Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Hypothalamus
Anterior end of diencephalon
received signals from multiple sources in nervous system
concerned with wellbeing of body
info used to cntrol secretion of pituiray ormones
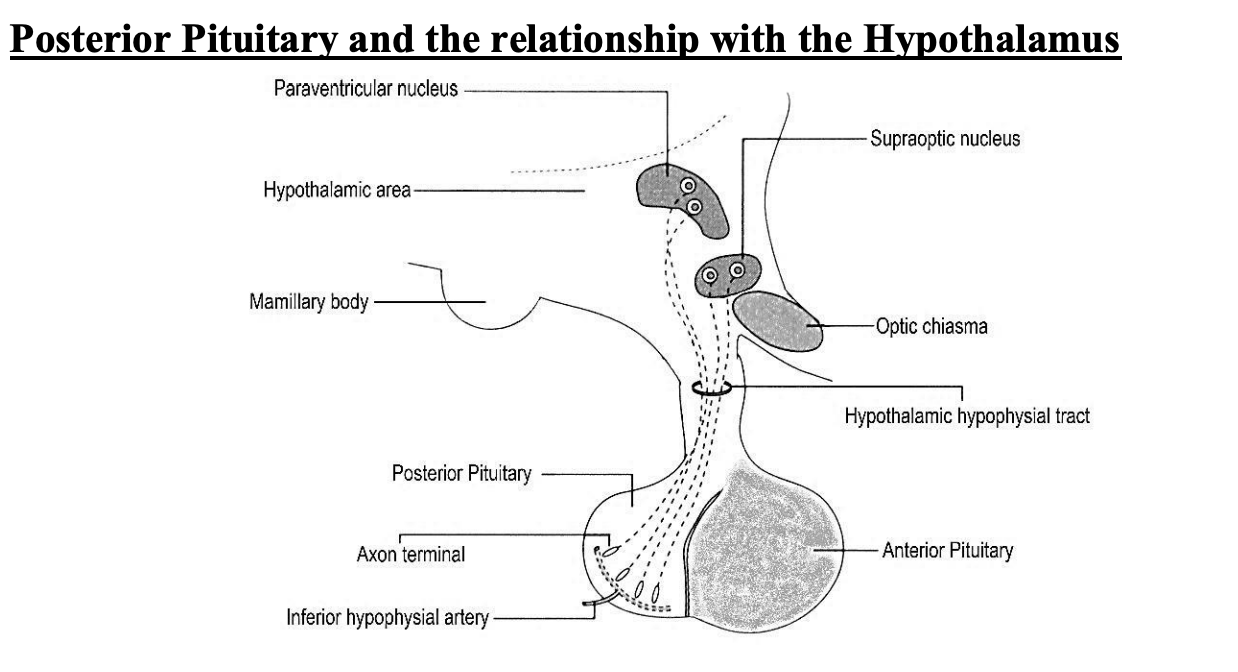
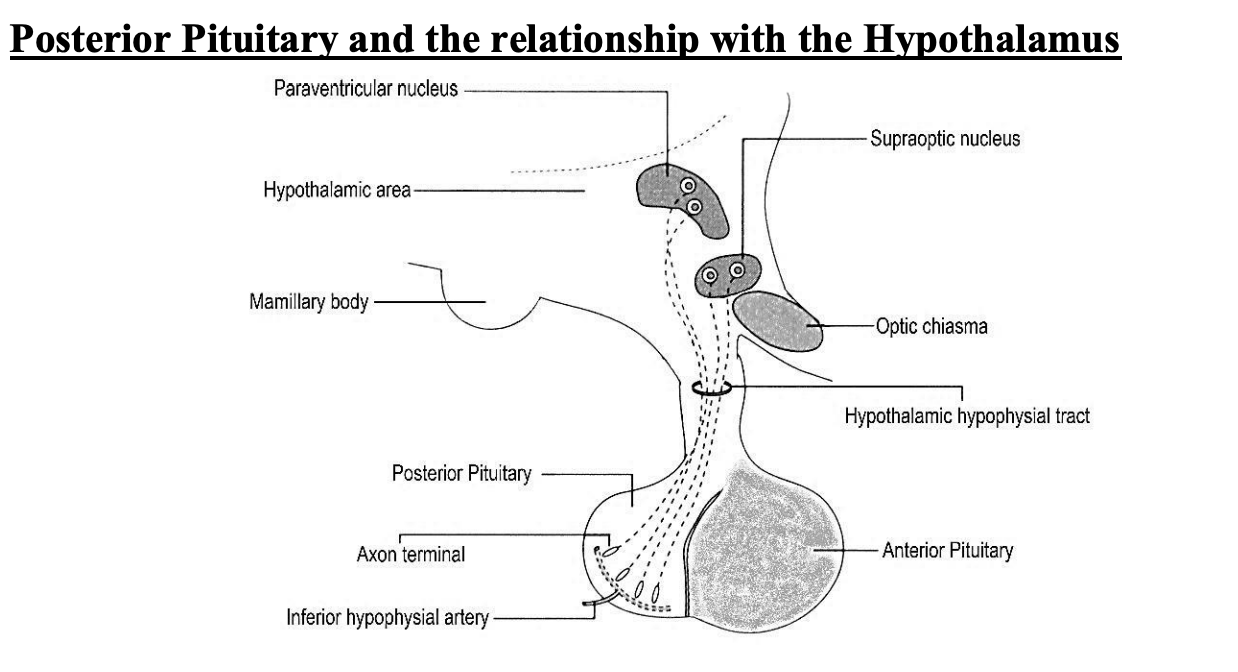
Links between hypothalamus and pituirtay
direct vascular links to ANTERIOR→ hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
special neurons synthesize and secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones
control secretion of anterior pituitray hormones
neural connections to POSTERIOR
Hypothalamic releasing and inhibitory hormones
Corticotrophin releasing hormone (CRH)
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH),
