Davies Abdomen
1/559
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
560 Terms
b. perform compression sonography
During abdominal sonography on a 68 year old male, you suspect an exophytic mass arising from the stomach. Which technique is most useful in analyzing this mass?
a. scan the area while the patient performs a Valsalva maneuver
b. perform compression sonography
c. scan the patient in both inspiration and expiration
d. rescan the patient following ingestion of a fatty meal
e. scan the patient in a Trendelenburg position
c. quadratus lumborum muscle
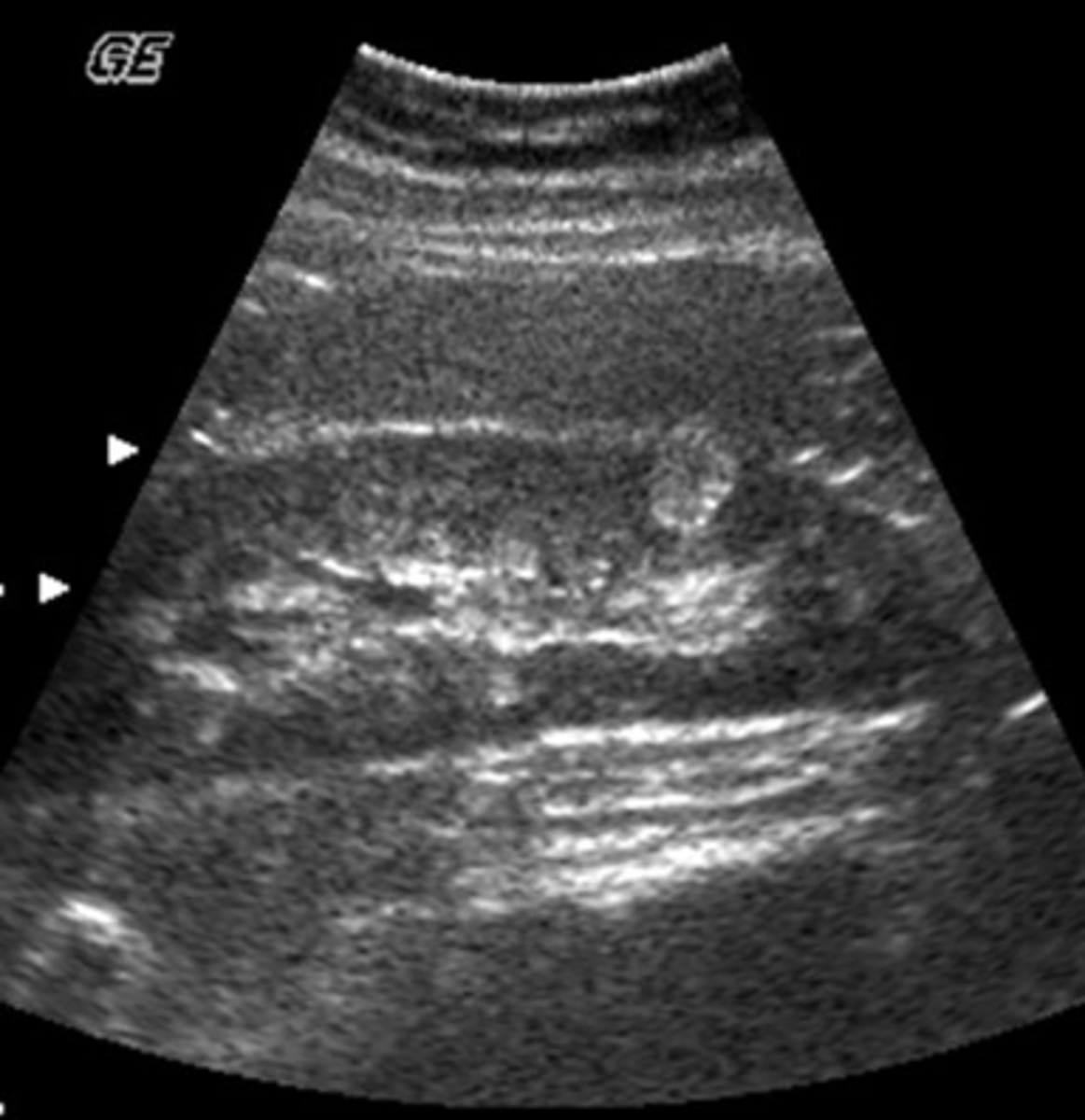
This TRV image was obtained in a 49 y.o. male with hematuria. What structure is represented by the letter "a"?
a. rib
b. lumbar spine
c. quadratus lumborum muscle
d. psoas muscle
e. obturator internus muscle
b. contraction of the gallbladder with diffuse wall thickening
The patient you are scanning has eaten breakfast prior to your study. What is the appearance of the gallbladder in the postprandial state?
a. dilatation of a thin-walled gallbladder
b. contraction of the gallbladder with diffuse wall thickening
c. nonvisibility of the gallbladder due to complete contraction
d. contraction of the gallbladder with asymmetric wall thickening
e. minimal contraction of the gallbladder with a sludge filled lumen
b. posterior to the neck
What is the relationship of the superior mesenteric artery to the pancreas?
a. posterior to the tail
b. posterior to the neck
c. superior to the body
d. cephalad to the head
e. lateral to the tail
c. a solitary thyroid nodule is usually malignant
Which of the following is NOT true regarding thyroid nodules?
a. the overwhelming majority of thyroid nodules are benign
b. thyroid nodules are very common
c. a solitary thyroid nodule is usually malignant
d. nodules with significant cystic component are usually benign
e. nodules may be hyperechoic or hypoechoic to the thyroid
b. shrunken caudate lobe
( with cirrhosis the caudate is usually enlarged compared to the right due to sparing)
You are scanning a patient with suspected liver cirrhosis. All of the following are sonographic features of cirrhosis EXCEPT:
a.surface nodularity
b. shrunken caudate lobe
c. altered echo texture
d. ascites
e. regenerative nodules
a. normal appearance
A patient has been referred to your ultrasound lab with a history of acute pyelonephritis. What is the most common sonographic appearance of this condition?
a. normal appearance
b. irregular renal surface contour
c. mottles appearance of both kidneys
d. focal hypoechoic masses throughout the kidney
e. gas within the renal parenchyma
c. dilated ureter
You have been asked to perform an ultrasound evaluation of a child with multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK). Which of the following is NOT a sign of this condition?
a. multiple variably sized cysts
b. nonmedial lobulation of the largest cyst
c. dilated ureter
d. no identifiable renal sinus
e. brightly echogenic tissue interfaces between cysts
d. hepatitis
You are scanning a patient with a history of fever, abnormal liver function tests, and RUQ tenderness. The liver is enlarged with decreased echogenicity, the GB wall is thickened and thick echogenic bands are noted surrounding the portal veins. Which of the following conditions is most likely?
a. fatty liver
b. cirrhosis
c. budd-chiari syndrome
d. hepatitis
e. normal liver
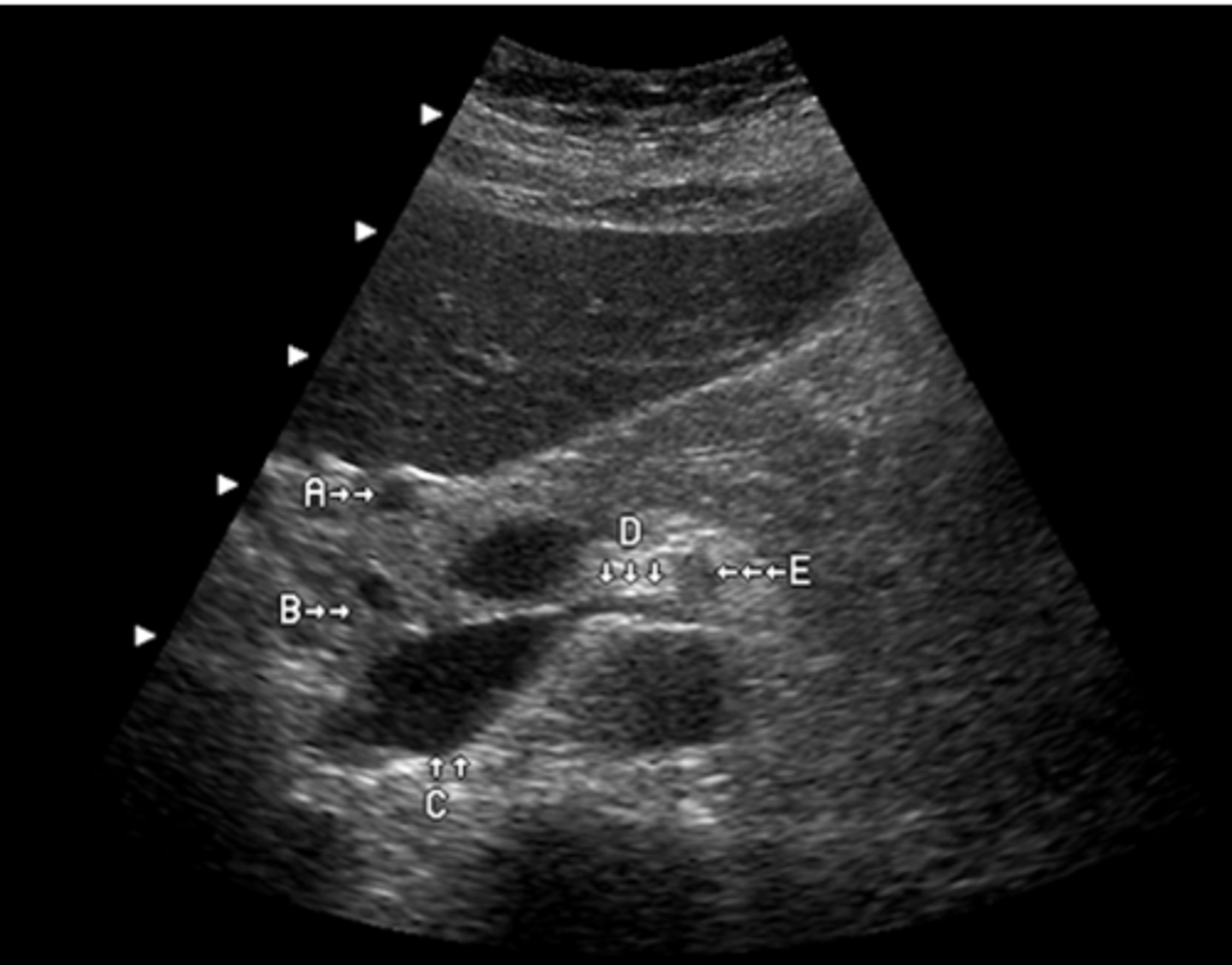
e. caudate lobe
The arrow labeled D is pointing to what lobe of the liver?
a. medial segment of left lobe
b. lateral segment left lobe
c. posterior segment right lobe
d. anterior segment right lobe
e. caudate lobe
b. small hyperechoic kidneys
A patient with a history of chronic medical renal disease has been referred for abdominal ultrasound. Which of the following describes the renal appearance you expect to see?
a. enlarged hypoechoic kidneys
b. small hyperechoic kidneys
c. normal appearance of kidneys
d. small hypoechoic kidneys
e. normal sized kidneys with calcified collecting system
b. kaposi's sarcoma
You have been asked to perform a liver sonogram on a patient with AIDS. Which of the following tumors is most commonly associated with this history?
a. hepatocellular carcinoma
b. kaposi's sarcoma
c. budd-chiari syndrome
d. hemangiosarcoma
e. hepatic adenoma
a. phlegmon
A nonencapsulated collection of necrotic and edematous peripancreatic tissues is termed:
a. phlegmon
b. pseudocyst
c. pseudoaneurysm
d. ascites
e. cystadenoma
a. caudal course, anterior to the pancreatic head
Which of the following describes the anatomic course of the gastroduodenal artery (GDA)?
