ap bio -- unit 3: cellular structure and function
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
actually one of the most important unit; you got this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
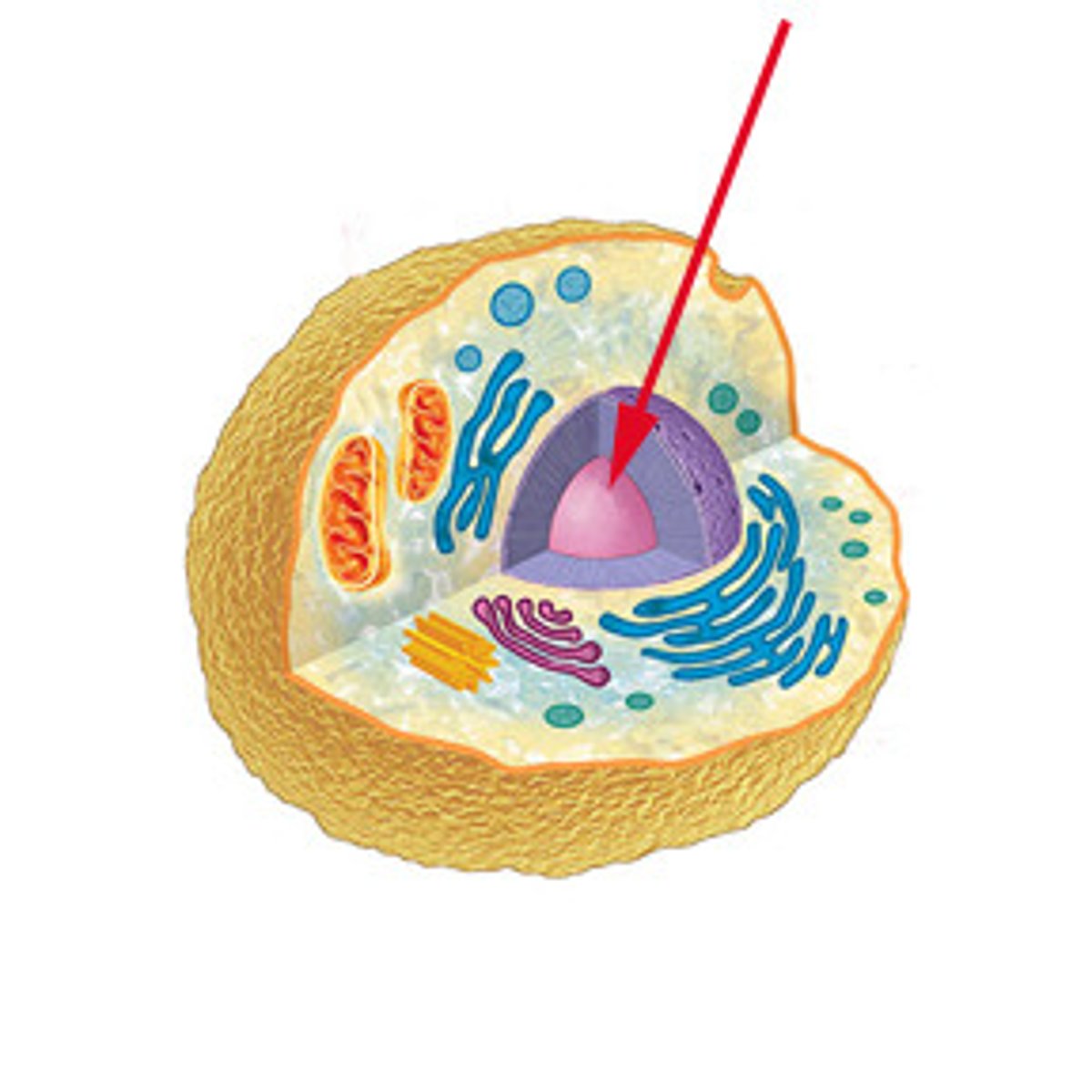
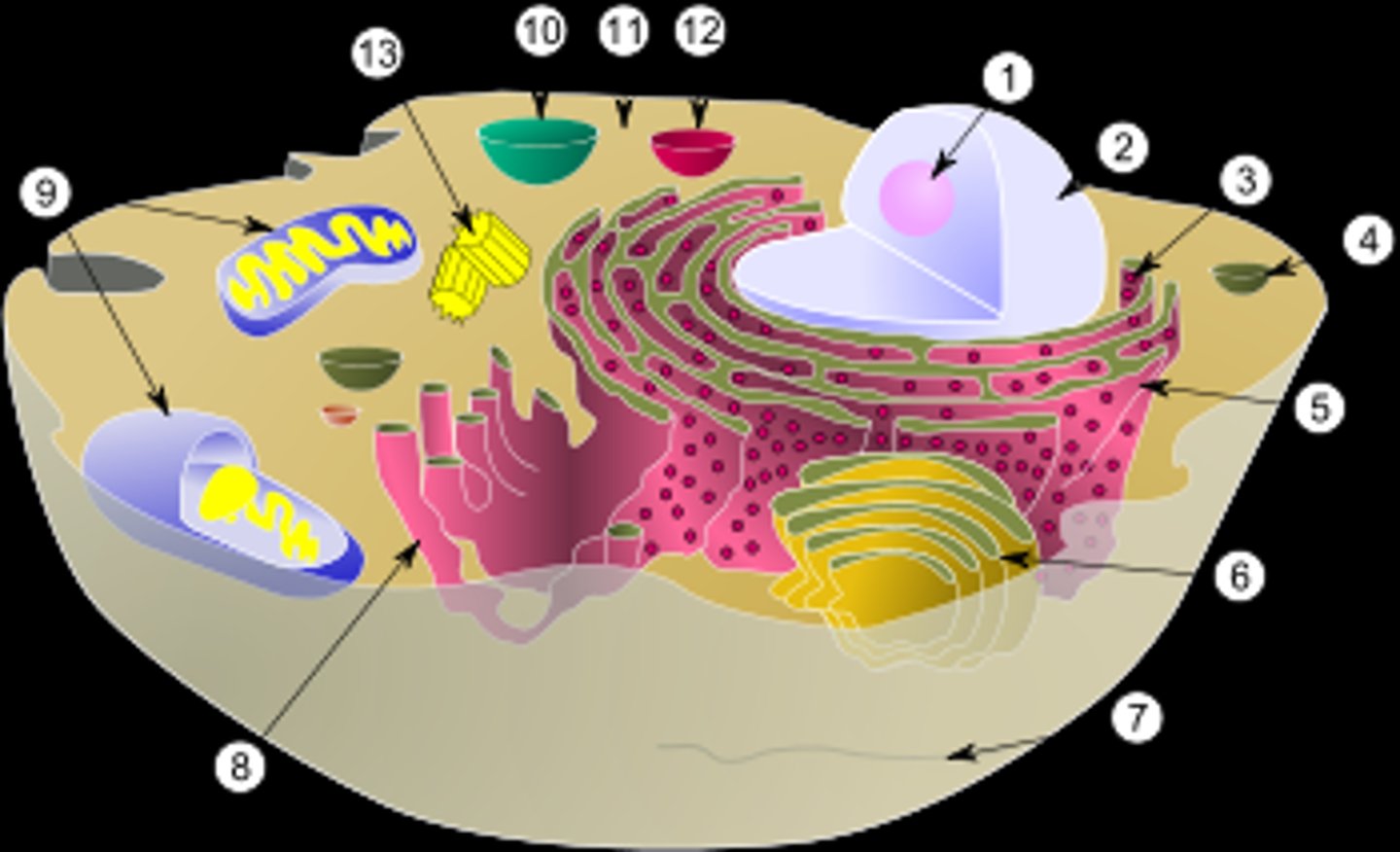
Nucleus
Dense organelle in eukaryotic cells, single rounded structure, has genetic material. Store the cells DNA and coordinates the cells activities. The brain of the cell.
