Topic 11 Speciation/Origin of Life 1-34
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
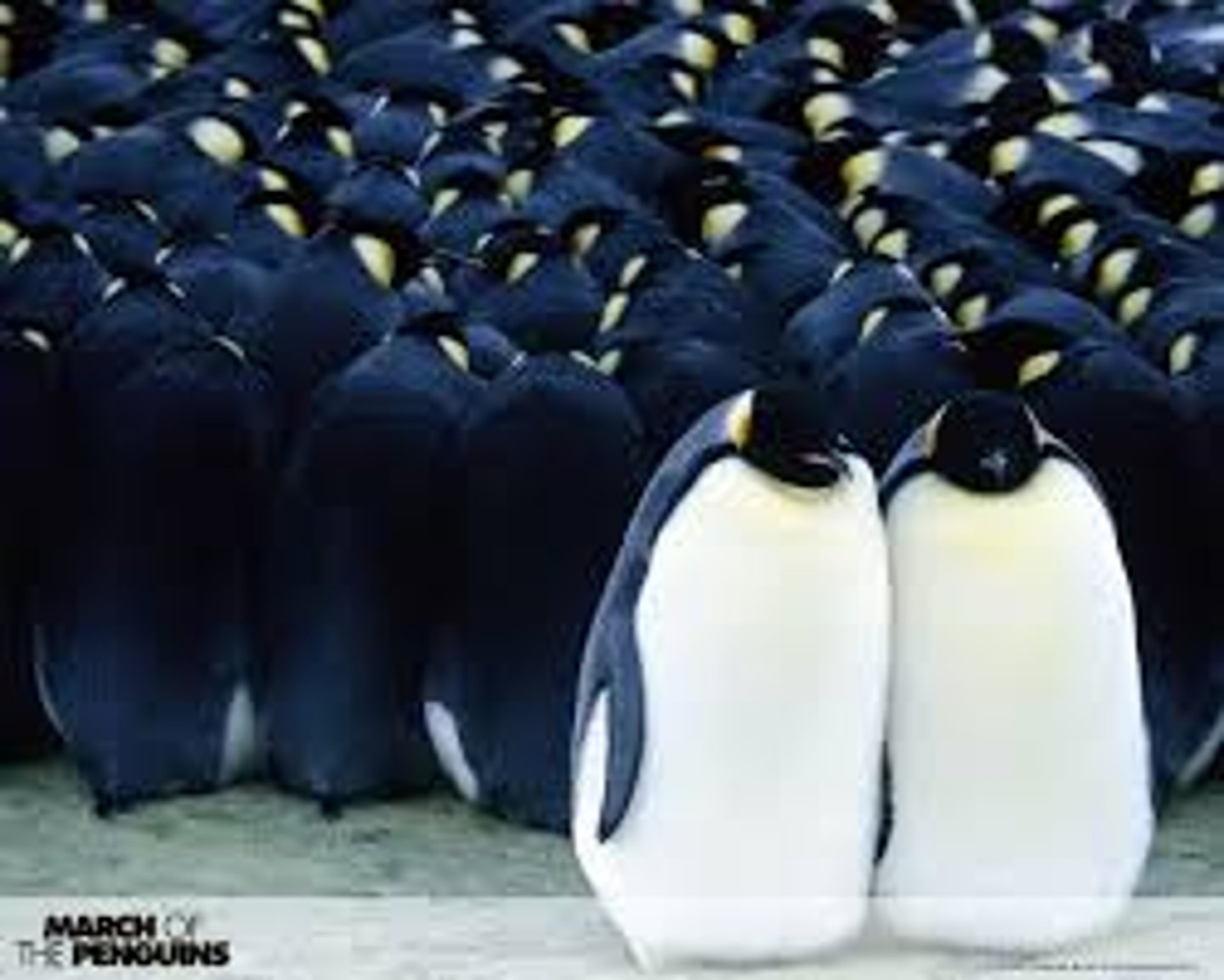

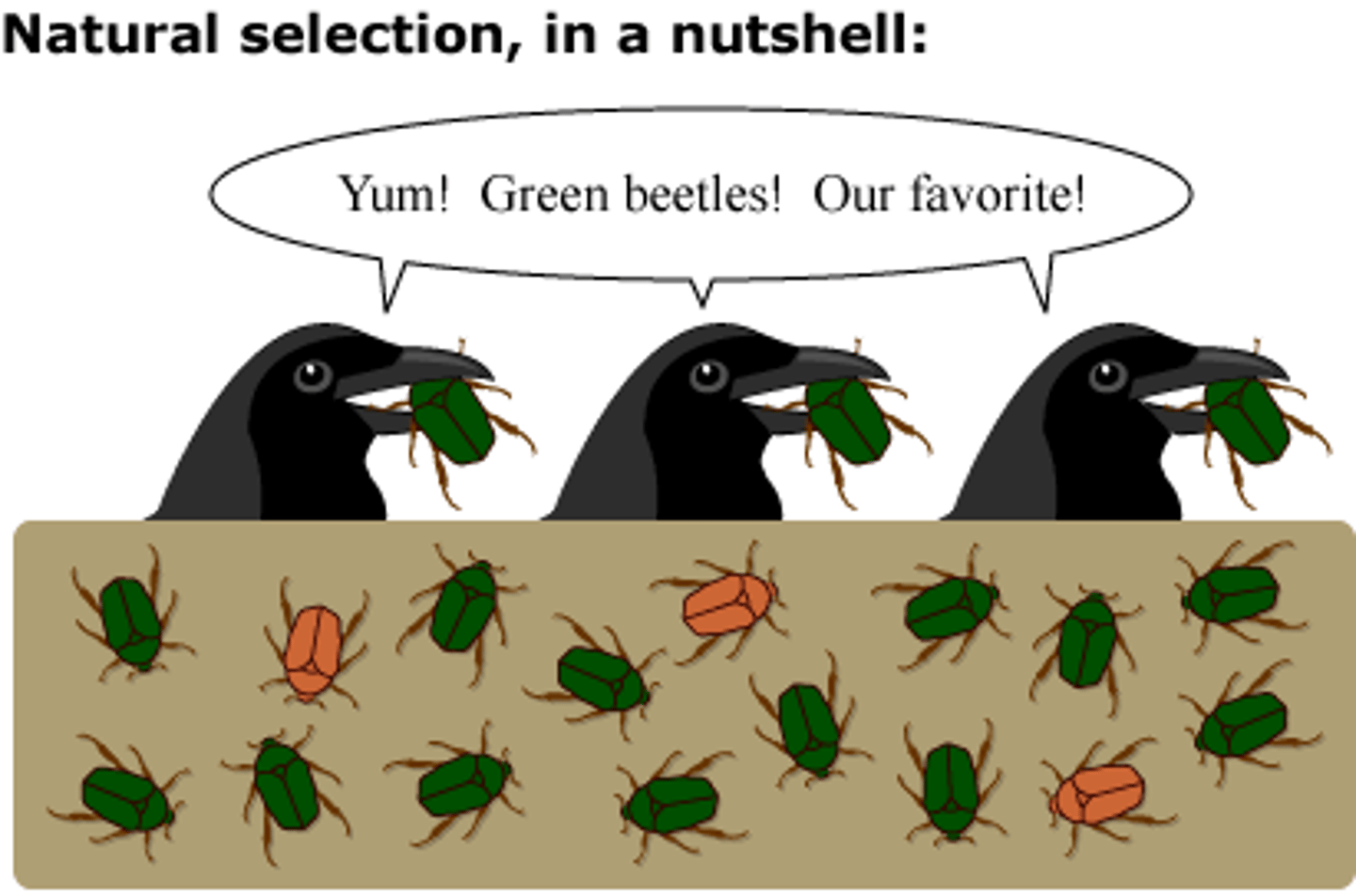
natural selection
A process in nature in which organisms possessing certain inherited traits are better able to survive and reproduce compared to others of their species.
modern synthesis
A comprehensive theory of evolution that incorporates genetics and includes most of Darwin's ideas, focusing on populations as the fundamental units of evolution
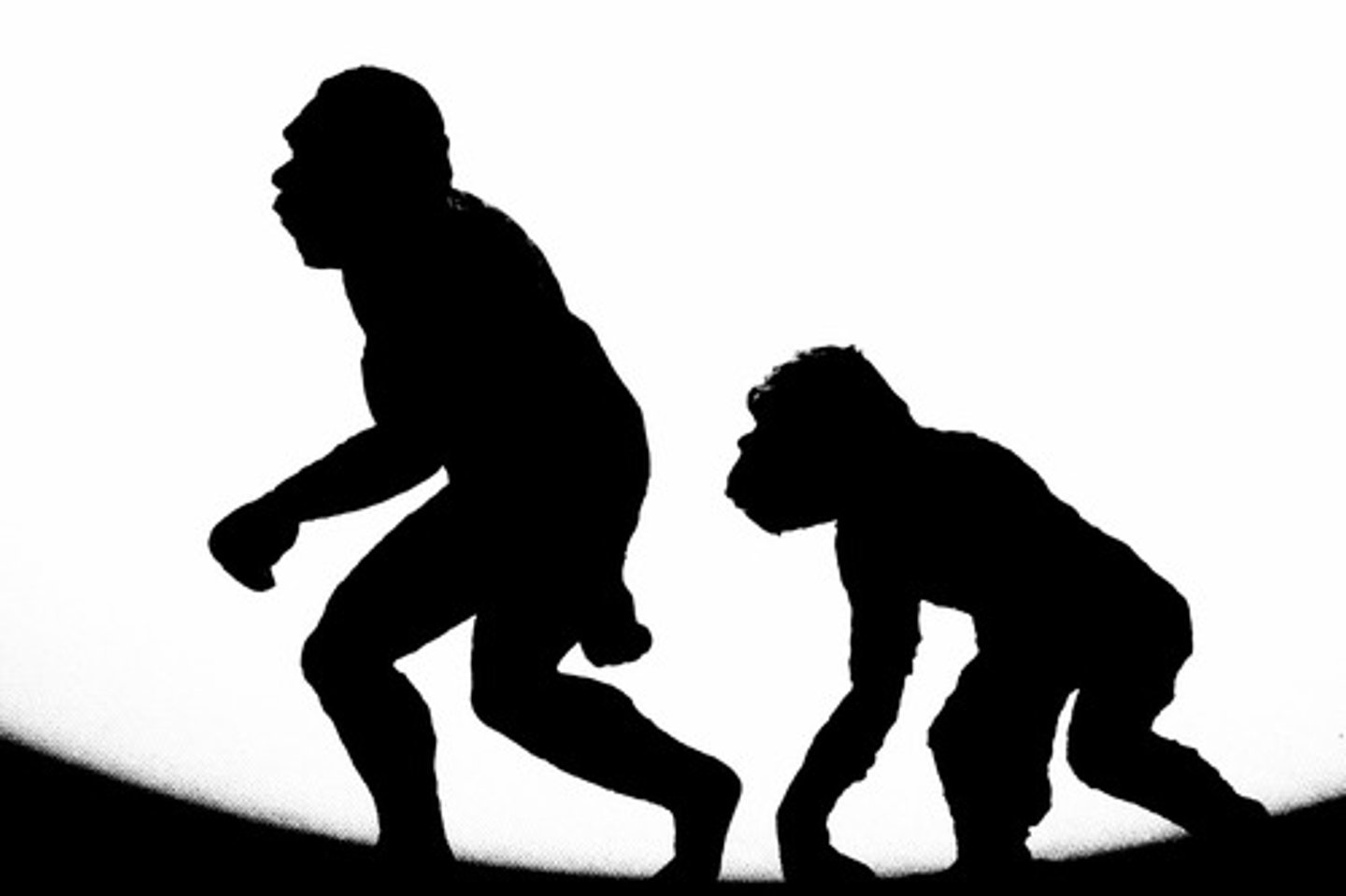

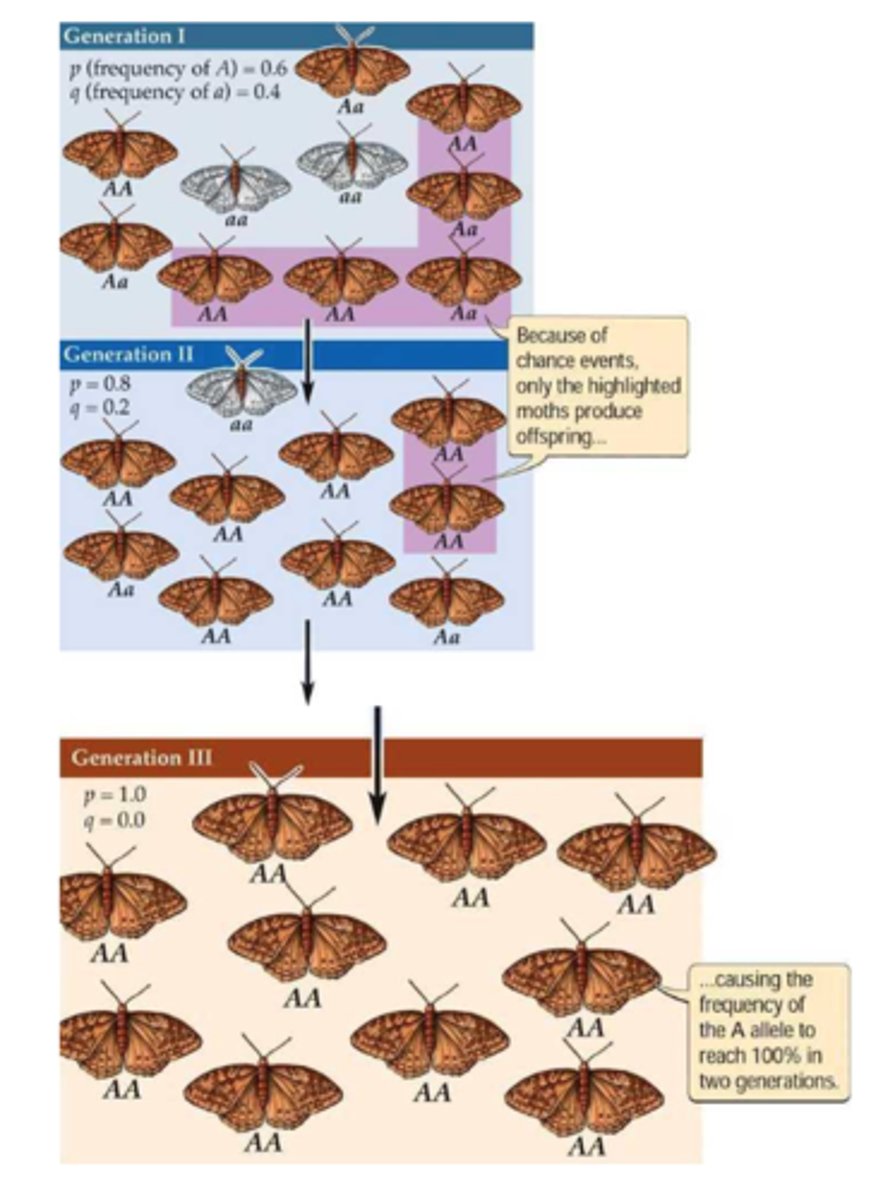
microevolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations
