[PART 2] SHOCK- CSI/ STI/MFT
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
cervical spine injury
are injuries to the cervical spine due csto crushing, stretching, and rotational shear forces exerted on the cord at the time of trauma that canproduce severeneurologic deficits.
Edema and cord swelling
this contribute further to the loss of aspinal cord function
True
T or F in assessing for cervical and spine injury, weakness or paralysis of the diaphragm may occur with lesion at or above C4
priaprism
persistent erection of penis
Hoffman’s sign
this is define in the action of flicking of the middle finger induces flexion of the ipsilateral thumb or index finger
done nasally
if the pt is experiencing CSI, he may b e intubated and should be done what way of ventilation
Methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg IV loading dose over 15 mins— 5.4 mg/kg/hr initiated 45 mins later and continue infusion for 23 hours—> reassess if there is improvement)
In CSI oatients what are the medications:
HIgh dose steroids
This med is given to decrease the inflammation and restore the functioning of the nerves
hypertension, hypothermia, and bradycardia
what are the indicative of spinal shock
MAXILLOFACIAL TRAUMA
Injuries to the head frequently result in facial lacerations and fractures to the facial bones (nasal, orbital, maxillary and mandibular fracture
Paralysis of the upward gaze (Inferioir rectuis muscle, inferior oblique muscle and infraorbital nerve affected)
Assessment (Maxillo): it is indicative of inferior orbit fracture (blowout fracture)
Crepitus (grating, crackling, or popping sensation) on palpation around the nose
assessment (maxillo): indicative of nasal fracture
malocclussion of teeth
ass of (maxillo): indicative of maxilla or mandible fracture
Palpable flattening of the cheek and loss of sensation below the orbit
ass (maxillo): - indicative of zygomatic (cheekbone) fracture
Trismus and mobility of the jaw
assess (maxillo): -indicative of maxillary fracture
Rhinorrhea and otorrhea
assess (Maxillo): indicative of CSF leak
opthalmologist
If maxillofacial trauma, if there is obvious optha, eye injury, we refer them to?
apply loose and bulky dressing
in controlling bleeding how will you do it as a nurse?
FALSE. no ice to eyes
Apply ice to eyes if injury is present, TRUE OR FALSE (maxillo)
Pain relievers and sedative
Drugs for maxillofacial trauma
meningitis and encephalititis
what are the possible complications when the brain become infected by the bacteria thru csf leaks by coughing, sneezing
CLOSED WOUND
an injury to the soft tissue without a break in the skin
CONTUSION
bleeding beneath the skin into the soft tissue (usually muscles)
Hematoma
well-defined pocket of blood and fluid beneath the skin
Blunt trauma
caused by a sudden force over the chest and abdomen, there is possible internal bleeding
Bruises, ecchymosis, hematoma
What you should assess to know if there is presence of blunt trauma?
closed wound
These patients have potential to develop shock, and may also present with other medical emergencies, what is the related trauma
open wound
an injury to the soft tissue with a break in the skin
abrasion (gas-gas)
superficial loss of skin resulting from rubbing or scraping the skin over a rough or uneven surface.
Laceration
tear in the skin; can be partial or full thickness cut. Can be defined as incisional (clean cut) or jagged
Puncture
occurs when the skin is penetrated by a pointed object. Can be penetrating or perforating. Don’t cause serious external bleeding but significant internal bleeding. (tusok
Avulsion
involves a tearing off or loss of a f lap of the skin. (wak-wak
Amputation
traumatic cutting or tearing off of a finger, toe, arm, or leg.
No
WHAT TO DO IN STI: if the dressing becomes saturated during direct pressure, will you remove the dressing?
above the level of the heart
Mgt in STI : if possible the injured area should be elevated how high?
Pressure points
These points are used when direct pressure and elevation cannot control bleeding alone or when direct pressure cannot be applied to a bleeding site due to protruding bone or an embedded object.
On the artery (proximal) to lessen flow to injury (distal)
In dealing with pressure points where will you put the pressure
temporal
Facial
carotid
subclavian
brachial
radial and ulnar
femoral
name the arteries: or the pressure points to stop hemorrhage
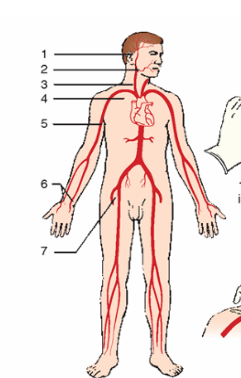
the site of injury and the heart
pressure points are located between
50 mL
As general rule in STI, irrigate wound with how many ml per inch of wound per hour of age of wound?
regional nerve block and wound margins
In managing wound preparation, through injection of anesthetic intradermally through what areas of wound?
True by Closure by primary Intent
T or F: Wound thst id repaired without delay after the injury; yields teh fastest healing may be by sutures, skin staples, or tissue adhesives
closure by secondary intent
Closure by what intent wherein the wound is allowed to granulate on its own without surgical closure
closure by secondary intent with delayed closure
closure by intent wherein the wound is cleaned and dressed, then the patient returns 3-4 days for definitive closure;
Hayaan muna mag-evaporate lahat ng debris, mag-nana or kung too much swelling. And then after 3-4 days, ire-reassess ang sugat, saka isasara
contact layer
wound dressing which is first layer, consist of a non absorbent hydrophilic dressing that will allow exudates to pass through to the second layer without wetting the contact layer4
non-absorbent hydrophilic dressing
dressing that will allow exudates to pass through to the second layer without wetting the contact laye
Absorbent layer
wound dressing which is the second layer, usually constructed of surgical dressing pads
outer wrap
wound dressing which is the : third layer, holds the dressing in place. consist of rolled gauze and tape.
surgical dressing pads
what consists the second layer or the absorbent layer of wound dressing which absorbs the pus
hydrophilic dressing
which dressing already has antibiotic with it
mefenamic acid
celecoxib
Tramadol (too much pain)
IV (paracetamol, diclofenac, tramadol)
Pain meds that is usually prescribed to patients: