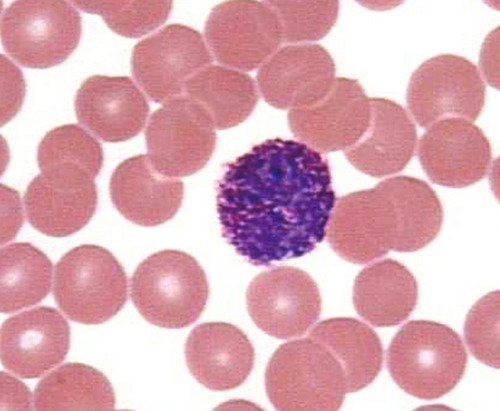
lymphocytes
make up 20-30% of WBCs; large spherical nucleus
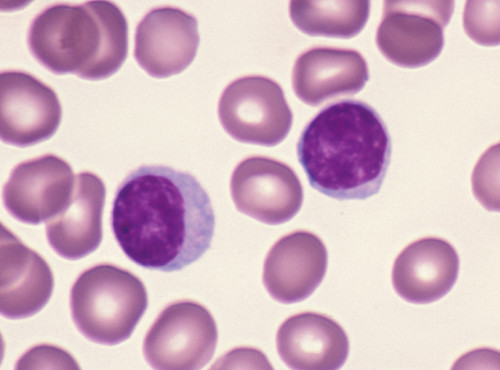
monocytes
make up 3-8% of WBCs; kidney-shaped nucleus
right atrium
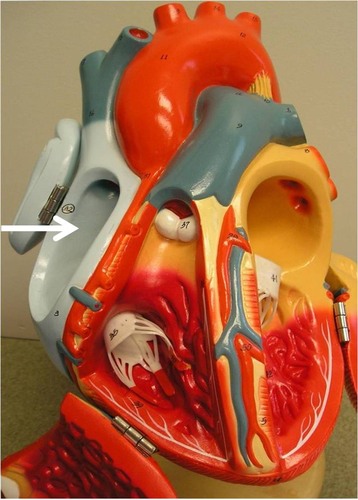
right ventricle
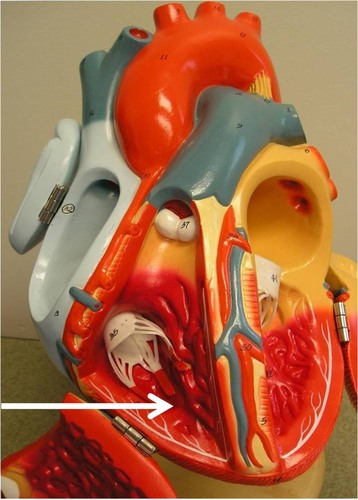
left atrium
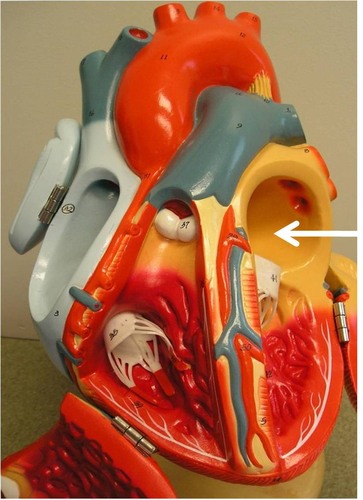
left ventricle
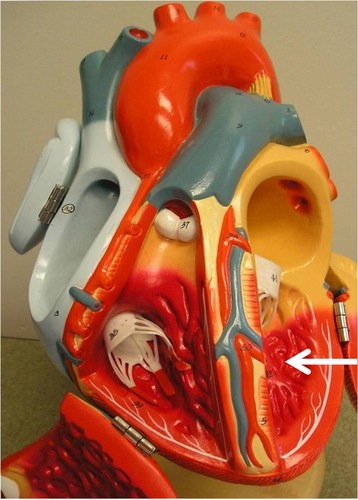
interventricular septum
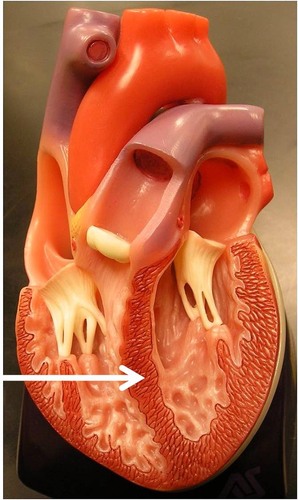
tricuspid valve
valve that lets blood from right atrium into right ventricle
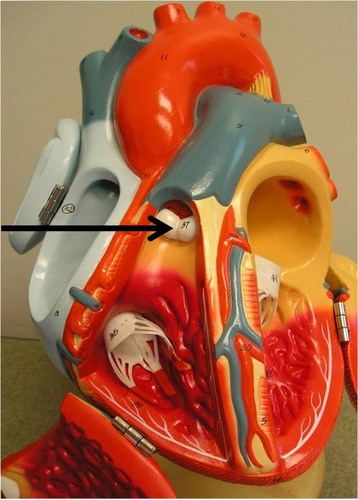
pulmonary valve
semilunar valve that lets blood from right ventricle to pulmonary trunk & arteries
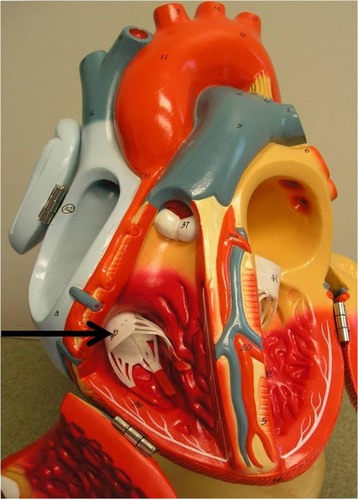
