AP Exam 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what are the differences between autocrine and paracrine signaling and how does it differ from endocrine signaling?
autocrine- chemicals that exert effects on same cells that secrete them
paracrine- locally acting chemicals that affect neighboring cells
what are the 2 types of hormones based on its composition? (amino-acid based, steroid based)?
steroids
synthesized from cholesterol
lipid soluble, can cross plasma membrane
includes gonadal and adrenocortical hormone
amino acid base- most hormones are this, amino acid derivatives, peptides, and proteins
water soluble (except thyroxine), cannot cross plasma membrane
what are eicosanoids? give examples of it
classified as paracrines and autocrines given their highly localized effects
ex.
prostaglandins: reg. inflammation, pain, fever, vasodilation, and uterine contractions
thromboxane: promote platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction: key in blood clotting
what are the mechanisms by which hormones take effect in the target cell? (water soluble hormones: 2nd messenger system signaling and steroid hormones/thyroid hormones: direct gene activation?
water soluble hormones- (insulin, epinephrine, FSH)- cannot pass through the cell membrane because they’re polar, they require a second messenger systems- cyclic AMP and PIP2- calcium signaling mechanism
steroid hormones/thyroid hormones: direct gene activation?
receptor hormone complex enters nucleus; binds to specific region of DNA
binding “turns on” gene to initiate DNA transcription to produce mRNA
mRNA is then translated into a specific protein
-proteins synthesized have various functions, including:
-metabolic activities, structural purposes, or extracellular functions (after being exported from cell)
what is the hypothalamic tract? (direct gene activation)
axons connecting hypothalamus to posterior pituitary form the tract
what is the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system? (direct gene activation)
releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus travel through portal to anterior pituitary gland to regulate secretion of 6 hormones:
GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, PRL
permissiveness
one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present
synergism
more than one hormone produces same effects at target cell and combined effects are amplified
e.g. glucagon causes liver to release glucose
antagonism
one or more hormones oppose action of another hormone
e.g. insulin and glucagon
what kind of interaction do calcitonin and insulin have in target cells?
synergism
parathyroid hormone
most important hormone in Ca2+ homeostasis
falling blood levels Ca2+ stimulate
rising blood inhibits
target organs: bones, kidneys, and small intestine
component of the blood
plasma- 55% of whole blood
buffy coat- <1% of WBCs and platelets
erythrocytes- 45% of whole blood (hematocrit)
what are the formed elements?
blood cells and platelets (thrombocytes), WBCs (leukocytes)
how are erythrocytes develop/form?
hypoxia (inadequate O2 levels)
kidney releases erythropoietin
erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow
enhanced erythropoiesis increases RBC count
O2 carrying ability of blood cells
what are the function of erythrocytes?
dedicated to respiratory gas transport
what are the functions of leukocytes?
defense against disease
make up <1% of total blood volume
cross capillary walls to leave the blood stream, called diapedesis
different kinds of leukocytes?
granulocytes and agranulocytes
what are granulocytes?
with cytoplasmic granules (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
what are agranulocytes?
lack cytoplasmic granules (lymphocytes, monocytes)
what is normal blood pH range?
7.35.7.45
what is albumin?
makes up 60% of plasma proteins involved in plasma osmotic pressure
plasma osmotic pressure
keeping water in blood
RBCs lack what?
nucleus (anucleate)
hormonal stimulus steps
hypothalamus
anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
endocrine glands
stimulus: hormones from hypothalamus
response: anterior lobe of pituitary gland secretes hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to secret hormones
how does blood typing work? what is the importance?
its important to determine blood group of both donor and recipient
blood is mixed with antibodies against common antigens
what is Rh factor?
Rh+ indicates presence of D antigen, comes from Rhesus monkey
what is hemolytic disease of the newborn?
occurs in Rh- mom and Rh+ baby
Rh- mom exposed to Rh+ baby during first pregnancy
second pregnancy: mom’s anti Rh antibodies cross placenta and destroy RBCs of Rh+ baby
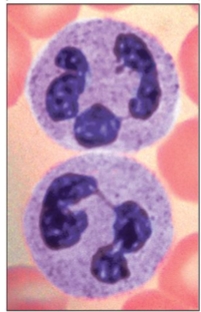
what is this granulocyte?
neutrophils
neutrophils
most numerous WBCs
bacteria slayers
ex. white stuff you see in your pimples, that is bacteria that has been engulfed by neutrophils
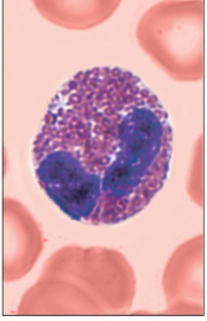
what is this?
eosinophil
eosinophil
plays a role in allergies and asthma
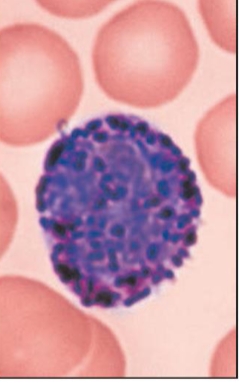
what is this?
basophil
basophil
inflammatory
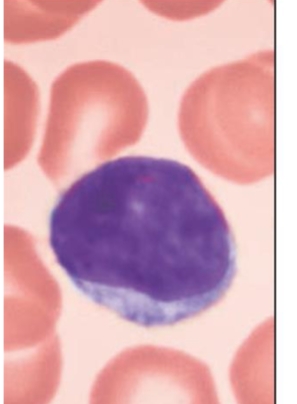
what is this?
lymphocyte
lymphocyte
T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes
found in lymphoid tissue and spleen
T lymphocytes (T cells)
act against virus infected cells and tumor cells
B lymphocytes (B cells)
give rise to plasma cells, which produce antibodies
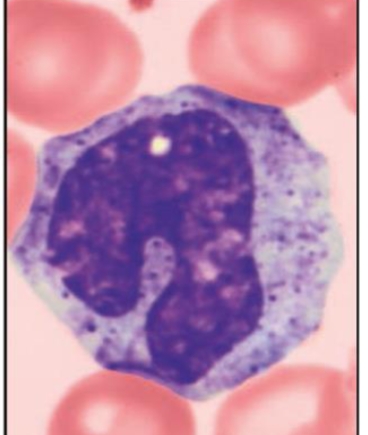
what is this?
monocyte
monocytes
leave circulation, enter tissues, and differentiate into highly mobile macrophages
what is hemostasis?
rapid series of reactions that stop bleeding
vascular spasm
platelet plug formation
coagulation
cAMP steps
hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor
receptor activates G protein
G protein activates adenylate cyclase
adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP (2nd messenger)
cAMP activates protein kinases