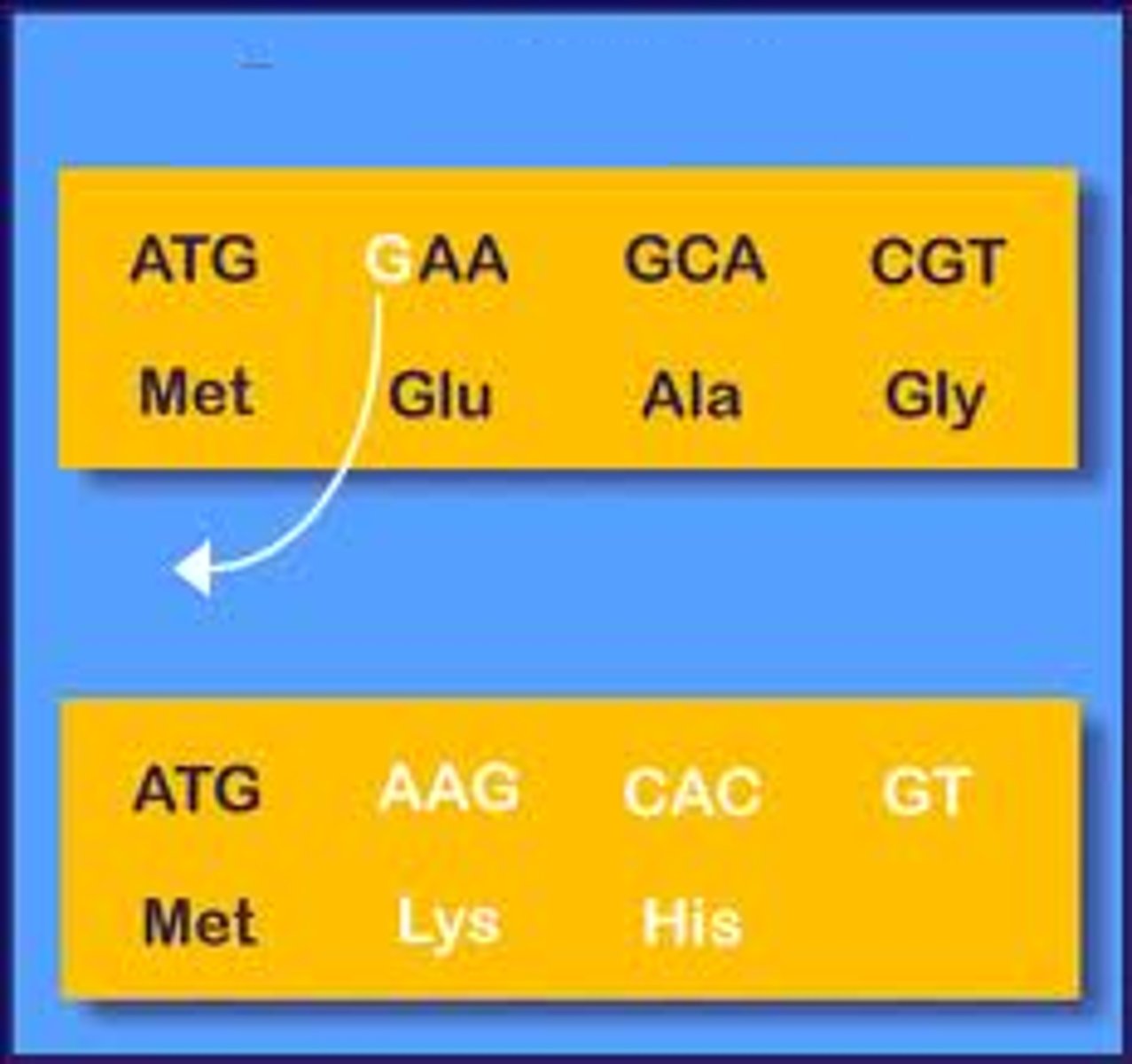
mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA, ultimately creating genetic diversity.
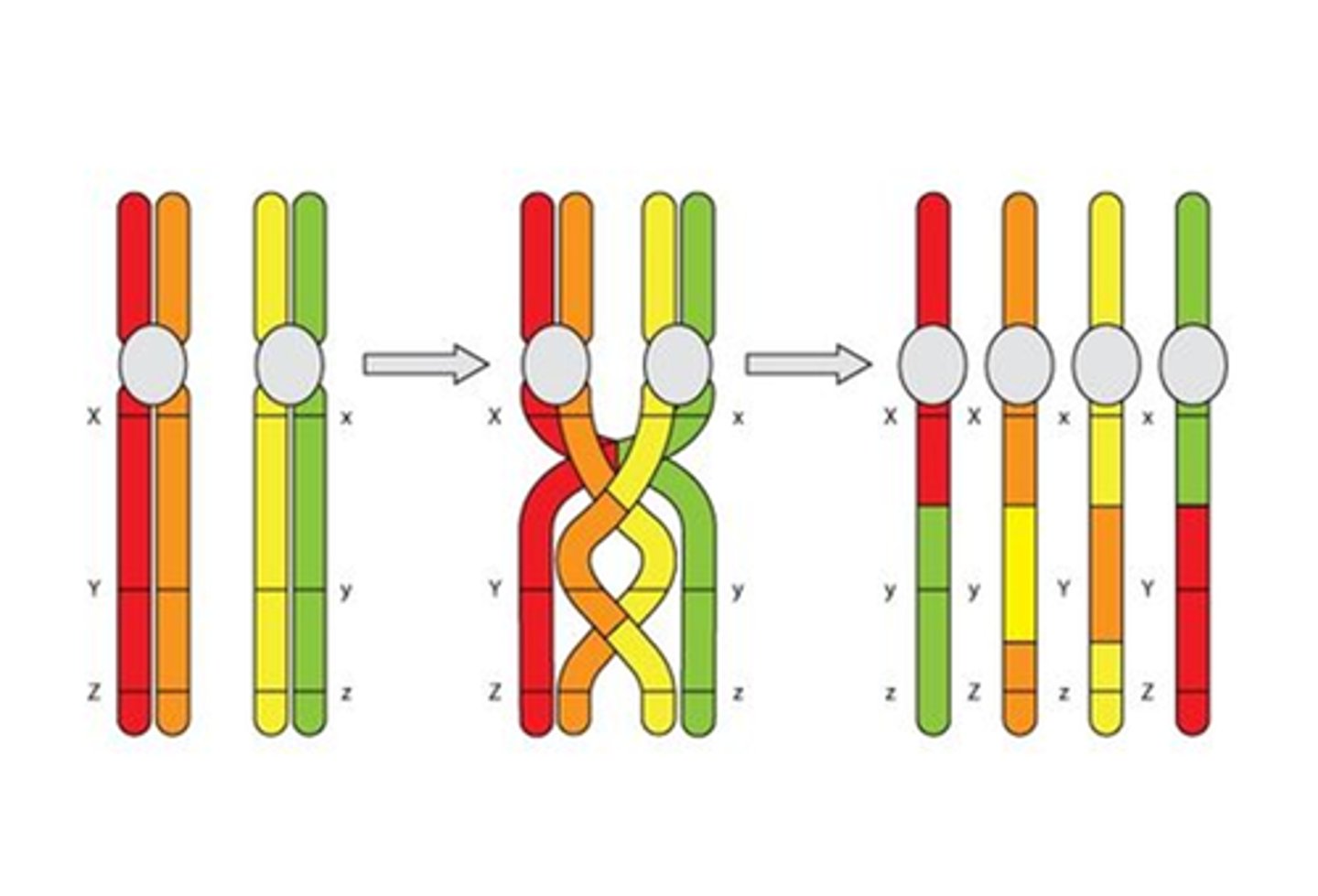
sexual recombination
In sexually reproducing populations, changes in genes from generation to generation that occur through meiosis and fertilization.
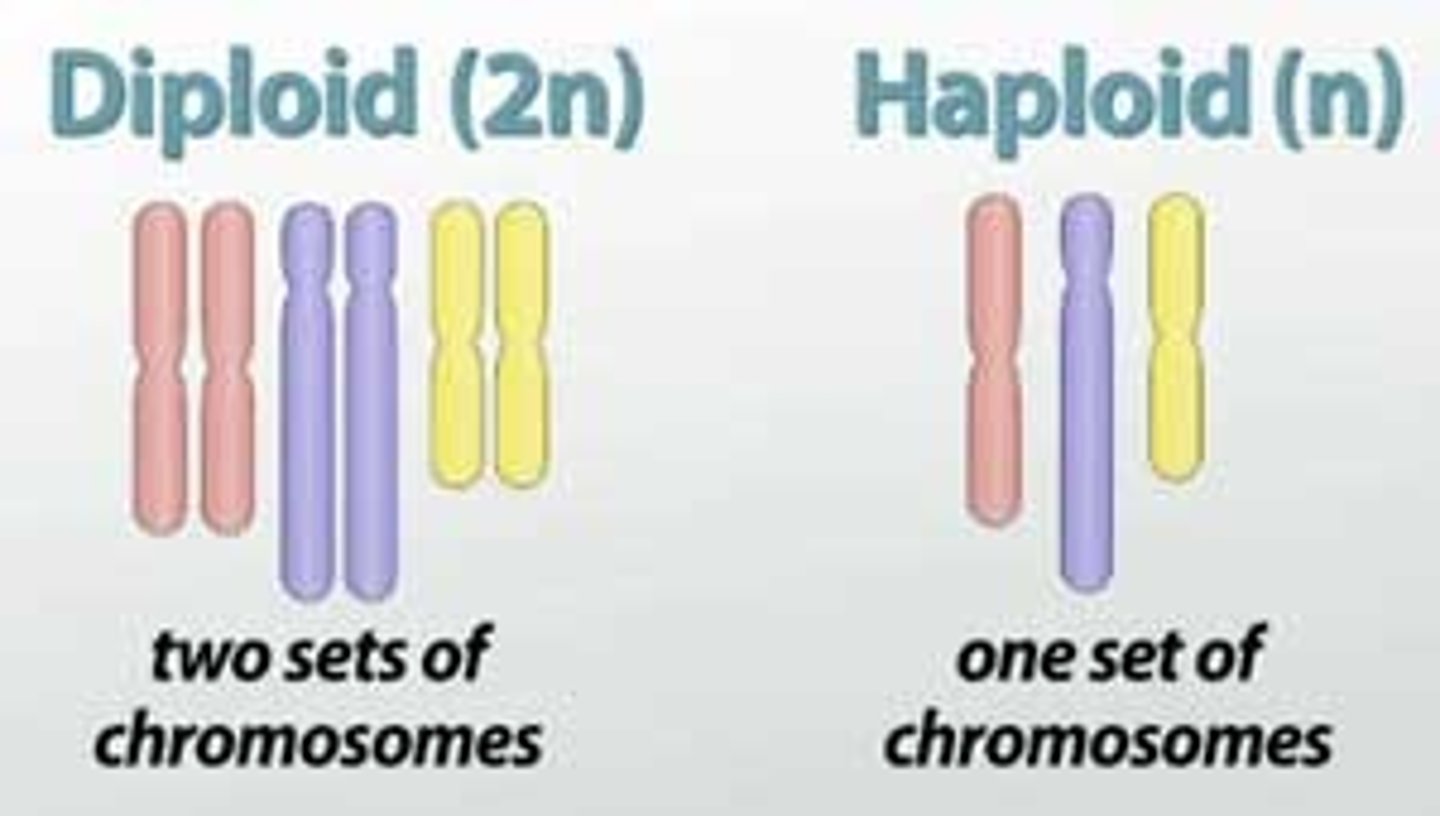
diploidy
Genetic status in which two copies of each chromosome are present in an individual.
neutral variation
Differences in DNA sequence that do not confer a selective advantage or disadvantage

balancing selection
Natural selection that maintains stable frequencies of two or more alelles in a population's gene pool.
