BIOL2030 - Mitosis, Meiosis, Cell Cycle review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
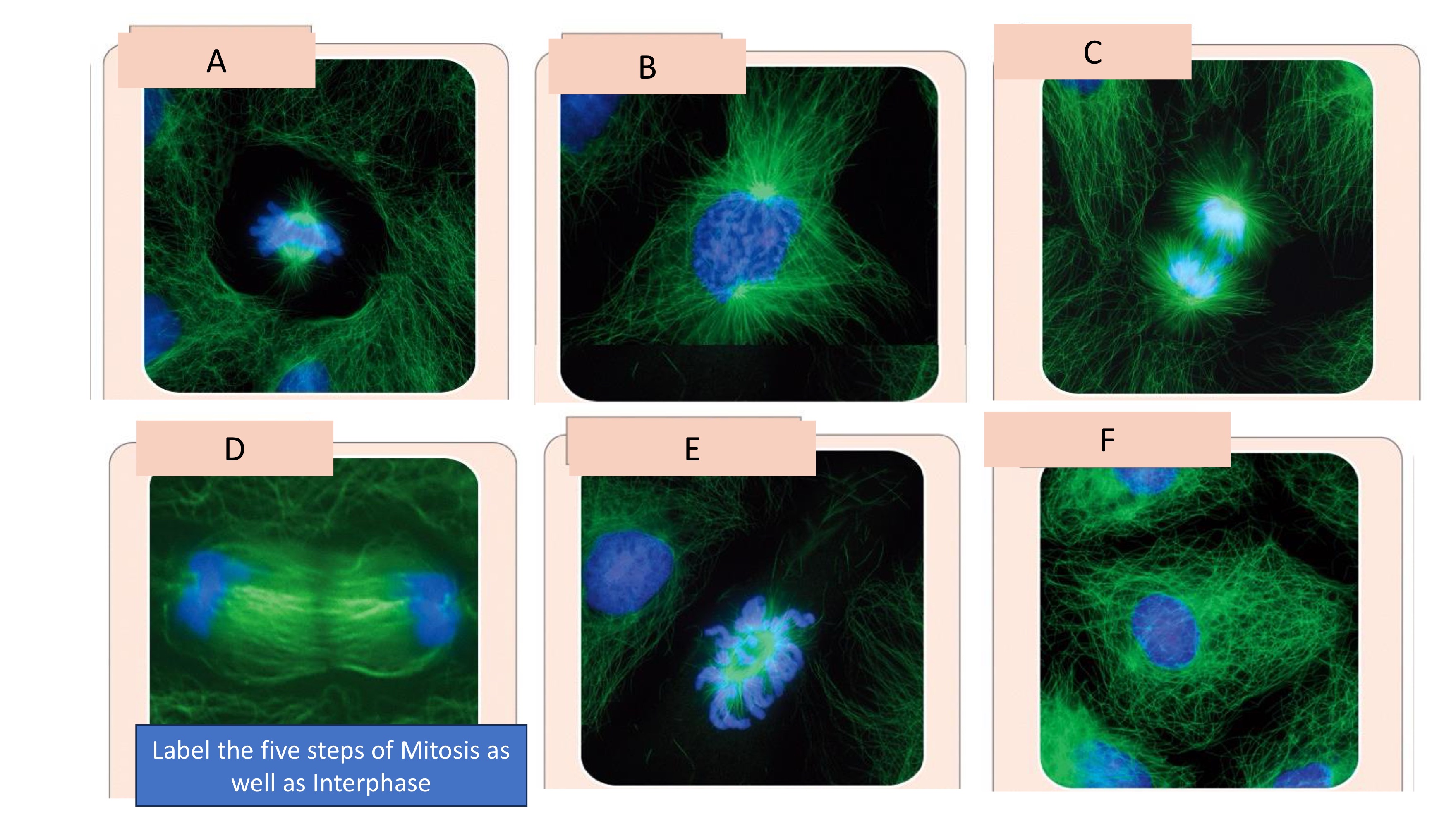
Label the five steps of mitosis as well as interphase
A. Metaphase
B. Prophase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
E. Prometaphase
F. Interphase
what is PP-MAT?
Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase of the Mitotic cycle
Number of chromosomes in the cell cycle?
G1: 4
S: 4
G2: 4
PP: 4
M: 4
A: 8
T & Cytokinesis: 4
Number of DNA molecules per cell in the cell cycle?
G1: 4
S: 4 --> 8
G2: 8
PP: 8
M: 8
A: 8
T & Cytokinesis: 4
How many chromosomes in the G1 phase?
2n = 4 chromosomes
- diploid chromosome number which means cell contains 2 complete sets of chromosomes.
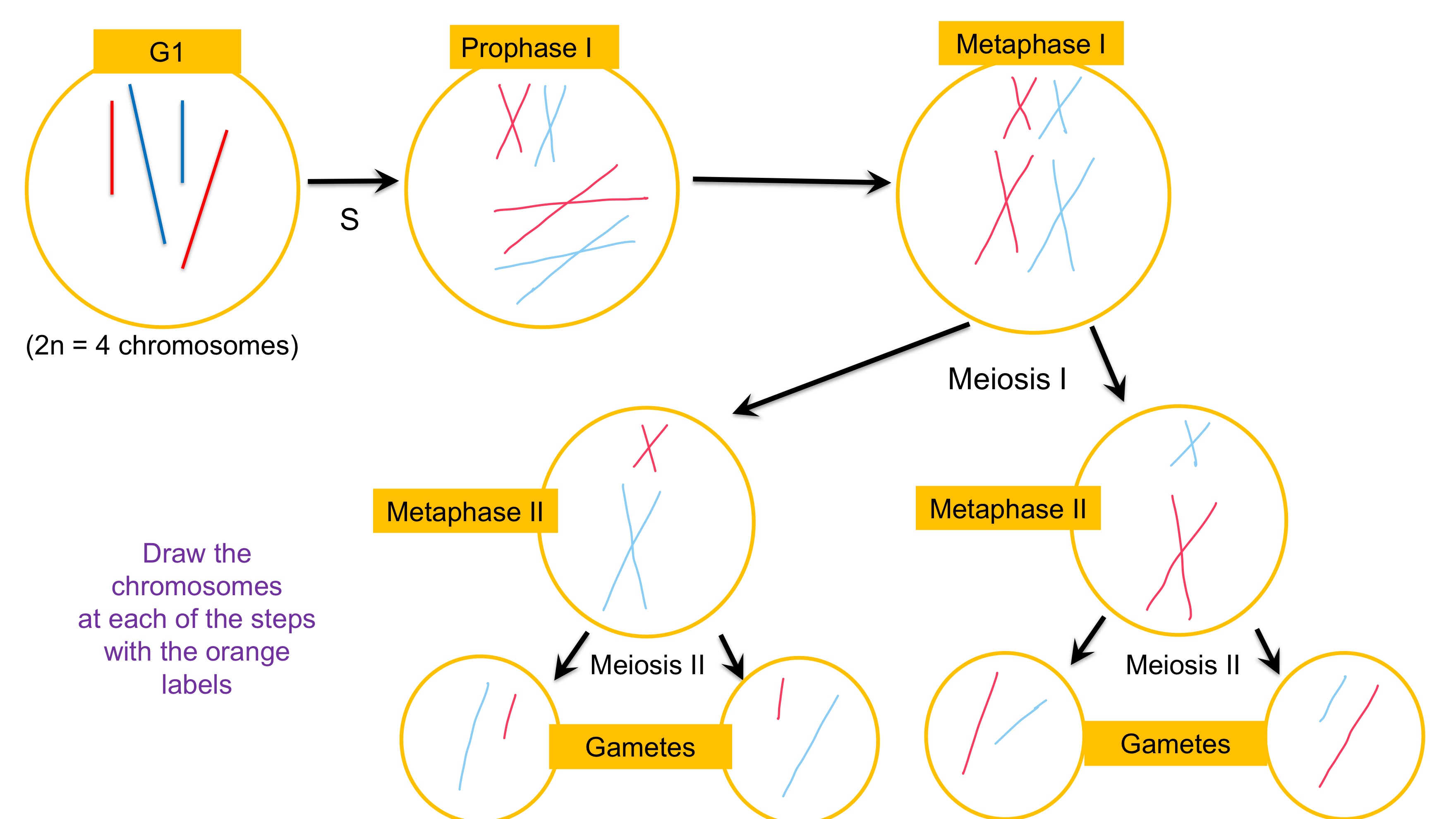
(T/F) these are the steps in Meiosis to produce two genetically unique haploid gametes from a single diploid cell?
