Aqueous Humor
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
scleral spur, trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular tissue, canal of Schlemm
what are the 4 structures of the anterior chamber angle?
scleral spur
located at posterior edge of internal scleral sulcus
posterior portion is attachment site for tendon of longitudinal ciliary muscle fibers
anterior portion is attachment site for trabecular meshwork sheets
collagen of trabeculae
collagen of the scleral spur is continuous with the ______
trabecular meshwork
encircles the circumference of the anterior chamber, occupying most of the inner aspect of internal scleral sulcus
triangular shape in cross-section
flattened, perforated sheets
inner face borders anterior chamber
outer side lies against corneal stroma, sclera, and Schlemm’s canal
C
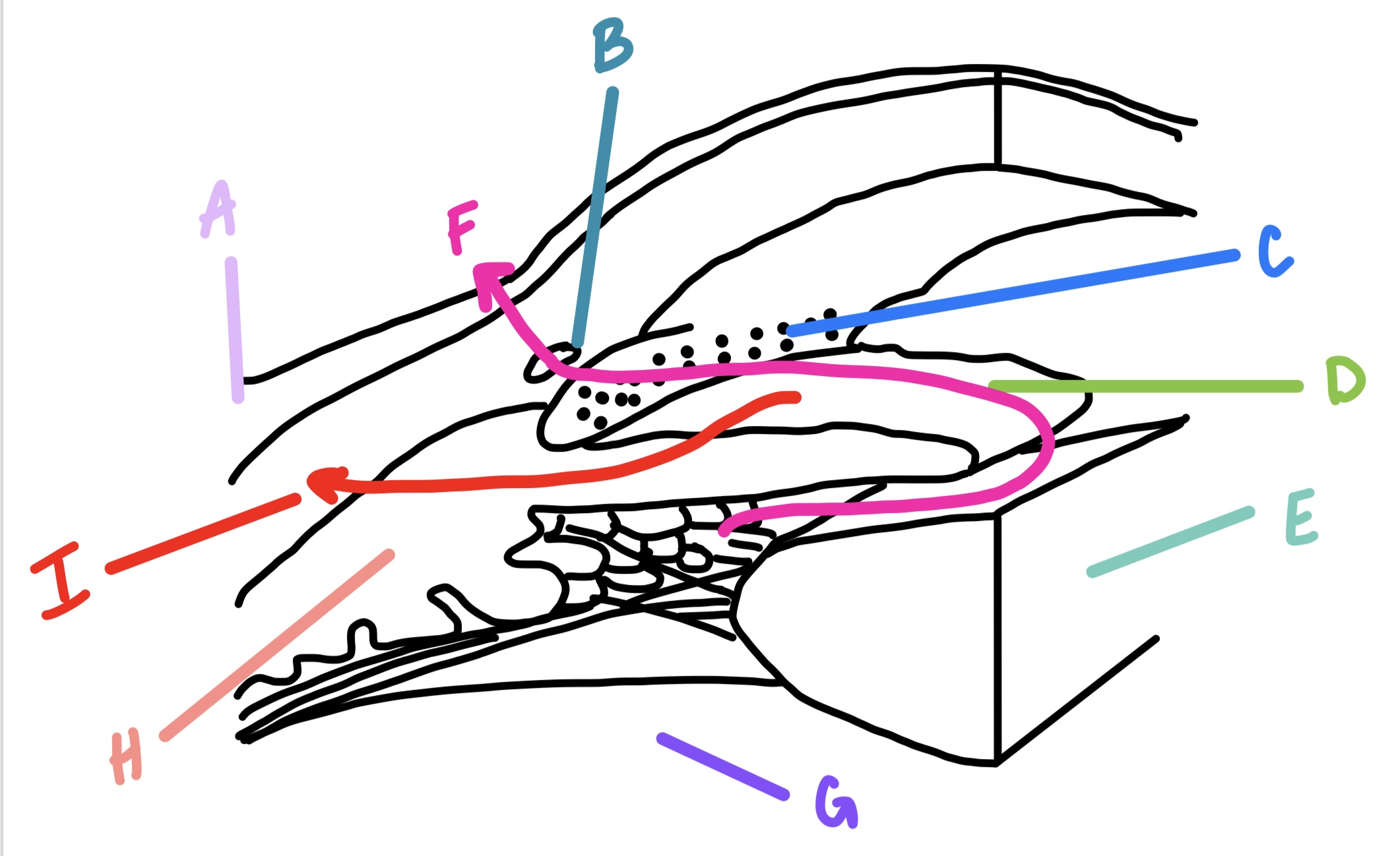
Descemet’s membrane
what structure is the apex termination of the trabecular meshwork?
scleral spur
what structure is the base termination of the trabecular meshwork?
