Part 5: Care of Site Specific Side Effects: VI. RTT to Abdomen/Pelvis
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
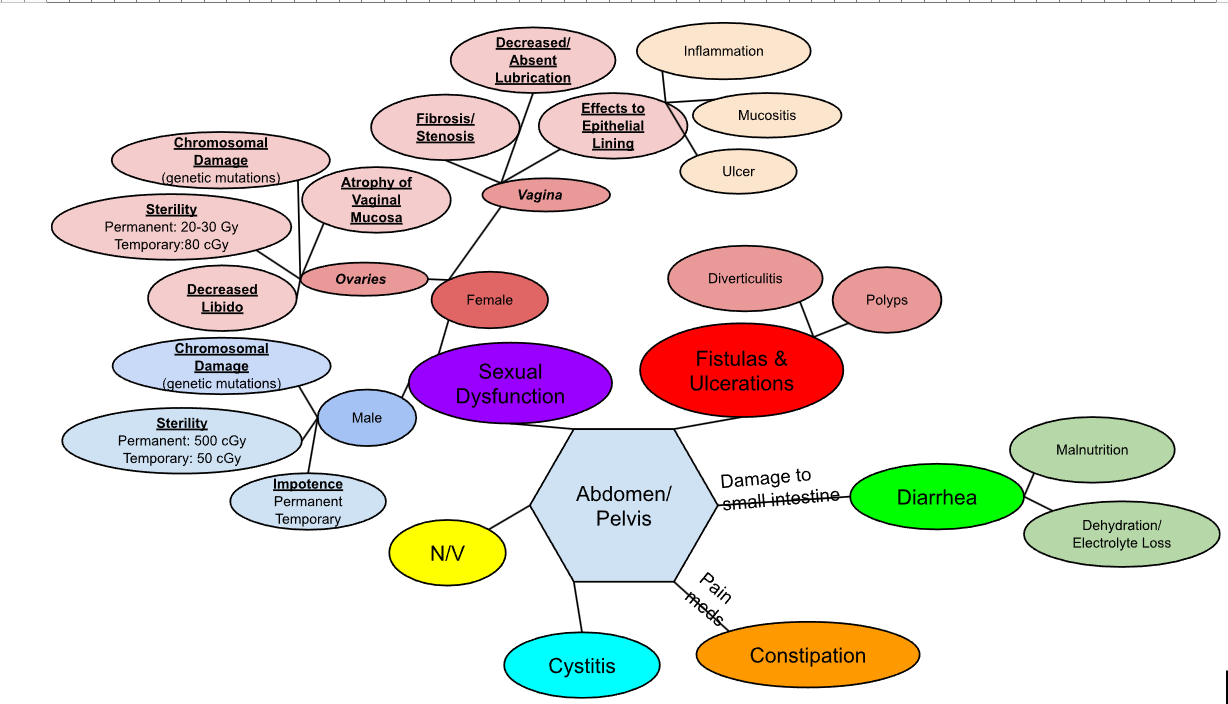
Mnemonic for Abdomen/Pelvis
FU! Don’t Come Close Now Sexual Predator!
Fistulas & Ulcerations
Diarrhea
Constipation
Cystitis
N/V
Sexual Dysfunction
Web for Abdomen/ Pelvis effects
NV
NV
Diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurs at what dose?
40 Gy & above
Irradiation to this organ is the primary cause of diarrhea?
small bowel
At a cellular level, how does RTT cause diarrhea
highly proliferative cells in intestinal lining
Highly proliferative- 20-50 Million cells sloughed off/minute
When does diarrhea occur?
