AP2 Heart to ECG - LECTURE REVIEW
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
atria
superior receiving chambers (space) of the heart
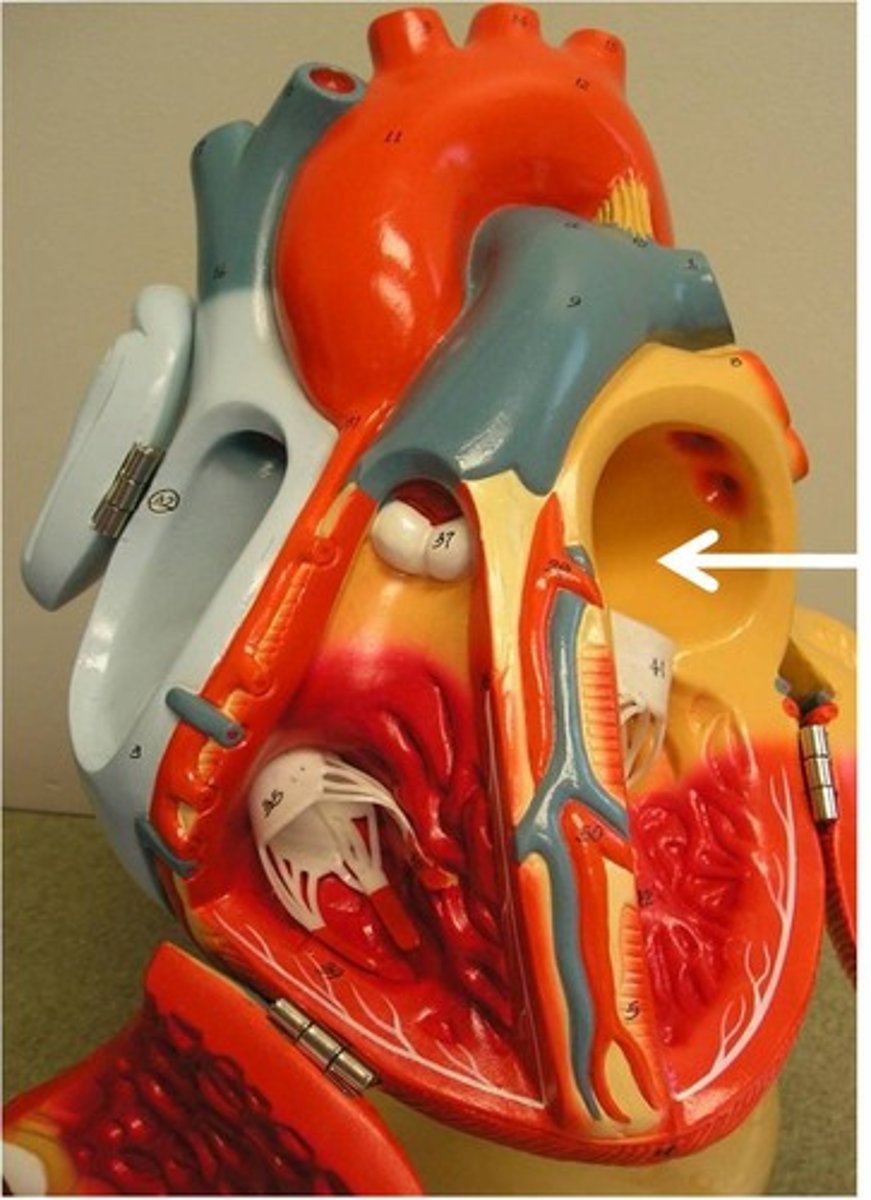
ventricles
inferior discharging chambers (space) of the heart
tricuspid
atrioventricular valve on the right side of the heart; between right atrium & right ventrical
mitral or bicuspid
atrioventricular valve on the left side of the heart; between the left atrium & left ventricle
pulmonary circuit
blood flow from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back to the left side of the heart; shorter & lower pressure; blood picks up oxygen "oxygen loading"