bicuspid valve
AKA the mitral valve; lets blood from left atrium to left ventricle
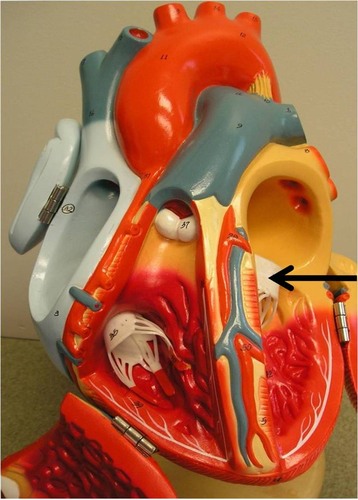
aortic valve
semillunar valve which lets blood from left ventricle into aorta
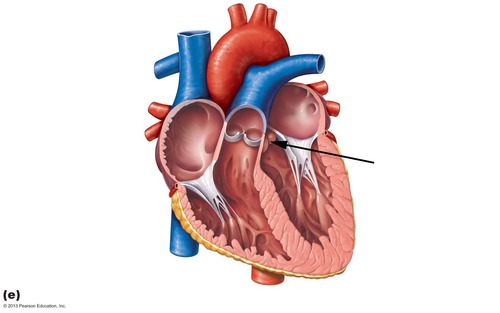
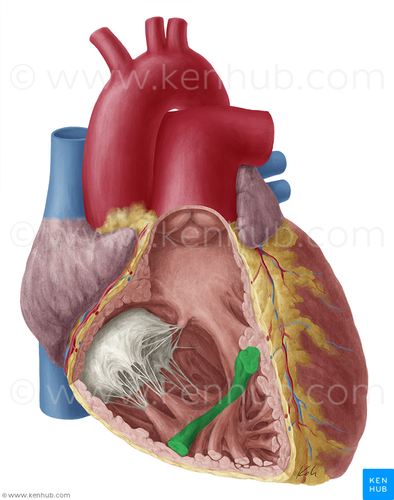
chordae tendineae
tiny white collagenic cords which anchor the cuspts of the tricuspid valve to the ventricular walls
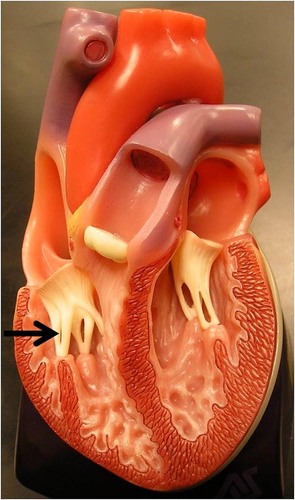
papillary muscles
small bundles of cardiac muscle that project from the myocardial wall & connect to chordae tendineae
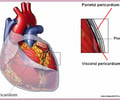
epicardium
AKA visceral pericardium; outer layer of heart wall
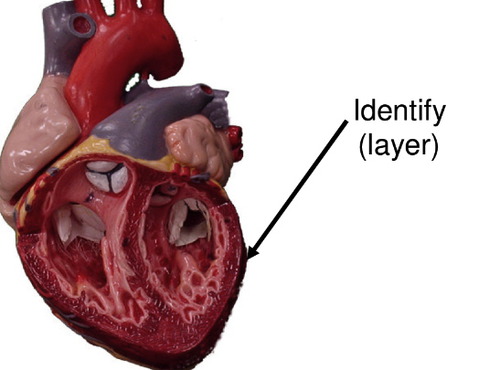
myocardium
muscular wall of heart; thickest layer