Starts: 2 weeks into tx
Ends: 2 weeks after tx ends
Small intestine has 3 features that increase the surface area to enhance absorption/ digestion. List them,
arrangement of small intestine in Peaks & Valleys
villi
microvilli
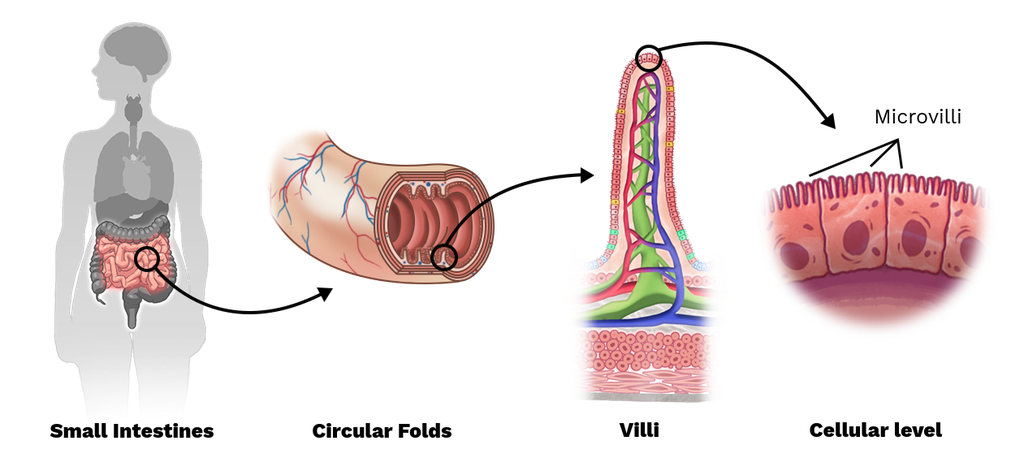
What is the functional unit of the small intestine?
villi
microvilli aka
brush border
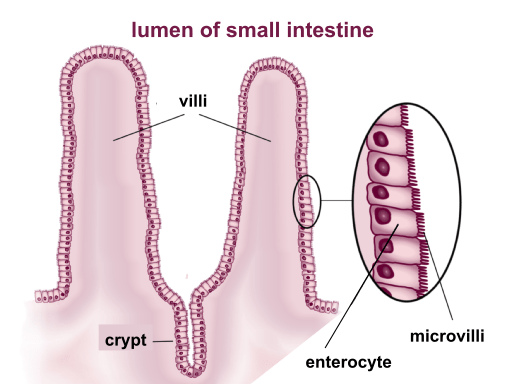
Effects of RT to villi and microvilli
villi and microvilli can easily slough off during tx, may be so bad as to require rest from tx
Diarrhea side effects
malnutrition
dehydration
electrolyte loss
Dietary interventions for diarrhea
Avoid foods that stimulate/ irritate the GI tract:
coffee/ tea
very hot/ cold foods/liquids
spicy food
lactose

What type of diet is recommended for diarrhea patients:
low residue diet
Medical interventions for diarrhea
anti-diarrheal
sitz bath (Epsom salts)
Anti-diarrheals
OTC
Prescription
OTC:
Pepto-Bismol
Imodium AD- BEST OTC
Paregoric (pare el gori gori)
Kaopectate (KaKao)
Prescription
Lomotil aka Loperamide (lo per amide)
Which side effect to abdomen/ pelvis is rare?
Constipation
(FYI: we usually cause diarrhea )
constipation
constipation
If constipation is not a side effect of radiation, why is it a common complaint amongst patients?