systemic circuit
blood flow from the left side of the heart through body tissues; longer & higher pressure; delivers oxygen to tissues "oxygen unloading"
bradycardia
slow heart rate below 60 bpm, may lead to inadequate blood circulation; may be desirable result of endurance training; R-R interval greater than 5 big boxes
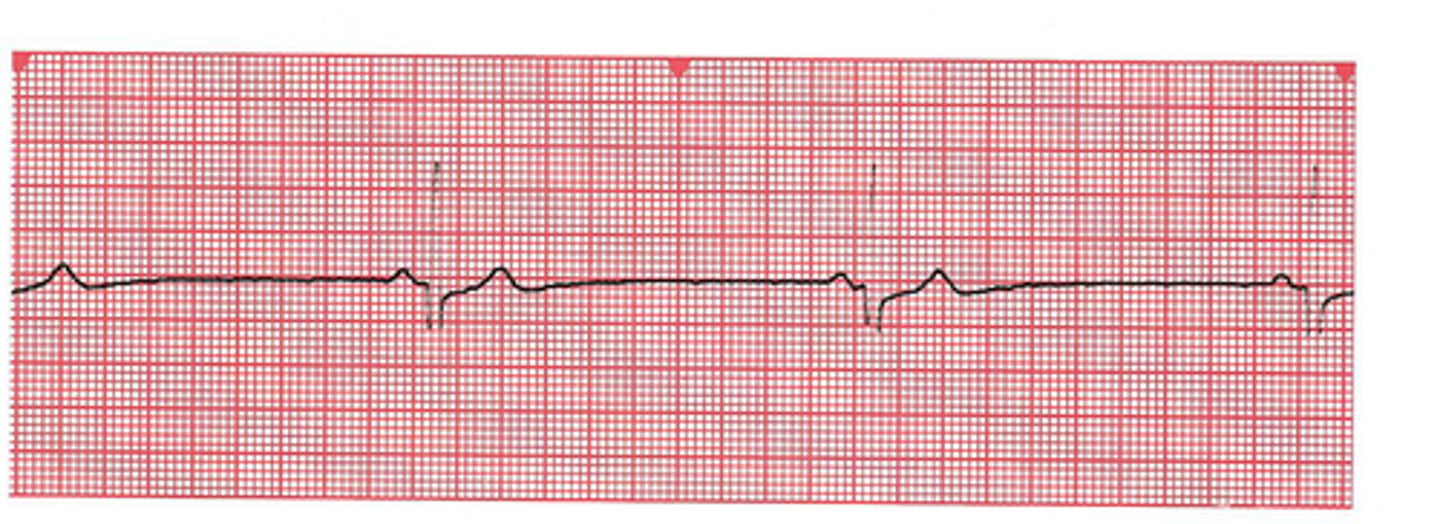
tachycardia
rapid heart rate over 100 bpm; less than 3 big boxes; may lead to fibrillation
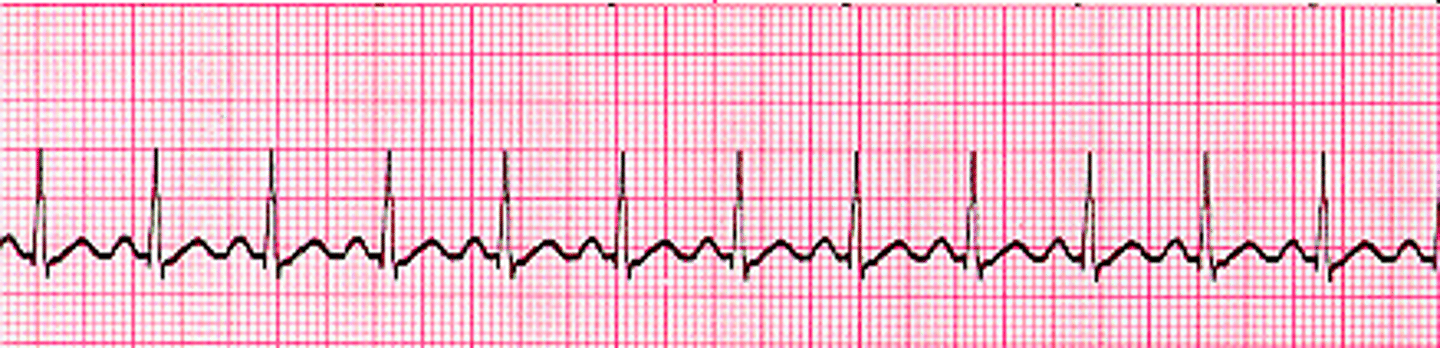
average heart rate
75 bpm
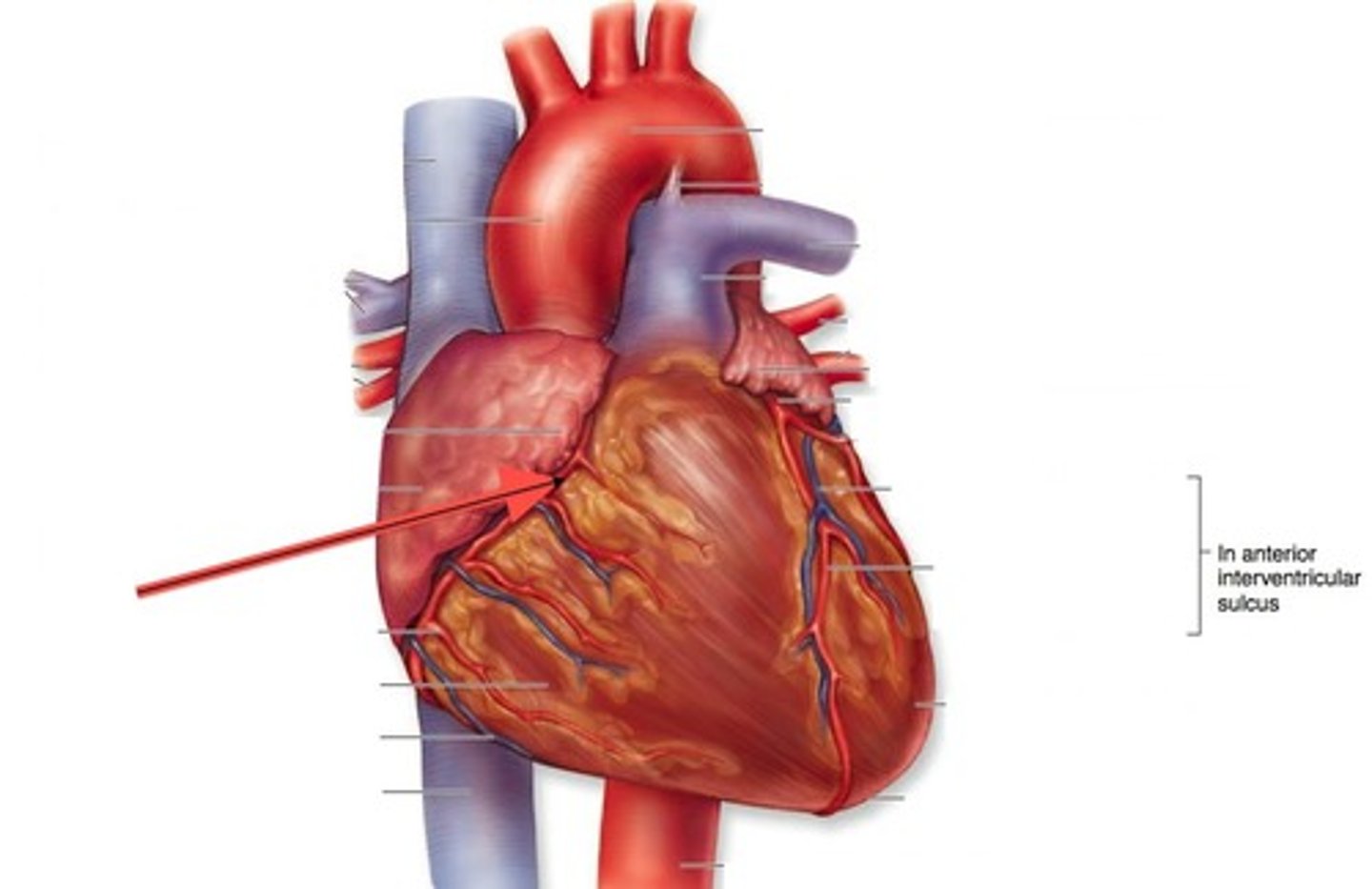
coronary