a. caudal course, anterior to the pancreatic head
b. caudal course, posterior to the pancreatic head
c. cranial course, anterior to the duodenum and medial to the pancreatic neck
d. cranial course, posterior ro the pancreatic head
e. lateral course, cephalic to the pancreatic head
b. Glisson's capsule
The thin capsule surrounding the liver is known as:
a. Reidel's capsule
b. Glisson's capsule
c. Teres capsule
d. Langerhan's capsule
e. Wirsung's capsule
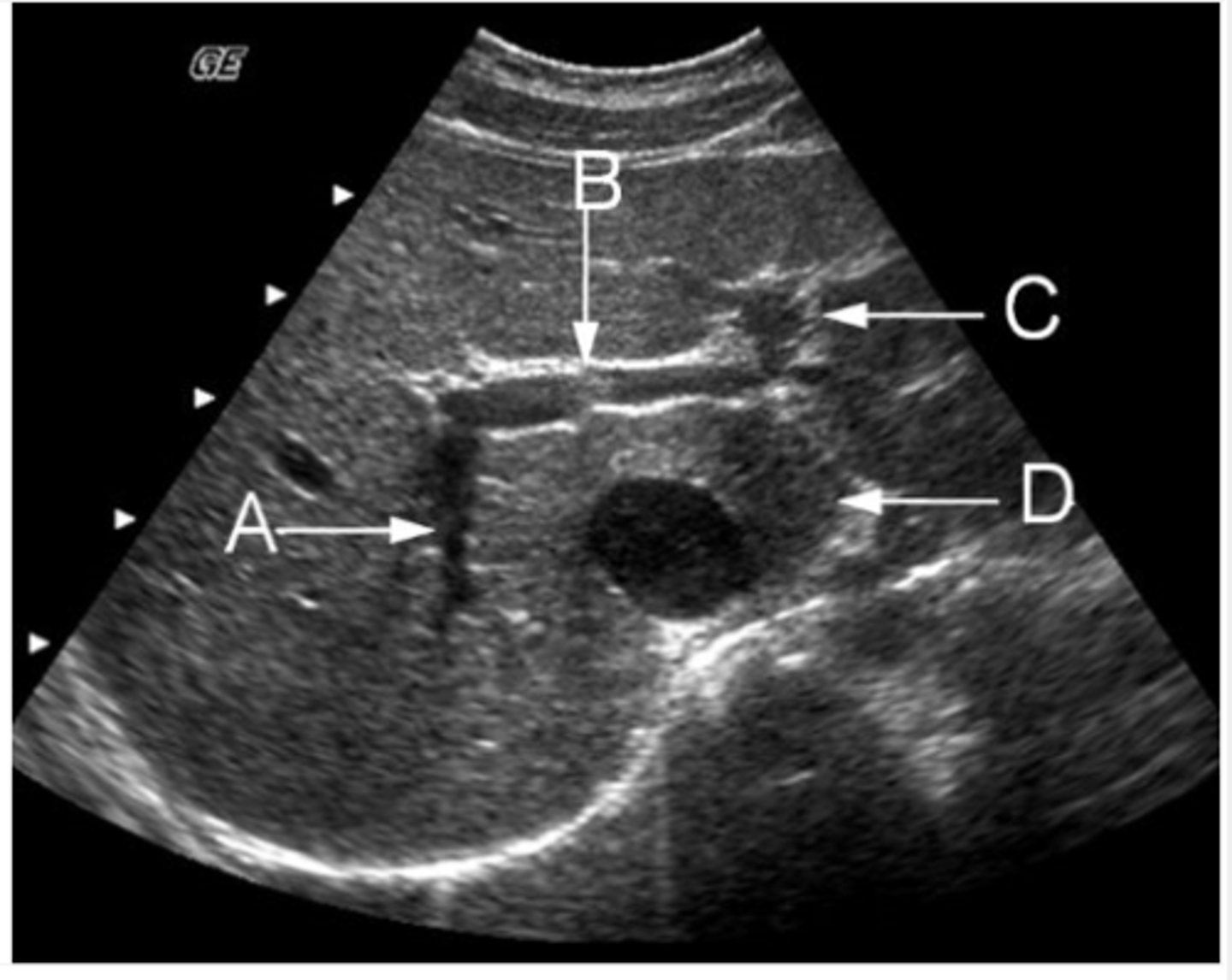
e. Inferior vena cava
Identify the anatomy labeled "C"
a. aorta
b. portal vein
c. superior mesenteric vein
d. inferior mesenteric vein
e. Inferior vena cava
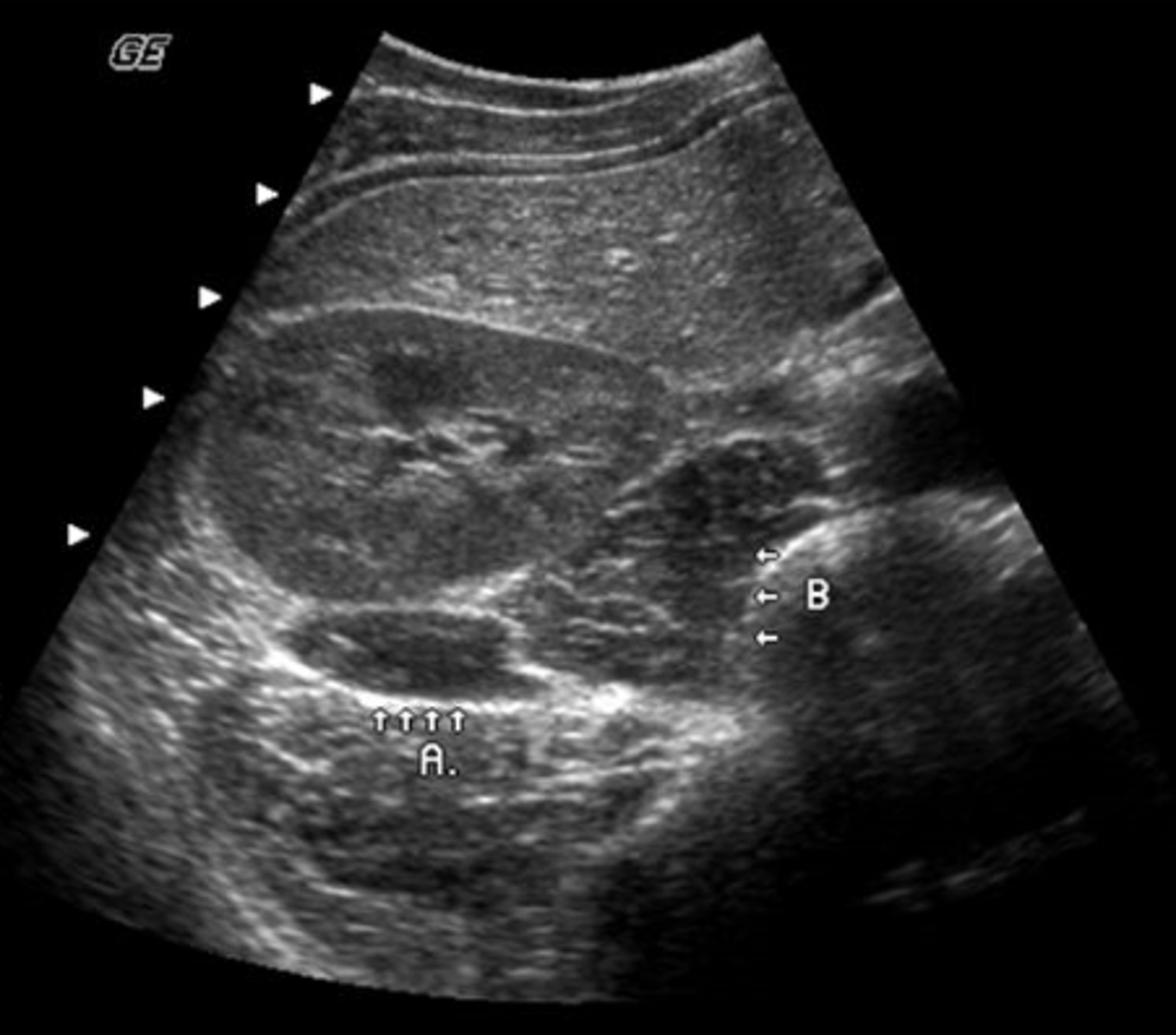
b. splenic and retroperitoneal varices
A 49-year-old male presented with a clinical history of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. In the transverse image below, multiple hypoechoic structures are seen at the splenic hilum and between the kidney and spleen. What is the most likely etiology of these structures.
a. multiple aneurysms of the splenic artery
b. splenic and retroperitoneal varices
c. loculated ascites
d. polycystic kidney disease
e. fluid-filled loops of bowel
d. concomitant elevation of both GGT and ALK phos indicates the source of the elevated ALK phos in the liver
(ALK phos can be elevated for a ton of things but if GGT is also elevated it means the ALK phos is raised by something in the liver)
You are reviewing lab work prior to performing an abdominal ultrasound exam. Elevated lab values include Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and alkaline phosphatase. Which statement below is true?
a. elevation of both GGT and ALK phos suggests the source of elevated ALK phos is due to metastatic bone cancer
b. elecation of both GGT and ALK phos is a sensitive indicator of pancreatitis
c. If both GGT and ALK phos are elevated, the lab work is invalid and must be repeated
d. concomitant elevation of both GGT and ALK phos indicates the source of the elevated ALK phos in the liver
e. concomitant elevation of both of these lab values is highly specific for hepatocellular carcinoma
b. 5.0 MHz curved linear array
You are requested to perform an ultrasound evaluation of the gallbladder and biliary tree on an elderly female with a small frame. Which of the following transduceres is most suited to this task?
a. 2.5 MHz phased array
b. 5.0 MHz curved linear array
c. 3.5 MFz linear array
d. 10 MHz curved linear array
e. 13 MHz linear array
a. roll the patient into a left lateral decubitus position
A patient is referred for gallbladder ultrasound with a history of RUQ pain and nausea. You suspect presence of a stone in the region of the gallbladder neck, but are not sure. Which of the following would be helpful in confirming the presence of a stone?
a. roll the patient into a left lateral decubitus position
b. have the patient perform a valsalva maneuver
c. place the patient in a trendelenburg position
d. increase the system dynamic range
e. increase the system overall gain
e. all of the above
This view is useful in the evaluation of what abnormality?
a. renal artery stenosis
b. multiple renal arteries
c. aortic aneurysm
d. IVC thrombosis
e. all of the above
e. hepatic veins
Which of the following course interlobar and intersegmental within the liver?
a. bile ducts
b. portal veins
c. hepatic arteries
d. lymphatics
e. hepatic veins
a. rejection
(liver biopsies are performed to rule out rejection)
What significant complication following liver transplantation is NOT detectable with ultrasound?
a. rejection
b. malignant disease
c. hepatic artery thrombosis
d. portal vein thrombosis
e. pseudoaneurysm
a. scan the patient in both deep inspiration and expiration
(the adrenal glands are fixed in position, so with deep inspiration the kidney moves downward but the adrenal wouldn't)
Abdominal sonography of a 42-year-old male reveals a solid mass located at the upper pole of the kidney. Which of the following would be most helpful in differentiating between a renal and adrenal mass?
a. scan the patient in both deep inspiration and expiration
b. ecaluate the mass with color doppler
c. have the patient drink 32 oz of water and rescan
d. give the patient a fatty meal and rescan in 20 minutes
e. perform spectral doppler resistive indices from vessels within the mass
c. occlusion of the left main renal artery
Ultrasound findings in a patient with hypertension include a left kidney measuring 6.8 cm and a right kidney measuring 11.7 cm. Which of the following is most consistant with these findings?
a. acute pyelonephritis in the left kidney
b. acute glomerulonephritis in the right kidney
c. occlusion of the left main renal artery
d. amyloidosis of the right kidney
e. none of the above
a. decrease pulse repetition frequency
During color doppler evaluation of the kidney, you observe inadequate fill of the intrarenal vasculature . Which doppler parameter will you adjust to improve sensitivity to flow?
a. decrease pulse repetition frequency
b. increase wall filter
c. decrease packet size
d. decreae color gain
e. decrease color resolution setting
d. hepatic adenoma
A patient is referred with RUQ tenderness and a history of oral contraceptive use. A solid, hypoechoic mass is identifies in the right lobe of the liver. Color doppler reveals hypervascularity of the mass. Which of the following scenarios is most likely?
a. hydatid liver disease
b. hepatic lipoma
c. hepatic abscess
d. hepatic adenoma
e. hepatocellular carcinoma
b. pancreatic carcinoma
You are performing an ultrasound examination on a patient with acute cholecystitis. Complications of acute cholecystitis that you should look for include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. pancreatitis
b. pancreatic carcinoma
c. gallbladder perforation
d. gangrenous cholecystitis
e. emphysematous cholecystitis
c. insulinoma
You are performing an ultrasound on an obese patient and notice a small, hypoechoic tumor located in the tail of the pancreas. This most likely represents:
a. adenocarcinoma
b. cystadenocarcinoma
c. insulinoma
d. Klatskin tumor
e. pancreaticblastoma
d. metastasis
You are perfoming an ultrasound study on a patient with malignant melanoma. Your ultrasound findings reveal multiple hyperechoic masses within the spleen. This most likely represents:
a. histoplasmosis
b. tuberculosis
c. pseudocyst
d. metastasis
e. infarction
b. gallstones
You have been requested to perform a gallbladder ultrasound to rule out cholelithiasis. What is cholelithiasis?
a. gallbladder carcinoma
b. gallstones
c. gallbladder polyps
d. adenomyosis
e. gallbladder wall thickening
a. left renal vein
The left renal artery is normally located immediately posterior to which of the following?
a. left renal vein
b. portal vein
c. common hepatic artery
d. splenic artery
e. none of the above
d. uncontrolled hypertension
What is the indication for a Doppler renal study to rule out renal artery stenosis?
a. hematuria
b. increased serum creatinine
c. leukocytosis and fever
d. uncontrolled hypertension
e. anemia, progressive azotemia and polyuria
d. increased attenuation
Which of the following is NOT a feature you would detect in a spenic cyst?
