AP Psych Unit 1 Vocabulary - Biological Bases of Behavior
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Central Nervous System
consists of our brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
consists of all nerves in your body other than the brain and spinal cord
Two Categories of Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic and Autonomic
Somatic Nervous System
controls our voluntary muscle movements
Autonomic Nervous System
controls the automatic functions of our body (heart, lungs, internal organs, glands, etc.)
Two Categories of Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic Nervous System
mobilizes our body to respond to stress and activates our flight or flight responses
Parasympathetic Nervous System
responsible for slowing down our body after a stress response
Glial Cells
provides physical and chemical support for neurons
Schwann Cells
supporting cells of the Peripheral Nervous System
Types of Neurons
Interneurons, Sensory Neurons, and Motor Neurons
Interneurons
take information from sensory neurons to different parts of the body, using the central nervous system
Sensory Neurons
take information from the senses to the brain, part of the peripheral nervous system
Motor Neurons
neurons that carry nerve impulses away from the Central Nervous System to the muscles, part of the peripheral nervous system
Dendrites
reaches out to receive information from other neurons, starts the electrical charge
Cell Body
keeps the cell structured and alive, doesn’t participate in information flow
Axon
tail where the information travels
Myelin Sheeth
covers the axon, makes info flow efficient, keeping it healthy
Terminal Branches
reaching out to send information at the bottom of the neuron
Terminal Button
neurotransmitters releasing to do an action
Synapse
space between the dendrite and terminal button, neurotransmitters are located here
Neurons
carry messages using electrical impulses
Parts of Neural Communication
Cell Body, Dendrites, Axon, Myelin Sheeth, Terminal Branches, Terminal Buttons, Synapses
Parts of Neural Firing
Resting Potential, Threshold, Action Potential, Refractory Period
Resting Potential
state of readiness (potential energy)
Threshold
minimum required in order for a neuron to fire, has to receive a certain amount of neurotransmitters
Action Potential
the neuron firing (kinetic energy)
Refractory Period
period of rest that is required between firing
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that move between neurons
Types of Neuortransmitters
excitatory and inhibitory
Excitatory
make it more likely that the next neuron fires, sends an activating message
Inhibitory
makes it less likely that the next neuron fires, send a calming message
Hormones
chemicals that can act similarly to neurotransmitters to activate neurons
Outside Influences on Neural Firing
Agonists and Antagonists
Agonists
substances that excite/cause the next neuron to fire (blocks reuptake)
Antagonists
blocks release of neurotransmitters and inhibits the next neuron to fire
Agonist Substances
stimulants
Antagonist Substances
depressants and pain relievers
Hallucinogens
mimic the neurotransmitter and causes the neurons to keep firing
Ventral View
view of the brain from the bottom
Sagittal View