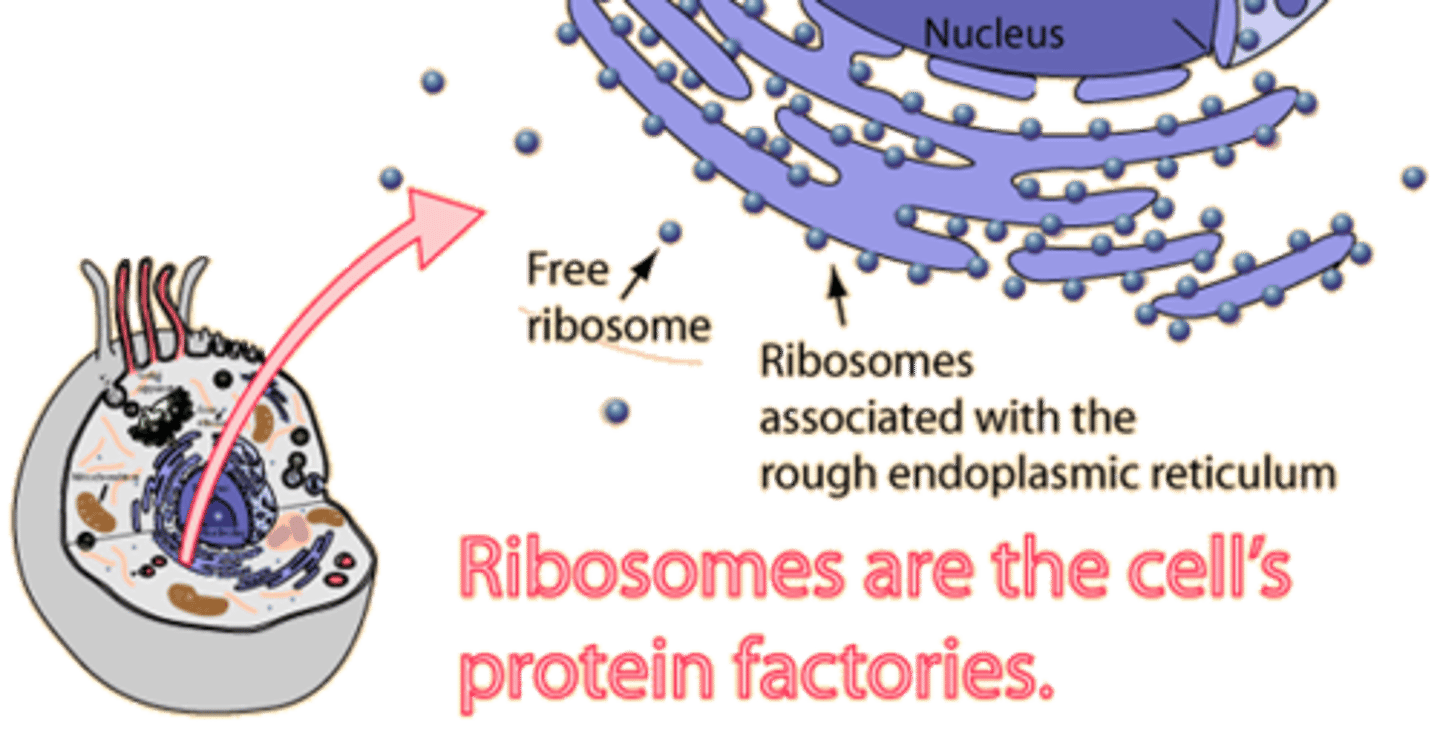
Ribosomes
Makes proteins, proteins do everything. can be on RER or free floating in the cytoplasm.
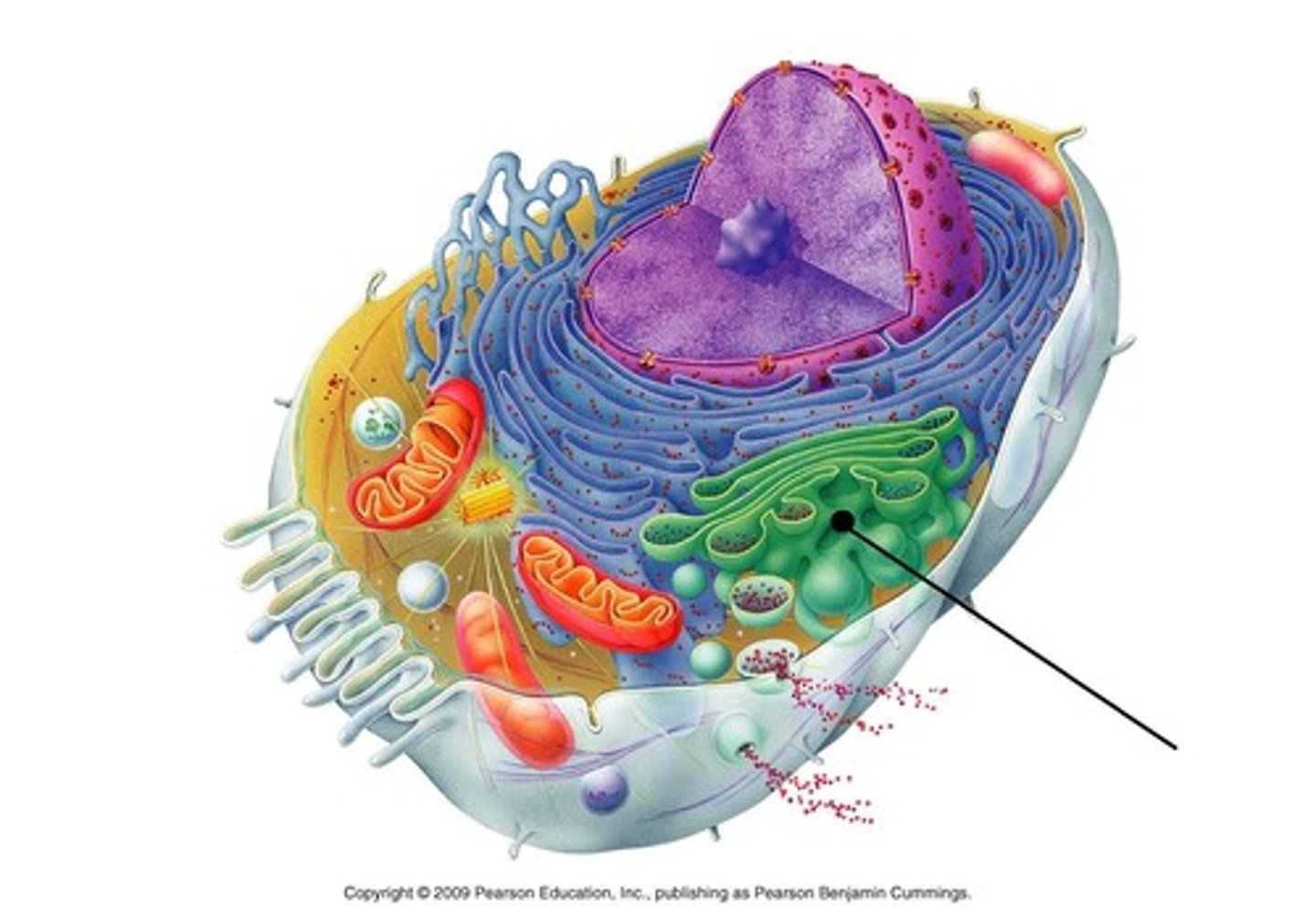
Golgi
involved in protein modification, distribution, and transport. this organelles looks like a stack of pancake-like membranes. Checks proteins and sends them to their appropriate location in or outside of the cell.