first R & L arteries to branch off aorta; supply the myocardium of the heart
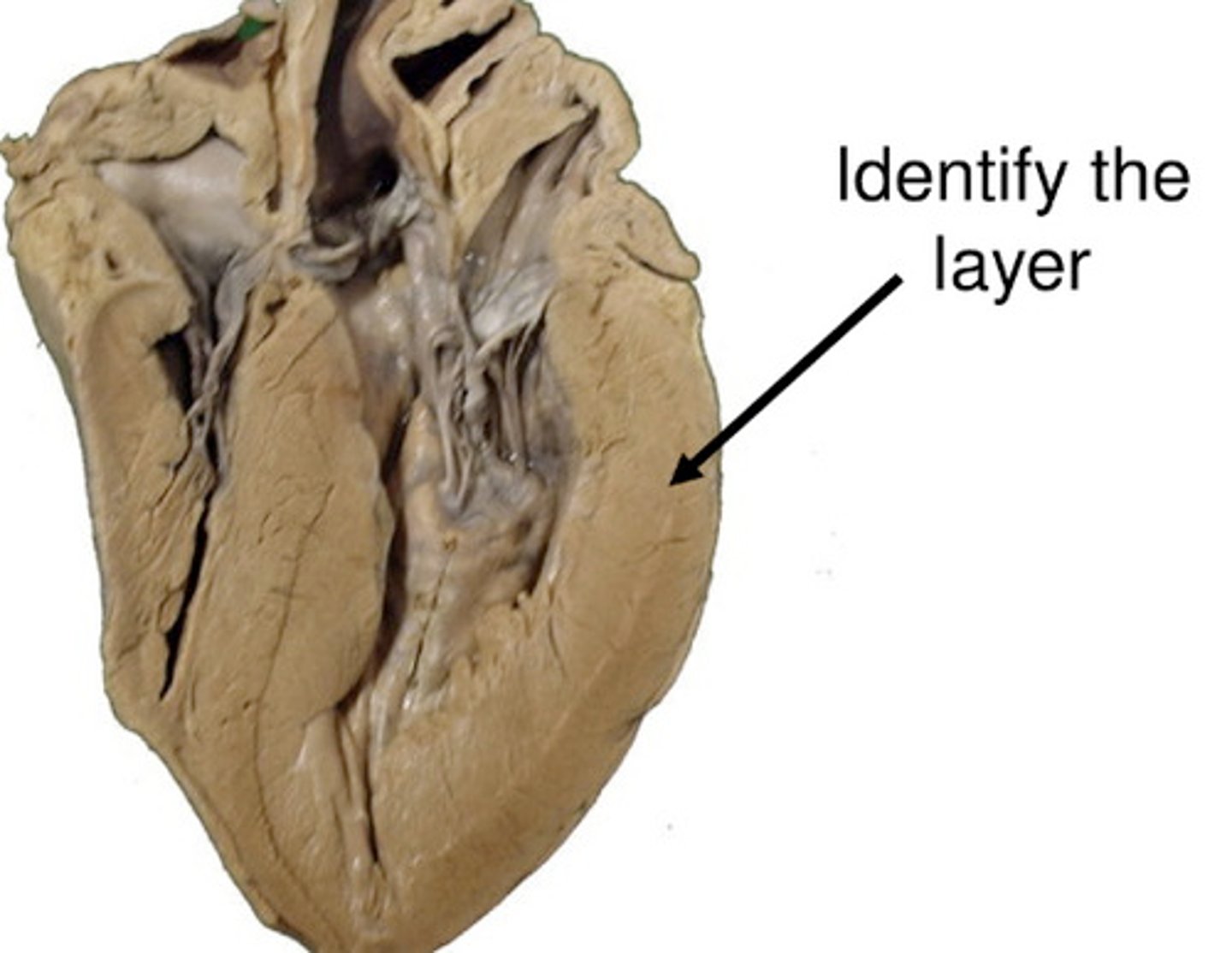
myocardium
term for heart muscle; middle layer; linked through gap junctions
pericardium
double walled sac around the heart that anchors and protects
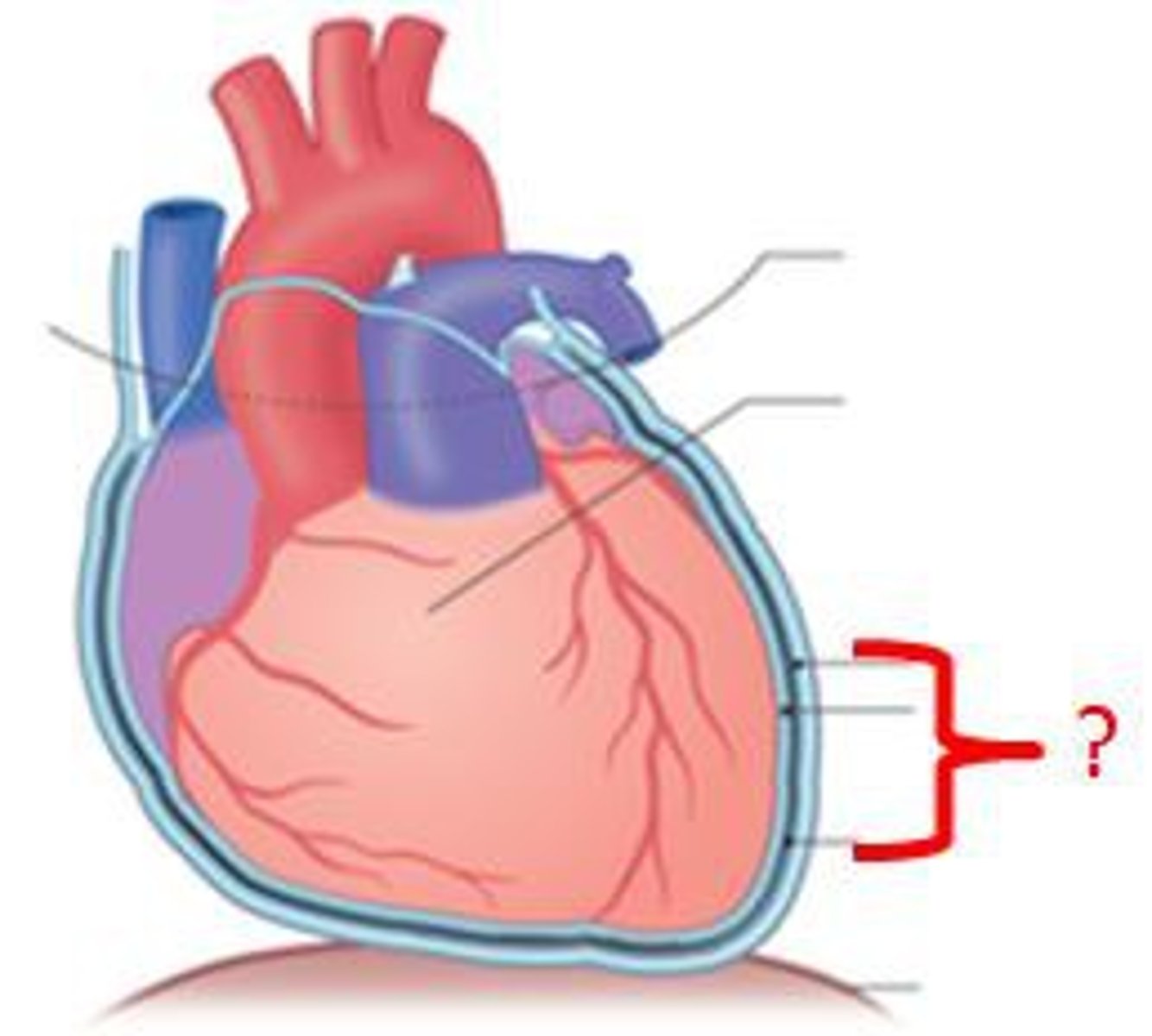
epicardium
layer of heart that is the same as the visceral layer of the heart
endocardium
continuous with endothelium of blood vessels, smooth inner lining of heart chambers; covers valves
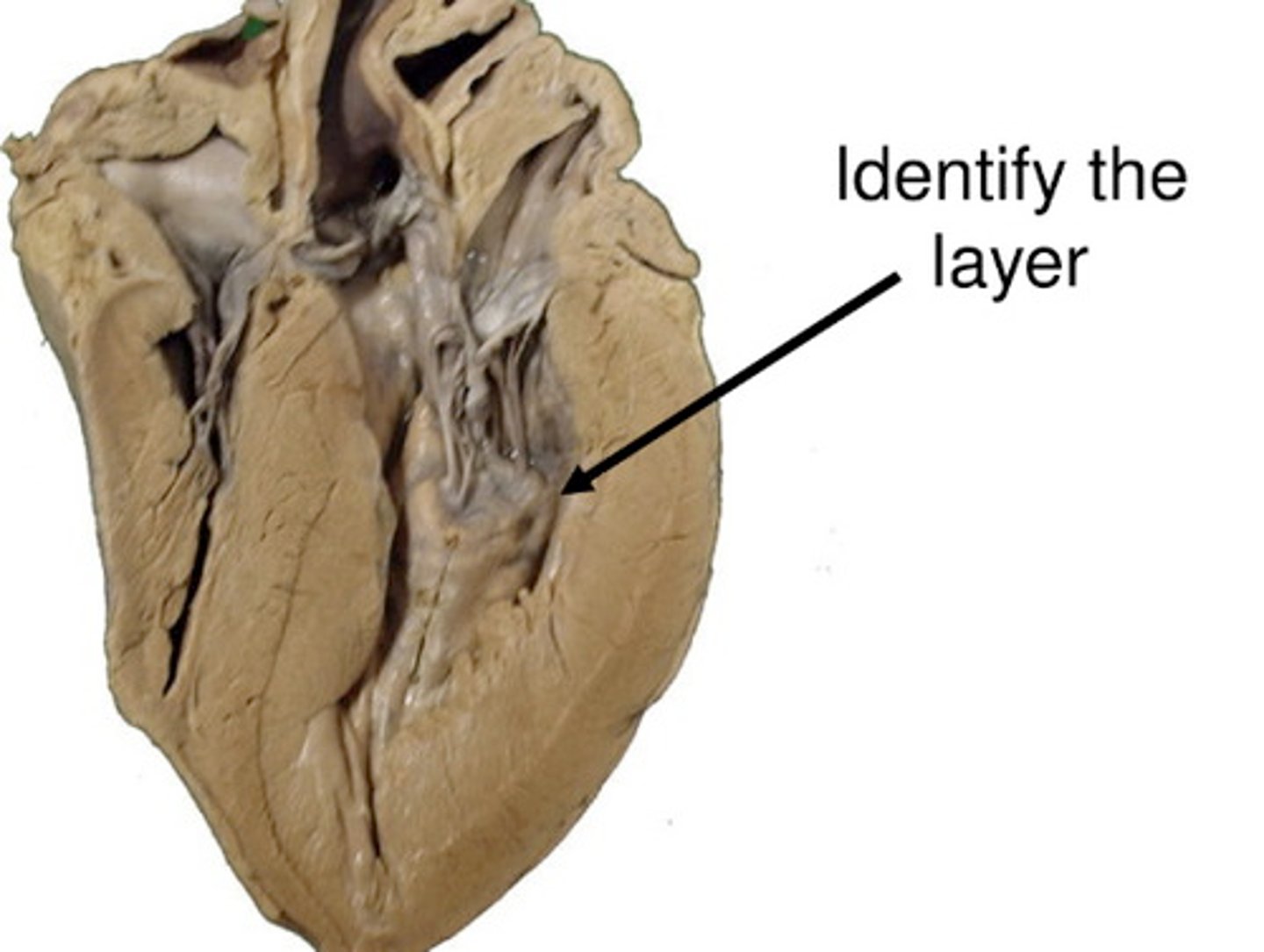
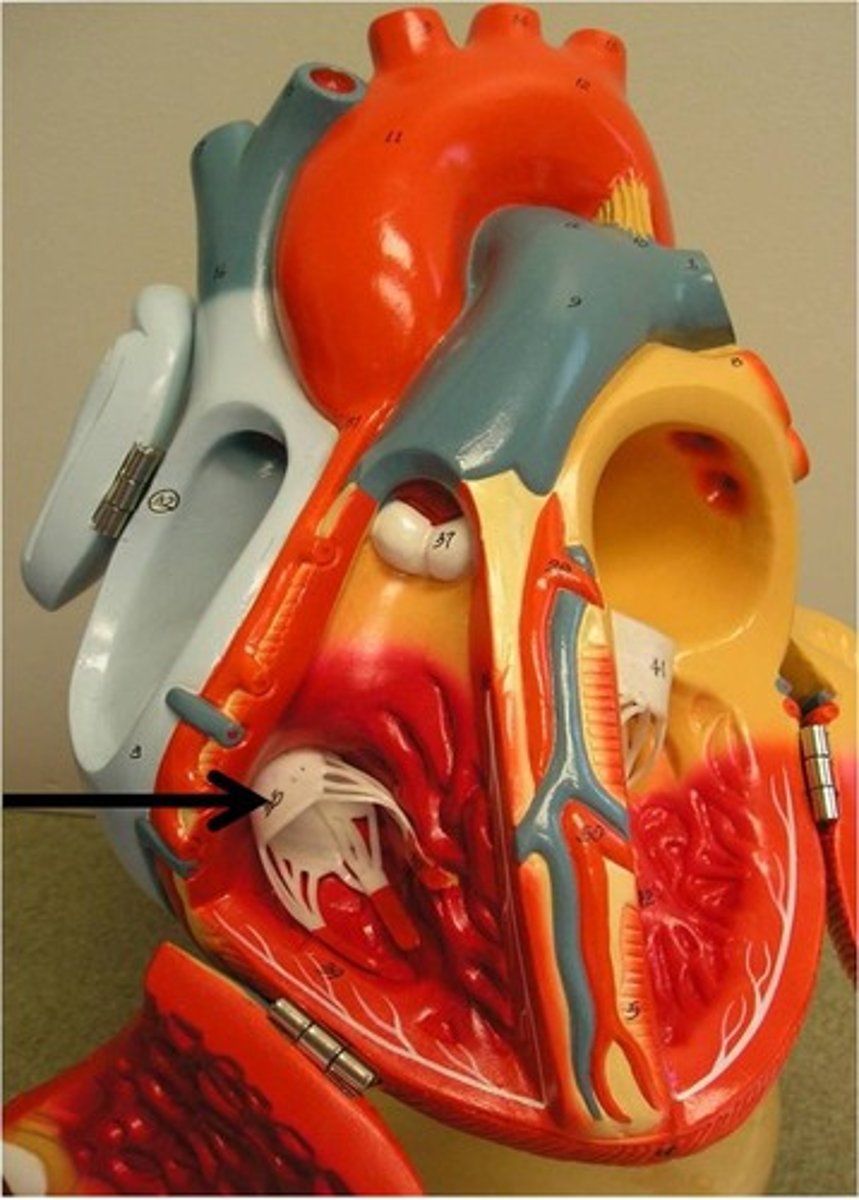
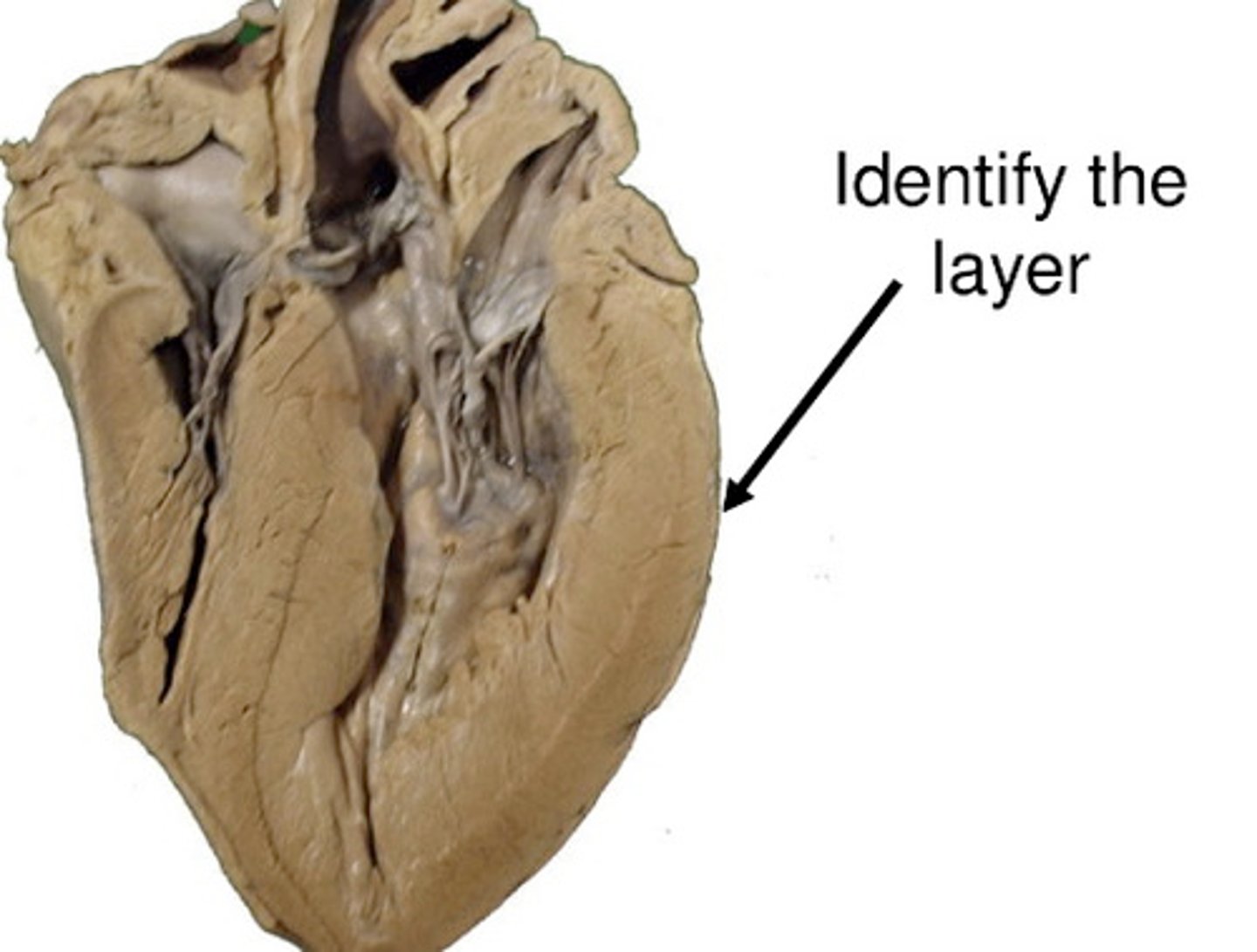
chordae tendineae