view of the brain from the side
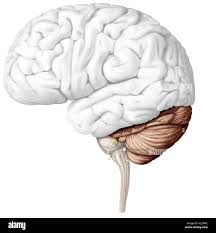
Cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movement and balance, and supports skill learning and memory
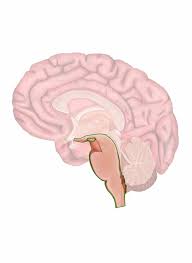
Brainstem
connects the brain to the spinal cord, consists of midbrain, pons, and medulla
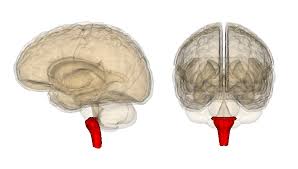
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
help coordinate movement and breathing
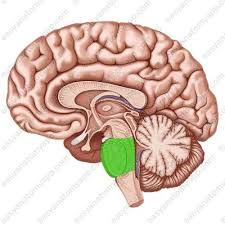
Optic Nerve
a bundle of nerve fibers at the back of the eye that transmit visual information from the retina to the brain
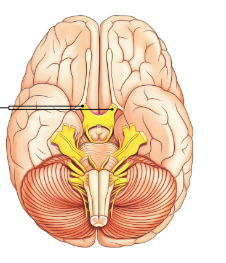
Olfactory Bulb
processes odor information from the nose to enable sense of smell
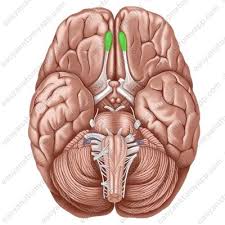
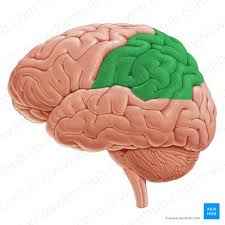
Frontal Lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead, enables linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher order thinking, and executive functioning
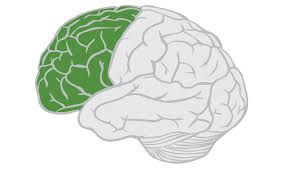
Motor Cortex
helps plan, control, and execute voluntary movements
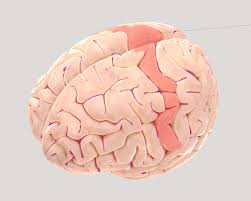
Parietal Lobe
taste, smell, and texture of food work because of this lobe, also supports reading and arithmetic
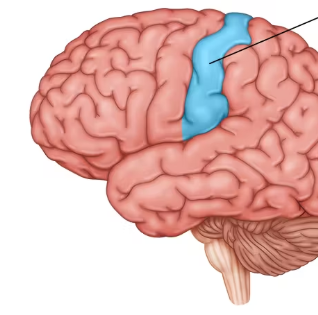
Sensory Cortex
receives information about temperature, taste, touch and movement from the rest of the body
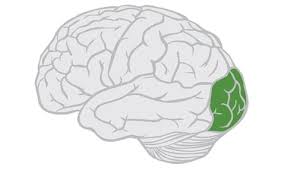
Occipital Lobe
processes images from the eyes that link that information with images stored in memory, damage here can cause blindness
Temporal Lobe
at the top of each lobe is an area responsible for receiving information through the ears, the bottom retrieves and forms memories, including memory with music, integrates taste, sound, sight, and touch
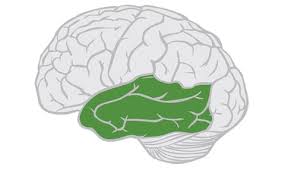
Auditory Cortex
receives information from your ears
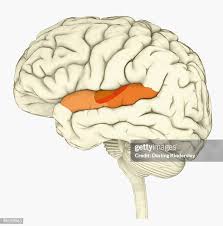
Wernick’s Area
located in the left temporal Lobe, crucial for language comprehension, particularly understanding spoken and written language
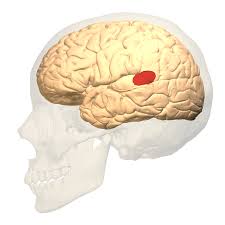
Broca’s Area
located in left frontal lobe, critical for speech production, articulation, and the generation of articulate language
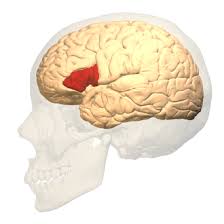
Reticular Formation
a diffuse network of nerve pathways in the brainstem connecting the spinal cord, cerebrum, cerebellum, and mediating overall levels of consciousness
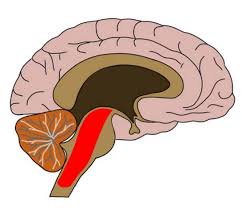
Visual Cortex
part of the brain located in occipital lobe, processes visual information, transforming it into conscious perception of the world
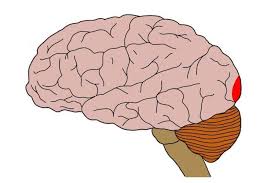
Corpus Callosum
a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain
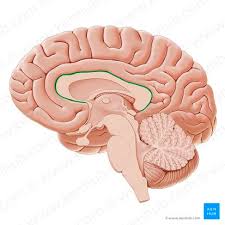
Thalamus
a major clearinghouse for information going to and from the spinal cord and cerebrum
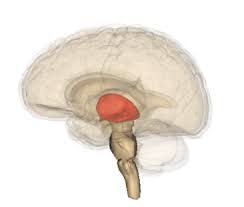
Hypothalamus
wakes you up, emotional center for feelings of exhilaration, anger, or unhappiness (adrenaline)
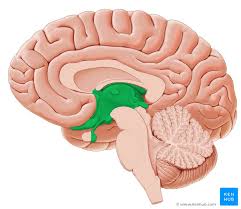
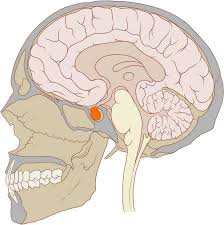
Pituitary Gland
the major endocrine gland, important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of other endocrine glands