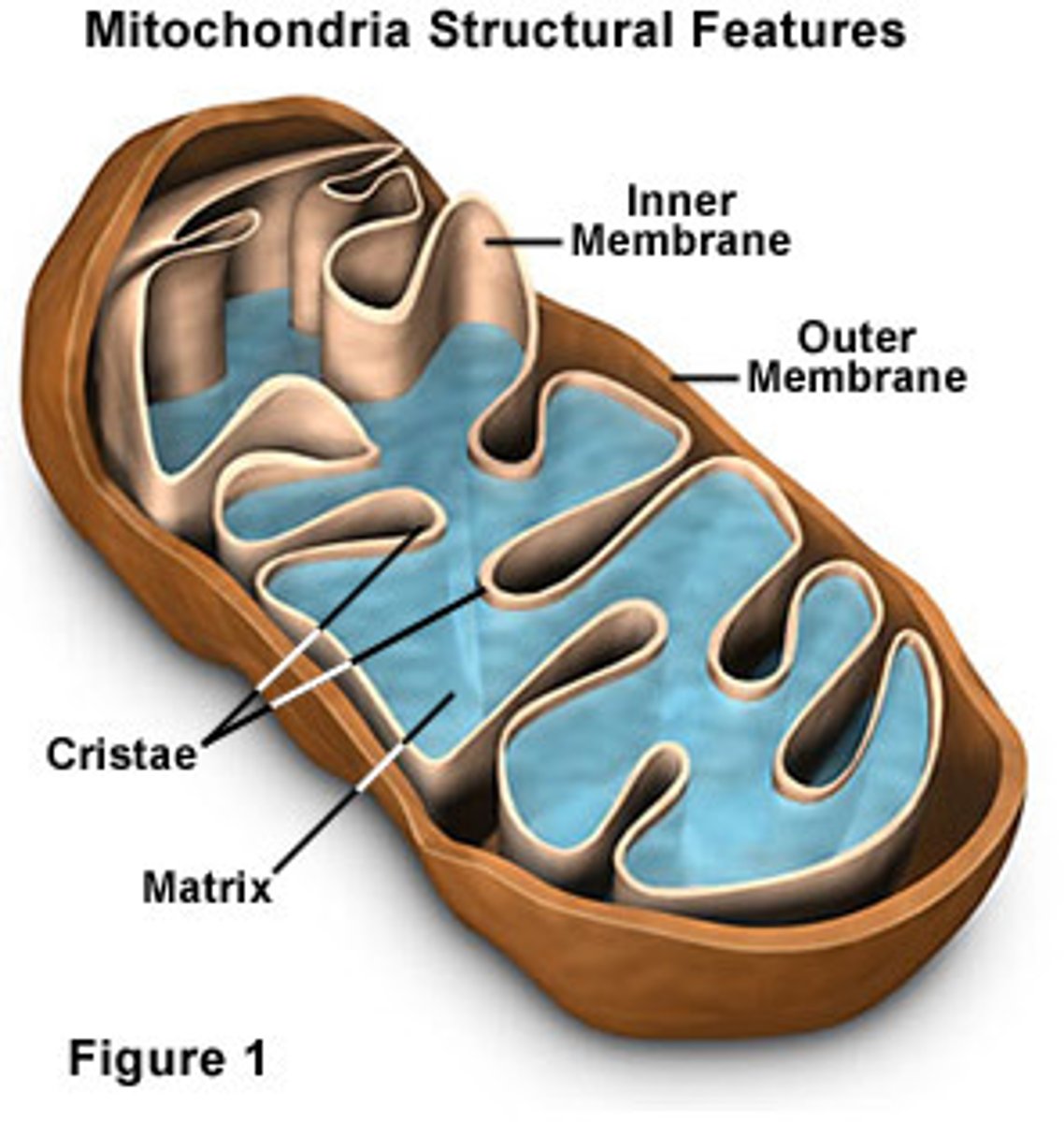
Mitochondria
makes (ATP) energy for the cell by breaking down sugar
Chloroplast
in plants, photosynthesis takes place here. light energy is converted into sugar for the plant as food. plants then break down this food in the mitochondria
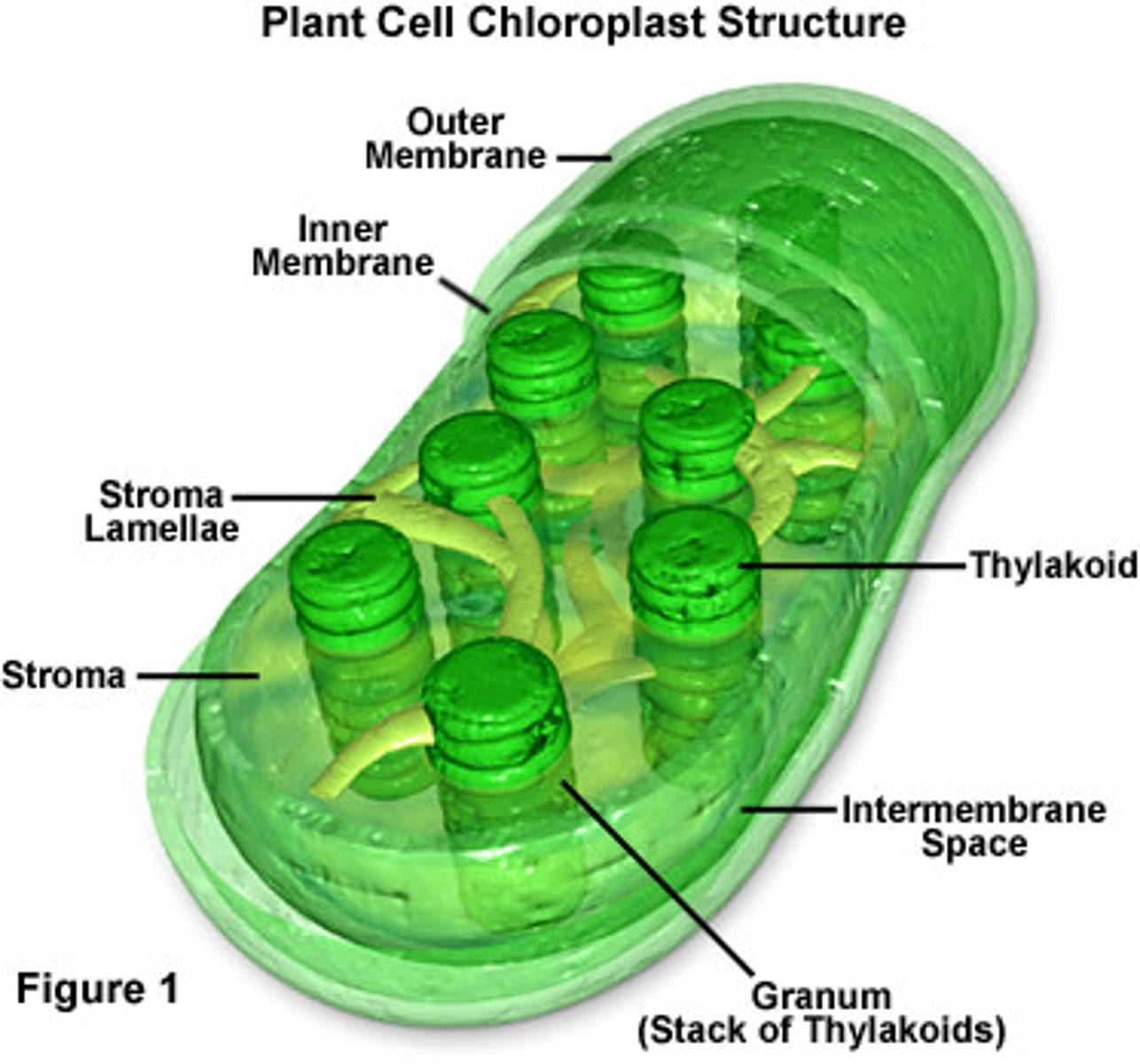
Lysosome
Recycles old organelles. Breaks down materials like wastes, food, or invaders.
Cell Wall
a rigid protective covering outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants and bacteria (prokaryotes). gives cells protection and structure.