anchors the AV valves and prevent valve prolapse and leakage
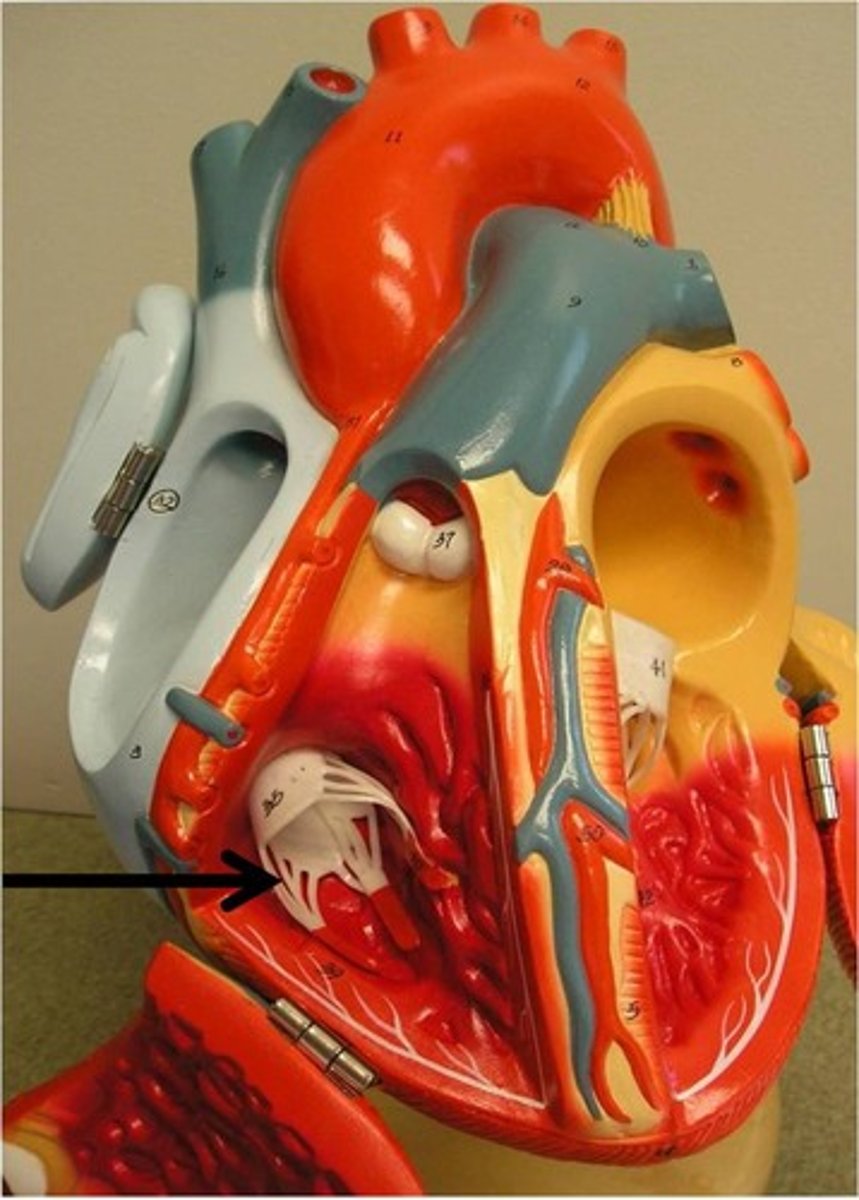
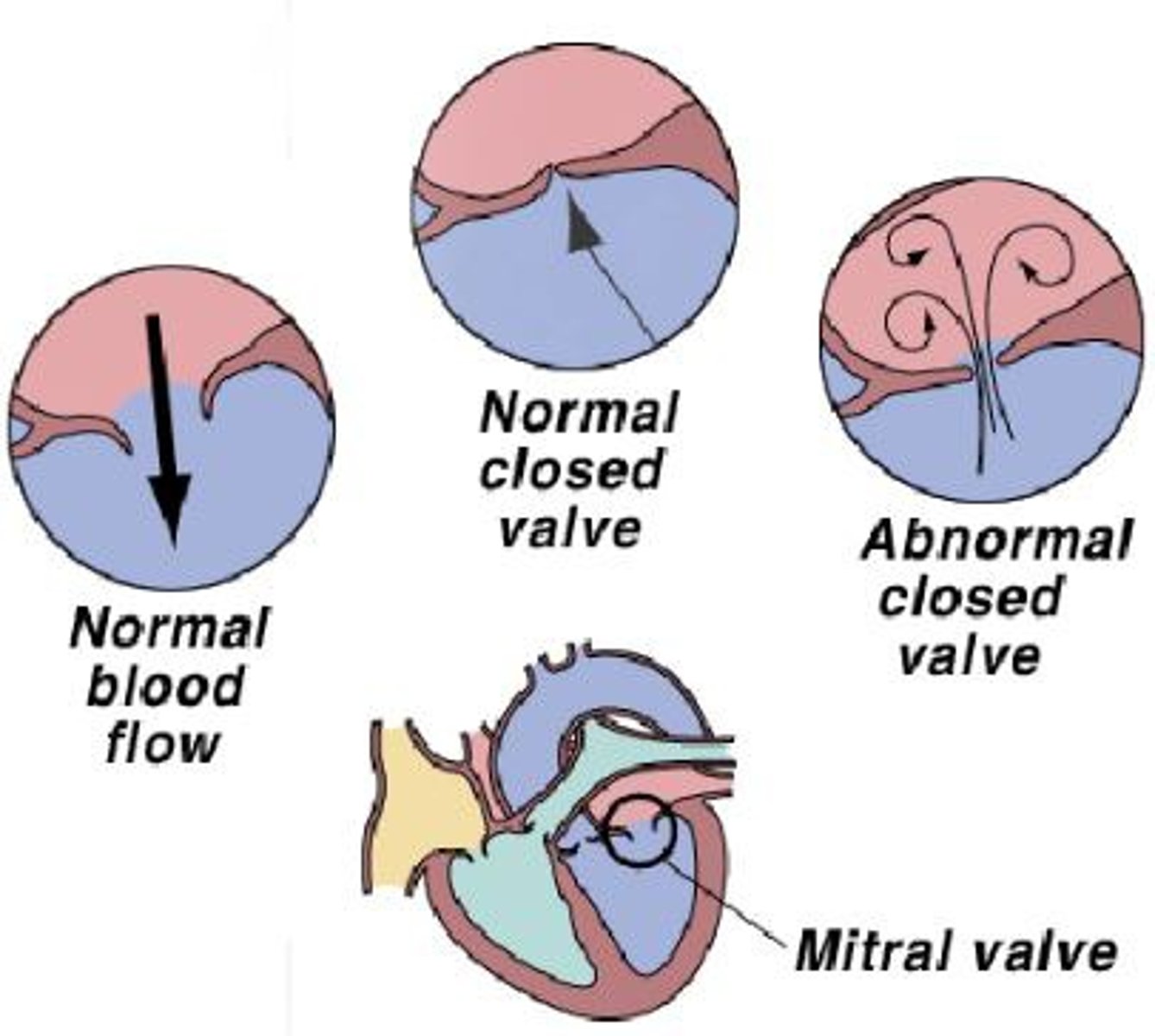
murmurs
abnormal heart sounds made by incompetent (leaky) or stenotic (stiff) valves
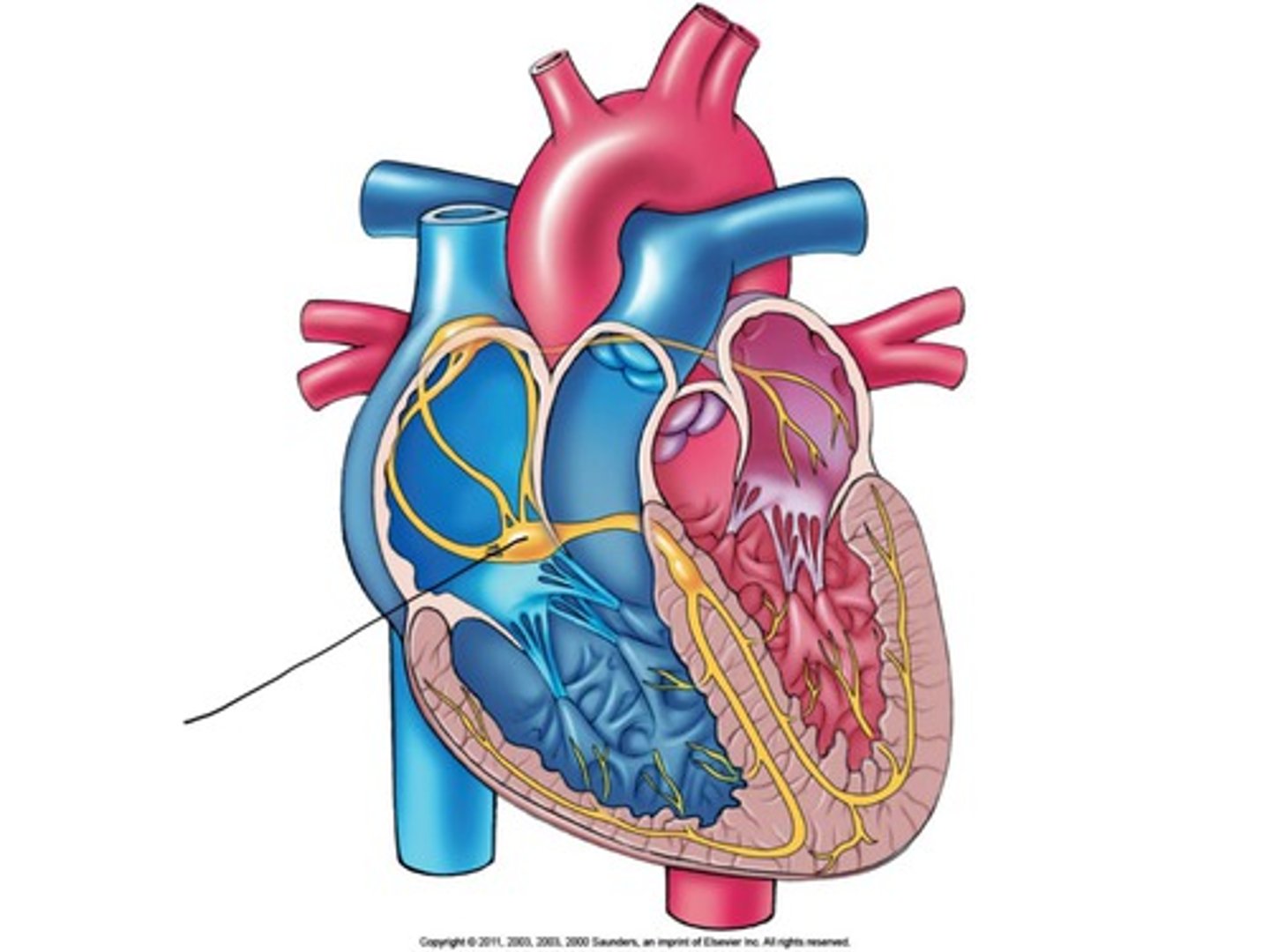
SA (sinoatrial) node
the pacemaker of the heart, 75 bpm
myocardial ischemia
reduced blood flow cutting off oxygen supply to the heart muscle; warning sign of impending heart attack
artery
blood vessel going away from the heart; efferent vessels
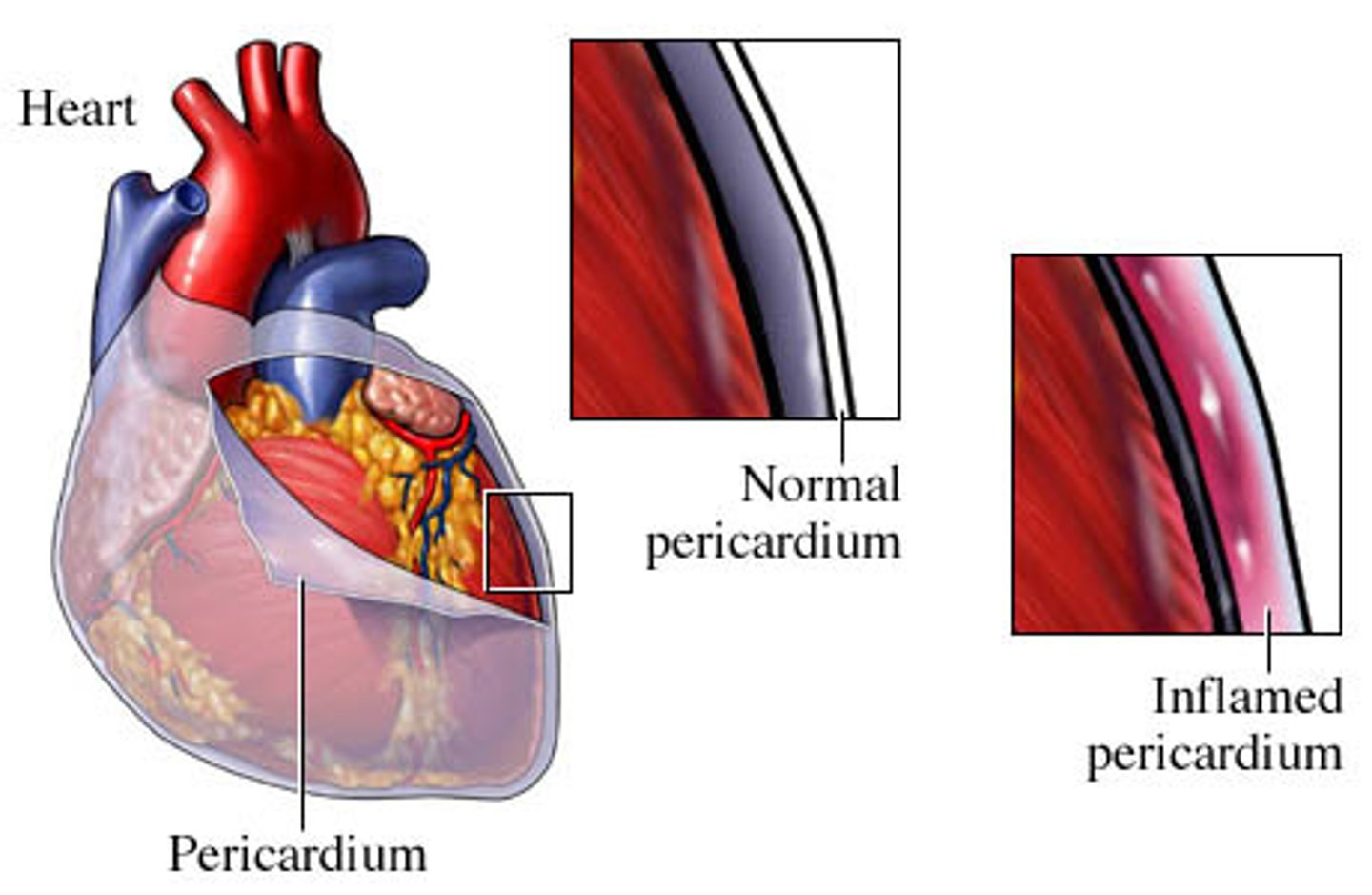
pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium; can be heard as friction rub during auscultation