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH),
gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH),
growth hormone release inhibiting hormone or somatostatin (SMS)
dopamine
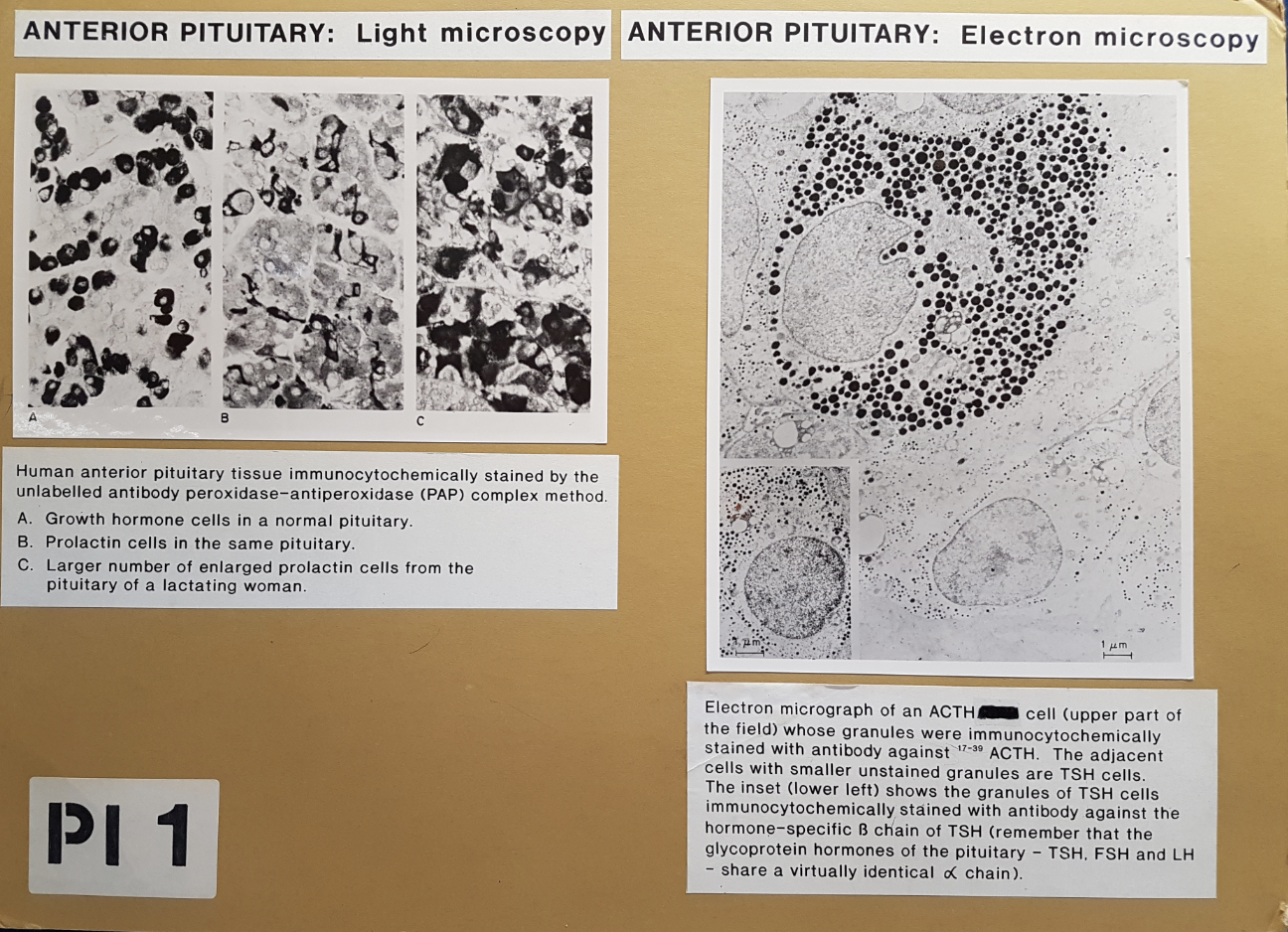
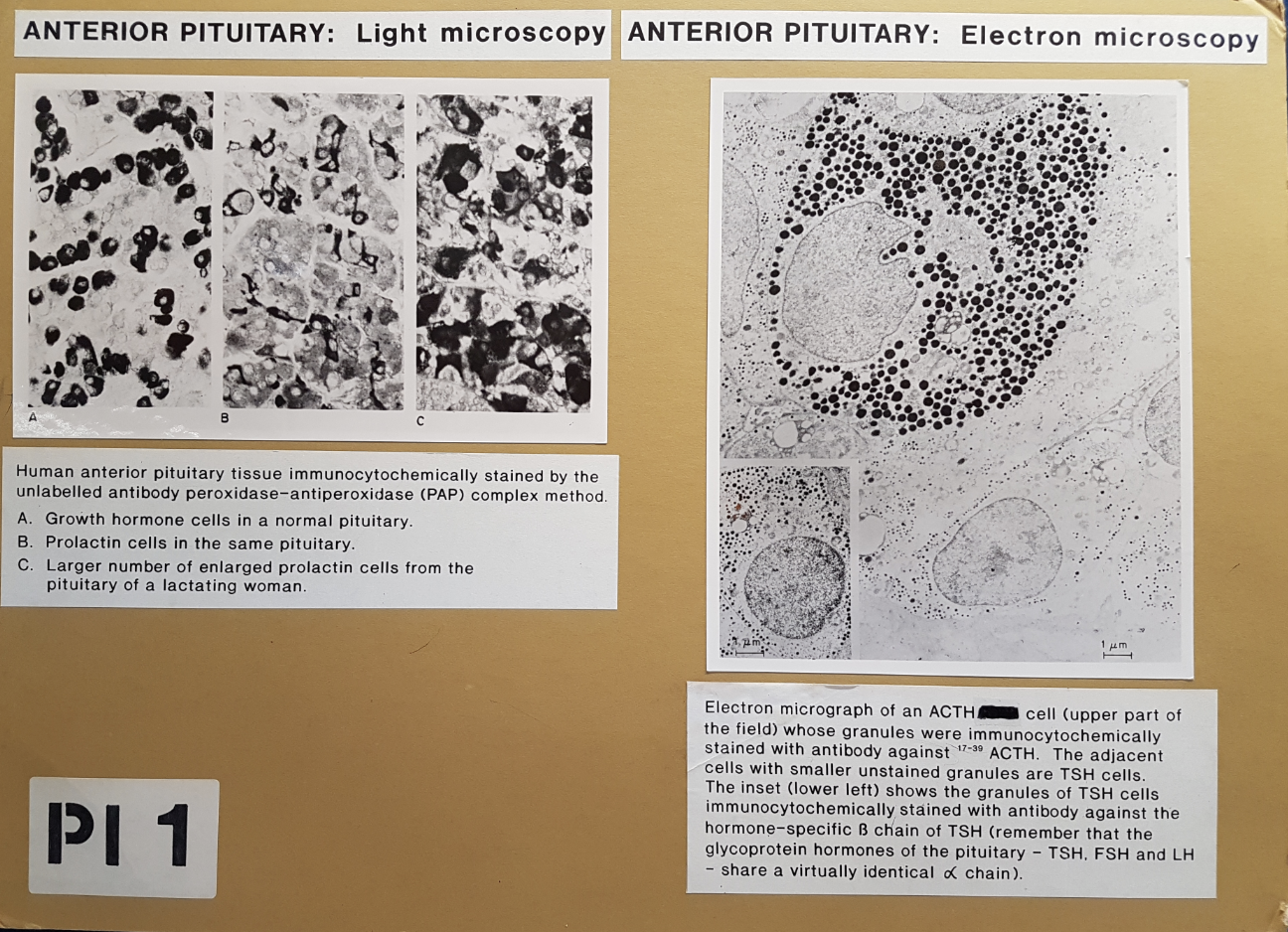
Blood supply and relationship between hypothalamus and pit gland: human anterior pit
stained with immunocytochemically
LM→ growth hormone cella and prolactin cells
enlarged prolactin cells in lactating women
EM-. ACTH and TSH cells
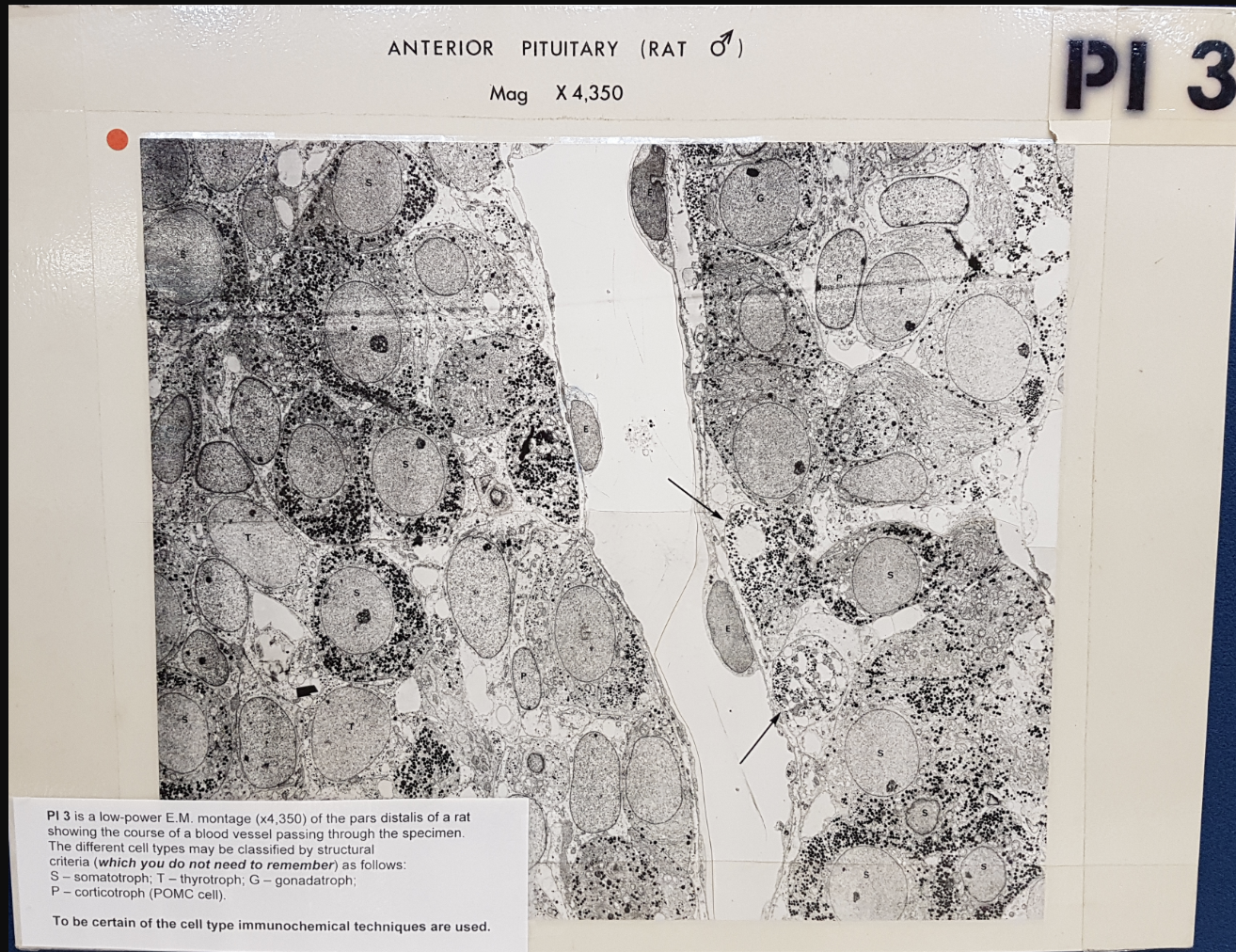
Anterior pituitary male rat
Various endocrine cell types
course of blood vessels passing through specimen
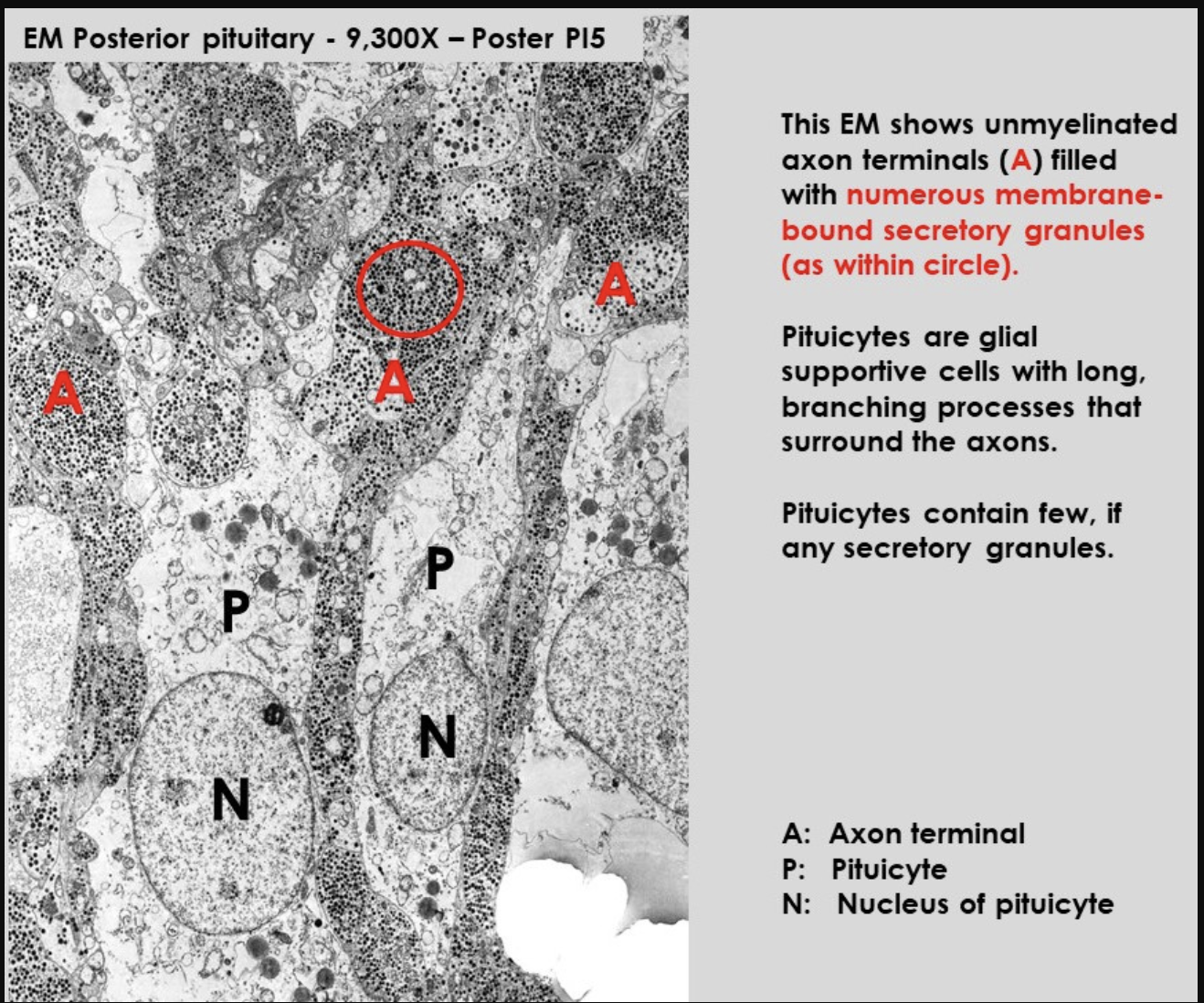
Rat Neurohypophysis