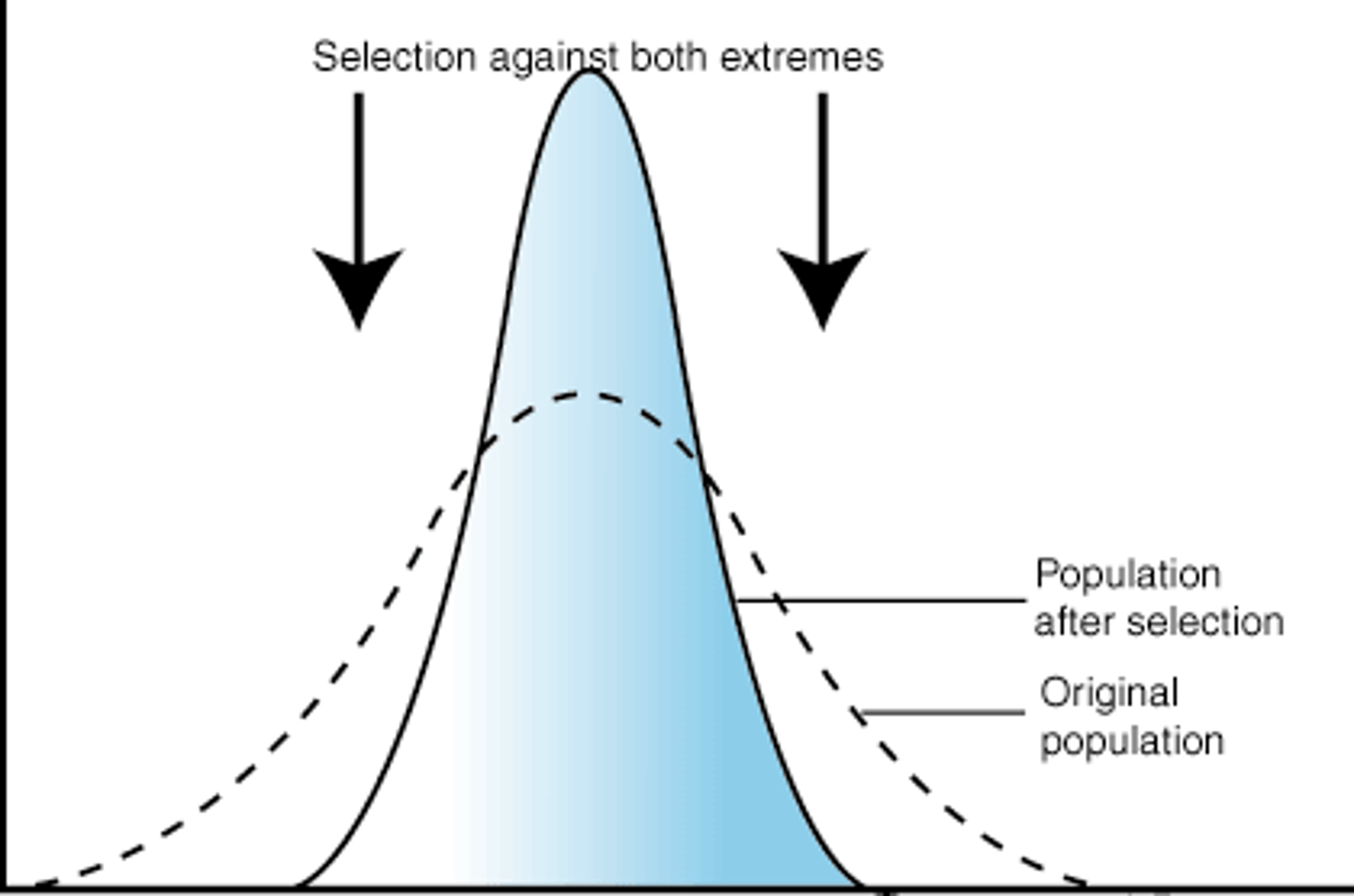
balanced polymorphism
The ability of natural selection to maintain stable frequencies of two or more phenotypic forms in a population.
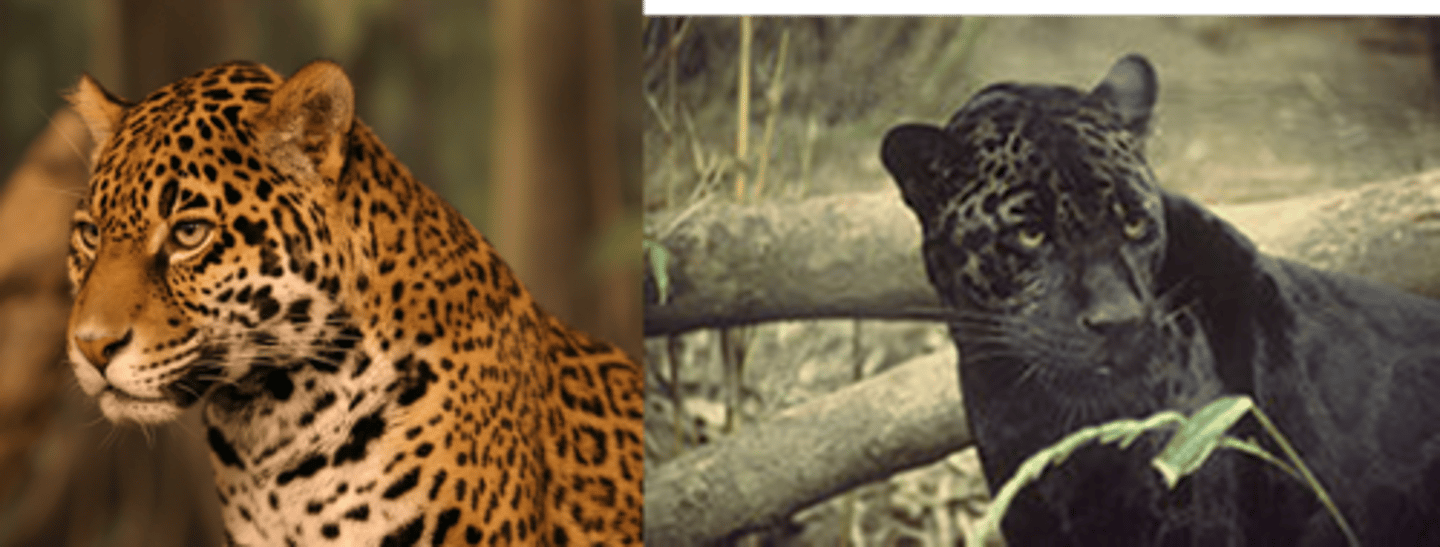

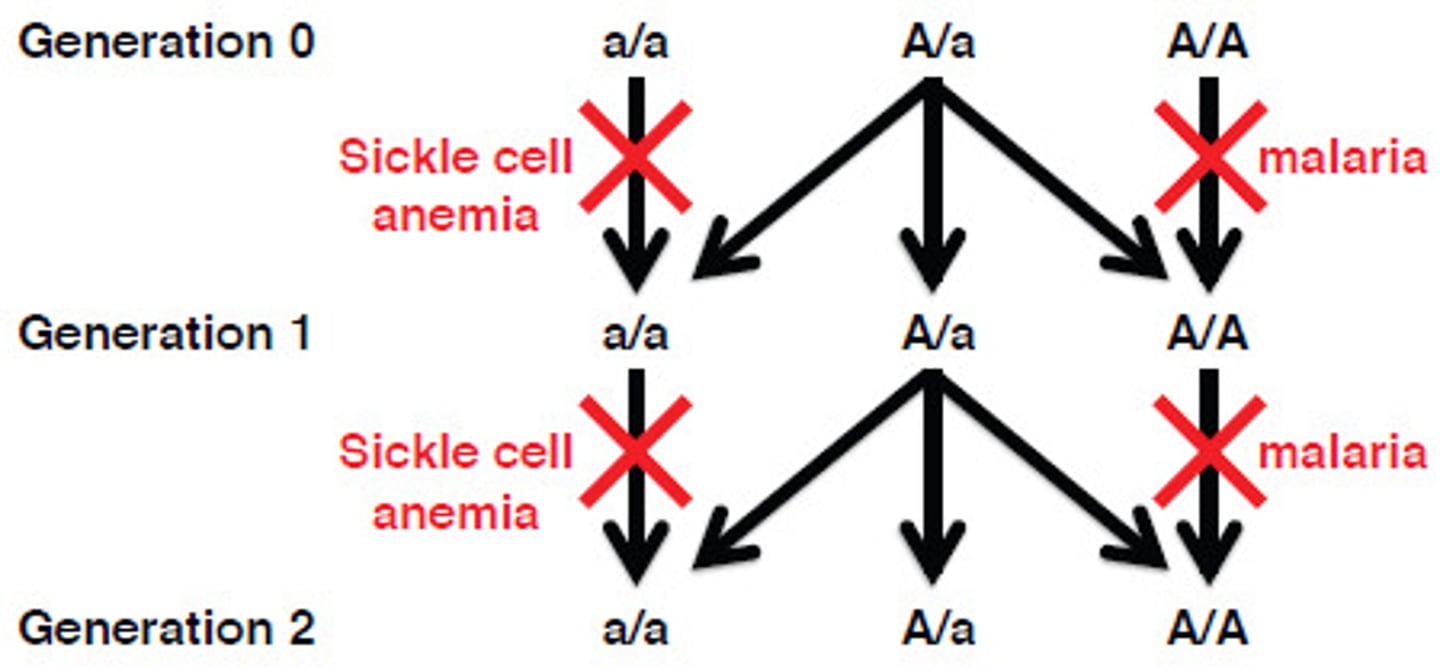
heterozygote advantage
Greater reproductive success of heterozygous individuals compared with homozygotes; tends to preserve variation in a gene pool
frequency dependent selection
A decline in the reproductive success of individuals that have a phenotype that has become too common in a population
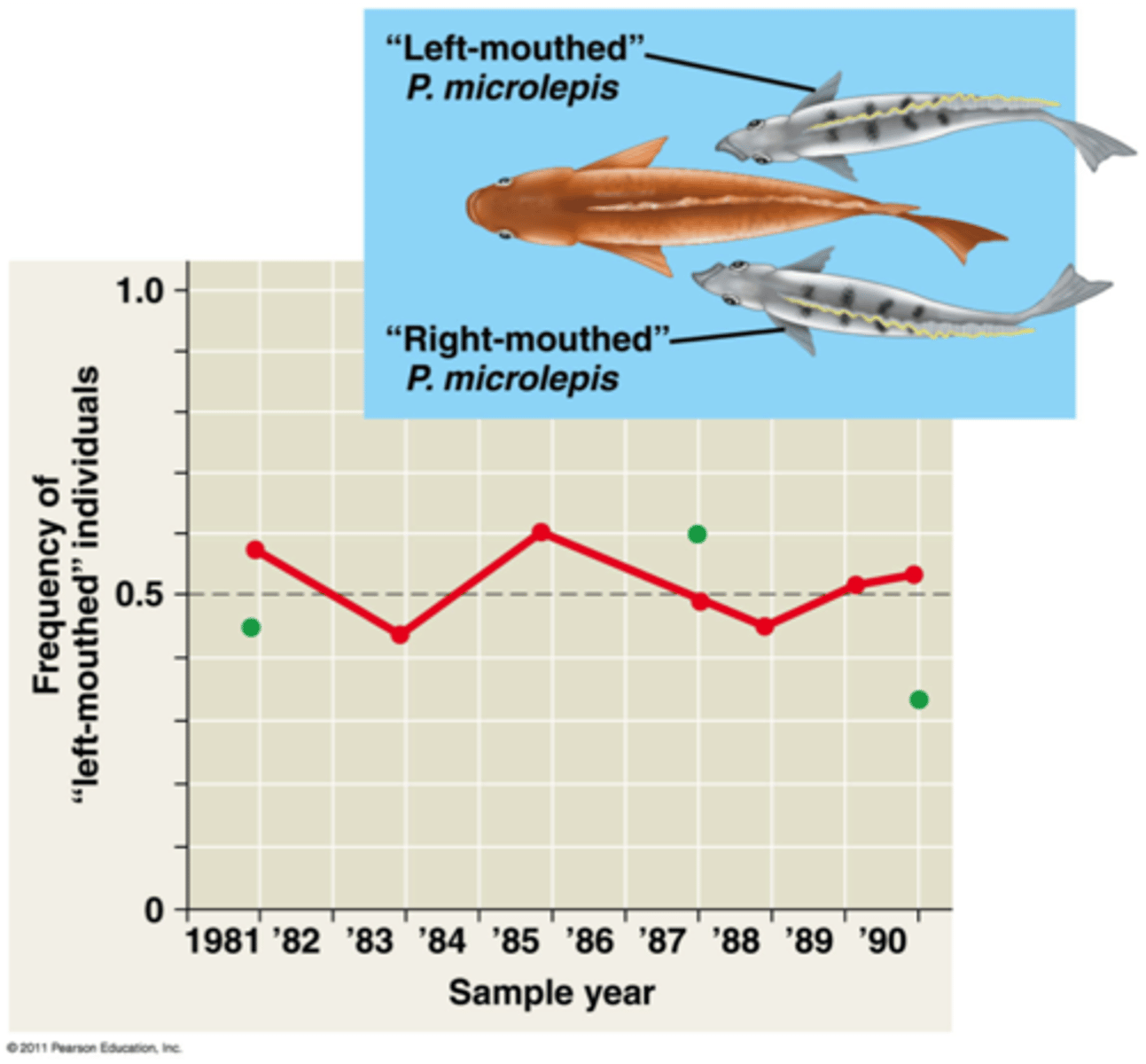
sexual selection
A form of selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates.
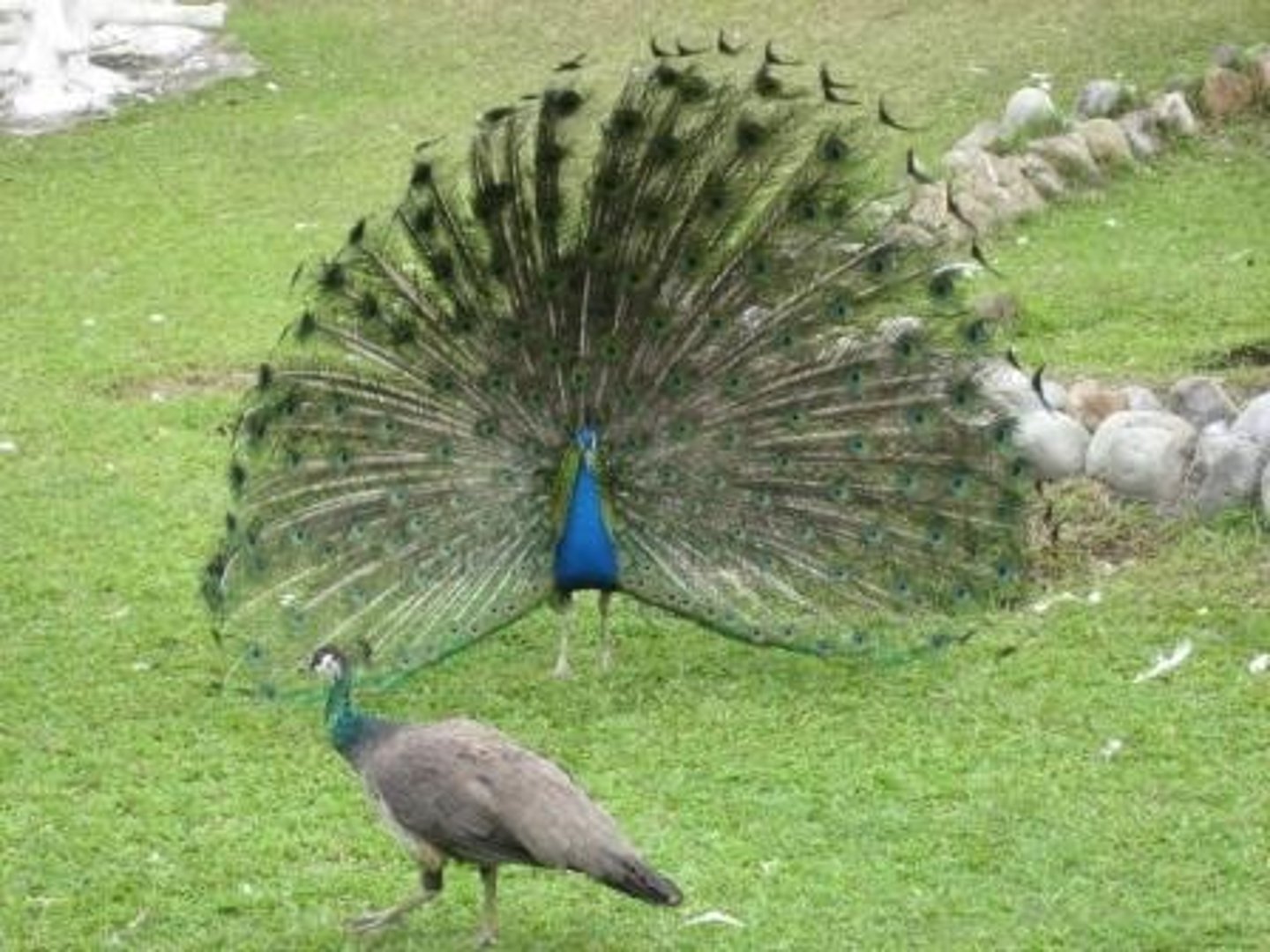

sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.