True
what is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The hereditary material in humans and almost all living organisms. It stores genetic information in the sequence of nucleotides, which directs protein production and influences an organism's phenotype. DNA is copied and passed on to offspring, while the phenotype itself is not inherited.
what are genes?
they are units of hereditary information and a chromosomal region that codes for a functional transcript.
what is an allele?
one of the different forms of a gene that exists at a single locus
What is a chromosome?
A large, threadlike structure made of DNA and proteins, visible during mitosis. It carries many genes essential for cellular functions and ensures genetic information is accurately passed to daughter cells.
Chromatin
a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic chromosomes
linear molecule of DNA associated with histone proteins and packaged into higher-order structures
Telomere
stabile ends of linear chromosmes
Centromere
constricted region of chromosomes where the kinetochore forms and spindle microtubules attach during cell division.
Where are sister chromatids held together?
centromere
locus (loci - plural)
position of gene on a chromosome, or particular location on a chromosome
what are the different morophologies of eukaryotic chromosomes?
Metacentric: centromere in middle
submetacentric: centromere slightly off center
acrocentric: centromere close to end
telocentric: centromere beside telomere
Haploid
N, one copy of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes
Diploid
2N, two copies of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes creating a homologous pair
Autosomes
chromosomes that are the same for both sexes
Sex chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes that differ between males and females
Eukaryotic cell reproduction
dealing with multiple linear chromosomes
Eukaryotic cell division
1. copy each chromosome
2. separate DNA into each daughter cell
a) accommodate nuclear envelope
b) ensure exactly one copy of each linear DNA strand ends up in each daughter cell
1 centromere =
1 chromosome
Prior to S-phase
1 linear strand of DNA
After S-phase:
2 linear strands of DNA
Are chromosomes maximally condensed?
no, chromosomes become maximally condensed only during mitosis
Is the cytoplasm often reduced during mitosis?
yes, by about 1/2
How many sets does each daughter cell get in mitosis?
each daughter gets exactly 2 haploid sets of chromosomes
Meiosis
the production of haploid (n) gametes
Fertilization
the restoration of diploid state (2n) in the next generation
How are diploid organisms produced?
By fusion of 2 haploid gametes
Gametogenesis (Meiosis)
production of gametes [ Ovum (n) and spermatozoa (n) ] to be fertilized
cell division after fertilization (Mitosis)
zygote (2n) produces organisms (2n)
What does sexual reproduction do?
maintains the correct diploid state across generations
meiotic cell "cycle"
-Interphase (G1, S, G2)
-Meiosis I - separation of homologous chromosomes (2N-->N)
- interkinesis
-Meiosis II - separation of sister chromatids
- 4 haploid cells
What are the 5 substages of prophase I?
- pairing of homologous chromosomes
- synapsis
- tetrad (bivalent) structures
- crossing over
- visible chiasmata
Meiosis yields
4 sets of haploid gametes, these haploid cells are genetically different from one another and are different from the parent
independant assortment (genetic variation 1)
independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes from paternal and maternal chromosomes
crossing over (genetic variation 2)
the physical exchange of genetic material among non-sister chromatids