it is a common side effect of many pain meds
fistulas & ulcerations
fistulas & ulcerations
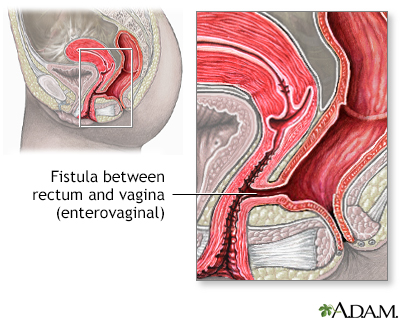
term. fistula
def. an abnormal tube-like passage from one cavity to another
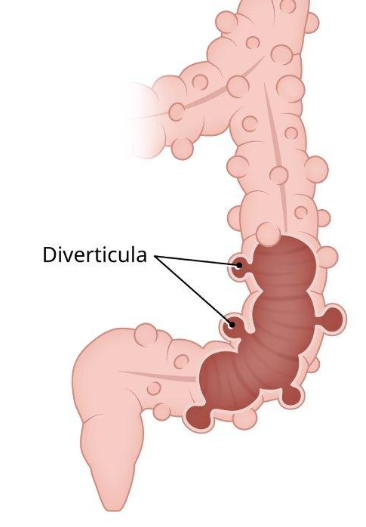
term. diverticuli
an outward sack or pouch
fyi: stuff can get stuck there
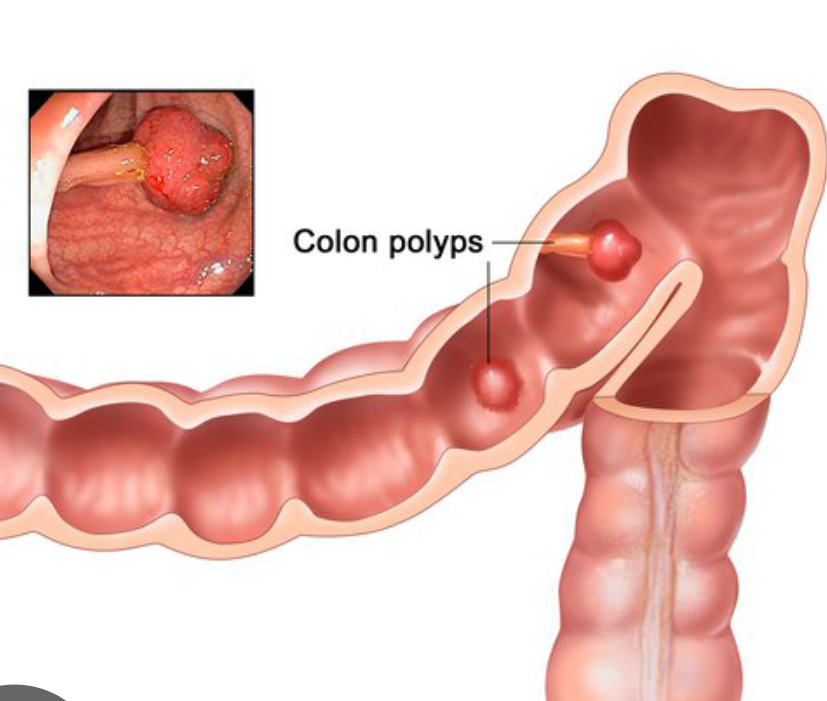
term. polyp
an inward, usually benign, growth
term. colostomy
an artificial opening into the colon for elimination purposes
May be temporary or permanent
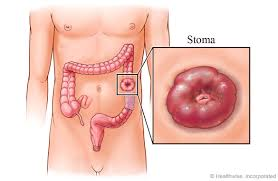