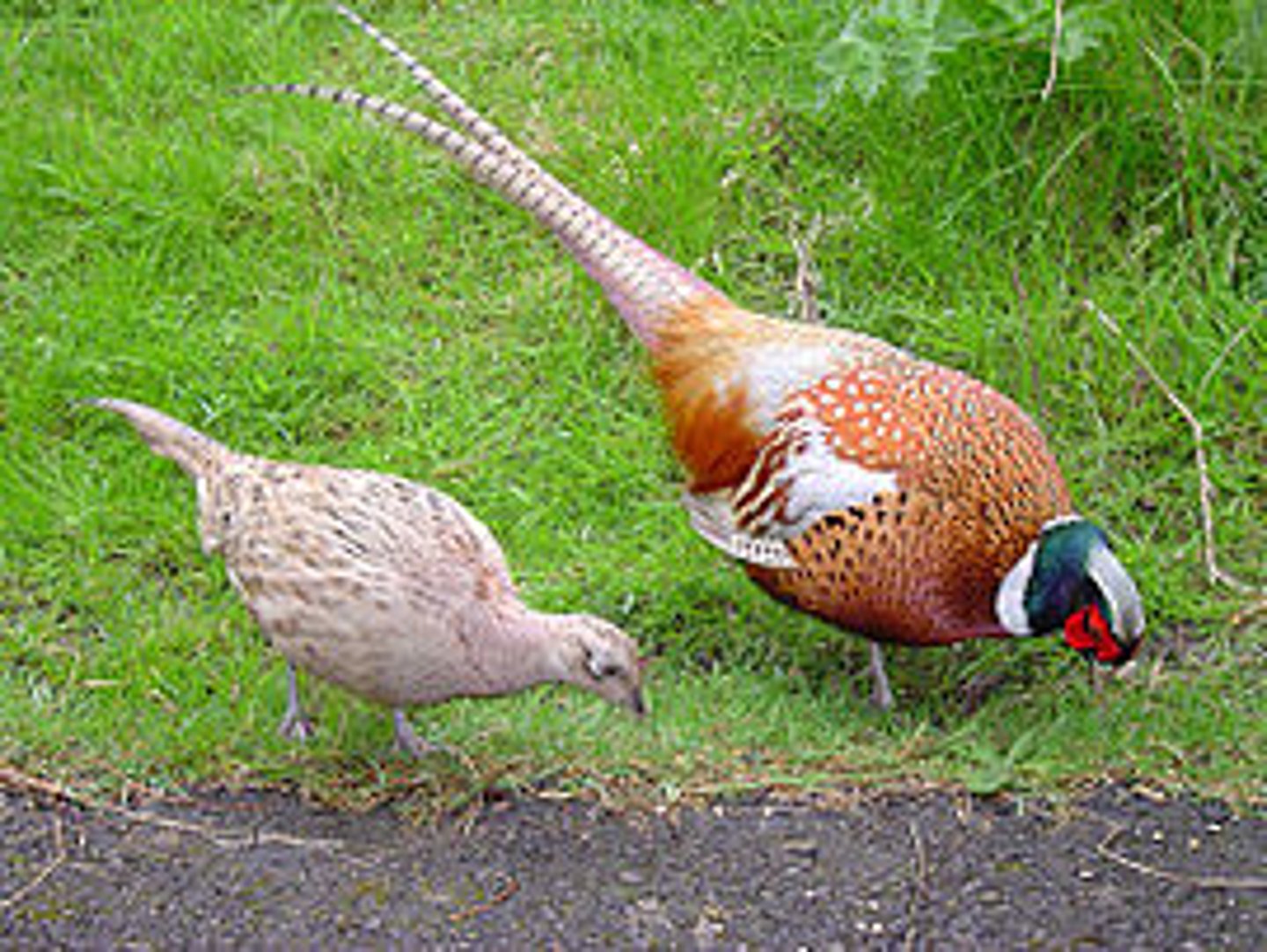

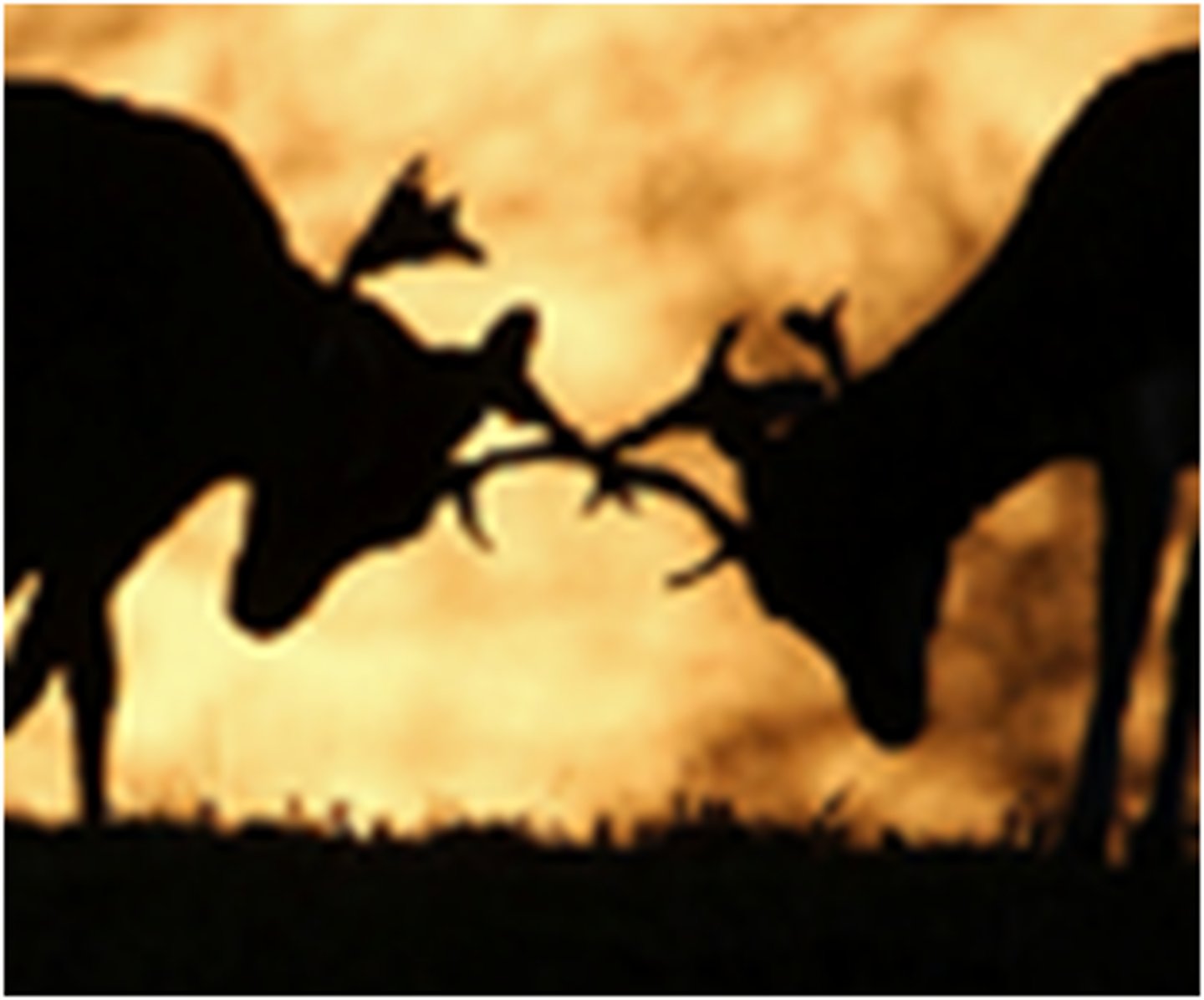
intrasexual selection
A direct competition among individuals of one sex (usually the males in vertebrates) for mates of the opposite sex.

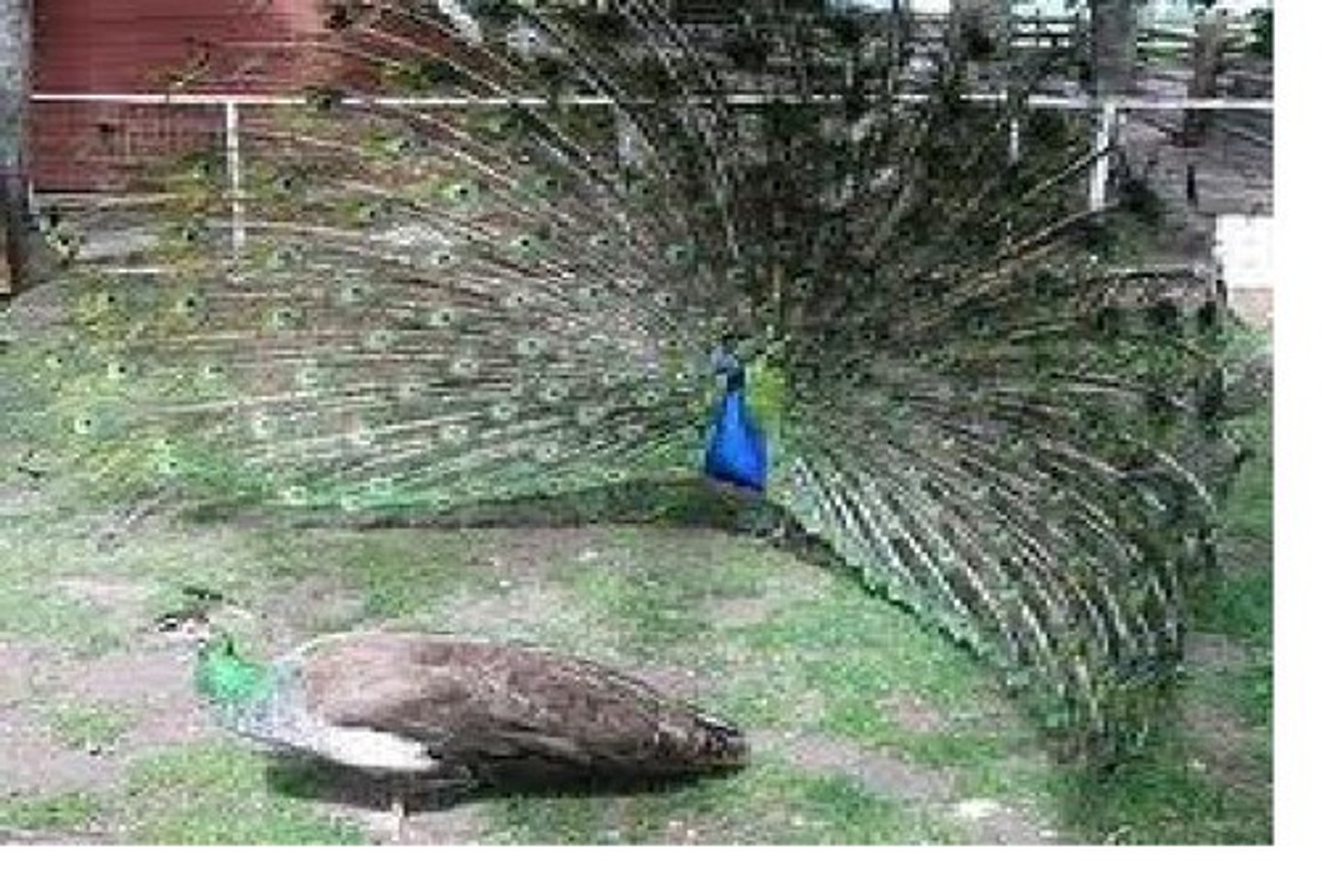
intersexual selection
Form of sexual selection in which members of one sex choose mates of the other based on the other's characteristics

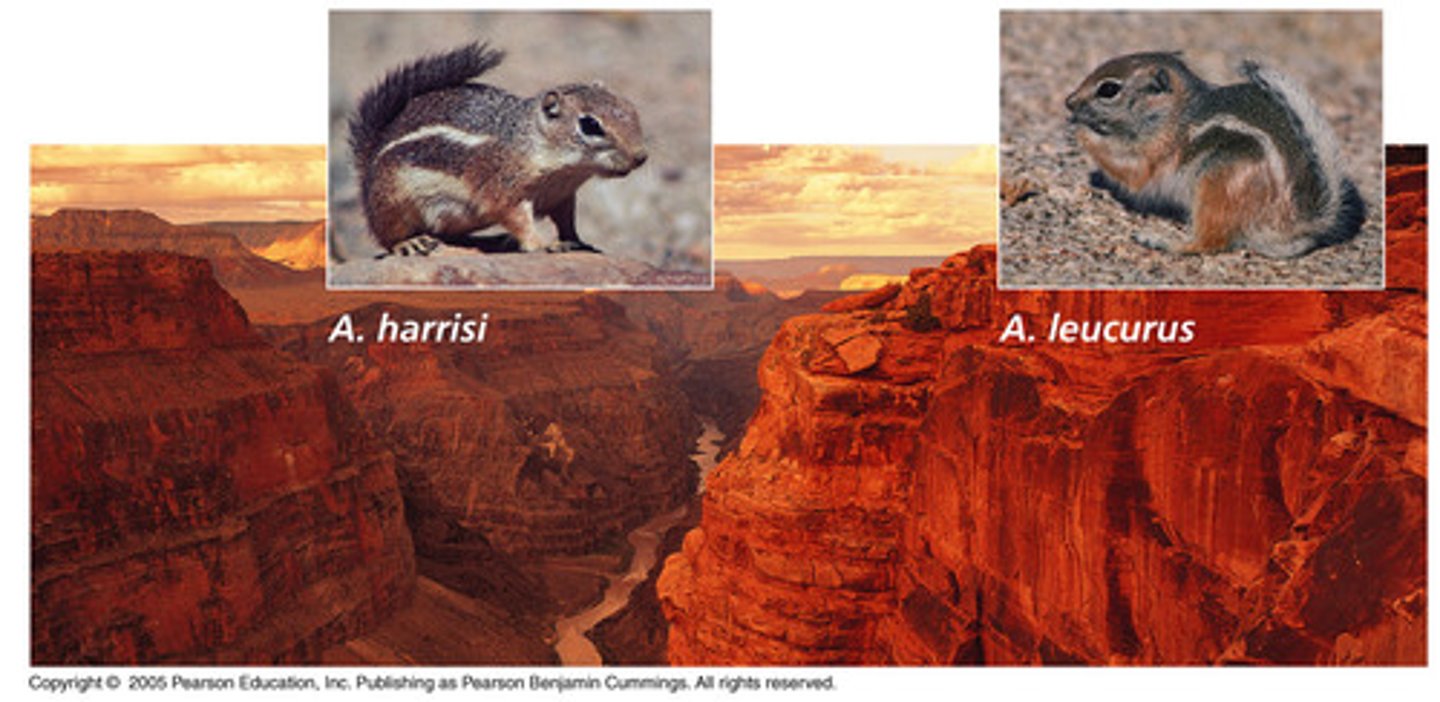
speciation
A process typically caused by the genetic isolation from a main population resulting in a new genetically distinct species.