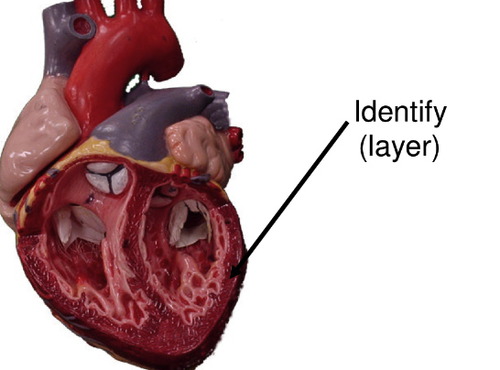
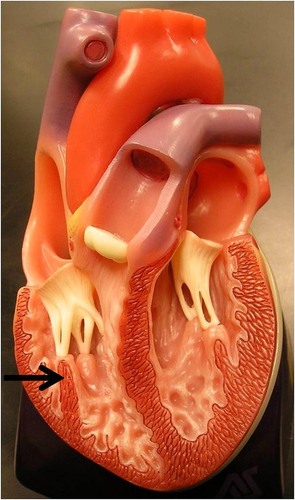
endocardium
inner surfaces of heart including valves
base of heart
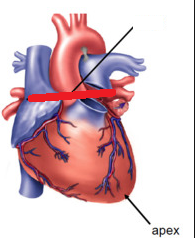
apex of heart
moderator band
bundle of cardiac muscle fibers connecting the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscles
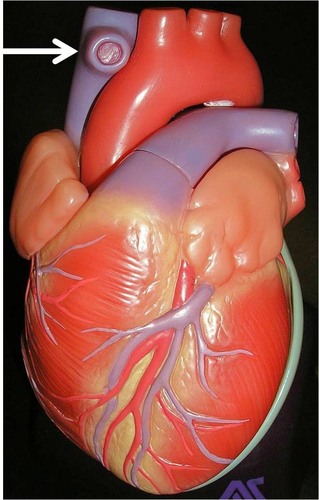
superior vena cava
large vein that brings oxygen-poor blood from the upper part of the body to the right atrium
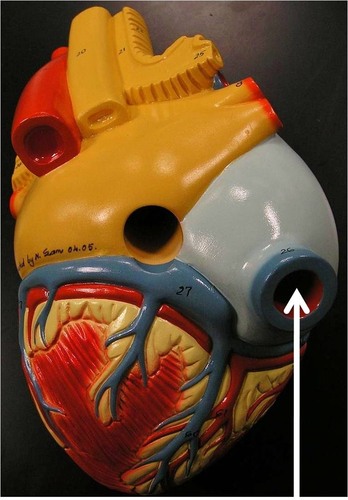
inferior vena cava
brings oxygen poor blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium
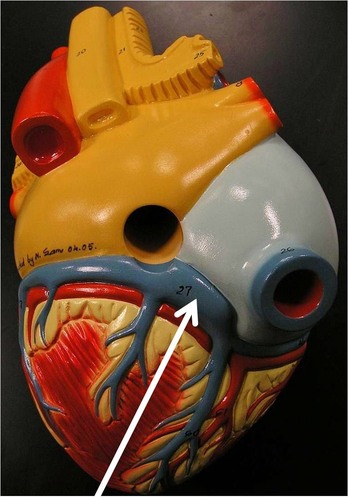
coronary sinus
enlarged vessel on the posterior aspect of the heart that empties blood into the right atrium