3-5
how many sheets of trabecular meshwork are at the apex?
15-20
how many sheets of trabecular meshwork do the apex sheets branch into?
open latticework
the trabecular meshwork is described as being what?
spaces of Fontana
historic name for the openings within trabecular meshwork sheets
smaller
openings in trabecular meshwork sheets become _____ as it nears Schlemm’s canal
no
are there any apertures that directly join the meshwork with the canal of Schlemm?
corneoscleral meshwork
outer region of the trabecular meshwork
sheets attach to the scleral spur
sheetlike
uveal meshwork
inner sheets of trabecular meshwork
inner to the spur and attach ciliary stroma and longitudinal muscle fibers
may attach to iris root
cordlike
largest pores
iris processes
projections from surface layer of the iris that connect to the trabeculae
inner core of collagen & elastic fibers
the meshwork trabeculae is described as ________________________ embedded in ground substance
basement membrane and endothelium
the trabecular meshwork is covered in what?
corneal endothelium
the endothelial cells of the trabecular meshwork are a continuation of what?
connective tissue components
what are the endothelial cells of the trabecular meshwork capable of replacing?
lysosomes
trabecular meshwork endothelial cells contain what to enable phagocytosis?
gap junctions
what sort of intercellular junction is found in the trabecular meshwork endothelial cells?
no
are any zonula occludens found in the trabecular meshwork?
cytoplasmic projections
what connects the cells of neighboring sheets in the trabecular meshwork endothelium?
scleral spur
where do the trabecular sheets lose their endothelial covering?
collagenous & elastic fibers
what part of the trabecular sheets continues into the connective tissue of the scleral spur and ciliary body?