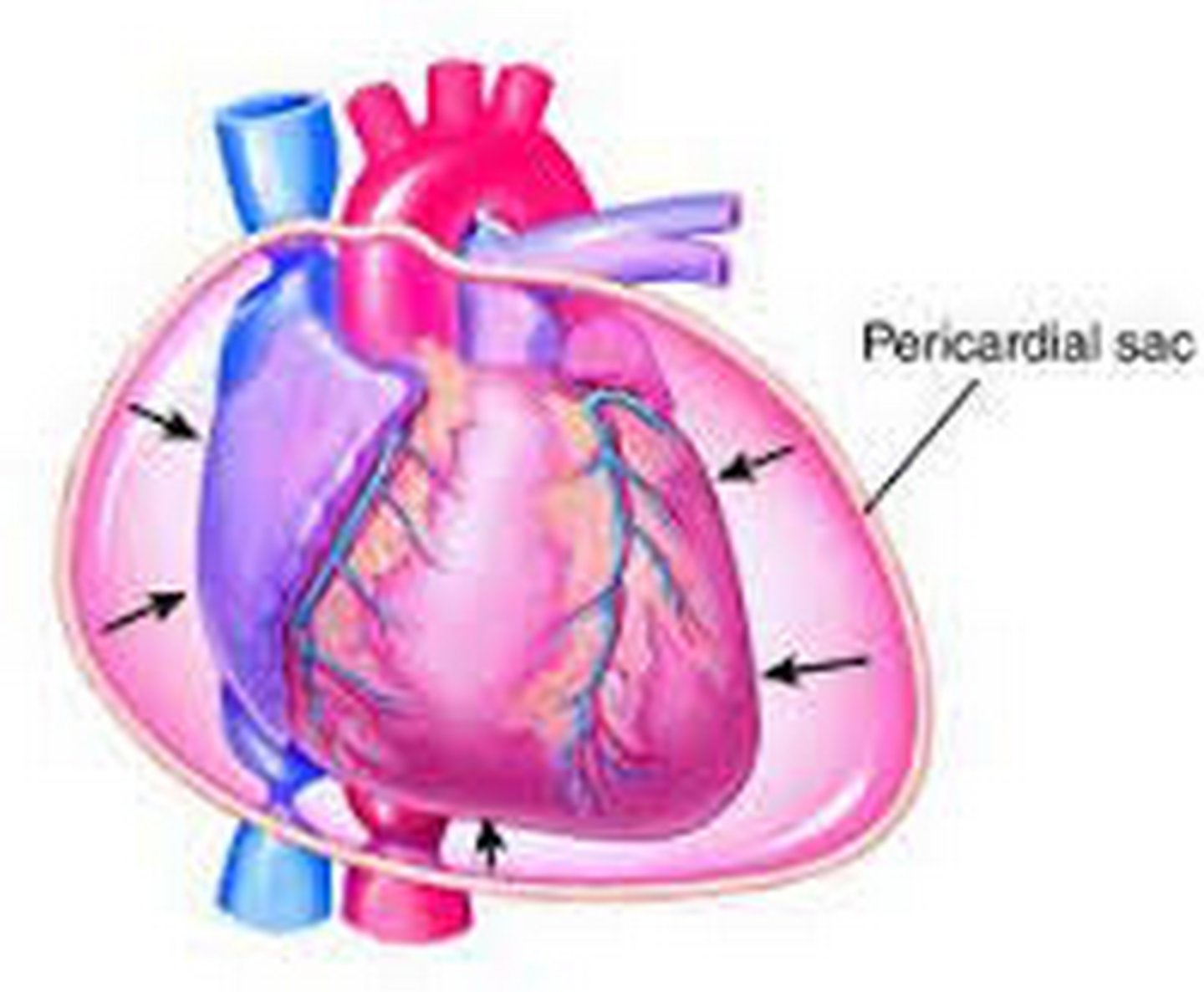
cardiac tamponade
excess pericardial fluid which limits the pumping ability of the heart
auricles
external ear or flap like appendages of the atria
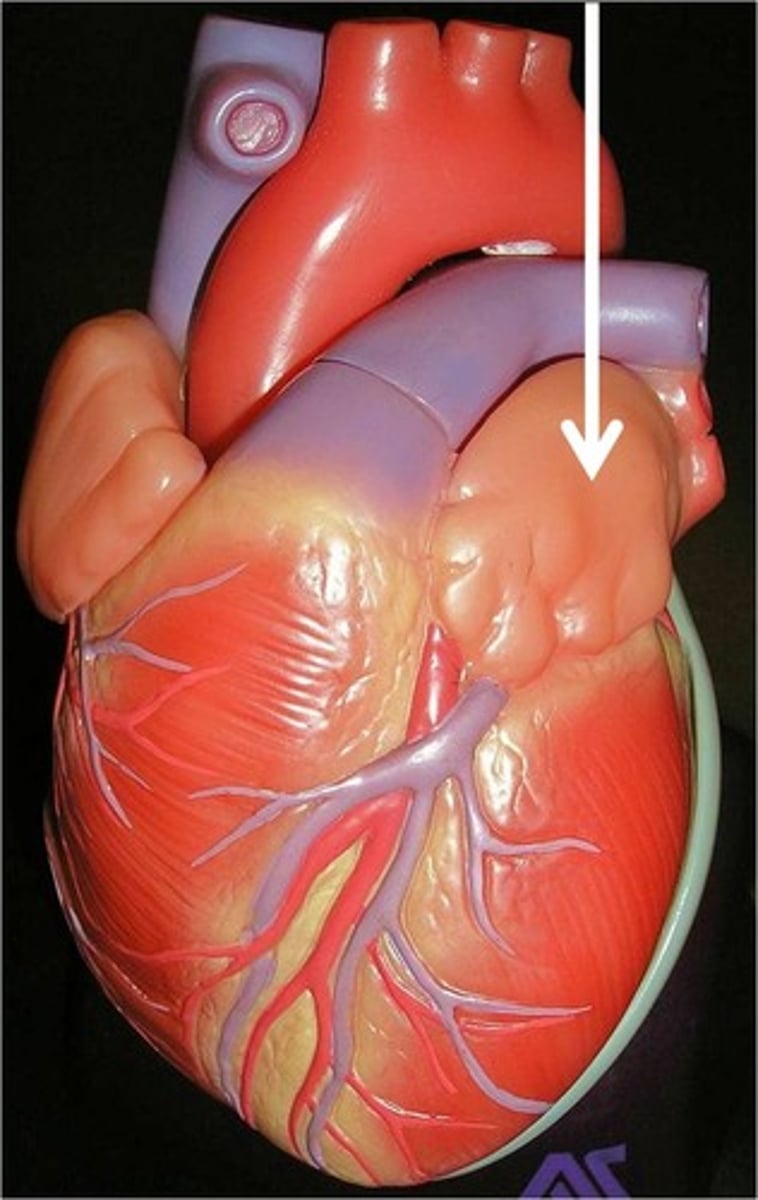
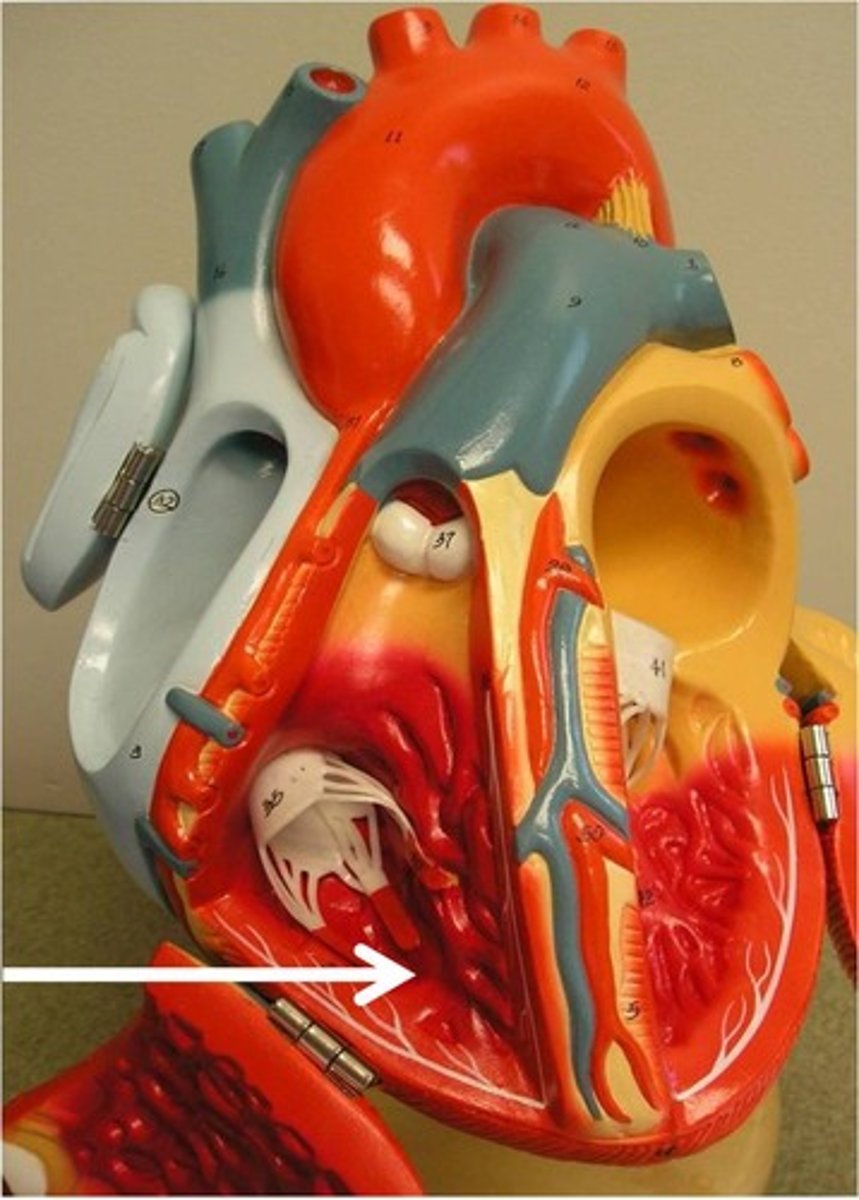
pectinate muscle
ridges of muscle found in the atria
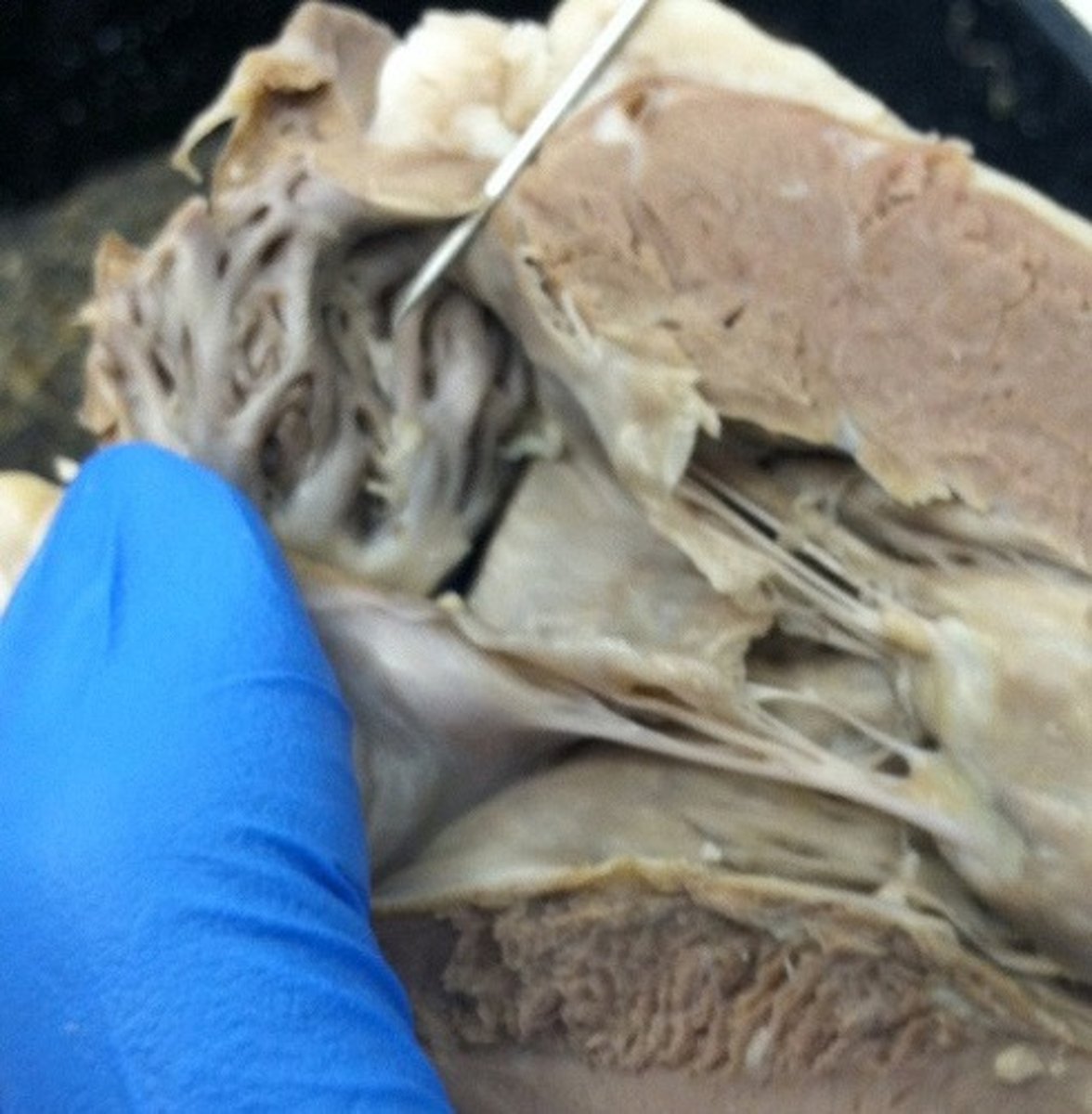
interatrial septum
wall between the atria
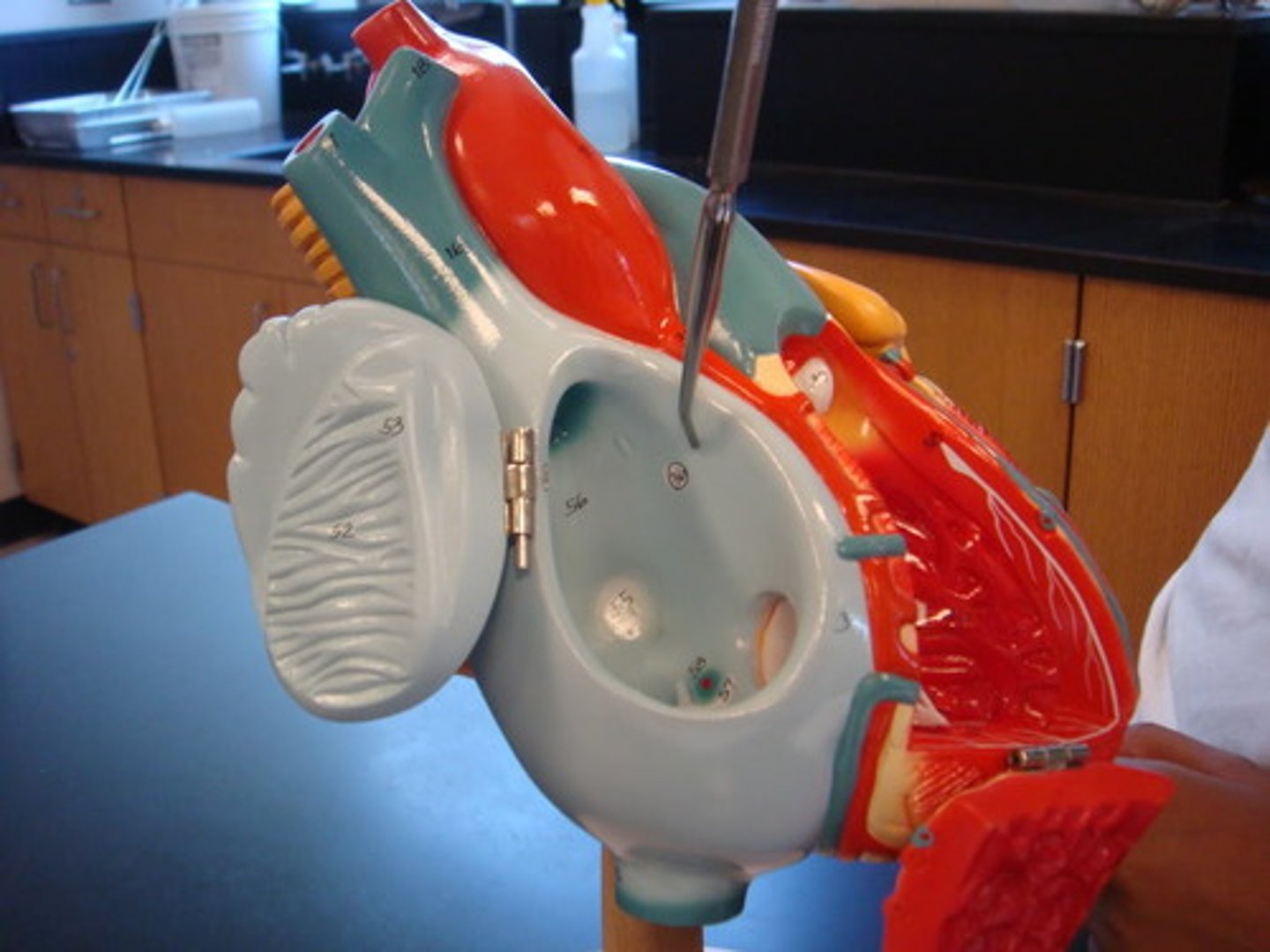

interventricular septum
wall between the ventricles
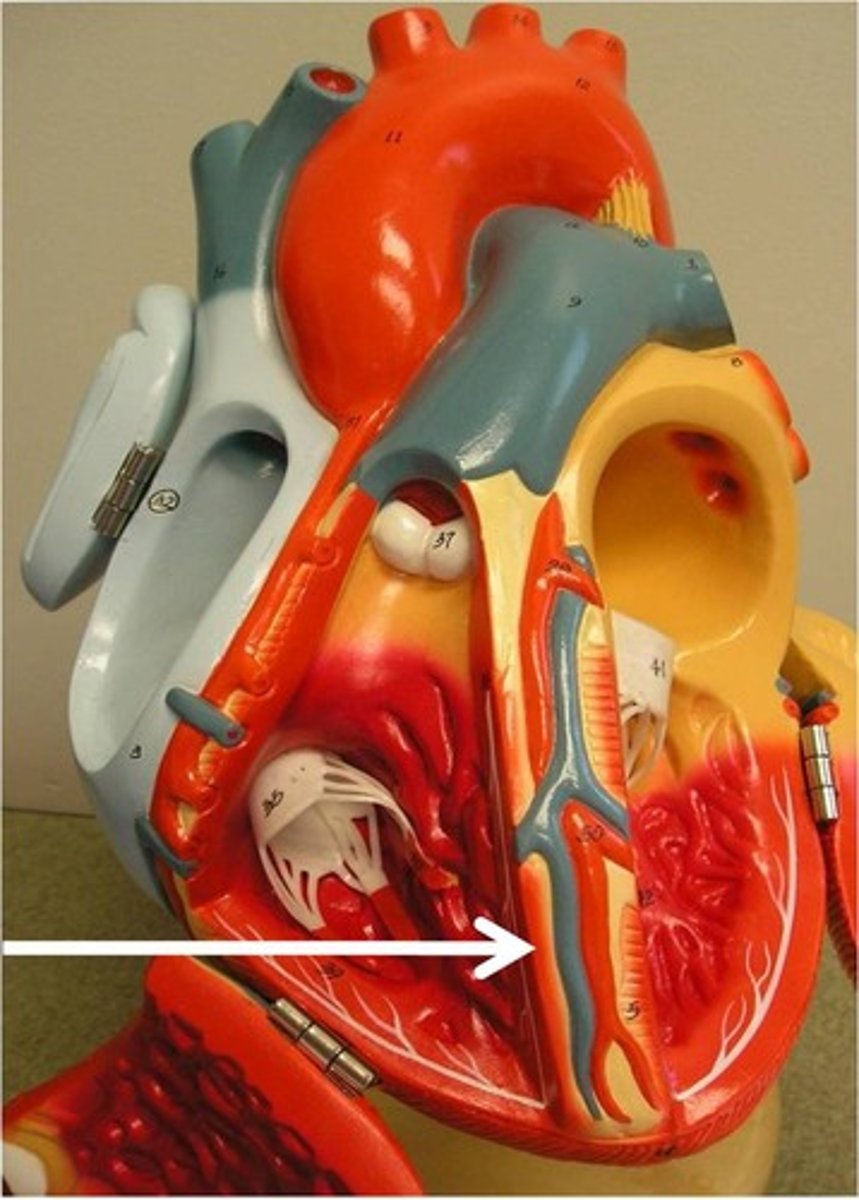
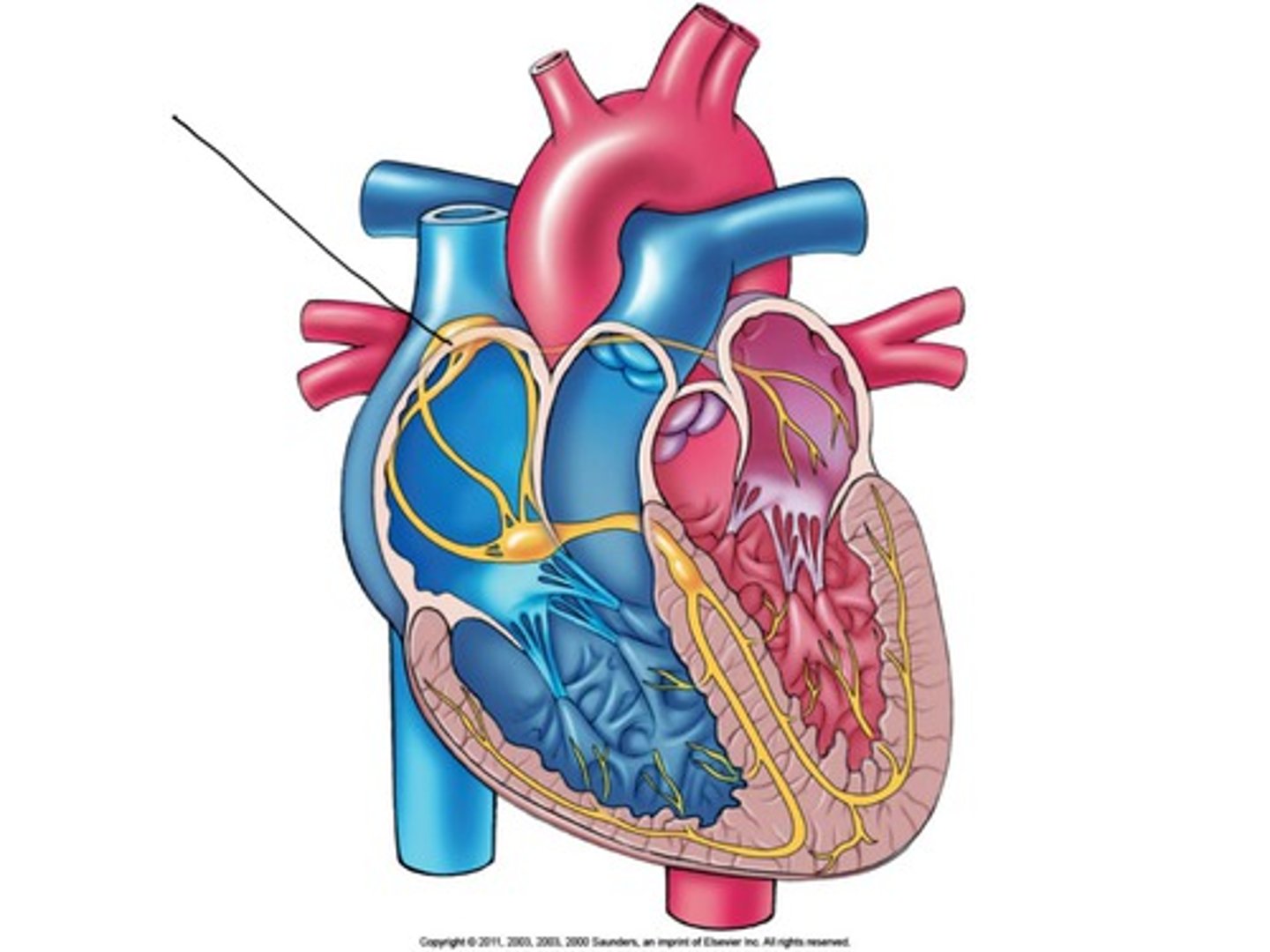