Colostomy may be permanent if:
tumor is closer to anus → no room to reattach colon after surgical excision
Colostomy may be temporary if:
tumor is more proximally located → reattachment after healing is complete
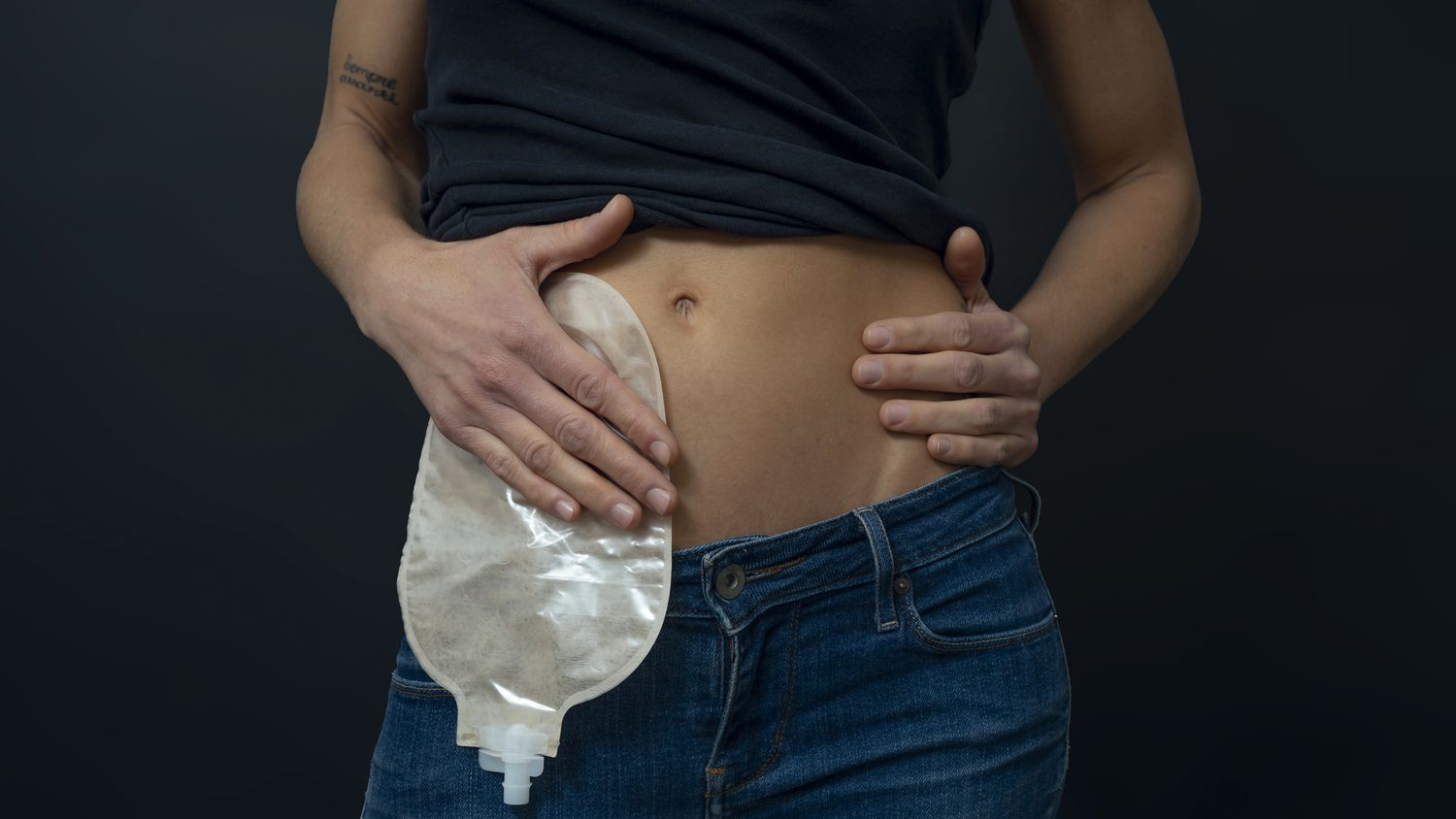
Illeostomy:
surgical opening by bringing out the ileum (end of small intestine) out onto the surface of the skin.
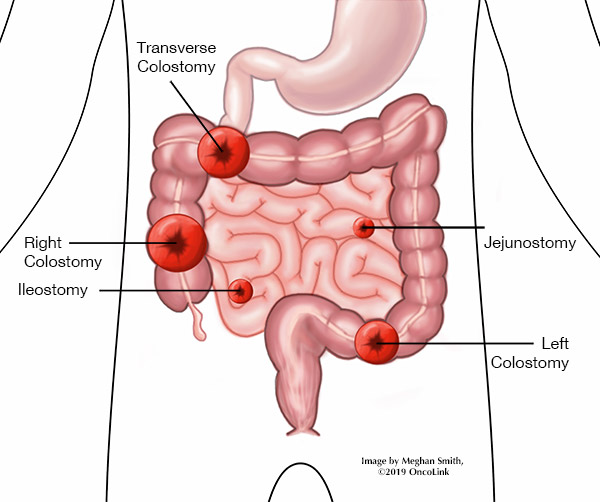
Internal waste passes out of the ileostomy and is collected in _
an external pouching system stuck to the skin
Where are ileostomies usually sited?