ciliary muscle
some connective tissue fibers of the ________ pass forward and merge with inner sheets of the meshwork
juxtacanalicular connective tissue
located b/t the deepest trabeculae of the corneoscleral meshwork and Schlemm’s canal
narrow strip of loose, cellular connective tissue
majority of aqueous humor outflow resistance
endothelial cells & fibroblasts embedded in a matrix of collagen, elastic-like fibers and ground substance
adhering & gap junctions
processes of cells in JCT are occasionally joined by what?
canal of Schlemm
circular vessel
venous channel
normally contains aqueous humor
“circular channel lined with bubble wrap”
outer to trabecular meshwork
anterior to scleral spur
B
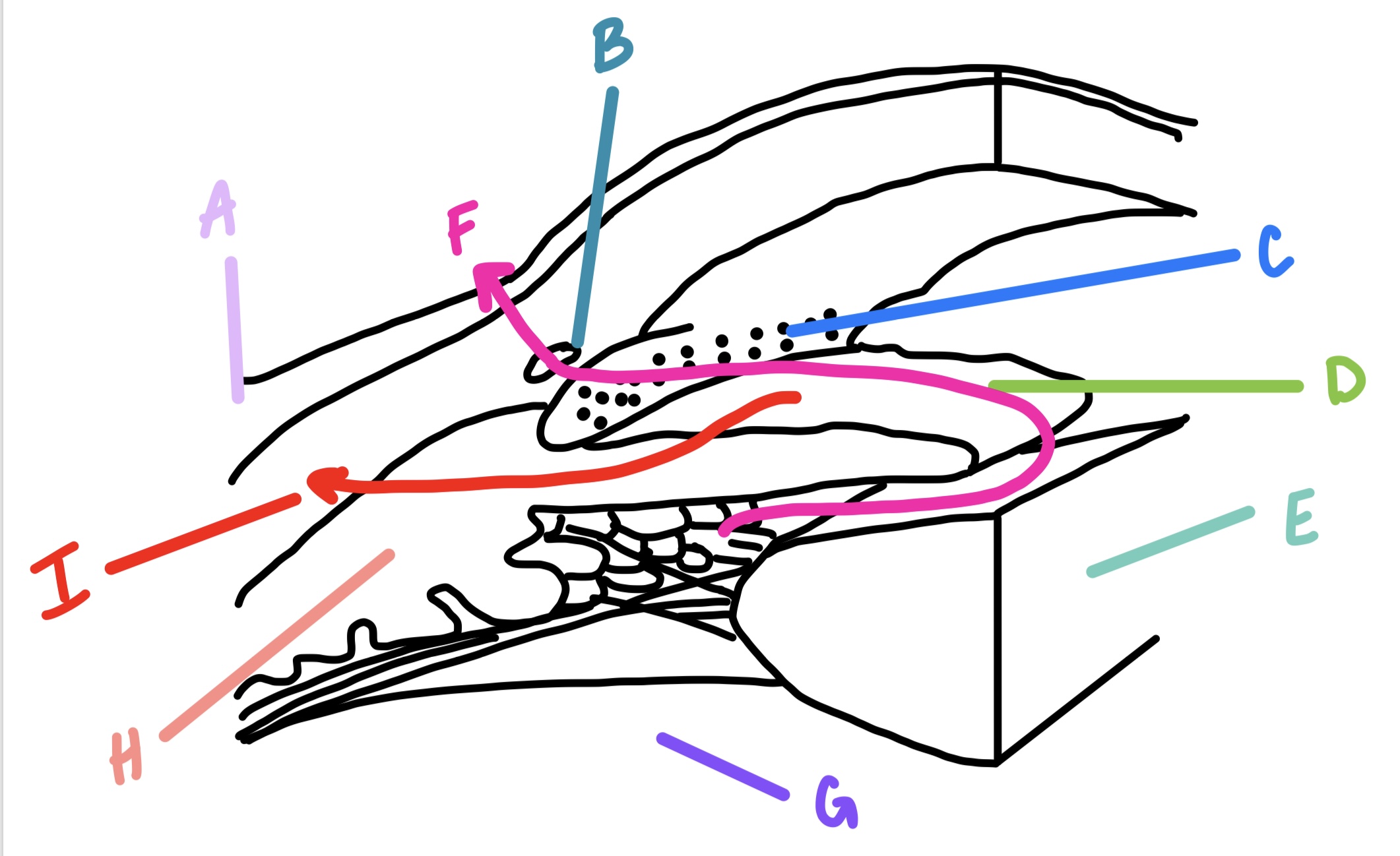
limbal sclera
external wall of canal of Schlemm lies against what?
JCT & scleral spur
inner wall of canal of Schlemm lies against what?
zonula occludens
what is the intercellular junction of the endothelial cells in the canal of Schlemm?
no
is the basement membrane of the canal of Schlemm complete?
giant vacuoles
pressure-dependent deformations of the inner wall of canal of schlemm that help move aqueous humor
provide an exit for aqueous humor, supply nutrients to avascular tissue
what are the functions of the filtration apparatus?
oxygen & glucose
aqueous humor provides what nutrients to the avascular lens and cornea?
pars plicata of ciliary body
where is aqueous humor produced?
convection currents
the aqueous humor circulates in what?
unconventional outflow
flow pattern of aqueous humor where it passes through spaces of uveal meshwork; less than 40% of outflow
I
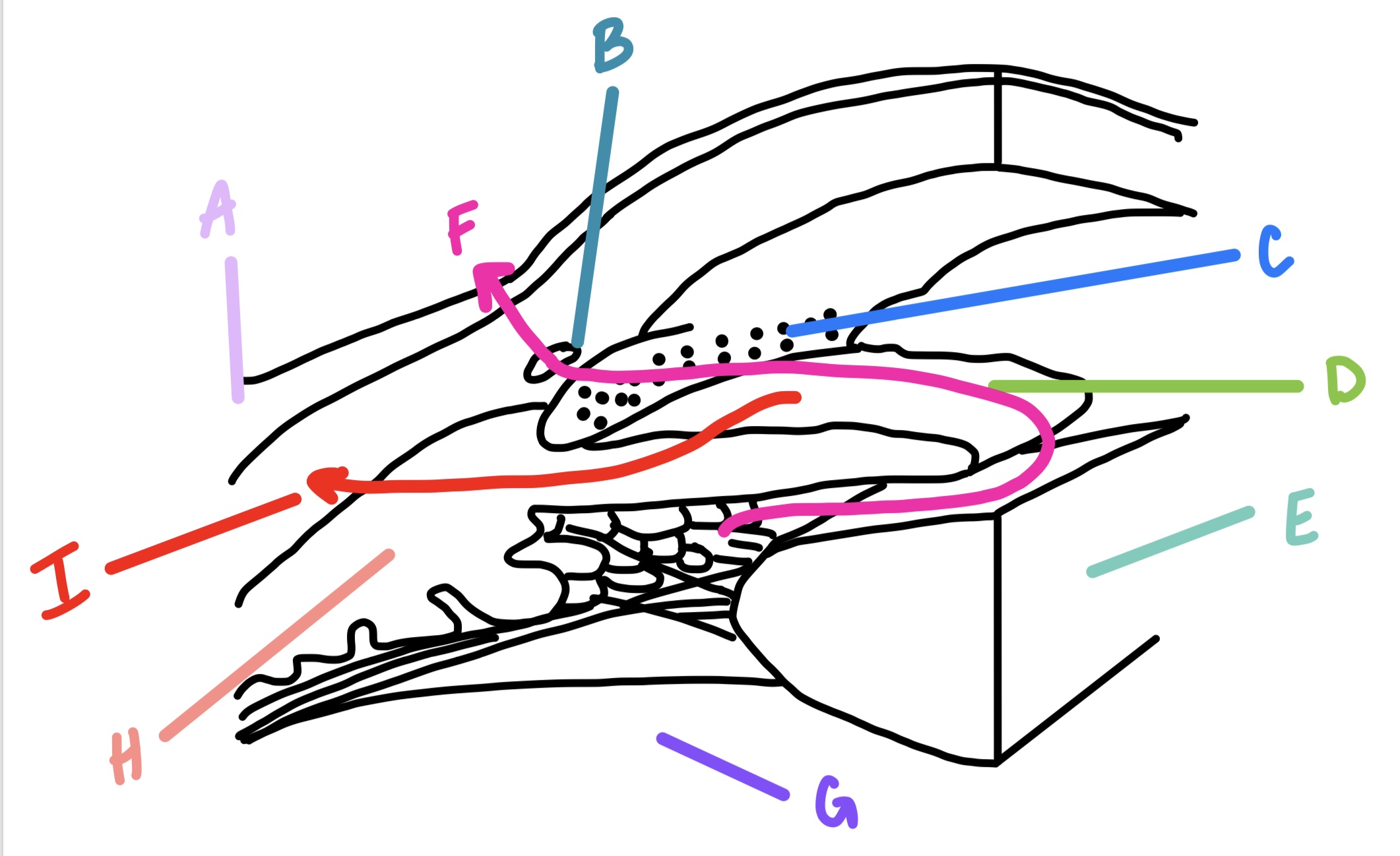
uveal meshwork → connective tissue around ciliary muscles → suprachoroidal space → sclera or vortex veins