a. smooth border
b. posterior acoustic enhancement
c. anechoic
d. increased attenuation
e. rounded shape
e. inferior vena cava
When imaging the pancreas, which vessels do you routinely visualize at the posterior border of the pancreatic head?
a. abdominal aorta
b. right renal artery
c. superior mesenteric artery
d. superior mesenteric vein
e. inferior vena cava
a. adenocarcinoma
(adenocarcinoma accounts for nearly 80% of all malignant tumors of the GI tract)
What is the most common malignant tumor of the gastrointestinal tract?
a. adenocarcinoma
b. mesenchymal tumors
c. lymphoma
d. metastatic tumors
e. cystadenocarcinoma
b. portal hypertension
(most common cause of portal hypertension is cirrhosis from alcohol abuse)
A 38-year-old female has been referred for a Doppler study of the liver with a history of ETOH abuse and cirrhosis. What vascular condition is associated with this history?
a. mesenteric ischemia
b. portal hypertension
c. hepatic artery fibromuscular dysplasia
d. splenic artery pseudoaneurysm
e. Budd-chiari syndrome
d. abdominal aortic aneurysm and horseshoe kidneys
This transverse image was obtained in the mid abdomen of a 57- year-old male with lower back pain. Which of the following correctly describes the sonographic findings?
a. leaking abdominal aortic aneurysm with hematoma
b. abdominal aortic aneurysm and para-aortic lymphadenopathy
c. inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm
d. abdominal aortic aneurysm and horseshoe kidneys
e. abdominal aortic aneurysm with retroperitoneal fibrosis
d. an avascular mass with low-level echoes
What is the sonographic appearance of tumefactive sludge within the gallbladder?
a. an echogenic mass with prominent color doppler signals
b. a mass with low-level echoes with prominent color doppler signals
c. a mass containing ringdown artifacts and no color doppler signals
d. an avascular mass with low-level echoes
e. an adherent, echogenic mass with weak color doppler signals
d. frequently only one kidney is involved
You are scanning a patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding this disease?
a. liver cysts may be present in up to 30% of patients
b. high blood pressure is common
c. cysts may be complicated by bleeding or infection
d. frequently only one kidney is involved
e. progressive renal failure is common
a. head
(head largest, neck smallest)
Which part of the pancreas generally has the largest dimensions?
a. head
b. neck
c. body
d. tail
e. uncinate process
d. portal vein and hepatic artery
Oxygenated blood is supplied to the liver via the:
a. portal vein and hepatic vein
b. hepatic vein and hepatic artery
c. hepatic vein and portal vein
d. portal vein and hepatic artery
e. hepatic artery only
c. search for other causes of right lower quadrant pain
You have performed a study to rule out appendicitis in a young female with RLQ pain. No evidence suggestin appendicitis was detected. What should you do?
a. nothing the study is complete
b. suggest the patient have a barium enema
c. search for other causes of right lower quadrant pain
d. have the patient return in 24-48 hours for a repeat study if symptoms have not subsided
e. both b and d
d. moderate hydration with no other specific preparation
What preperation should you require of your patient scheduled for renal sonograms?
a. fasting for 24 hours prior to examination
b. ingestion of 100 mg simethicome 5 minutes before examination
c. water enema
d. moderate hydration with no other specific preparation
e. faty meal within 30 minutes of examination
b. epididymal cyst
You have obtained this image while performing a scrotal ultrasound on a patient with a history of a palpable right sctrotal mass. What pathology is present?
a. seminoma
b. epididymal cyst
c. epididymitis
d. orchitis
e. hydrocele
c. low resistance
Which of the following describes the normal waveform of the main renal artery?
a. triphasic
b. high resistance
c. low resistance
d. phasic
e. bidirectional
b. mass in the head of the pancreas
You are performing an abdominal ultrasound study and detect a dilated, nontender gallbladder. What should you look for?
a. right kidney hydronephrosis
b. mass in the head of the pancreas
c. mass in the posterior right lobe of the liver
d. abdominal aortic aneurysm
e. portal vein thrombosis
d. 7 MHz linear array
( during intraoperative scanning the transducer is placed directly on the exposed liver, for this reason you need a higher frequency, but not too high where you cannot penetrate the whole liver)
You have been asked to provide ultrasound imaging during liver surgery. What transducer would be best suited for this purpose?
a. 3.5 MHz curved linear array
b. 10 MHz linear array
c. 2.25 MHz phased array
d. 7 MHz linear array
e. 12 MHz curved linear array
c. search for the presence of portosystemic collaterals
You are performing an ultrasound exam in a patient with a history of alcoholic liver cirrhosis. You have documented the presence of splenomegaly and dilated veins at the splenic hilum. Considering the patient's history and findings, what else should you look for?
a. search for signs of acute cholecystitis
b. carefully scan the spleen for presence of infarcts
c. search for the presence of portosystemic collaterals
d. check the pelvis for a left side mass
e. rule out the presence of an aortic aneurysm
c. arcuate
What arteries course on top of the renal pyramids and give rise to the tiny intralobular arteries?
a. segmental
b. interlobar
c. arcuate
d. vasa recta
e. capsular
d. hyperechoic
What term best describes this lower pole renal mass?
a. hypoechoic
b. anechoic
c. isoechoic
d. hyperechoic
e. none of the above
d. fusiform
You are asked to perform a follow-up study on a patient with a known abdominal aortic aneurysm. Which of the following terms correctly describes this aneurysm?
a. pseudoaneurysm
b. saccular
c. dissecting
d. fusiform
e. dumbbell
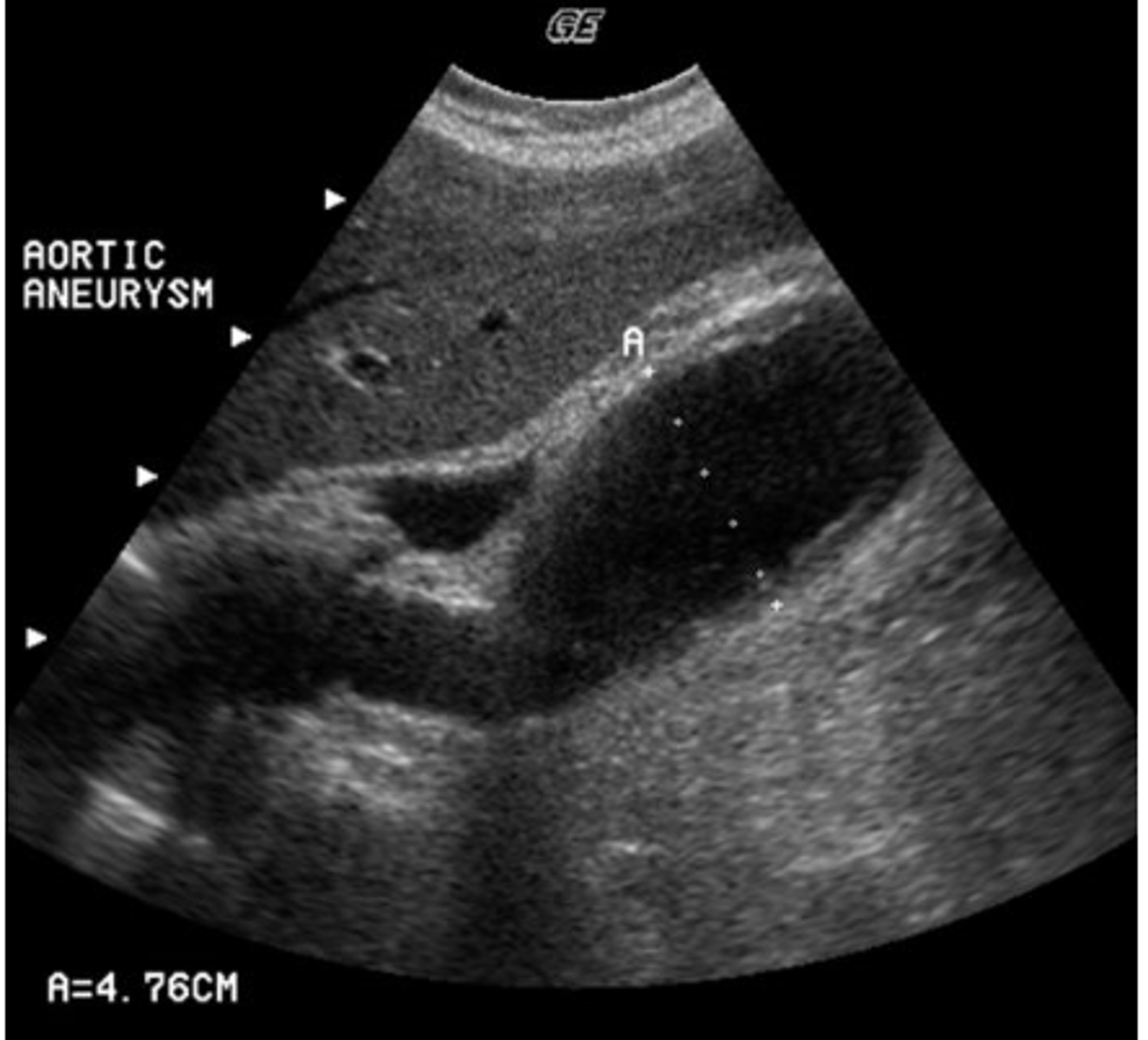
c. the patient has sludge most likely due to bile stasis
You are scanning a patient in ICU and notice low-level echoes within the gallbladder consistent with sludge. The gallbladder wall is not thickened. Which statement below is true?
a. the patient most likely has acute acalculus cholecystitis
b. these findings represent gallbladder perforation
c. the patient has sludge most likely due to bile stasis
d. the patient has a porcelain gallbladder
e. the patient has a pancreatic abnormality
b. sequential linear array
Which of the following transduceres does NOT demonstrate a sector view?
a. phased array
b. sequential linear array
c. curved linear array
d. annular array
e. all of these transducers produce a sector field of view
d. 9-14 cm
You are performin a sonogram on a patient with bilaterally small kidneys. What is the normal range in size for a kidney?
a. 2-4 cm
b. 4-7 cm
c. 7-9 cm
d. 9-14 cm
e. 13-17 cm
a. scan the patient in deep inspiration
You are imaging a patient with a high liver. Subcostal images do not clearly demonstrate the liver tissue. What should you do?
a. scan the patient in deep inspiration
b. scan the patient in expiration
c. place the patient in trendelenburg position and rescan
d. have the patient drink 32 oz of water and rescan
e. scan with the patient in quiet respiration
c. mildly undulating
(smooth wavelike motion and low velocity is normal)
You have been asked to perform a doppler analysis of the portal venous system. Which of the following describes the waveform you will see in the portal vein in a normal study?
a. bidirectional
b. triphasic
c. mildly undulating
d. highly pulsatile
e. continuous
e. all of the above
You have detected an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Considering this finding, you should tailor your exam to include which of the following?
a. evaluation of the common iliac arteries
b. measurement of the transverse and anteroposterior diameter
c. assessment of intraluminal thrombus
d. location of the aneurysm in relation to the renal arteries
e. all of the above
d. centripetal artery
Which of the following arteries courses within the testicular parenchyma?
a. testicular artery
b. deferential artery
c. cremasteric artery
d. centripetal artery
e. all of the above
e. horseshoe kidney
You are scanning a patient and notice that the right and left kidneys are attached at their lower poles. What anomaly is this?
a. duplicated collecting system
b. supernumerary kidney
c. ureterocele
d. pelvic kidney
e. horseshoe kidney
a. pleural effusion
What pathology is present in this image obtained from the left upper quadrant?