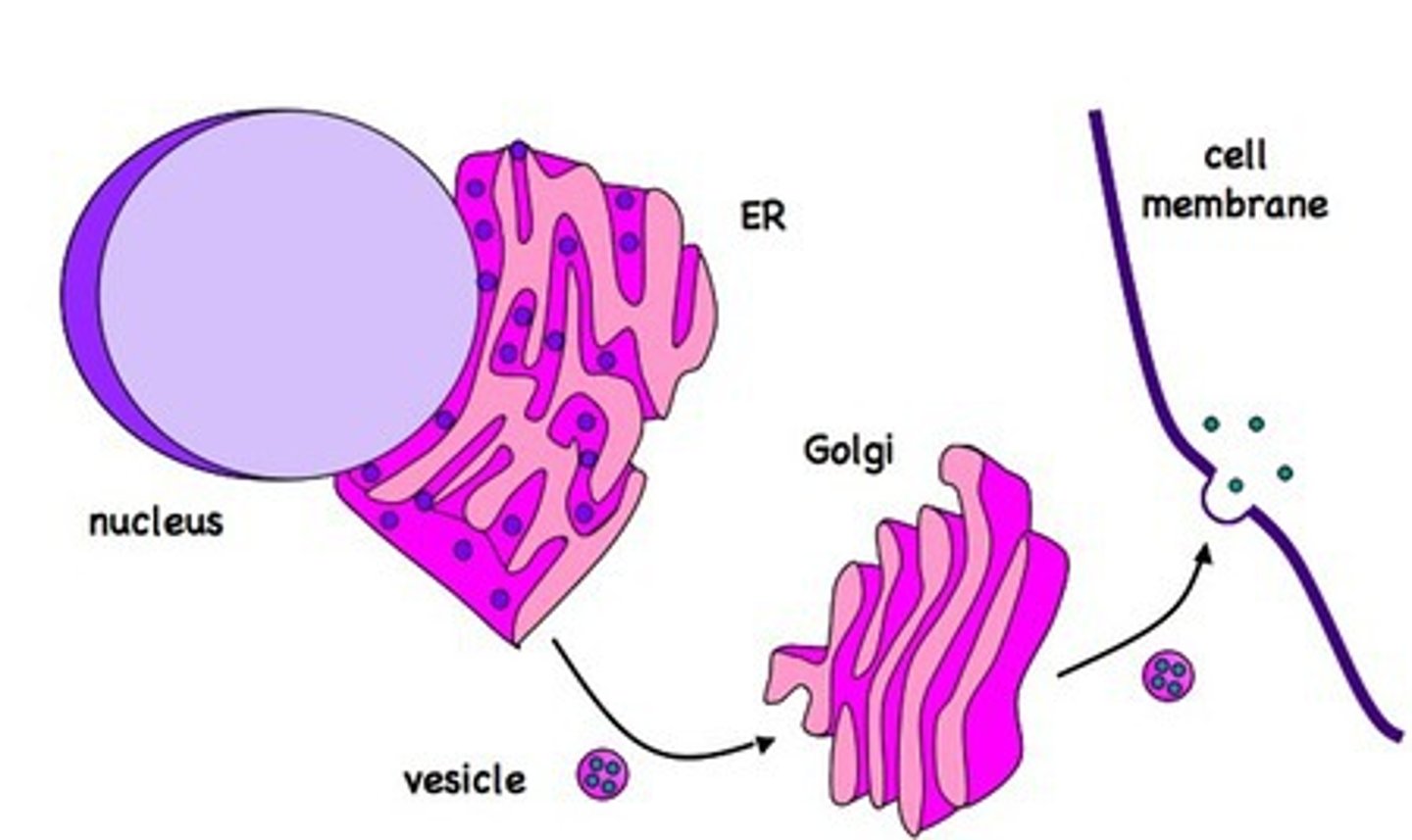
Transport vesicles
small sacs of membrane that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
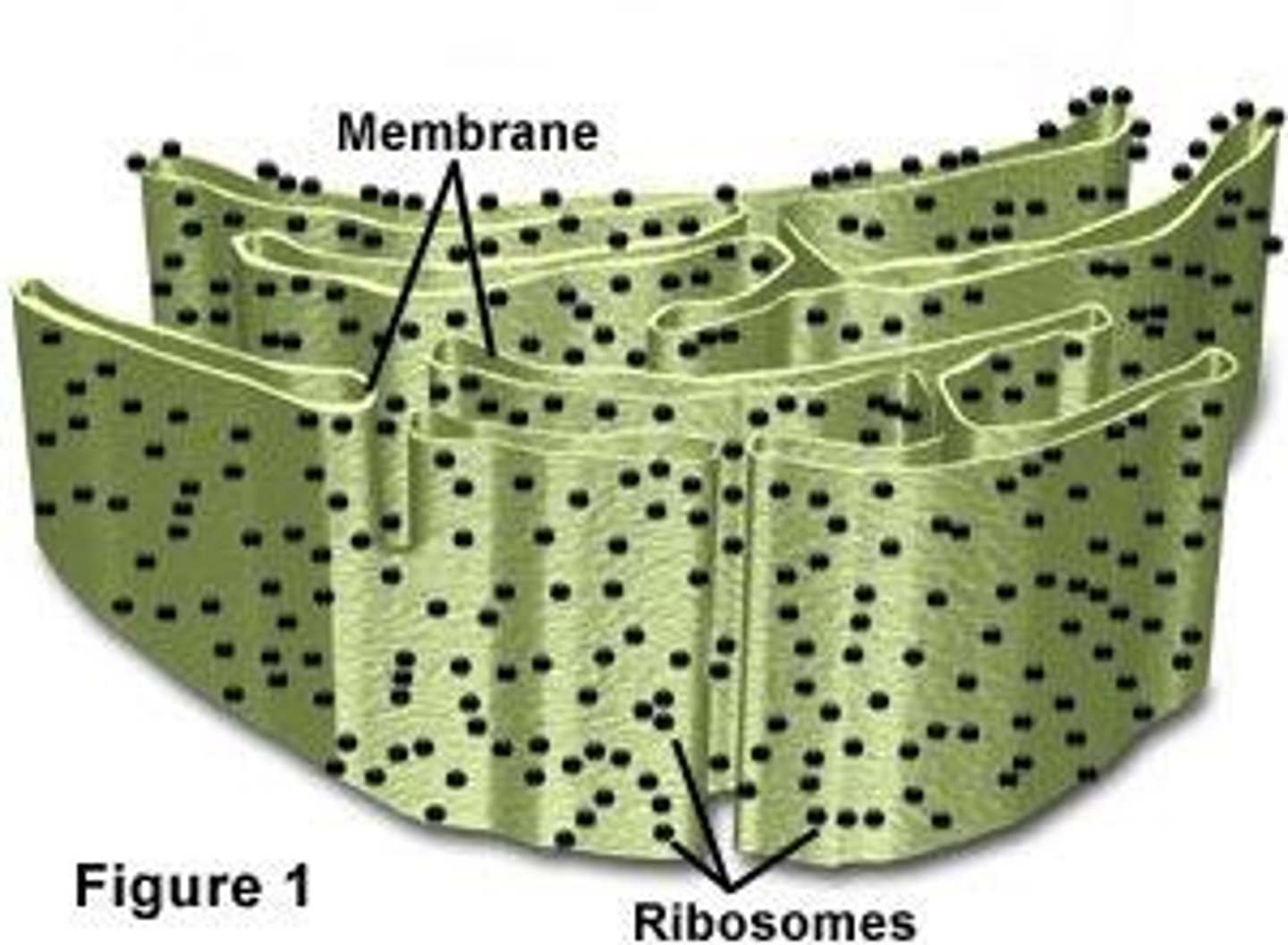
Rough ER
Has ribosomes attached. packages newly made proteins and send them to be further processed.