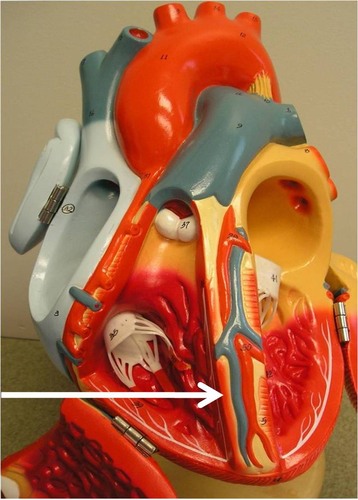
right coronary artery
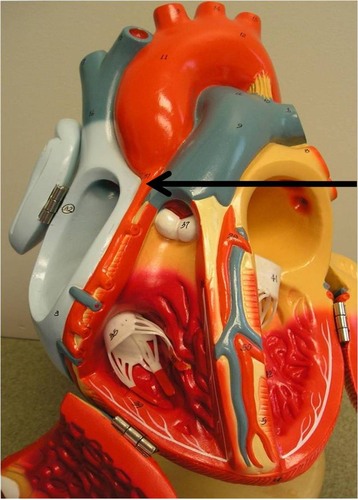
left coronary artery
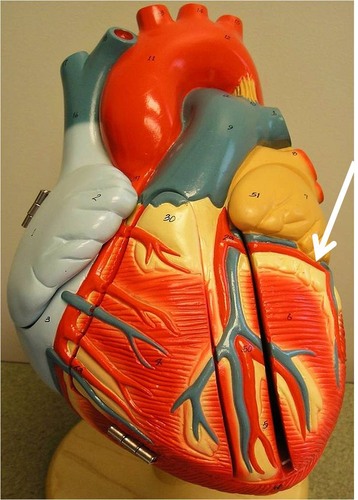
circumflex artery
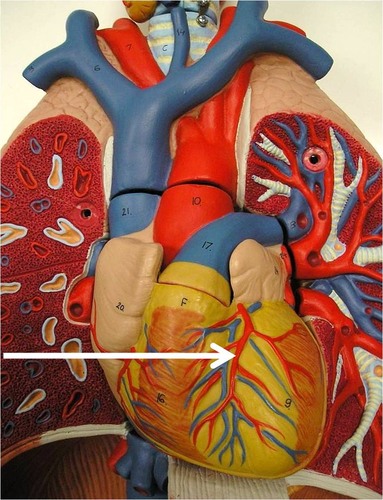
anterior interventricular artery
pulmonary veins
The four veins that return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
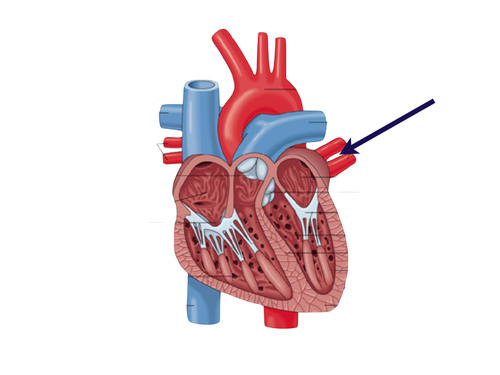
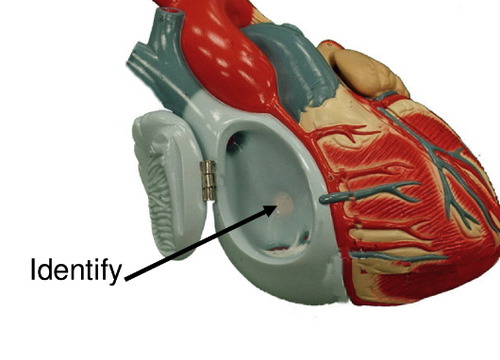
fossa ovalis
a remnant site of foramen ovale in fetus; right atrium
pulmonary trunk
branches into R & L pulmonary arteries
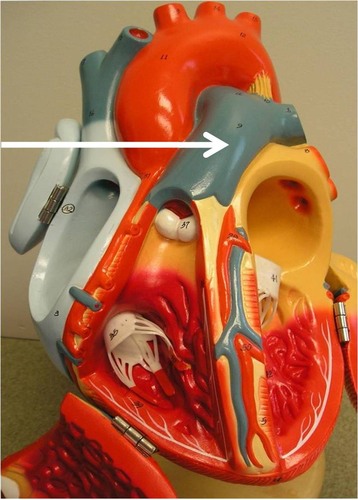
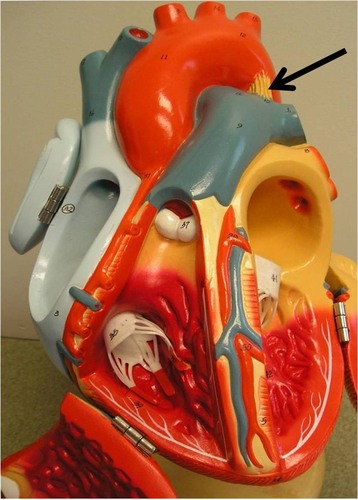
ligamentum arteriosum
remnant of ductus arteriosus in fetus
parietal pericardium