a. pleural effusion
b. splenomegaly
c. ascites
d. splenic metastases
e. splenic cysts
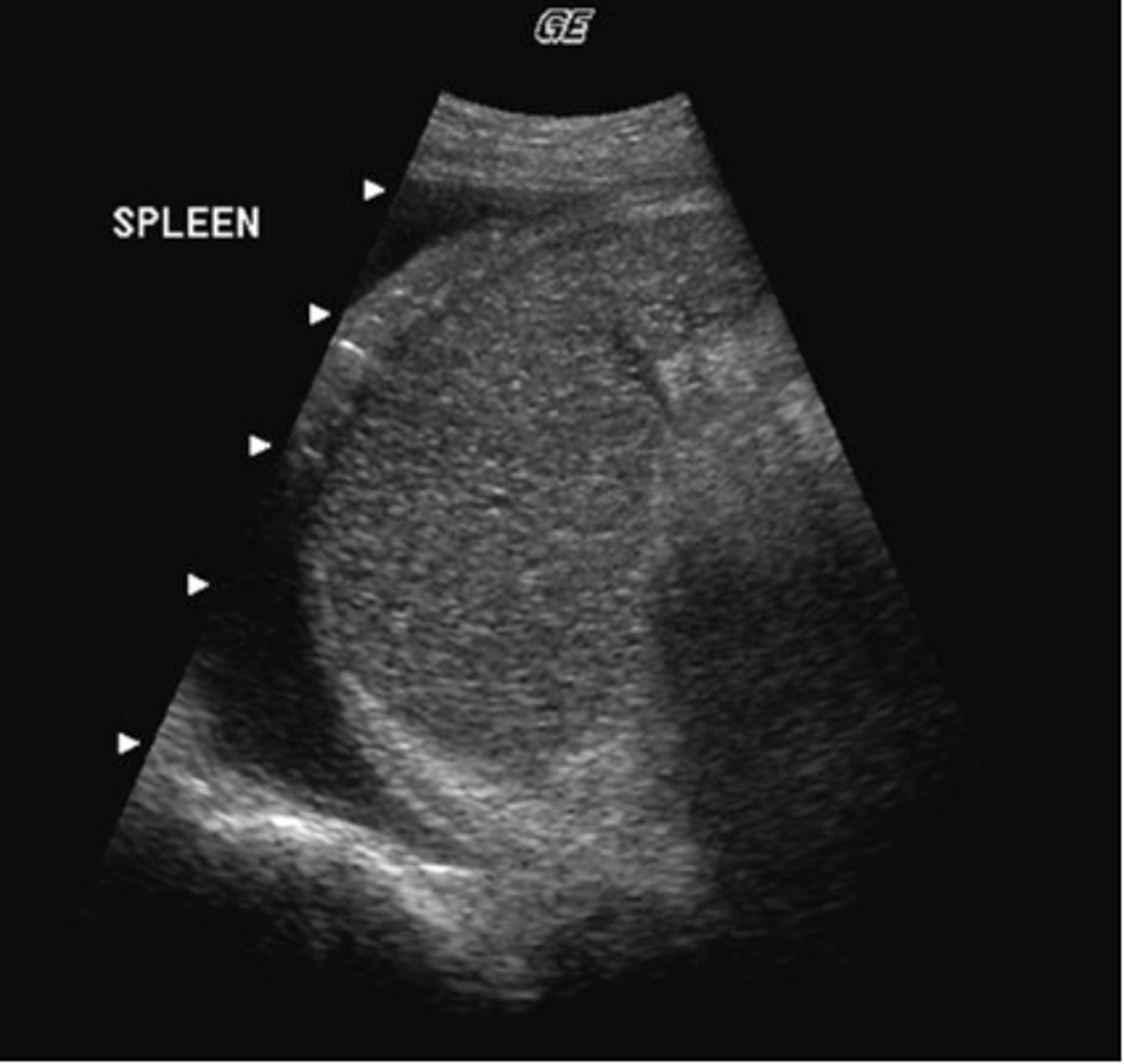
c. evaluate the lesion with color doppler
( the spleen is highly vacular, an infarct would show no color and would stand out from it's surrounding vascularity)
You detect a wedge-shaped, hypoechoic lesion within the spleen. Which of the following would increase diagnostic confidence the most?
a. have the patient perform a valsalva maneuver
b. evaluate the lesion in both inspiration and expiration
c. evaluate the lesion with color doppler
d. have the patient drink 48 o of water and rescan
e. rescan the patient in an upright position
c.posterior and caudal
What is the relationship of the splenic vein to the pancreas?
a. superior
b.anteromedial
c.posterior and caudal
d. inferior and anterior
e. ventral
b. splenic vein
Which structures will you detect at the splenic hilum?
a. diaphragm
b. splenic vein
c. left kidney
d. duodenum
e. left lobe of the liver
d. proper hepatic artery and gastroduodenal artery
You are imaging the common hepatic artery and detect its division into two branches. What are these two branches?
a. proper hepatic artery and right gastric artery
b. right gastric artery and gastroduodenal artery
c. left gastric artery and proper hepatic artery
d. proper hepatic artery and gastroduodenal artery
e. gastroduodenal artery and left gastric artery
a. hypertrophy
You are performing a follow-up study on a patient with a renal transplant. Which of the following changes normally occurs in renal transplants compared to the immediate postoperative study?
a. hypertrophy
b. increased echogenicity
c. hydronephrosis
d. shrinkage
e. calcified pyramids
b. phrygian cap
In what anatomic variant is the fundus of the gallbladder folded over the body?
a. choledochal cyst
b. phrygian cap
c. duplicated collecting system
d. biliary atresia
e. junctional fold
b. hypoechoic, symmetrical, irregularly shaped structures
Which of the following describes the most common appearance of seminal vesicles by transrectal prostate sonography?
a. hyperechoic, symmetrical, irregularly shaped structures
b. hypoechoic, symmetrical, irregularly shaped structures
c. hyperechoic, asymmetrical, smooth structures
d. hyperechoic, asymmetrical, irregularly shaped structures
e. hypoechoic, asymmetrical, smooth structures
c. microlithiasis
What pathology is present in this image?
a. spermatocele
b. seminoma
c. microlithiasis
d. metastatic disease
e. orchitis
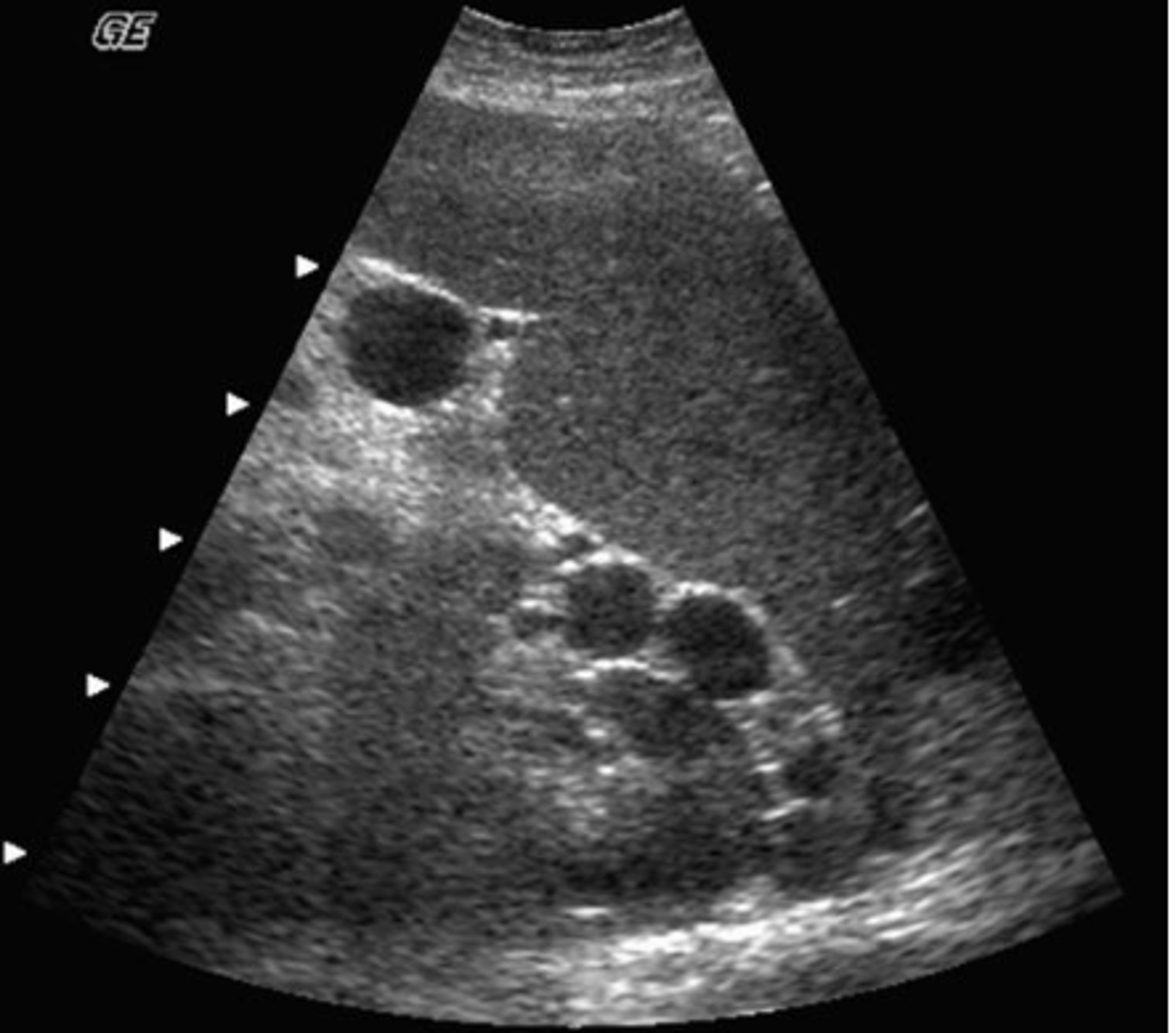
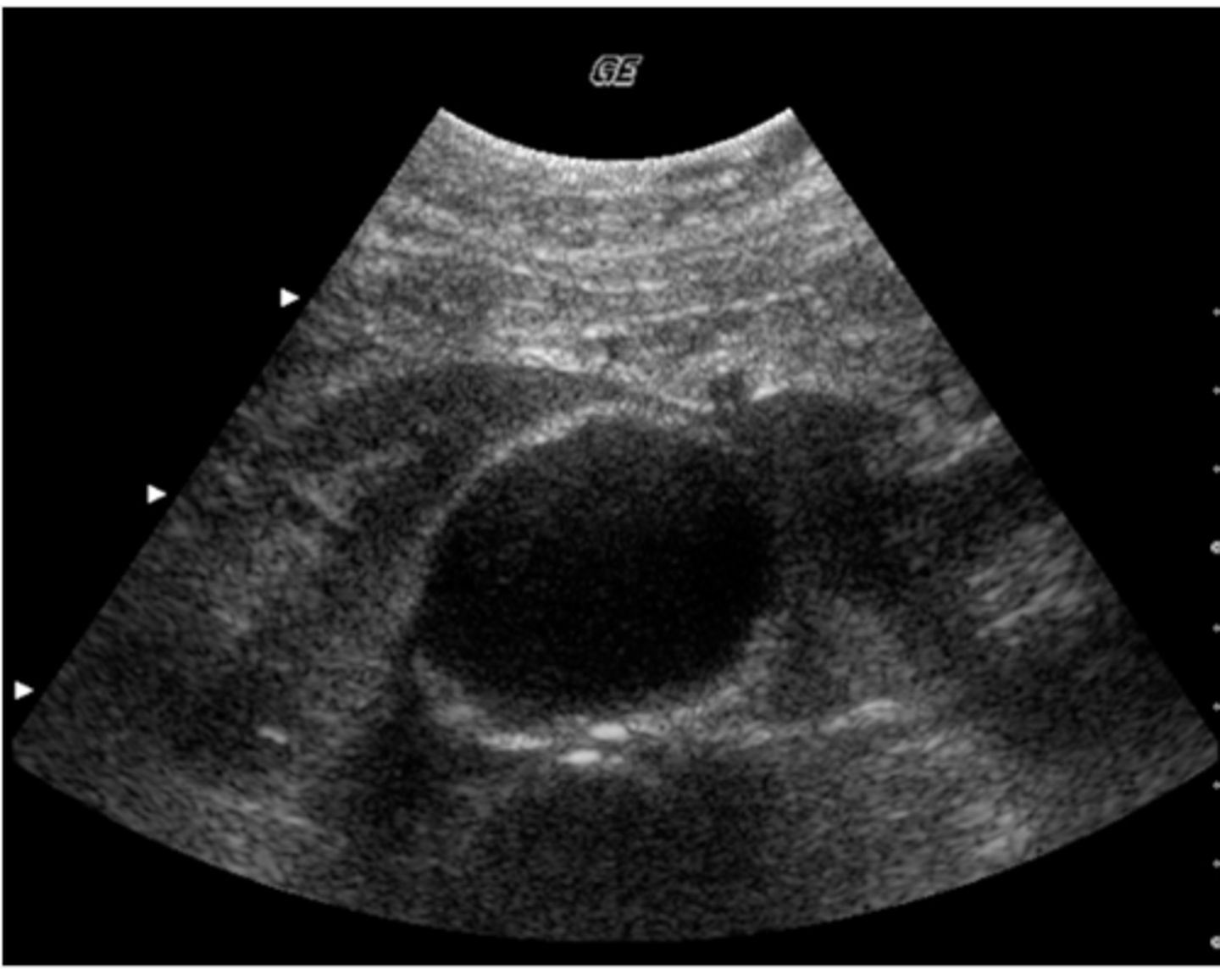
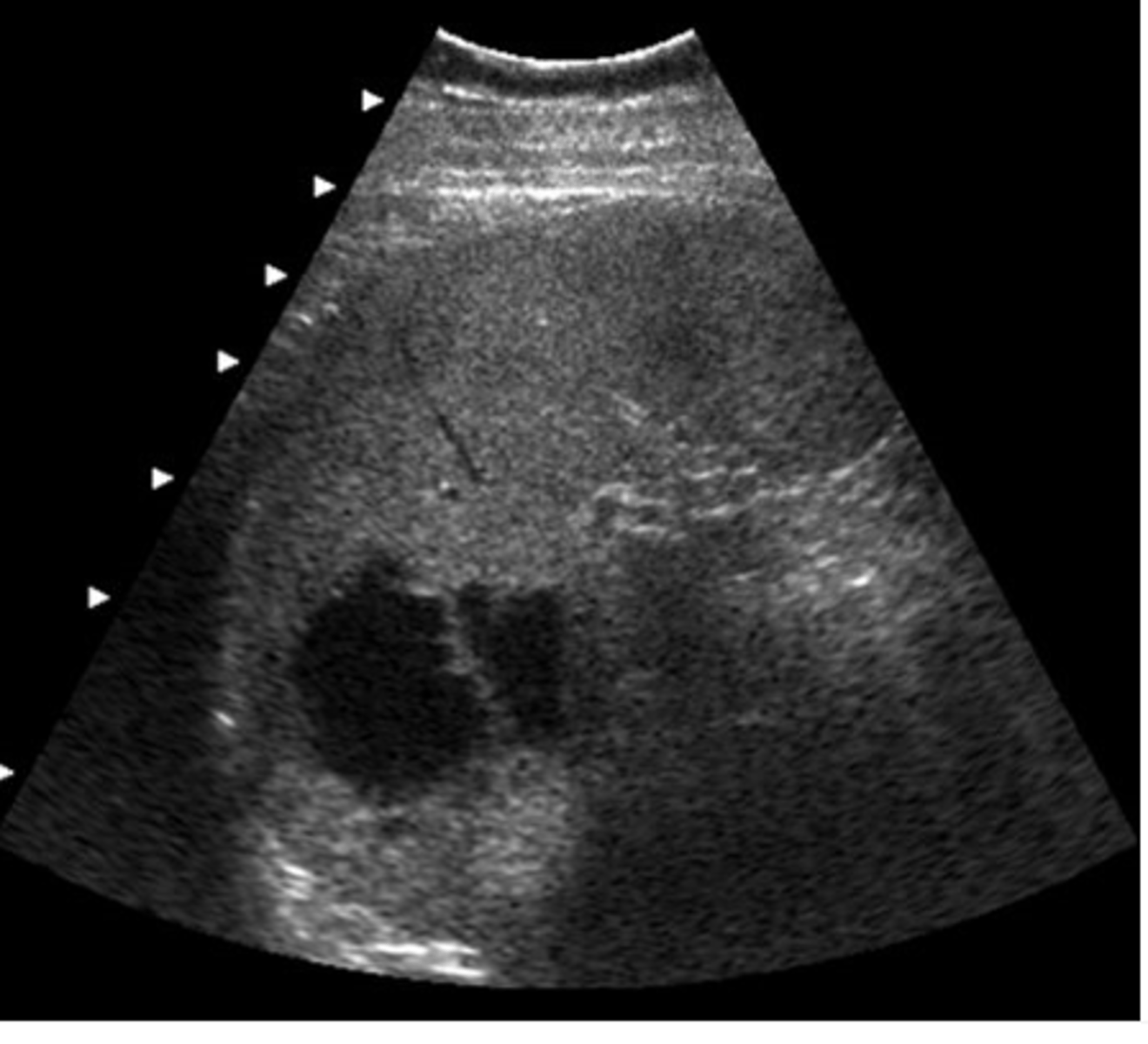
e. splenic cysts
This patient was regerred for an abdominal ultrasound because of epigastric pain and tenderness. This image was obtained from the left upper quadrant. Which of the following describes the ultrasound findings?