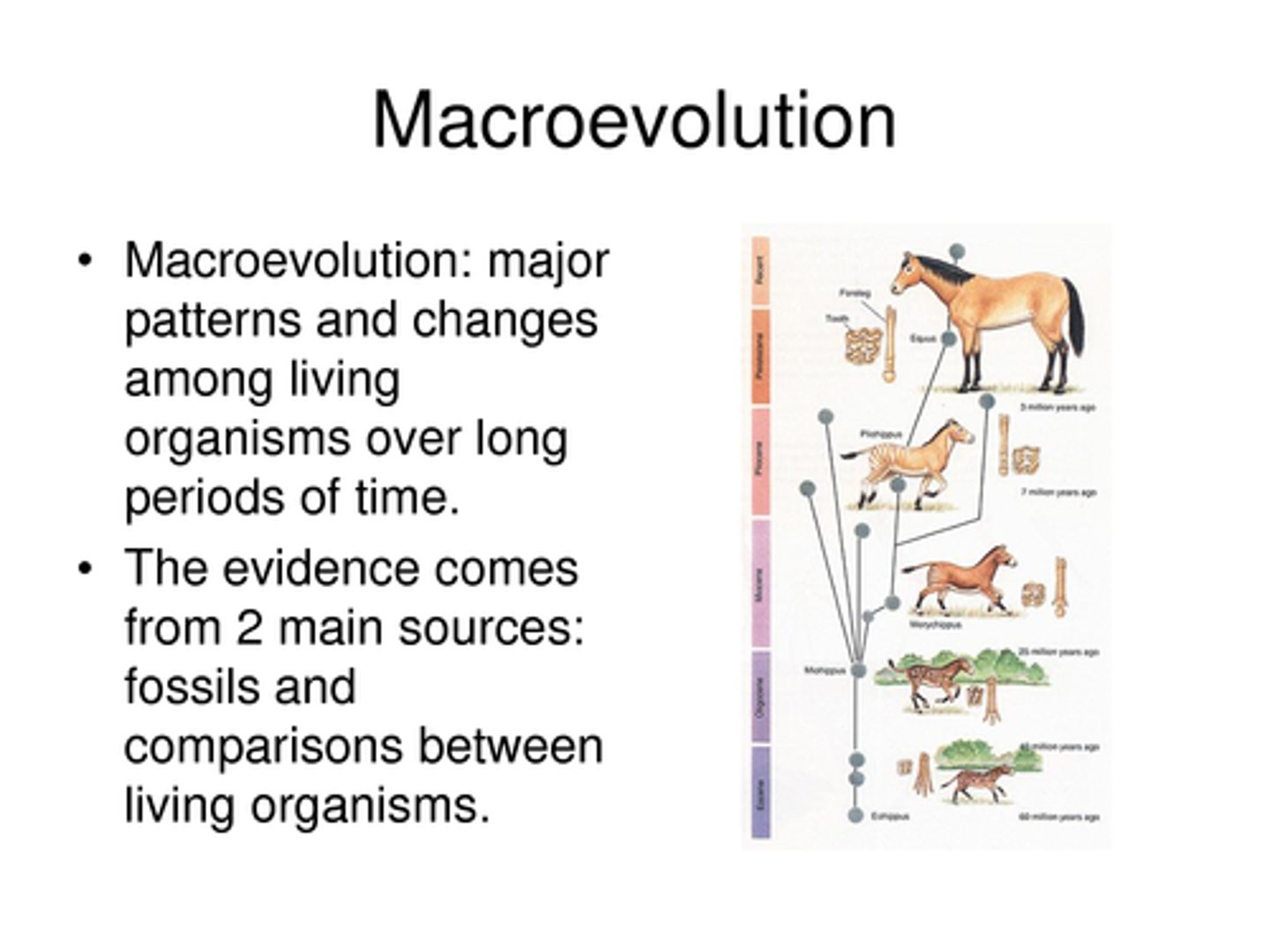
macroevolution
Evolutionary change above the species level
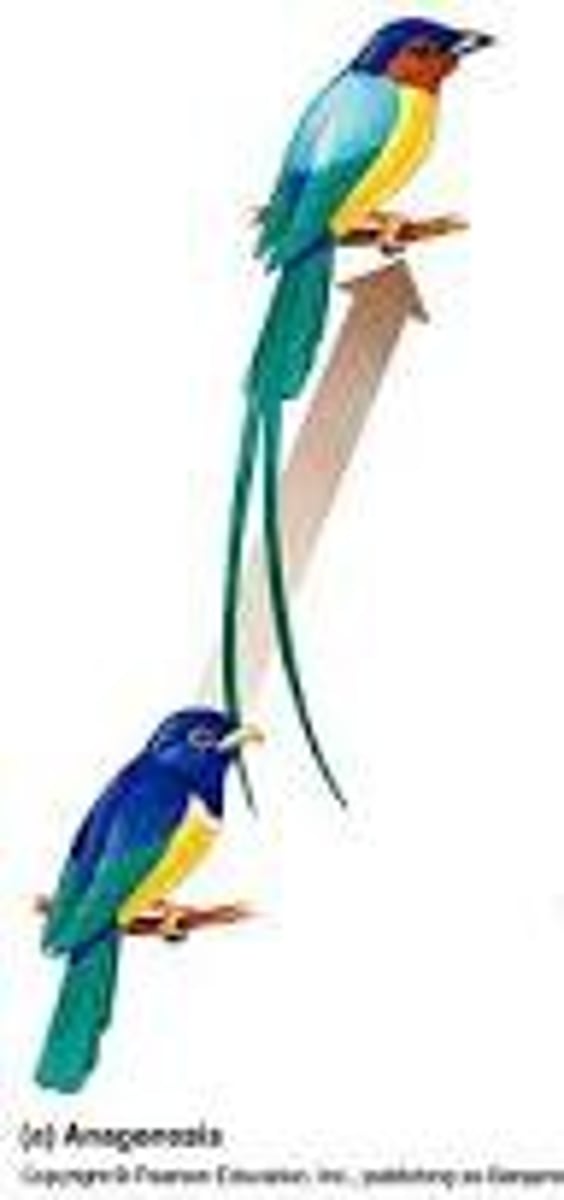
anagenesis
The change of a species into another species

cladogenesis
Evolution that consist of the splitting of a species into two new species

biological species concept
A species is a group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile offspring.
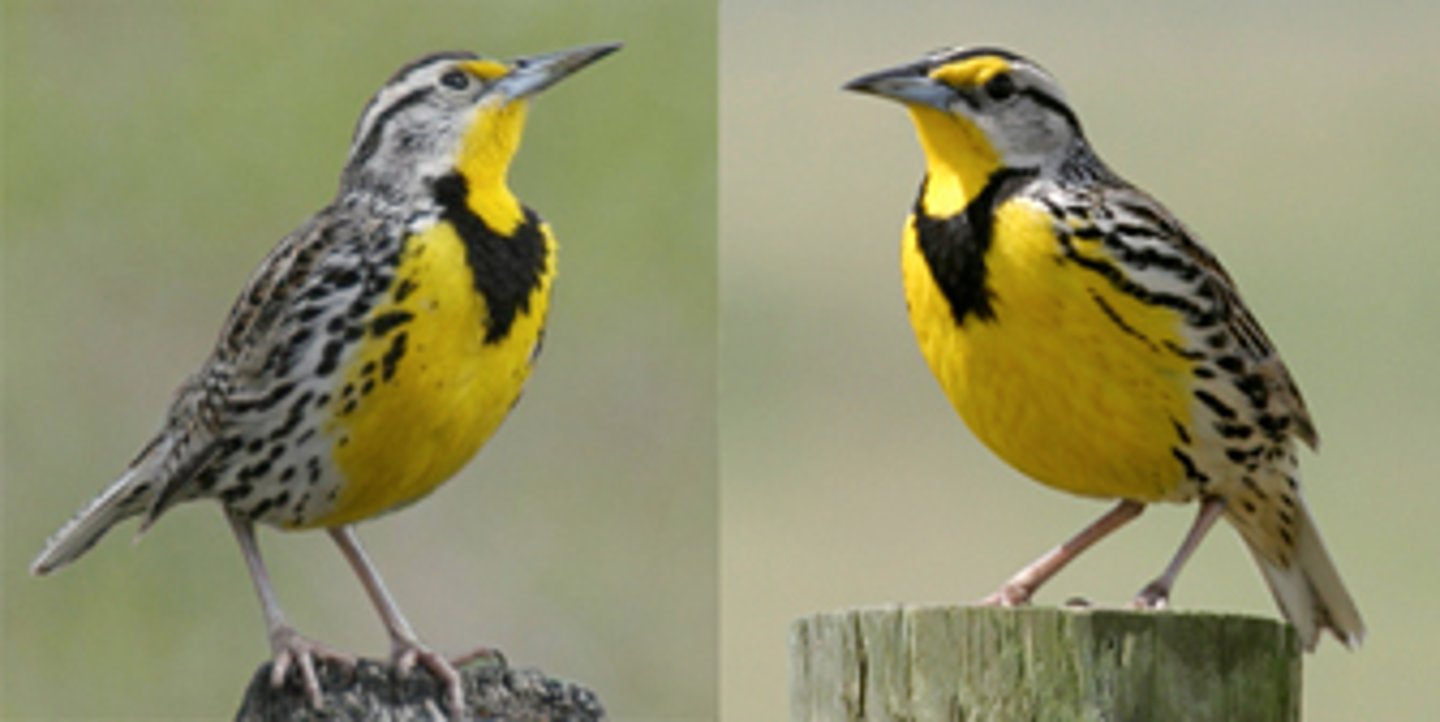

reproductive isolation
Any factors that impede members of two species from interbreeding and producing viable, fertile offspring
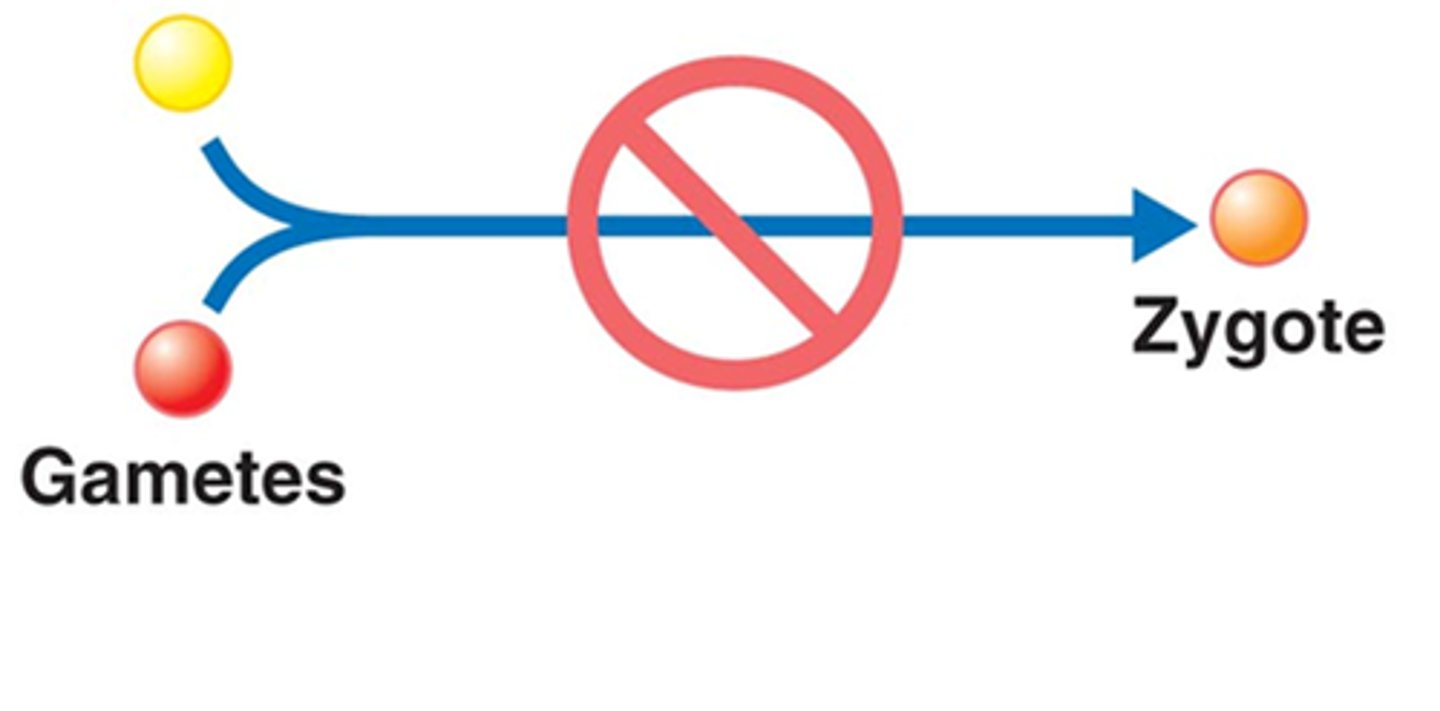
prezygotic barriers
Barriers that prevent different species from producing offspring by preventing an attempted mating or by hindering fertilization if mating is completed successfully
postzygotic barriers
Any of several species-isolating mechanisms that prevent hybrids produced by two different species from developing into viable, fertile adults.