above the groin,
right side of abdomen
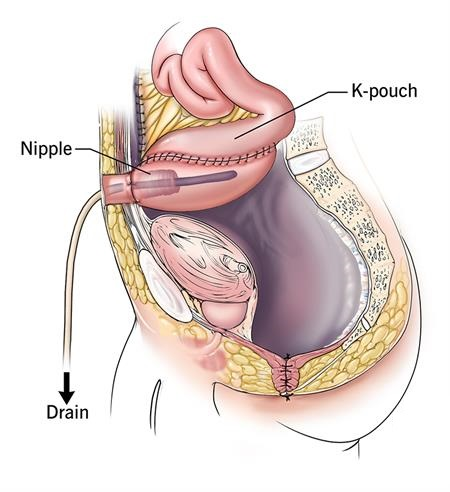
Ileostomies are being replaced by the proffered alternative:
K-Pouch or BCIR
This surgery turns the small intestine into an internal reservoir (no external appliance needed)
FYI: poop is stored there and patient can manually get ride of it by turning a valve
cystitis
cystitis
FYI: what is cystitis
inflammation of the bladder
urostomy aka
ureteroileostomy
ureter(o) ile(um) ostomy
urostomy / ureteroileostomy
anastomosis (ana stoma osmosis) of the ureters to (an isolated loop) of the ileum drained trough a stoma on the abdominal wall
symptoms of cystitis
frequency & urgency of voiding
burning sensation
low back pain
hematuria (blood in urine)
Interventions for cystitis
force fluids
Avoid irritating foods/ substances:
coffee/tea
alcohol
tobacco
pepper
curry
Role of pH in cystitis
↓ (acidic) pH = ↓ risk of infection
FYI: so get some vitamin C
UCD stand for
Urinary collection devices
def. a simple utensil that allows an individual to empty their bladder into a container hygienically without spilling urine
term urinary collection device

a type of urinary collection device is a/an ___
Catheter
urinary catheterization aka
cathing
term. urinary catheterization
a catheter (plastic tube) is inserted into a patient’s bladder via their urethra
What are the 2 purposes of urinary catheterization?
drain urine freely from bladder
inject liquids for tx or diagnosis of bladder conditions
The procedure or catheterization is usually done by ___
a clinician often a nurse
tho self-catheterization is possible as well
Types of catheters list (3)
Foley catheter
Robinson catheter
External Texas/ Condom catheter
term. Foley catheter
def. indwelling retention catheter
What holds a Foley catheter in position?
an inflatable balloon
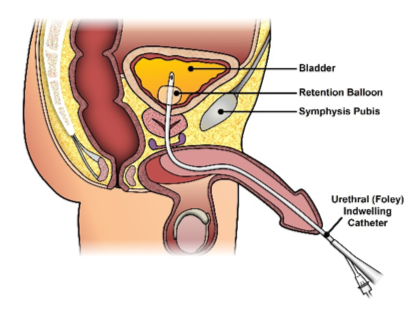
Besides holding the catheter in place, what is another purpose of the balloon in a Foley catheter?
air in balloon can be used as a contrast agent
Biggest downside of catheters?
they are a common source of infection
What types of catheters are the most commonly used
#16 or #14 French tip catheters
term. Robinson catheter
def. a flexible catheter used for short-term drainage of urine

True or False: The Robinson catheter has a balloon to hold it in place
False , it has no balloon, so it cannot stay in place unaided

term. External Texas/ Condom catheter
def. catheter used for incontinent males.
