Extensions and modifications of basic principles
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are factors that can affect the results of a genetic cross?
type od dominance, level of expression, multiple alleles, lethal alleles
The phenotype of the heterzygote is the same as one of the phenotypes of the homozygotes. red flower + blue flower =? if the red flower is dominant
Red, it is complete dominance
The phenotyoe of the heterozygote is a blend of the phenotypes of the homozygote. red flower + blue flower =?
Purple, incomplete dominance
The phenotype of the heterozygote includes the phenotypes of both homozygotes. red flower + blue flower =?
Blue/Red, codominance
In radishes, red (R) and white (w) are true-breeding colors, while hybrids are purple (RW).
What kind of inheritance is this?
If a red radish is crossed with a white radish, what are the resulting genotypic & phenotypic ratios?
If the F1s are crossed together, what are the genotypic & phenotypic ratios in F2 generation?
Incomplete dominance
100% RW, 100% Purple
25% RR, 25% WW, 50% RW, 25% red, 25% white, 50% purple
In some chickens, the alles for the feather color gene follows a codomiance mode of inheritance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W.
What do you expect the heterozygous phenotyoe to look like?
If you cross 2 erminette (BW) chickens together, what are the phenotypic & genotypic ratios of their progeny?
100% BW (erminette)
25% black, 25% white, 50% erminette
In some cattle, when a red individual is crossed with a white individual, all offspring are roan (red and white). What kind of inheritance is this?
There is another gene in cattle responsible for the presence or absence of horns. The absence of horns is called polled, and its allele is dominant over the allele for horns. What kind of inheritance is this?
You cross a true-breeding red, horned bull to a true-breeding white, polled cow. What are the genotypic & phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
If you cross the F1s together, what are the genotypic & phenotypic ratios of the F2 generation?
codominance
complete
100% RWHh, 100% roan
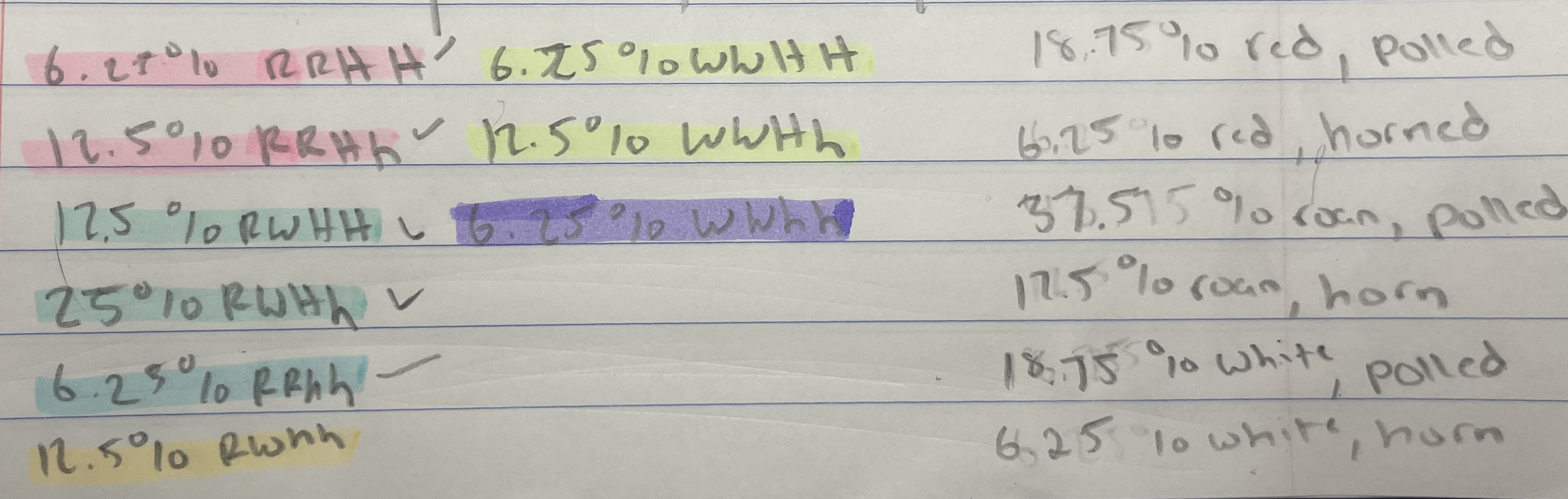
Proportion of individuals having a genotype that expressed the expected phenotype
penetrance
The degress to which at trait is expressed
expressivity
Polydacrtyly.