intrinsic cardiac conduction system
sinoatrial SA node, atrioventricular AV node, atrioventricular AV bundle, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers or subendocardial conduction network; ensures coordinated heart contraction
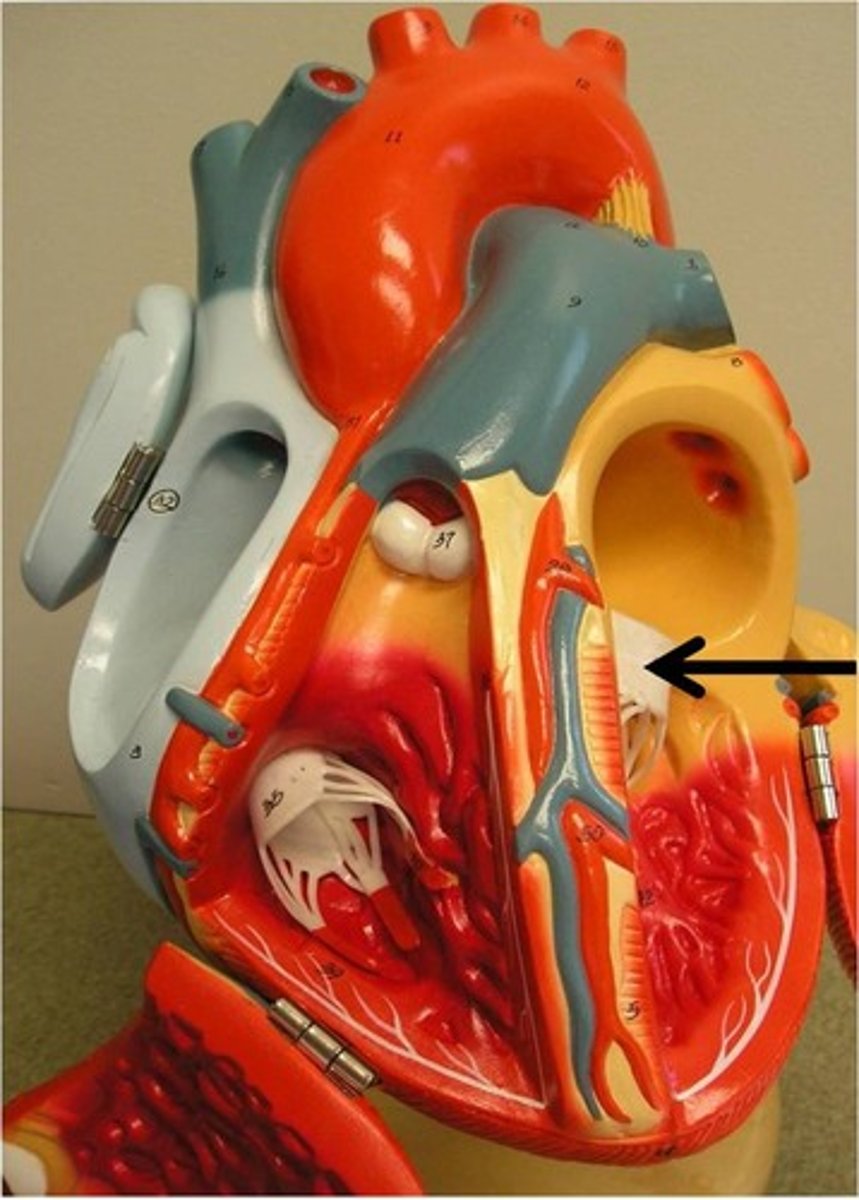
papillary muscles
cone-like muscular extensions of the myocardium, attached to chordae tendinea and AV valves; contract to keep valves closed and prevent prolapse (valvular inversion)
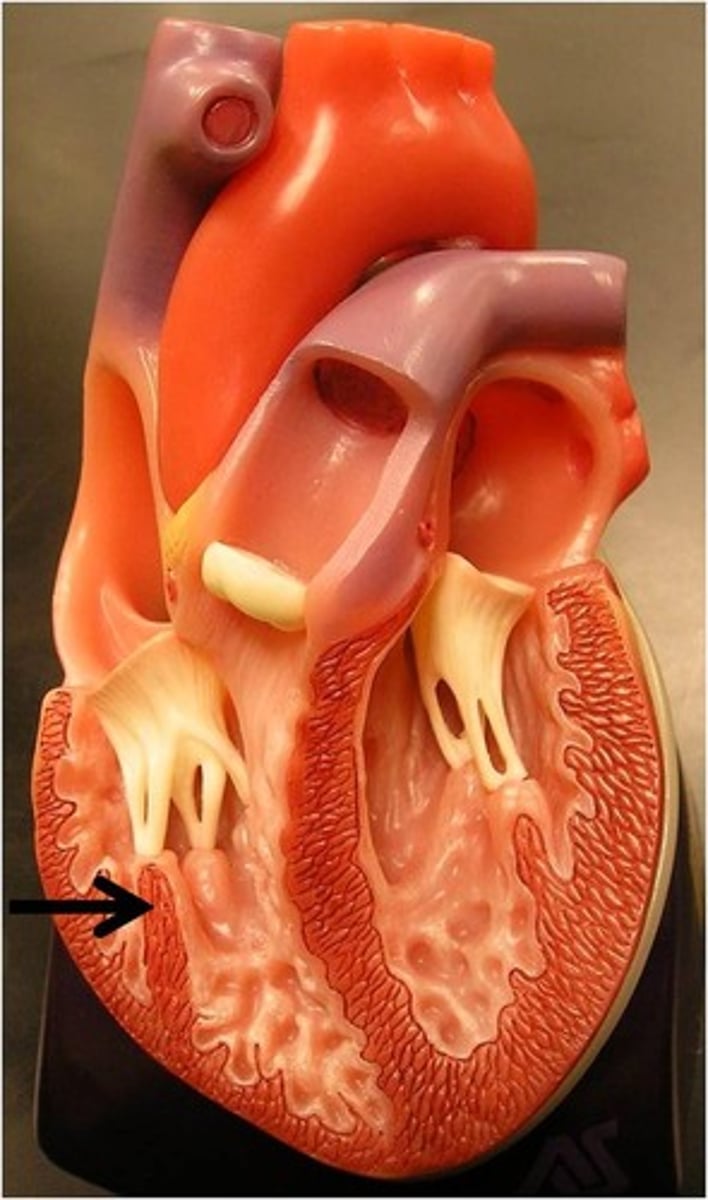
causes of valve disease
congenital, acquired thru infections like endocarditis or rheumatic fever or due to stiffening with age.