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
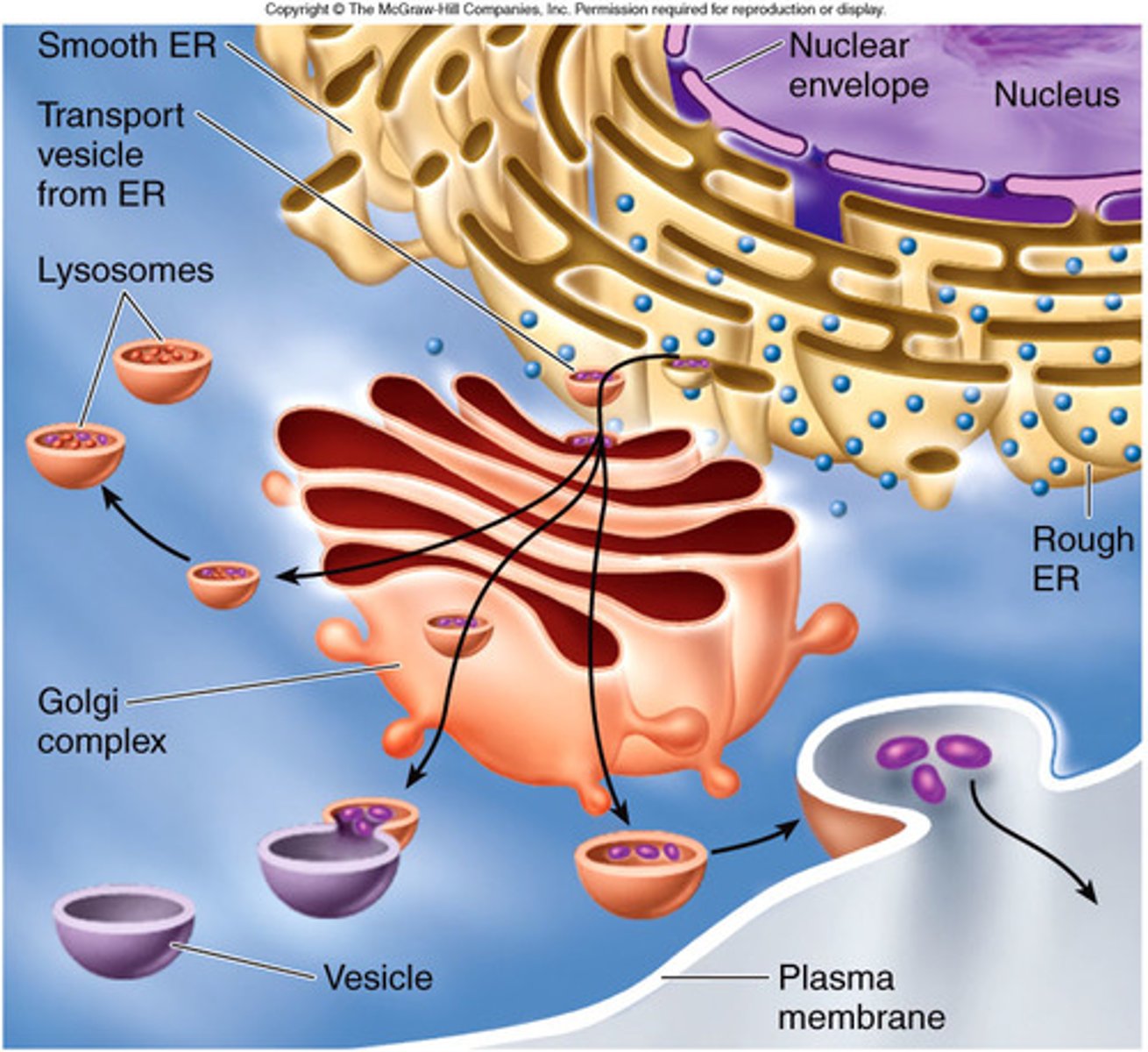
Organelles involved in protein synthesis
Nucleus (code for proteins), ribosomes (protein factory), Endoplasmic Reticulum (packs proteins), Golgi Apparatus (modifies and distributes proteins), Vesicles (transports proteins).