Not all individuals with the polydactyl allele will have abnormal numbers of fingers/toes, what is this an example of?
Furthermore, some affected individuals may have 1 extra finger while another individual has 3 extra fingers, what is this an example of?
incomplete pentarence
Varability expressivity
3+ alleles are present for a given locus
Multiple alleles
If someone heterozygous for A blood has a child with someone iwth AB blood, what is the probability that their child will have B blood?
25% chance their child will have B blood
Dominance hierarchy in duck plumage.
Mᴿ (restricted) > M (mallard) > mᵈ (dusky)
If an Mᴿmᵈ duck mates with an Mmᵈ duck, what is the probaility that their progeny will have dusky plumage?
25% their progeny will have a dusky plumage
Assiciated with a phenotype tht causes death at early stage of development.
Affects mendelian genotypic and phenotypic ratios in the progeny
lethal alleles
What are the typical genotypic & phenotypic ratios between 2 heterozygotes at 1 locus (Aa x Aa)
What are the genotypic & phenotypic ratios for a recessive lethal allele?
50% Aa, 25% AA, 25% aa
33.33% AA, 66.66% Aa
The BRCA allele is associated with a significantly higher chance of breast and ovarian cancer. Inheriting 1 BRCA allele will increase the risk, but inheriting 2 BRCA alleles actually results in a condition called Fanconi anemia ( a bone marrow disorder), which is embryonically lethal.
If two people are carriers of the BRCA, what is the probability that their child will develop Fanconi in utero?
If a carrier ofthe BRCA allele mates with someone who does not possess any BRCA alleles, what is the probability that their child will be a carrier?
25% chance their child will develop it in utero
50% chance their child will be a carrier or BRCA
Relativley few phenotypes, there are distinct categories
Discontinuos variation
Continuous distribution of phenotypes; occurs when genes at many loci interact, there are no distinct categories
Continuous variation
Characteristics encoded by genes at many loci
polygenic
One gene affects multiple characteristics
Pleiotropy
Milk production in cattle is influenced by the accumulation of small effects from many genes. Is this polu geneic inheritance or pleiotropy?
polygenic
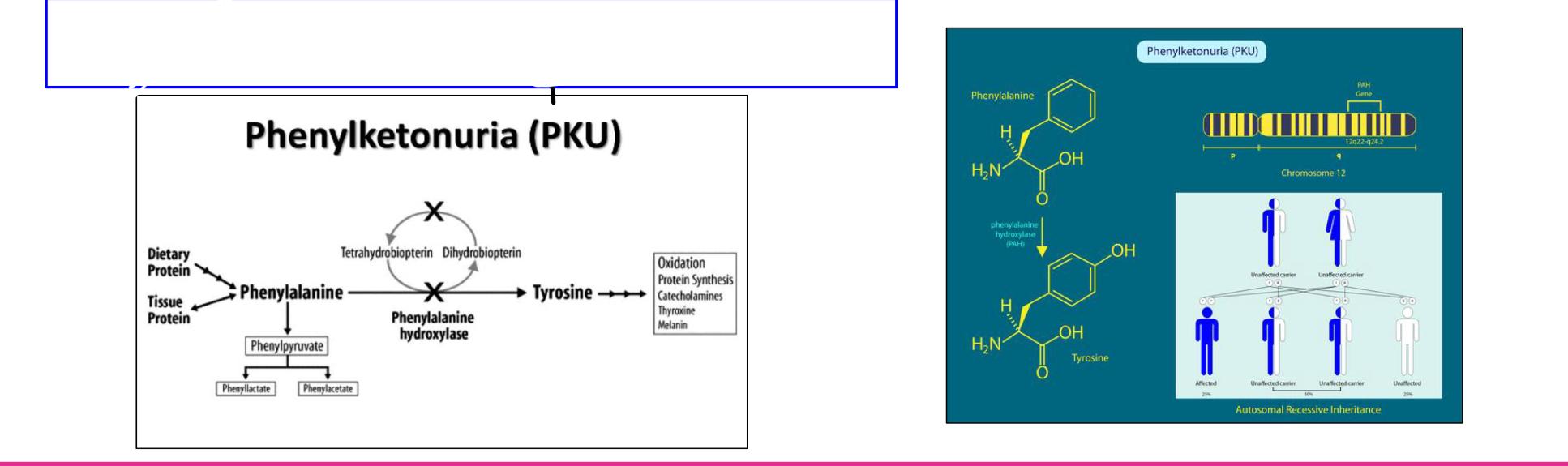
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a mutation in which affected individuals
have a deficiency in the enzyme required to break down phenylalanine
(phenylalanine hydroxylase). This disruption of the phenylalanine pathway
can affect brain development, behavior, and neurological processes.