shows pituicytes and axons
notice:
difference between number and secretory granules in each of them
Posterior pit→ composed of non-myellinated axons of neurons located in hypothalamus
axons contain numerous secretory granules
supported by glial cells→ pituicytes
numerous sinusoid capillaries present
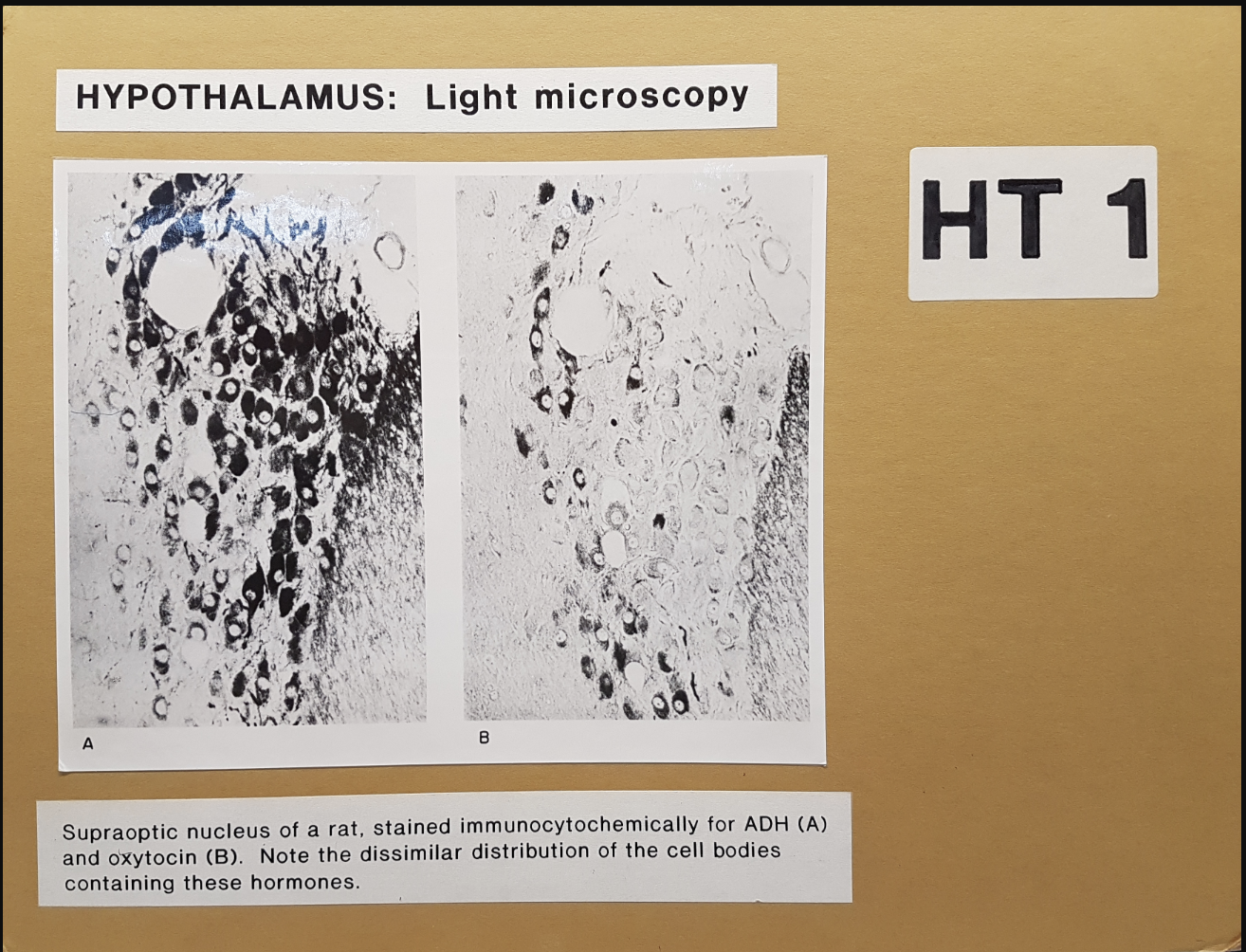
Rat hypothalamus
immunocytochemically stained for ADH and oxytocin
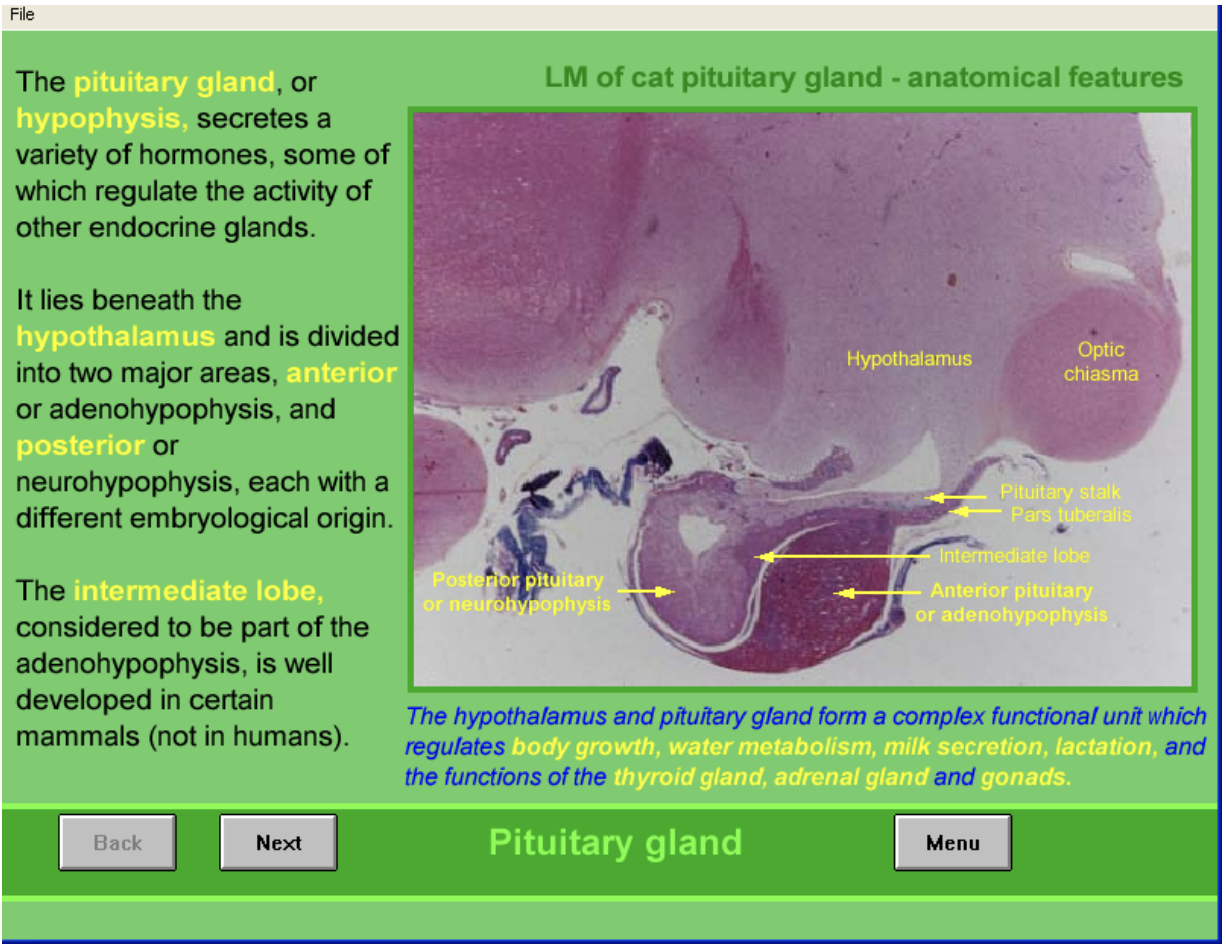
Pituitary gland (hypophysis) what it does
secretes variety of hormones
some regulate other endocrine glands
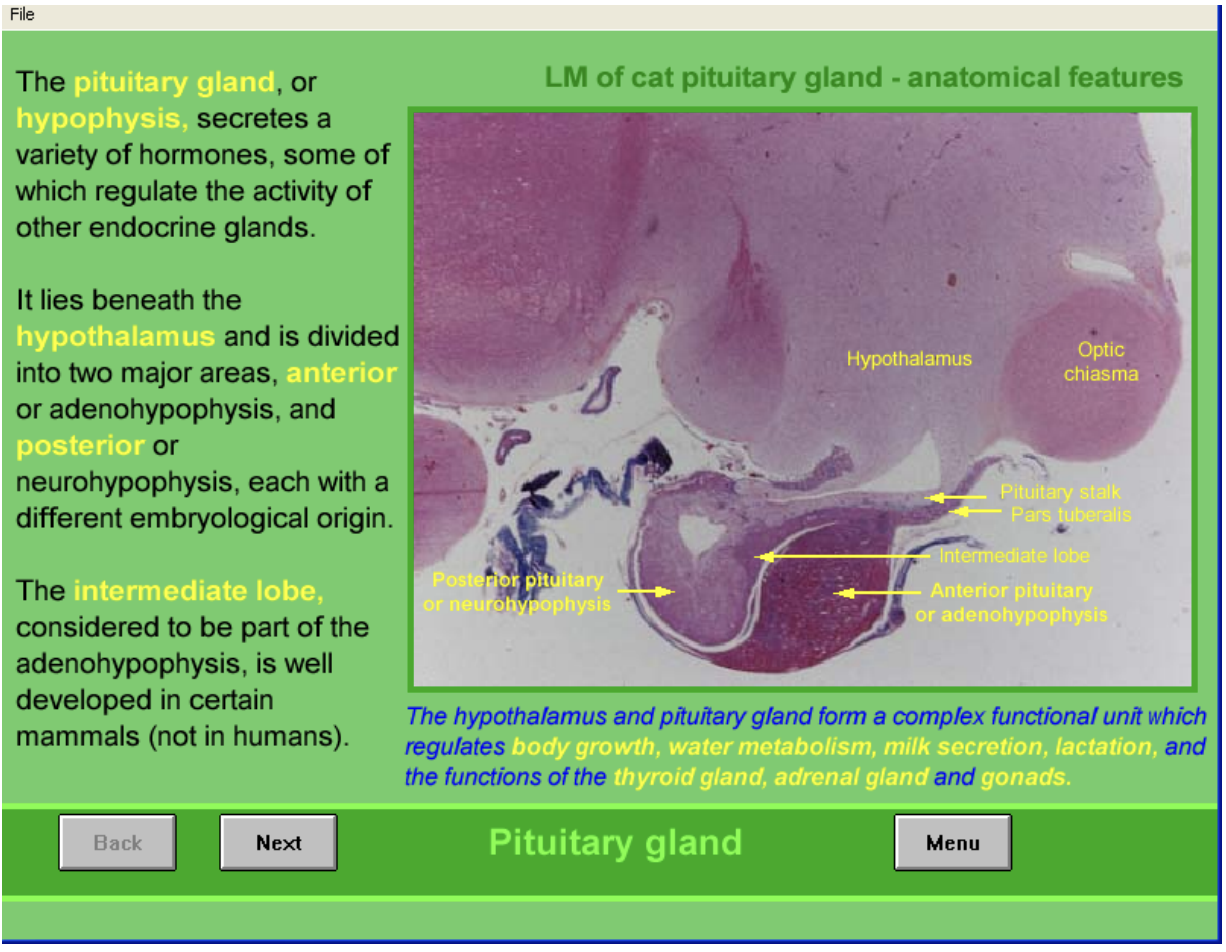
Where found and strucuture
Beneath hypothalamus
Divided into two
Anterior (andenohypophysis)
contains intermdeiate lobe
well developed in certain mammals (not in humans)