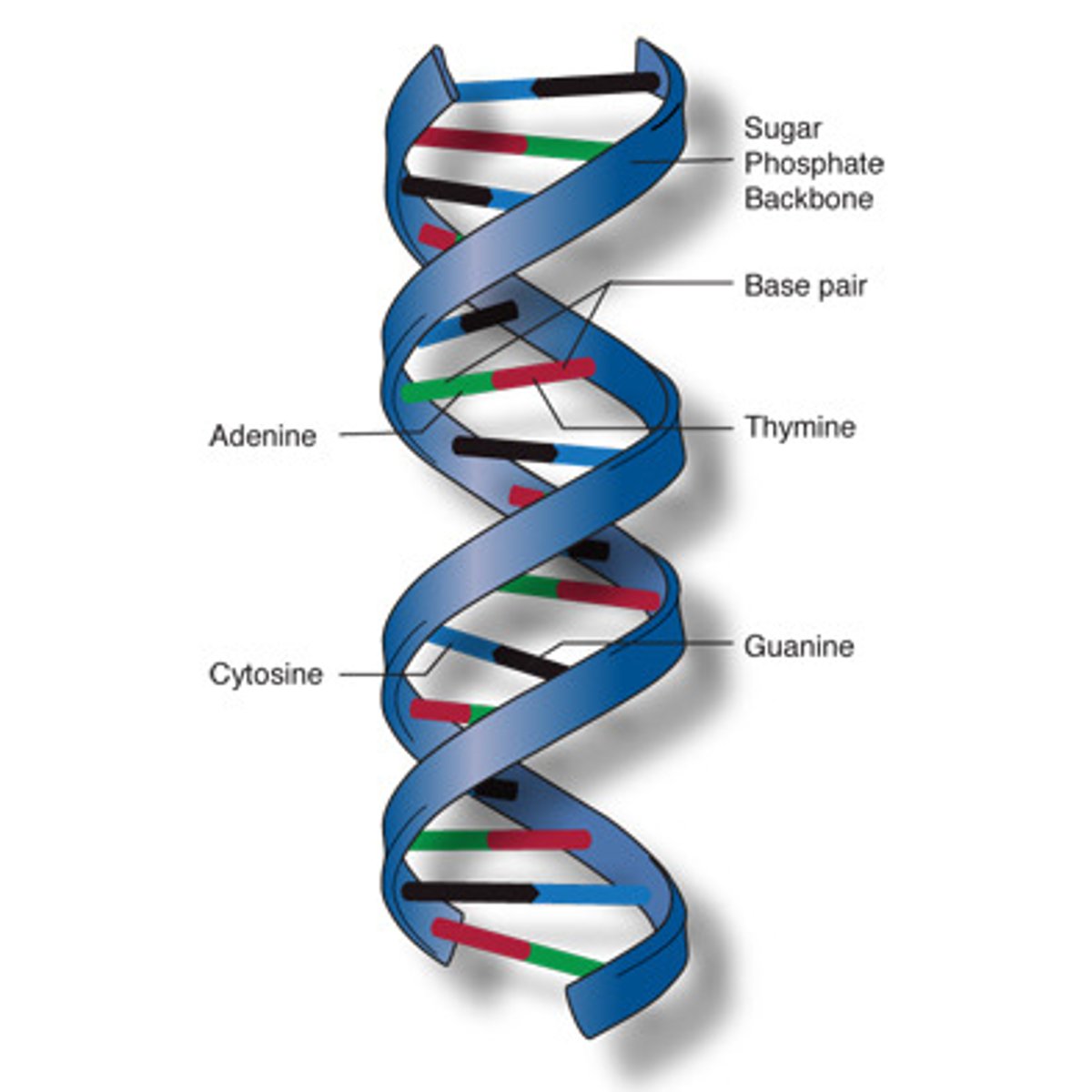
DNA
A macromolecule containing the genetic information
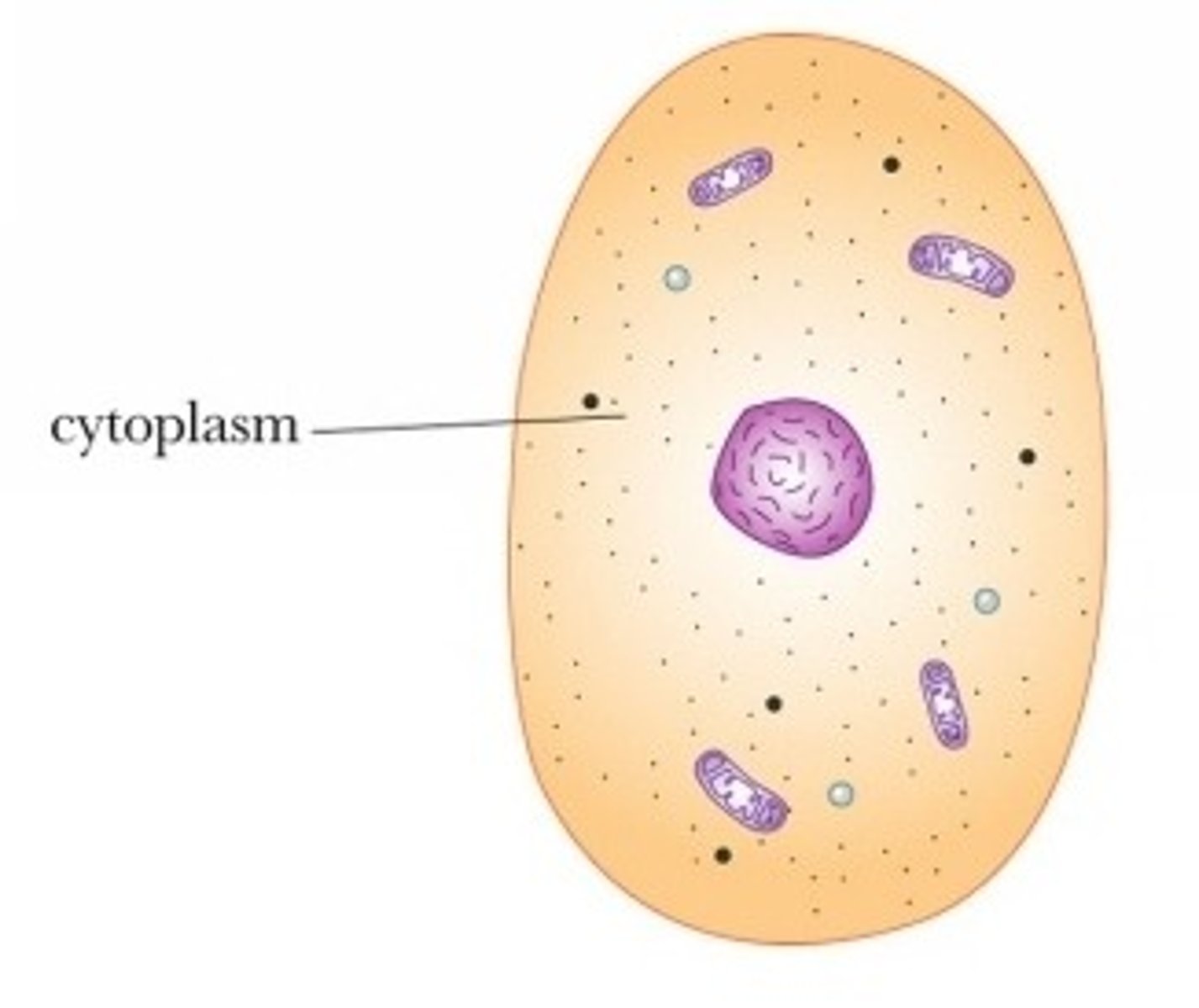
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
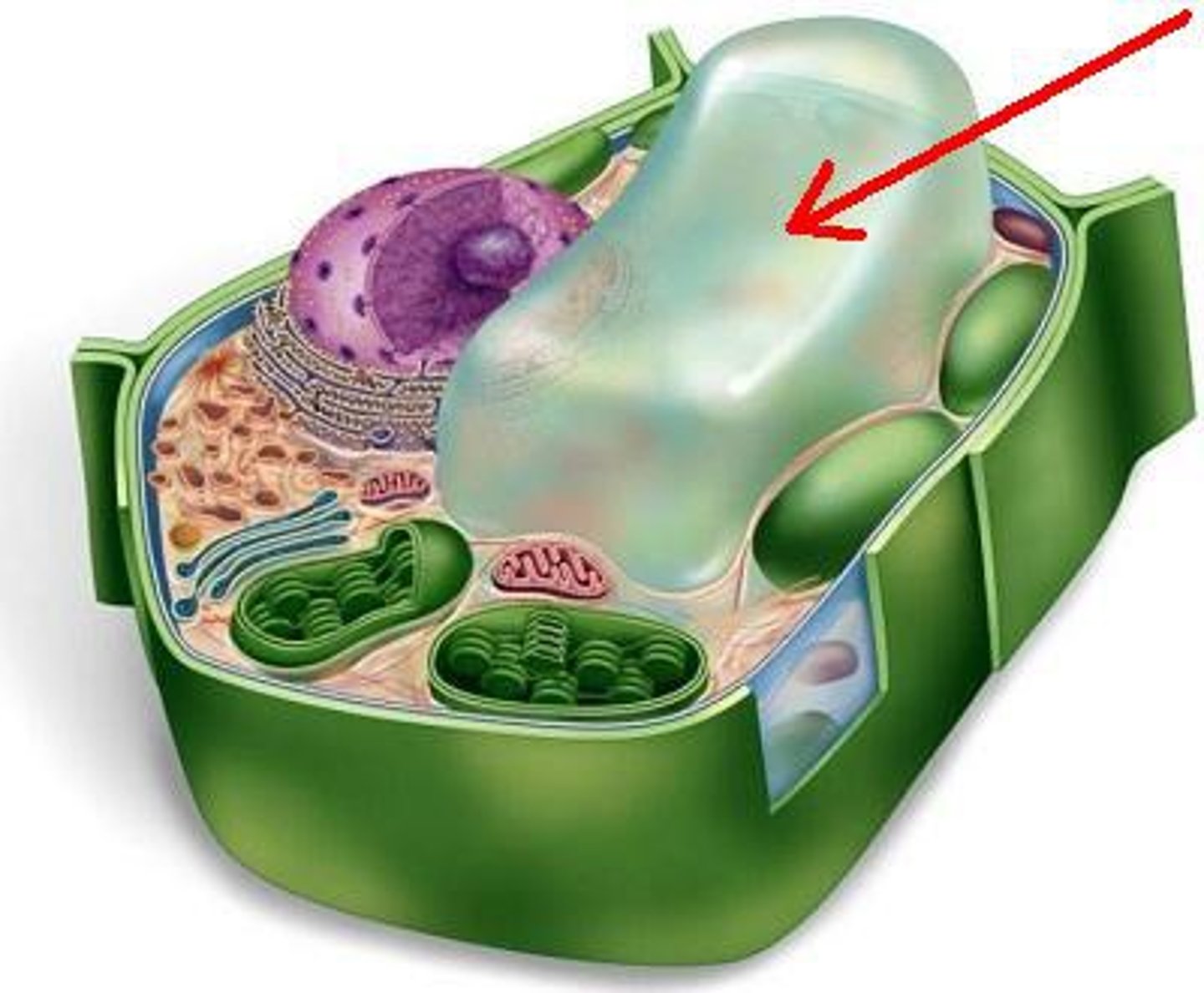
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. is very large in plants to store water.