Is this an example of polygenic inheritance or pleiotropy?
Pleiotrophy
One gene masks effect of another gene
Epistasis
Labs can be black, chocolate brown, or yellow. This is the result of 2 genes. At the B-locus, black (B0 is dominant to brown (b). At the E-locus, for labs, the recessive e is epistasis.
What does that mean?
it will mask the B-locus if it is present.
Labs can be black, chocolate brown, or yellow. This is the result of 2 genes. At the B-locus, black (B0 is dominant to brown (b). At the E-locus, yellow (e) is recessive & epistatic.
What phenotype is represented by this genotype: BbEe?
What phenotype is represented by this genotype: BBEE?
What phenotype is represented by this genotype: bbee?
Black
Black
Yellow
Used to determine whether mutations are at the same locus or different locus. When mutations are in different genes, each true-breeding mutant supplies the WT allele.
Complementation testing
Assume you discover new recessive mutations in a type of flower. Wild-type = white flower petals, New mutations = blue flower petals & red flower petals.
What would the pffspring of a mutant x mutant cross look like if these traits were the result of 1 gene?
What would the offspring of a mutant x mutant cross look like if thesd traits were the result of 2 genes?
aa mutant (blue or red)
aa+bb+ (WT = white)
Characteristics are associated with genes found on a sex chromosome
sex-linked
autosomal traits that are influenced by sex
sex-influenced
Autosomal traits that are only visible within one sex
Sex-limited
Pattern baldness is a phenotype associated with a characteristic pattern of hair loss from the scalp. However, the patter is expressed differently between genetic males and genetic females.
What is this trait considered?
Sex-linked
There are several autosomal genes responsible for milk yield in cattle, however milk-associated phenotypes are only observed in cows, despite bulls having the same genotypes at these loci.
What is this trait considered?
sex-limited
The gene responsible for hairy ears is found on the Y chromosome.
What is this trait considered?
sex-linked
The genotype of the maternal parent determines the phenotype of the offspring. Due to mother supplying particular mRNA or protein to the egg
Gene products from maternal nuclear genes.
Maternal effect
The coiling phenotype seen in the offspring in controlled by the mother’s genotype. Right-coil (A) is dominant over left-coil (a)
If the parental is Aa x Aa, what will the aa offspring form as?
Right-coil the mother is A
Transmission of genes that occur outside the nucleus
Cytoplasmic inheritance
When only one parent contributes extranuclear DNA to offspring
Uniparental cytoplasmic inheritance
DNA that is nonnuclearr inherited from the mother
maternal inheritance
When both parents contribute extranuclear DNA to offspring
Biparental cytoplasmic inheritance
Different a, expression of genetic material, depending on whether it is inherited from the maternal or paternal parent
Genomic imprinting
What happens to the paternal and maternal copy when dealing with the Igf2 gene
The paternal is underlined, while the maternal is crossed out
What happens to a Lion x Tiger offspring when dealing with genomic imprinting?
What happens when a male lion breeds with a female tiger? What of a Female lion with a male tiger?
In lions
Paternal: grow really big
Maternal: don’t grow that much
In tigers
Paternal & Maternal: grow medium sized
really big ligar
A medium sized tigon