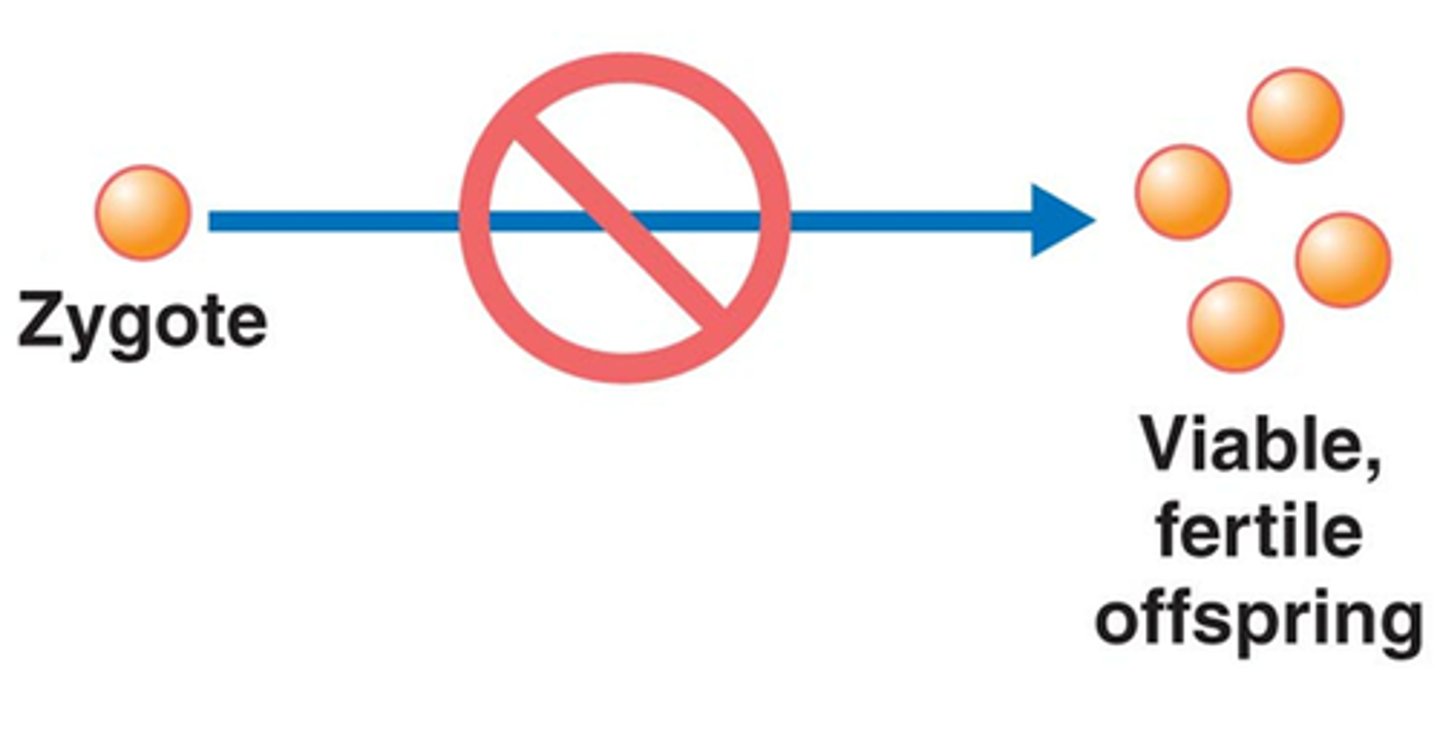
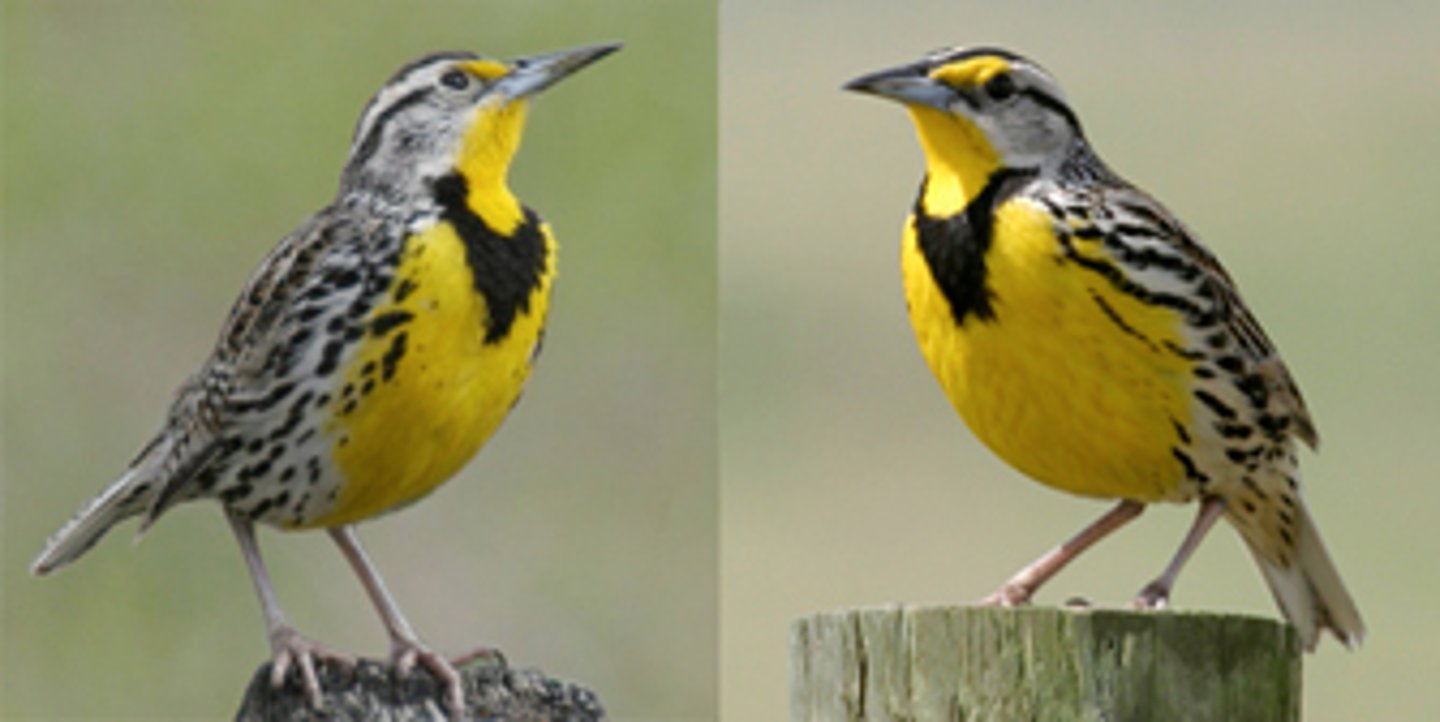
morphological species concept
A way to characterize a species by body shape and other structural features

paleontological species concept
A way to characterize species based on morphological differences known only from the fossil record.
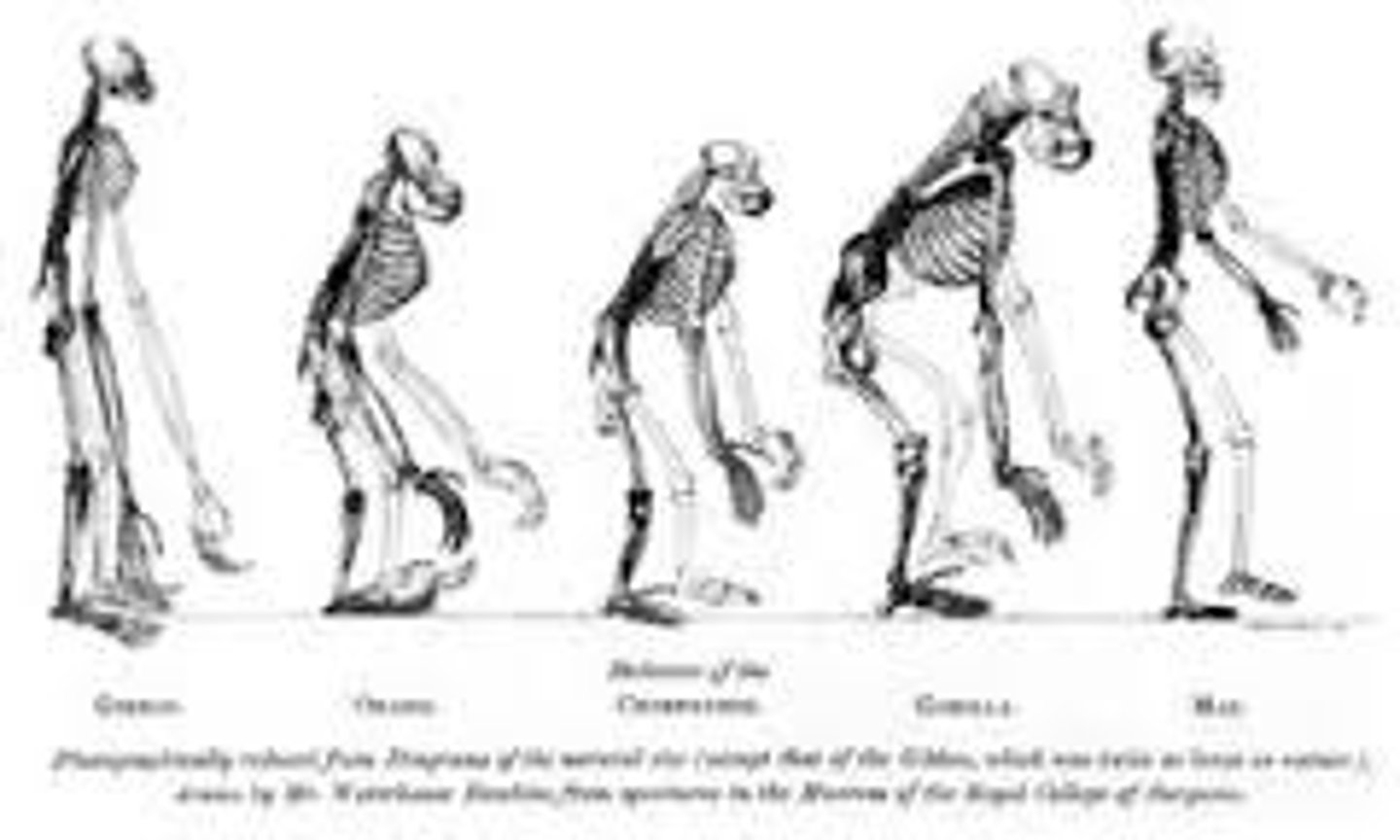
ecological species concept
A way to characterize species based on their ecological niche
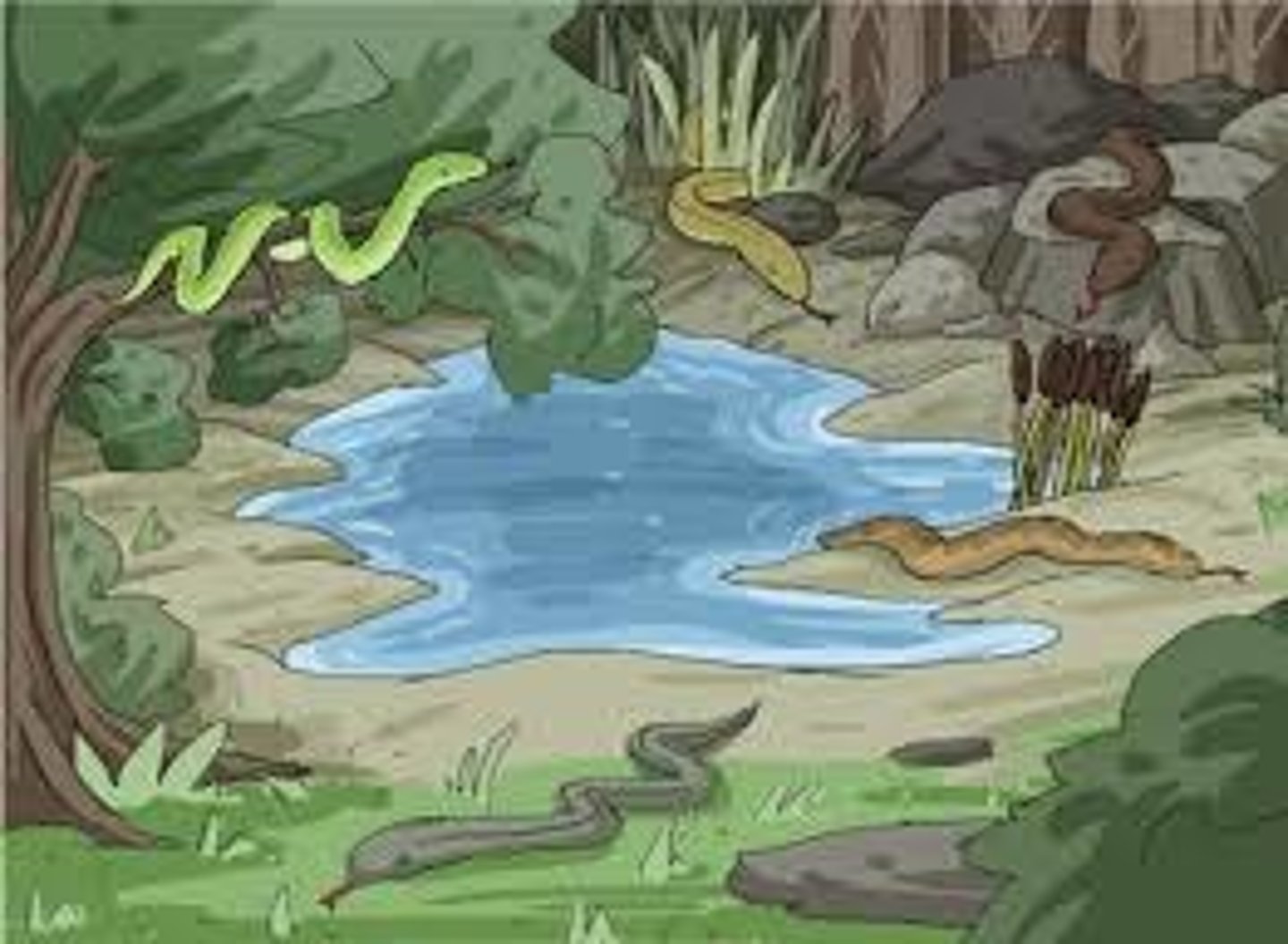

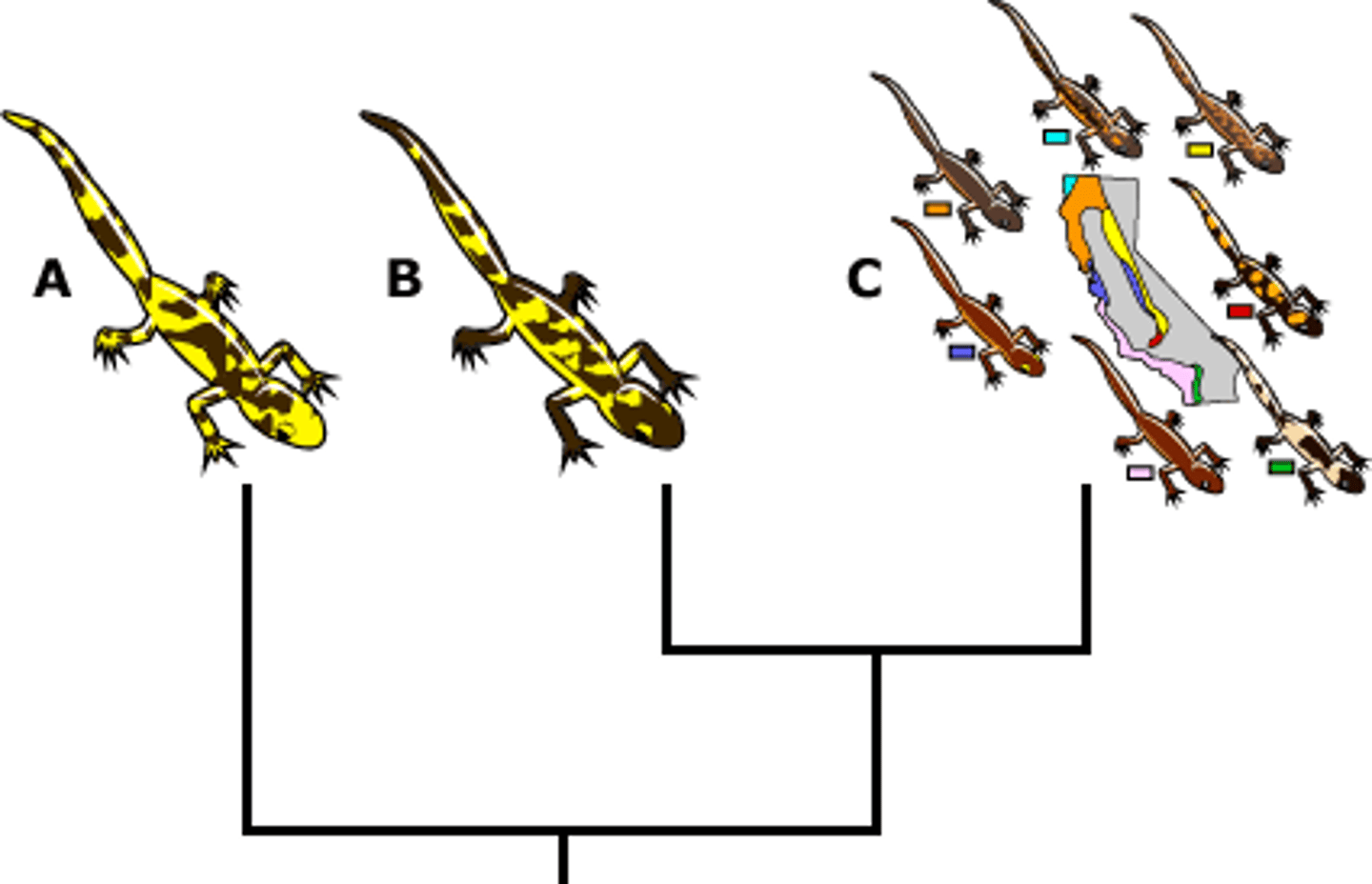