Posterior (neurohypophysis) (pars nervosa)
Have different embryological origin
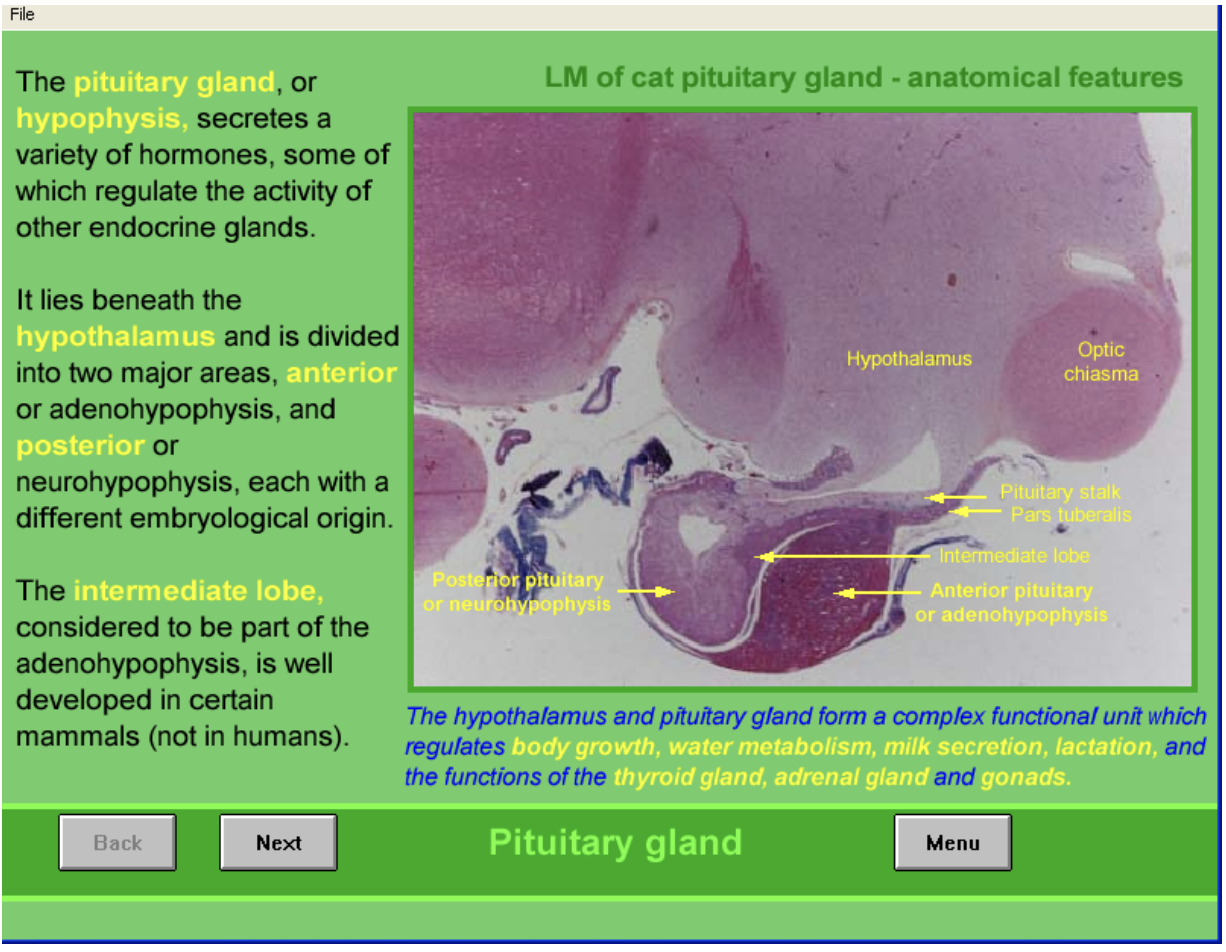
Hypothalamus and pituitary as a unit
complex functional unit
regulates
body growth
water metabolism
milk secretion
lactation
functions of
thyroid, adrenal and gonads
HYpothalamus is main regulator of pituitary secretions
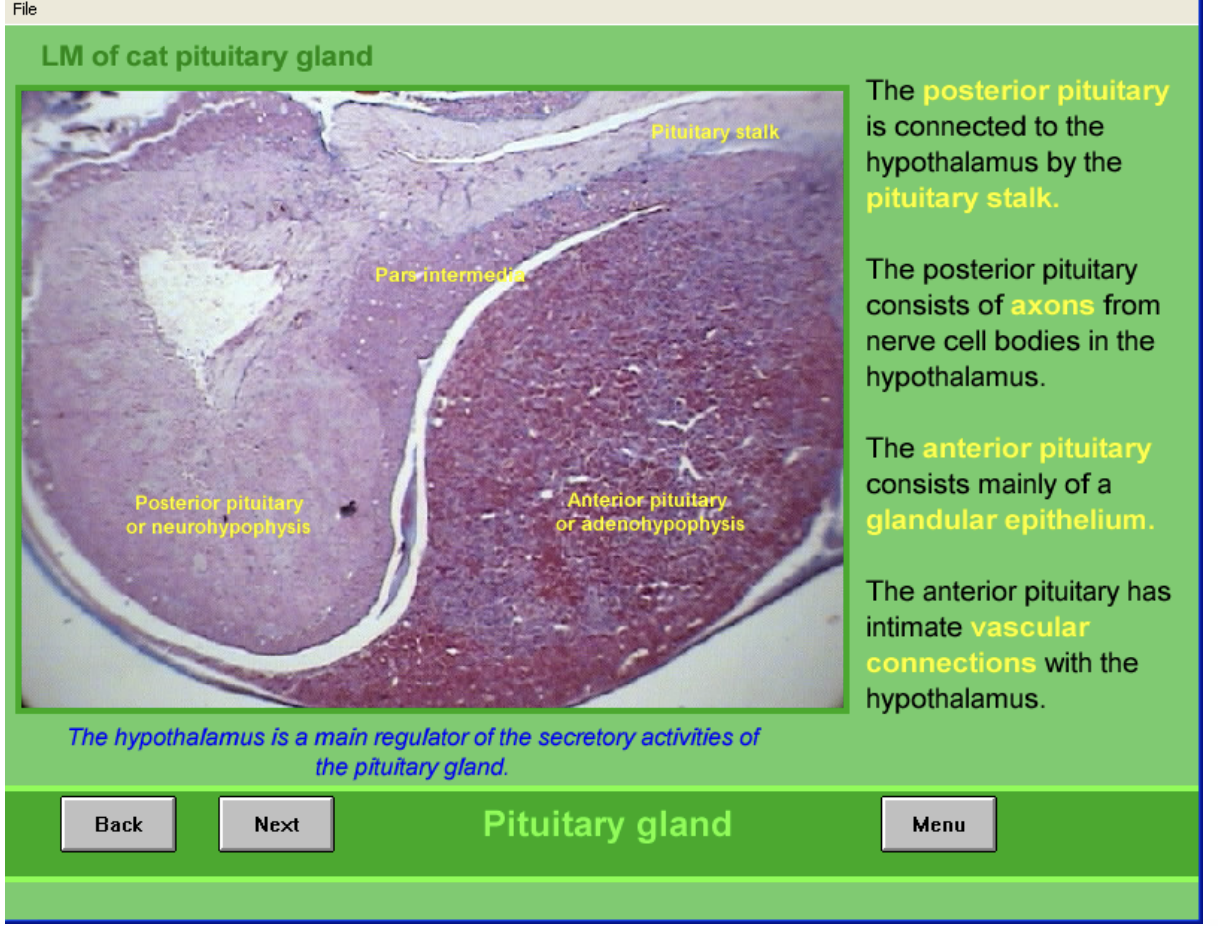
Posterior vs Anterior connections with hypo
Posterior
connected to hypo via pituitary stalk
consists of axons from nerve cell bodies→ in hypothalamus
Anterior
Mainly glandular epithelium
intimate vascular connections with hypothalamus
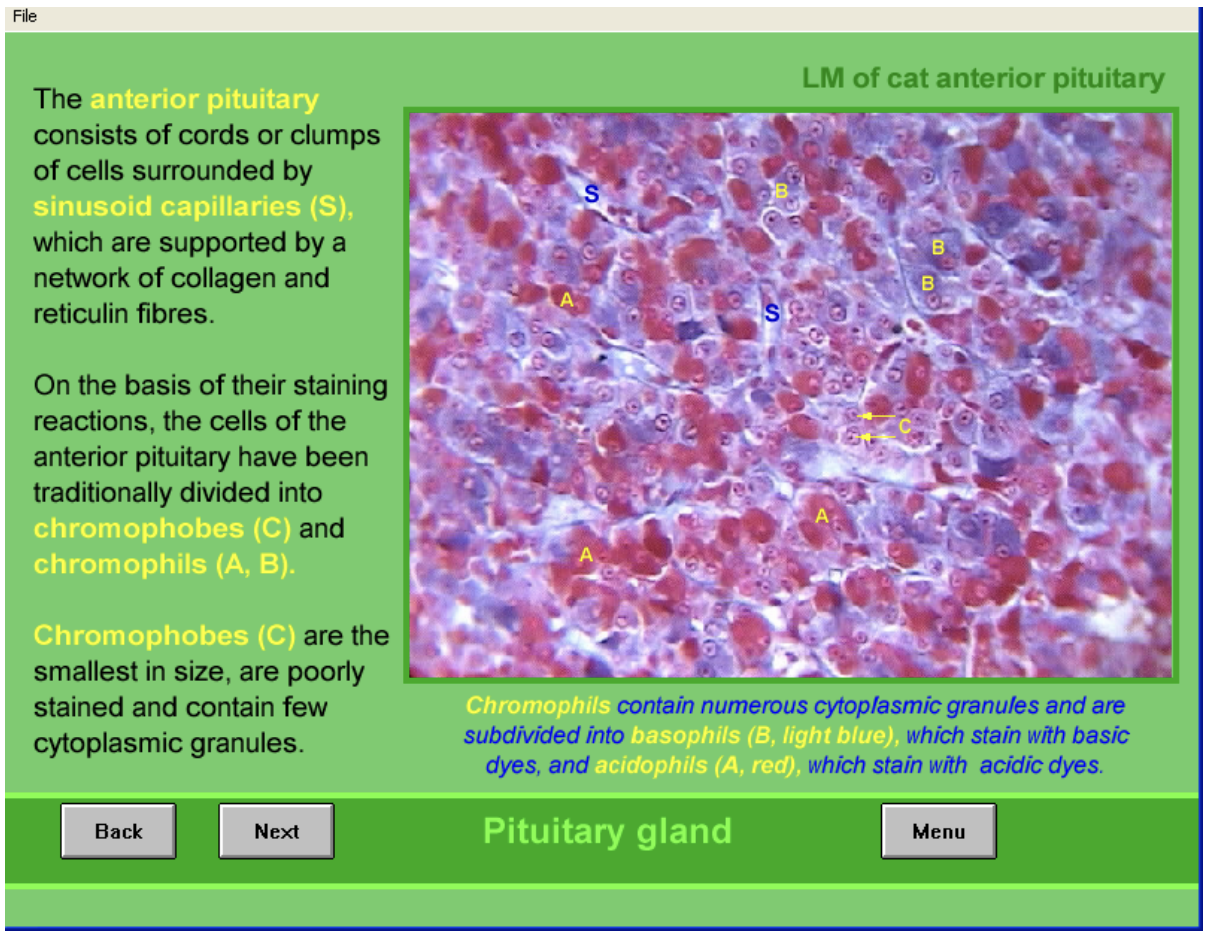
Anterior pituitary structure
consists of cords or clumps of cells