a. pleural effusion
b. splenomegaly
c. ascites
d. splenic metastases
e. splenic cysts
e. A and C only
You suspect intrahepatic bile duct dilatation in a patient with RUQ pain and tenderness. How can you differentiate the dilated bile ducts from intrahepatic veins?
a. dilated bile ducts demonstrate irregular tortuous walls
b. intrahepatic portal veins show increased through transmission compared to the dilated bile ducts
c. bile ducts will not demonstrate flow with color doppler
d. all of the above
e. A and C only
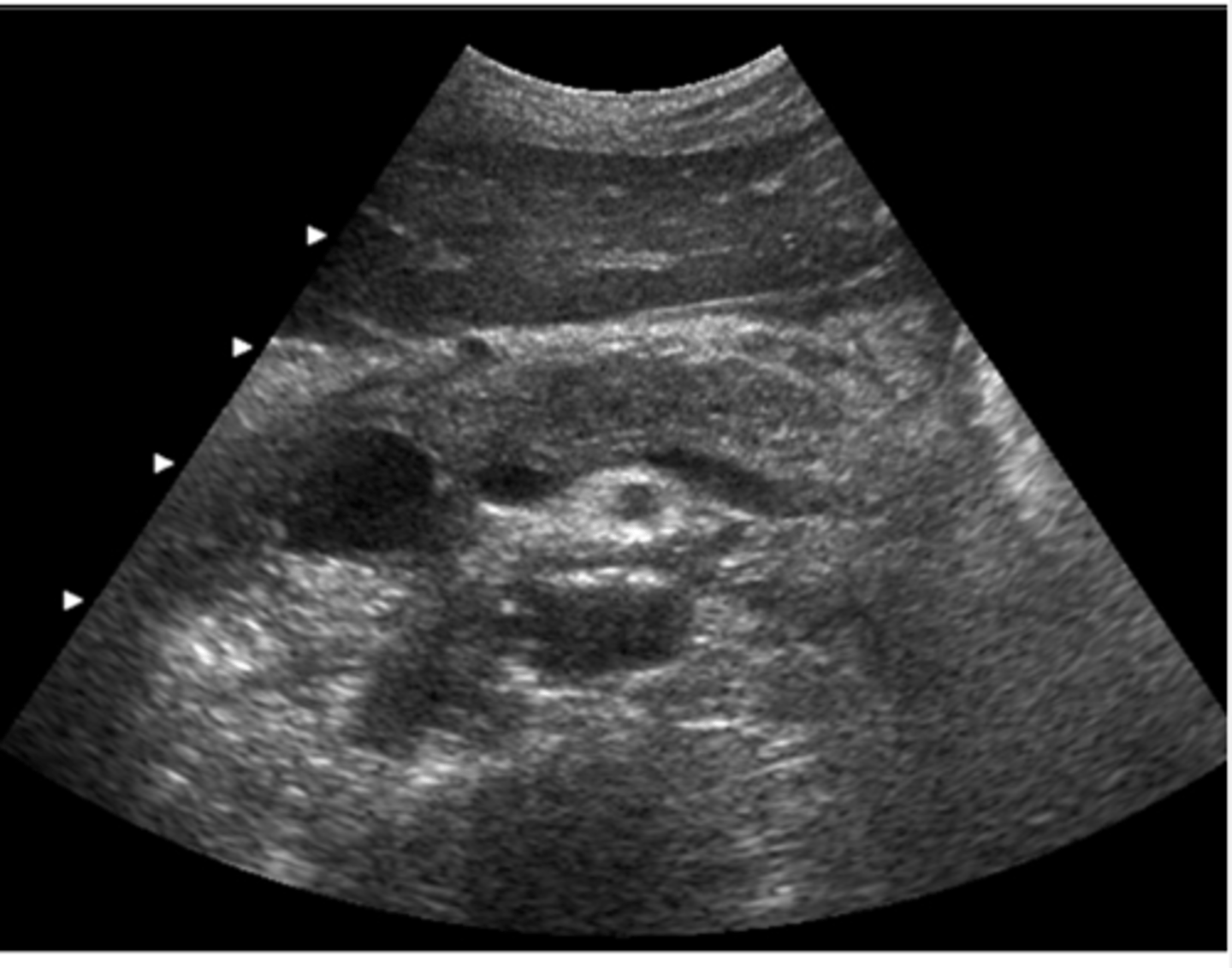
a. angiomyolipoma
Which of the following is most consistent with the sonographic appearance of this renal mass?
a. angiomyolipoma
b. staghorn calculus
c. lymphomatous involvement
d. complex renal cyst
e. transitional cell tumor
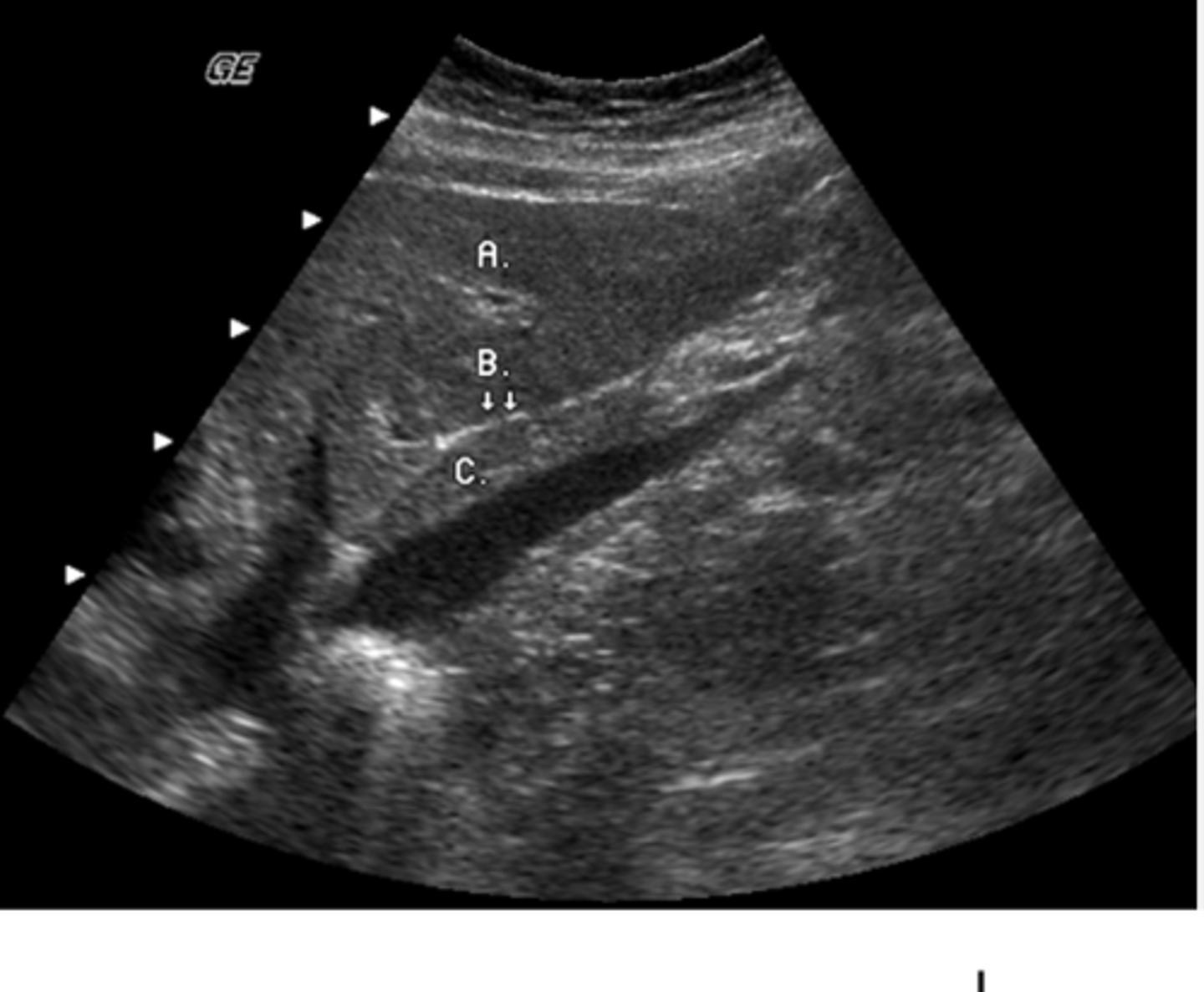
b. aorta
What vessel is seen posterior to the vessel labeled D?
a. IVC
b. aorta
c. right renal artery
d. IMV
e. splenic vein
d. angiomyolipoma
A renal mass that is highly echogenic due to its high-fat content is:
a. renal cell carcinoma
b. wilm's tumor
c. renal hamartoma
d. angiomyolipoma
e. renal lymphoma
c. 60 degrees
You are performing a doppler study on a patient with a TIPS stent. What is the greatest doppler angle of incidence you should use to get accurate velocity measurements in this exam?
a. 0 degrees
b. 45 degrees
c. 60 degrees
d. 70 degrees
e. 90 degrees
d. the two pancreatic ducts have not fused
You are reviewing a CT report on a patient referred for abdominal sonography. The report states that pancreatic divisum is present. What does this mean?
a. the pancreas is split into two pieces on each side of the abdomen
b. the pancreas head is separate from the body and tail
c. the pancreatic duct is duplicated
d. the two pancreatic ducts have not fused
e. the pancreas is malrotated
d. posterior to ivc
Which of the following descrives the normal course of the right renal artery?
