Computer Hardware🔌
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Digital Technology Unit 1: Digital Technology (Core)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Microphone
Accepts sound input into computer and can convert it to text
Faster to speak using a microphone than typing and is hands free
Recognition rate can be slow if there is other noise and files require greater storage
Mouse
Controls cursor using built in sensors to detect movements and buttons to select
Easy to use with little to no training and quicker to interact with than a keyboard
Experienced users find it slower than ‘hot keys’ and needs a flat surface
Graphic digitiser
Allows hand drawn images on a flat interactive surface with stylus
More natural to draw diagrams with accurate and detailed drawings
Not suitable for selecting menus and more expensive than a mouse
Touch screen
Similar to ordinary screens but with touch sensitive surface, calculating position with x, y
Not much IT competence required and much faster than a keyboard
Limited number of options available and can become dirty quickly
Speaker
Outputs sound, internal or external, and requires a sound card
Read out text for visually impaired and natural way to communicate
Requires additional desk space and can distract people surrounding
Laser printer
Laser beam scans image and attracts ink to reproduce page
Faster to print in bulk compared to inkjet printers and high quality output
Colour laser printers are expensive, hard to use and not compact
3D printer
Gradually prints a solid 3D object one layer at a time
Time taken to produce an object is much faster with a variety of surfaces
Limited form of printing, only prototypes, and not economical for large-scale
Hard disk drive (HDD)
rigid discs stacked on spindle and enclosed, dividing surface into tracks and sectors that rotate at high speeds, back and forth
Cost per gigabyte is cheaper with a greater capacity
Prone to breaking down and access speeds are slower than ‘flash’ memory devices as moving parts

Solid state drive (SDD)
'Flash memory’ and non-volatile such as USB sticks
Are compact, portable and have a large storage capacity which does not require a driver
Memory cards
Electronic flash memory storage devices
Used in a range of digital devices like mobile phones as a sim
Smart cards
Bank cards use a form of flash memory known as ‘chip and PIN’
Contains small embedded IC, allowing data to be written and read with a reader
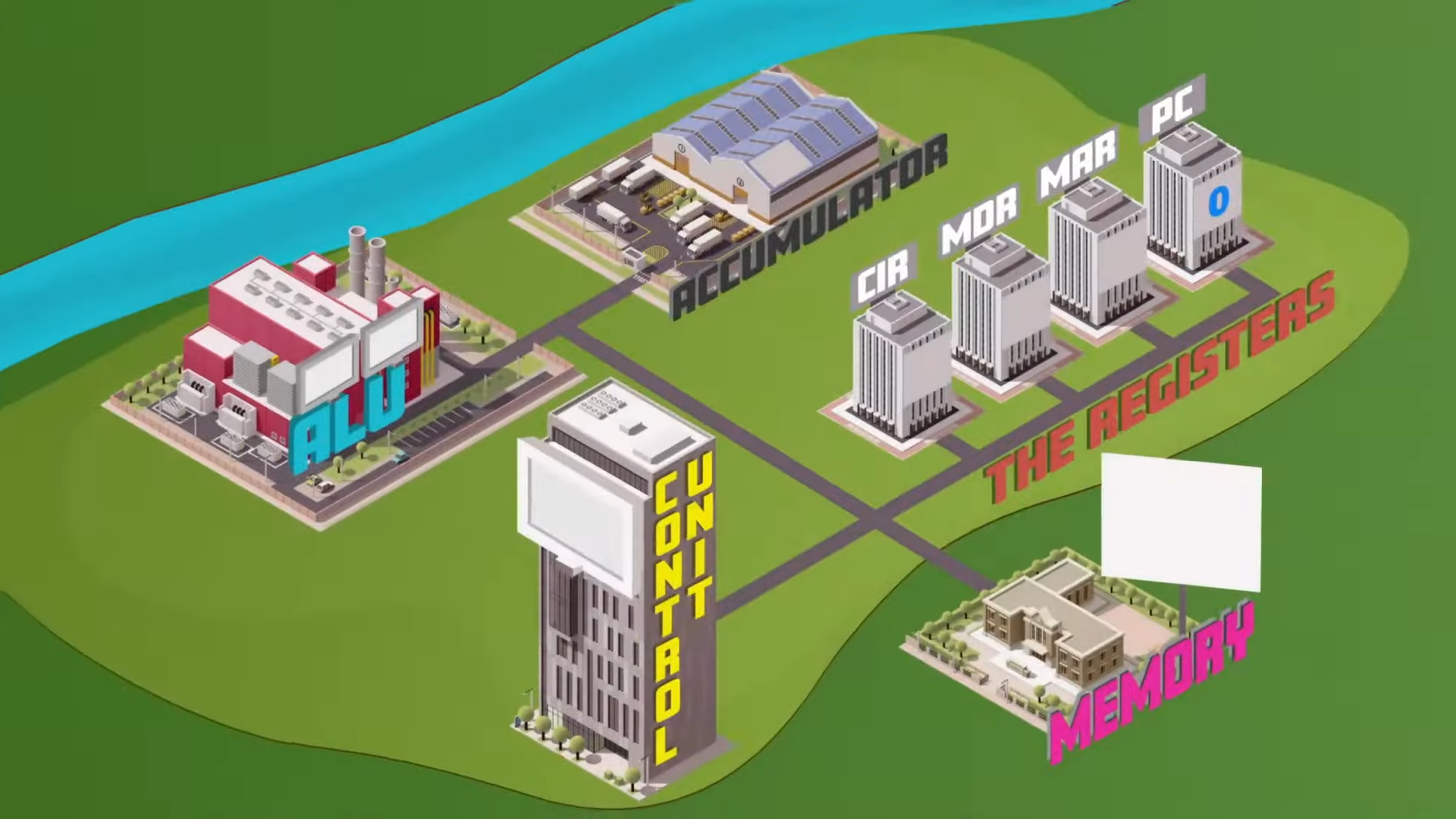
Fetch stage
Memory address held in the PC is copied into the MAR
Address bus carries it to the memory
It’s instruction is sent back to the MDR via the data bus
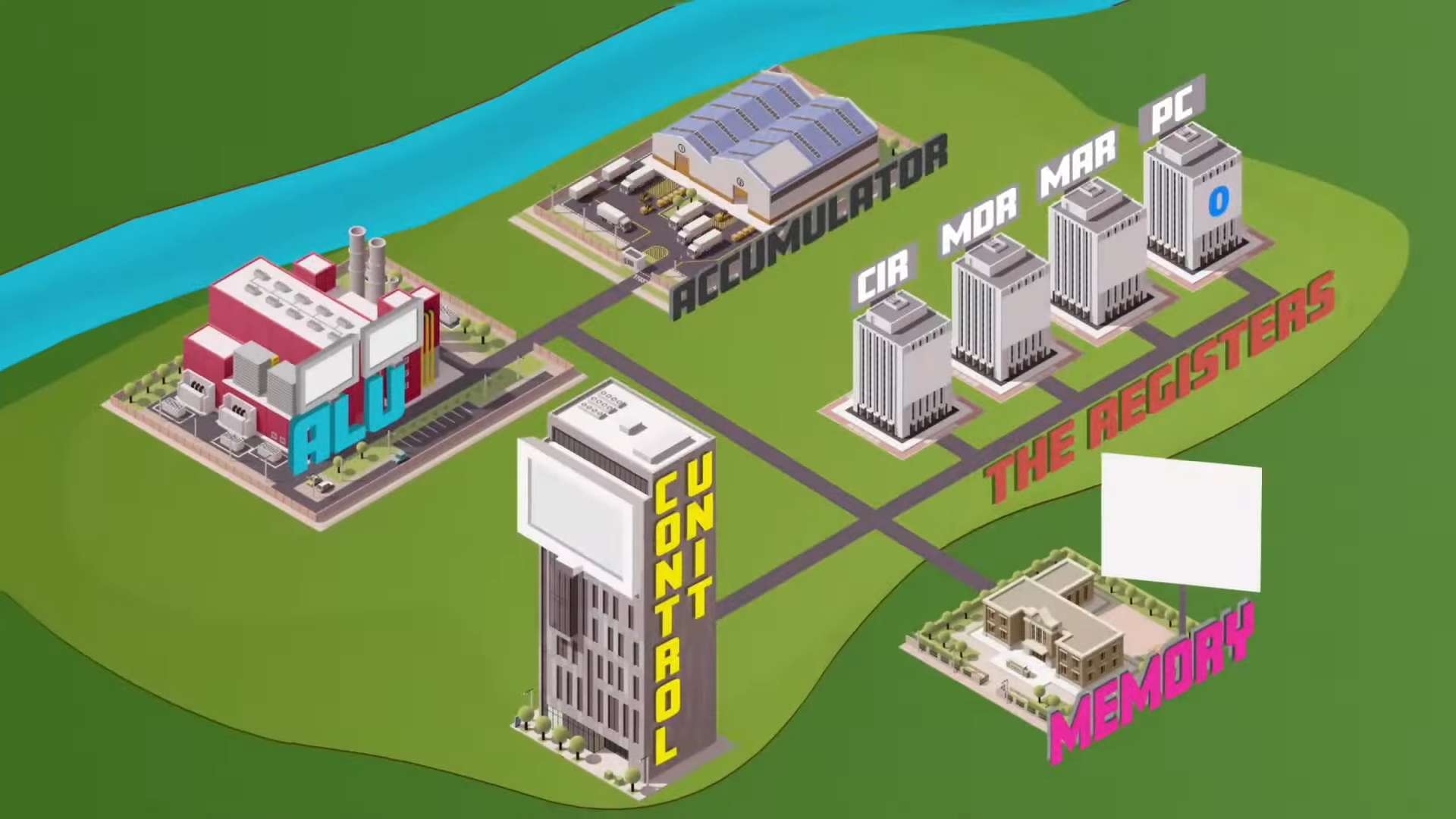
Decode stage
It is then copied into the IAR and sent to the CU
CU finds out what it means (decodes)
PC is incremented by 1
Execute stage