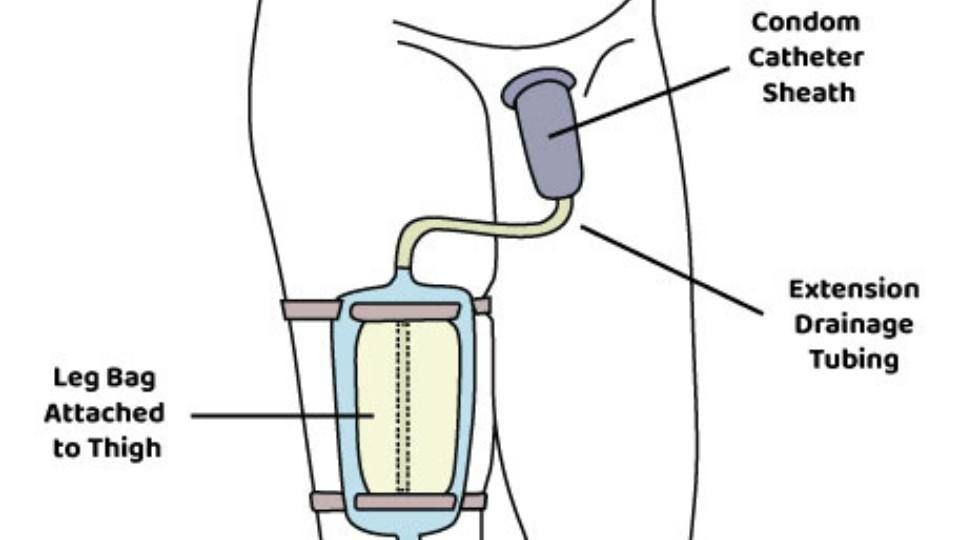
main benefit of External Texas/ Condom catheter
lower risk of infection than an indwelling catheter
sexual dysfunction- when testes/ ovaries are in the field
sexual dysfunction
Sexual Dysfunction in males:
List the 3 primary effects:
permanent/ temporary Sterility (FYI: decreased sperm count)
permanent/ temporary Impotence
Chromosomal Damage (genetic mutations)
____ are much more sensitive than mature sperm
spermatogonia
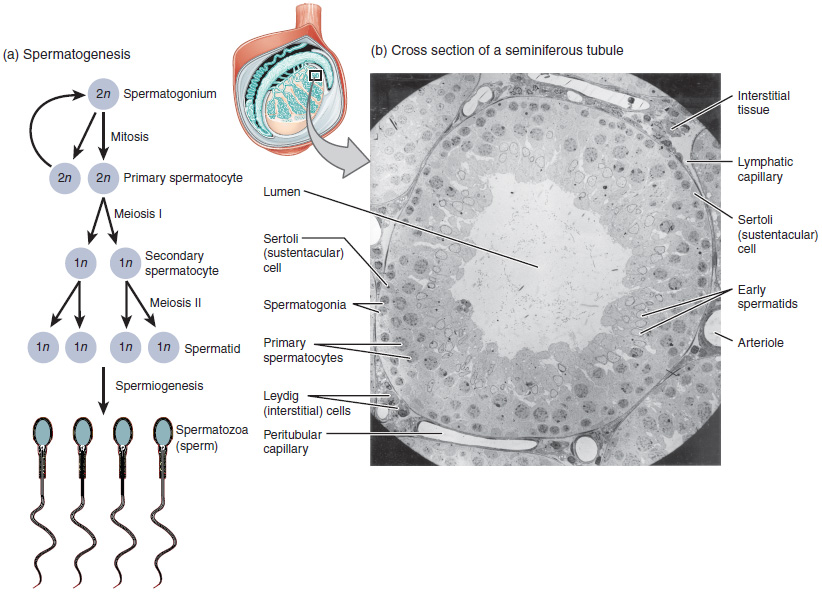
name of the cells that produce testosterone
Leydig cells
True or False: Spermatogonia and Leydig cells are very radiosensitive
False:
Spermatogonia- very radiosensitive
Leydig Cells- radioresistant
What is a result of Leydig cells being radioresistant?
testosterone levels remain the same UNLESS very high doses are used
Fields that can involve the testes?