valvular stenosis
stiffening and narrowing of heart valves; hard to pump through, heard as a murmur
3 vessels that feed into the right atrium
superior and inferior vena cavae and coronary sinus; carrying deoxygenated blood
vessels that feed into the left atrium
4 pulmonary veins; carrying oxygenated blood
angina pectoris
means "choked chest"; caused by restricted blood flow to myocardium especially during exertion and hypoxia (low oxygen)
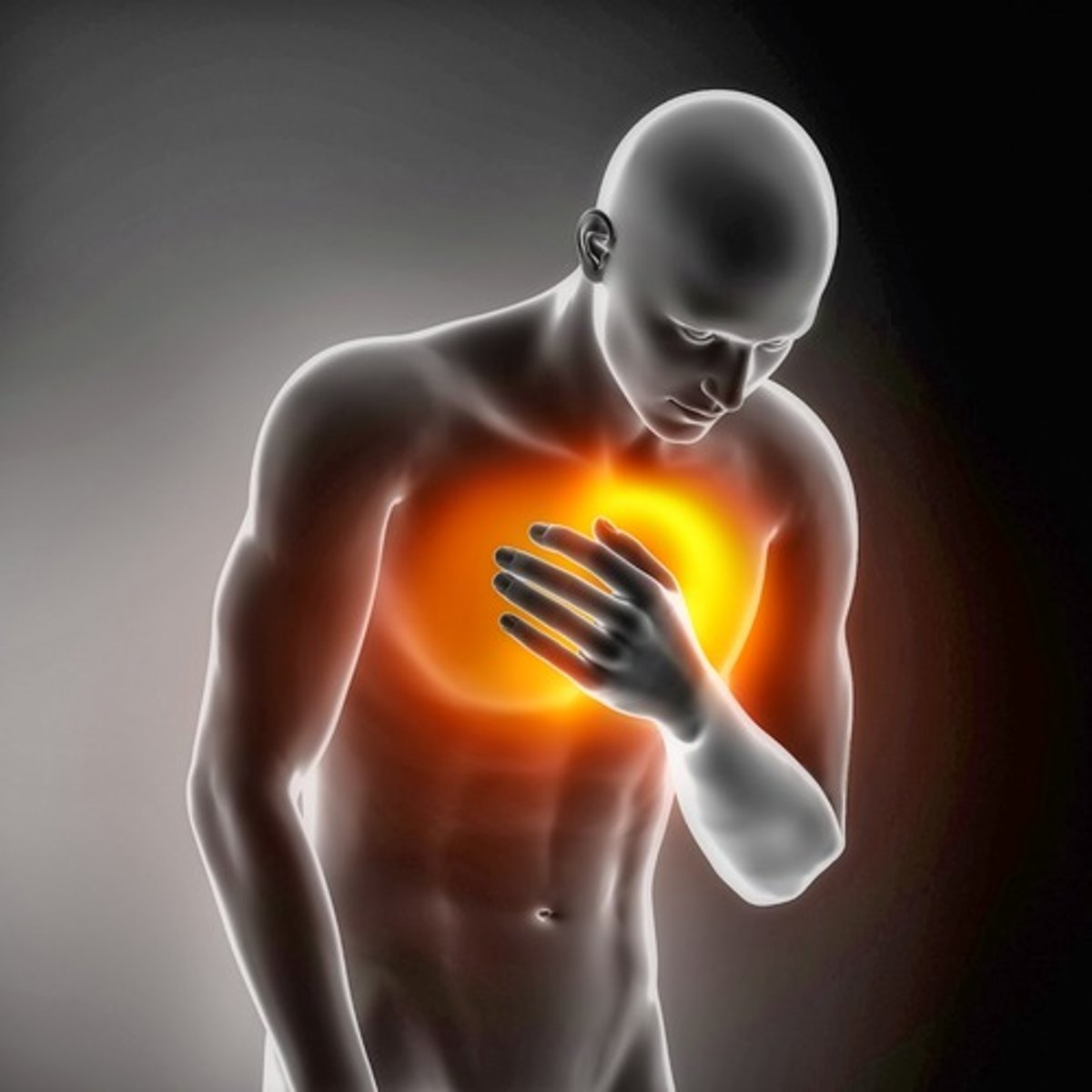

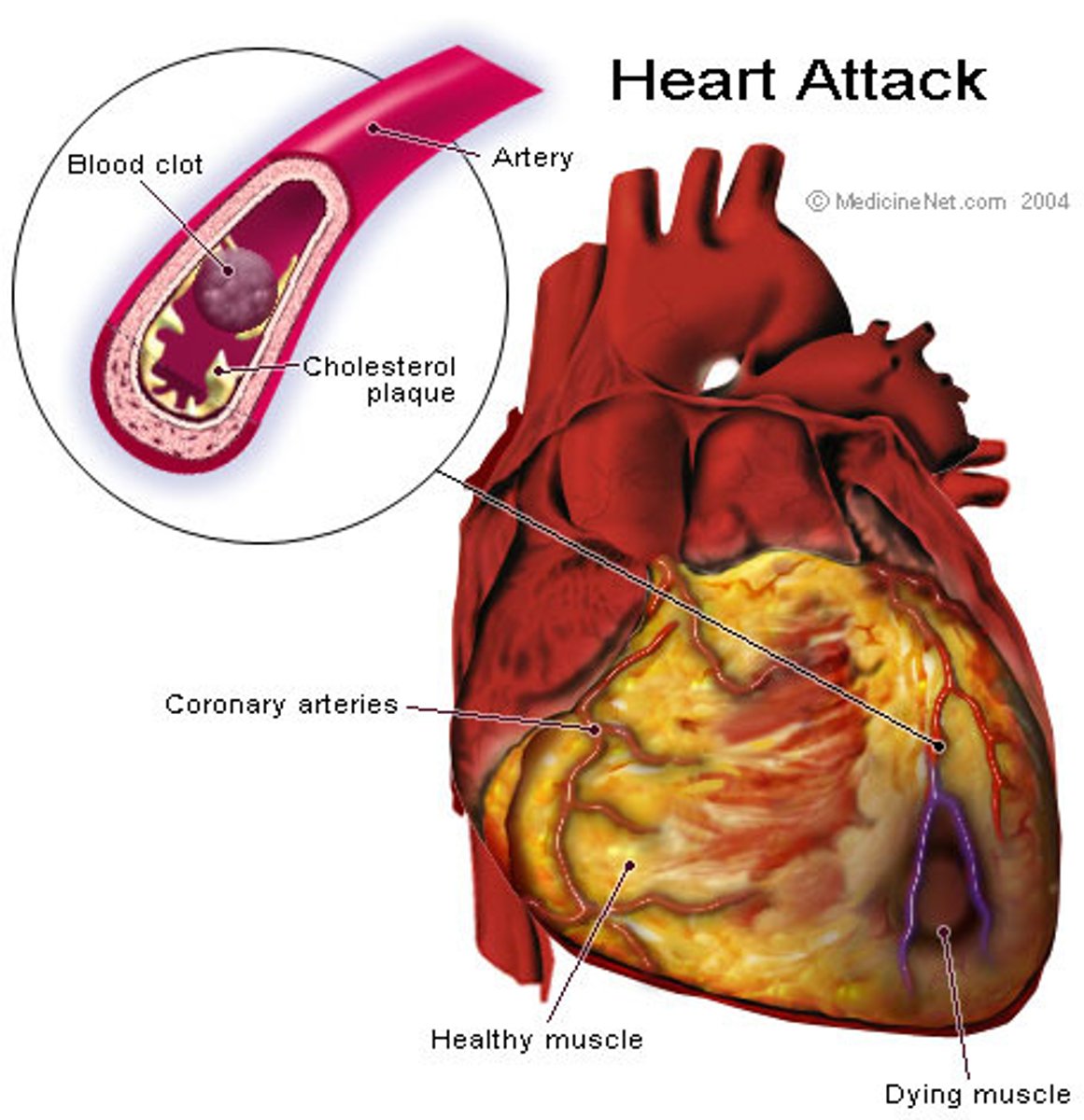
myocardial infarction
heart attack; obstruction of blood supply to a portion of the cardiac muscle resulting in tissue death
first
Which heart sound is from the AV valves closing (tricuspid and mitral/bicuspid)- "LUB"?
second
Which heart sound is from the semilunar valves closing (pulmonary and aortic)- "DUB"?
Intercalated discs
junctions between cardiac myocytes (cardiac muscle cells); have gap junctions for communication & desmosomes for attachment
moderator band or septomarginal trabecula
found in right ventricle, carries impulse to right ventricular wall
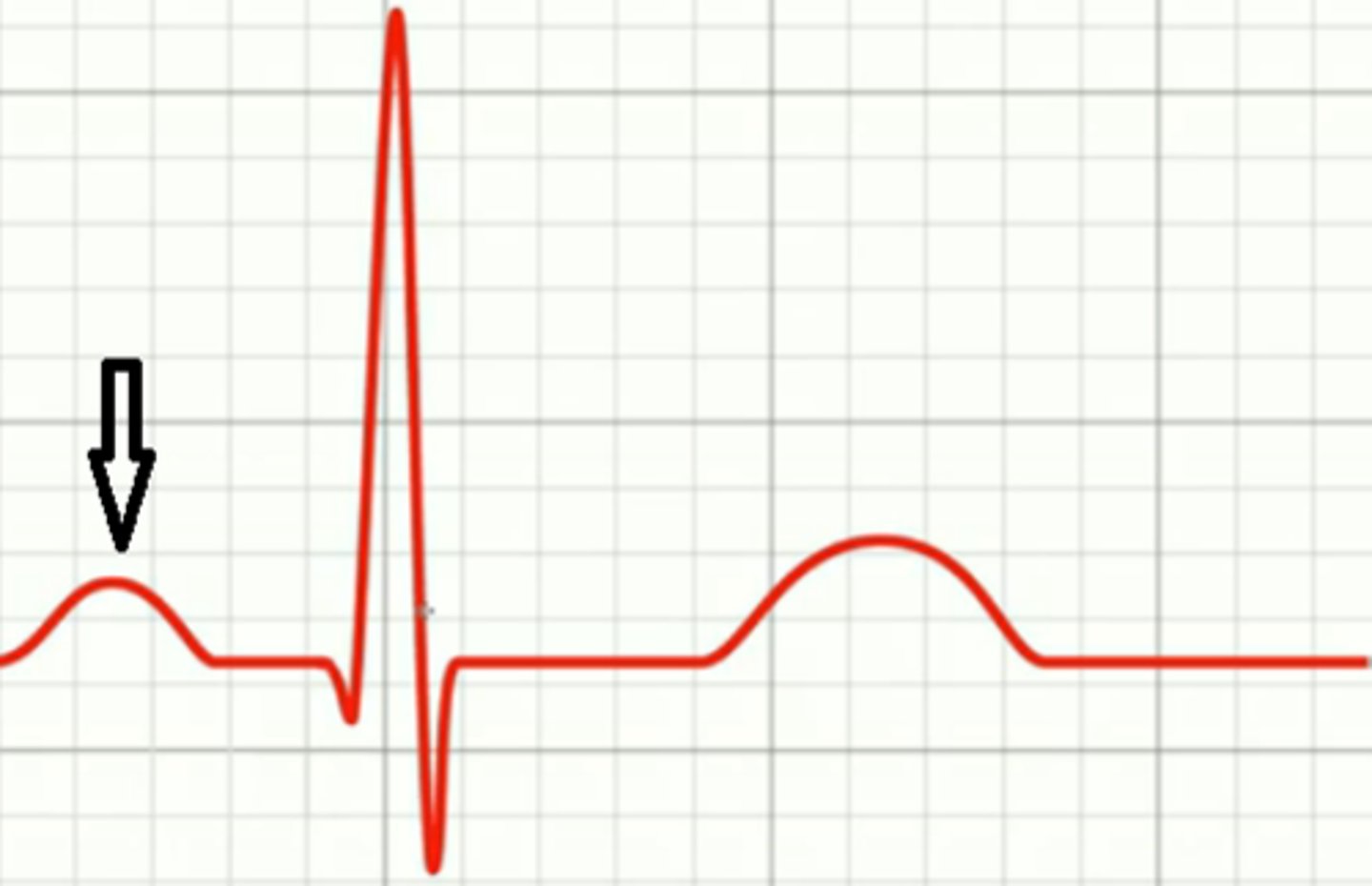
P wave
shows depolarization/excitation of atria, followed by atrial systole (contraction)
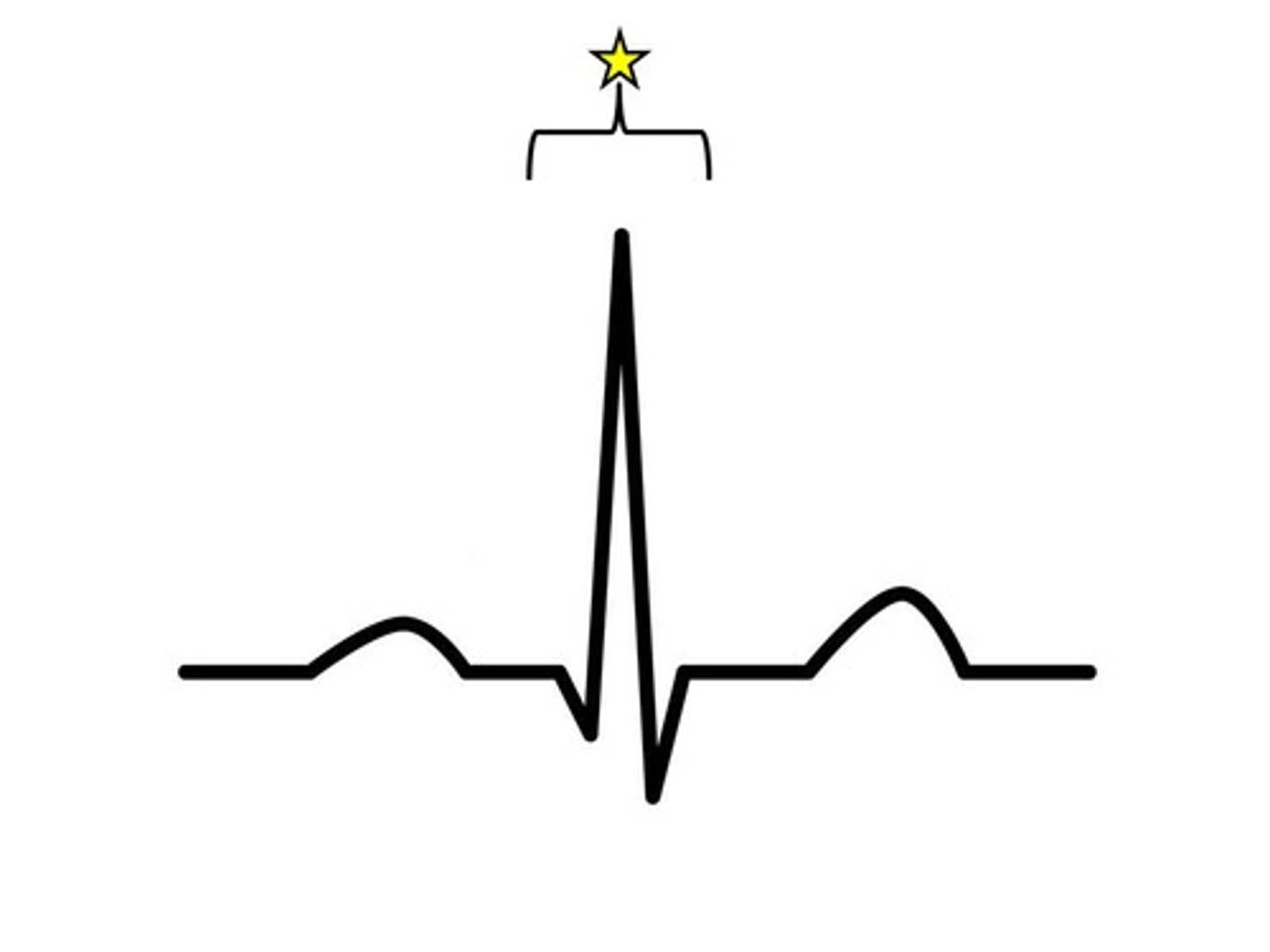
QRS complex
shows depolarization/excitation of ventricles, followed by ventricular systole (contraction)
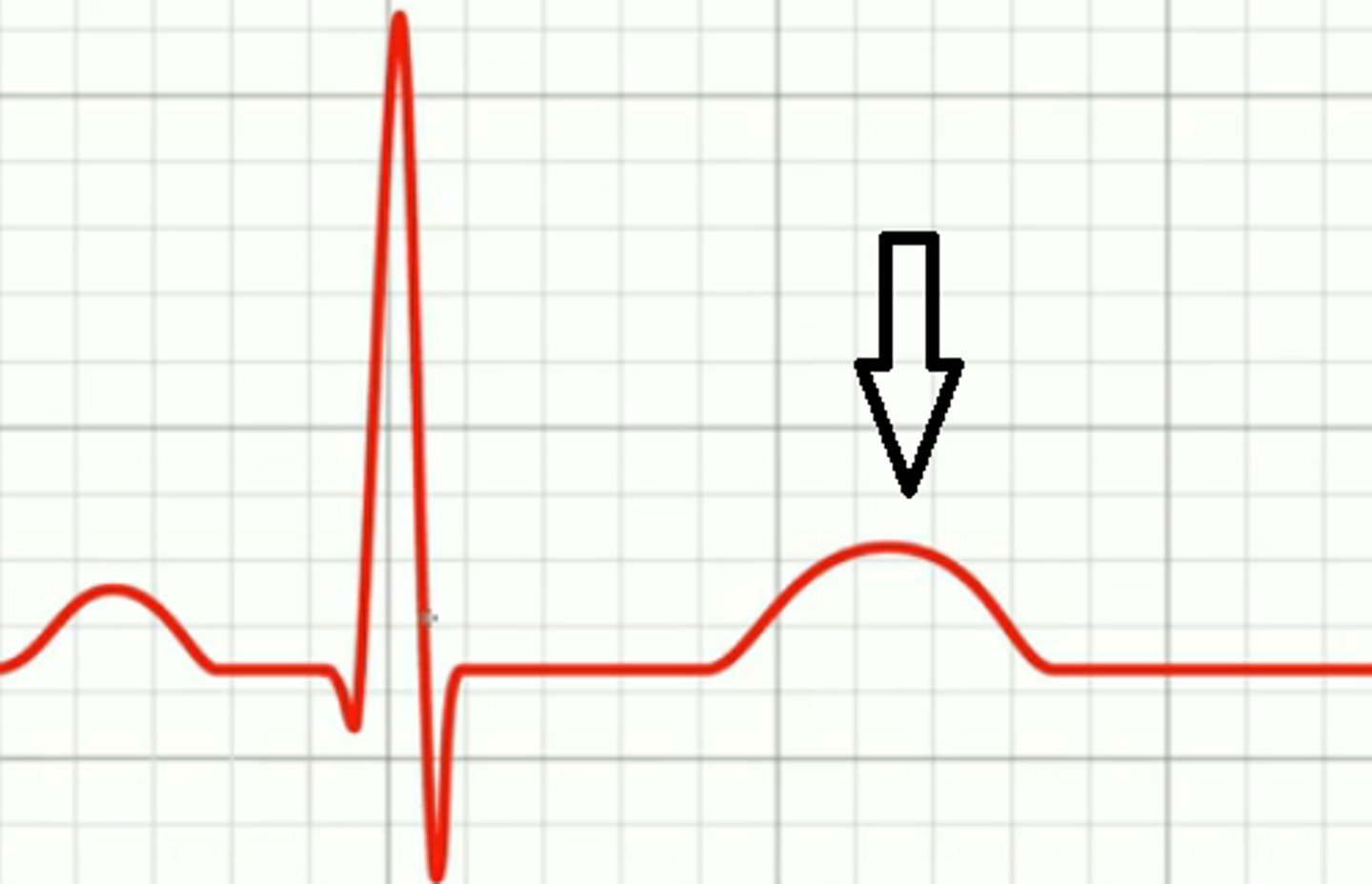
T wave
shows repolarization/relaxation of the ventricles, followed by ventricular diastole (relaxation)
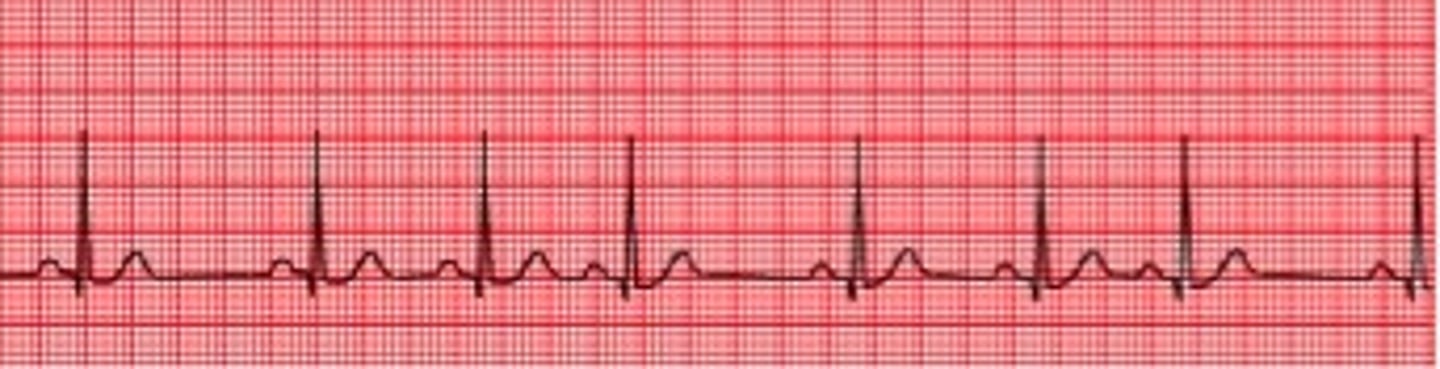
arrhythmias
irregular heartbeat
pericardial cavity
space between parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium (epicardium); filled with serous fluid; reduces friction
atrial fibrillation
rapid, random, ineffective contractions of the atrium; can lead to blot clots, stroke & other heart complications
ventricular fibrillation
the rapid, irregular, and useless contractions of the ventricles; leads to cardiac arrest
before a P wave