a. retroaortic
b. between the sma and aorta
c. anterior to sma and ivc
d. posterior to ivc
e. between sma and splenic vein
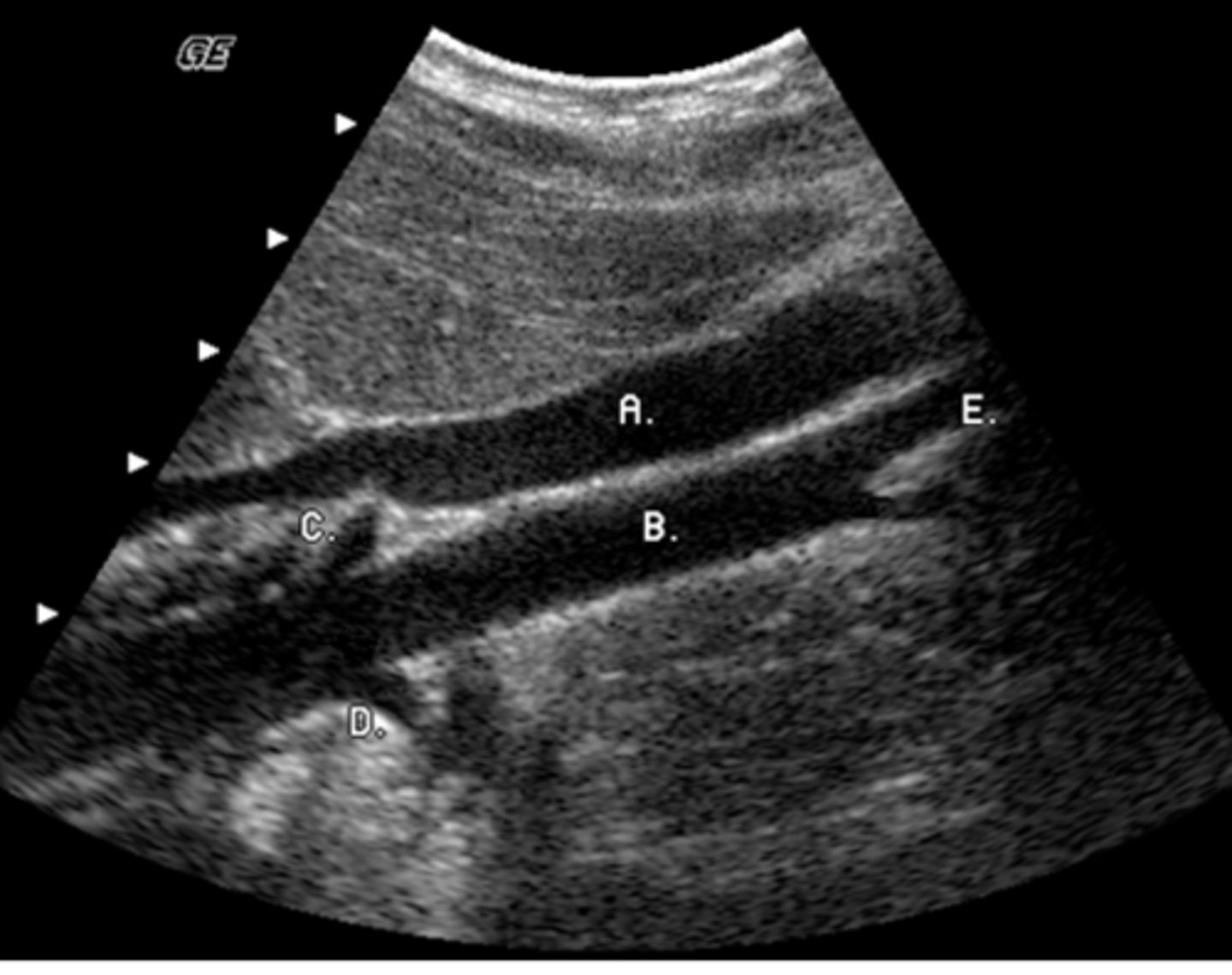
a. left lobe
What lobe of the liver does the letter A represent?
a. left lobe
b. caudate lobe
c. posterior right lobe
d. anterior right lobe
e. quadrate lobe
c. varicocele
A 33-year-old male has been referred for a scrotal ultrasound as a part of an infertility work-up. You will tailor your ultrasound exam to include an evaluation for which of the following?
a. epididymal cyst
b. torsion of the appendix testis
c. varicocele
d. testicular artery aneurysm
e. testicular cyst
c. pancreatic head pseudocyst
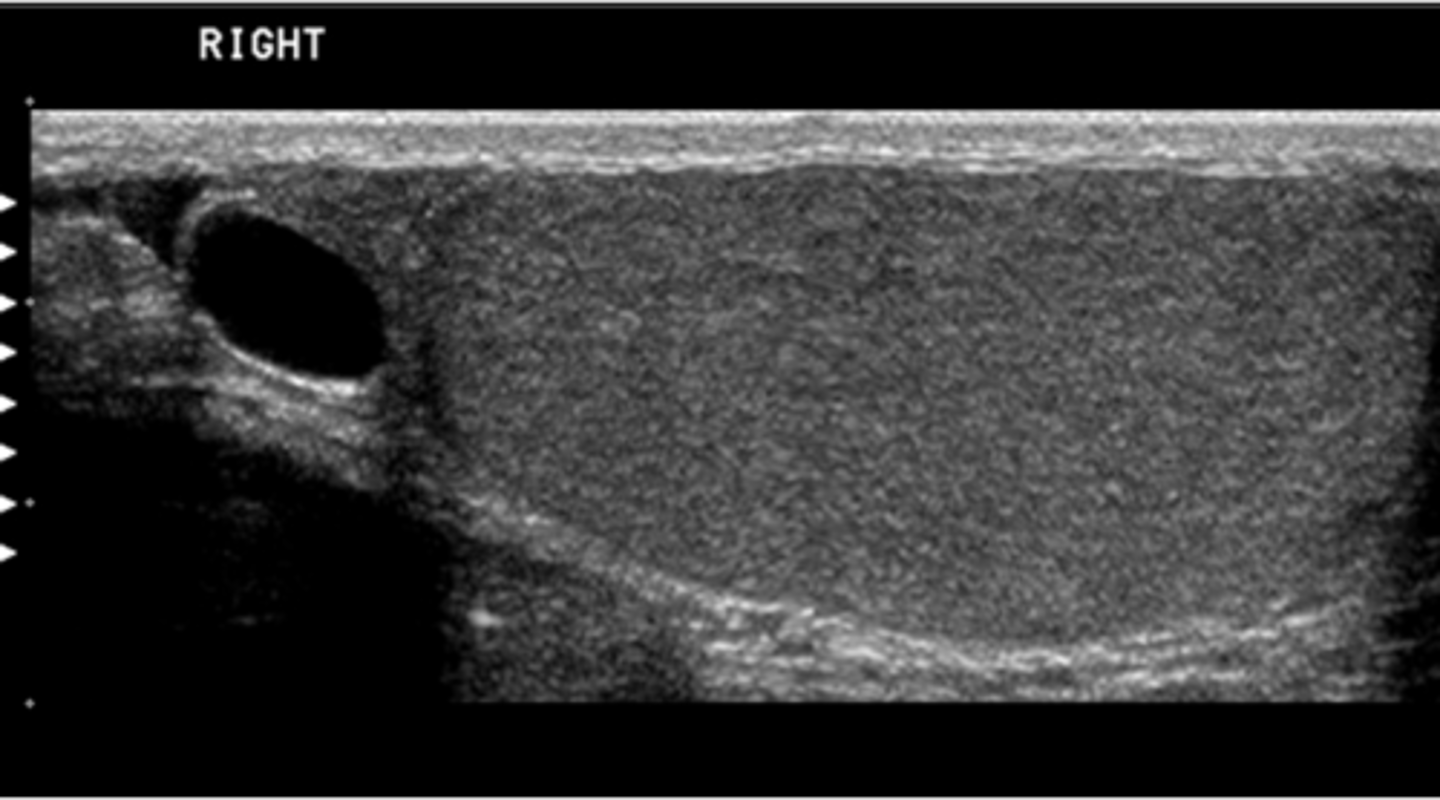
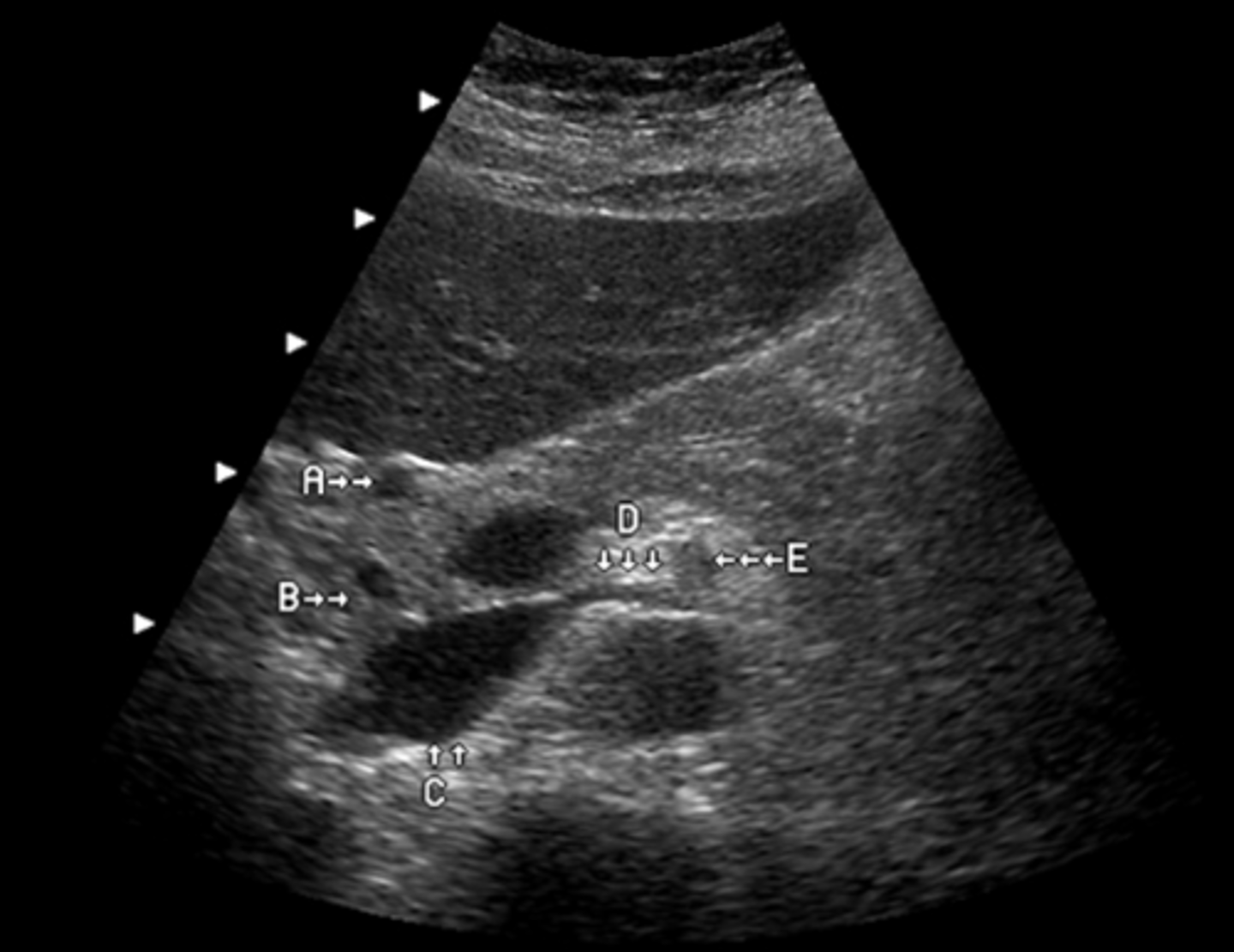
This image was obtained in a 48-year-old male referred for an abdominal ultrasound because of abnormal liver function tests. Which of the following best describes the findings?
a. ectopic location of gallbladder
b. pancreatic head carcinoma
c. pancreatic head pseudocyst
d. fluid in the duodenum
e. peripancreatic lymphadenopathy
d. fasting for 8-12 hours prior to study
You have a patient scheduled for a gallbladder sonogram. What preparation is required?
a. there is no necessary prep
b. patient should drink 4-6 8 oz glasses of water to improve hydration prior to the study
c. eat a fatty meal 30 minutes prior to study
d. fasting for 8-12 hours prior to study
e. fasting at least 24 hours prior to study and ingest an anti-gas medication
a. papillary carcinoma
YOu are performing a thyroid sonogram on a patient with a nodule suspicious for malignancy. What is the most common form of thyroid cancer?
a. papillary carcinoma
b. follicular carcinoma
c. medullary carcinoma
d. lymphoma
e. metastatic disease
d. >/= 10 mm
You are scanning a patient with a history of renal infections. You suspect thinning of the renal cortex. What is the normal measurement of the renal cortex?
a. <3mm
b. 3-6 mm
c. 6-9 mm
d. >/= 10 mm
e. the renal cortex cannot be measured sonographically
c. middle hepatic vein
Which vessel courses within the main lobar fissure?