phylogenetic species concept
A way to characterize species as the smallest group of individuals that share a common ancestor
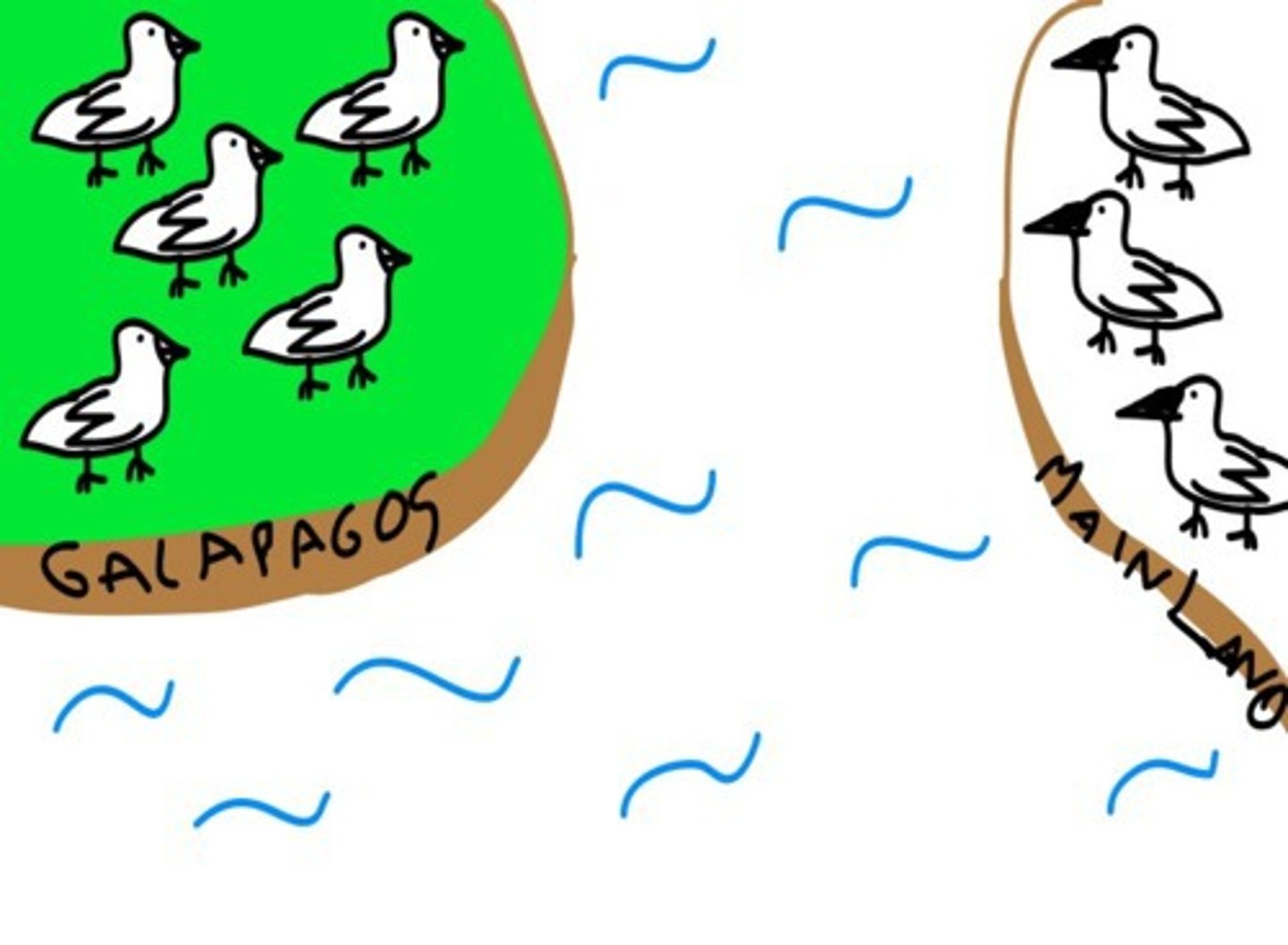
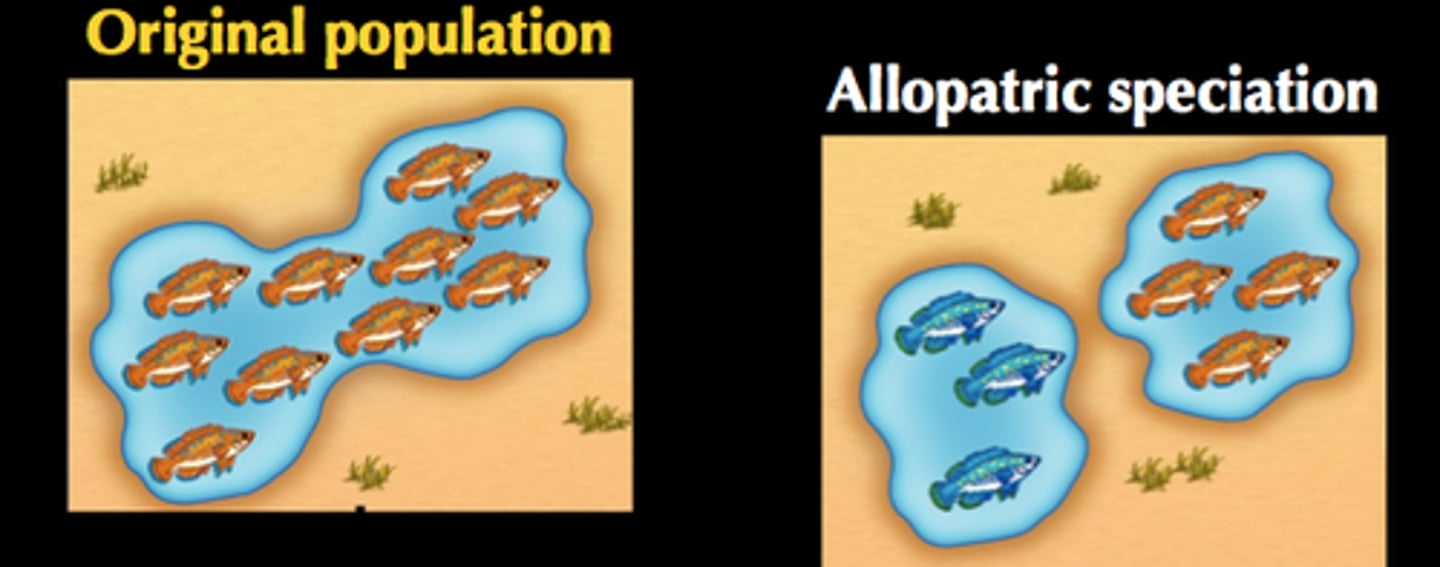
allopatric speciation
Speciation that occurs when a population is disrupted into geographically isolated populations
sympatric speciation
Speciation that occurs in populations that live in the same geographic area
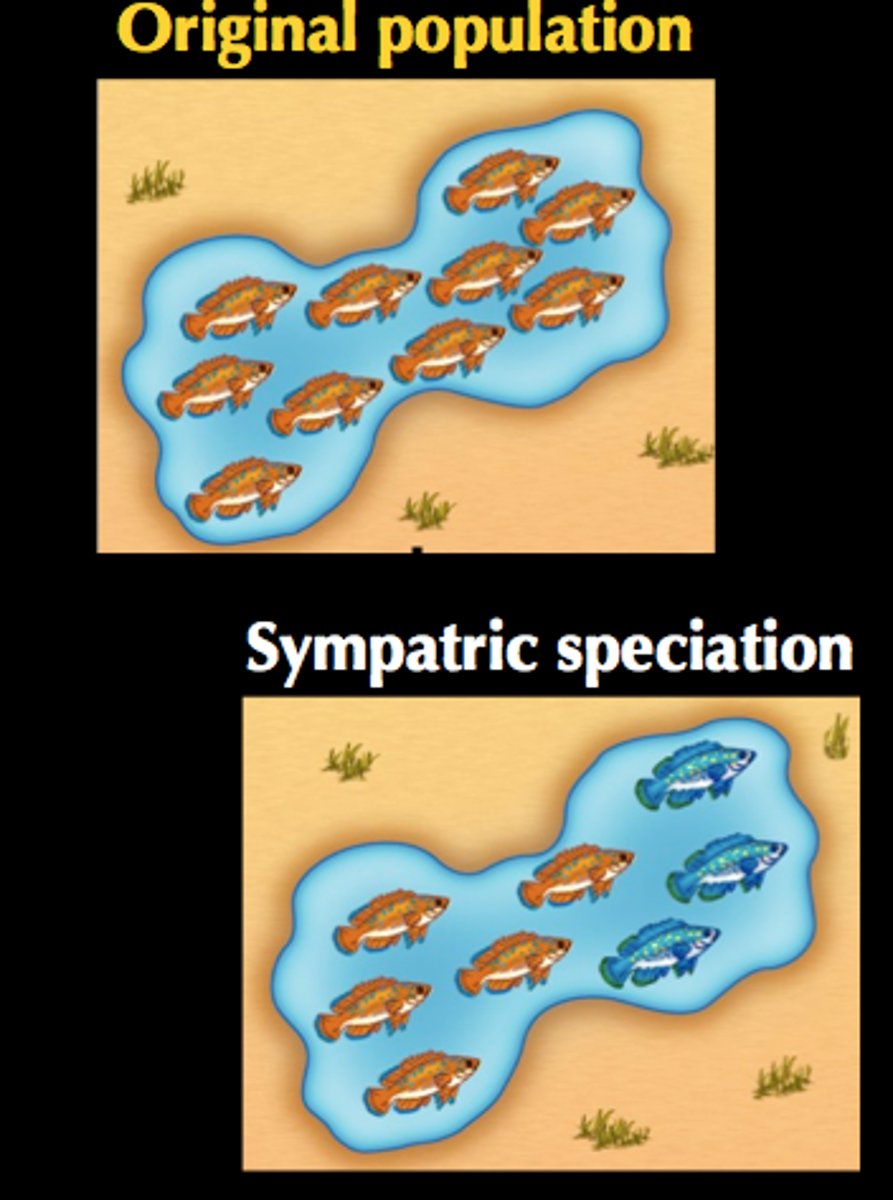
polyploidy
A chromosomal condition in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets.