what is the flow route for the unconventional outflow pathway?
decreases with age
over the lifespan, the percentage of aqueous humor outflow that occurs via the alternate pathway …
contraction of ciliary muscle
what reduces the uveoscleral outflow?
scleral spur location
what determines whether aqueous humor enters the trabecular outflow pathway or the uveoscleral pathway?
above scleral spur
aqueous humor located _________ leaves the anterior chamber via the conventional pathway
below scleral spur
aqueous humor located ___________ leaves the anterior chamber via the unconventional pathway
unidirectional into the canal
what is the flow pattern through the giant vacuoles of the endothelial cells in the canal of Schlemm?
indentation forms in basal surface, gradually enlarges, and eventually opens to apical side, basal eventually occludes opening
what are the steps to a giant vacuole flow?
pinocytic vesicles
what provides additional transport into the canal of Schlemm?
passive diffusion
how does the bulk of aqueous humor go into the canal of schlemm?
cellular factors, increase
endothelial cells of trabecular meshwork may release ________ that can _______ permeability of inner wall of Schlemm’s canal
internal collector channels of Sondermann
evaginations, blind pouches, of the internal wall of Schlemm’s canal that extend into the JCT toward the trabecular meshwork
can be fairly long and branching
serve to increase surface area
arise near posterior canal wall
sheet of connective tissue
what always separates the endothelium of collector channels from the trabecular space?
frequently, bridges
corneoscleral trabecular sheets branch _______ and their endothelial cells often form ______ between adjacent sheets
ophthalmic veins
what carries aqueous humor out of the orbit?