a. main portal vein
b. left portal vein
c. middle hepatic vein
d. proper hepatic vein
e. right hepatic vein
b. internal jugular vein
Identify the structure labeled E
a. common carotid artery
b. internal jugular vein
c. external jugular vein
d. longus coli muscle
e. subclavian vein
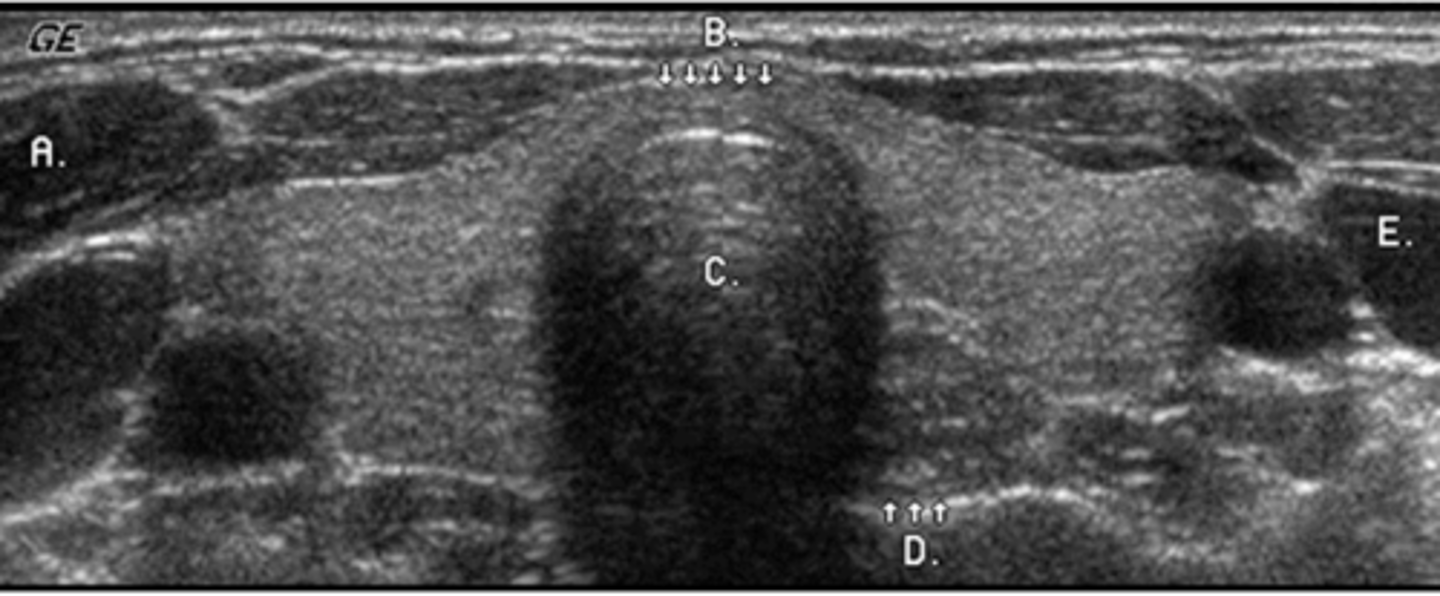
c
For correct orientation when performing a transverse scan through the left thyroid, which letter represents the patient's right side?
a. a
b. b
c. c
d. d
e. e
d. calcified pyramids
A patient has been referred to the ultrasound department with a history of medullary nephrocalcinosis. What do you expect to see?
a. a calcified renal capsule
b. a calcified ureter
c. a calcified urinary bladder
d. calcified pyramids
e. all of the above
a. rectus sheath hematoma
You have obtained this image from the mid abdomen of a patient with a history of severe sneezing and a palpable abdominal mass. What pathology is present in this image?
a. rectus sheath hematoma
b. aortic aneurysm
c. lymphadenopathy
d. bowel tumor
e. abdominal hernia
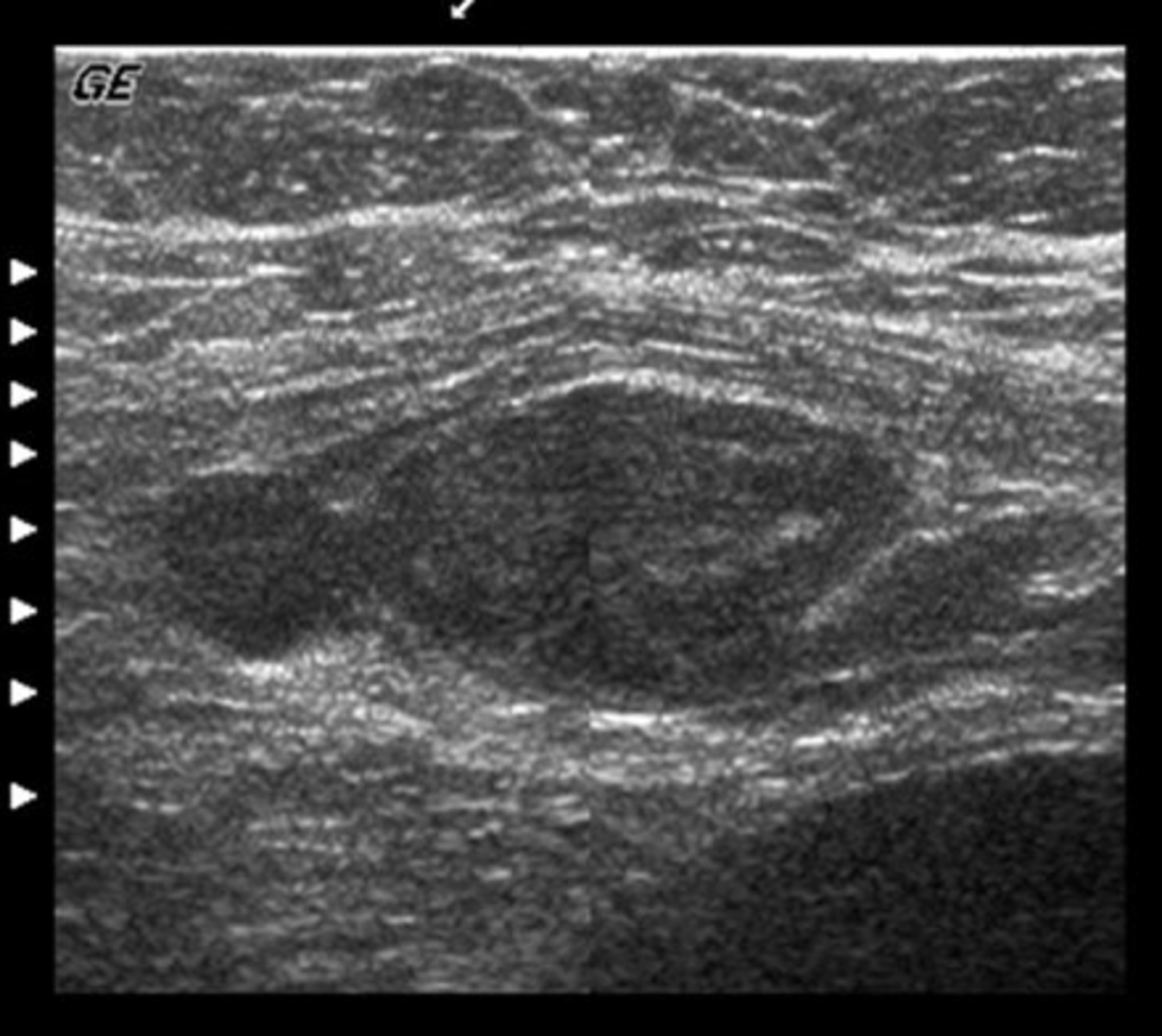
c. acute cholecystitis complicated by gallbladder perforation
You are scanning a 34-year-old multiparois woman with symptoms of severe RUQ pain, nausea and vomiting. The gallbladder is thick-walled with stones and an adjacent complex fluid collection is seen. These findings most likely represent:
a. adenomyomatosis complicated by gallstones
b. gallbladder carcinoma
c. acute cholecystitis complicated by gallbladder perforation
d. acalculous cholecystitis
e. emphysematous cholecystitis
a. left lobe
You have detected a mass anterior and to the left of ligamentum venosum. This mass is located in what lobe of the liver?
a. left lobe
b. caudate lobe
c. reidel's lobe
d. right lobe
e. quadrate lobe
b. intussesception
You have detected a dilated bowel with multiple concentric rings within it in a patient with severe abdominal pain. This finding is consistent with which of the following?
a. crohn's disease
b. intussesception
c. adenocarcinoma
d. lymphoma
e. acute diverticulitis
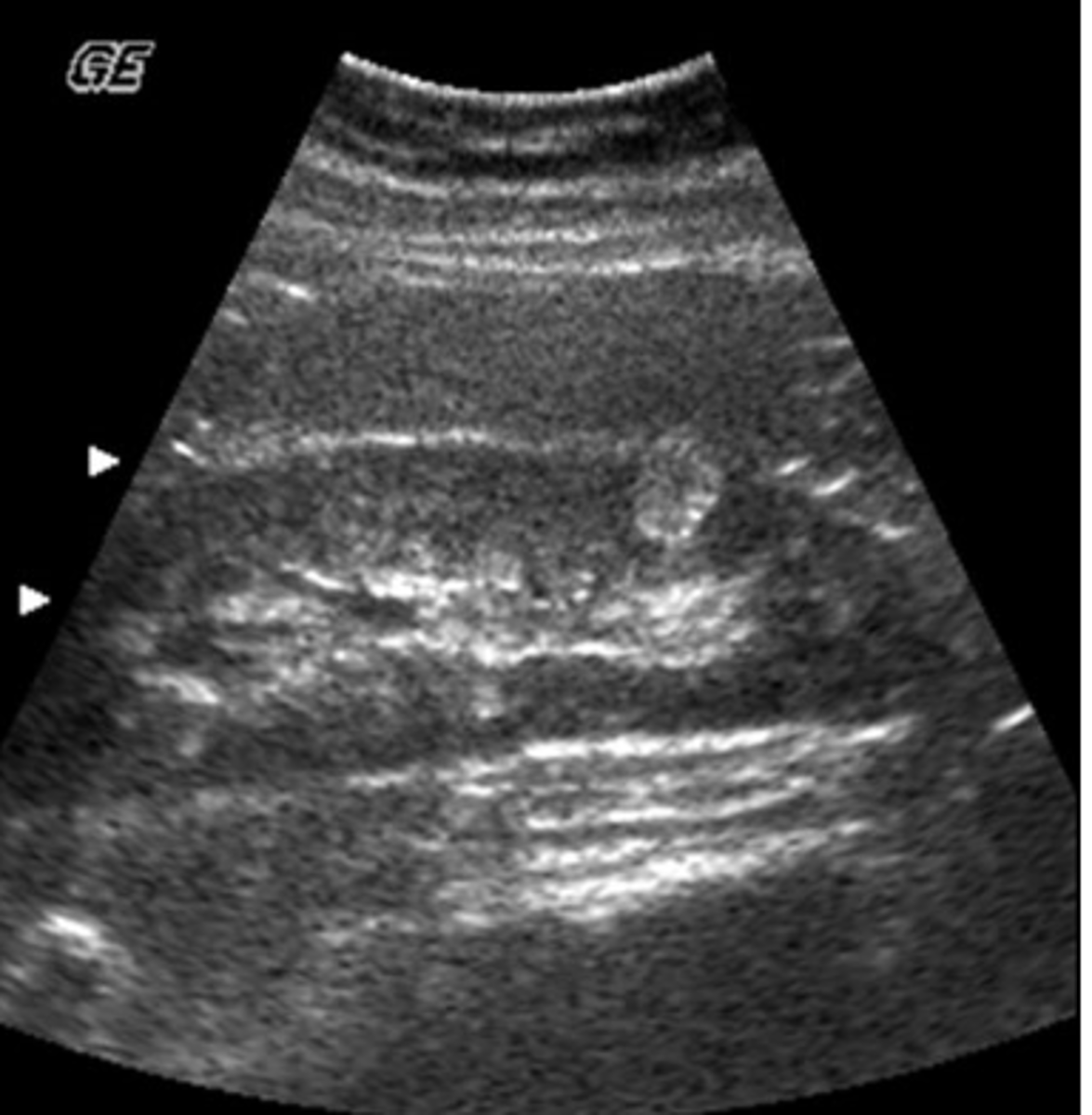
a. cirrhosis
In the image below, the surface nodularity of the liver is indicative of:
a. cirrhosis
b. metastatic disease
c. hepatitis
d. fatty infiltration
e. hydatid disease
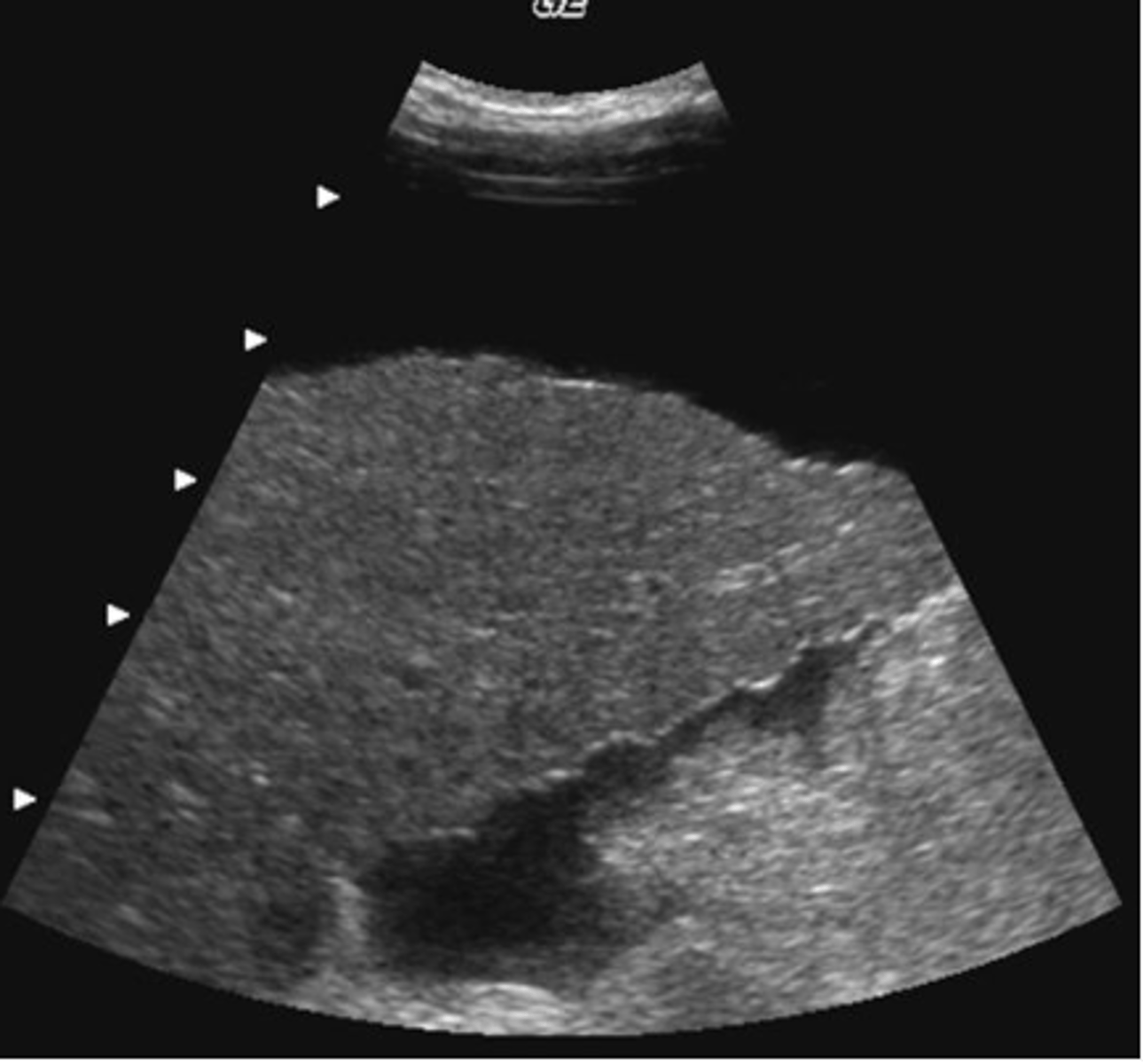
e. all of the above
Which of the following describes an abnormal sonographic appearance of the gut?
