Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
homeostasis
the maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment
CNS
brain and sp. cord
PNS
sensory and motor
somatic
skeletal muscles/voluntarily controlled
autonomic (parasympathetic and sympathetic)
involuntarily controlled
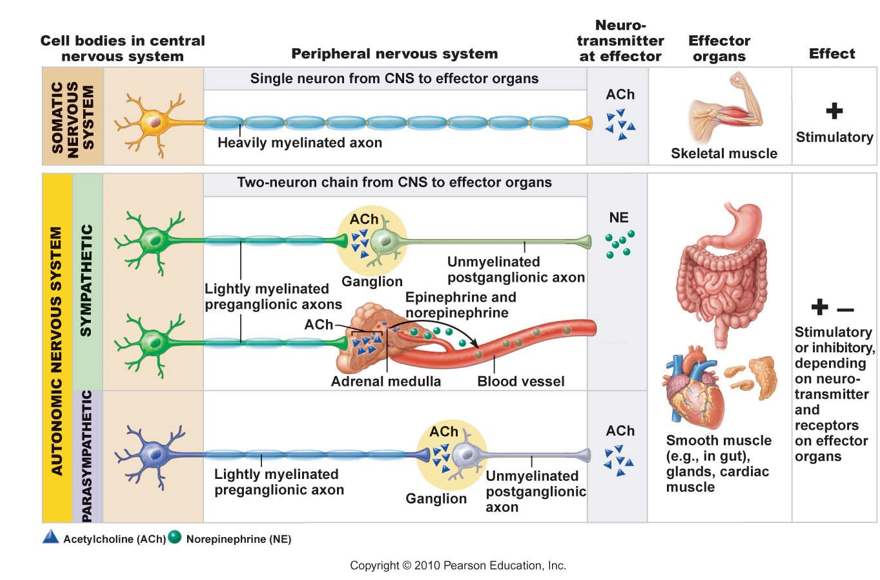
autonomic nervous system
functions in total body homeostasis at the unconscious level (routine homeostatic adjustments in physiological systems, to include the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive systems)
organization of ANS
commands from autonomic centers in the brain/ brainstem are sent to the sp. cord
Organization of ANS
messages are sent out via visceral motor neurons:
preganglionic neurons (1st order)
located in CNS, are myelinated axons, quite divergent
Organization of ANS
messages are sent out via visceral motor neurons:
post ganglionic neurons (2nd order)
located in PNS, are unmyelinated axons, to target tissue Eg.) target tissue= heart, visceral smooth muscle, glands, adipose tissue
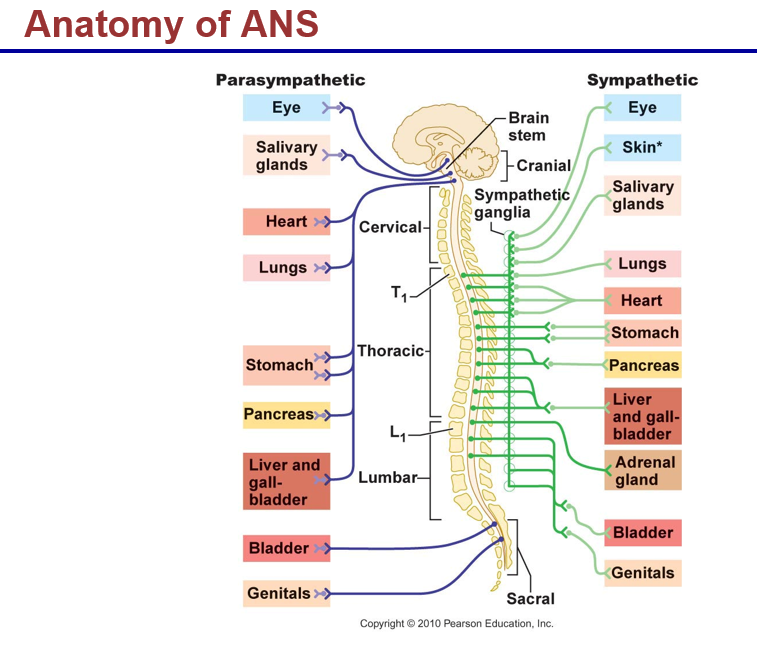
subdivisions of ANS:
sympathetic
fight or flight responses
systems are altered in order to deal with emergencies, increased alertness, increased metabolism
for example: increased heart rate
increased perspiration
increased blood flow to skeletal muscles
increased breathing rate
subdivisions of ANS:
parasympathetic
rest and repose or rest and digest responses
systems altered to converse energy, digest, promote sedentary activities
For example: decreased heart rate
increased digestive secretions and movement
increased blood flow to intrstine
increased bladder contractions