Now it’s executed, generally the ALU carrying out a calculation
Results of processing are stored in the ACC
Cycle returns to step one
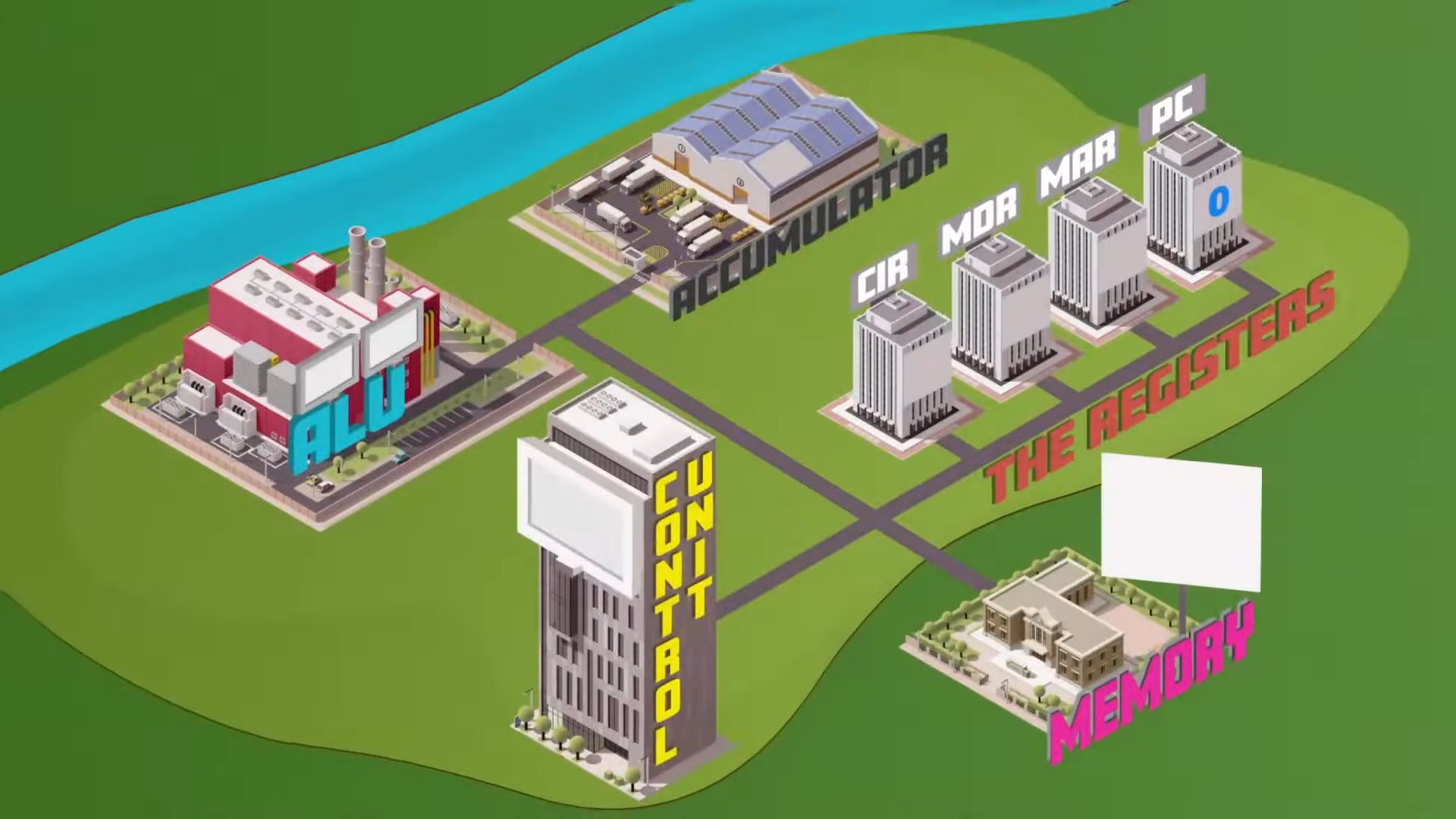
CPU consists of
high speed memory locations used for specific purposes (registers)
Registers
Program Counter (PC)
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Instruction Address Register (IAR)
Accumulator (ACC)
Program Counter (PC)
stores address of first instruction to be fetched and automatically increments by 1 each time
Memory Address Register (MAR)
temporarily stores address of current instruction or data being executed
Memory Data Register (MDR)
temporarily stores data being fetched from or written to the main memory
Instruction Address Register (IAR)
temporarily stores the current instruction to be decoded and then executed
Accumulator
initially stores results during calculations before transferring to the main memory
CPU
referred to as ‘brain’ of computer, manages functions by processing data and instructions
How does the CPU work?
repeatedly fetching an instruction from memory and executing it
Components of CPU
control unit, arithmetic and logic unit, immediate access store
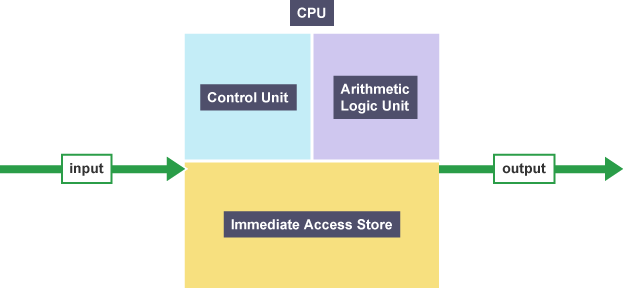
Control unit
Decides which instruction to carry out next and fetches it from memory
Decodes the instruction to execute and informs how to respond
Manages how data is processed and communicated
Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
Processes all data inside CPU
Carries out arithmetic calculations
Makes logical comparisons using operators
Immediate access store (IAS)
Stores all programs and data temporarily while they are in use
allows CPU to access them immediately
instructions are fetched from their location using a unique address
Clock speed
measure of instruction cycles in a second, showing speed CPU can process instructions
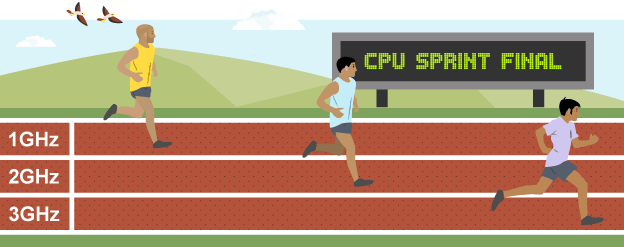
Unit for clock speed
gigahertz, 3 gHz = 3 billion cycles per second
Impact of clock speed
faster clock speed means more powerful computer so quicker the CPU will work
Cache
temporarily stores frequently used instructions and data, extremely fast access so quicker to search through than RAM
Impact of cache
greatly reduces processing time so greater cache size means quicker CPU
Cache server
dedicated network server, or service, to save webpages and other Internet content locally
Processor core
a single processor, more cores increases ability to run many programs at the same time
Volatile memory
can be read from or written to, whereas non-volatile can only be read

Random Access Memory (RAM)
Stores programs and data currently in use, affecting the speed e.g applications like word
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Stores programs that the computer frequently requires e.g booting up program (BIOS)
BIOS
Basic Input Output System