surrounded by sinusoid capillaries (S)
supported by network of collagen and reticulin fibres
Due to staining→ divided into
Chromophobes (C)
smallest in size
poorely stained
contain few cytoplasmic granules
Chromophils (A,B)
numerous cytoplasmic granules
subdivided into
basophils (light blue) BASIC
Acidophils (red) ACIDIC
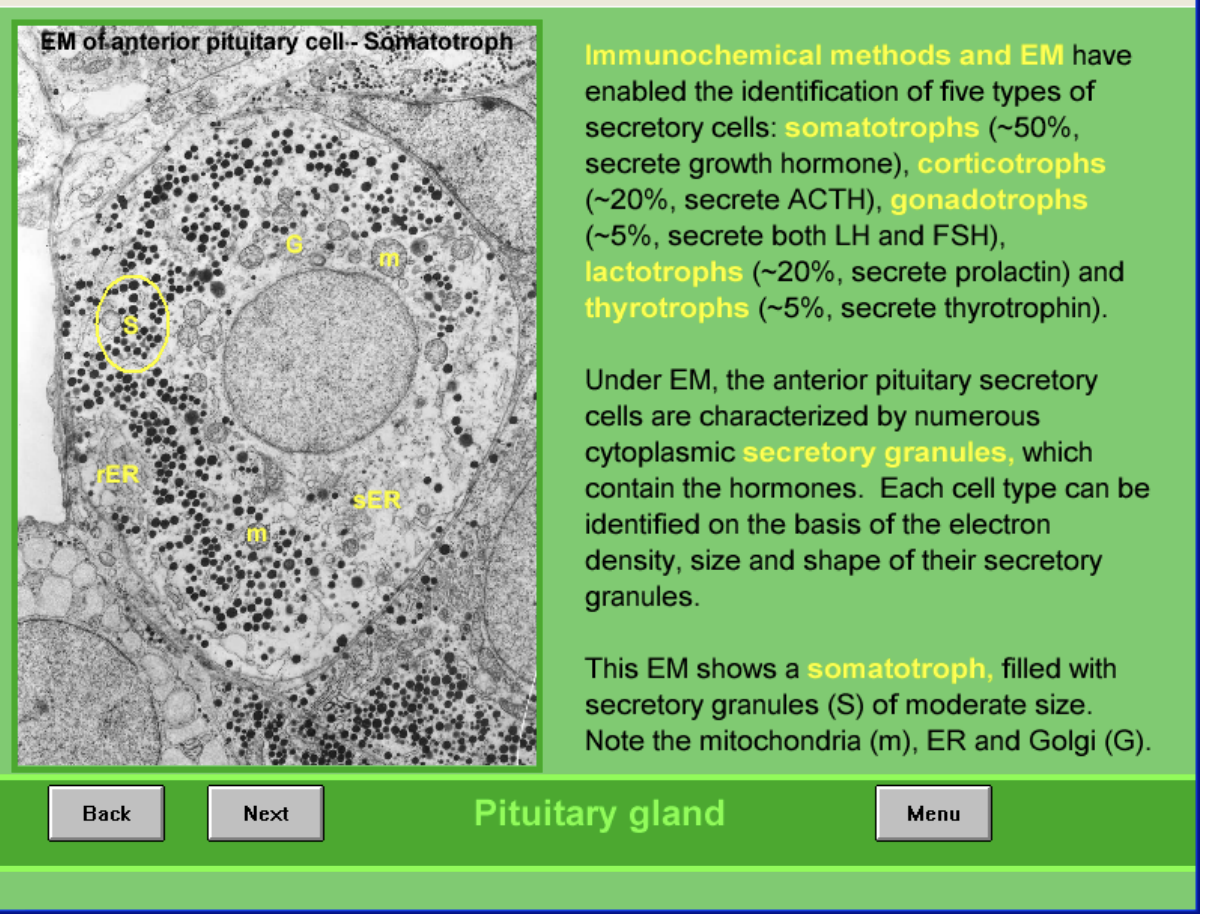
Immunochemical methods and EM of Anterior
Found 5 types of secretory cells
somatotrophs→ 50%→ growth hormones
corticotrophs→ 20%→ ACTH
gonadotrophs→ 5%→ LH and FSH
lactotrophs→ 20%→ prolactin
thyrotrophs→ 5%→ thyrotrophin
image shows:
somatotroph filled with secretory granules (S) of moderate size
also with mitochondria m, ED and Golgi G