portion of pericardium close to the chest wall
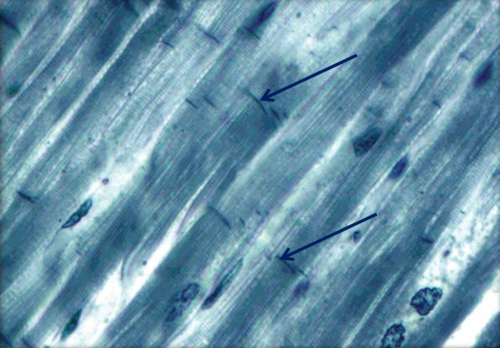
intercalated discs
monocytic leukemia
a form of leukemia in which there is dominance/large amounts of monocytes
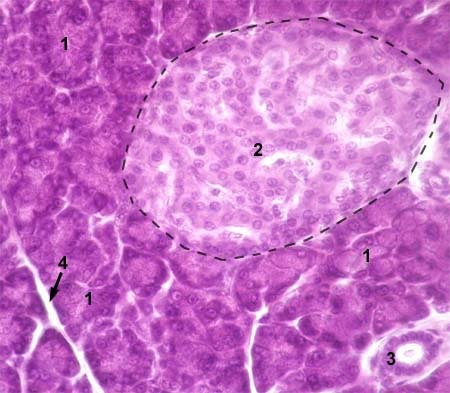
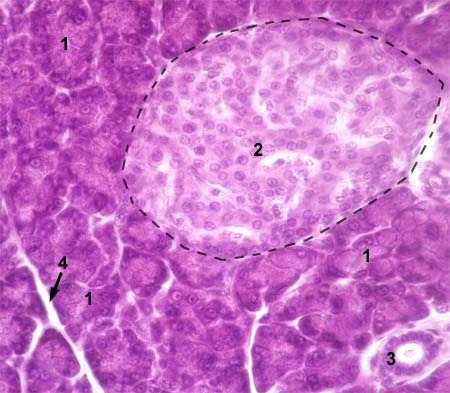
pancreatic islet (islet of Langerhans)
clusters in pancreas tissue filled with endocrine cells (alpha (A) cells and beta (B) cells); usually a lighter color
Romburg (Balance) test
test done by standing flat with feet both on the ground and eyes closed, then again with one leg up; tests to see if static equilibrium receptors are working
vertigo
sensation of circular motion either of oneself or external objects; severe cases may be accompanied by nystagmus