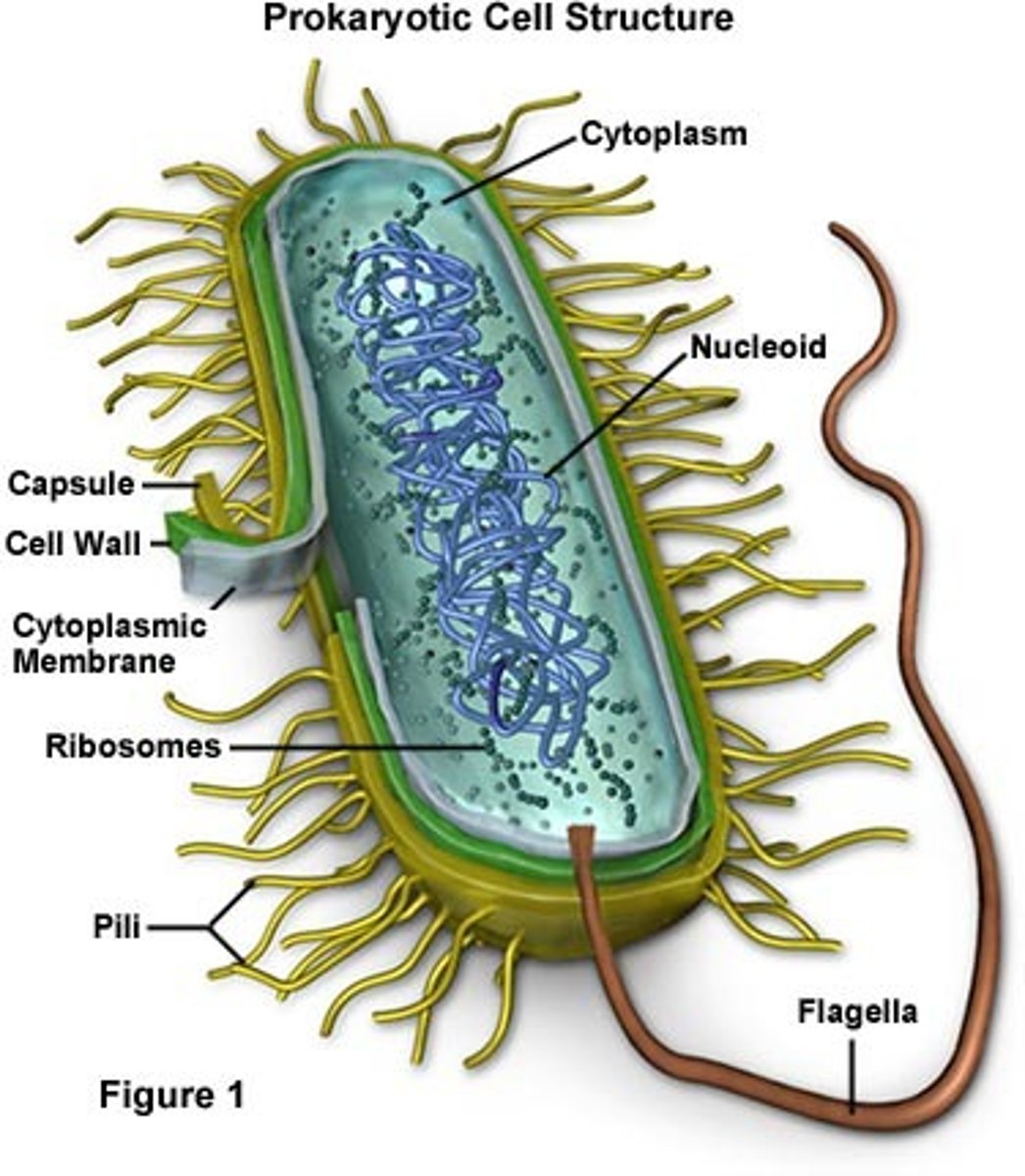
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
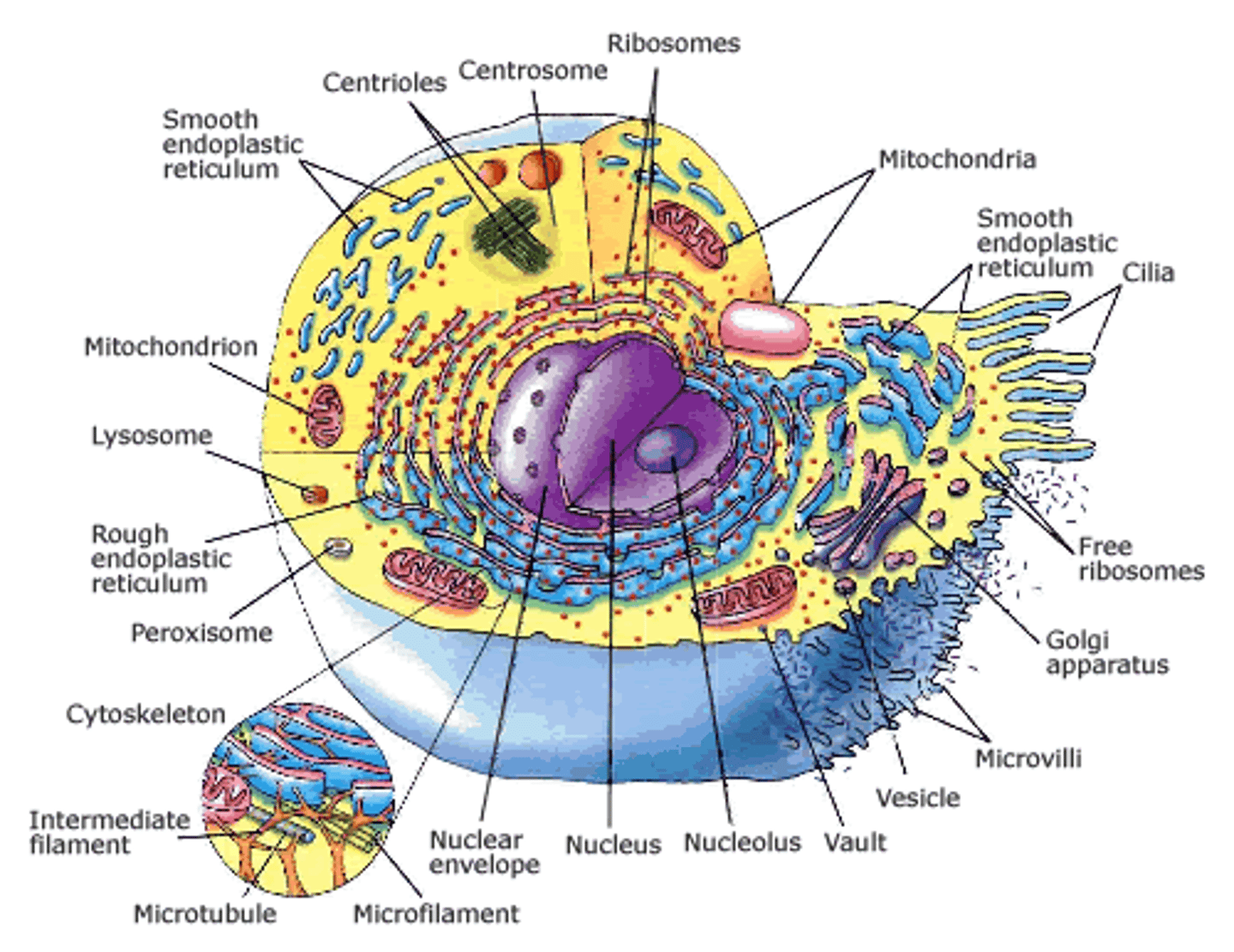
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. very complex. plants, animals, and fungi
Organelle
A tiny membrane bound structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
Cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and helps move materials around the cell like a highway.
what structures do prokaryotes and eukaryotes share
cell membrane, cytosplam, ribosomes, DNA, (cell wall sometimes. plants/fungi are the only eukaryotes with a cell wall)
Properties of eukaryotic cells
Large in size, many pieces of linear DNA. can have specialized functions. more complex
have membrane bound organelles: Nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, Mitochondria, Chloroplast, smooth ER ect.
Properties of prokaryotic cells
- free floating DNA (no nucleus)
- no membrane bound organelles
- size: very small
- unicellular
-reproduce fast!
-evolve fast!