Size and electron density of granules varies among the different cell types and the hormones they secrete
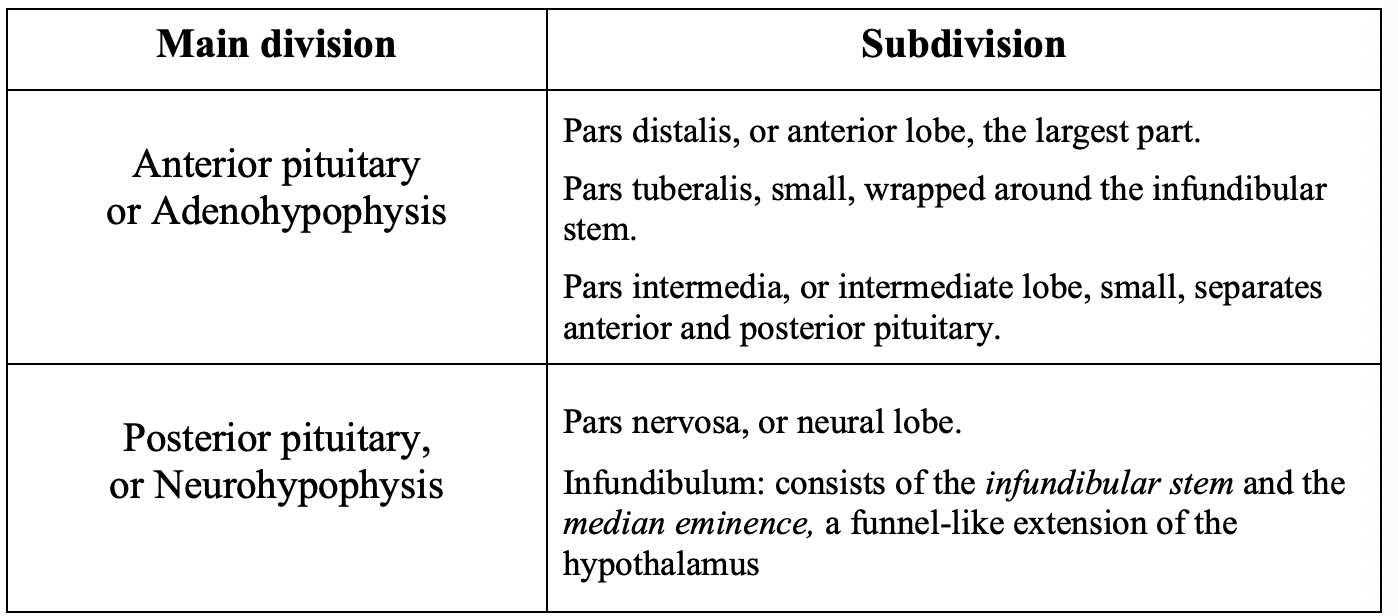
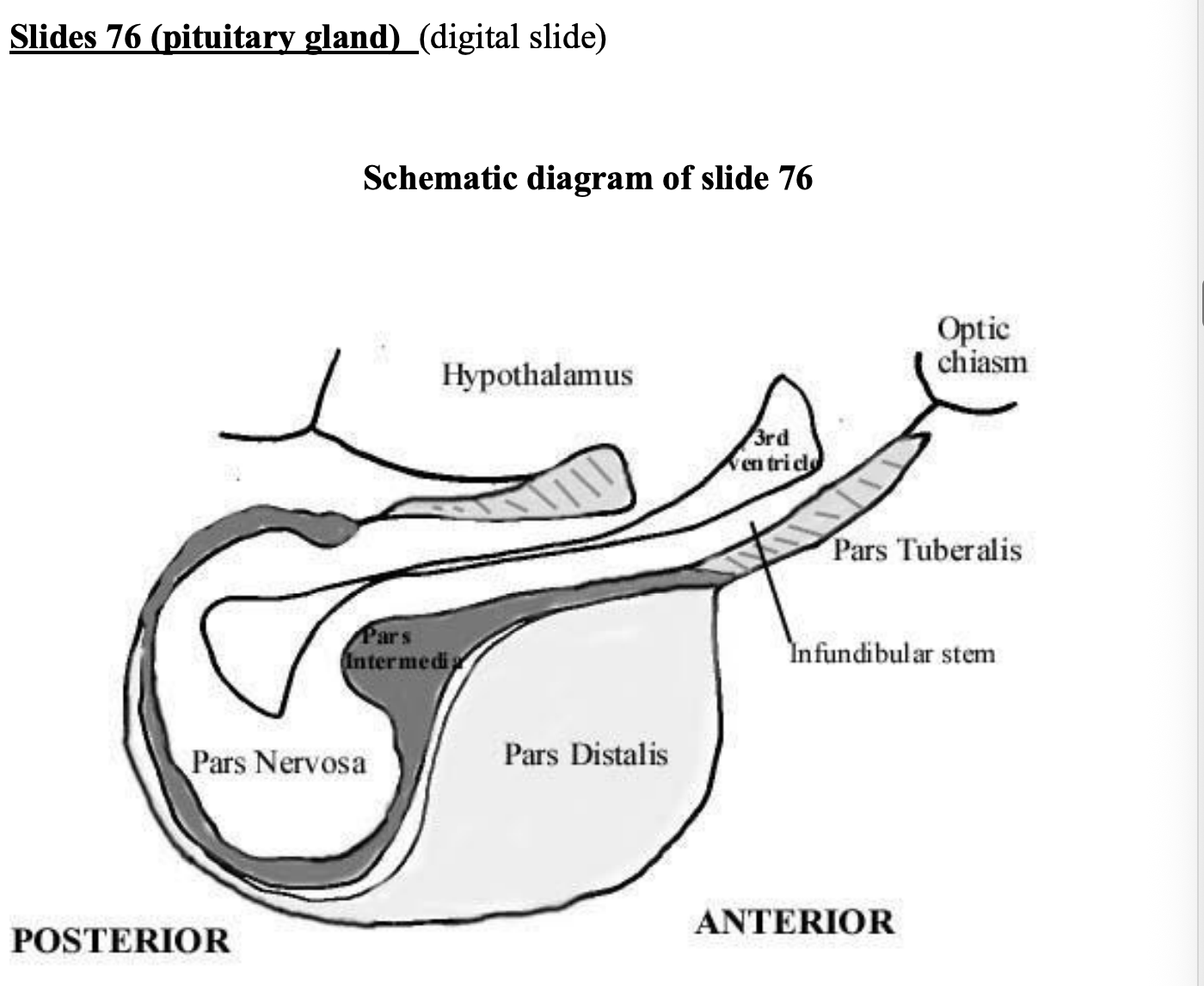
Major parts of anterior pituitary
par distalis (anterior lobe)→ major parts
separated from posterior by pars intermedia
Pars tuberalis→ upward extension of anterior pituitary, forms a partial or total collar of cells around the infundibular stem (neural component)
together make the pituitary stalk
pars intermedia (intermediate lobe)→ thin area of tissue lying against posterior pituitary
rudimentary in humans compared to other mammals
secretes mealocyte-stimulating hormones (MSH)
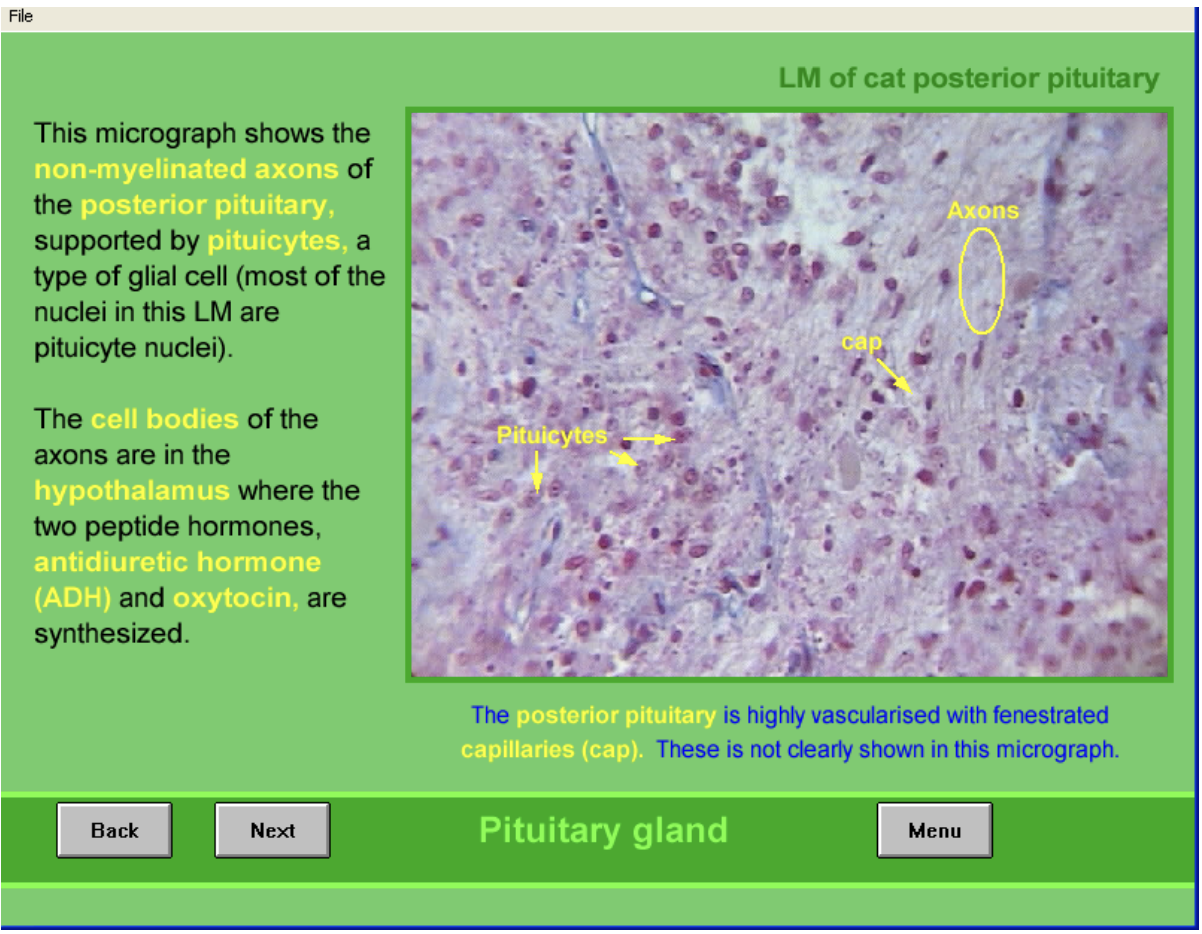
Posterior structure
non-meylinated axons
