genetic fingerprinting and gel electrophoresis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
give and explain 5 uses of genetic fingerprinting:
forensic science - comparing samples of DNA collected from crime scenes to samples of DNA from possible suspects
medical diagnosis - screening/identifying genetic diseases
animal and plant breeding - finding evolutionary relationships to prevent inbreeding
why may someone use genetic fingerprinting over sequencing?
sequencing more time consuming and expensive
fingerprinting eliminates these issues while maintaining accuracy
what are VNTRs? describe their key features:
variable number tandem repeats - short base sequence made up of introns repeated multiple times
inherited!
no. and length unique so diff in all individuals
describe the steps of genetic fingerprinting:
DNA extracted from donor - use PCR to amplify
DNA digested using restriction endonucleases
electrophoresis
DNA transferred onto membrane and hybridised with complementary radioactive/fluorescent DNA probes which bind
position compared to other samples - often using radiography/UV light
what is gel electrophoresis?
technique used to separate molecules e.g. DNA/RNA/proteins based on size by using an electric current applied to an agarose gel matrix
describe the process of gel electrophoresis:
DNA mixture placed into a well in a slab of gel and covered in a buffer solution that conducts electricity
electrical current passed through gel - DNA fragments negatively charged so move towards +ve electrode at far end of gel
small DNA fragments move faster and travel further through the gel so DNA fragments separate according to size
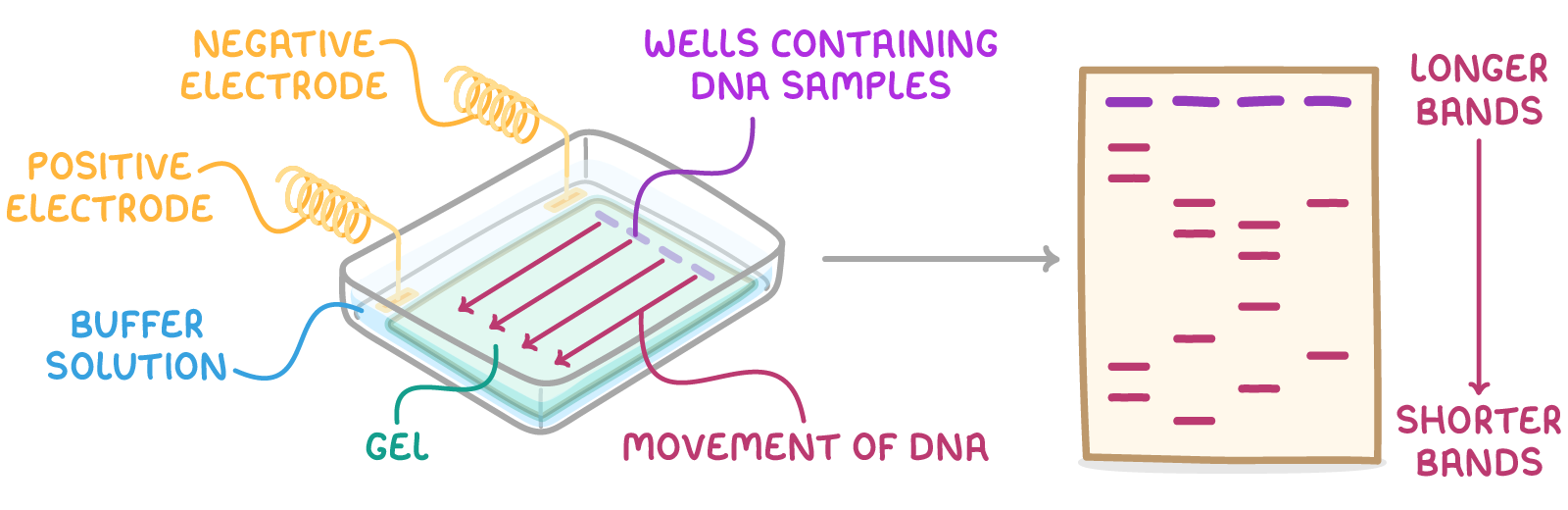
what is the ladder in gel electrophoresis? what is its purpose?
mixture of DNA fragments of known lengths that allows you to work oout the length of the bands in electrophoresis
allows comparison and identification of DNA bands
why is it important to