TNI, Inverted Y, Hockey Stick/ Dog Leg
TNI, Inverted Y and Hockey Stick/Dog Leg are also used for
Hodgkin’s Disease
FYI: TNI treats almost all lymph nodes of the body
(Inverted Y/ Hockey Stick) field is mostly associated with Hodgkins Disease, while (Inverted Y/ Hockey Stick) is mostly associated with testicular cancer
(Inverted Y/ Hockey Stick) field is mostly associated with Hodgkins Disease, while (Inverted Y/ Hockey Stick) is mostly associated with testicular cancer =
Field used to treat 1 testicle
hockey stick/ dog leg
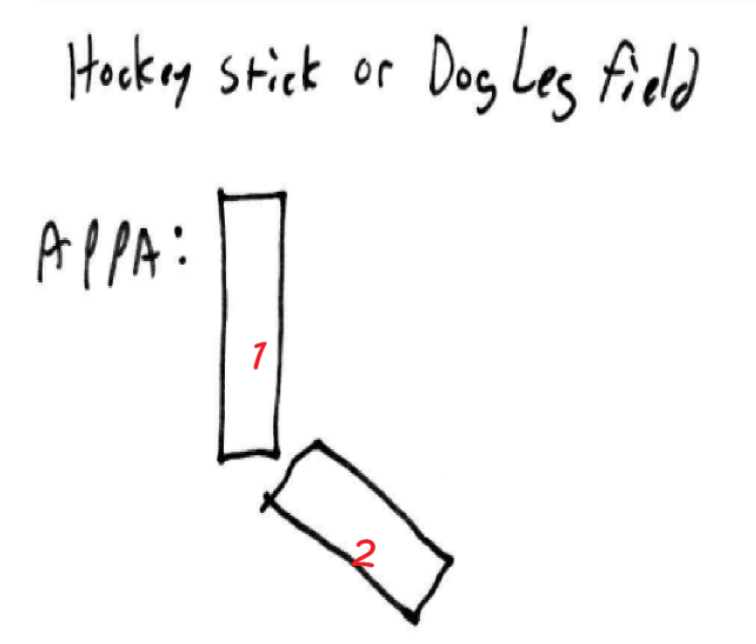
WITH SHIELDING
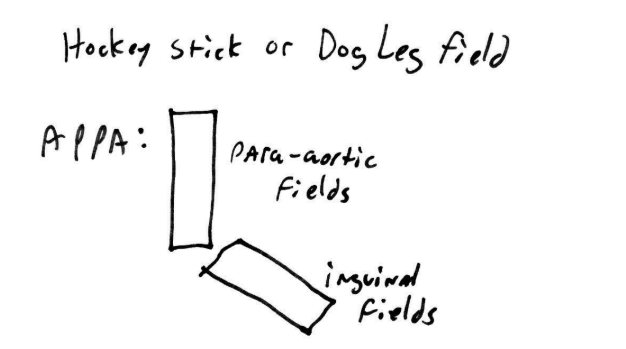
Hockey stick field uses doses of _____
400cGy dogs have 4 legs
Even with shielding, hocky stick fields expose the testicles to ____ rads
80-250 rads (enough to cause temporary sterility)
Sterility in males doses:
temporary
permanent
temporary: 50 cGy
permanent: 500 cGy
When does reduction of sperm count happen?
Begins: 6-8 weeks into tx
Ends: continues for several months- years
Most oncologist recommend from childbearing for a period of ___
2 years (to prevent genetic mutations)
Intervention for sterility
sperm banks before tx
Impotence
When does it happen?