30
how many external collector channels are there?
external collector channels
exhibit smooth muscle, 30 located around the eye, lead from outer wall of canal of Schlemm and toward vessels of episclera
deep scleral plexus
from the external collector channels, aqueous passes into this tortuous system of vessels within the thickness of the sclera
superficial intrascleral venous plexus
deep scleral plexus leads to this
aqueous and blood get mixed
tortuous route of draining of canal of schlemm causes what?
aqueous veins of Ascher
unique vessels in 10% of eyes that allow aqueous to bypass the tortuous pathway and connect directly from Schlemm’s canal to episcleral veins
near limbus at 3 or 9 o’clock
where are aqueous veins of Ascher located if present?
remains constant
how does aqueous humor production change over time?
decreased outflow
most cases of increased IOP are caused by what?
uveoscleral
which outflow pathway is said to be fairly constant and not affected by IOP
widening space between sheets and decreasing outflow resistance
how does ciliary muscle contraction alter the geometry of the trabecula?
JCT → endothelium of Schlemm’s canal
what are the elastic fibers of the scleral spur continuous with?
increases
interaction between elastic fibers of scleral spur, JCT, and Schlemm’s canal during accommodation ______ lumen diameter
Fin=Fout
ideal aqueous balance
tonometer
device to measure IOP
indentation/impression tonometer
measure the depth of indentation made by a plunger of known weight placed onto the cornea
applanation tonometer
measure the force required to flatten a known area of the corneal surface
applanation
which form of tonometry is the most widely used?
goldmann tonometry
measures the force required to flatten a known area of the cornea, based on imbert-fick law
non contact tonometry
time required to applanate 3.6mm diameter of central cornea with a standardized air pressure puff
central corneal thickness
measurements of eye pressure are affected by what?
555um
what is the average central corneal thickness
artificially high
increased CCT may lead to an _____ IOP
artificially low
decreased CCT may lead to an _____ IOP
LASIK
procedure that reduces corneal thickness and thus may reduce IOP readings
cholinergic agonist
drug that affects IOP
causes iris sphincter and ciliary muscles to contract, changing the configuration of trabecular sheets to facilitate outflow
uncomfortable side effects of miosis and ciliary spasm
not commonly used anymore
Pilocarpine
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
drug that affects IOP
not well tolerated
inhibit key enzymes for ionic transport across epithelial layers
prostaglandins
drugs that affect IOP
currently most effective
well tolerated, good compliance
enhance outflow through uveoscleral pathway
relax ciliary muscle tone
remodel extracellular matrix w/in CT b/t muscle bundles, increasing spacing and tissue permeability
rho-kinase inhibitors
drugs that affect IOP
loosen intercellular junctions along Schlemm canal and decrease production of ECM, thus widening spaces in TM
Rhopressa
argon laser trabeculoplasty
uses higher laser energy that damages the TM causing it to contract and scar
opens up pores to increase outflow
recruits macrophages to treatment site where they remodel ECM to increase outflow
one time permanent procedure
selective laser trabeculoplasty
lower laser energy absorbed selectively by pigmented trabecular meshwork to recruit macrophages to clean up meshwork and increase outflow
no damaging effects
can be repeated as effects wear off
trabeculectomy
last resort treatment for glaucoma
wedge of TM is removed and often a scleral flap is formed so that aqueous can percolate through trabecular opening and accumulate beneath the flap to be absorbed into episcleral tissue
endoscopic cyclophotoagulation
recent surgical procedure that reduces aqueous production by applying a laser to damage tissue of ciliary processes
TM thickens, loss of uveal endothelial cells, hypertrophy of leftover cells, plaque formation, compacting uveal strands, reduced forming of giant vacuoles, atrophy of ciliary muscle, decrease in facility offset by decrease in aqueous production
what are aging changes in the TM?
beta blockers
medication that inhibits the receptor that upregulates sympathetic innervation to aqueous production; yellow cap
alpha2 agonists
medication that stimulates the receptor that downregulates sympathetic innervation to aqueous production; purple caps
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
interferes with the regulator of bicarbonate transport that regulates fluid transport; orange cap
rho kinase inhibitor
medication that increases aqueous outflow through the conventional pathway; white cap
prostaglandin analog
medication that increases aqueous outflow through the unconventional pathway; blue cap
gonioscopy
allows a direct view of the anterior chamber angle
lens contains mirrors to look in and around the limbus to view angle structures
ciliary body, scleral spur, TM, Schwalbe’s line
what are the structures in the anterior chamber angle that can be viewed through gonioscopy? + iris
no
can Schlemm’s canal normally be seen in gonioscopy?
van herick angle estimation
used to estimate how wide open the anterior chamber angle might be to know if you can apply dilation
iris, ciliary body, scleral spur, TM, schwalbe’s line
what are the structures viewed in gonioscopy from posterior to anterior?