- bacteria
chromosome
piece of DNA
binary fission
copy DNA and divide a cell into 2 cells
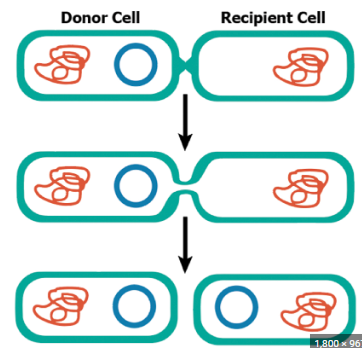
conjugation
transmission of plasmids from one prokaryotic cell to another via sex pilis
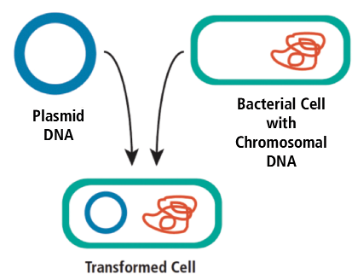
transformation
the uptake and use of DNA (plasmids) from surroundings and environment
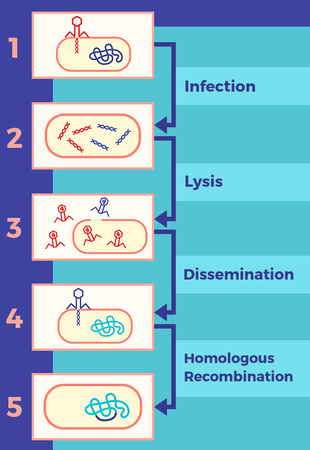
transduction
the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one prokaryote to another, occurs when viruses infect prokaryotes and result of malfunction of viral infection
horizontal gene transfer
transmission of DNA within one generation
selectively permeable
only allow certain molecules in/out of cell due to molecule structure
homeostasis
maintaining internal conditions separate from external conditions
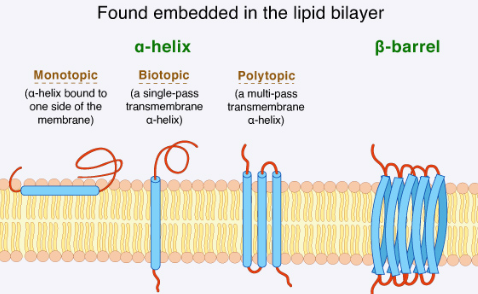
integral/transmembrane proteins
proteins that span the membrane (embedded in membrane)
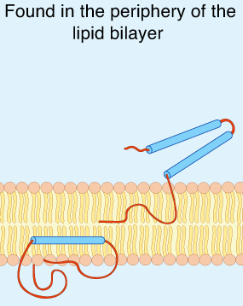
peripheral proteins
loosely bound to surface of membrane and extent outward
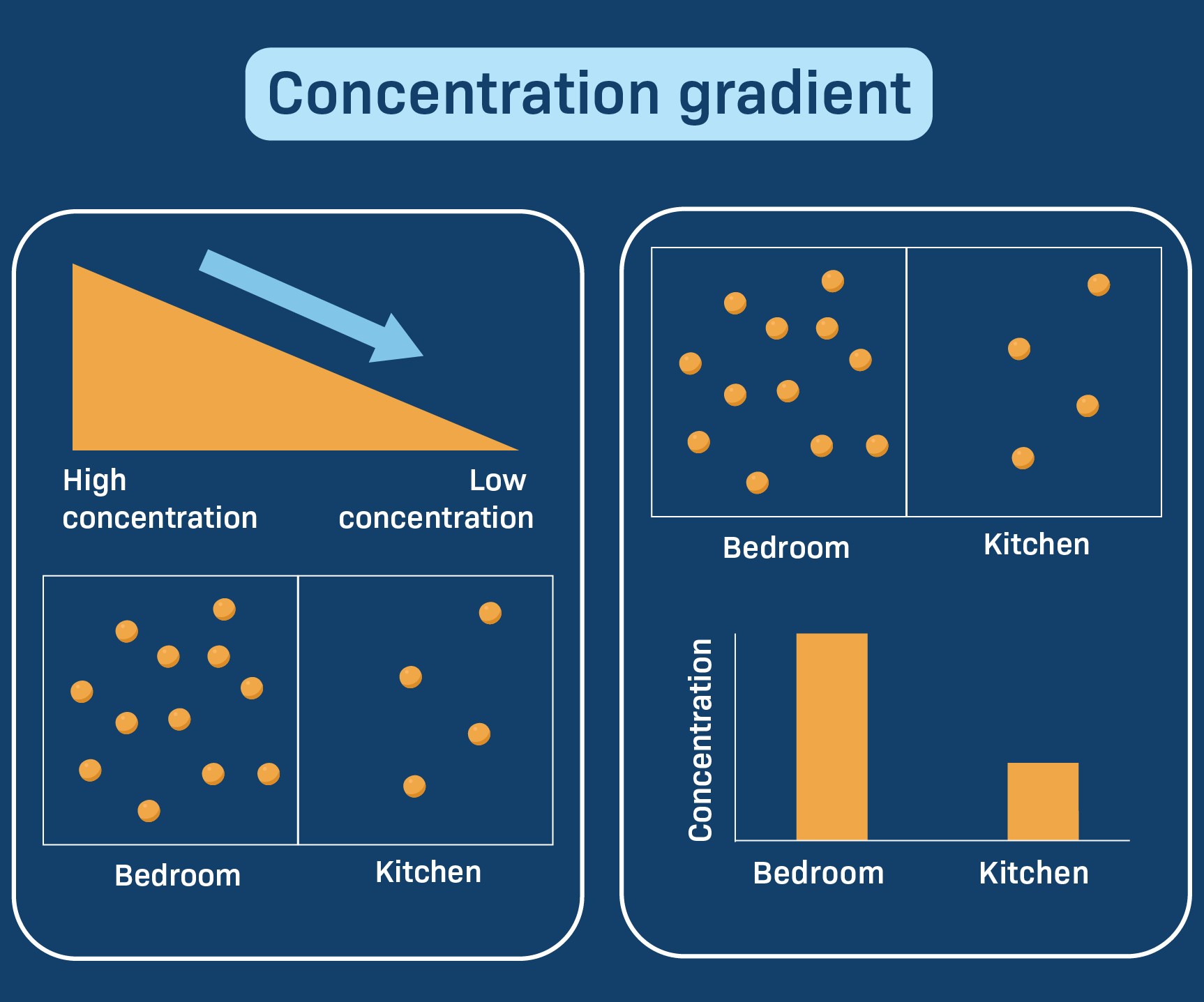
concentration gradient
the difference in concentration of a substance between two areas
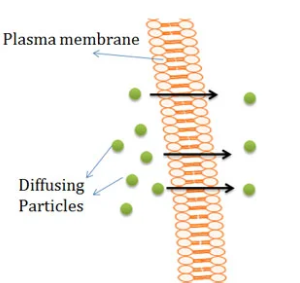
simple diffusion
natural, small nonpolar movement of molecules from high to low concentration (down con. gradient / passive transport)
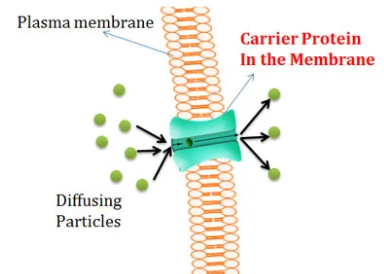
facilitated diffusion
movement of polar molecules through a channel (down con. gradient / passive transport)
osmosis
movement of water from an area of high water con. to low water con. (like a combo of facilitated and simple diff.)
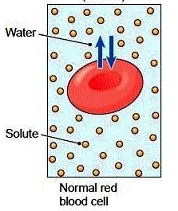
isotonic solutions
surrounding solutions that have an equal solute (and water) con. as the cell, in equilibrium
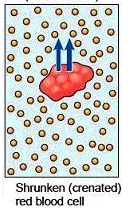
hypertonic solution
solutions that have a higher solute con. than the cell
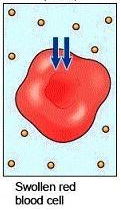
hypotonic solution
solutions that have less solute con. than the cell
active transport
transport of molecules against con. gradient (from low to high) and requires input of energy
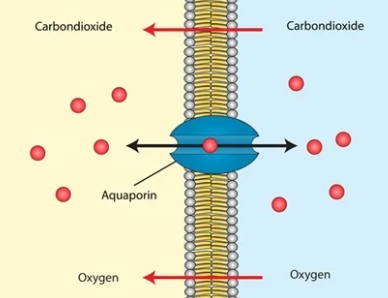
aquaporins
proteins embedded in membranes that move water (water protein channel)
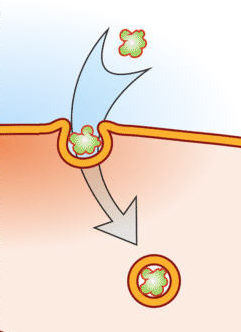
endocytosis
cells take in very large macromolecules or whole viruses by enclosing then in vesicles derived from plasma membrane (enter)
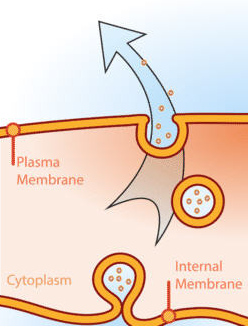
exocytosis
vesicles containing molecules produced in the cell, fuse w/ plasma membrane and release contents outside the cell (exit)
some membrane protein functions
transport proteins embedded in membrane
signal molecule reception by binding to receptors
cell to cell recognition via markers
anchoring
enzymatic activity