a. target
b. asymmetric target
c. pseudokidney
d. a and b only
e. all of the above
c. difficult initiation of voiding, nocturia, and small stream
A patient has been referred for transrectal sonography due to symptoms of prostatism.WHat are the most commmon symptoms of prostatism?
a. neausea, painful urination, pressure sensation on urinary bladder
b. weight loss, nocturia, hematura, and small stream
c. difficult initiation of voiding, nocturia, and small stream
d. hematuria, dysuria, and nocturia
e. swelling, lethargy, dysuria, and nocturia
d. renal cell carcinoma
A patient is referred for ultrasound evaluation to rule out the presence of renal malignancy. What is the most common solid renal mass in the adult?
a. oncocytoma
b. transitional cell carcinoma
c. angiomyolipoma
d. renal cell carcinoma
e. adenoma
b. dilated common bile duct
You have obtained this image from the RUQ of a patient with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. What pathology is present?
a. gallstones
b. dilated common bile duct
c. portal vein thrombosis
d. pneumobilia
e. pancreatic pseudocyst
e. all of the above appearances of liver metastasis may be encountered
A patient is referred for a sonogram of the liver to rule out metastatic disease. Which of the following describes the sonographic appearance of liver metastasis?
a. single hypoechoic mass
b. multiple hyperechoic masses
c. masses of mixed echogenicity
d. cystic masses
e. all of the above appearances of liver metastasis may be encountered
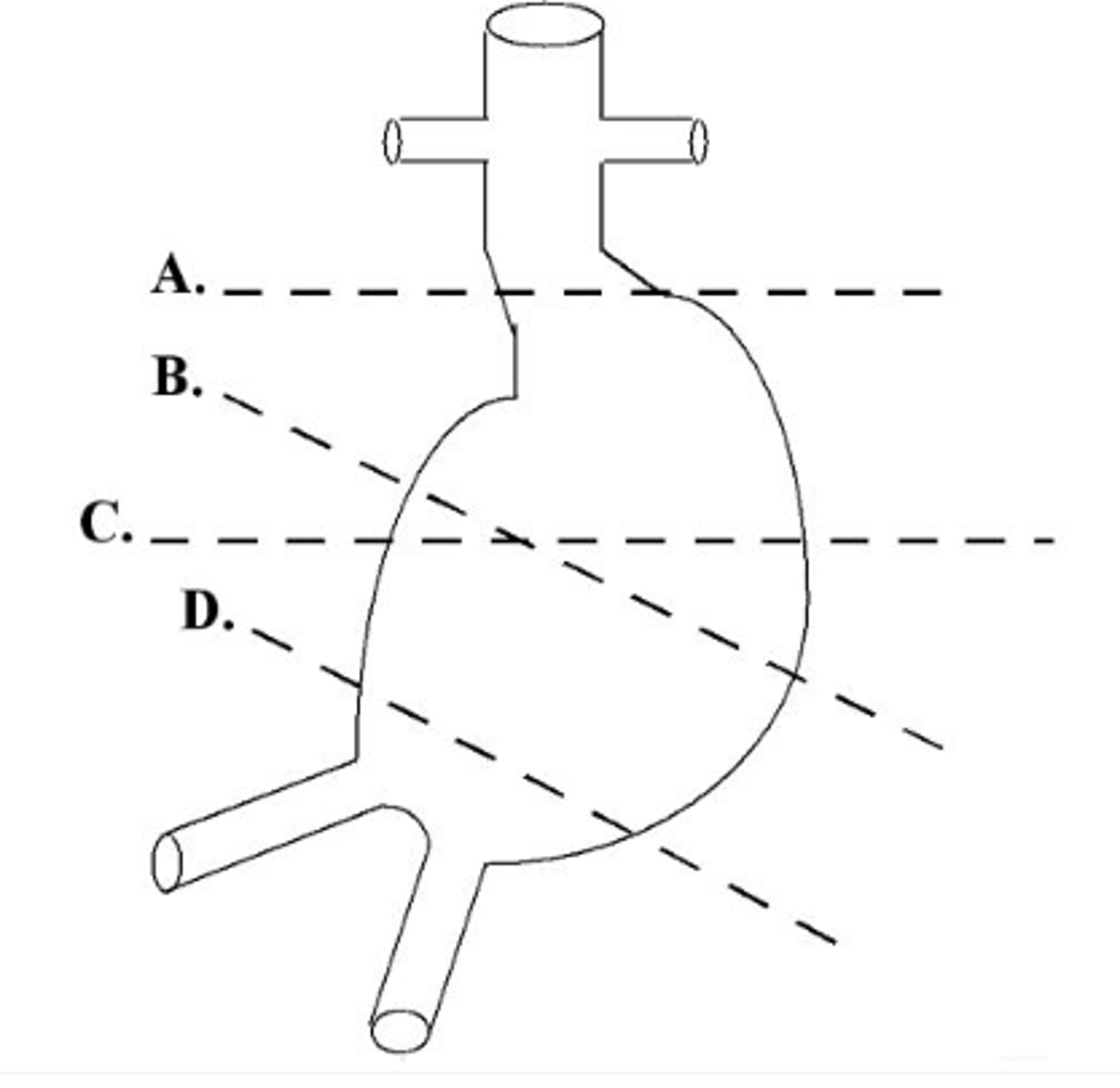
b. b
Which of the following shows the correct plane for measuring the diameter of this aortic aneurysm?
a. a
b. b
c. c
d. d
e. both b and c are correct
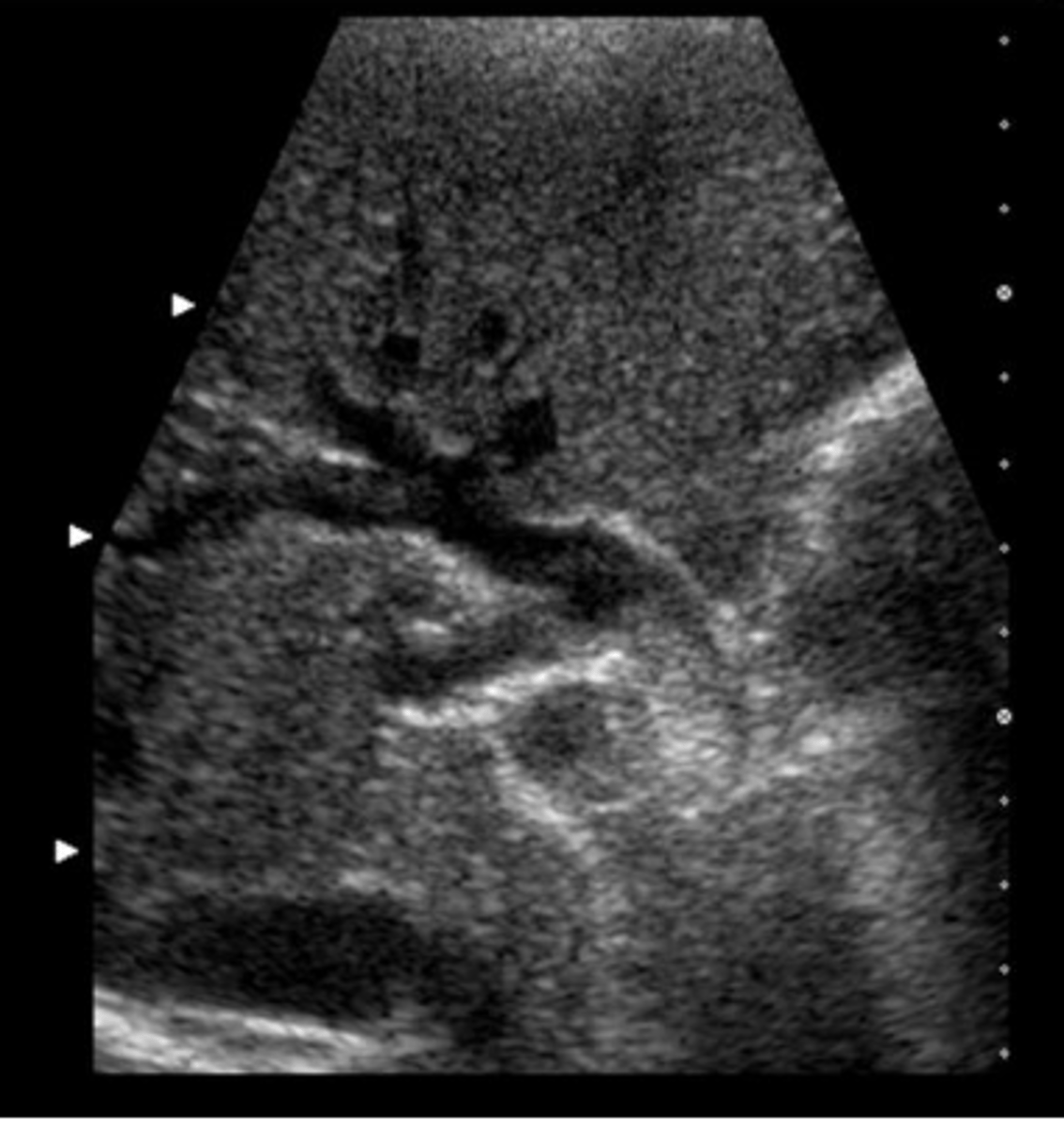
c. fatty metamorphosis of the liver with focal sparing
A liver ultrasound on a 49-year-old obese male demonstrates diffuse increased echogenicity with a focal hypoechoic area anterior to the portal vein. This most likely represents:
a. liver cirrhosis with hepatocellular carcinoma
b. hydatid disease
c. fatty metamorphosis of the liver with focal sparing
d. metastatic disease most likely due to a colon primary
e. normal liver parenchyma with a simple cyst
c. psoas
During ultrasound evaluation of the kidney, you detect a striated structure located posteromedial in relation to the kidney. What muscle are you imaging?
a. quadratus lumborum
b. rectus sheath
c. psoas
d. iliacus
e. piriformis