cell bodies are in hypothalamus, supraoptic and paraventricular nuceli
where ADH (supraoptic) and oxytocin (paraventricular) are made
supported by pituicytes→ type of glial cell
most nuclei in this are from these
Highly vascularised
fenestrated capillaries (not clearly shown here)
EM of posterior pituitary
Shows
Pituicytes (P)→ some organelles in cytoplasm but FEW secretory granules
Non-myelinated axon terminals→ many secretory granules
ADH and oxytocin synthezied as precursoler molecules packed in granules and transported down to axons
cleavage of percursor into free hormones occurs during transport
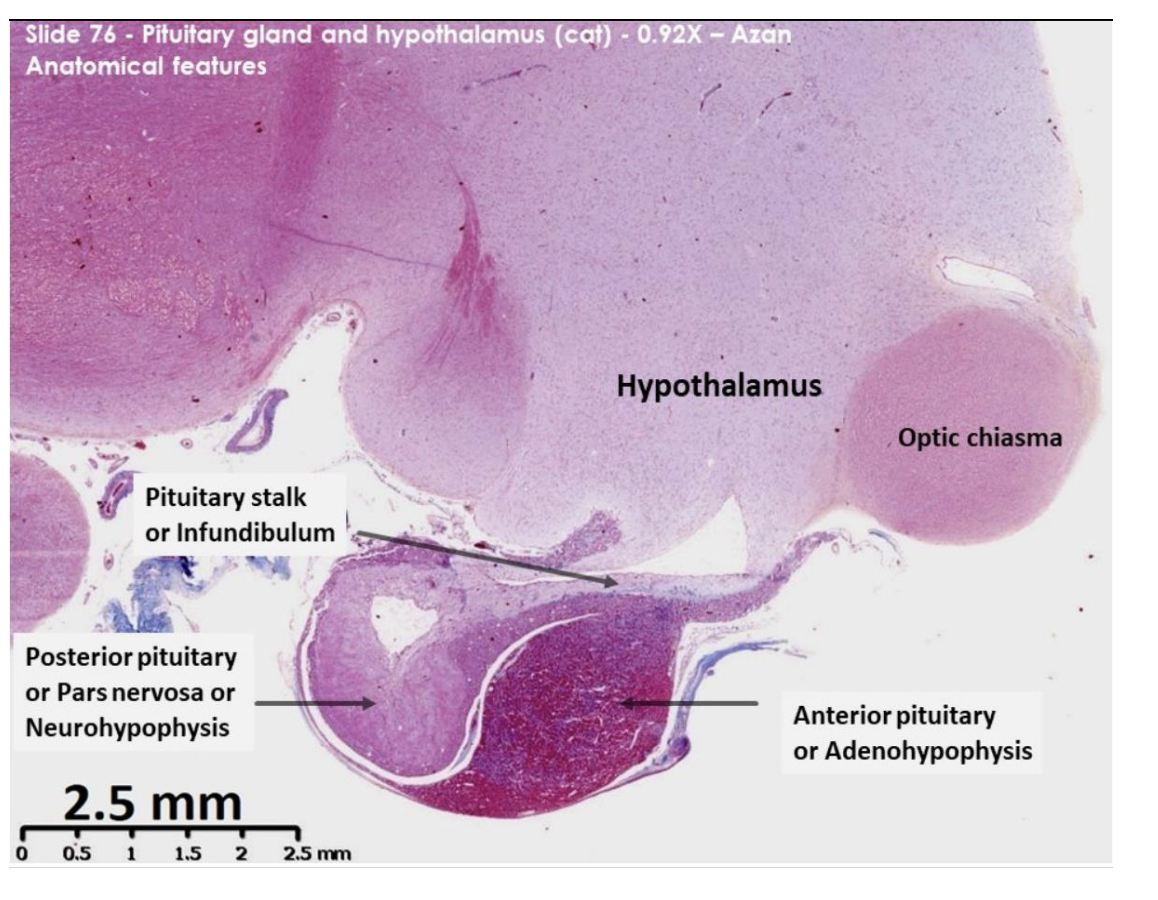
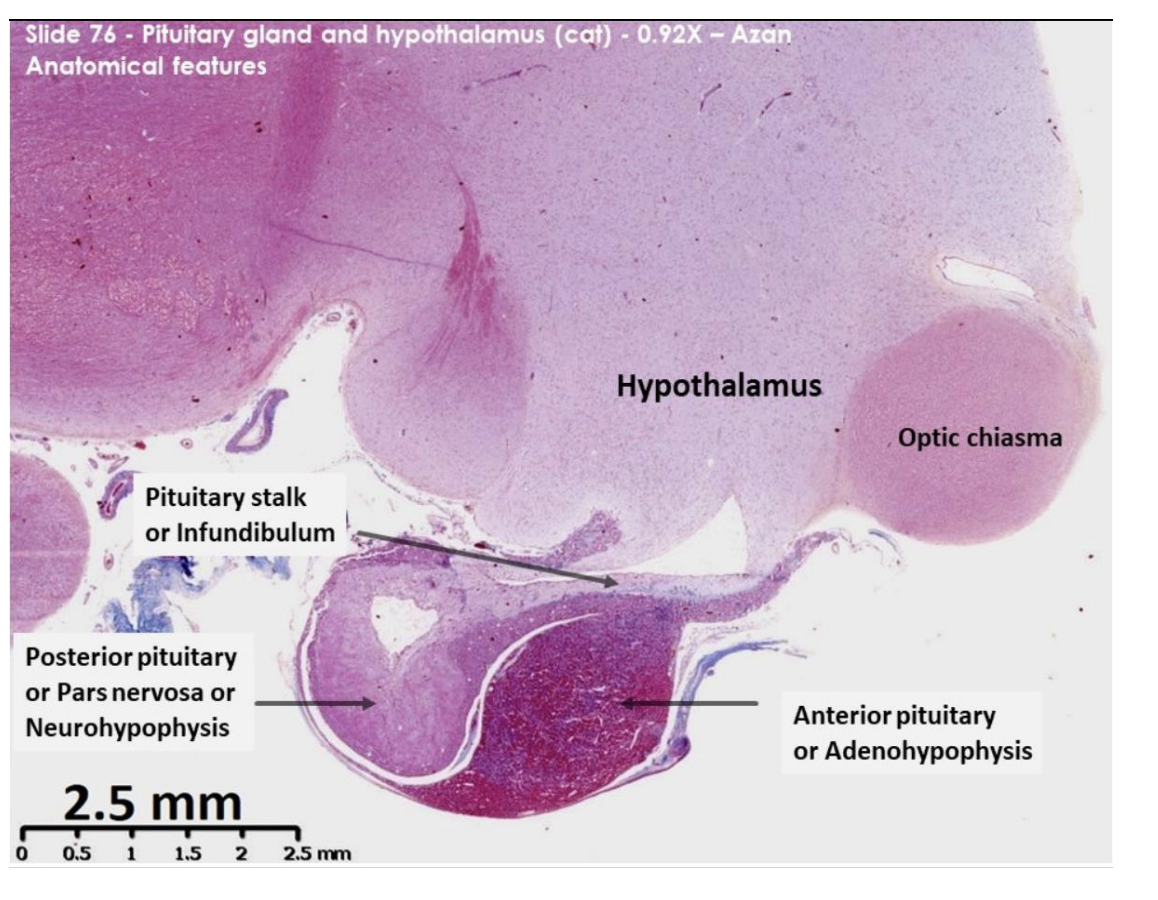
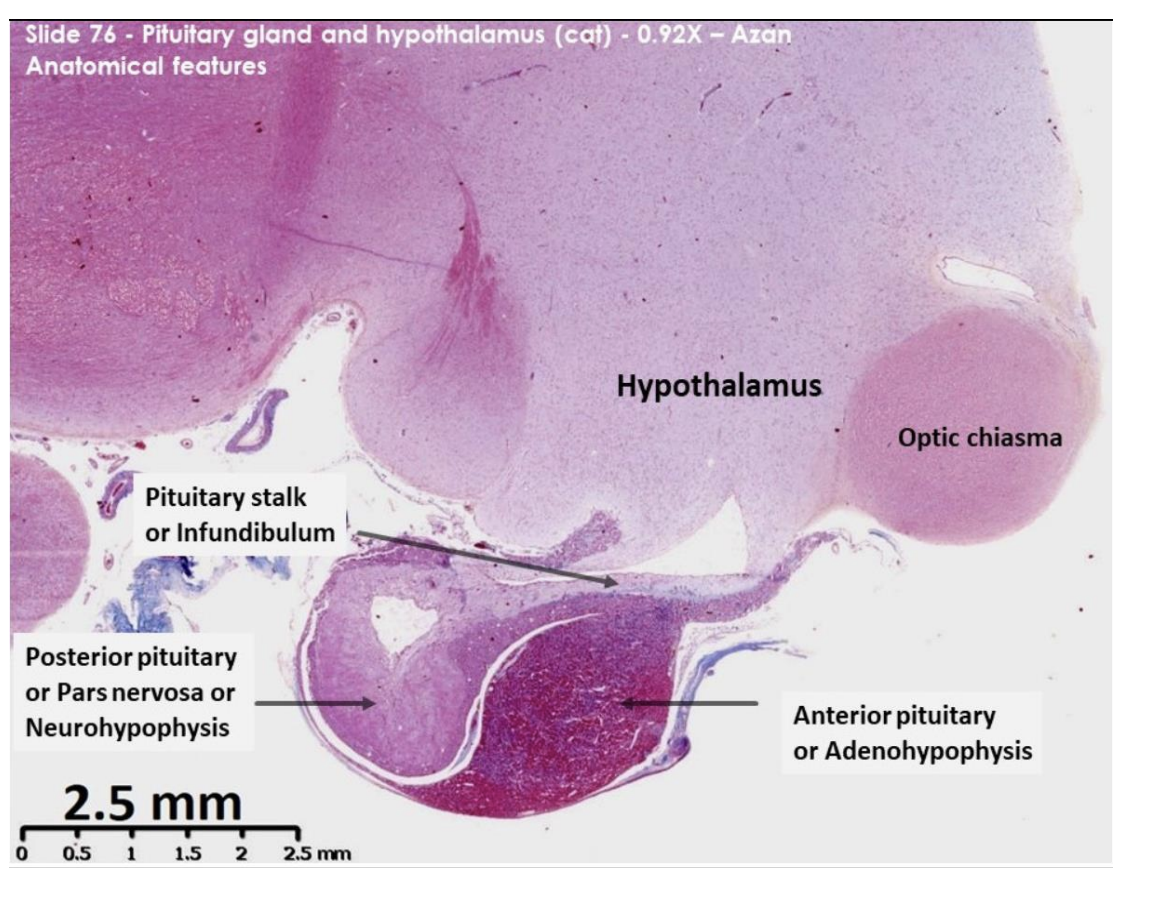
Pit and hypothalamus of cat: anatomical features
Nuclei - brilliant red
Collagen and reticulin – blue
Basophilic cytoplasm – blue/purple
Acidophilic cytoplasm – orange/red
Identify:
hypo
pit
optic chiasm→ mass of nerve fibres at the anterior limit of hypothalamus
Par distalis (anterior lobe or anterior pit)
deeply staining area
dark red, pale pink and purple cytoplasm
these are secretory cell in anterior pit, stained different colours due to different hormones
GH and PRL→ peptides→ acidophilic
ACTH, FSH, TSH and LH→ glycoproteins→ basophilic
Depleted hormone contect→ chromophobes→ PALE PINK
Posterior appearance here
pale staining tissue
many sections surrounds a fluid filled lumen
created as the pituitary stalk grows down from the neural tube
during embryonic development