Beings: a couple of weeks into tx
Ends: extends for several weeks after tx
How RTT affects testosterone levels:
Testosterone levels unaffected by RTT, there might be a mild decrease in some patients
For females, if ___or ___ is in the tx field, there might be side effects
ovaries
vagina
Ovaries in tx field side effects
Decreased libido
Permanent/ Temporary Sterility
Chromosomal Damage
Atrophy of Vaginal Mucosa
Sterility in females doses:
temporary
permanent
temporary: 800cGy (8 = OOva)
Permanent: 20-30 Gy
term. atrophy of vaginal mucosa
shrinkage of the vaginal size & decrease in lubrication
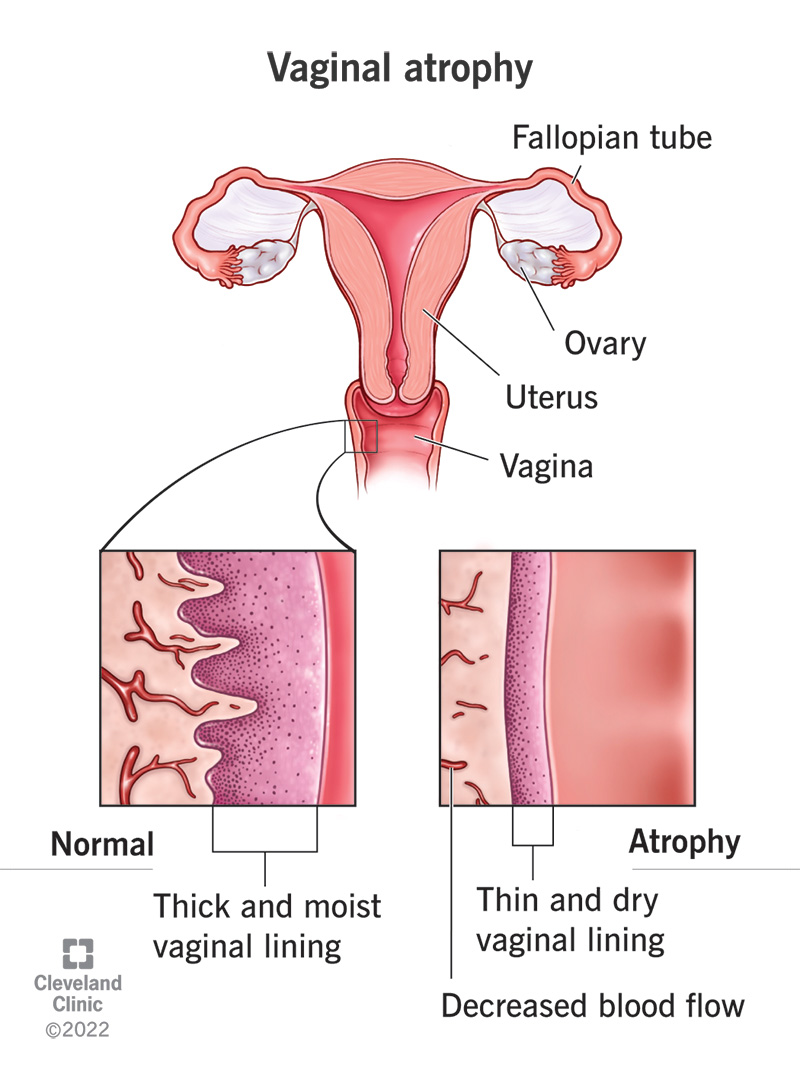
vagina in tx field side effects
fibrosis & stenosis (FYI: narrowing or closing)
decreased or absent lubrication
May effect epithelial lining like any other epithelium: inflammation, mucositis, ulcer etc.
Prophylactic medical innervation for RTT where ovaries would be in the tx field
Ovaries can be surgically displaced
How often after RTT should women wait for childbearing
2 years (to prevent genetic mutations)
Intervention for decreased lubrication of vagina:
KY Jelly or Lubrifax (NOT VASELINE)
Intervention for preventing vaginal stenosis:
intercourse
vaginal dilator
Intervention for yeast infections for women
Diflucan
Other interventions for females for genital side effects
sitz bath
steroid based cream
sexual counseling