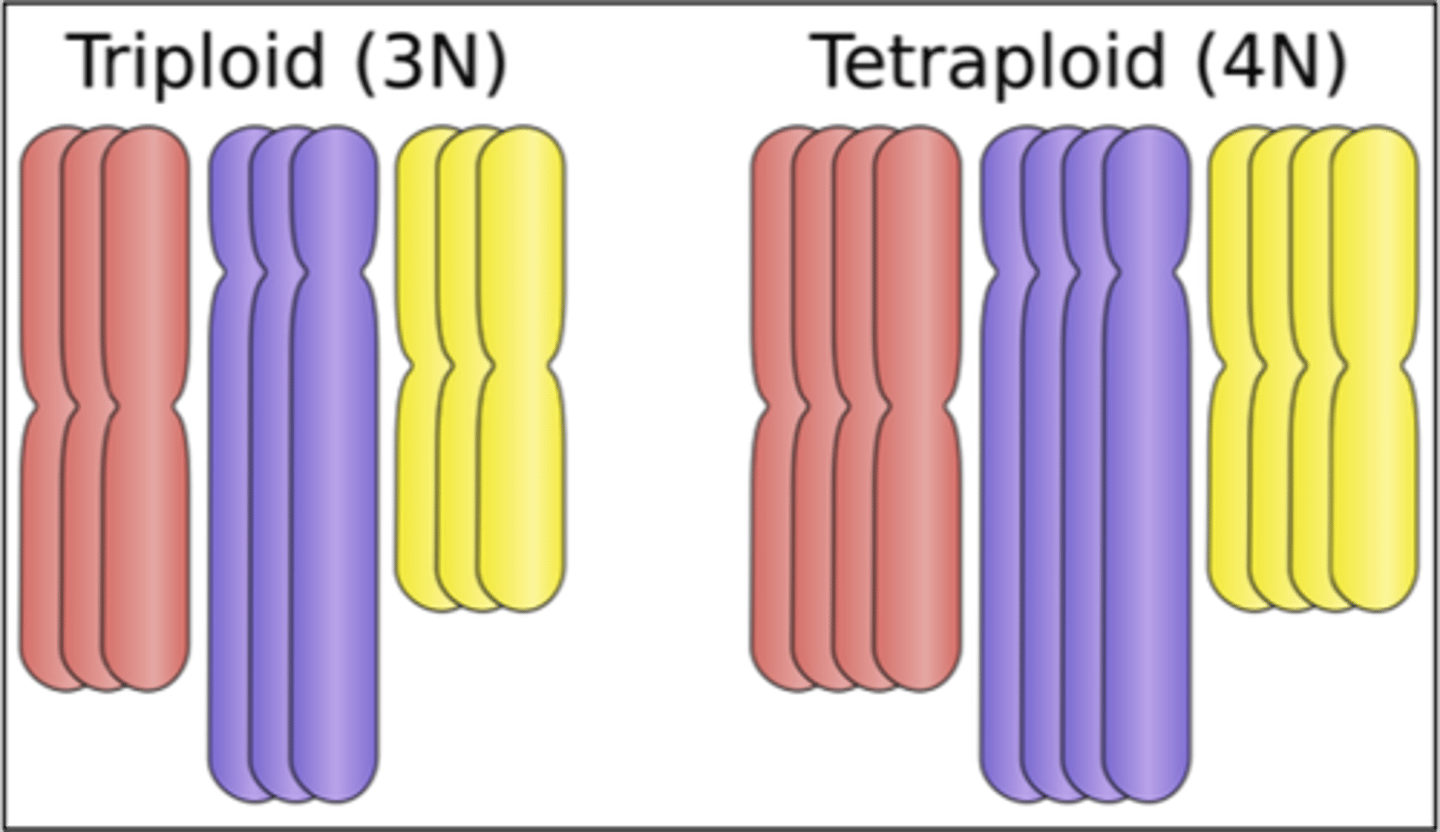
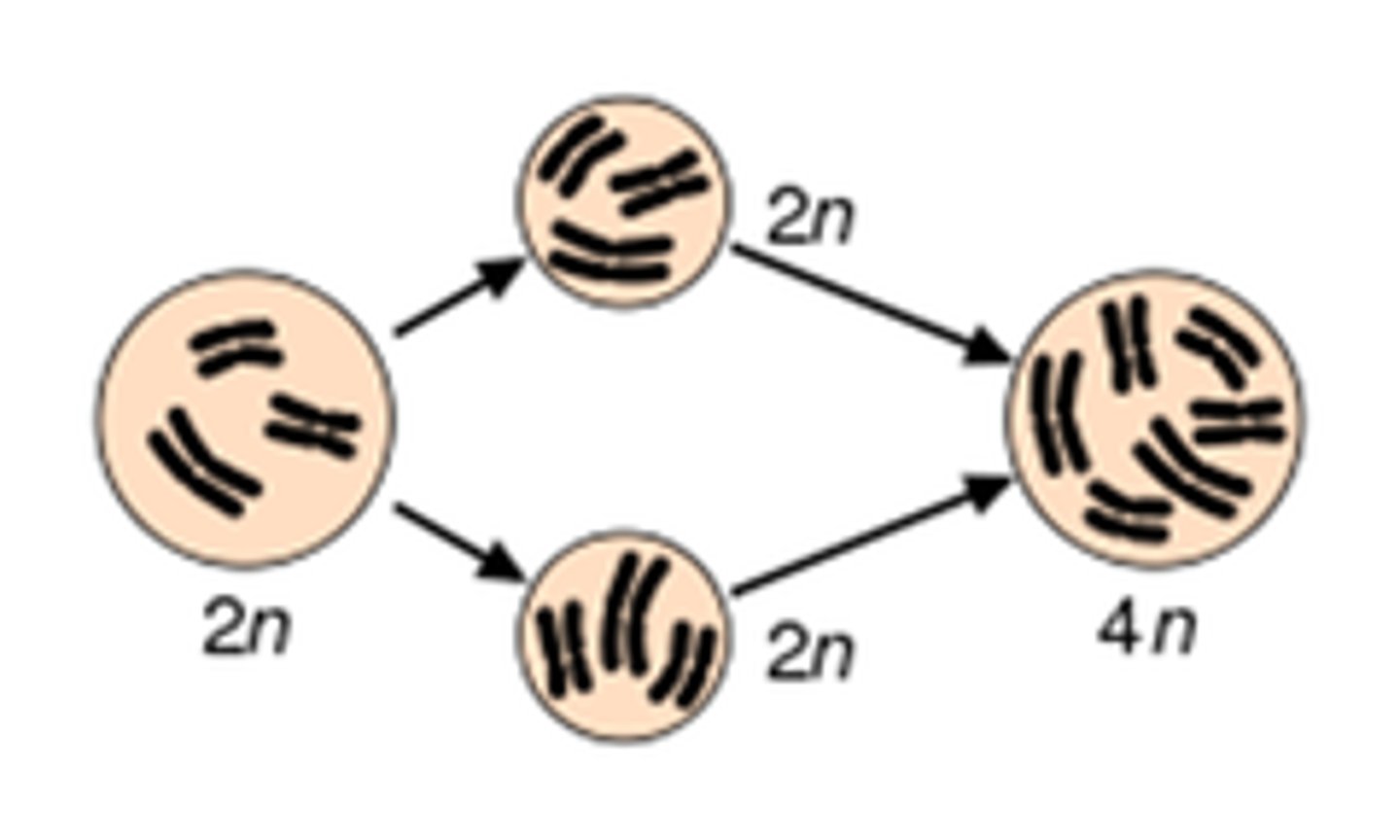
autopolyploidy
A form of polyploidy in which individuals have more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species
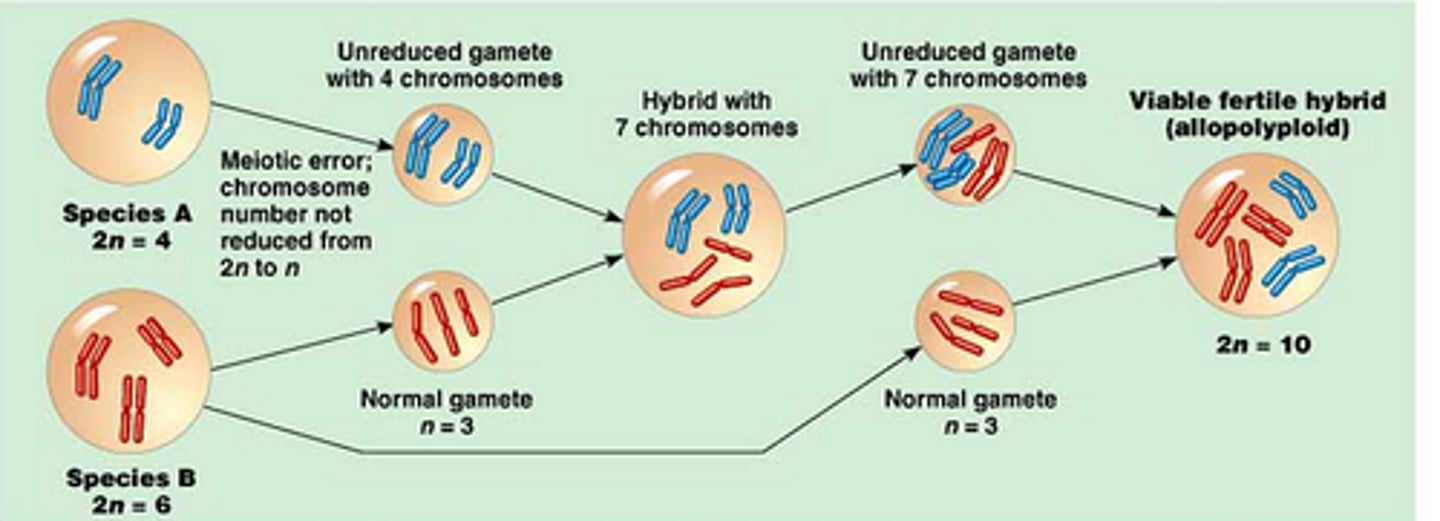
allopolyploidy
A form of polyploidy that forms when two different species interbreed and produce hybrid offspring that over generations can produce fertile offspring with each other, but not with either parent species
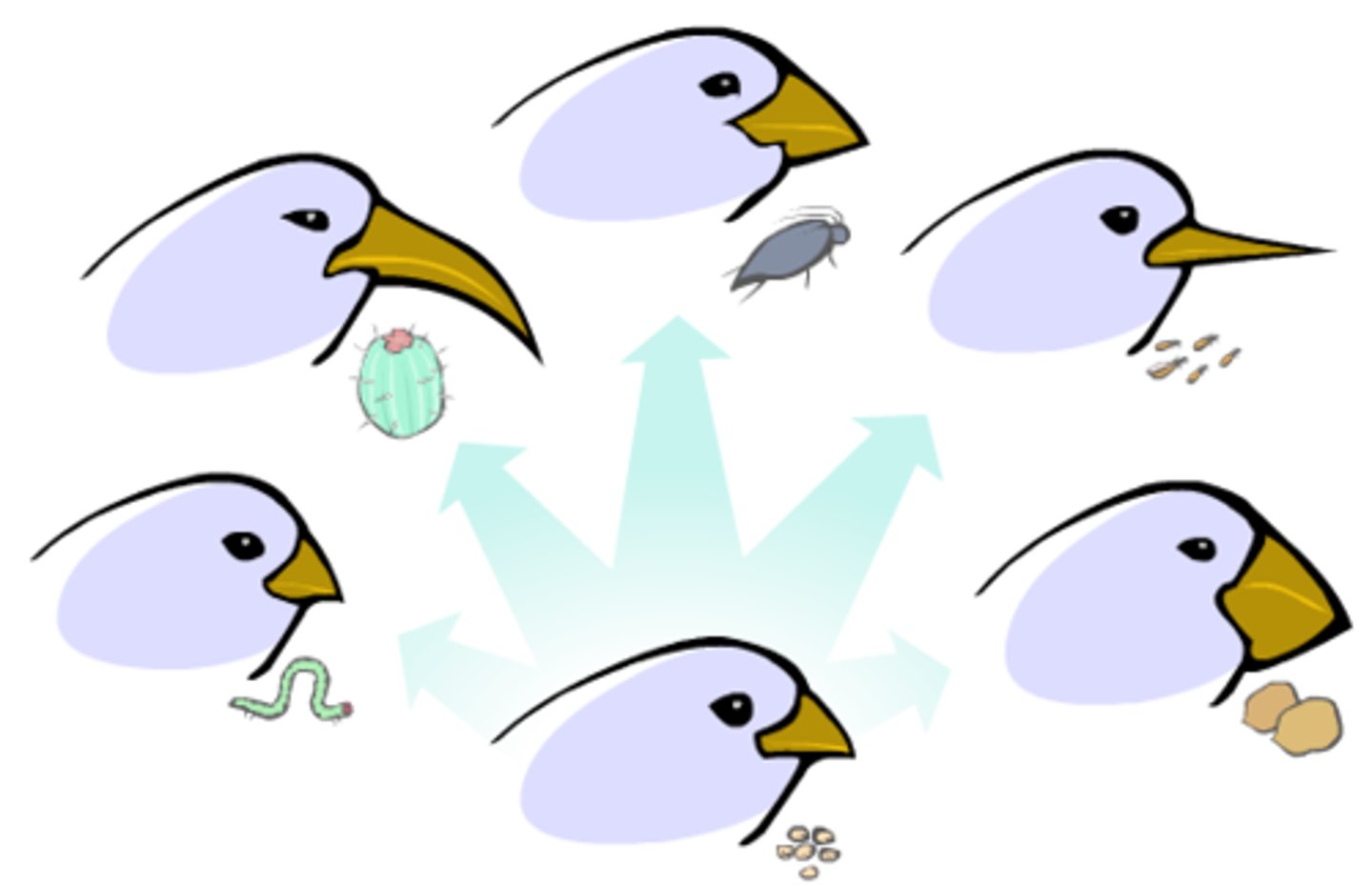
adaptive radiation
A process in which organisms diversify rapidly into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available