part of ECG showing when heart is in diastole
heart block
condition where AV node is defective and few or no impulses reach ventricles

STEMI (ST elevated myocardial infarction)
heart attack in progress due to blockage of a coronary artery
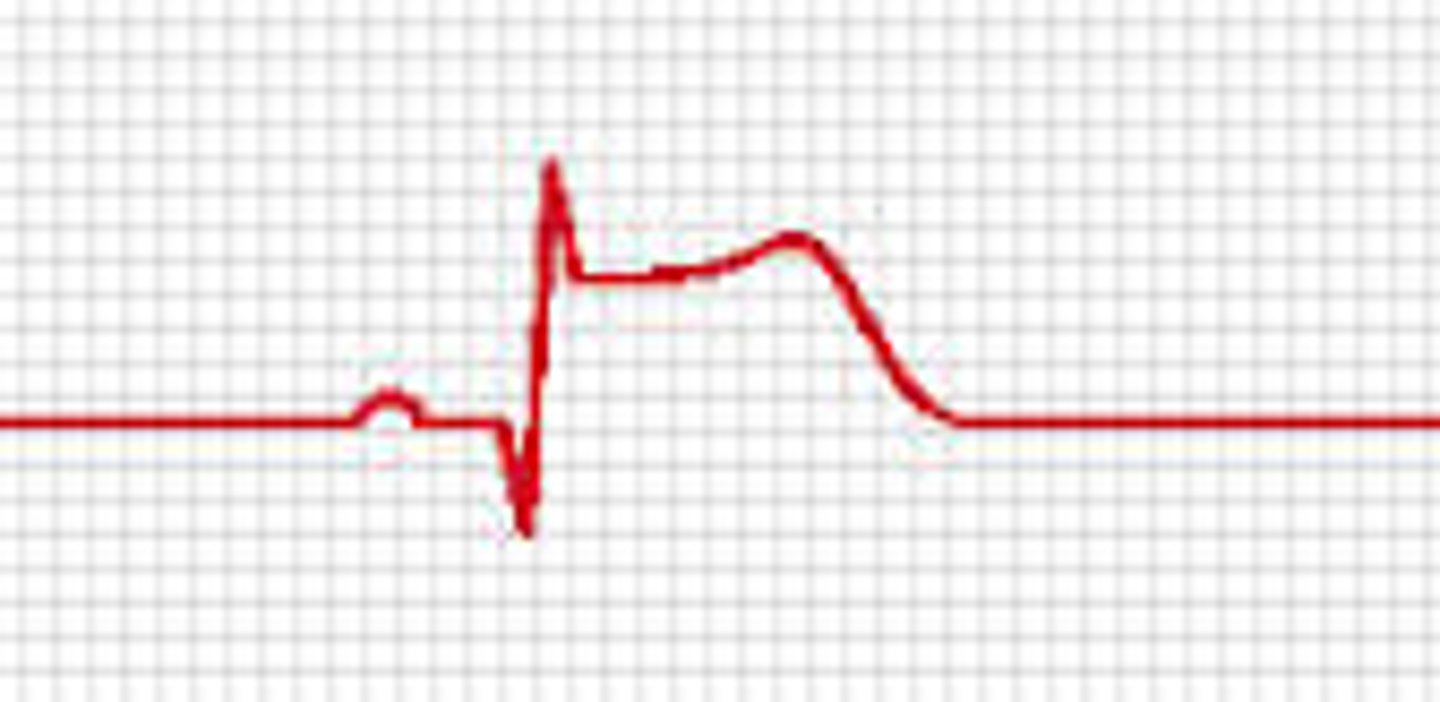
nSTEMI (non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction)
a heart attack that is not diagnosed on the EKG but is diagnosed by an elevated cardiac enzyme panel = troponin on blood test; caused by an obstructed arteriole
t-PA (tissue plasminogen activator)
a fibrinolytic or thrombolytic agent; actively dissoves blood clots; a clot buster
bypass surgery
usually a vein from the leg is taken and used as an alternate route for a clogged coronary artery
past heart attack
a depressed Q-wave means a __________.
artery
A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart- efferent vessel
vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart- afferent vessel
AV node (atrioventricular node)
node between the atria and ventricles where the signal pauses to allow for atrial contraction
first
Heart sound heard at the beginning of ventricular systole?
second
Heart sound heart at the beginning of ventricular diastole?
mitral or bicuspid
Which valve is closure is best detected in the 5th intercostal space on the left side of the sternum at mid-clavicle?
tricuspid
Which valve closure is best detected in the 5th intercostal space just right of the sternal margin?
aortic
Which valve closure is best detected in the 2nd intercostal space just right of the sternal margin?
pulmonary
Which valve closure is best detected in the 2nd intercostal space just left of the sternal margin?
aortic
Which valve is between the left ventricle and the systemic circulation?
pulmonary
Which valve is between the right ventricle and the circulation to the lungs?
ischemia
an inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body
anastomosis (pl. anastomoses)
an alternate or collateral route of circulation common in the coronary blood supply